Deep Neural Network Approach for Pose, Illumination, and Occlusion Invariant Driver Emotion Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Proposed System Methodology
3.1. Pre-Processing
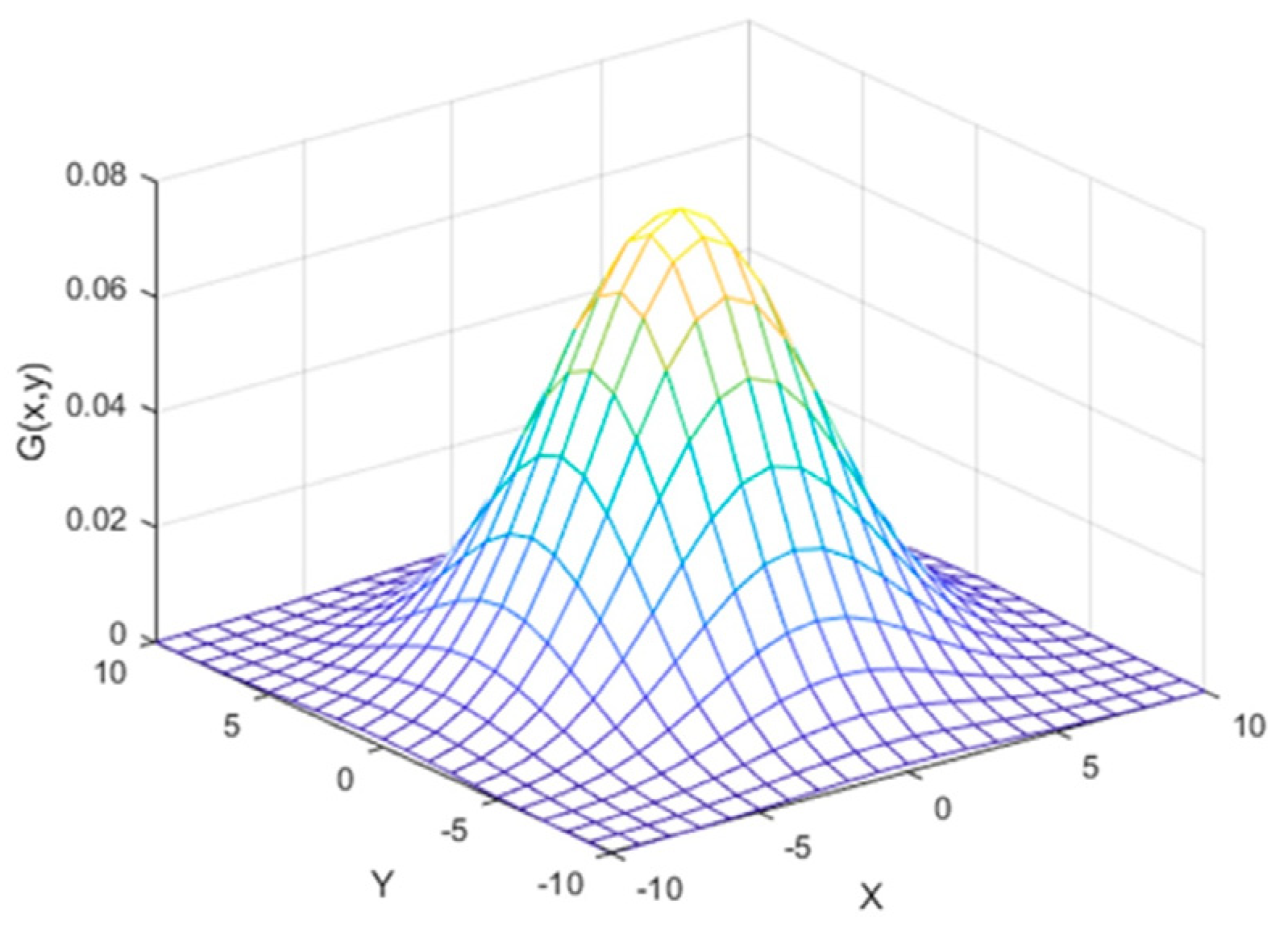
3.1.1. 2D Gaussian Filter
3.1.2. Median Filter
3.1.3. Image Enhancement
Histogram Equalization
3.2. First Proposed Approach for Driver Emotion Detection Using Viola–Jones Face Detection and K.L.T. Feature Tracking with a Deep Neural Network
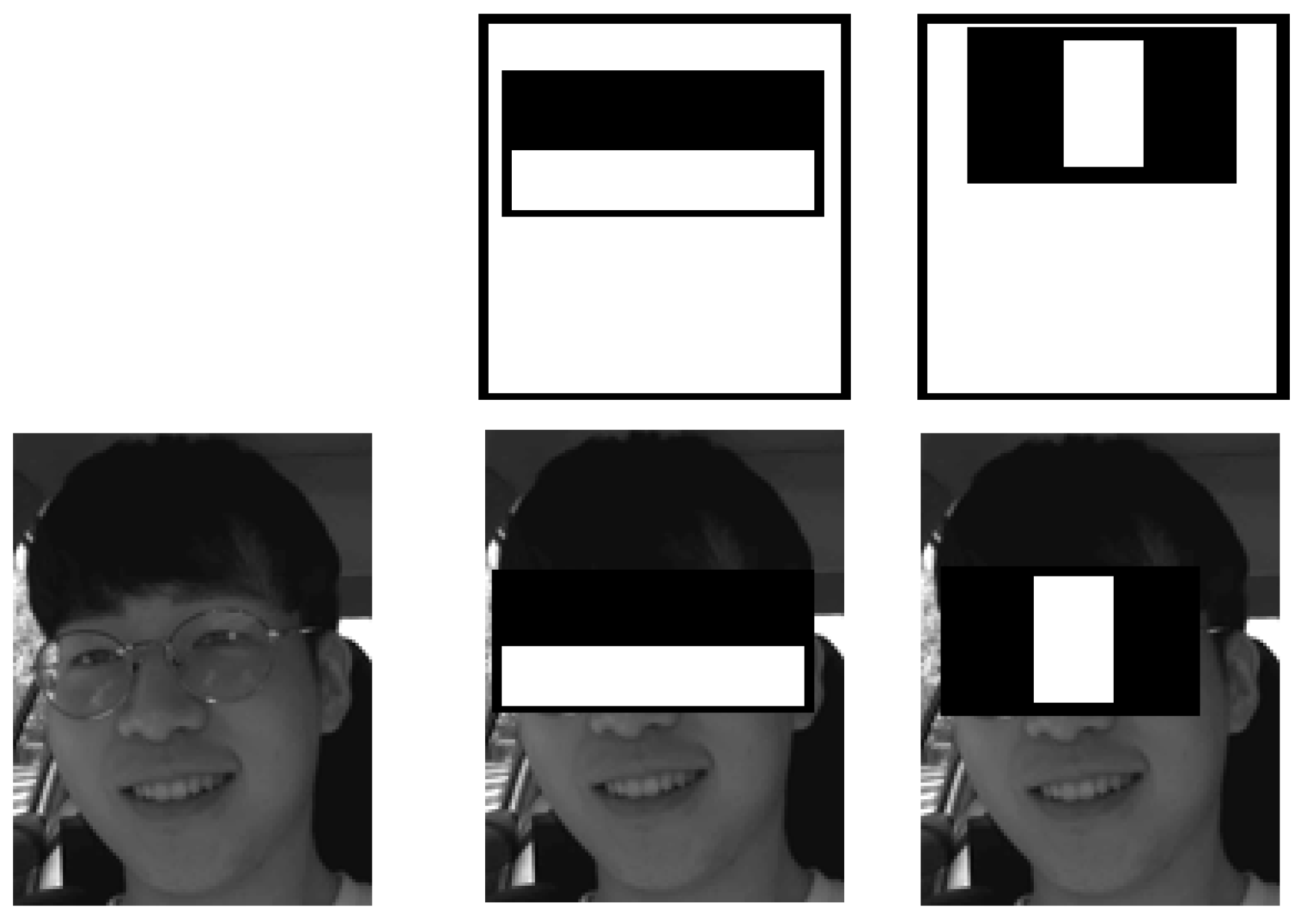
3.2.1. Face Detection and R.O.I. (Region of Interest) Extraction
Viola–Jones Face Detection Algorithm
3.2.2. Feature Extraction with K.L.T. (Kanade Lucas Tomasi)
3.2.3. Classification
Deep Neural Network (DeepNet)
3.3. Proposed Algorithm for Driver Emotion Detection Using a Multi-Task Cascaded Convolutional Neural Network with a Deep Neural Network
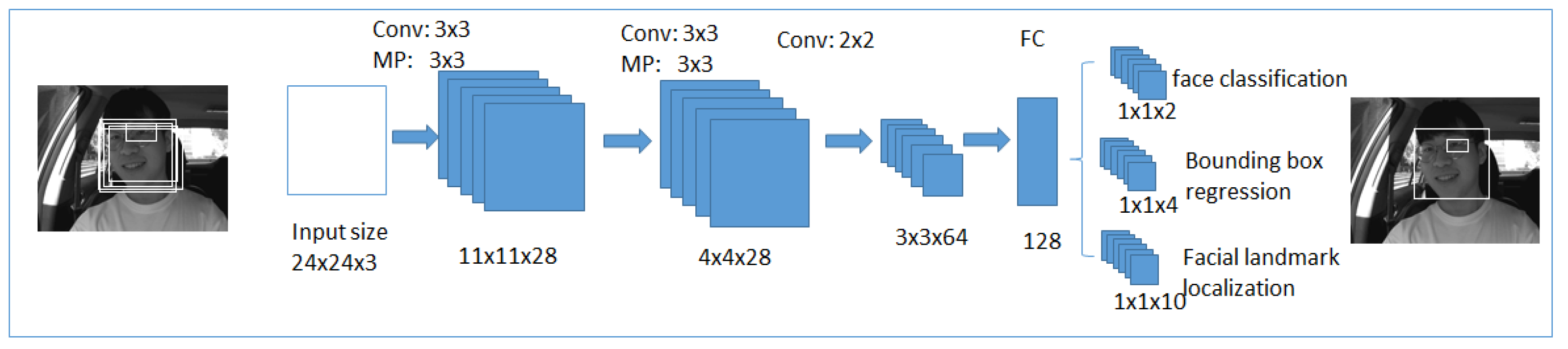
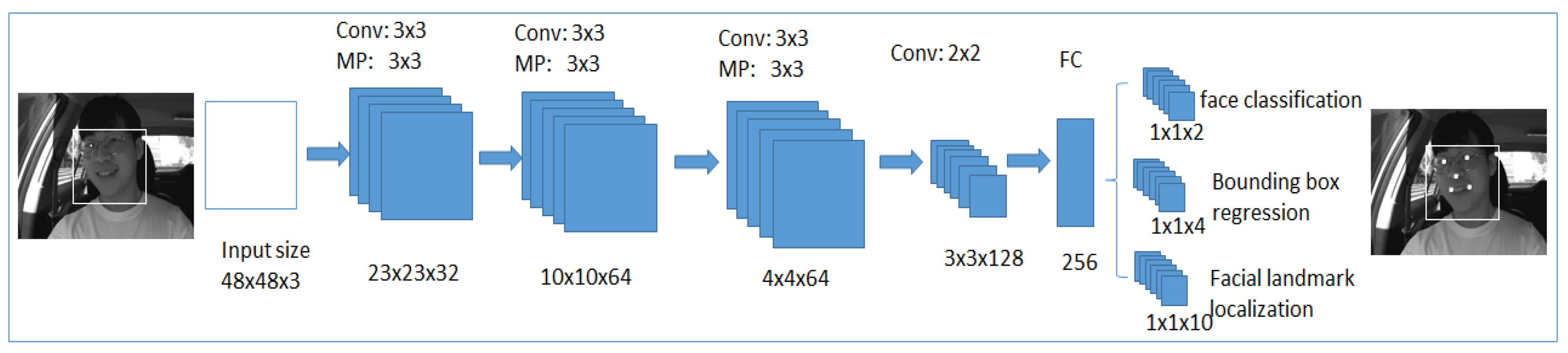
3.3.1. Multi-Task Cascaded Convolutional Neural Networks
First Stage
Second Stage
Third Stage
4. Experimental Results
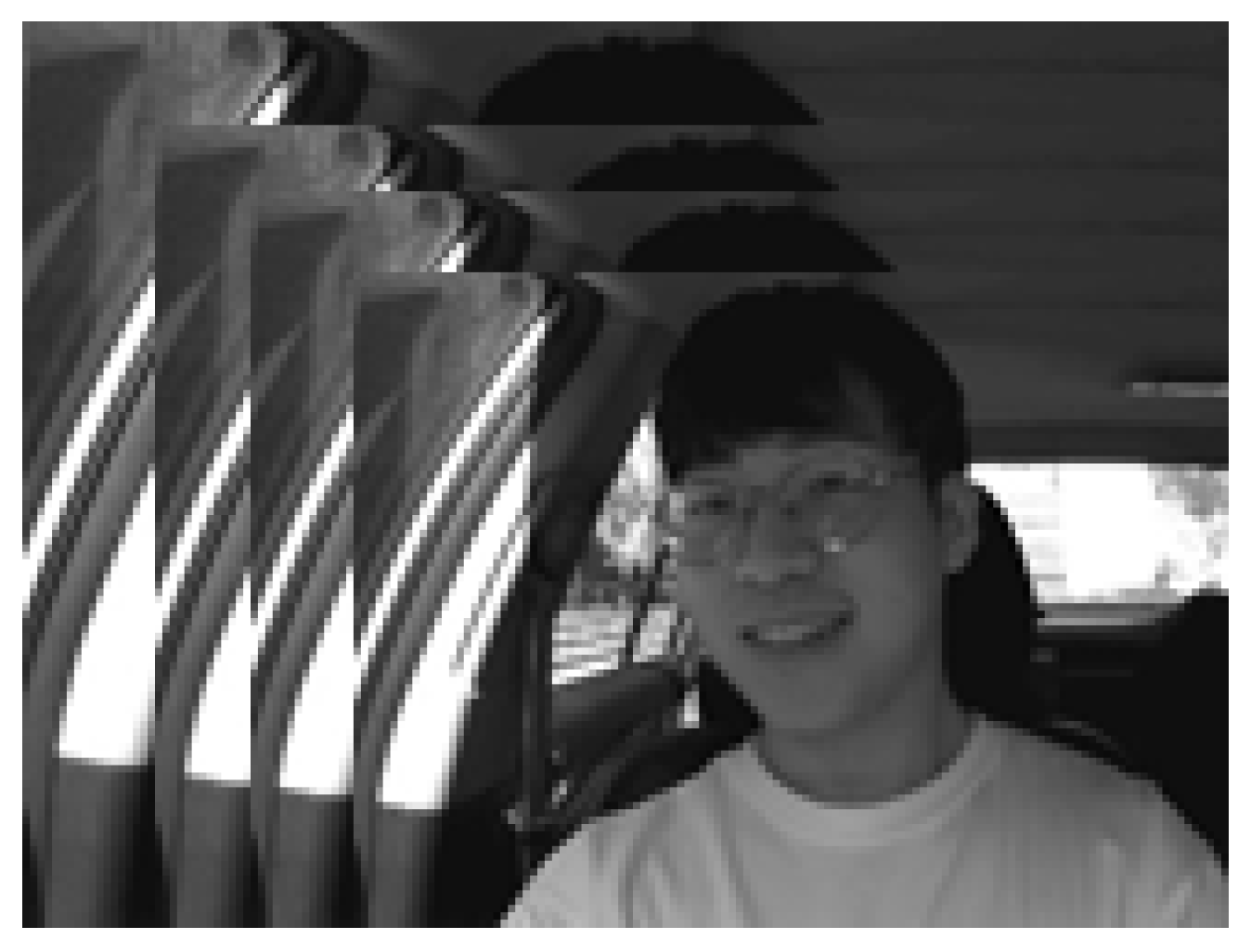
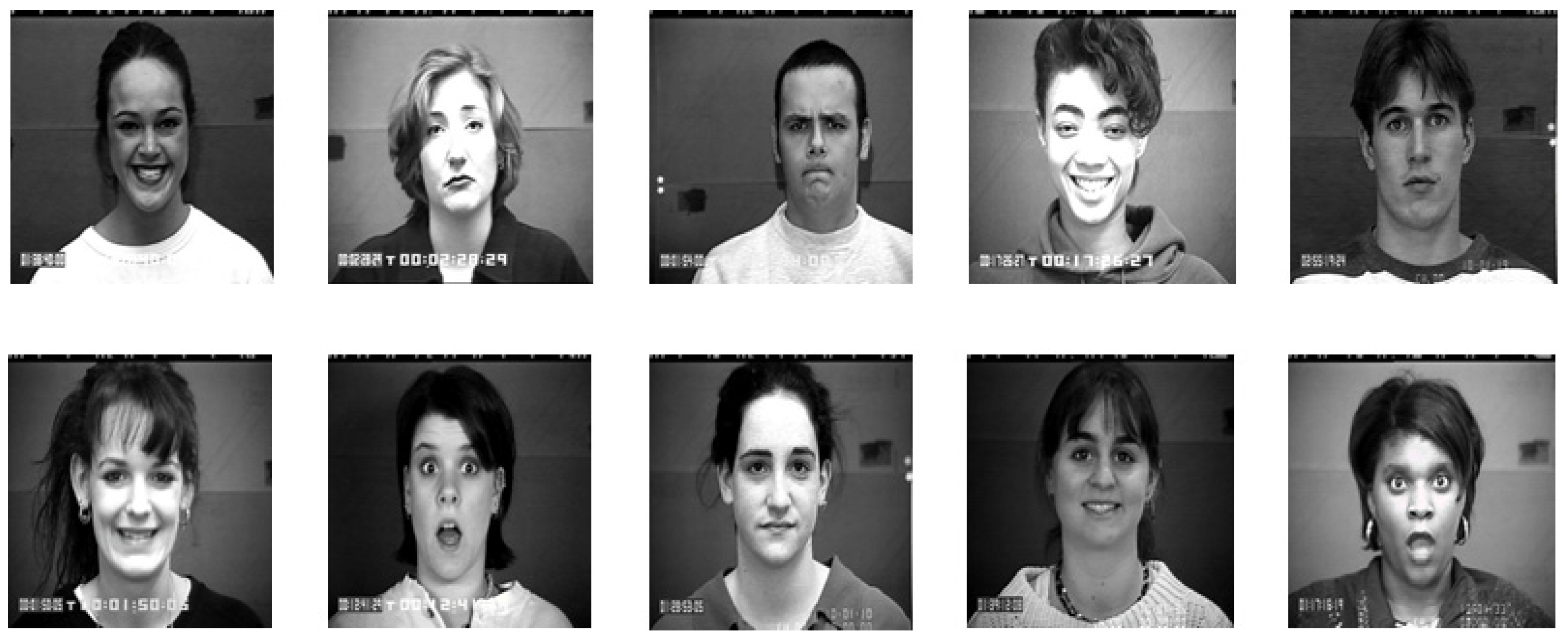
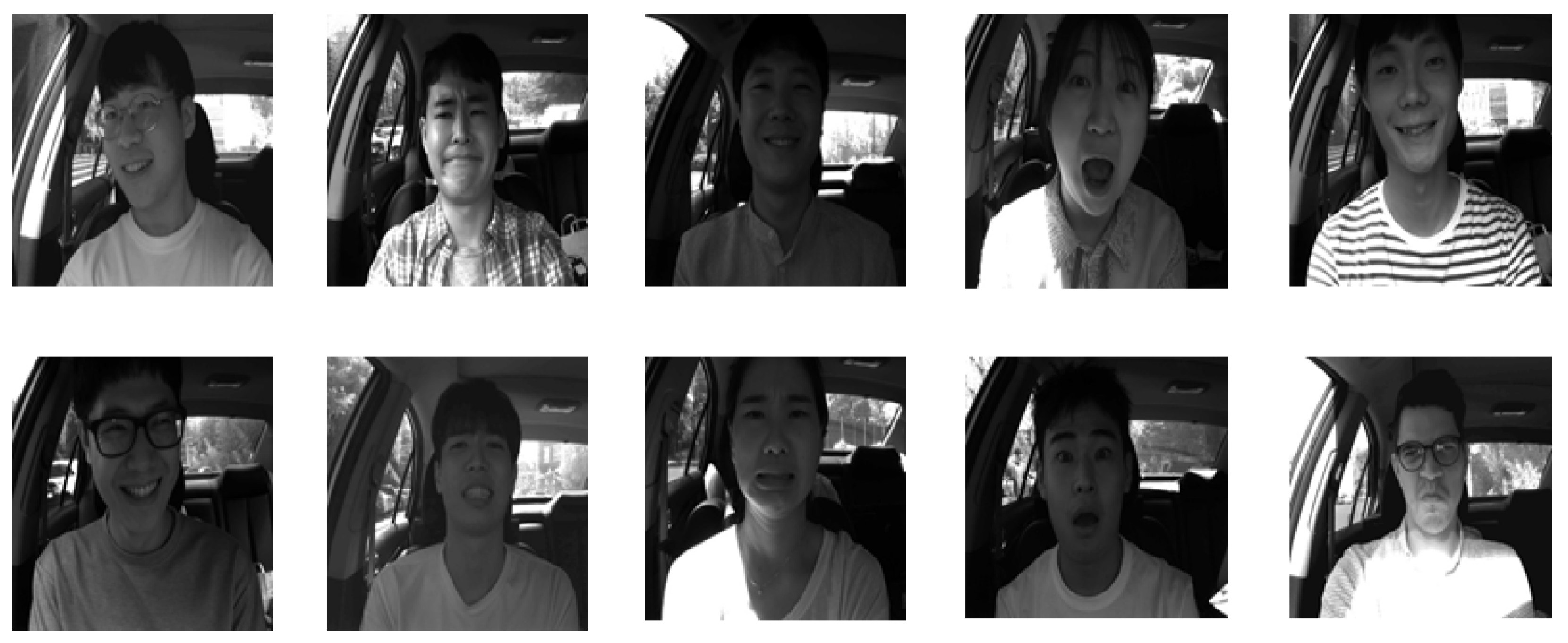
4.1. Databases
- (I)
- CK+
- (II)
- FER 2013
- (III)
- KDEF
- (IV)
- KMU-FED
4.2. Performance Evaluation
4.2.1. Experiments on CK+ Database
4.2.2. Experiments on the FER 2013 Database
4.2.3. Experiments on KDEF Database
4.2.4. Experiments on KMU-FED Database
4.3. Emotion Recognition Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Road Traffic Injuries. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/road-traffic-injuries (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Sariyanidi, E.; Gunes, H.; Cavallaro, A. Automatic analysis of facial affect: A survey of registration, representation, and recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intel. 2014, 37, 1113–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafeiriou, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z. A survey on face detection in the wild: Past, present and future. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2015, 138, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinges, D.; Grace, R. PERCLOS: A Valid Psychophysiological Measure of Alertness as Assessed by Psychomotor Vigilance; Publication Number FHWA-MCRT-98-006; U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- Tawari, A.; Trivedi, M.M. Speech emotion analysis: Exploring the role of context. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2010, 12, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Mahmoud, M.; Robinson, P.; Dias, E.; Skrypchuk, L. Automatic detection of a driver’s complex mental states. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications, Trieste, Italy, 3–6 July 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 678–691. [Google Scholar]
- Bergasa, L.M.; Nuevo, J.; Sotelo, M.A.; Barea, R.; Lopez, M.E. Real-time system for monitoring driver vigilance. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2006, 7, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, T.; Leo, M.; Guaragnella, C.; Distante, A. A visual approach for driver inattention detection. Pattern Recognit. 2007, 40, 2341–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, M.; Kurt, M.B.; Sezgin, N.; Bayram, M. Estimating vigilance level by using E.E.G. and E.M.G. signals. Neural Comput. Appl. 2008, 17, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Lin, Y.; Bhattacharya, P. A driver fatigue recognition model based on information fusion and dynamic Bayesian network. Inf. Sci. 2010, 180, 1942–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, J.S.; Ahmad, S.A.; Chong, Y.Z.; Ali, S.H.; Ai, G.; Wagatsuma, H. Driver emotion recognition framework based on electrodermal activity measurements during simulated driving conditions. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), Kaula Lumpur, Malaysia, 4–8 December 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 365–369. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yihong, G. Recognition of multiple drivers’ emotional state. In Proceedings of the 2008 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–11 December 2008; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Karaduman, O.; Eren, H.; Kurum, H.; Celenk, M. An effective variable selection algorithm for Aggressive/Calm Driving detection via CAN bus. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Connected Vehicles and Expo (ICCVE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2–6 December 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 586–591. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, R.; Picard, R.W. Modeling drivers’ speech under stress. Speech Commun. 2003, 40, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, M.; Kroschel, K.; Harris, H.; Nass, C.; Schuller, B.; Rigoll, G.; Moosmayr, T. On the necessity and feasibility of detecting a driver’s emotional state while driving. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, Lisbon, Portugal, 12–14 September 2007; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 126–138. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.; Jonsson, I.M. Using paralinguistic cues in speech to recognize emotions in older car drivers. In Affect and Emotion in Human-Computer Interaction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.M.; Jonsson, I.M. Automatic recognition of affective cues in the speech of car drivers to allow appropriate responses. In Proceedings of the 17th Australia Conference on Computer-Human Interaction: Citizens Online: Considerations for Today and the Future, Canberra, Australia, 23–25 November 2005; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.M.; Jonsson, I.M. Performance analysis of acoustic emotion recognition for in-car conversational interfaces. In International Conference on Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 411–420. [Google Scholar]
- Schuller, B.W. Speaker, noise, and acoustic space adaptation for emotion recognition in the automotive environment. In I.T.G. Conference on Voice Communication [8. ITG-Fachtagung]; V.D.E.: Frankfurt, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tawari, A.; Trivedi, M. Speech based emotion classification framework for driver assistance system. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, La Jolla, CA, USA, 21–24 June 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Bořil, H.; Kleinschmidt, T.; Boyraz, P.; Hansen, J.H. Impact of cognitive load and frustration on drivers’ speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boril, H.; Seyed, O.S.; Hansen, J.H.L. UTDrive: Emotion and cognitive load classification for in-vehicle scenarios. In Proceedings of the 5th Biennial Workshop on Digital Signal Processing for In-Vehicle Systems, Kiel, Germany, 4–7 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, I.; Lopez-de Ipiña, K.; Daily, S.B.; Gilbert, J.E. Emotional Adaptive Vehicle User Interfaces: Moderating negative effects of failed technology interactions while driving. In Proceedings of the Workshop of Automotive Natural Interfaces, Together with International Conference on Automotive User Interfaces, Portsmouth, NH, USA, 17–19 October 2012; pp. 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tews, T.K.; Oehl, M.; Siebert, F.W.; Höger, R.; Faasch, H. Emotional human-machine interaction: Cues from facial expressions. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Human Interface, Orlando, FL, USA, 9–14 July 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 641–650. [Google Scholar]
- Paschero, M.; Del Vescovo, G.; Benucci, L.; Rizzi, A.; Santello, M.; Fabbri, G.; Mascioli, F.F. A real time classifier for emotion and stress recognition in a vehicle driver. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Hangzhou, China, 28–31 May 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1690–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama, T.; Abdelaziz, K.; Shimomura, N. Face analysis of aggressive moods in automobile driving using mutual subspace method. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR2012), Tsukuba, Japan, 11–15 November 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 2898–2901. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, U.; Giripunje, S.; Bajaj, P. Emotion and gesture recognition with soft computing tool for drivers assistance system in human centered transportation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Manchester, UK, 13–16 October 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 4612–4616. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Yüce, A.; Thiran, J.P. Detecting emotional stress from facial expressions for driving safety. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 5961–5965. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, A.C.; Rinaldi, A. Video summarization for expression analysis of motor vehicle operators. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–14 July 2017; pp. 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihme, K.; Dömeland, C.; Freese, M.; Jipp, M. Frustration in the face of the driver: A simulator study on facial muscle activity during frustrated driving. Interact. Stud. 2018, 19, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, S.; Althoff, F.; McGlaun, G.; Rigoll, G. Bimodal fusion of emotional data in an automotive environment. In Proceedings of the (ICASSP’05) IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–25 March 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 2, p. ii-1085. [Google Scholar]
- Tischler, M.A.; Peter, C.; Wimmer, M.; Voskamp, J. Application of emotion recognition methods in automotive research. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Emotion and Computing—Current Research and Future Impact, Osnabruck, Germany, 10–13 September 2007; Volume 1, pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Schuller, B.; Wimmer, M.; Arsic, D.; Moosmayr, T.; Rigoll, G. Detection of security related affect and behaviour in passenger transport. In Proceedings of the 9th Interspeech 2008 incorp. 12th Australasian Int. Conf. on Speech Science and Technology S.S.T. 2008, Brisbane, Australia, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 265–268. [Google Scholar]
- Hynek, B.; Boyraz, P.; Hansen, J.H.L. Towards multimodal driver’s stress detection. In Digital Signal Processing for In-Vehicle Systems and Safety; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, I.C.; Lee, D.H.; Park, S.W.; Ko, J.I.; Yoon, H.R. Automobile driver’s stress index provision system that utilizes electrocardiogram. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–15 June 2007; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 652–656. [Google Scholar]
- Begum, S.; Ahmed, M.U.; Funk, P.; Filla, R. Mental state monitoring system for the professional drivers based on Heart Rate Variability analysis and Case-Based Reasoning. In Proceedings of the 2012 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems (FedCSIS), Wrolcaw, Poland, 9–12 September 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Keshan, N.; Parimi, P.V.; Bichindaritz, I. Machine learning for stress detection from E.C.G. signals in automobile drivers. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 29 October–1 November 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 2661–2669. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhavasi, S.B.; Sukhavasi, S.B.; Elleithy, K.; Abuzneid, S.; Elleithy, A. Human Body-Related Disease Diagnosis Systems Using CMOS Image Sensors: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasoz, F.; Lisetti, C.L.; Vasilakos, A.V. Affectively intelligent and adaptive car interfaces. Inf. Sci. 2010, 180, 3817–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conjeti, S.; Singh, R.R.; Banerjee, R. Bio-inspired wearable computing architecture and physiological signal processing for on-road stress monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics, Hong Kong, China, 5–7 January 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 479–482. [Google Scholar]
- Rebolledo-Mendez, G.; Reyes, A.; Paszkowicz, S.; Domingo, M.C.; Skrypchuk, L. Developing a body sensor network to detect emotions during driving. IEEE Trans. Intel. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 1850–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haouij, N.; Poggi, J.-M.; Ghozi, R.; Sevestre-Ghalila, S.; Jaïdane, M. Random forest-based approach for physiological functional variable selection for driver’s stress level classification. Stat. Methods Appl. 2019, 28, 157–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, L.; Chiyomi, M.; Norihide, K.; Kazuya, T. Analysis of real-world driver’s frustration. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2010, 12, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollahosseini, A.; Chan, D.; Mahoor, M.H. Going deeper in facial expression recognition using deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 7–10 March 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Ma, N.; Deng, Y. Multi-network fusion based on cnn for facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computer Science, Electronics and Communication Engineering (CSECE 2018), Wuhan, China, 7–8 February 2018; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2018; pp. 166–169. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, A.; Mittal, N. Using CNN for facial expression recognition: A study of the effects of kernel size and number of filters on accuracy. Vis. Comput. 2020, 36, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, R.M.; Shen, Y.; Sohail, M.; Guo, M. Exnet: An efficient approach for emotion recognition in the wild. Sensors 2020, 20, 1087. [Google Scholar]
- Minaee, S.; Minaei, M.; Abdolrashidi, A. Deep-emotion: Facial expression recognition using attentional convolutional network. Sensors 2021, 21, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shi, B.E. Action unit selective feature maps in deep networks for facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 2031–2038. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Shan, S.; Zheng, Z. Multichannel pose-aware convolution neural networks for multi-view facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (F.G. 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 458–465. [Google Scholar]
- Ariel, R.-G.; Palade, V.; Elshaw, M.; Almakky, I. Deep learning for illumination invariant facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, R.K.; Karmakar, S.; Ramakrishnan, A.G.; Saha, N. Improving facial emotion recognition systems using gradient and laplacian images. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.05411. [Google Scholar]
- Shehu, H.A.; Sharif, M.H.; Uyaver, S. Facial expression recognition using deep learning. In Proceedings of the A.I.P. Conference Proceedings, Istanbul, Turkey, 17–21 June 2021; Volume 2334, p. 070003. [Google Scholar]
- Mahesh, V.G.V.; Chen, C.; Rajangam, V.; Raj, A.N.J.; Krishnan, P.T. Shape and Texture Aware Facial Expression Recognition Using Spatial Pyramid Zernike Moments and Law’s Textures Feature Set. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 52509–52522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, B.; Mahoor, M.H. Facial expression recognition using enhanced deep 3D convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Hu, H. Facial expression recognition using hierarchical features with deep comprehensive multipatches aggregation convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 21, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.; Ko, B.C. Driver’s facial expression recognition in real-time for safe driving. Sensors 2018, 18, 4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, M.; Veni, S. Driver emotion recognition for enhancement of human machine interface in vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Chennai, India, 4–6 April 2019; pp. 0420–0424. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, M.; Nam, J.; Ko, B.C. Lightweight multilayer random forests for monitoring driver emotional status. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 60344–60354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putatunda, S. Machine learning: An introduction. In Advances in Analytics and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Lecun, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning for A.I. Commun. ACM 2021, 64, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, L.; Zotin, A.; Cadena, F.; Korneeva, A.; Legalov, A.; Morales, B. Noise reduction techniques for processing of medical images. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, London, UK, 5–7 July 2017; Volume 1, pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Allagwail, S.; Gedik, O.S.; Rahebi, J. Face recognition with symmetrical face training samples based on local binary patterns and the Gabor filter. Symmetry 2019, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, W.A.; Kader, M.M. A review of histogram equalization techniques in image enhancement application. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1019, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.owlnet.rice.edu/~elec539/Projects99/BACH/proj2/wiener.html (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Alghamdi, J.; Alharthi, R.; Alghamdi, R.; Alsubaie, W.; Alsubaie, R.; Alqahtani, D.; Alqarni, L.; Alshammari, R. A survey on face recognition algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Computer Applications & Information Security (ICCAIS), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 19–21 March 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, F.P.; Habib, M.; Ahad, M.; Rahman, A.; Mckeever, S.; Moslehuddin, A.S.; Vasant, P. Face recognition-based real-time system for surveillance. Intel. Decis. Technol. 2017, 11, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.wikiwand.com/en/Kanade%E2%80%93Lucas%E2%80%93Tomasi_feature_tracker (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Bin, L.; Lima, D. Facial expression recognition via ResNet-50. Int. J. Cognit. Comput. Eng. 2021, 2, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, R.; Li, H.; Pan, J.; Ma, W.; Lin, J. Face recognition based on MTCNN and Facenet. 2021. Available online: https://jasonyanglu.github.io/files/lecture_notes/%E6%B7%B1%E5%BA%A6%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0_2020/Project/Face%20Recognition%20Based%20on%20MTCNN%20and%20FaceNet.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Zhang, N.; Luo, J.; Gao, W. Research on Face Detection Technology Based on MTCNN. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Network, Electronic and Automation (ICCNEA), Xi’an, China, 25–27 September 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.; Cohn, J.F.; Kanade, T.; Saragih, J.; Ambadar, Z.; Matthews, I. The extended Cohn-kanade dataset (ck+): A complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition-Workshops, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Erhan, D.; Carrier, P.L.; Courville, A.; Mirza, M.; Hamner, B.; Cukierski, W.; Tang, Y.; Thaler, D.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Challenges in representation learning: A report on three machine learning contests. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Daegu, Korea, 3–7 November 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Lundqvist, D.; Flykt, A.; Öhman, A. Karolinska directed emotional faces. Cognit. Emot. 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KMU-FED. Available online: http://cvpr.kmu.ac.kr/KMU-FED.htm (accessed on 4 December 2018).
- Zhang, J.; Mei, X.; Liu, H.; Yuan, S.; Qian, T. Detecting negative emotional stress based on facial expression in real time. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Wuxi, China, 19–21 July 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 430–434. [Google Scholar]
- Leone, A.; Caroppo, A.; Manni, A.; Siciliano, P. Vision-based road rage detection framework in automotive safety applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhavasi, S.B.; Sukhavasi, S.B.; Elleithy, K.; Abuzneid, S.; Elleithy, A. CMOS image sensors in surveillance system applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundmann, F.; Epstude, K.; Scheibe, S. Face masks reduce emotion-recognition accuracy and perceived closeness. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbon, C.C. Wearing face masks strongly confuses counterparts in reading emotions. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazhoohi, F.; Forby, L.; Kingstone, A. Facial masks affect emotion recognition in the general population and individuals with autistic traits. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziccardi, S.; Crescenzo, F.; Calabrese, M. What is hidden behind the mask? Facial emotion recognition at the time of COVID-19 pandemic in cognitively normal multiple sclerosis patients. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Databases | Parameters | First Approach-Values | Second Approach-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Size | 256 × 256 | 256 × 256 | |
| Optimizer | Stochastic Gradient Descent (S.G.D.) | Adam | |
| CK+ | Loss Function | Cross-Entropy | Cross-Entropy |
| FER 2013 | Activation Function | ReLU | ReLU |
| KDEF | Batch Size | 128 | 128 |
| KMU-FED | Learning Rate | 0.01 | 0.001 |
| Epochs | 100 | 100 | |
| Momentum | 0.9 | 0.9 | |
| Validation Frequency | 30 | 30 |
| Comparison Methods | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| DNN [44] | 93.2 |
| Inception-Resnet and LSTM [55] | 93.2 |
| Single-WRF [57] | 92.2 |
| Hierarchical W.R.F. with Normal Information Gain [57] | 90.9 |
| Hierarchical W.R.F. with Data Similarity [57] | 92.6 |
| DCMA-CNN [56] | 93.4 |
| LMRF [59] | 93.4 |
| First Proposed Approach | 93.4 |
| Second Proposed Approach | 96.1 |
| Comparison Methods | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| D.N.N. [44] | 66.4 |
| CNN-MNF [45] | 70.3 |
| Simple CNN Model [46] | 65.7 |
| eXnet [47] | 73.5 |
| eXnet-Resnet [47] | 71.1 |
| eXnet-DeXpression [47] | 68.0 |
| Deep-Emotion [48] | 70.0 |
| First Proposed Approach | 83.6 |
| Second Proposed Approach | 84.5 |
| Comparison Methods | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| TLCNN [49] | 86.4 |
| TLCNN-FOS [49] | 88.2 |
| MPCNN [50] | 86.9 |
| DSCAE-CNN [51] | 95.5 |
| STL + GRADIENT + LAPLACIAN RTCNN [52] | 88.1 |
| DL-FER [53] | 96.6 |
| RBFNN [54] | 88.8 |
| First Proposed Approach | 98.4 |
| Second Proposed Approach | 99.1 |
| Comparison Methods | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| Facial Landmarks + WRF [57] | 94.0 |
| CNN [76] | 97.3 |
| SqueezeNet [59] | 89.7 |
| MobileNetV2 [59] | 93.8 |
| MobileNetV3 [59] | 94.9 |
| LMRF [59] | 95.1 |
| VGG16 [77] | 94.2 |
| First Proposed Approach | 98.1 |
| Second Proposed Approach | 99.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sukhavasi, S.B.; Sukhavasi, S.B.; Elleithy, K.; El-Sayed, A.; Elleithy, A. Deep Neural Network Approach for Pose, Illumination, and Occlusion Invariant Driver Emotion Detection. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042352
Sukhavasi SB, Sukhavasi SB, Elleithy K, El-Sayed A, Elleithy A. Deep Neural Network Approach for Pose, Illumination, and Occlusion Invariant Driver Emotion Detection. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(4):2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042352
Chicago/Turabian StyleSukhavasi, Susrutha Babu, Suparshya Babu Sukhavasi, Khaled Elleithy, Ahmed El-Sayed, and Abdelrahman Elleithy. 2022. "Deep Neural Network Approach for Pose, Illumination, and Occlusion Invariant Driver Emotion Detection" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 4: 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042352
APA StyleSukhavasi, S. B., Sukhavasi, S. B., Elleithy, K., El-Sayed, A., & Elleithy, A. (2022). Deep Neural Network Approach for Pose, Illumination, and Occlusion Invariant Driver Emotion Detection. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(4), 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042352








