The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: What Lessons Are We Learning on 4IR and the Sustainable Development Goals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
3. Telemedicine/Telehealth and Goal Three, Ensure Healthy Lives and Promote Wellbeing for All at All Ages
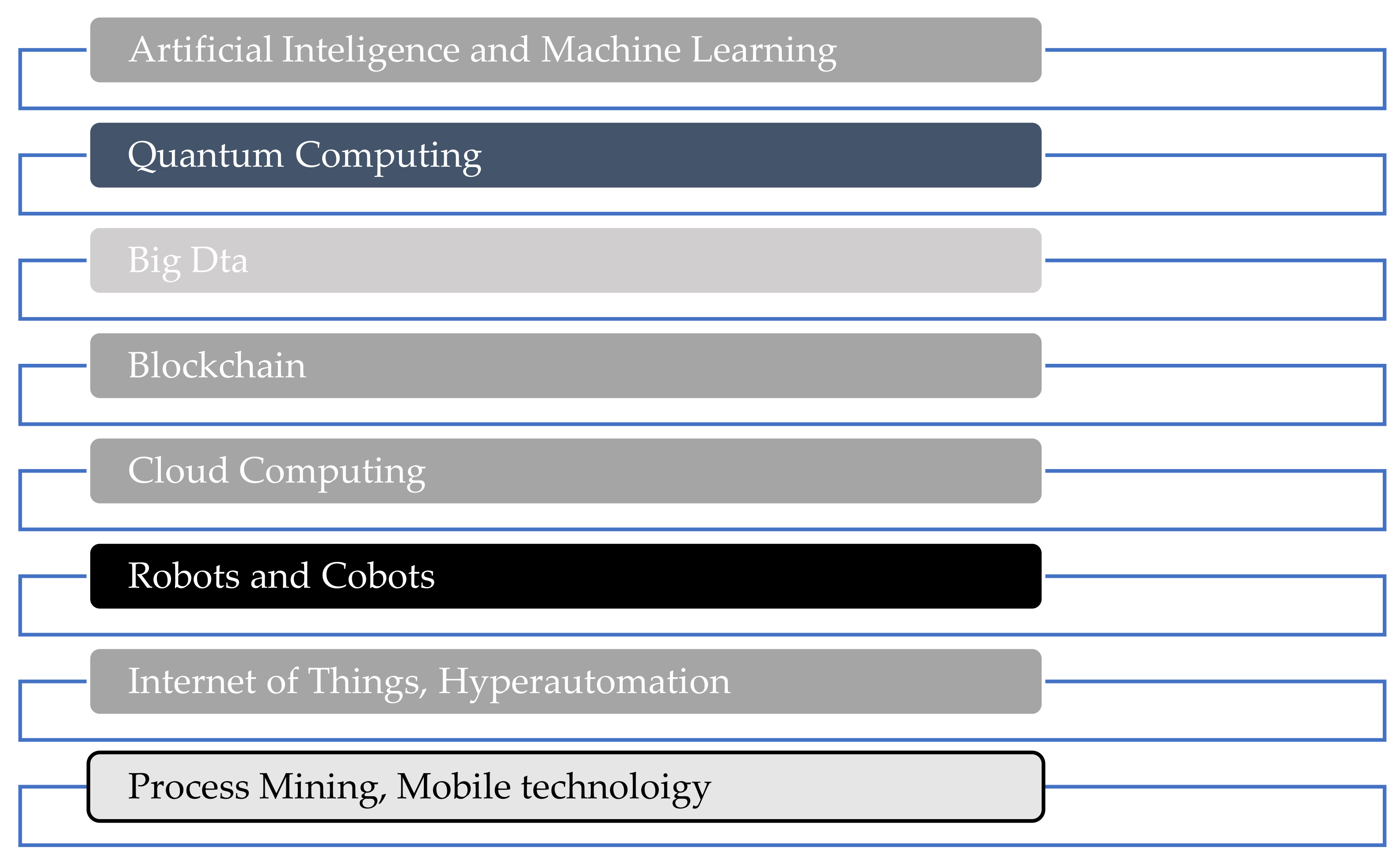
4. The Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR)
5. Brief Description of AI
6. Brief Outline COVID-19 and the Global Economy
7. Brief Review of Literature
8. Methodology
9. Results and Discussion
9.1. Speeding up Research and Treatment of the COVID-19 Related Complications
9.2. AI and Forecasting and Scaling Customer Communications during the Pandemic
9.3. Diagnosis, Containment and Monitoring
9.4. AI and Understanding How COVID-19 Spreads, Treatments and Cures
9.5. AI Lessons on the Fourth Industrial and Sustainable Development Goals
10. Conclusions and Policy Recommendation
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fegert, J.M.; Vitiello, B.; Plener, P.L.; Clemens, V. Challenges and burden of the Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic for child and adolescent mental health: A narrative review to highlight clinical and research needs in the acute phase and the long return to normality. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2020, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razu, S.R.; Yasmin, T.; Arif, T.B.; Islam, S.; Islam, S.M.S.; Gesesew, H.A.; Ward, P. Challenges Faced by Healthcare Professionals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Inquiry from Bangladesh. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagherazzi, G.; Goetzinger, C.; Rashid, M.A.A.; Aguayo, G.; Huiart, L. Digital Health Strategies to Fight COVID-19 Worldwide: Challenges, Recommendations, and a Call for Papers. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e19284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M. Medical 4.0 and Its Role in Healthcare During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review. J. Ind. Integr. Manag. 2020, 5, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Poly, T.; Alsinglawi, B.; Lin, L.-F.; Chien, S.-C.; Liu, J.-C.; Jian, W.-S. Application of Artificial Intelligence in COVID-19 Pandemic: Bibliometric Analysis. Healthcare 2021, 9, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilraja, M. Application of Artificial Intelligence to Address Issues Related to the COVID-19 Virus. SLAS Technol. Transl. Life Sci. Innov. 2021, 26, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrus, I.; Wyndham, J. Artificial Intelligence and COVID-19: Applications and Impact Assessment. Available online: https://www.aaas.org/sites/default/files/2021-05/AIandCOVID19_2021_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Vaishya, R.; Javaid, M.; Khan, I.H.; Haleem, A. Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications for COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Mehran, M.T.; Haq, Z.U.; Ullah, Z.; Naqvi, S.R. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comprehensive Review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 185, 115695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://www.unfpa.org/resources/transforming-our-world-2030-agenda-sustainable-development (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Assembly, G. Sustainable Development Goals. SDGs Transform Our World, 2030. Available online: http://www.igbp.net/download/18.62dc35801456272b46d51/1399290813740/NL82-SDGs.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Mhlanga, D. Artificial Intelligence in the Industry 4.0, and Its Impact on Poverty, Innovation, Infrastructure Development, and the Sustainable Development Goals: Lessons from Emerging Economies? Sustainability 2021, 13, 5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhlanga, D.; Garidzirai, R. The Influence of Racial Differences in the Demand for Healthcare in South Africa: A Case of Public Healthcare. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, J.; Petterson, V. Introduction to the Practice of Telemedicine. J. Telemed. Telecare 2005, 11, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjelm, N.M. Benefits and drawbacks of telemedicine. J. Telemed. Telecare 2005, 11, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portnoy, J.; Waller, M.; Elliott, T. Telemedicine in the era of COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 8, 1489–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohannessian, R.; Duong, T.A.; Odone, A. Global Telemedicine Implementation and Integration Within Health Systems to Fight the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Call to Action. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020, 6, e18810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, K. The Fourth Industrial Revolution: What it Means, How to Respond? Available online: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/01/the-fourth-industrial-revolution-what-it-means-and-how-to-respond/ (accessed on 13 November 2021).
- D’Alfonso, S. Al in mental health. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2020, 36, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, A.; Memarzadeh, K. The rise of artificial intelligence in healthcare applications. Artif. Intell. Healthc. 2020, 25–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Economic Situation and Prospects as of Mid-2021. Available online: https://www.un-ilibrary.org/content/9789210054980_10 (accessed on 16 November 2021).
- OECD. The Impact of COVID-19 on Health and Health Systems. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/health/covid-19.htm (accessed on 16 November 2021).
- World Health Organisation. COVID-19 Responsible for at Least 3 Million Excess Deaths in 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/the-impact-of-covid-19-on-global-health-goals (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Adadi, A.; Lahmer, M.; Nasiri, S. Artificial Intelligence and COVID-19: A Systematic umbrella review and roads ahead. J. King Saud. Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.-H.; Beam, A.L.; Kohane, I.S. Artificial intelligence in healthcare. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, T.; Kalakota, R. The potential for artificial intelligence in healthcare. Future Health J. 2019, 6, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, S.; Fox, J.; Purohit, M.P. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Healthcare Delivery. J. R. Soc. Med. 2019, 112, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipior, J.C. Considerations for development and use of AI in response to COVID-19. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 55, 102170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemler, S.E. Content analysis. In Emerging Trends in the Social and Behavioral Sciences: An Interdisciplinary, Searchable, and Linkable Resource; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.D. Content Analysis—Research Methods for Social Work; Rawat Publications: New Delhi, India, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, D. Addressing COVID-19 Drug Development with Artificial Intelligence. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 200070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FDA. The Beginnings: Laboratory and Animal Studies. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/druginformation-consumers/beginnings-laboratory-and-animal-studies (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- DiMasi, J.A.; Grabowski, H.G.; Hansen, R.W. Innovation in the pharmaceutical industry: New estimates of R&D costs. J. Health Econ. 2016, 47, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smalley, E. AI-powered drug discovery captures pharma interest. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 604–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, P.; Griffin, I.; Tucker, C.; Smith, D.; Oechsle, O.; Phelan, A.; Rawling, M.; Savory, E.; Stebbing, J. Baricitinib as potential treatment for 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease. Lancet 2020, 395, e30–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lilly, E. Baricitinib Has Significant Effect on Recovery Time, Most Impactful in COVID-19 Patients Requiring Oxygen. Available online: https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/baricitinib-has-significant-effect-recovery-time-most-impactful (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Simonite, T. AI Uncovers a Potential Treatment for COVID-19 Patients. Available online: https://www.wired.com/story/ai-uncovers-potential-treatment-covid-19-patients/ (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Neiiler, E. An AI Epidemiologist Sent the First Warnings of the Wuhan Virus, Wired Magzine. Available online: https://www.wired.com/story/ai-epidemiologist-wuhan-public-health-warnings/ (accessed on 11 September 2021).
- Li, L.; Yang, Z.; Dang, Z.; Meng, C.; Huang, J.; Meng, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Peng, H.; et al. Propagation analysis and prediction of the COVID-19. Infect. Dis. Model. 2020, 5, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Saputra, Y.M.; Van Huynh, N.; Nguyen, N.T.; Khoa, T.V.; Tuan, B.M.; Ottersten, B. Enabling and Emerging Technologies for Social Distancing: A Comprehensive Survey. arxiv 2020, arXiv:2005.02816. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y.; Yao, W.; Huang, J.; Qu, J. Improved Deep Learning Model for Differentiating Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia and Influenza Pneumonia. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castiglioni, I.; Ippolito, D.; Interlenghi, M.; Monti, C.B.; Salvatore, C.; Schiaffino, S.; Polidori, A.; Gandola, D.; Messa, C.; Sardanelli, F. Artificial Intelligence Applied on Chest X-ray Can Aid in the Diagnosis of COVID-19 Infection: A First Experience from Lombardy, Italy. 2020. Available online: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.08.20040907v1 (accessed on 11 September 2021).
- Kondylakis, H.; Katehakis, D.G.; Kouroubali, A.; Logothetidis, F.; Triantafyllidis, A.; Kalamaras, I.; Votis, K.; Tzovaras, D. COVID-19 Mobile Apps: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e23170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.J.L.; Couch, D.; Yap, K. Mobile Health Apps That Help With COVID-19 Management: Scoping Review. JMIR Nurs. 2020, 3, e20596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S. ACM Keynote: New Ways of Thinking of the Mobile Phone for Healthcare and the Current Pandemic. Available online: https://aiforgood.itu.int/events/acm-keynote-new-ways-of-thinking-of-the-mobile-phone-for-healthcare-and-the-current-pandemic/ (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Hui, M. Hong-Kong Is Using Tracker Wristbands to Geofence People Under Coronavirus Quarantine. Available online: https://finance.yahoo.com/news/hong-kong-using-tracker-wristbands-111714176.html (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Culham, D. Geofencing Informs COVID-19 Response. Tyler Technologies Blog. Available online: https://www.tylertech.com/resources/blog-articles/geofencing-informs-covid-19-response (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Wesner, K.L. Is the Grass Greener on the Other Side of the Geofence: The First Amendment and Privacy Implications of Unauthorized Smartphone Messages? Case W. Res. JL Tech. Internet 2019, 10, 3. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Ensure Healthy Lives and Promote Well-Being for All at All Ages. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/health/ (accessed on 13 November 2021).
- Vinuesa, R.; Azizpour, H.; Leite, I.; Balaam, M.; Dignum, V.; Domisch, S.; Nerini, F.F. The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, S.; Allan, S.; Coghlan, S.; Cooper, P. A governance model for the application of AI in health care. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2019, 27, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, A.; Weippl, E.; Tjoa, A.M.; Kieseberg, P. Digital transformation for sustainable development goals (SDGs)—A security, safety and privacy perspective on AI. In International Cross-Domain Conference for Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.; Machado, C.C.V.; Burr, C.; Cowls, J.; Joshi, I.; Taddeo, M.; Floridi, L. The Ethics of AI in Health Care: A Mapping Review. Soc. Sci. Med. 2021, 313–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truby, J. Governing Artificial Intelligence to benefit the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhlanga, D. A Dynamic Analysis of the Demand for Health Care in Post-Apartheid South Africa. Nurs. Rep. 2021, 11, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sustainable Development Goals | Description |
|---|---|
| Goal 1 | Put an end to poverty in all of its manifestations around the world. |
| Goal 2 | Put an end to hunger and attain food security enhance sustainable agriculture and boost nutrition. |
| Goal 3 | Ensure that all people of all ages enjoy healthy lives and are happy. |
| Goal 4 | Ensure that all students receive a high-quality education that is inclusive and equitable, and that lifelong learning opportunities are available to all. |
| Goal 5 | Assist all women and girls in achieving gender equality. |
| Goal 6 | Ensure that all people of all ages enjoy healthy lives and are happy. |
| Goal 7 | Ensure that everyone has access to energy that is affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern. |
| Goal 8 | Encourage long-term, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, as well as full and productive employment and decent work for everyone. |
| Goal 9 | Build a more resilient infrastructure, encourage inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and encourage innovation. |
| Goal 10 | Reduce intra- and inter-country inequity. |
| Goal 11 | Ensure that cities and human settlements be inclusive, safe, resilient, and long-lasting. |
| Goal 12 | Ensure that consumption and production trends are sustainable. |
| Goal 13 | Take immediate action to address climate change and its consequences. |
| Goal 14 | For sustainable development, conserve and sustainably utilise the oceans, seas, and marine resources. |
| Goal 15 | Defend, rebuild, and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, manage forests sustainably, prevent desertification, halt and reverse land degradation, and stop biodiversity loss. |
| Goal 16 | To ensure long-term development, promote peaceful and inclusive societies, ensure universal access to justice, and construct effective, responsible, and inclusive institutions at all levels. |
| Goal 17 | Strengthen and revive the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development’s implementation mechanisms. |
| 2019 GDP Growth | 2020 GDP Growth | 2021 Projected Growth | 2022 Projected Growth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| World Output | 2.5 | −3.6 | 5.4 | 4.1 |
| Developed Economies | 1.7 | −5.0 | 5.0 | 3.4 |
| United States of America | 2.2 | −3.5 | 6.2 | 3.2 |
| Japan | 0.3 | −4.8 | 3.3 | 2.2 |
| The United Kingdom Great Britain and Northern Island | 1.3 | −9.9 | 5.1 | 5.5 |
| Other developed Nations | 1.7 | −3.5 | 3.6 | 2.9 |
| 2019 GDP Growth | 2020 GDP Growth | 2021 Projected Growth | 2022 Projected Growth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economies in Transition | 2.2 | −2.7 | 3.3 | 3.3 |
| South-Eastern Europe | 3.7 | −3.5 | 4.2 | 3.5 |
| Commonwealth of the Independent States and Georgia | 2.2 | −2.6 | 3.3 | 3.3 |
| Russia Federation | 1.3 | −3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| 2019 GDP Growth | 2020 GDP Growth | 2021 Projected Growth | 2022 Projected Growth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developing Economies | 3.6 | −1.7 | 6.1 | 5.0 |
| Africa | 2.9 | −3.5 | 3.6 | 3.7 |
| Northern Africa | 3.2 | −5.5 | 5.6 | 4.0 |
| East Africa | 6.5 | 0.1 | 3.3 | 4.5 |
| Central Africa | 1.9 | −1.8 | 3.0 | 3.2 |
| West Africa | 3.3 | −1.0 | 2.7 | 3.6 |
| Southern Africa | −0.2 | −6.1 | 2.2 | 2.6 |
| East and South Asia | 4.9 | −0.1 | 7.1 | 5.7 |
| East Asia | 5.3 | 1.0 | 7.1 | 5.2 |
| China | 6.1 | 2.3 | 8.2 | 5.8 |
| South Asia | 3.1 | −5.6 | 6.9 | 8.3 |
| India | 4.6 | −6.8 | 7.5 | 10.1 |
| Western Asia | 1.2 | −3.2 | 3.7 | 3.4 |
| Latin America and the Caribbean | −0.3 | −7.3 | 4.3 | 3.3 |
| South America | −0.7 | −6.8 | 4.1 | 3.1 |
| Brazil | 1.4 | −4.1 | 3.0 | 2.4 |
| Mexico and Central America | 0.6 | −8.2 | 4.7 | 3.6 |
| Caribbean | 0.5 | −8.1 | 4.3 | 6.8 |
| Least developed countries | 4.9 | −0.3 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| World trade of Goods and Services | 1.2 | −8.1 | 9.4 | 5.7 |
| Journal Articles | Reports | Media Articles | Others |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 25 | 25 | 55 |
| Journals targeted were those published from the year 2000 up wards though Work from previous years was considered. Publishers-Springer Nature, Multidisciplinary Publishing, Es, Elsevier Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. | United Nations, The World Bank, The World Health Organization Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) among others | Media articles from Various countries were used for instance United State of America, South Africa, the United Kingdom among other nations. | Various other documents were consulted to come up with the ideas that shaped the trajectory of the study. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mhlanga, D. The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: What Lessons Are We Learning on 4IR and the Sustainable Development Goals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031879
Mhlanga D. The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: What Lessons Are We Learning on 4IR and the Sustainable Development Goals. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031879
Chicago/Turabian StyleMhlanga, David. 2022. "The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: What Lessons Are We Learning on 4IR and the Sustainable Development Goals" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031879
APA StyleMhlanga, D. (2022). The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: What Lessons Are We Learning on 4IR and the Sustainable Development Goals. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031879





