Renoprotective Effects of Mangiferin: Pharmacological Advances and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
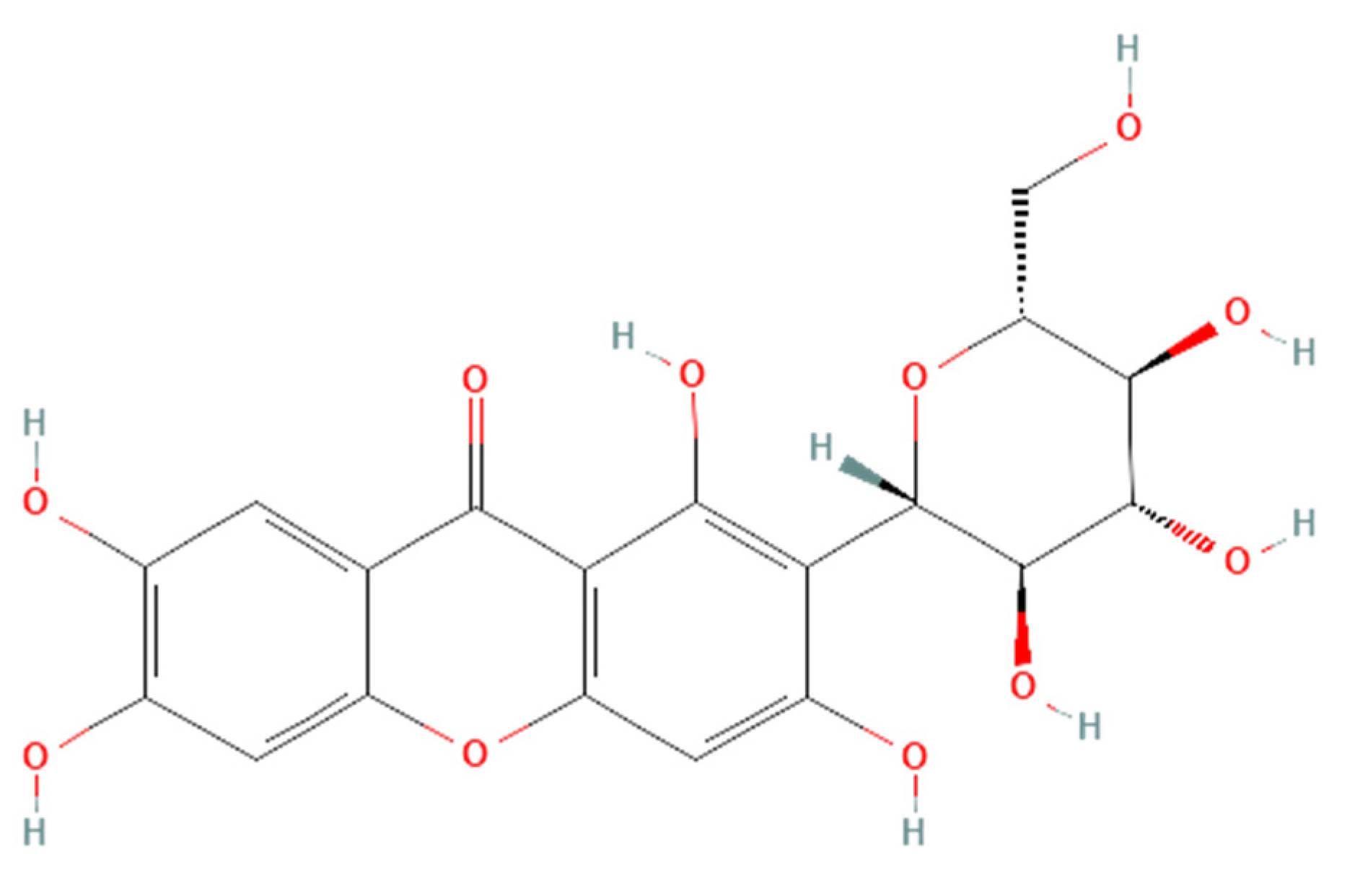
3. Mangiferin: Natural Sources and Extraction Methods
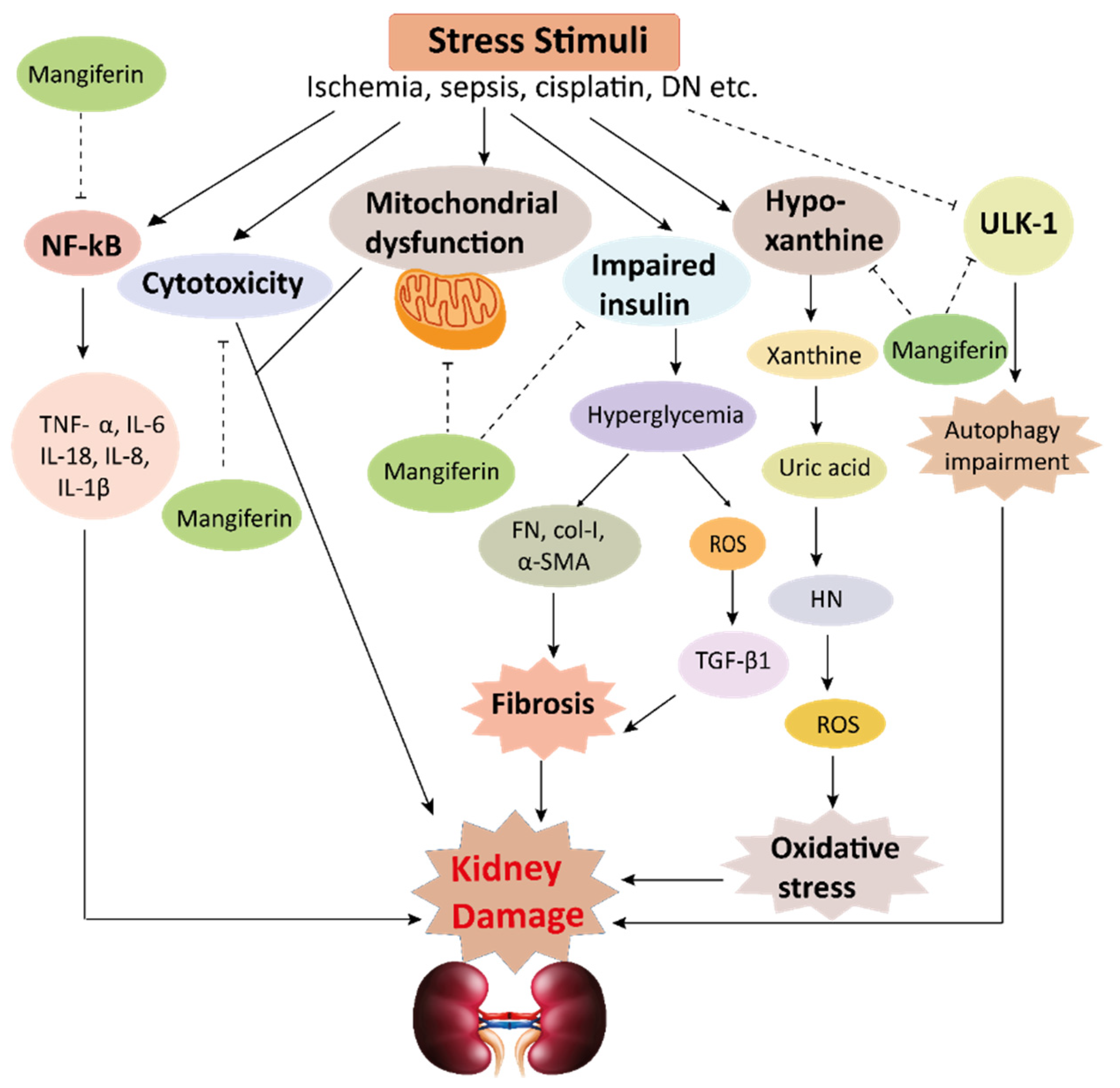
4. Pharmacological Effects of Mangiferin on Kidney Diseases
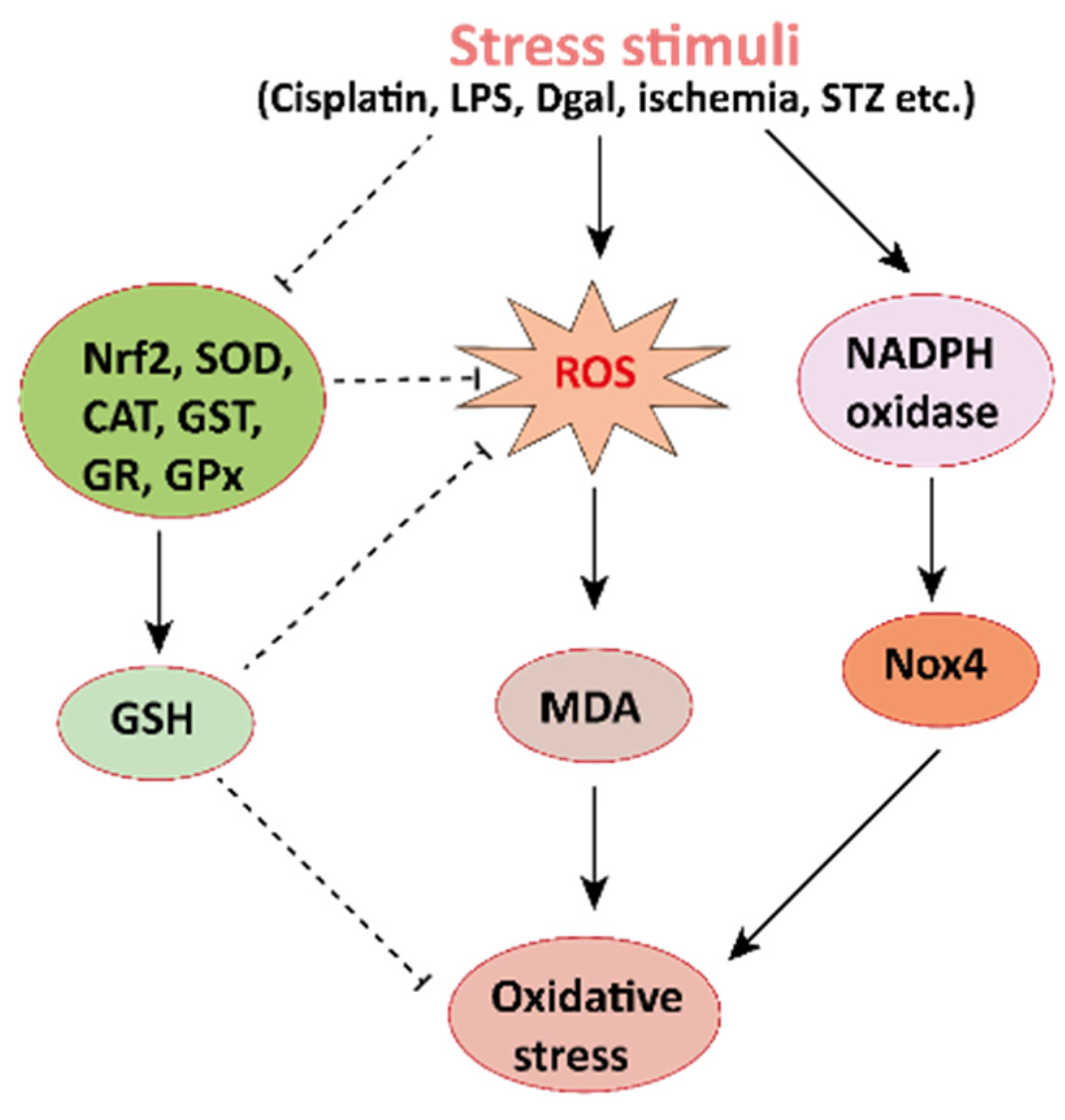
4.1. Effects of Mangiferin on Renal Oxidative Stress
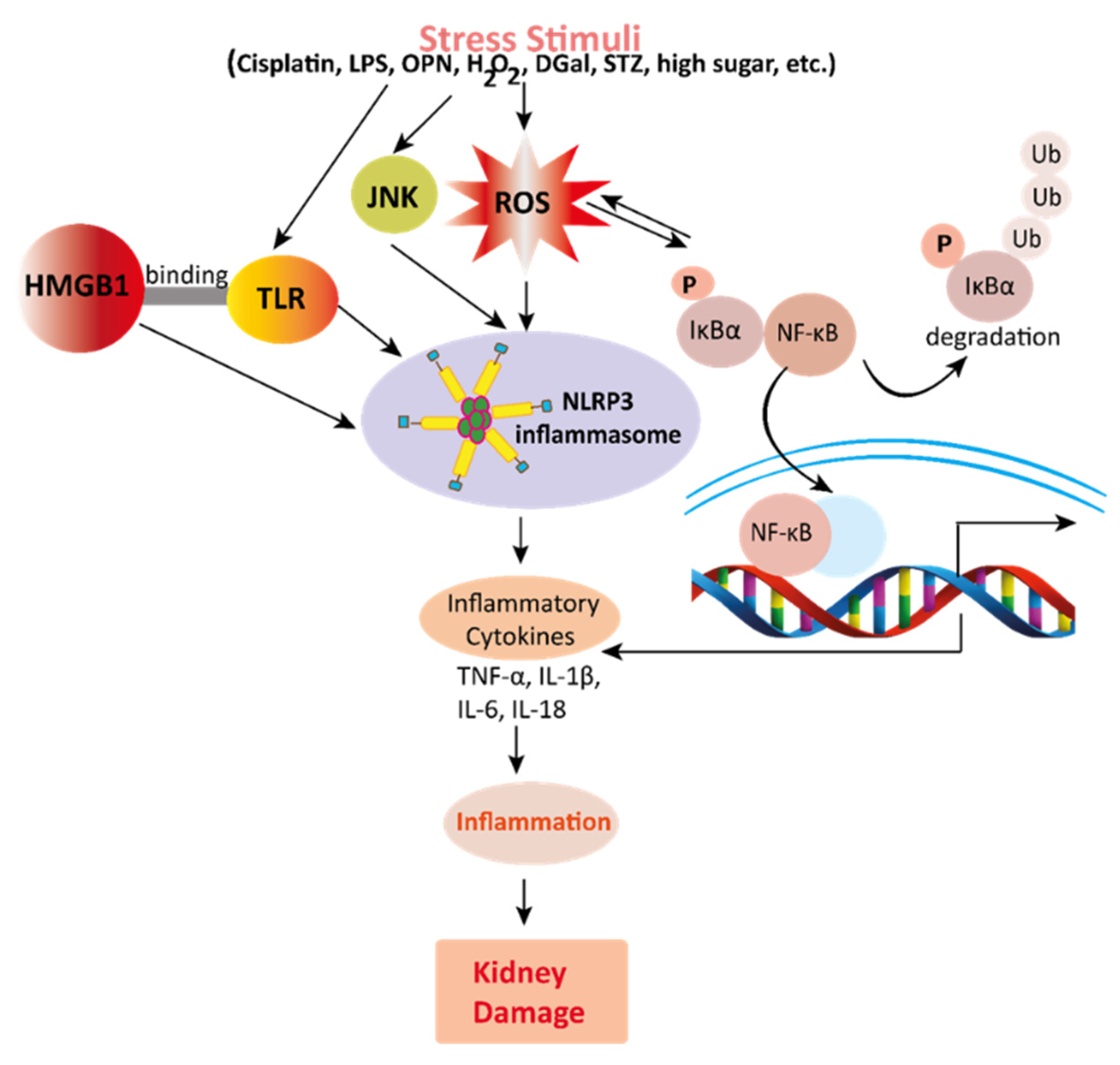
4.2. Effects of Mangiferin on Renal Inflammation
4.3. Effects of Mangiferin on Renal Fibrosis
4.4. Effects of Mangiferin against Other Kidney Pathologies
5. Biosynthesis and Bioavailability of Mangiferin
6. Pharmacological Advances of Mangiferin-Based Drug Development
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kassebaum, N.J.; Arora, M.; Barber, R.M.; Brown, J.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Coates, M.M.; Coggeshall, M.; Cornaby, L.; et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 315 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE), 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1603–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chawla, L.S.; Eggers, P.W.; Star, R.A.; Kimmel, P.L. Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease as Interconnected Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matkowski, A.; Kus, P.; Goralska, E.; Wozniak, D. Mangiferin—A bioactive xanthonoid, not only from mango and not just antioxidant. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekar, M. Molecules of interest-mangiferin—A review. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2015, 5, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyotshna; Khare, P.; Shanker, K. Mangiferin: A review of sources and interventions for biological activities. BioFactors 2016, 42, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, O.; Chi, Y. Medicinal properties of mangiferin, structural features, derivative synthesis, pharmacokinetics and biological activities. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Liu, W.; Tang, K.; Zang, J.; Li, D.; Gao, H. Mangiferin alleviates renal interstitial fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice through regulating the PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 9481720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Sadhukhan, P.; Sil, P.C. Mangiferin: A xanthonoid with multipotent anti-inflammatory potential. BioFactors 2016, 42, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.-B.; Xia, E.-Q.; He, T.-P.; Huang, M.-Y.; Jia, Q.; Li, H.-W. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of mangiferin from mango (Mangifera indica L.) Leaves Using Response Surface Methodology. Molecules 2014, 19, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; Jia, Q.; Song, G. Comparison of microwave-assisted and conventional extraction of mangiferin from mango (Mangifera indica L.) leaves. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 3457–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loan, N.T.T.; Long, D.T.; Yen, P.N.D.; Hanh, T.T.M.; Pham, T.N.; Pham, D.T.N. Purification process of mangiferin from Mangifera indica L. leaves and evaluation of its bioactivities. Processes 2021, 9, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerma-Torres, J.M.; Navarro-Ocaña, A.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Hernández-Vázquez, L.; Ruiz-Montañez, G.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A. Preparative scale extraction of mangiferin and lupeol from mango (Mangifera indica L.) leaves and bark by different extraction methods. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4625–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Lv, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, G.; Huang, G.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C.; Li, X.; Chen, K. Quantification and purification of mangiferin from Chinese mango (Mangifera indica L.) cultivars and its protective effect on human umbilical vein endothelial cells under H2O2-induced stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11260–11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, V.M.; Rathod, V.K. Extraction of mangiferin from Mangifera indica leaves using three phase partitioning coupled with ultrasound. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 52, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, K.; Kumar, M.M.; Ilango, K.; Mohankumar, R.; Priya, R.L. Prelusive scale extraction of mangiferin from Mangifera indica leaves: Assessing solvent competency, process optimization, kinetic study and diffusion modelling. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 140, 111703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alara, O.R.; Abdul Mudalip, S.K.; Olalere, O.A. Optimization of mangiferin extrated from Phaleria macrocarpa fruits using response surface methodology. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2017, 5, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, J.J.; Kshirsagar, P.R.; Jadhav, S.G.; Nalavade, V.M.; Gurme, S.T.; Pai, S.R. Elicitor-mediated enhancement of biomass, polyphenols, mangiferin production and antioxidant activities in callus cultures of Salacia chinensis L. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Tzen, J.T.C. A feasible UHPLC-MS/MS method for concurrent quantification of 10 bioactive principles in Aquilaria leaf tea by the multiple reaction monitoring analytical mode. Phytochem. Anal. 2020, 31, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grauzdytė, D.; Pukalskas, A.; El Kalamouni, C.; Venskutonis, P.R. Mangiferin rich products from Aphloia theiformis (Vahl) Benn leaves: Extraction, fractionation, phytochemical characterization, and antioxidant properties. Molecules 2020, 25, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhukhan, P.; Saha, S.; Dutta, S.; Sil, P.C. Mangiferin ameliorates cisplatin induced acute kidney injury by upregulating Nrf-2 via the activation of PI3K and exhibits synergistic anticancer activity with cisplatin. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.K.; Verma, V.K.; Mutneja, E.; Malik, S.; Nag, T.C.; Dinda, A.K.; Arya, D.S.; Bhatia, J. Mangiferin attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats mediating modulation of MAPK pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 452, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, P.B.; Sinha, K.; Sil, P.C. Mangiferin attenuates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress mediated signaling cascade, TNFα related and mitochondrial dependent apoptotic pathways in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekar, V.; Mani, S.; Malarvizhi, R.; Barathidasan, R.; Vasanthi, H.R. Positive interaction of mangiferin with selected oral hypoglycemic drugs: A therapeutic strategy to alleviate diabetic nephropathy in experimental rats. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 4465–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Lin, H.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Li, L. Mangiferin prevents diabetic nephropathy progression and protects podocyte function via autophagy in diabetic rat glomeruli. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 824, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellamuthu, P.S.; Arulselvan, P.; Kamalraj, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Kandasamy, M. Protective nature of mangiferin on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in tissues of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. ISRN Pharmacol. 2013, 2013, 750109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muruganandan, S.; Gupta, S.; Kataria, M.; Lal, J.; Gupta, P. Mangiferin protects the streptozotocin-induced oxidative damage to cardiac and renal tissues in rats. Toxicology 2002, 176, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-W.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Q.; Wang, J.-Y.; Zhang, F.; Guo, H.; Yin, J.-L.; Yin, X.-X. Up-regulation of glyoxalase 1 by mangiferin prevents diabetic nephropathy progression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 721, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Han, S.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, B.; Wang, X. Therapeutic effects of mangiferin on sepsis-associated acute lung and kidney injuries via the downregulation of vascular permeability and protection of inflammatory and oxidative damages. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Peng, X.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Tang, C.; Dong, Z.; Liu, F.; Peng, Y. Mangiferin attenuate sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 40, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, Z.; Carlström, M.; Tian, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, S.; Ye, F. Mangiferin ameliorates hyperuricemic nephropathy which is associated with downregulation of AQP2 and increased urinary uric acid excretion. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S.; Song, J.; Xie, T.; Tian, J.; Wu, S.; Du, G. Antihyperuricemic effect of mangiferin aglycon derivative J99745 by inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity and urate transporter 1 expression in mice. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Gao, L.; Niu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, H.; Jiang, J.; Kong, X.; Liu, X.; Li, L. Mangiferin inhibits renal urate reabsorption by modulating urate transporters in experimental hyperuricemia. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Cheng, Y.-Q.; Du, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Guo, H.; Liu, Y.-W.; Yin, X.-X. Mangiferin attenuates renal fibrosis through down-regulation of osteopontin in diabetic rats. Phyther. Res. 2015, 29, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Mahalanobish, S.; Dutta, S.; Sil, P.C. Mangiferin ameliorates collateral neuropathy in t BHP induced apoptotic nephropathy by inflammation mediated kidney to brain crosstalk. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5981–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, M.; Das, J.; Sil, P.C. D(+) galactosamine induced oxidative and nitrosative stress-mediated renal damage in rats via NF-κB and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) pathways is ameliorated by a polyphenol xanthone, mangiferin. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wan, J.; Gong, X.; Kuang, G.; Cheng, X.; Min, S. Mangiferin attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting inflammation and inducing adenosine production. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 25, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadarsi, R.; Dutta, D. Anti-oxidative effect of mangiferin-chitosan nanoparticles on oxidative stress-induced renal cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Rengarajan, T.; Nishigaki, Y.; Palaniswami, R.; Nishigaki, I. In vitro studies on mangiferin protection against cadmium-induced human renal endothelial damage and cell death via the MAP kinase and NF-κB pathways. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2016, 36, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-K.; Sun, C.-Y.; Qin, X.-Y.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, G.-Y.; Min-Jian, Q. Effects of ethanol extract of Bombax ceiba leaves and its main constituent mangiferin on diabetic nephropathy in mice. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 15, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, M.P.; Ang, D.S.; Pall, A.; Struthers, A.D. Oxidative stress in renal dysfunction: Mechanisms, clinical sequelae and therapeutic options. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2010, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gyurászová, M.; Gurecká, R.; Bábíčková, J.; Tóthová, Ľ. Oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of kidney disease: Implications for noninvasive monitoring and identification of biomarkers. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 5478708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uddin, M.J.; Kim, E.H.; Hannan, M.A.; Ha, H. Pharmacotherapy against oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease: Promising small molecule natural products targeting nrf2-ho-1 signaling. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, G.; Uddin, M.J.; Lee, G.; Jiang, S.; Cho, A.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.R.; Bae, Y.S.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; et al. A novel pan-Nox inhibitor, APX-115, protects kidney injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice: Possible role of peroxisomal and mitochondrial biogenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 74217–74232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Fu, X.; Chen, Q.; Patra, J.K.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Gai, Z. Arachidonic acid metabolism and kidney inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uddin, M.J.; Jeong, J.; Pak, E.S.; Ha, H. CO-releasing molecule-2 prevents acute kidney injury through suppression of ROS-Fyn-ER stress signaling in mouse model. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9947772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Dorotea, D.; Pak, E.S.; Ha, H. Fyn kinase: A potential therapeutic target in acute kidney injury. Biomol. Ther. 2020, 28, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Pak, E.S.; Ha, H. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-2 protects mice against acute kidney injury through inhibition of ER stress. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 22, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moni, A.; Iqbal, A.; Uddin, M. Resveratrol attenuates inflammation through tristetraprolin expression in human hepatocytes. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 1, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, M.; Kim, K.; Uddin, M.J.; Lee, G.; Hwang, I.; Kang, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Ha, H. Delayed treatment with fenofibrate protects against high-fat diet-induced kidney injury in mice: The possible role of ampk autophagy. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2017, 312, F323–F334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeong, B.Y.; Uddin, M.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.B.; Miyata, T.; Ha, H. Novel plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitors prevent diabetic kidney injury in a mouse model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.; Uddin, M.J.; Lee, G.; Jiang, S.; Pak, E.S.; Ha, H. Peroxiredoxin 3 deficiency accelerates chronic kidney injury in mice through interactions between macrophages and tubular epithelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 131, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Ahmmed, S.M.; Saha, B.P.; Mukherjee, P.K. Soya phospholipid complex of mangiferin enhances its hepatoprotectivity by improving its bioavailability and pharmacokinetics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Inoue, T. Biosynthesis of mangiferin in Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge. I. The origin of the xanthone nucleus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1980, 28, 2476–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehianeta, T.S.; Laval, S.; Yu, B. Bio- and chemical syntheses of mangiferin and congeners. BioFactors 2016, 42, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telange, D.R.; Sohail, N.K.; Hemke, A.T.; Kharkar, P.S.; Pethe, A.M. Phospholipid complex-loaded self-assembled phytosomal soft nanoparticles: Evidence of enhanced solubility, dissolution rate, ex vivo permeability, oral bioavailability, and antioxidant potential of mangiferin. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1056–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, N.; Dehury, N.; Pal, A.; Behera, A.; Patra, S. Preparation and mechanistic aspect of natural xanthone functionalized gold nanoparticle. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Karmakar, T.; Ghosh, N.; Basak, S.; Gopal Sahoo, N. Targeting mangiferin loaded N-succinyl chitosan-alginate grafted nanoparticles against atherosclerosis—A case study against diabetes mediated hyperlipidemia in rat. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoobchandani, M.; Khan, A.; Katti, K.K.; Thipe, V.C.; Al-Yasiri, A.Y.; MohanDoss, D.K.D.; Nicholl, M.B.; Lugão, A.B.; Hans, C.P.; Katti, K.V. Green nanotechnology of MGF-AuNPs for immunomodulatory intervention in prostate cancer therapy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeyer, S.; Athipornchai, A.; Pabunrueang, P.; Trakulsujaritchok, T. Development of mangiferin loaded chitosan-silica hybrid scaffolds: Physicochemical and bioactivity characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozkina, S.N.; Nhung Vu, T.H.; Generalova, Y.E.; Snetkov, P.P.; Uspenskaya, M.V. Mangiferin as new potential anti-cancer agent and mangiferin-integrated polymer systems—A novel research direction. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Model Animals | Disease Inducing Agents | Mangiferin Dosages | Effects of Mangiferin | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | Route | Duration | Oxidative Stress | Inflammation | Fibrosis | Other Pathologies | |||
| Mice | Cisplatin | 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg | orally | 21 days | ↓ ROS ↑ GSH, SOD, CAT, GST, GR, GPx | ↓ TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, NF-κB | − | ↓ Caspase-3 | [20] |
| Rats | Cisplatin | 20 and 40 mg/kg | i.p. | 10 days | ↓ ROS, MDA ↑ GSH, SOD, CAT | ↓ TNF-α, IL-6 | − | ↓Bax, caspase-3 ↑ Bcl-2↓ MAPK pathway | [21] |
| Mice | STZ | 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg/day | orally | 4 Weeks | ↓ ROS, MDA ↑ SOD, CAT, andGSH-Px | ↓TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β | ↓TGF-β1, FN, Col I, and α-SMA | ↓Phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt | [7] |
| Rats | STZ | 10, 20, 40, 60 and 80 mg/kg; | orally | 30 days | ↓ ROS, MDA ↑ SOD, CAT, GPX, GR | ↓ NF-kB, TNF-α | − | ↓ Cytochrome C ↓ Bax, Caspase-9, Caspase-3↑ Bcl-2↓ MAPK pathway | [22] |
| Rats | STZ | 40 mg/kg | orally | 28 days | ↓ ROS ↑ CAT, GST, GS, GSH, GPx, SOD | ↓ NF-κB, TNF-α, VEGF, PKC | ↓ TGFβ1 | − | [23] |
| Rats | STZ | 12.5, 25, or 50 mg/kg | orally | 12 weeks | − | − | − | ↑ AMPK ↓ mTOR ↑ pULK1 | [24] |
| Rats | STZ | 40 mg/kg/day | orally | 30 days | ↑ SOD, CAT, GPx and GSH ↓ ROS, MDA | − | − | − | [25] |
| Rats | STZ | 10 and 20 mg/kg | i.p | 28 days | ↓ ROS, MDA ↑ SOD, CAT | − | − | − | [26] |
| Rats | STZ | 15, 30, and 60 mg/kg | orally | 9 weeks | ↓ ROS, MDA, AGEs ↑ GSH | − | − | − | [27] |
| Mice | LPS | 20, 50, and 100 mg/kg | i.p. | 7 days | ↓ ROS, MDA ↑ SOD | ↓ NF-κB, HMGB1 | − | − | [28] |
| Rats | LPS | 10, 50, 100 μM | 1 h | ↓ ROS, MDA | ↓ IL-1β, IL-18 and NLRP3 | − | ↓ caspase-9 and caspase-3 | [29] | |
| Mice | Uric acid | 50 mg/kg/day | orally | 7 days | ↓ ROS, XO ↑ SOD | ↓ IL-1b, IL-18 | − | − | [30] |
| Mice | Uric Acid | 10, and 30 mg/kg | 7 days | ↓ ROS, MDA | − | − | − | [31] | |
| Rats and mice | Uric acid | 1.5–6.0 mg/kg | i.p. | 5 days | − | − | − | ↓ URAT1, OAT10, and GLUT9 | [32] |
| Rats | OPN | 15, 30, and 60 mg/kg/day | orally | 9 weeks | − | ↓ TNF-α, COX-2, IL-1β, NF-κB, p65 | ↓ Col IV, α-SMA | − | [33] |
| Mice | tBHP | 75 mg/kg | orally | 2 weeks | ↑ SOD, CAT, GST, GRGPX | ↓ TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β | − | ↓ Bax, caspase-8 caspase-3 ↑ Bcl-2 | [34] |
| Rats | DGal | 25 mg/kg | i.p. | 14 days | ↓ ROS, MDA ↑ CAT, GST, GS, GPx, SOD | ↓ NF-κB a, NO, TNF-α | − | ↓ Bax, cytochrome c, caspase-9 and caspase-3 ↑ Bcl-2, Bcl-xL | [35] |
| Mice | Ischemia | 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg | i.p. | 30 min | − | ↓ TNF-α and IL-1β | − | ↓ Caspase-3 | [36] |
| Cell Lines | Model Drug | Mangiferin | Effects of Mangiferin | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | Duration | Oxidative Stress | Inflammation | Other Pathologies | |||
| NKE cells | Cisplatin | 5–30 µM | 2 h | ↓ ROS ↑ GSH, SOD, CAT, GST, GR, GPx | − | ↓ Caspase-3 | [20] |
| NKE Cells | NaF | 100–1000 μg/mL | ↓ ROS ↑ CAT, peroxidase and GHS | − | − | [37] | |
| HRGEC | Cadmium | 75 μM | 24 h | ↓ ROS, MDA ↑ SOD, GSH, GR, GSH-Px | ↓ NF-kB, IL-6, IL-8 | ↓ Bax, Cytochrome C, Caspase ↑ Bcl-2 | [38] |
| Mesangial Cells (SV40 MES 13) | High glucose (25 mM) | 50 mg/kg | 48 hr | ↓ ROS ↓ NOX4 | − | ↓ Caspase-3 ↑ Mitochondrial membranepotential | [39] |
| Nano-Particles | Cells/Tissues/Others | Method of Preparation | Size | Zeta Potential | Dose | Experimental Models | Indication | Benefits | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCNs | NKE cells | Ionic gelation method | <80 nm | +25 ± 0.2 mV | 100–1000 μg/mL | Nephropathic model | Nephro-protection | Decreases oxidative stress Enhances anti-oxidant activity, solubility and bioavailability | [37] |
| MGF treated-ZnO | Bone tissue | Sol-gel synthesis and freeze-drying | 25–60 nm | Bone substitute material | Increases bone regeneration | [60] | |||
| MGF-AuNP | Prostate cell | Clathrin-mediated pathway | 35 ± 2 nm | −40 ± 2 mv | 41 µM | Xenograft model | Prostate protection | Reduces pro-tumor cytokines | [59] |
| MPLC SNPs | Hepatic tissue | Solvent evaporation and nanoprecipitation | 1 nm to 10 μm | −200 to + 200 mV | 100 μg/mL | Albino rat model | Hepatoprotection | Increases anti-oxidant activity and oral bioavailability of MPLC SNPs | [56] |
| MGF treated-AuNP | Human breast cell | 0.025 mM to 10 mM | 100 μg | Non-toxic | Reduces toxicity | [57] | |||
| NSC-MGF nanoconjugate | Blood serum | Ionotropic gelation method | 100~200 nm | −30 mV | 10 mg/kg | Wistar rat model | Anti-diabetes Anti-hyperlipidemia | Reduces blood glucose level and total plasma cholesterol | [58] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akter, S.; Moni, A.; Faisal, G.M.; Uddin, M.R.; Jahan, N.; Hannan, M.A.; Rahman, A.; Uddin, M.J. Renoprotective Effects of Mangiferin: Pharmacological Advances and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031864
Akter S, Moni A, Faisal GM, Uddin MR, Jahan N, Hannan MA, Rahman A, Uddin MJ. Renoprotective Effects of Mangiferin: Pharmacological Advances and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031864
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkter, Sumaya, Akhi Moni, Golam Mahbub Faisal, Muhammad Ramiz Uddin, Nourin Jahan, Md Abdul Hannan, Asadur Rahman, and Md Jamal Uddin. 2022. "Renoprotective Effects of Mangiferin: Pharmacological Advances and Future Perspectives" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031864
APA StyleAkter, S., Moni, A., Faisal, G. M., Uddin, M. R., Jahan, N., Hannan, M. A., Rahman, A., & Uddin, M. J. (2022). Renoprotective Effects of Mangiferin: Pharmacological Advances and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031864








