Mitigating the Health Effects of Aqueous Cr(VI) with Iron-Modified Biochar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Preparation of the Biochar and Modified Biochar
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.3. Synthesis of Cr(VI)-Containing Wastewater
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sample Characterization
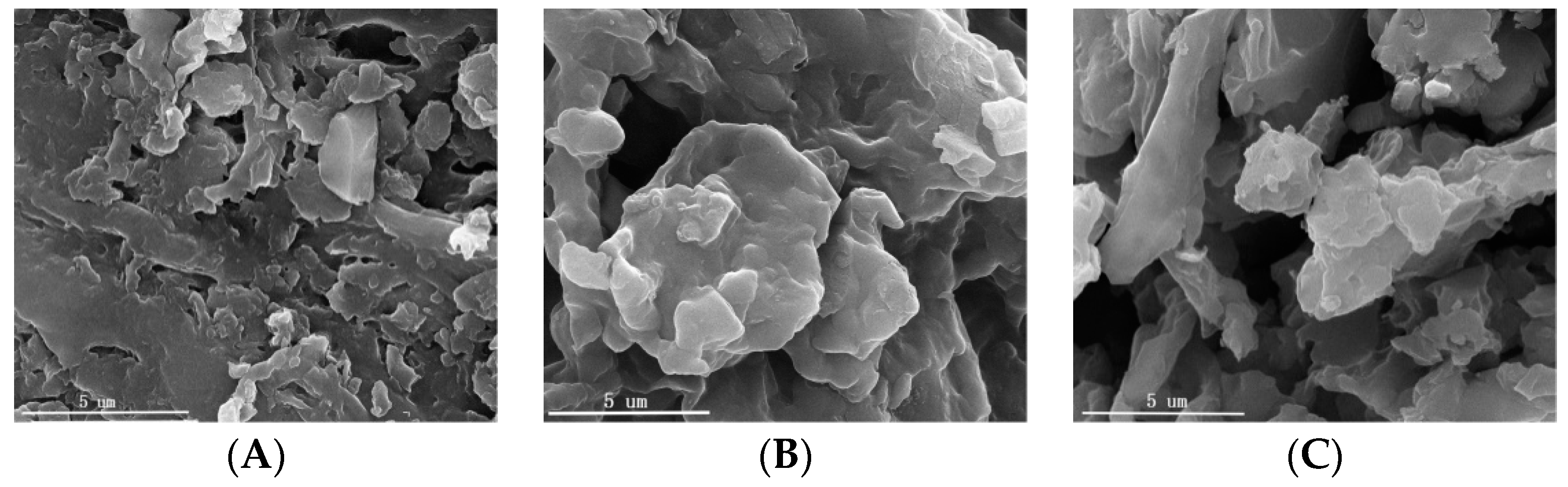
3.1.1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Images
3.1.2. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) Analysis
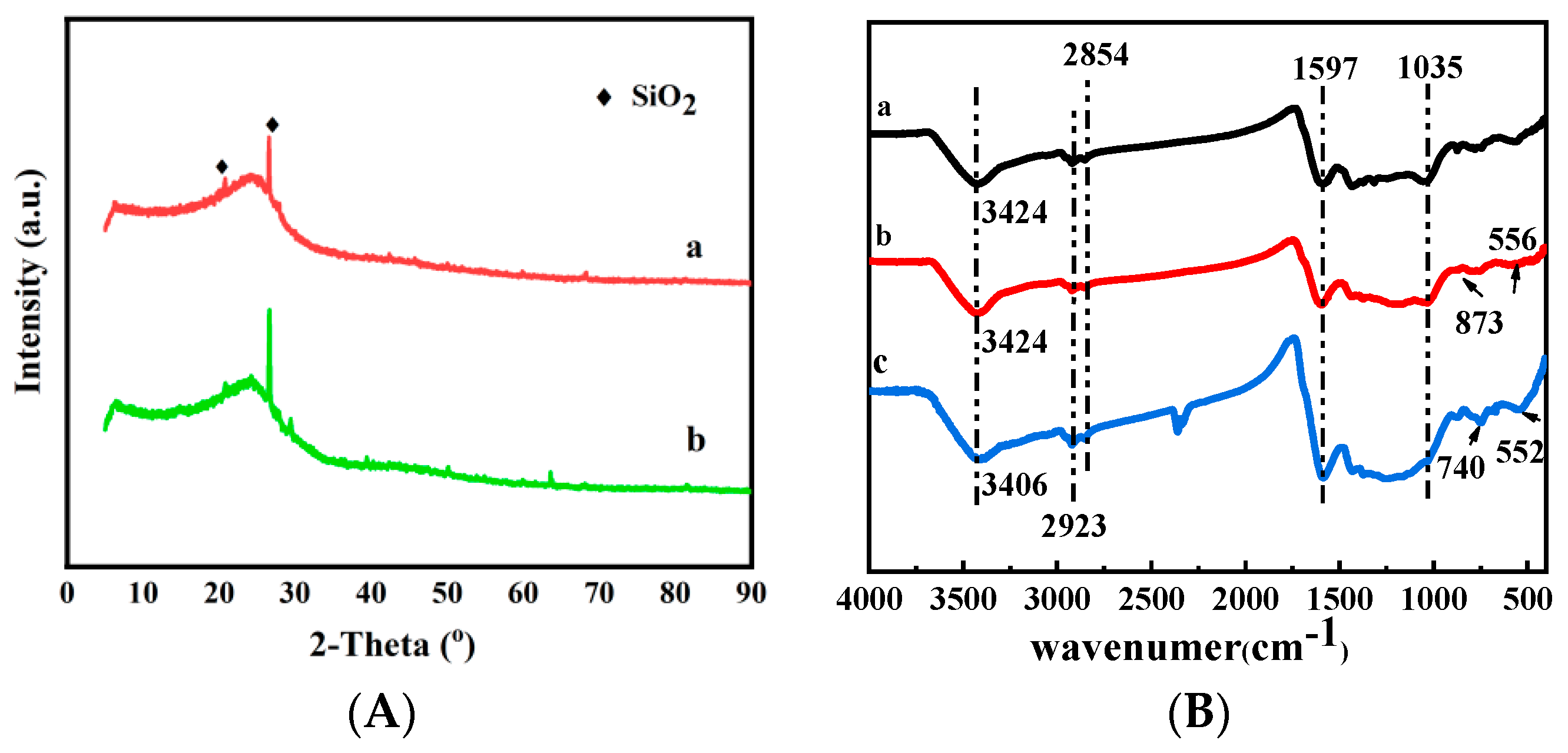
3.1.3. X-ray Diffractometer (XRD) Analysis
3.1.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
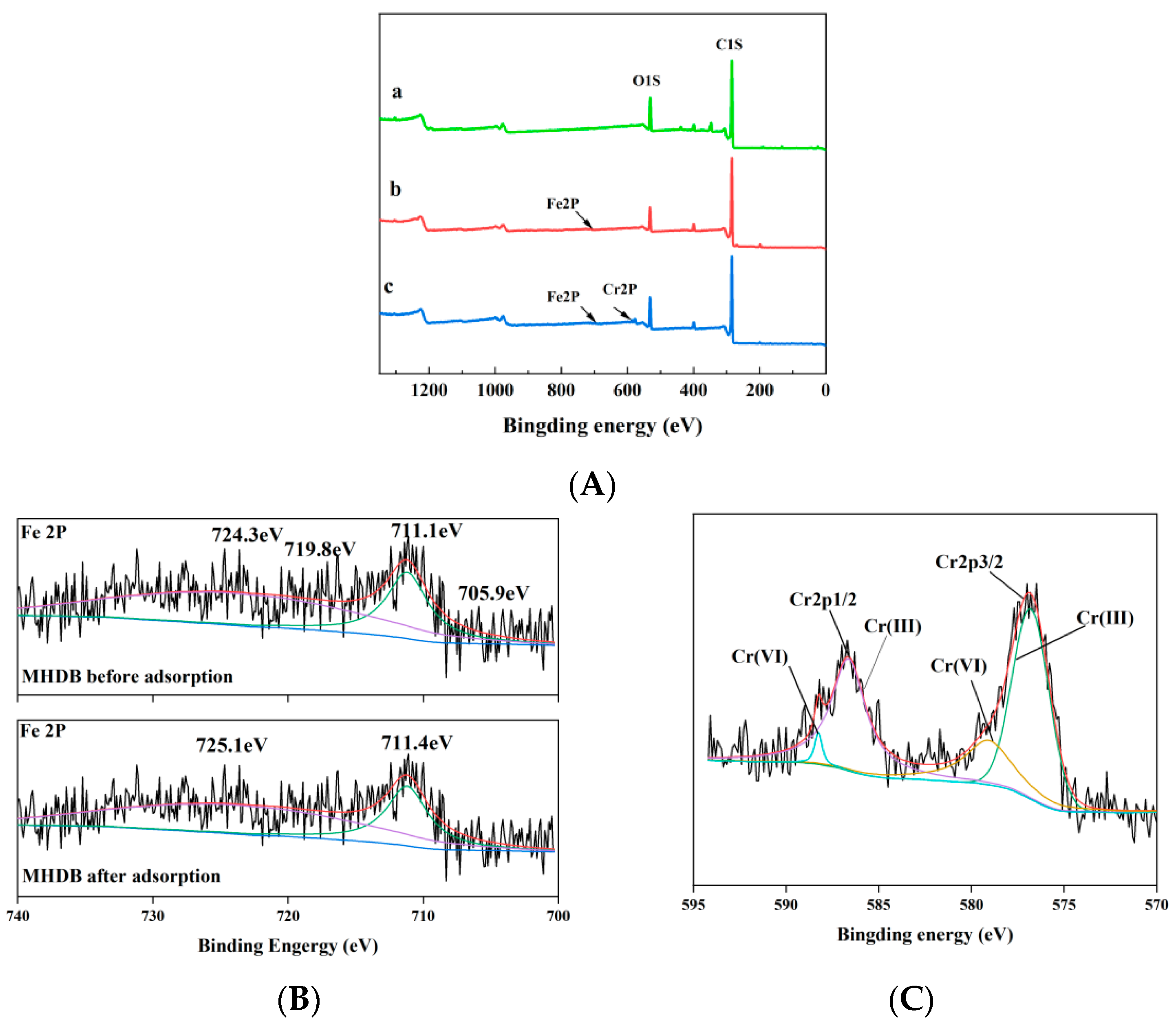
3.1.5. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Analysis
3.2. Adsorption Study
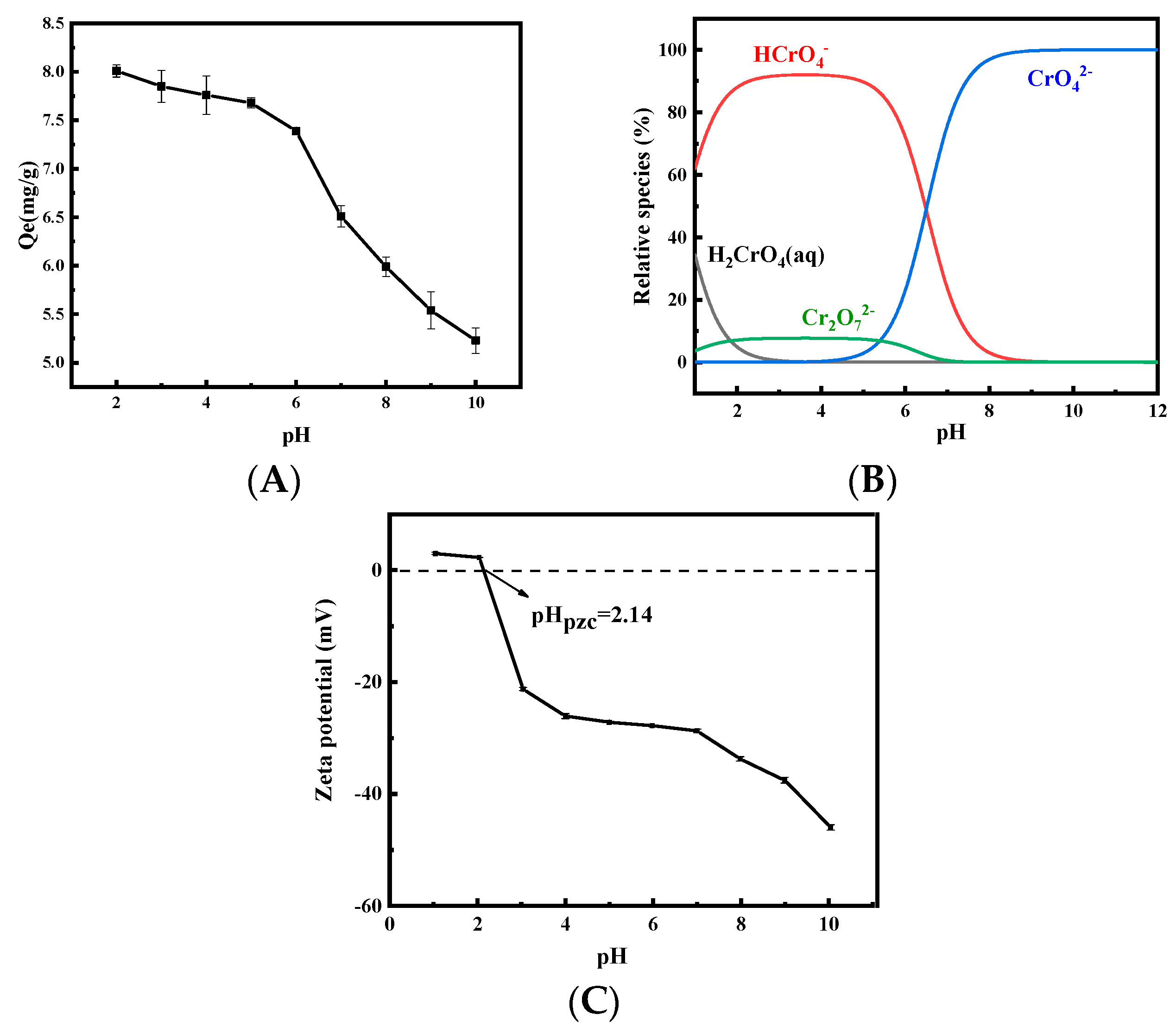
3.2.1. Effect of Initial Solution pH
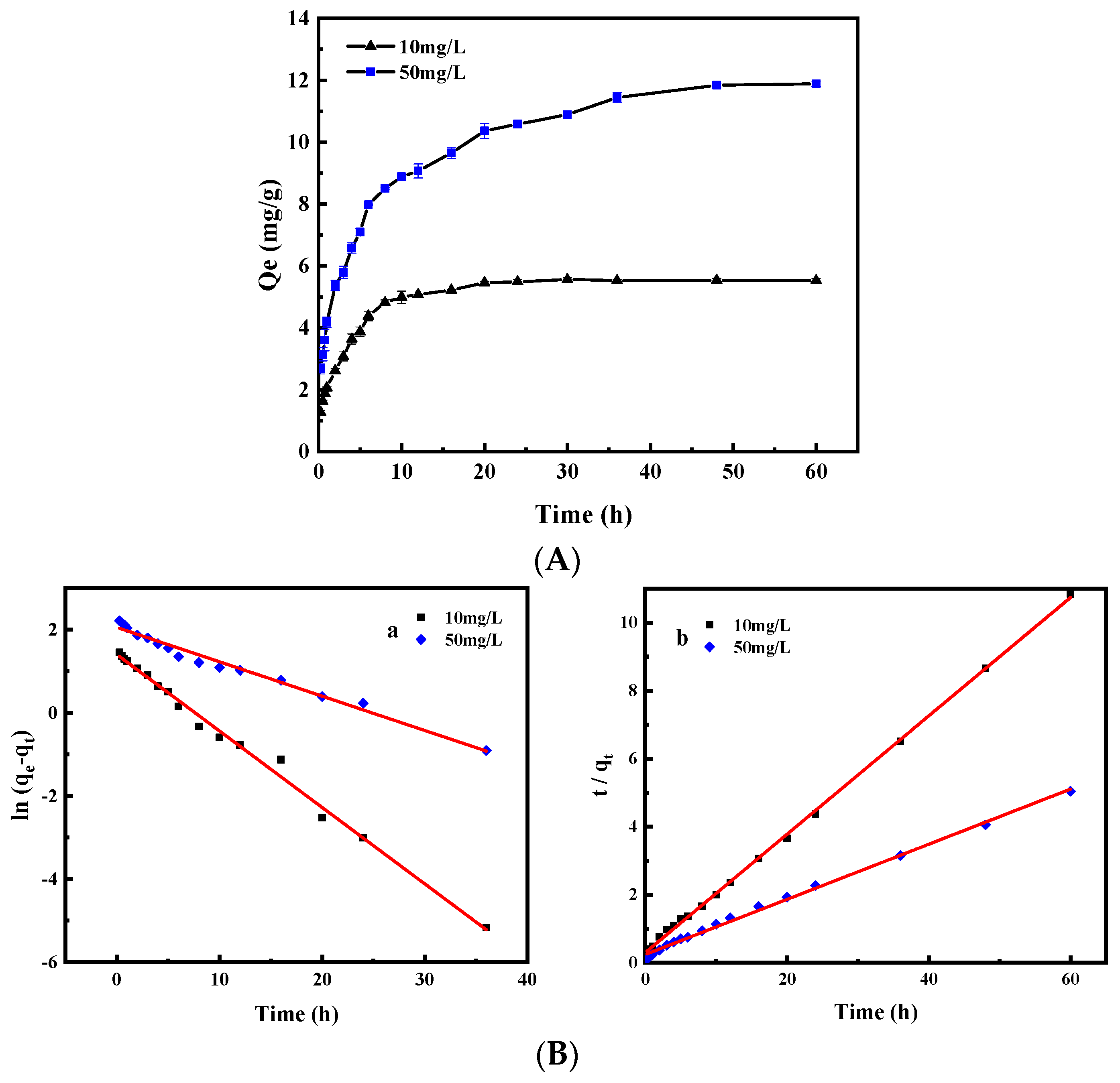
3.2.2. Effect of Adsorption Time and Adsorption Kinetics
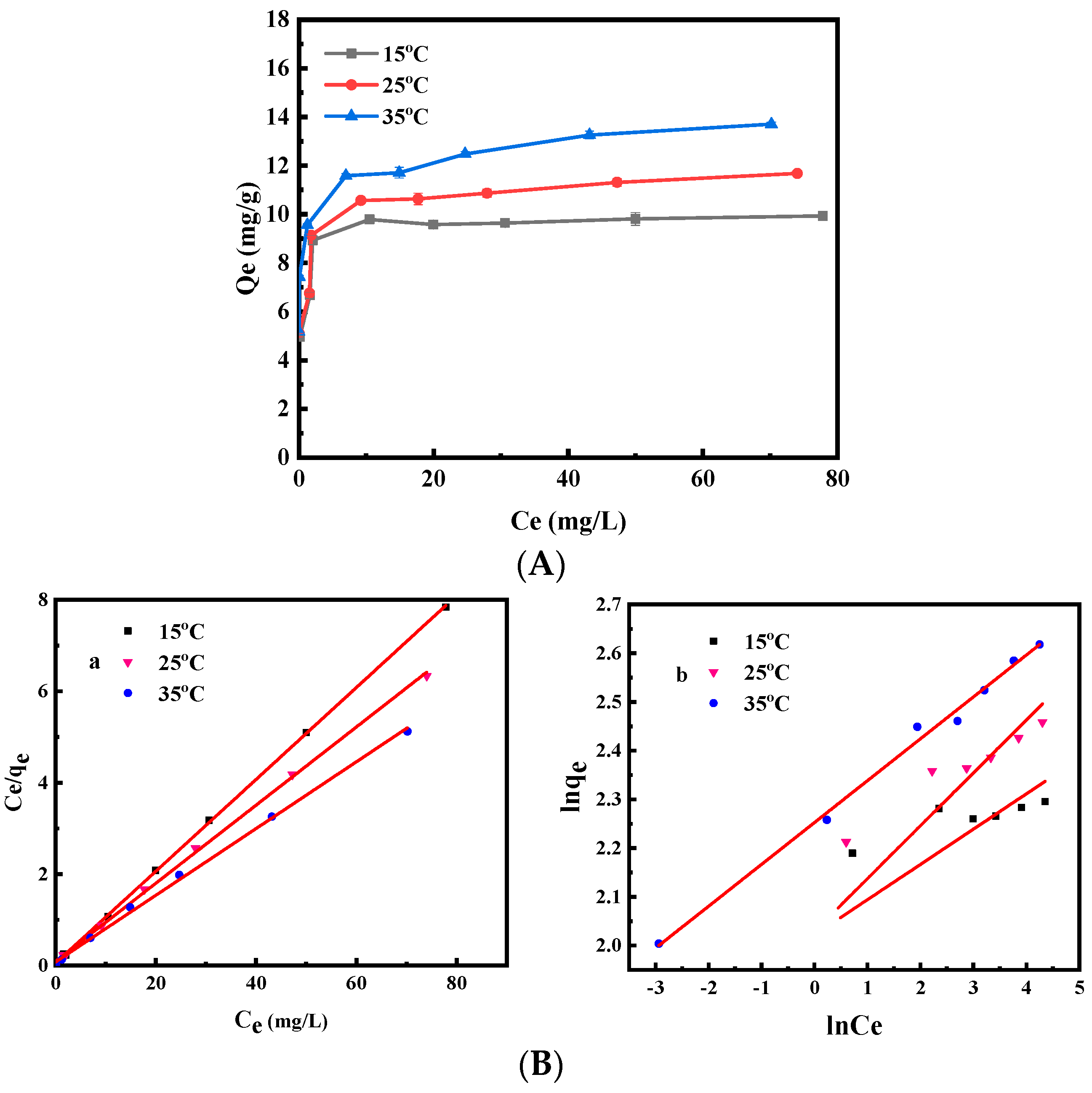
3.2.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3.2.4. Adsorption Thermodynamics
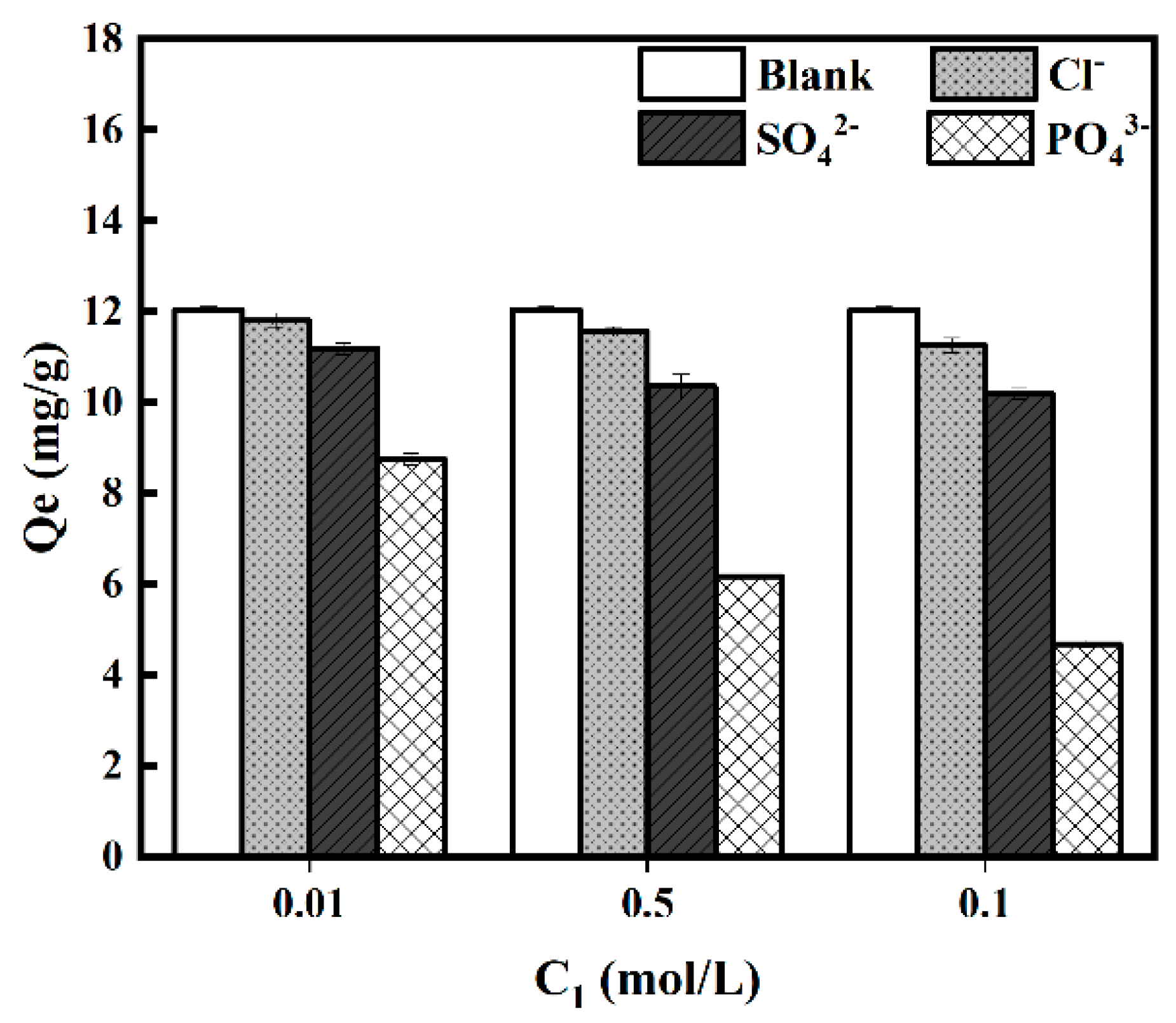
3.2.5. Effect of Co-Existing Ions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, X.; Zhao, H.P.; Liang, Y.; Chen, R. Energy level mediation of (BiO)2CO3 via Br doping for effificient molecular oxygen activation and ciproflfloxacin photodegradation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 258, 117966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhang, L.X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Bai, Y.C.; Guan, Y.T. Facile assembled N, S-codoped corn straw biochar loaded Bi2WO6 with the enhanced electron-rich feature for the efficient photocatalytic removal of ciprofloxacin and Cr(VI). Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, R.R.; Yue, C.L.; Qiu, J.L.; Liu, F.Q.; Li, A.M. Highly effificient sunlight-driven reduction of Cr(VI) by TiO2@NH2-MIL-88B(Fe) heterostructures under neutral conditions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 251, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Santanen, A.; Mäkelä, P.S.A. Recycling sludge on cropland as fertilizer-Advantages and risks. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 155, 104647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.R.; He, Q.; Zeng, G.M.; Tang, L.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.K.; Zeng, Y.L.; Zhao, F.; Wu, Y.A. Chromate removal by surface-modifified nanoscale zero-valent iron: Effect of different surface coatings and water chemistry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 471, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.P.; Wei, J.Y.; Hu, Y.; Wei, C.H. Fabrication of terminal amino hyperbranched polymer modified graphene oxide and its prominent adsorption performance towards Cr(VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 363, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, G.S.; Manna, A.; Baskaran, S.; Puhazhendi, P.; Ramchary, A.; Niraikulam, A.; Ramudu, K.N. Non-enzymatic reduction of Cr(VI) and it’s effective biosorption using heat-inactivated biomass: A fermentation waste material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, R.; Shi, Y.Y.; Gu, J.; Bi, J.W.; Yuan, H.R.; Luo, B.; Chen, Y. Aqueous Cr(VI) removal by biochar derived from waste mangosteen shells: Role of pyrolysis and modifification on its absorption process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Shahab, A.; Zhang, K.; Zeng, H.T.; Bacha, A.; Nabi, I.; Ullah, H. Comparative study on characterization and adsorption properties of phosphoric acid activated biochar and nitrogen-containing modified biochar employing Eucalyptus as a precursor. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 303, 127046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Ali, S.; Refay, Y.; Rizwan, M.; Alhammad, B.A.; El-Hendawy, S.E. Chromium resistant microbes and melatonin reduced Cr uptake and toxicity, improved physio-biochemical traits and yield of wheat in contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shan, R.; Lu, L.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. High-efficiency removal of Cr(VI) by modified biochar derived from glue residue. J. Clean. 2020, 254, 119935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, F.C.; Bourg, A.C.M. Aqueous geochemistry of chromium: A review. Water Res. 1991, 25, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Xie, X.J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, W.F.; Liu, P. Chemical processes of Cr(VI) removal by Fe-modified biochar under aerobic and anaerobic conditions and mechanism characterization under aerobic conditions using synchrotron-related techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.J.; Boada, R.; Cibin, C.; Palet, C. Enhancement of selective adsorption of Cr species via modifification of pine biomass. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.C.; Shao, J.G.; Li, Z.Q.; Yang, H.P.; Zhang, S.H.; Chen, H.P. Nano nickel embedded in N-doped CNTs-supported porous biochar for adsorption-reduction of hexavalent chromium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, U.; Shakoor, M.B.; Ali, S.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L. Adsorption-reduction performance of tea waste and rice husk biochars for Cr(VI) elimination from wastewater. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.M.; Tian, X.L.; Wang, C.H.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Chen, C.L. Metal-organic frameworks-derived 3D yolk shell-like structure Ni@carbon as a recyclable catalyst for Cr(VI) reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 123428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Tang, Y.P.; Tao, S.R. Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic study on removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions using low-cost adsorbent Alligator weed. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 148, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, H.T.; Pehlivan, E. Cr6+ rovemal using oleaster (Elaeagnus) seed and cherry (Prunus avium) stone biochar. Powder Technol. 2017, 306, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.W.; Yin, W.Z.; Li, Y.T.; Li, P.; Wu, J.H.; Jiang, G.B.; Gu, J.J.; Liang, H. Column study of enhanced Cr(VI) removal and longevity by coupled abiotic and biotic processes using Fe0 and mixed anaerobic culture. Water Res. 2017, 122, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.I.; Usman, A.R.; Ahmad, M.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Immobilization and mitigation of chromium toxicity in aqueous solutions and tannery waste-contaminated soil using biochar and polymer-modified biochar. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 129198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Yun, Z.J.; Shi, J.B.; Jiang, G.B. Research progress of heavy metal pollution in China: Sources, analytical methods, status, and toxicity. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Basumatary, A.K.; Kumar, R.V.; Ghoshal, A.K.; Pugazhenthi, G. Cross flow ultrafiltration of Cr (VI) using MCM-41, MCM-48 and Faujasite (FAU) zeolite-ceramic composite membranes. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakade, V.E.; Tavengwa, N.T.; Madikizela, L.M. Recent advances in hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solutions by adsorptive methods. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 26142–26164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiadi, N.; Dash, R.R.; Mohanty, C.R.; Patel, A.M. Comparative Studies of Adsorption of Chromium(VI) Ions onto Different Industrial Wastes. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2020, 24, 04020021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, E.; Almeida, O.; Brasil, H.; Moraes, D.; Reis, M.A.L. Adsorption of chromium(VI) on hydrotalcitehydroxyapatite material doped with carbon nanotubes: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 172, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.Q.; Yu, G.W.; Ndagijimana, P.; Wang, Y.; You, F.T.; Xing, Z.J.; Wang, Y. Effective adsorption of Direct Red 23 by sludge biochar based adsorbent: Adsorption kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanisms study. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 2424–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Dey, U.; Chattoraj, S.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Mondal, N.K. Modeling of the adsorptive removal of arsenic(III) using plant biomass: A bioremedial approach. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1307–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, H.R.; Deng, J.M.; Xie, Y.K.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, Y.J.; Hou, K.J.; Zeng, G.M. Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ge, C.Z.; Li, X.L.; Li, L.; Wang, B.; Lin, A.J.; Yang, W.J. Does soluble starch improve the removal of Cr(VI) by nZVI loaded on biochar? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.H.; Liu, Y.G.; Liu, S.B.; Jiang, L.H.; Tan, X.F.; Zeng, G.M.; Li, M.F.; Liu, S.J.; Tian, S.R.; Fang, Y. Activated magnetic biochar by one-step synthesis: Enhanced adsorption and coadsorption for 17β-estradiol and copper. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1530–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Liu, H.B.; Li, M.X.; Chen, T.H.; Chen, D.; Zou, X.H.; Frost, R.L. Green preparation of magnetic biochar for the effective accumulation of Pb(Ⅱ): Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.H.; Tang, J.C.; Huang, Y.; Gai, L.S.; Zeng, E.Y.; Liber, K.; Gong, Y.Y. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by a novel biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Jiao, X.Q.; Liu, N.; Lv, J.; Yang, Y.D. Enhanced removal of aqueous Cr( VI) by a green synthesized nano scale zero-valent iron supported on oak wood biochar. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.Q.; Dong, Y.P.; Zhang, T.H.; Dong, L.; Guo, C.W.; Rao, Z.H. Experimental Study on Herb Residue Gasifification in an Air-Blown Circulating Fluidized Bed Gasififier. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 13264–13273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.T.; Zeng, H.Z.; Zhang, H.; Shahab, A.; Zhang, K.; Lu, Y.Q.; Nabi, I.; Naseem, F.; Ullah, H. Efficient adsorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous environments by phosphoric acid activated eucalyptus biochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.G.; Shin, J.W.; Kwak, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Son, C.J.; Kim, G.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Chon, K.M. Enhanced Adsorption Capacities of Fungicides Using Peanut Shell Biochar via Successive Chemical Modifification with KMnO4 and KOH. Separations 2021, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Y.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.P.; Gao, Y. Mechanisms of Cr(VI) removal by FeCl3-modifified lotus stem-based biochar (FeCl3@LS-BC) using mass-balance and functional group expressions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 551, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.X.; Yu, G.W.; Mo, W.T.; Zhang, C.J.; Huang, H.; Li, S.; Gao, M.; Lu, X.J.; Zhang, B.P.; Zhu, H.P. Enhanced phosphate sequestration by Fe(III) modifified biochar derived from coconut shell. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 10425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, D.; Yoon, K.; Kwon, E.E.; Biswas, J.K.; Song, H. Fabrication of magnetic biochar as a treatment medium for As(V) via pyrolysis of FeCl3-pretreated spent coffee ground. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.Y.; Sun, X.H.; Xie, D.L.; Wang, M.J.; Fan, A.; Chen, Y.Y.; Shu, C.; Zheng, C.M.; Hu, W.B. Mesoporous Graphitic Carbon-Encapsulated Fe2O3 Nanocomposite as High-Rate Anode Material for Sodium-Ion Batteries. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 14786–14793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Ding, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.Q.; Li, H.H.; Lu, L. Removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by magnetic biochar derived from bagasse. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.S.; Ho, S.; Huang, X.C.; Wang, D.W.; Yang, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Cao, X.D.; Ma, F. Magnetic Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron Assisted Biochar: Interfacial Chemical Behaviors and Heavy Metals Remediation Performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9673–9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, J.P. Biosorption of hexavalent chromium onto raw and chemically modified Sargassum sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Yan, C.Z.; Luo, Z.X.; Fang, H.D.; Hu, S.G.; Cao, Y.L. Synthesis of a novel ternary HA/Fe-Mn oxide-loaded biochar composite and its application in cadmium(II) and arsenic(V) adsorption. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 85, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.C.; Leivisk, T.; Taskila, S.; Tanskanen, J. Iron-loaded Sphagnum moss extract residue for phosphate removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 218, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.H.; Mishra, S.; Poonguzhali, E.; Rajesh, M.; Tamilarasan, K. Fractionation and characterization of lignin from waste rice straw: Biomass surface chemical composition analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benis, K.Z.; Soltan, J.; Mcphedran, K.N. Electrochemically modified adsorbents for treatment of aqueous arsenic: Pore diffusion in modified biomass vs. Biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.A.Q.; Zhao, Z.W.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.P.; Lei, Z.F.; Zhang, Z.Y. Insight into effificient phosphorus removal/recovery from enhanced methane production of waste activated sludge with chitosan-Fe supplementation. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, P.; Xiao, J.; Li, H.B.; Wang, C.X.; Yang, G.W. A microfifibre assembly of an iron-carbon composite with giant magnetisation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Wu, T.; Geng, X.; Ru, J.J.; Hua, Y.X.; Bu, J.J.; Xue, Y.; Wang, D. The role of electrolyte ratio in electrodeposition of nanoscale Fe-Cr alloy from choline chloride-ethylene glycol ionic liquid: A suitable layer for corrosion resistance. J. Mol. Liq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Yang, X.N.; Sun, R.H.; Wang, X.Z.; Yin, W.Q.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, J. The contribution of lignocellulosic constituents to Cr(VI) reduction capacity of biochar-supported zerovalent iron. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.X.; Huang, X.B.; Tang, Z.W.; Huang, Q.F.; Niu, F.L.; Wang, X.K. Polymer-based nanocomposites for heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solution: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 3562–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.H.; Tian, X.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, B.; Akindolie, M.S.; Hu, Q.; Feng, C.C.; Feng, Y.; Meng, X.L.; Zhang, Y. Multi-component adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) onto microwave-functionalized cellulose: Kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, mechanisms and application for electroplating wastewater purifification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, F.B.; Tian, Q.W.; Nie, C.R.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhu, Z.L.; Fang, L.P.; Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, S.W. A highly porous animal bone-derived char with a superiority of promoting nZVI for Cr(VI) sequestration in agricultural soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 104, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahanty, B.; Mondal, S. Synthesis of Magnetic Biochar Using Agricultural Waste for the Separation of Cr(VI) From Aqueous Solution. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 10803–10818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.G.; Wei, J.X.; Li, F.X.; Qu, X.L.; Liang, S.; Zhang, H.D.; Yu, Q.J. Synthesis, characterization and hexavalent chromium adsorption characteristics of Aluminum and sucrose-incorporated tobermorite. Materials. 2017, 10, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, M.X.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhang, R.Q.; Yang, X.; Tang, C.F.; Hu, X.J. A novel preparation of S-nZVI and its high efficient removal of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezak, N.; Bahmani, A.; Bettahar, N. Adsorptive removal of P(V) and Cr(VI) by calcined Zn-Al-Fe ternary LDHs. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 2504–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Gu, L.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Cao, L.; Hu, X.X. Sorption behavior of Cr(VI) on pineapple-peel-derived biochar and the inflfluence of coexisting pyrene. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 111, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, H.; Kar, Y. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by bio-chars obtained during biomass pyrolysis. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, N.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lyu, T. Sustainable Chromium (VI) Removal from Contaminated Groundwater Using Nano-Magnetite-Modifified Biochar via Rapid Microwave Synthesis. Molecules 2021, 26, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Zanli, B.L.G.L.; Chen, J. O/N/P-doped biochar induced to enhance adsorption of sulfonamide with coexisting Cu2+/Cr(VI) by air pre-oxidation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qhubu, M.C.; Mgidlana, L.G.; Madikizela, L.M.; Pakade, V.E. Preparation, characterization and application of activated clay biochar composite for removal of Cr(VI) in water: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 260, 124165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.H.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Tufail, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Shang, J.Y. Green Sustainable and Highly Efficient Hematite Nanoparticles Modified Biochar-clay Granular Composite for Cr(VI) Removal and Related Mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zhao, C.F.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Liu, K.Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.T.; Qiu, R.L. Microscopic mechanism about the selective adsorption of Cr(VI) from salt solution on O-rich and N-rich biochars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| C0 mg/L | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe | k1 | R2 | qe | k2 | R2 | |
| 10 | 4.05 | 0.1838 | 0.9925 | 5.74 | 0.1741 | 0.9991 |
| 50 | 7.78 | 0.0826 | 0.9789 | 12.33 | 0.0811 | 0.9962 |
| Reaction Temperature °C | Langmuir Equation | Freundlich Equation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm | KL | R2 | Kf | 1/n | R2 | |
| 15 | 9.95 | 2.039 | 0.9998 | 7.551 | 0.0724 | 0.5089 |
| 25 | 11.70 | 0.972 | 0.9989 | 7.605 | 0.1085 | 0.7089 |
| 35 | 13.70 | 0.979 | 0.9979 | 9.511 | 0.0859 | 0.9924 |
| Reaction Temperature | ΔG0 | ΔH0 | ΔS0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 288 K | −0.15 | 14.74 | 51.73 |
| 298 K | −0.67 | ||
| 308 K | −1.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Z.; Duan, X. Mitigating the Health Effects of Aqueous Cr(VI) with Iron-Modified Biochar. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031481
Zheng Z, Duan X. Mitigating the Health Effects of Aqueous Cr(VI) with Iron-Modified Biochar. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031481
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Zhihong, and Xiaohan Duan. 2022. "Mitigating the Health Effects of Aqueous Cr(VI) with Iron-Modified Biochar" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031481
APA StyleZheng, Z., & Duan, X. (2022). Mitigating the Health Effects of Aqueous Cr(VI) with Iron-Modified Biochar. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031481






