A Bayesian Hierarchical Spatial Model to Correct for Misreporting in Count Data: Application to State-Level COVID-19 Data in the United States
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Poisson-Logistic Model
- What value is most likely for the reporting probability?
- What value would be considered unusually high?
2.2. Model with False Positives
3. A Simulation Study
4. Application
4.1. Data
4.2. Priors
4.3. Results
4.4. Model Checking
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Explicit Forms for M1 to M5
Appendix B. Sensitivity Analysis for M5
| Priors | Beta (7, 55), Gamma (5, 1) | Beta (5, 78), Gamma (5, 1) | Beta (5, 78), Gamma (30, 1) | Beta (7, 55), Gamma (30, 1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M 1 | L | U | M | L | U | M | L | U | M | L | U | |
| Intercept | 9.653 | 9.133 | 10.253 | 10.253 | 9.643 | 10.956 | 10.213 | 9.653 | 10.863 | 9.635 | 9.145 | 10.209 |
| Uninsured | −0.103 | −0.278 | 0.078 | −0.101 | −0.287 | 0.072 | −0.102 | −0.286 | 0.072 | −0.097 | −0.289 | 0.095 |
| Obesity | −0.199 | −0.415 | 0.02 | −0.196 | −0.423 | 0.017 | −0.196 | −0.403 | 0.021 | −0.205 | −0.426 | 0.013 |
| Alcoholism | 0.204 | 0.023 | 0.387 | 0.201 | 0.022 | 0.377 | 0.209 | 0.029 | 0.389 | 0.213 | 0.037 | 0.39 |
| AirPollution | 0.012 | −0.182 | 0.208 | 0.005 | −0.191 | 0.217 | −0.002 | −0.205 | 0.191 | 0.018 | −0.182 | 0.218 |
| Drug_death | −0.07 | −0.263 | 0.119 | −0.07 | −0.265 | 0.117 | −0.065 | −0.275 | 0.138 | −0.071 | −0.27 | 0.128 |
| MDI | 0.038 | −0.147 | 0.242 | 0.049 | −0.147 | 0.236 | 0.048 | −0.154 | 0.251 | 0.038 | -0.158 | 0.234 |
| Smoking | −0.369 | −0.629 | −0.098 | −0.375 | −0.639 | −0.092 | −0.392 | −0.653 | −0.129 | −0.37 | −0.63 | −0.107 |
| Inactivity | 0.417 | 0.149 | 0.666 | 0.415 | 0.149 | 0.683 | 0.427 | 0.152 | 0.7 | 0.413 | 0.129 | 0.694 |
| Popdensity | −0.025 | −0.216 | 0.17 | −0.023 | −0.216 | 0.169 | −0.022 | −0.227 | 0.182 | −0.034 | −0.213 | 0.146 |
| Intercept | −1.88 | −2.572 | −1.254 | −2.557 | −3.301 | −1.891 | −2.53 | −3.224 | −1.898 | −1.877 | −2.525 | −1.294 |
| Testing | 0.415 | 0.187 | 0.682 | 0.358 | 0.176 | 0.572 | 0.362 | 0.162 | 0.579 | 0.426 | 0.202 | 0.688 |
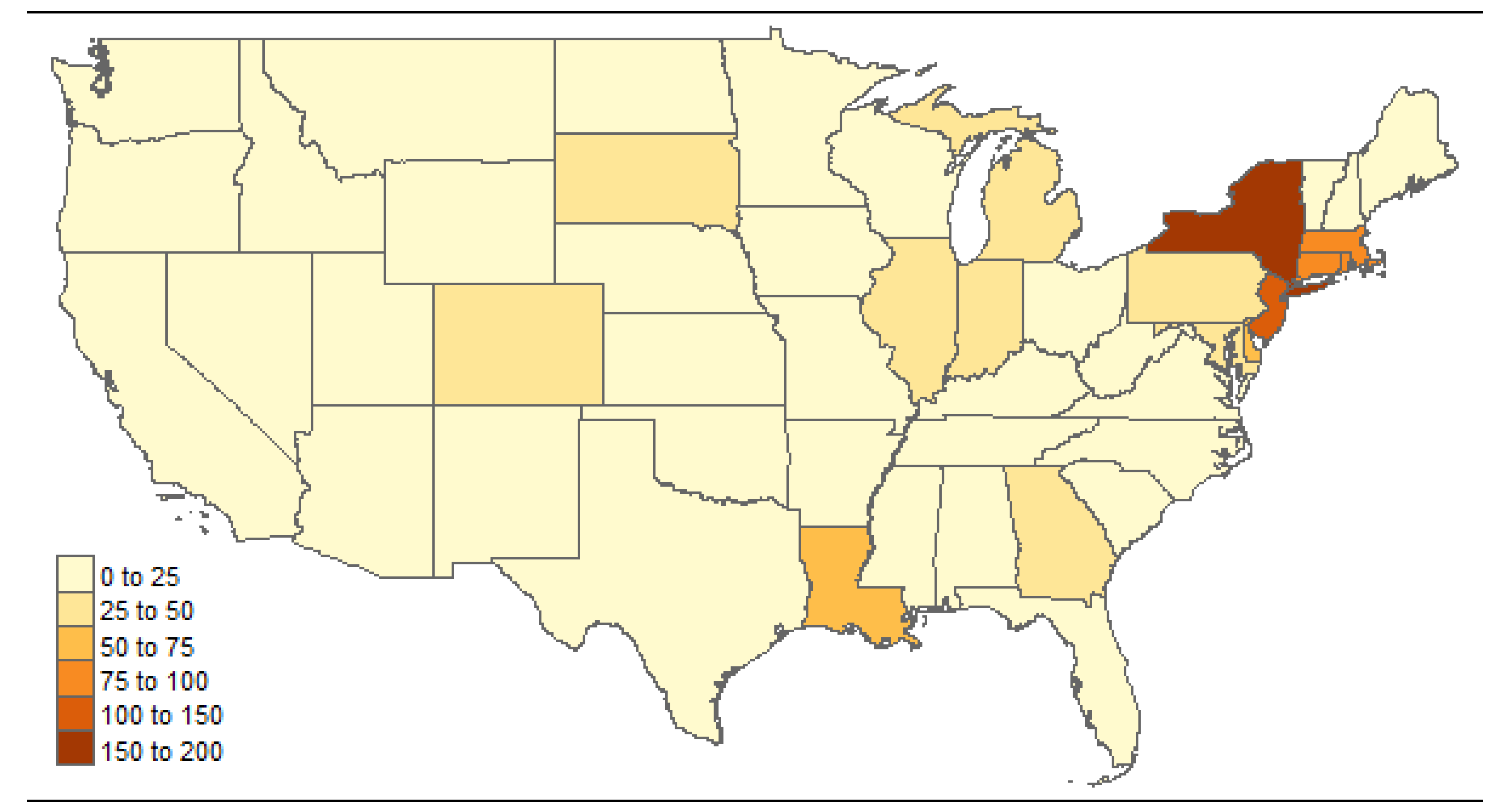
Appendix C. Posterior Estimation of Reporting Rate for Each State

Appendix D



Appendix E. Codes
Appendix E.1. Stan Code for Model 5
Appendix E.2. R Code for Beta_elicit Function
Appendix E.3. R Code for Gamma_elicit Function
References
- Bailey, T.; Carvalho, M.S.; Lapa, T.; Souza, W.; Brewer, M. Modeling of under-detection of cases in disease surveillance. Ann. Epidemiol. 2005, 15, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, G.L.; Loschi, R.H.; Assunção, R.M. A random-censoring Poisson model for underreported data. Stat. Med. 2017, 36, 4873–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelmann, R.; Zimmermann, K.F. Poisson–Logistic Regression; Volkswirtschaftl. Fakultät d. Ludwig-Maximilians-Univ. München: Munich, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Dvorzak, M.; Wagner, H. Sparse Bayesian modelling of underreported count data. Stat. Model. 2016, 16, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamey, J.D.; Young, D.M.; Boese, D. A Bayesian hierarchical model for Poisson rate and reporting-probability inference using double sampling. Aust. N. Z. J. Stat. 2006, 48, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaweno, D.; Trauer, J.M.; Denholm, J.T.; McBryde, E.S. A novel Bayesian geospatial method for estimating tuberculosis incidence reveals many missed TB cases in Ethiopia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoner, O.; Economou, T.; Drummond Marques da Silva, G. A hierarchical framework for correcting under-reporting in count data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2019, 114, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Besag, J.; York, J.; Mollié, A. Bayesian image restoration, with two applications in spatial statistics. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1991, 43, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebler, A.; Sørbye, S.H.; Simpson, D.; Rue, H. An intuitive Bayesian spatial model for disease mapping that accounts for scaling. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2016, 25, 1145–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simpson, D.; Rue, H.; Riebler, A.; Martins, T.G.; Sørbye, S.H. Penalising model component complexity: A principled, practical approach to constructing priors. Stat. Sci. 2017, 32, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, B.; Gelman, A.; Hoffman, M.D.; Lee, D.; Goodrich, B.; Betancourt, M.; Brubaker, M.A.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Riddell, A. Stan: A probabilistic programming language. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 76, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Valpine, P.; Turek, D.; Paciorek, C.J.; Anderson-Bergman, C.; Lang, D.T.; Bodik, R. Programming with models: Writing statistical algorithms for general model structures with NIMBLE. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2017, 26, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sood, N.; Simon, P.; Ebner, P.; Eichner, D.; Reynolds, J.; Bendavid, E.; Bhattacharya, J. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2–Specific Antibodies among Adults in Los Angeles County, California, on April 10–11, 2020. JAMA 2020, 323, 2425–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendavid, E.; Mulaney, B.; Sood, N.; Shah, S.; Ling, E.; Bromley-Dulfano, R.; Lai, C.; Weissberg, Z.; Saavedra, R.; Tedrow, J.; et al. COVID-19 Antibody Seroprevalence in Santa Clara County, California. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 50, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortacsu, A.; Liu, J.; Schwieg, T. Estimating the Fraction of Unreported Infections in Epidemics with a Known Epicenter: An Application to COVID-19. J. Econom. 2020, 220, 106–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, L.C.; Bernardes, A.T. Estimate of Underreporting of COVID-19 in Brazil by Acute Respiratory Syndrome Hospitalization Reports; IDEAS; Cedeplar, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.; Wheeler-Martin, K.; Simpson, D.; Mooney, S.J.; Gelman, A.; DiMaggio, C. Bayesian hierarchical spatial models: Implementing the Besag York Mollié model in stan. Spat. Spatio-Temporal Epidemiol. 2019, 31, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freni-Sterrantino, A.; Ventrucci, M.; Rue, H. A note on intrinsic conditional autoregressive models for disconnected graphs. Spat. Spatio-Temporal Epidemiol. 2018, 26, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindgren, F.; Rue, H. Bayesian spatial modelling with R-INLA. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 63, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rue, H.; Martino, S.; Chopin, N. Approximate Bayesian inference for latent Gaussian models by using integrated nested Laplace approximations. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2009, 71, 319–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratcher, T.L.; Stamey, J.D. Estimation of Poisson rates with misclassified counts. Biom. J. J. Math. Methods Biosci. 2002, 44, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrick, E.J.; Christensen, R.; Johnson, W. A new perspective on priors for generalized linear models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1996, 91, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihaka, R.; Gentleman, R. R: A language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar]

| Average Bias | MSE | Coverage | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Truth | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 |
| −2 | (N/A) | 0.672 | (N/A) | 0.252 | 0.24 | (N/A) | 9.697 | (N/A) | 0.082 | 0.076 | (N/A) | 0.33 | (N/A) | 1 | 1 | |
| 0.5 | (N/A) | 0.958 | (N/A) | 0.046 | 0.076 | (N/A) | 9.844 | (N/A) | 0.079 | 0.087 | (N/A) | 0.2 | (N/A) | 1 | 1 | |
| 5 | −0.121 | 0.456 | −0.213 | 0.102 | 0.004 | 0.019 | 0.558 | 0.047 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| −1 | −0.018 | −0.024 | 0.065 | 0.061 | −0.021 | 0.025 | 0.027 | 0.01 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.96 | |
| 2 | −0.073 | −0.075 | −0.161 | −0.162 | −0.016 | 0.036 | 0.035 | 0.031 | 0.031 | 0.007 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.99 | |
| 6 | (N/A) | (N/A) | (N/A) | (N/A) | −0.497 | (N/A) | (N/A) | (N/A) | (N/A) | 1.635 | (N/A) | (N/A) | (N/A) | (N/A) | 1 | |
| Variable | Description | Max | Min | Mean | Median | sd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AirPollution | The average exposure of the general public to particulate matter of 2.5 microns or less measured in micrograms per cubic meter (3-year estimate) | 12.80 | 4.40 | 7.48 | 7.40 | 1.45 |
| Uninsured (%) | Percentage of population not covered by private or public health insurance | 17.50 | 2.80 | 8.09 | 8.10 | 2.99 |
| Inactive (%) | Percentage of adults who reported doing no physical activity or exercise other than their regular job in the past 30 days | 32.40 | 16.40 | 24.17 | 23.80 | 3.84 |
| Obesity (%) | Percentage of adults with a body mass index of 30.0 or higher based on reported height and weight | 39.50 | 22.90 | 31.46 | 30.90 | 3.86 |
| Smoking (%) | Percentage of adults who reported smoking at least 100 cigarettes in their lifetime and currently smoke daily or some days | 25.20 | 9.00 | 16.61 | 16.10 | 3.32 |
| Alcoholism (%) | Percentage of adults who reported binge drinking (four or more (women) or five or more (men) drinks on one occasion in the past 30 days) or heavy drinking (eight or more (women) or 15 or more (men) drinks per week) | 26.30 | 11.30 | 18.17 | 18.20 | 3.10 |
| Drug deaths | Number of deaths due to drug injury (unintentional, suicide, homicide or undetermined) per 100,000 population | 48.30 | 7.20 | 20.78 | 19.90 | 8.87 |
| MDI | An index of seventeen socioeconomic indicators from the American Community Survey 5-year sample at the block group level | 21.45 | 8.23 | 13.81 | 13.48 | 3.43 |
| Popdensity | Population per square mile | 11,011.00 | 6.00 | 424.33 | 106.00 | 1566.86 |
| Pop | Population | 39,144,818 | 586,107 | 6,515,301 | 4,670,724 | 7,268,509 |
| Testing | The total number of testing per 1000 people as of the cut-off date | 62.81 | 10.86 | 22.09 | 17.95 | 11.03 |
| Variable | M1 | M2 | M3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept1(γ0) | |||
| Uninsured () | |||
| Obesity () | |||
| Alcoholism () | |||
| AirPollution () | |||
| Drug deaths () | |||
| MDI () | |||
| Smoking () | |||
| Inactivity () | |||
| Popdensity () | |||
| Intercept () | (N/A) | (N/A) | |
| Testing () | (N/A) | (N/A) | |
| DIC | 152,001 | 131,129 | 633.1 |
| M4 | M5 | ||
| Intercept() | |||
| Uninsured () | |||
| Obesity () | |||
| Alcoholism () | |||
| AirPollution () | 0.02 | 0.017 | |
| Drug deaths () | |||
| MDI () | 0.039 | 0.043 | |
| Smoking () | |||
| Inactivity () | |||
| Popdensity () | |||
| Intercept () | |||
| Testing() | |||
| DIC | 631.1 | 631.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Song, J.J.; Stamey, J.D. A Bayesian Hierarchical Spatial Model to Correct for Misreporting in Count Data: Application to State-Level COVID-19 Data in the United States. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063327
Chen J, Song JJ, Stamey JD. A Bayesian Hierarchical Spatial Model to Correct for Misreporting in Count Data: Application to State-Level COVID-19 Data in the United States. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(6):3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063327
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jinjie, Joon Jin Song, and James D. Stamey. 2022. "A Bayesian Hierarchical Spatial Model to Correct for Misreporting in Count Data: Application to State-Level COVID-19 Data in the United States" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 6: 3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063327
APA StyleChen, J., Song, J. J., & Stamey, J. D. (2022). A Bayesian Hierarchical Spatial Model to Correct for Misreporting in Count Data: Application to State-Level COVID-19 Data in the United States. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(6), 3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063327






