Electrochemical Disinfection of Simulated Ballast Water Using RuO2-TiO2/Ti Electrode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
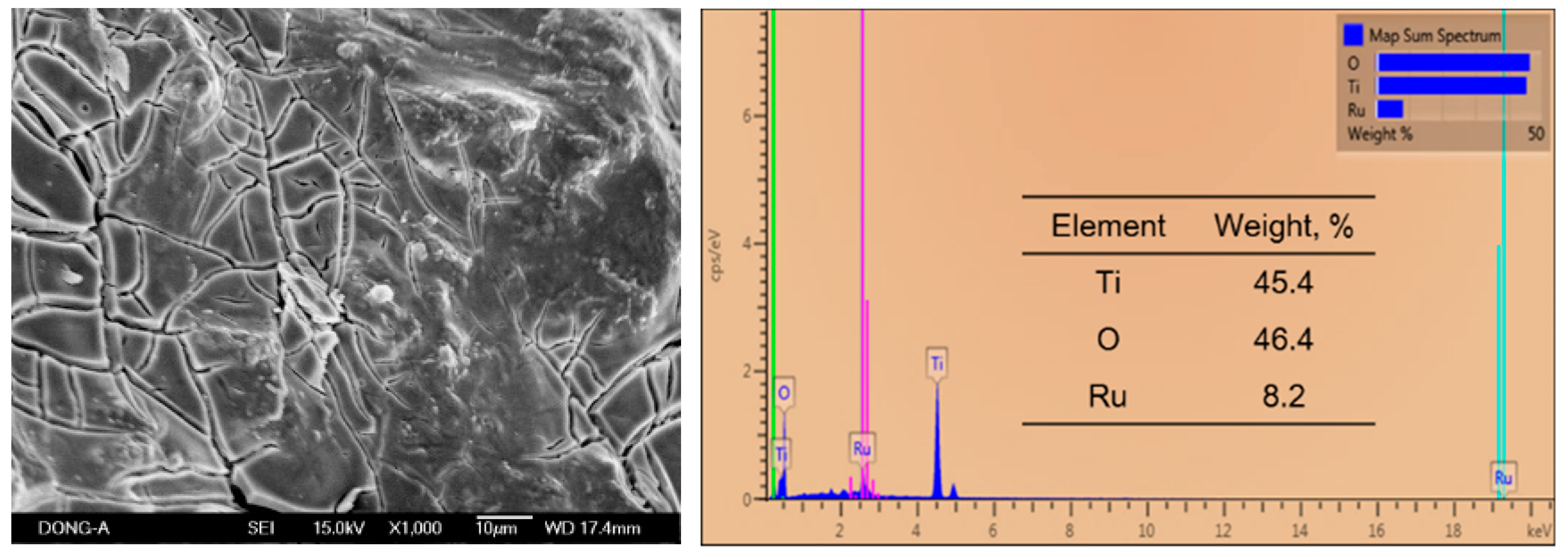
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Electrode
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.3. Set-Up of the Electrochemical Reactor
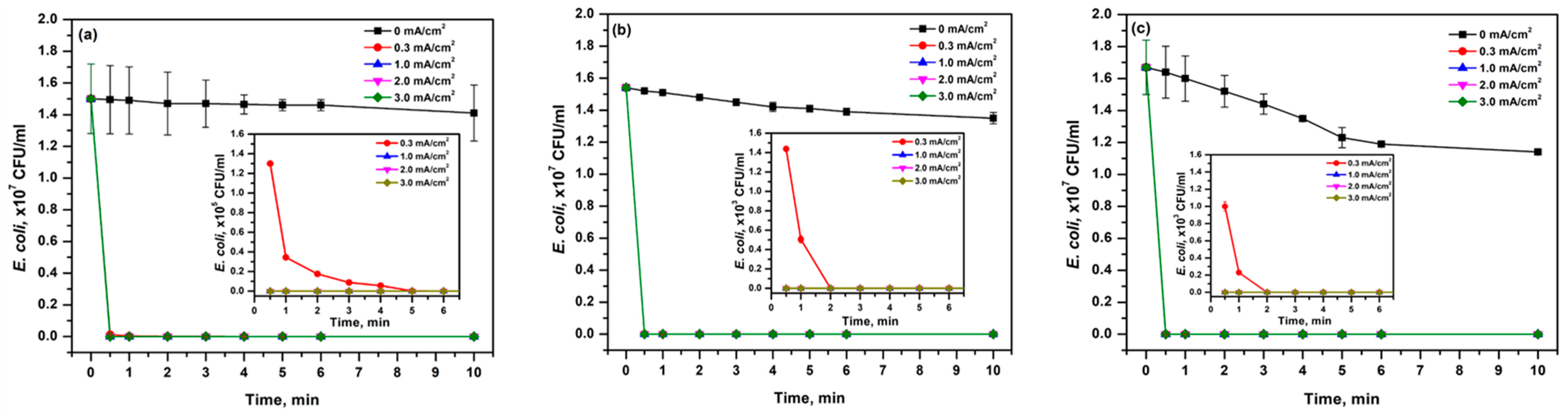
2.4. Disinfection Experiments
2.5. Bacterial Sample Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization and Surface Morphology Analysis
3.2. Effect of Current Density
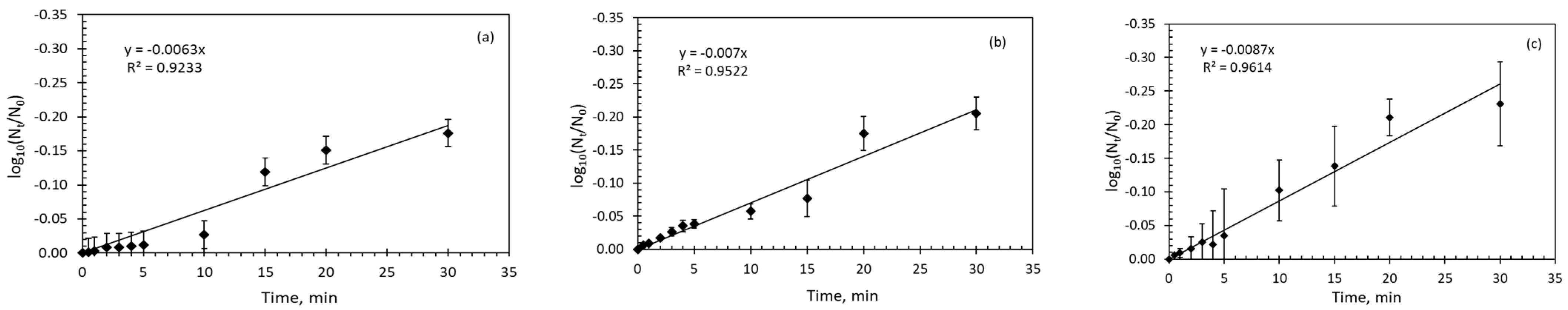
3.3. Kinetics of E. coli Inactivation
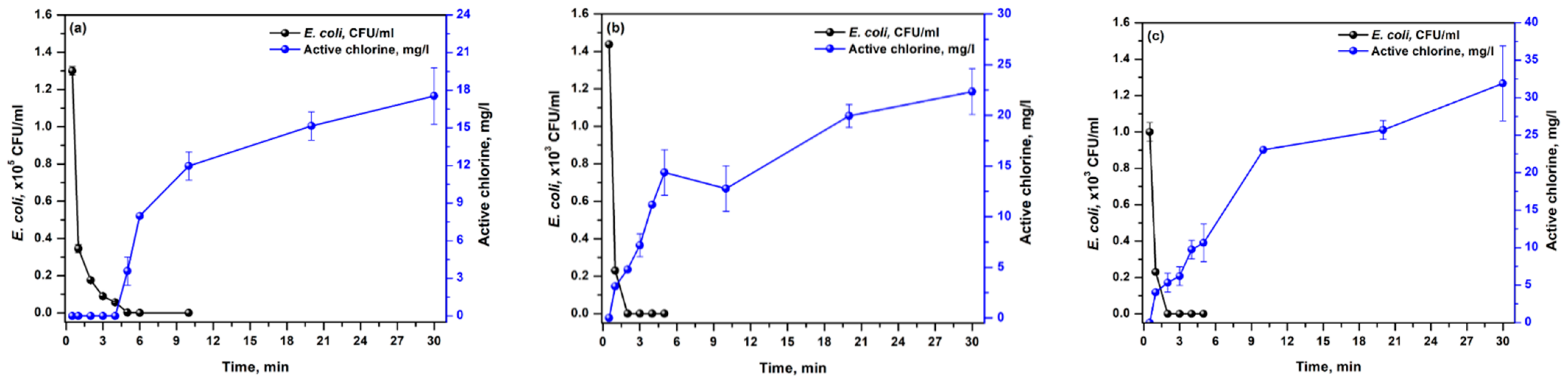
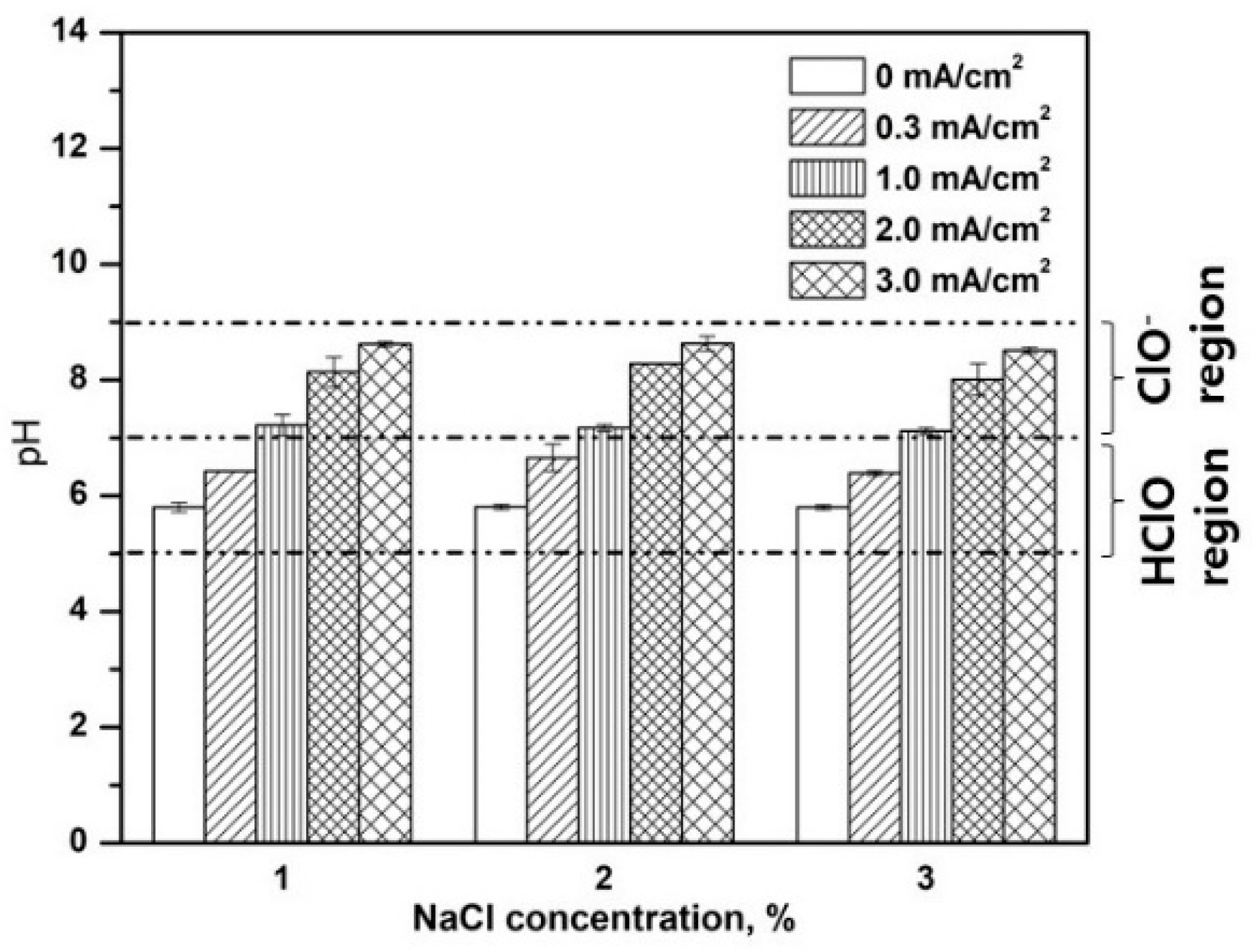
3.4. Effect of NaCl Concentration
3.5. Mechanism of E. coli Inactivation
3.6. Energy Consumption and Cost Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lakshmi, E.; Priya, M.; Achari, V.S. An overview on the treatment of ballast water in ships. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 199, 105296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayinli, B.; Dong, Y.; Park, Y.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Recent progress and challenges facing ballast water treatment—A review. Chemosphere 2021, 132776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.M.; Fofonoff, P.W.; Carlton, J.T.; Wonham, M.J.; Hines, A.H. Invasion of coastal marine communities in North America: Apparent patterns, processes, and biases. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2000, 31, 481–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallegraeff, G.M.; Bolch, C.J. Transport of toxic dinoflagellate cysts via ships’ ballast water. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1991, 22, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.W.; Frazier, M.; Smith, G.E.; Perry, E.S.; Ruiz, G.M.; Tamburri, M.N. Enumerating sparse organisms in ships’ ballast water: Why counting to 10 is not so easy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3539–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollasch, S.; David, M.; Voigt, M.L.; Dragsund, E.; Hewitt, C.L.; Fukuyo, Y. Critical review of the IMO international convention on the management of ships’ ballast water and sediments. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.F.; Mahamud, M.M.; Lavin, A.G.; Bueno, J.L. The regrowth of phytoplankton cultures after UV disinfection. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 67, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelossi, E.; Faimali, M. Comparative assessment of antimicrobial efficacy of new potential biocides for treatment of cooling and ballast waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 356, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.D.; Liu, Z.Q.; Salhi, E.; Höfer, T.; Werschkun, B.; Von Gunten, U. Formation of disinfection by-products during ballast water treatment with ozone, chlorine, and peracetic acid: Influence of water quality parameters. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2015, 1, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavand, M.R.; McClintock, J.B.; Amsler, C.D.; Peters, R.W.; Angus, R.A. Effects of sonication and advanced chemical oxidants on the unicellular green alga Dunaliella tertiolecta and cysts, larvae and adults of the brine shrimp Artemia salina: A prospective treatment to eradicate invasive organisms from ballast water. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.K.; Ahn, Y. Electrochemical removal and recovery of iron from groundwater using non-corrosive electrodes. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 211, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.K.; Ha, M.; Shin, S.; Seo, M.; Jang, J.; Jo, S.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y.; Kang, P.; et al. Electrochemical effect on bioleaching of arsenic and manganese from tungsten mine wastes using Acidithiobacillus spp. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Brillas, E. A critical review over the electrochemical disinfection of bacteria in synthetic and real wastewaters using a boron-doped diamond anode. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2021, 25, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, H. Electrochemical disinfection—State of the art and tendencies. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 28, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Särkkä, H.; Vepsäläinen, M.; Pulliainen, M.; Sillanpää, M. Electrochemical inactivation of paper mill bacteria with mixed metal oxide electrode. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanayakkara, K.G.N.; Alam, A.K.M.K.; Zheng, Y.M.; Chen, J.P. A low-energy intensive electrochemical system for the eradication of Escherichia coli from ballast water: Process development, disinfection chemistry, and kinetics modeling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemian, S.; Asadishad, B.; Omanovic, S.; Tufenkji, N. Electrochemical disinfection of bacteria-laden water using antimony-doped tin-tungsten-oxide electrodes. Water Res. 2017, 126, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annamalai, S.; Santhanam, M.; Sudanthiramoorthy, S.; Pandian, K.; Pazos, M. Greener technology for organic reactive dye degradation in textile dye-contaminated field soil and in-situ formation of “electroactive species” at the anode by electrokinetics. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3552–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Logan, B.E. Electrochemical technologies for wastewater treatment and resource reclamation. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 800–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalz, V.; Dittmar, T.; Haaken, D.; Worch, E. Electrochemical disinfection of biologically treated wastewater from small treatment systems by using boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrodes—Contribution for direct reuse of domestic wastewater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 5260–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Hu, W.; Hong, J.; Sandoe, S. Electrochemical disinfection of simulated ballast water on PbO2/graphite felt electrode. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 105, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacasa, E.; Tsolaki, E.; Sbokou, Z.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Mantzavinos, D.; Diamadopoulos, E. Electrochemical disinfection of simulated ballast water on conductive diamond electrodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusmão, I.C.C.P.; Moraes, P.B.; Bidoia, E.D. Studies on the electrochemical disinfection of water containing Escherichia coli using a dimensionally stable anode. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2010, 53, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.J.; Finn, D.D.; Wyeth, M.S.; Teel, A.L. Performance comparison of tin oxide anodes to commercially available dimensionally stable anodes. Water Environ. Res. 2008, 80, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, S.; Cusick, R.D. Electrochemical disinfection in water and wastewater treatment: Identifying impacts of water quality and operating conditions on performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3470–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirés, I.; Brillas, E.; Oturan, M.A.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Panizza, M. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: Today and tomorrow. A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8336–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Bai, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lu, G. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over Ru-doped ceria catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 126, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Suntivich, J.; May, K.J.; Perry, E.E.; Shao-Horn, Y. Synthesis and Activities of Rutile IrO2 and RuO2 Nanoparticles for Oxygen Evolution in Acid and Alkaline Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panić, V.V.; Jovanović, V.M.; Terzić, S.I.; Barsoum, M.W.; Jović, V.D.; Dekanski, A.B. The properties of electroactive ruthenium oxide coatings supported by titanium-based ternary carbides. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanam, M.; Annamalai, S.; Sudanthiramoorthy, S.; Gopalakrishnan, R. A simple strategy for monitoring of aromatic degradation in chloride mediated electrooxidation process. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 75528–75532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, P.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Asokan, K.; Subramanian, K.; Arumugam, V. An Improved Process for the Preparation of Insoluble Non-Precious Metal Oxide Anode Doped with Platinum Group Metal Oxide to Be Used in Electrochemical Processes. Indian Patent 178184, 18 December 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Tsolaki, E.; Pitta, P.; Diamadopoulos, E. Electrochemical disinfection of simulated ballast water using Artemia salina as indicator. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, S.; Sundaram, M.; Curras, M.P. Integrated approach of chemical and electrodialysis process in textile effluent contaminated groundwater for irrigation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3190–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, S.R.; Moore, J.A. Modeling enteric bacterial die-off: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1986, 27, 411–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deborde, M.; von Gunten, U. Reactions of chlorine with inorganic and organic compounds during water treatment—Kinetics and mechanisms: A critical review. Water Res. 2008, 42, 13–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Kim, C.; Yoon, J. The effect of electrode material on the generation of oxidants and microbial inactivation in the electrochemical disinfection processes. Water Res. 2009, 43, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Qu, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Lei, P. Inactivation of Microcystis aeruginosa by continuous electrochemical cycling process in tube using Ti/RuO2 electrodes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4633–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; McCarthy, D.T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Deletic, A. Stormwater disinfection using electrochemical oxidation: A feasibility investigation. Water Res. 2018, 140, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, M.V.B.; Sene, J.J.; Selcuk, H.; Anderson, M.A. Photoelectrocatalytic production of active chlorine on nanocrystalline titanium dioxide thin-film electrodes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 3203–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, C.; Ureña de Vivanco, M.; Rajab, M.; Müller, E.; Letzel, T.; Helmreich, B. Rapid inactivation of waterborne bacteria using boron-doped diamond electrodes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3061–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Current Density, mA/cm2 | Kinetics | NaCl conc., % (w/v) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 0 | First-order | |||
| R2 * | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.96 | |
| 0.3 | First-order | |||
| R2 | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.84 | |
| NaCl, % (w/v) | Current Density, mA/cm2 | Electroactive Chlorine Species, mg/L |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.3 | 17.50 ± 2.25 * |
| 1 | 55.83 ± 1.12 | |
| 2 | 156.34 ± 10.15 | |
| 3 | 207.39 ± 13.15 | |
| 2 | 0.3 | 22.30 ± 2.25 |
| 1 | 60.62 ± 7.89 | |
| 2 | 169.11 ± 14.66 | |
| 3 | 252.06 ± 1.12 | |
| 3 | 0.3 | 31.90 ± 5.01 |
| 1 | 79.76 ± 9.02 | |
| 2 | 162.72 ± 15.79 | |
| 3 | 262.35 ± 41.36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Annamalai, S.; Futalan, C.C.; Ahn, Y. Electrochemical Disinfection of Simulated Ballast Water Using RuO2-TiO2/Ti Electrode. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031835
Annamalai S, Futalan CC, Ahn Y. Electrochemical Disinfection of Simulated Ballast Water Using RuO2-TiO2/Ti Electrode. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031835
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnnamalai, Sivasankar, Cybelle Concepcion Futalan, and Yeonghee Ahn. 2022. "Electrochemical Disinfection of Simulated Ballast Water Using RuO2-TiO2/Ti Electrode" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031835
APA StyleAnnamalai, S., Futalan, C. C., & Ahn, Y. (2022). Electrochemical Disinfection of Simulated Ballast Water Using RuO2-TiO2/Ti Electrode. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031835







