Effectiveness of Exogenous Fe2+ on Nutrient Removal in Gravel-Based Constructed Wetlands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
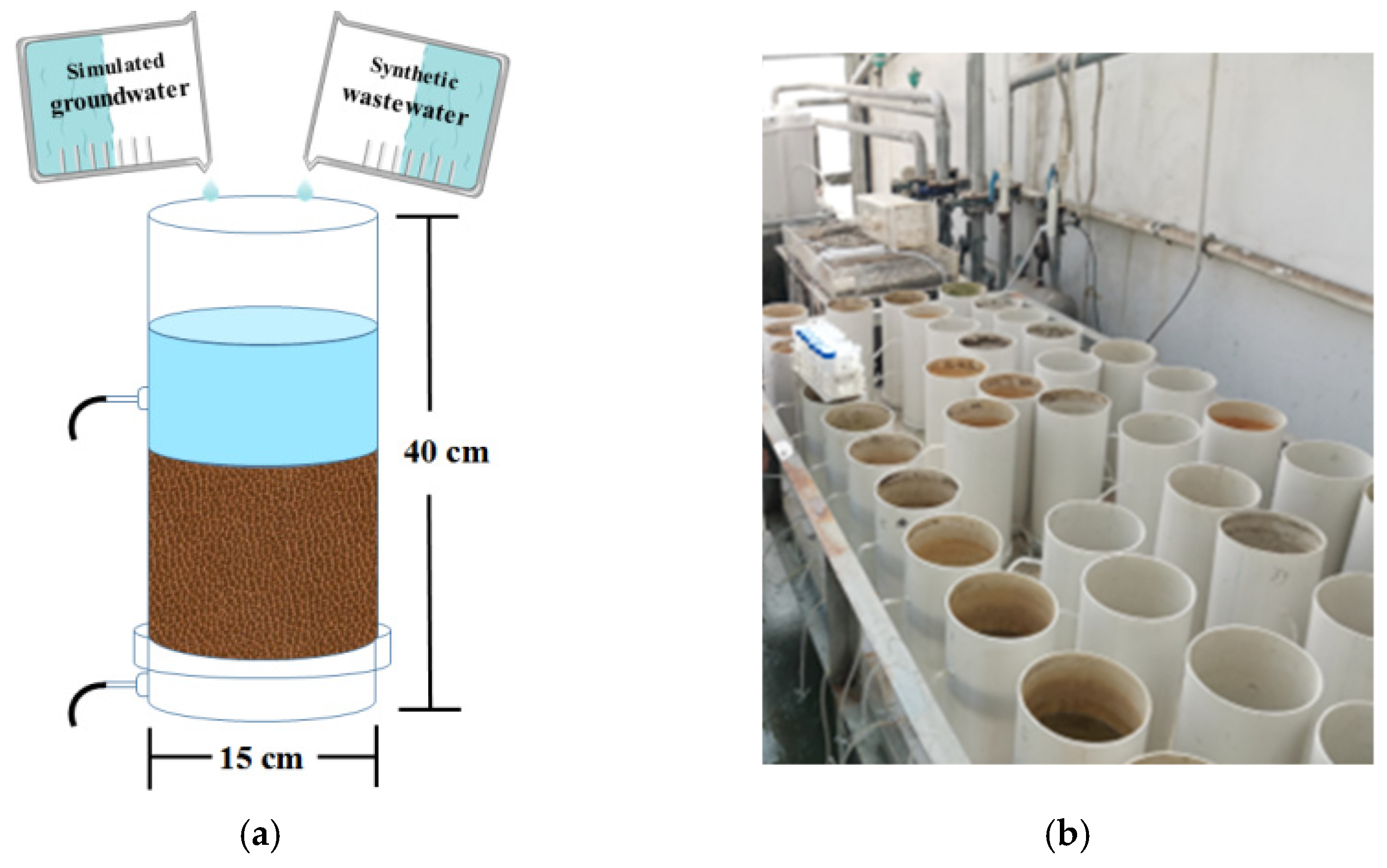
2.1. Experimental Description
2.2. Synthetic Wastewater and System Operation
2.3. Sample Collection and Determination
2.4. Microbial Community Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
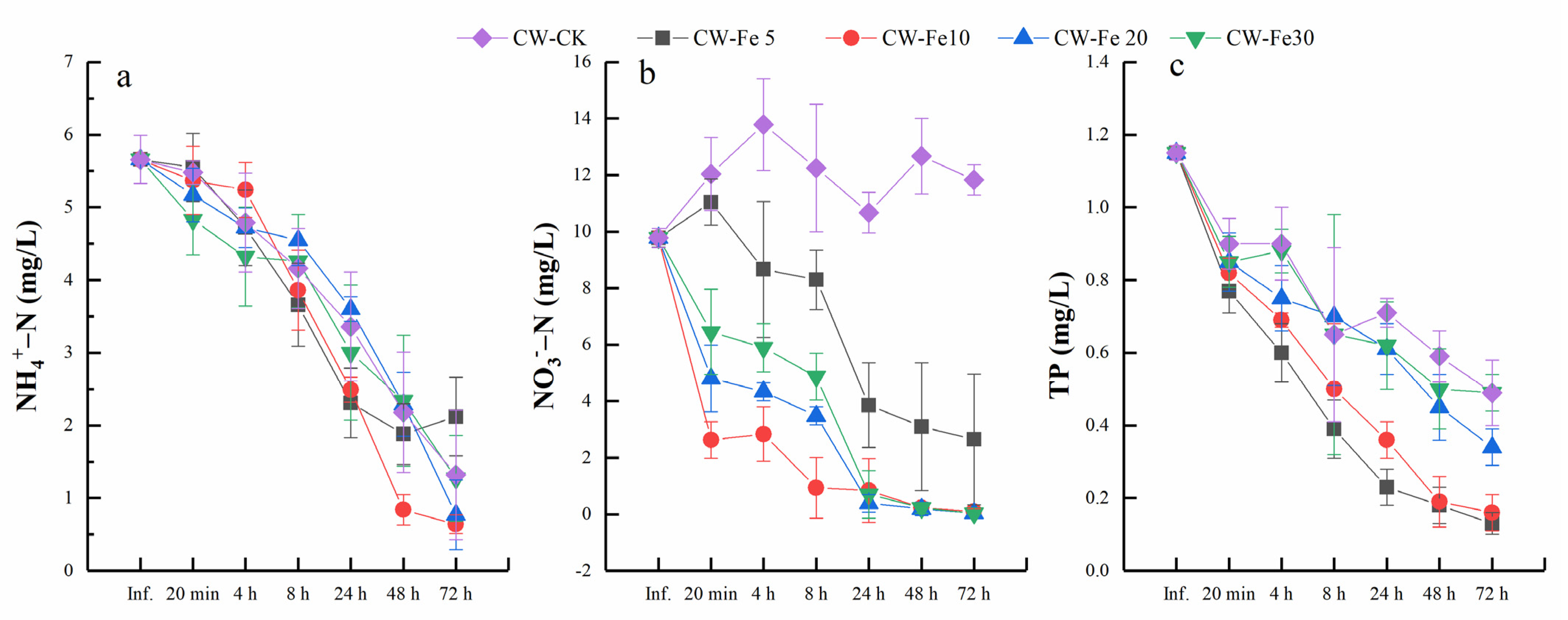
3.1. Nutrients Removal Efficiency
3.2. Effluent Dissolved Fe2+, Total Iron and Fe3+, and pH Value Concentrations
3.3. Microbial Community Characteristics in Substrates
3.3.1. Microbial Richness and Diversity
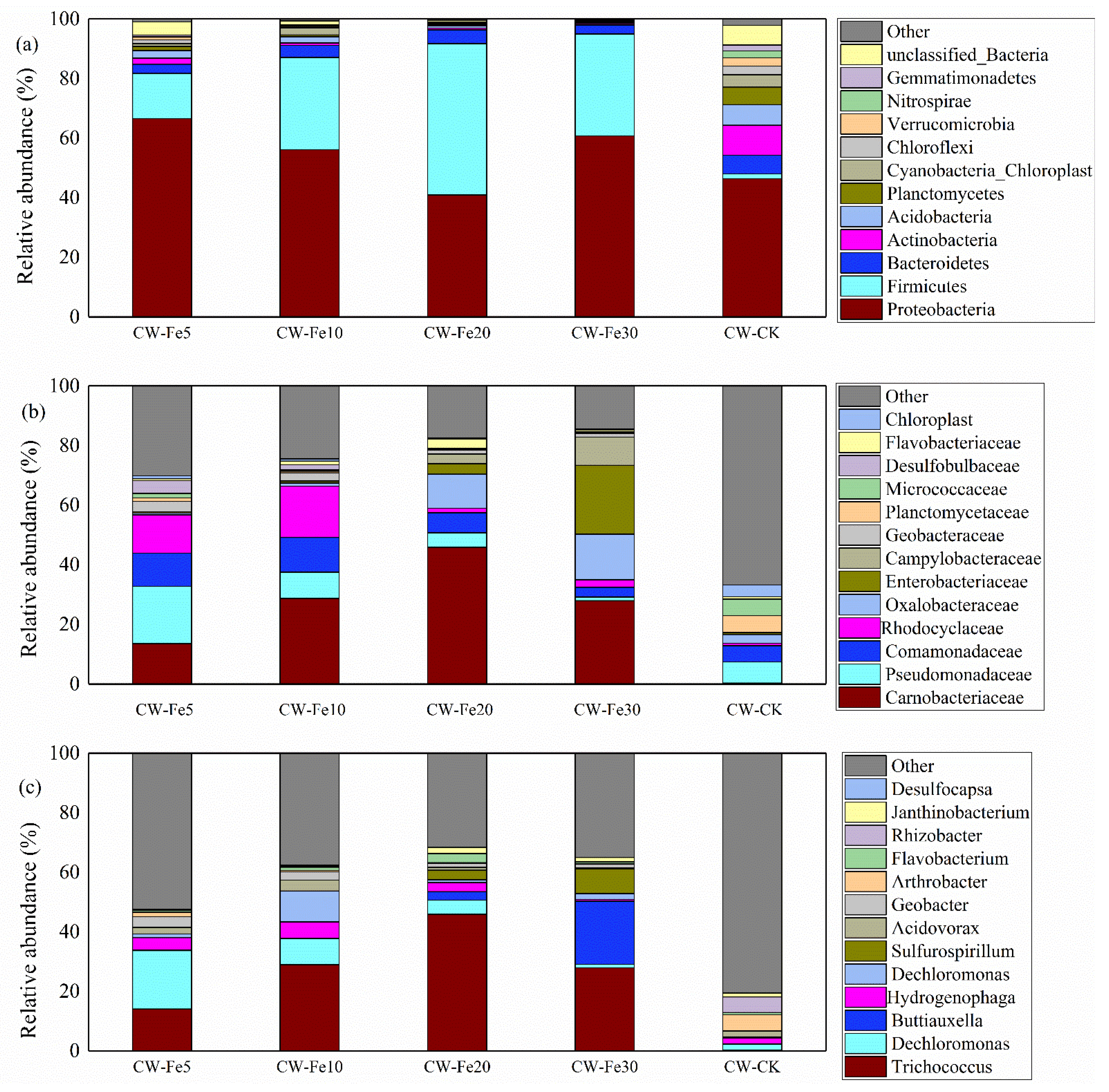
3.3.2. Bacterial Community Composition
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Fe2+ Addition on Nitrogen Removal in CWs
4.2. Influence of Fe2+ Addition on Phosphorus Removal Performance in CWs
4.3. Influence of Fe2+ Addition on the Features of Bacterial Communities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, F.; Du, S. Assessment and analysis of non-point source nitrogen and phosphorus loads in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of Hubei Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 412, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boers, P.C.M. Nutrient emissions from agriculture in The Netherlands, causes and remedies. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 33, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Hou, P.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, M.; Liu, F.; Yang, L. Application of systematic strategy for agricultural non-point source pollution control in Yangtze River basin, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 304, 107148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X. Assessment and analysis of agricultural non-point source pollution loads in China: 1978–2017. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.; Han, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z. Application of the source-sink landscape method in the evaluation of agricultural non-point source pollution: First estimation of an orchard-dominated area in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 252, 106910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupas, R.; Delmas, M.; Dorioz, J.-M.; Garnier, J.; Moatar, F.; Gascuel-Odoux, C. Assessing the impact of agricultural pressures on N and P loads and eutrophication risk. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhao, N.; Ni, Y.; Yi, J.; Wilson, J.P.; He, L.; Du, Y.; Pei, T.; Zhou, C.; Song, C.; et al. China’s improving inland surface water quality since 2003. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaau3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Si, Z.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, X. Natural pyrite improves nitrate removal in constructed wetlands and makes wetland a sink for phosphorus in cold climates. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Wei, D.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, R. Natural pyrite to enhance simultaneous long-term nitrogen and phosphorus removal in constructed wetland: Three years of pilot study. Water Res. 2019, 148, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, K.L.; Benz, M.; Schink, B.; Widdel, F. Anaerobic, nitrate-dependent microbial oxidation of ferrous iron. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1996, 62, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Vymazal, J.; Brix, H. Critical Review: Biogeochemical Networking of Iron, Is It Important in Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7930–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Anaerobic Ammonium Removal Pathway Driven by the Fe (II)/Fe (III) Cycle through Intermittent Aeration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7615–7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.P.; Yan, B.X.; Lu, Y.Z.; Yang, Z.X.; Zhang, F.Y. Distribution of Water-soluble Iron in Water Environment of Sanjiang Plain. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2007, 27, 820–824. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, L.; Yin, H.; Fan, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Ge, C.; Song, H. Enhanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal by natural pyrite-based constructed wetland with intermittent aeration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 69012–69028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, X.; Sand, W. Untangling the nitrate removal pathways for a constructed wetland- sponge iron coupled system and the impacts of sponge iron on a wetland ecosystem. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Fu, C.Y.; Li, X.H.; Yan, B.X.; Shi, T.H. Effect of Fe2+ addition on chemical oxygen demand and nitrogen removal in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.J.; Bruell, C.J.; Marley, M.C.; Sperry, K.L. Persulfate oxidation for in situ remediation of TCE. I. Activated by ferrous ion with and without a persulfate-thiosulfate redox couple. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wan, J.-Q.; Ma, Y.-W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.-Z.; Lan, M. Influences of pH and complexing agents on degradation of reactive brilliant blue KN-R by ferrous activated persulfate. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2012, 33, 871–878. [Google Scholar]
- Melton, E.D.; Swanner, E.D.; Behrens, S.; Schmidt, C.; Kappler, A. The interplay of microbially mediated and abiotic reactions in the biogeochemical Fe cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dai, W.; Zheng, P.; Zheng, X.; He, S.; Zhao, M. Iron scraps enhance simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.; Chung, Y.C.; Jung, J.Y. Microbial community structure and occurrence of diverse autotrophic ammonium oxidizing microorganisms in the anammox process. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2723–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, T.; Oh, Y.-K.; Nguyen, V.K.; Cho, S. Correlation of microbial community with salinity and nitrogen removal in an anammox-based denitrification system. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liu, H.; Tong, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, P.; Liu, D.; Yuan, S.H. Impact of Fe (II) oxidation in the presence of iron-reducing bacteria on subsequent Fe (III) bio-reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Zhu, H.; Yan, B.; Su, S.; Wang, X.; Li, P. Simulation Research of Effect of Exogenous Iron on Removal of Nitrogen in Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands. Wetl. Sci. 2015, 13, 350–355. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.; Lin, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, H.; Yu, G.; Chong, Y. The production of ferrous ions driven by anaerobic degradation of plant biomass and improved phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, C.Y.; Li, X.H.; Dong, H.Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Shi, T.H.; Yan, B.X.; Liu, X.L. Effect of Ferrous Iron Addition on Ammonium Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Communities in Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands. Wetlands 2020, 40, 2109–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Douglas, G.B.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Cui, L.; Ye, Z. Microbial reduction of nitrate in the presence of zero-valent iron. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Roberts, K.L.; Grace, M.R.; Kessler, A.J.; Cook, P.L.M. Role of organic carbon, nitrate and ferrous iron on the partitioning between denitrification and DNRA in constructed stormwater urban wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.L.; Nielsen, P.H. Microbial nitrate-dependent oxidation of ferrous iron in activated sludge. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 3556–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cai, Z. Ferrous Iron Involved in Denitrification in Subtropical Soils Under Anaerobic Condition. Soils 2015, 47, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zheng, P.; Li, W.; Wang, R.; Ding, S.; Abbas, G. Performance of nitrate-dependent anaerobic ferrous oxidizing (NAFO) process: A novel prospective technology for autotrophic denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardal, F. Abiotic and microbial interactions during anaerobic transformations of Fe (II) and NOX. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tai, Y.-L.; Dempsey, B.A. Nitrite reduction with hydrous ferric oxide and Fe (II): Stoichiometry, rate, and mechanism. Water Res. 2009, 43, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, J.; Prommer, H.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Sun, J.; Siade, A.J.; Yusov, A.; Bostick, B. Identifying and Quantifying the Intermediate Processes during Nitrate-Dependent Iron (II) Oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5771–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehe, E.M.; Gerhardt, S.; Schink, B.; Kappler, A. Ecophysiology and the energetic benefit of mixotrophic Fe (II) oxidation by various strains of nitrate-reducing bacteria. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 70, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, B.; Wang, S.; Cao, S.; Miao, Y.; Jia, F.; Du, R.; Peng, Y. Biological nitrogen removal from sewage via anammox: Recent advances. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Q.; Elliott, D.W.; Zhang, W.-X. Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for abatement of environmental pollutants: Materials and engineering aspects. Crit. Rev. Solid State. 2006, 31, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.Y.F. Phosphorus fractions and fluxes in the soils of a free surface flow constructed wetland in Hong Kong. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.; Scholz, M. Treatment of artificial wastewater containing two azo textile dyes by vertical-flow constructed wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2018, 25, 6870–6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vymazal, J. Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 380, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, R.; Morgan, D. Global development of various emerged substrates utilized in constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilfert, P.; Kumar, P.S.; Korving, L.; Witkamp, G.-J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. The Relevance of Phosphorus and Iron Chemistry to the Recovery of Phosphorus from Wastewater: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9400–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Shao, M.-F.; Zhang, T.; Tong, A.H.Y.; Lok, S. Analysis of the bacterial community in a laboratory-scale nitrification reactor and a wastewater treatment plant by 454-pyrosequencing. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4390–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ma, S.; Jiang, H.; Yang, F. Start-up of the anaerobic hydrolysis acidification (ANHA)simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD)/enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) process for simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal for domestic sewage treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130094. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, T.; Morrison, L.; Gerrity, S.; Collins, G.; Porca, E.; Li, R.; Zhan, X. Nanostructured pyrrhotite supports autotrophic denitrification for simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal from secondary effluents. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.; Pearson, V.K.; Schwenzer, S.P.; Miot, J.; Olsson-Francis, K. Nitrate-Dependent Iron Oxidation: A Potential Mars Metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, N.; Chen, Y. Insight into the mechanisms of biochar addition on pollutant removal enhancement and nitrous oxide emission reduction in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Microbial community structure, functional genes and enzyme activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Ma, J.; Murinda, S.; Reddy, G.B. Bacterial community dynamics in surface flow constructed wetlands for the treatment of swine waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.A.; Achenbach, L.A.; Coates, J.D. Microorganisms pumping iron: Anaerobic microbial iron oxidation and reduction. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Q.-A.; Shaaban, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, F.; Hu, R.; Wang, B. Nitrate dependent Fe-oxidizing bacterial diversity in subtropical soils of China. Catena 2019, 176, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Cao, X.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Si, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Tesfahunegn, A.A. Bioenergy generation and simultaneous nitrate and phosphorus removal in a pyrite-based constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 296, 122350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; He, Y.; Peng, Y. Achieving partial nitrification in a continuous post- denitrification reactor treating low C/N sewage. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, C.; Yin, W. Enhanced simultaneous organics and nutrients removal in tidal flow constructed wetland using activated alumina as substrate treating domestic wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.; Batstone, D.J.; Keller, J. Biological phosphorus removal from abattoir wastewater at very short sludge ages mediated by novel PAO clade Comamonadaceae. Water Res. 2015, 69, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.; Shin, S.G.; Jannat, M.A.H.; Tongco, J.V.; Hwang, S. Use of food waste-recycling wastewater as an alternative carbon source for denitrification process: A full-scale study. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xiong, P.; Liu, L.; Bao, Y.; Zhao, Z. Link between characteristics of Fe (III) oxides and critical role in enhancing anaerobic methanogenic degradation of complex organic compounds. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, G.; Kim, J.; Cho, K.; Bae, H.; Lee, C. The biostimulation of anaerobic digestion with (semi)conductive ferric oxides: Their potential for enhanced biomethanation. Appl. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10355–10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, C.; Lv, N.; Pan, X.; Cai, G.; Ning, J.; Zhu, G. Deeper insights into effect of activated carbon and nano-zero-valent iron addition on acidogenesis and whole anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 324, 124671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.H.; Song, X.S.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.F.; Ge, X.Y.; Tesfahunegn, A.A. Nitrate removal to its fate in wetland mesocosm filled with sponge iron: Impact of influent COD/N ratio. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y. Nitrogen loss from anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to Iron (III) reduction in a riparian zone. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CW-CK | CW-Fe5 | CW-Fe10 | CW-Fe20 | CW-Fe30 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4Cl | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| KNO3 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| K2HPO4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| FeSO4•7H2O | 0 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 60 |
| C6H10O8C6 | 0 | 262.68 | 525.35 | 1050.7 | 1576.05 |
| Systems | OTUs | Shannon | Chao1 | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW-CK | 1454.67 ± 24.44 a | 5.74 ± 0.24 a | 1589.20 ± 65.24 a | 1.000 ± 0.001 a |
| CW-Fe5 | 1255.34 ± 61.65 b | 4.26 ± 0.40 b | 1513.32 ± 82.05 a | 0.994 ± 0.001 b |
| CW-Fe10 | 1114.33 ± 105.83 b | 3.66 ± 0.33 b | 1405.91 ± 130.45 ab | 0.994 ± 0.001 b |
| CW-Fe20 | 914.00 ± 117.85 c | 2.92 ± 0.22 c | 1264.73 ± 127.85 bc | 0.993 ± 0.001 b |
| CW-Fe30 | 797.33 ± 53.89 c | 2.72 ± 0.16 d | 1105.40 ± 122.96 c | 0.994 ± 0.001 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, L.; Yan, B.; Ou, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, L.; Jiao, P. Effectiveness of Exogenous Fe2+ on Nutrient Removal in Gravel-Based Constructed Wetlands. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031475
Tian L, Yan B, Ou Y, Liu H, Cheng L, Jiao P. Effectiveness of Exogenous Fe2+ on Nutrient Removal in Gravel-Based Constructed Wetlands. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031475
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Liping, Baixing Yan, Yang Ou, Huiping Liu, Lei Cheng, and Peng Jiao. 2022. "Effectiveness of Exogenous Fe2+ on Nutrient Removal in Gravel-Based Constructed Wetlands" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031475
APA StyleTian, L., Yan, B., Ou, Y., Liu, H., Cheng, L., & Jiao, P. (2022). Effectiveness of Exogenous Fe2+ on Nutrient Removal in Gravel-Based Constructed Wetlands. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031475





