Spatiotemporal Variation and Influencing Factors of TSP and Anions in Coastal Atmosphere of Zhanjiang City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site and Time Schedule
2.2. Sampling Instruments and Methods
2.3. Sample Pretreatment and Testing
2.3.1. Sample Pretreatment
2.3.2. Sample Testing
Testing of TSP Concentration
Testing of Anion Concentration in Atmospheric Absorption Liquid
2.4. Data Analysis and Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Seasonal Meteorological Environments Variation in Zhanjiang
3.2. Seasonal Air Pollutant Concentration Variation in Zhanjiang Atmosphere
3.3. Coastal Atmospheric Pollutants Concentrations Variation with Meteorological Factors
3.3.1. Coastal Atmospheric Pollutants Concentrations Variation Affected by Temperature
3.3.2. Coastal Atmospheric Pollutants Concentrations Variation with Relative Humidity
3.3.3. Coastal Atmospheric Pollutants Concentrations Variation with Atmospheric Pressure
3.3.4. Coastal Atmospheric Pollutants Concentrations Variation with Wind Speed and Direction
3.3.5. Correlation Analysis of Coastal Atmospheric Anion Concentrations and Meteorological Factors
3.4. Seasonal Variation of Coastal Atmospheric Pollutants Concentration
3.5. Changes in Atmospheric Pollutant Concentration in Different Sites
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Meteorological Factors on Coastal Atmospheric Pollutants Concentrations
4.2. Effects of Different Seasons on Coastal Atmospheric Pollutants Concentrations
4.3. Impact of Different Environmental Types on Coastal Atmospheric Pollutants Concentrations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.M.; Zhang, H.F. Six sources mainly contributing to the haze episodes and health risk assessment of PM2.5 at Beijing suburb in winter 2016. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2018, 166, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andini, A.; Bonnet, S.; Rousset, P.; Hasanudin, U. Impact of open burning of crop residues on air pollution and climate change in Indonesia. Curr. Sci. 2018, 115, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszman, P.E.; Derbisz, K.; Kwasiborski, P.; Chrząszcz, P.; Mularska, M.; Baron, D.; Sobieszek, A.; Mendyk, A.; Skoczylas, P.; Cisowski, M.; et al. Impact of air pollution on hospital patients admitted with ST- and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in heavily polluted cities within the European Union. Cardiol. J. 2020, 27, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, C.C.; Li, Y.W.; Liu, J.Y.; Meng, C.S.; Han, J.X.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xu, D.Q. Short-term effects of ambient air pollution exposure on lung function: A longitudinal study among healthy primary school children in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Cheng, Q.; Luo, X.L.; Bai, L.J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.S.; Xu, Z.H.; Gao, J.J.; Zhang, Y.W.; Su, H. Is the serious ambient air pollution associated with increased admissions for schizophrenia? Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.Y.; Hsu, W.H.; Lin, C.L.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, C.H.; Wang, I.K.; Hsu, C.Y.; Kao, C.H. Association of Exposure to Fine-Particulate Air Pollution and Acidic Gases with Incidence of Nephrotic Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Vigotti, M.A.; Zanobetti, A.; Repetto, F.; Gianelle, V.; Schwartz, J. Air pollution and cause-specific mortality in Milan, Italy, 1980–1989. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1999, 54, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.H.; Ferris, B.G.; Dockery, D.W.; Spengler, J.D.; Stram, D.O.; Speizer, F.E. Effects of ambiemt sulfur oxides and suspended particles on respiratory health of preadolescent children. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1986, 135, 834–842. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Q.Q.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.H.; Xing, C.Z.; Tan, W.; Liu, H.R.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.S.; Geng, T.Z.; et al. Evolution of the vertical structure of air pollutants during winter heavy pollution episodes: The role of regional transport and potential sources. Atmo. Res. 2019, 228, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, J.H.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.J.; Shi, J.H.; Gao, H.W. Seasonal distribution of water-soluble inorganic ions in the atmospheric aerosol in Qingdao. Huanjing Kexue 2012, 33, 2180–2190. [Google Scholar]
- Manju, A.; Kalaiselvi, K.; Dhananjayan, V.; Palanivel, M.; Banupriya, G.S.; Vidhya, M.H.; Panjakumar, K.; Ravichandran, B. Spatio-seasonal variation in ambient air pollutants and influence of meteorological factors in Coimbatore, Southern India. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.J.; Ma, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Q. Aerosol and gaseous pollutant characteristics during the heating season (winter-spring transition) in the Harbin-Changchun megalopolis, northeastern China. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2019, 188, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Tong, L.; Huang, Z.W.; Zhang, H.L.; He, M.M.; Dai, X.R.; Zheng, J.; Xiao, H. Seasonal variation and size distributions of water-soluble inorganic ions and carbonaceous aerosols at a coastal site in Ningbo, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.S.; Xu, M.X.; Snape, C.; He, J.; Behera, S.N.; Xu, H.H.; Ji, D.S.; Wang, C.J.; Yu, H.; Xiao, H.; et al. Temporal and spatial variation in major ion chemistry and source identification of secondary inorganic aerosols in Northern Zhejiang Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 179, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.P.; Hao, Q.J.; Wen, T.X.; Ji, D.S.; Liu, Z.R.; Wang, Y.S.; Jiang, C.S. Mass Concentrations and Size Distributions of Water-soluble Inorganic Ions in Atmospheric Aerosols in Beibei District, Chongqing. Huanjing Kexue 2018, 39, 4002–4013. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cesari, D.; Genga, A.; Ielpo, P.; Siciliano, M.; Mascolo, G.; Grasso, F.M.; Contini, D. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in the harbour–industrial area of Brindisi (Italy): Identification and estimation of the contribution of in-port ship emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arideep, M.; Madhoolika, A. Assessment of local and distant sources of urban PM2.5, in middle Indo-Gangetic plain of India using statistical modeling. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 275–287. [Google Scholar]
- Bozkurt, Z.; Uzmez, O.O.; Dogeroglu, T.; Artun, G.; Gaga, E.O. Atmospheric concentrations of SO2, NO2, ozone and VOCs in Duzce, Turkey using passive air samplers: Sources, spatial and seasonal variations and health risk estimation. Atmos. Res. 2018, 9, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeričević, A.; Gašparac, G.; Maslać, M.M.; Kumar, P.; Prtenjak, M.T. Identification of diverse air pollution sources in a complex urban area of Croatia. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimtriou, K.; Kassomenos, P. A meteorological analysis of PM10 episodes at a high altitude city and a low altitude city in central Greece—The impact of wood burning heating devices. Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddows, D.C.S.; Harrison, R.M. Identification of specific sources of airborne particles emitted from within a complex industrial (steelworks) site. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 183, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, G.W.; Roest, G. Source apportionment of non-methane hydrocarbons, NOx and H2S data from a central monitoring station in the Eagle Ford shale, Texas. Elementa-Sci. Anthrop. 2018, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, M.G.; Vratolis, S.; Georgieva, E.; Torok, S.; Sega, K.; Veleva, B.; Osan, J.; Beslic, I.; Kertesz, Z.; Pernigotti, D.; et al. Sources and geographic origin of particulate matter in urban areas of the Danube macro-region: The cases of Zagreb (Croatia), Budapest (Hungary) and Sofia (Bulgaria). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.C.; Chen, W.H.; Yuan, C.S.; Wu, S.P.; Wang, X.H. Physicochemical Characteristics and Source Apportionment of Atmospheric Aerosol Particles in Kinmen-Xiamen Airshed. Environ. Eng. 2013, 13, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.M.; Zhang, X.H.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, R.Q.; Ma, Y.L.; He, K.B. Characteristics of aerosol pollution during heavy haze events in Suzhou, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7357–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahino, J.; Yoboue, V.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Adon, M.; Akpo, A.; Keita, S.; Liousse, C.; Gardrat, E.; Chiron, C.; Ossohou, M.; et al. A pilot study of gaseous pollutants’ measurement (NO2, SO2, NH3, HNO3 and O3) in Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire:contribution to an overview of gaseous pollution in African cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 243, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.B.; Yang, B.; Chen, T.; Sun, X.L.; Chen, C.L. Metal speciation and pollution assessment of Cd and Pb in intertidal sediments of Donghai Island, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 6, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- George, S.K.; Nair, P.R.; Parameswaran, K.; Jacob, S.; Abraham, A. Seasonal trends in chemical composition of aerosols at a tropical coastal site of India. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2008, 113, D16209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branis, M. Air quality of Prague: Traffic as a main pollution source. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 156, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehra, B. Seasonal variation of water-soluble inorganic ions in PM10 in a city of northwestern Turkey. Environ. Forensics 2018, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, J.; González, A.E. Analysis of the Relation between Particle Matter Concentration and Meteorological Parameter at Montevideo City. Sci. Res. Pub. 2018, 6, 120–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xie, J.L.; Liao, Z.H.; Fang, X.Q.; Xu, X.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Fan, S.J.; Wang, B.M. The characteristics of hourly wind field and its impacts on air quality in the Pearl River Delta region during 2013–2017. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusino-Atresino, R.; Anderson, J.; Gao, Y. Ionic and elemental composition of PM2.5 aerosols over the Caribbean Sea in the Tropical Atlantic. J. Atmos. Chem. 2016, 73, 427–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.S.; Braban, C.F.; Dragosit, U.; Simmons, I.; Leaver, D.; van Dijk, N.; Poskitt, J.; Thacker, S.; Patel, M.; Carter, H.; et al. Acid gases and aerosol measurements in the UK (1999–2015): Regional distributions and trends. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16293–16324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.D.; Song, J.M.; Li, X.G.; Yuan, H.M.; Li, N.; Duan, L.Q.; Ren, C.Z. Geochemical characteristics and potential biogeochemical effect of water-soluble ions in atmospheric aerosols over the western boundary regions of Pacific Ocean. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.P.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.Z.; Wang, W.X. PM2.5 Characteristics in Qingdao and across Coastal Cities in China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbatt, J.P.D.; Leaitch, W.R.; Aliabadi, A.A. Overview paper: New insights into aerosol and climate in the Arctic. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2527–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enami, S.; Sakamoto, Y.; Hara, K.; Osada, K.; Hoffmann, M.R.; Colussi, A.J. “Sizing” Heterogeneous Chemistry in the Conversion of Gaseous Dimethyl Sulfide to Atmospheric Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1834–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.R.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.Q.; Liu, Y.S.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.L.; Tao, M.H.; Wang, G.H. Analysis of Different Particle Sizes, Pollution Characteristics, and Sources of Atmospheric Aerosols During the Spring Dust Period in Beijing. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 5315–5322. [Google Scholar]
- Adame, J.A.; Lope, L.; Hidalgo, P.J.; Sorribas, M.; Gutierrez-Alvarez, I.; del Aguila, A.; Saiz-Lopez, A.; Yela, M. Study of the exceptional meteorological conditions, trace gases and particulate matter measured during the 2017 forest fire in Donana Natural Park, Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brønnum-Hansen, H.; Bender, A.M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Sorensen, J.; Bonlokke, J.H.; Boshuizen, H.; Becker, T.; Diderichsen, F.; Loft, S. Assessment of impact of traffic-related air pollution on morbidity and mortality in Copenhagen Municipality and the health gain of reduced exposure. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, P.; Molero, F.; Fernandez, A.J.; Tobias, A.; Pandolfi, M.; Gomez-Moreno, F.J.; Barreiro, M.; Perez, N. Synergistic effect of the occurrence of African dust outbreaks on atmospheric pollutant levels in the Madrid metropolitan area. Atmos. Res. 2019, 226, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, A.J.; Zhang, F. Roadside atmospheric pollution: Still a serious environmental problem in Beijing, China. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocoste, T.; Dorville, J.F.; Monjoly, S.; Jacoby-Koaly, S.; Andre, M. Assessment of nitrogen oxides and ground-level ozone behavior in a dense air quality station network: Case study in the Lesser Antilles Arc. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2018, 68, 1278–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul, H.N.D.; Latif, M.T.; Ahamad, F.; Dominick, D.; Chung, J.X.; Juneng, L.; Khan, M.F. The long-term assessment of air quality on an island in Malaysia. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeniran, J.A.; Yusuf, R.O.; Fakinle, B.S.; Sonibare, J.A. Air quality assessment and modelling of pollutants emission from a major cement plant complex in Nigeria. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; de la Rosa, J.; Sanchez-de-la-Campa, A.; Plana, F.; Ruiz, C.R. Source apportionment analysis of atmospheric particulates in an industrialised urban site in southwestern Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3113–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, R.; Chan, Y.C.; Gardner, T.; Shaw, G.; Chapman, H. Characterisation of atmospheric deposition as a source of contaminants in urban rainwater tanks. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, K.; Gupta, A.K. Seasonal variations and chemical characterization of ambient PM10 at residential and industrial sites of an urban region of Kolkata (Calcutta), India. Atmos. Res. 2006, 81, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ma, M.; Shi, J.H.; Gao, H.W.; Yao, X.H. Concentrations, Sources, and Dry Deposition Fluxes of Different Forms of Phosphorus in Qingdao Aerosols in Summer. Huanjing Kexue 2018, 39, 4034–4041. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.H.; Liu, X.H.; Yao, X.H.; Zhang, R.F.; Chen, X.J.; Lin, X.H.; Gao, H.W.; Liu, R.H. The concentration, source and deposition flux of ammonium and nitrate in atmospheric particles during dust events at a coastal site in northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojano, R.E.; Arregoces, H.A.; Angulo, L.C.; Restrepo, G.M. Analysis and Origin of PM10 and PM 10 Concentrations in Open-pit Coal Mining using Polar Plots. Inf. Technol. 2018, 29, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, W.J.; Liang, J.L.; Cheng, S.Y.; Jia, J.; Wang, X.Q. Air Pollutant Emission Inventory from Iron and Steel Industry in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region and Its Impact on PM(2.5). Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Ding, G.L.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Q.P.; Feng, K.L. Field Evaluation of the Dust Impacts from Construction Sites on Surrounding Areas: A City Case Study in China. Sustainability. 2019, 11, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Du, W.; Chen, Y.C.; Shen, G.F.; Su, S.; Lin, N.; Shen, H.Z.; Zhu, D.; Yuan, C.Y.; Duan, Y.H.; et al. Household air pollution and personal inhalation exposure to particles (TSP/PM2.5/PM1.0/PM0.25) in rural Shanxi, North China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeniran, J.A.; Yusuf, R.O.; Olajire, A.A. Exposure to coarse and fine particulate matter at and around major intra-urban traffic intersections of Ilorin metropolis, Nigeria. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Gao, X.; Zhu, T.Y.; Luo, L.; Zheng, Y. Chemical profiles of PM emitted from the iron and steel industry in northern China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 150, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.N.; Zhuang, G.S.; Huang, K.; Lin, J.; Wang, Q.Z.; Deng, C.R.; Fu, J.S. A Typical Formation Mechanism of Heavy Haze-Fog Induced by Coal Combustion in an Inland City in North-Western China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Nazeer, M.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L.C.; Kumar, K.R.; Ho, H.C.; Mazhar, U. Characteristics of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) over Urban, Suburban, and Rural Areas of Hong Kong. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Mutuku, J.K.; Chang, K.H. Various Sources of PM2.5 and their Impact on the Air Quality in Tainan City, Taiwan. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 601–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Q.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, J.X.; Wu, J.Z. Assessment of multi-air emissions: Case of particulate matter (dust), SO2, NOx and CO2 from iron and steel industry of China. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 232, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
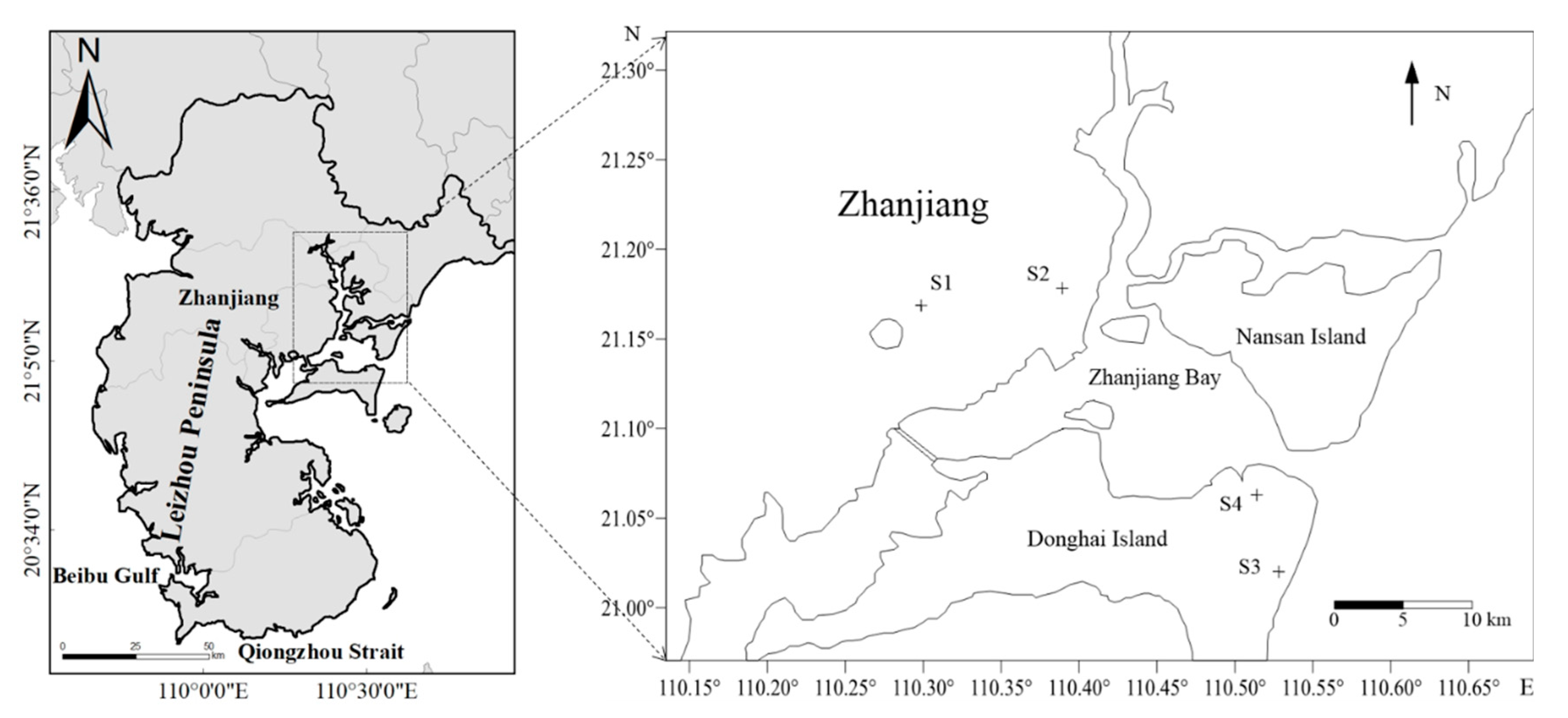







| Station | Longitude (N) | Latitude (E) | Distance from Sea (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 21°9′40.68″ | 110°17′43.44″ | 6.3 |
| S2 | 21°11′8.52″ | 110°23′35.52″ | 0.9 |
| S3 | 21°1′33.59″ | 110°31′32.52″ | 0.3 |
| S4 | 21°1′33.95″ | 110°31′13.44″ | 2.0 |
| Season | T(℃) | RH (%) | Air Pressure (hPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 24.9 | 86.1 | 1009.8 |
| Summer | 30.8 | 79.6 | 998.6 |
| Autumn | 24.9 | 81.4 | 1011.7 |
| Winter | 19.6 | 81.2 | 1015.2 |
| Maximum | 34.1 | 100.0 | 1019.7 |
| Minimum | 16.5 | 55.5 | 989.1 |
| Average | 25.2 | 82.0 | 1008.6 |
| Station | Range and Average | Cl− (μg/m3) | NO3− (μg/m3) | SO42− (μg/m3) | PO43− (μg/m3) | TSP (mg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Maximum | 53.5 | 29.7 | 52.0 | 31.2 | 0.45 |
| Minimum | 12.1 | 5.3 | 8.5 | 5.0 | 0.08 | |
| Average | 26.4 ± 17.6 | 19.0 ± 5.2 | 29.6 ± 14.9 | 10.6 ± 13.6 | 0.26 ± 0.17 | |
| S2 | Maximum | 69.5 | 51.6 | 72.2 | 32.5 | 0.59 |
| Minimum | 12.7 | 10.8 | 28.6 | 3.6 | 0.05 | |
| Average | 33.0 ± 19.5 | 25.1 ± 7.0 | 50.3 ± 13.7 | 15.1 ± 11.1 | 0.34 ± 0.22 | |
| S3 | Maximum | 60.8 | 24.8 | 70.6 | 29.0 | 0.58 |
| Minimum | 11.0 | 7.6 | 15.0 | 8.1 | 0.03 | |
| Average | 30.5 ± 16.1 | 14.7 ± 4.6 | 49.1 ± 16.2 | 17.2 ± 10.7 | 0.25 ± 0.20 | |
| S4 | Maximum | 62.1 | 32.0 | 84.3 | 40.1 | 0.41 |
| Minimum | 17.2 | 11.5 | 10.5 | 5.4 | 0.12 | |
| Average | 29.3 ± 16.5 | 19.5 ± 3.9 | 53.2 ± 18.1 | 11.0 ± 11.0 | 0.28 ± 0.19 | |
| Sum | Maximum | 69.5 | 51.6 | 84.3 | 40.1 | 0.59 |
| Minimum | 11.0 | 5.3 | 8.5 | 3.6 | 0.03 | |
| Average | 29.8 ± 11.1 | 19.6 ± 4.7 | 45.6 ± 16.1 | 13.5 ± 12.4 | 0.28 ± 0.18 |
| Correlation Coefficient | Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) | Atmospheric Pressure (hPa) | Wind Speed (m·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl− | 0.343 ** | 0.315 ** | −0.238 * | −0.204 * |
| NO3− | 0.027 | −0.014 | −0.010 | −0.021 |
| SO42− | 0.140 | −0.197 | −0.249 * | −0.266 * |
| PO43− | −0.216 * | 0.224 * | 0.217 * | −0.202 * |
| TSP | −0.303 ** | −0.224 * | 0.291 * | −0.325 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.-B.; Rong, Y.-M.; Yin, Q.-F.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, L.-R.; Chen, C.-L. Spatiotemporal Variation and Influencing Factors of TSP and Anions in Coastal Atmosphere of Zhanjiang City, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042030
Zhang J-B, Rong Y-M, Yin Q-F, Zhang P, Zhao L-R, Chen C-L. Spatiotemporal Variation and Influencing Factors of TSP and Anions in Coastal Atmosphere of Zhanjiang City, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(4):2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042030
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ji-Biao, Yu-Mei Rong, Qi-Feng Yin, Peng Zhang, Li-Rong Zhao, and Chun-Liang Chen. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Variation and Influencing Factors of TSP and Anions in Coastal Atmosphere of Zhanjiang City, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 4: 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042030
APA StyleZhang, J.-B., Rong, Y.-M., Yin, Q.-F., Zhang, P., Zhao, L.-R., & Chen, C.-L. (2022). Spatiotemporal Variation and Influencing Factors of TSP and Anions in Coastal Atmosphere of Zhanjiang City, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(4), 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042030






