Amino Acid Complexes of Zirconium in a Carbon Composite for the Efficient Removal of Fluoride Ions from Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Graphite Oxide
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Zr-Amino Acid-Graphite Oxide Compounds
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results
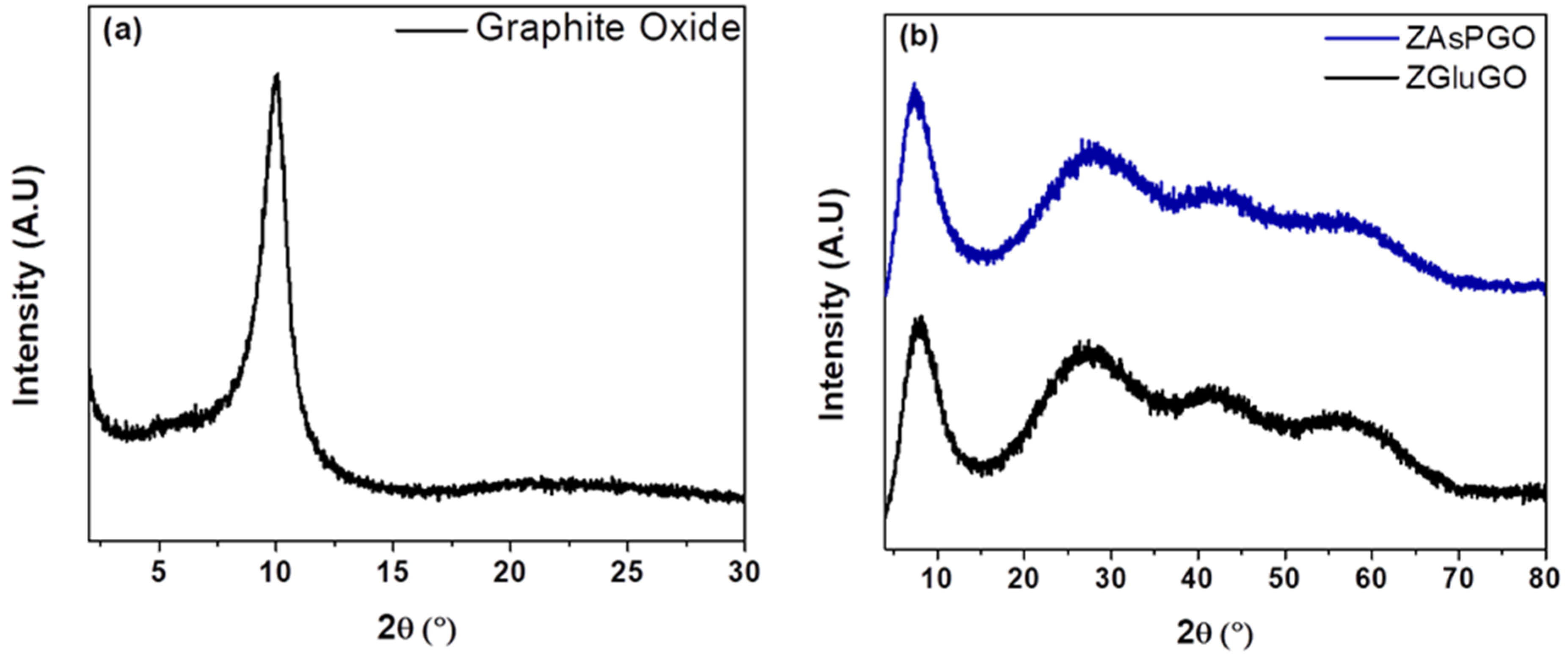
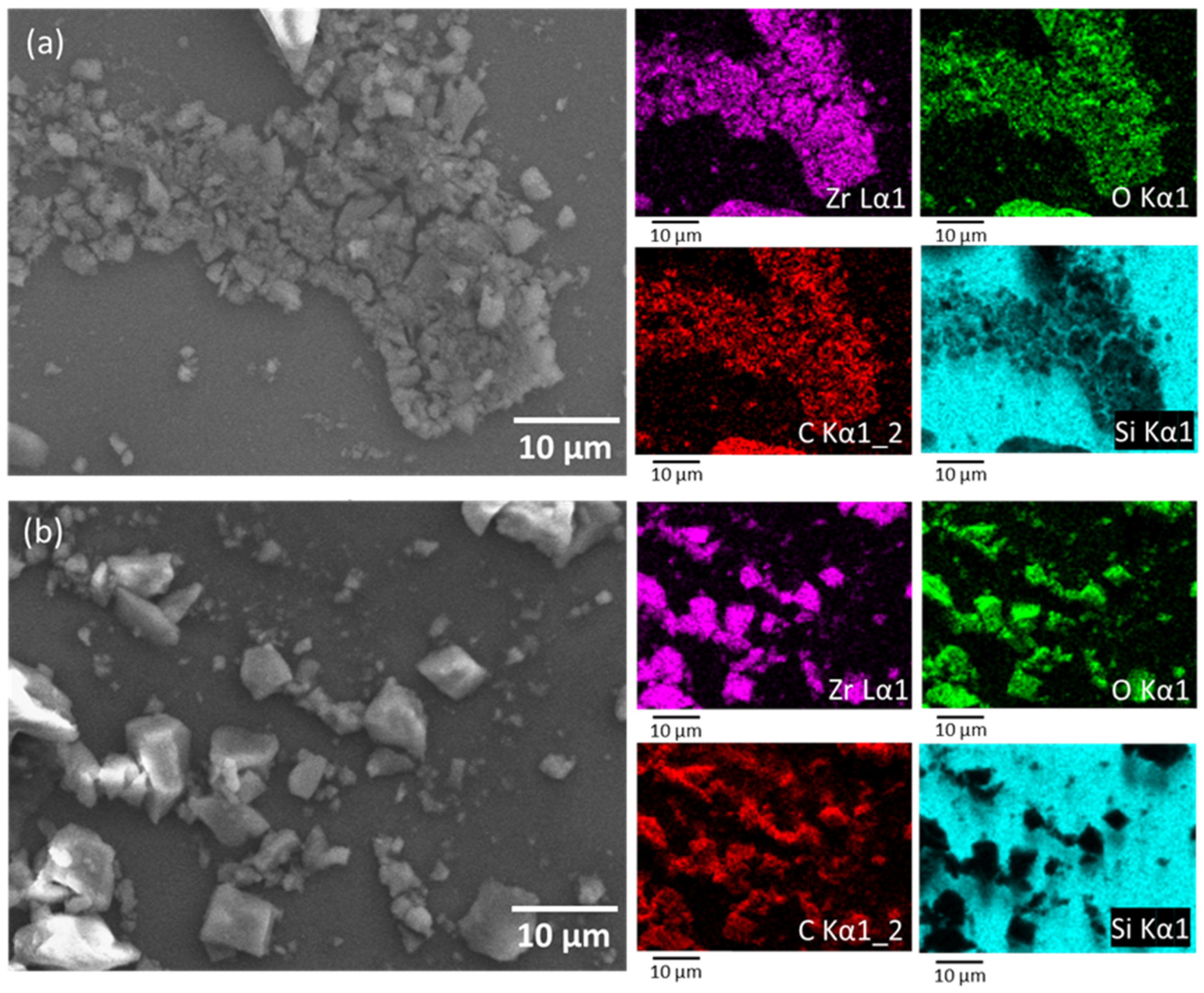
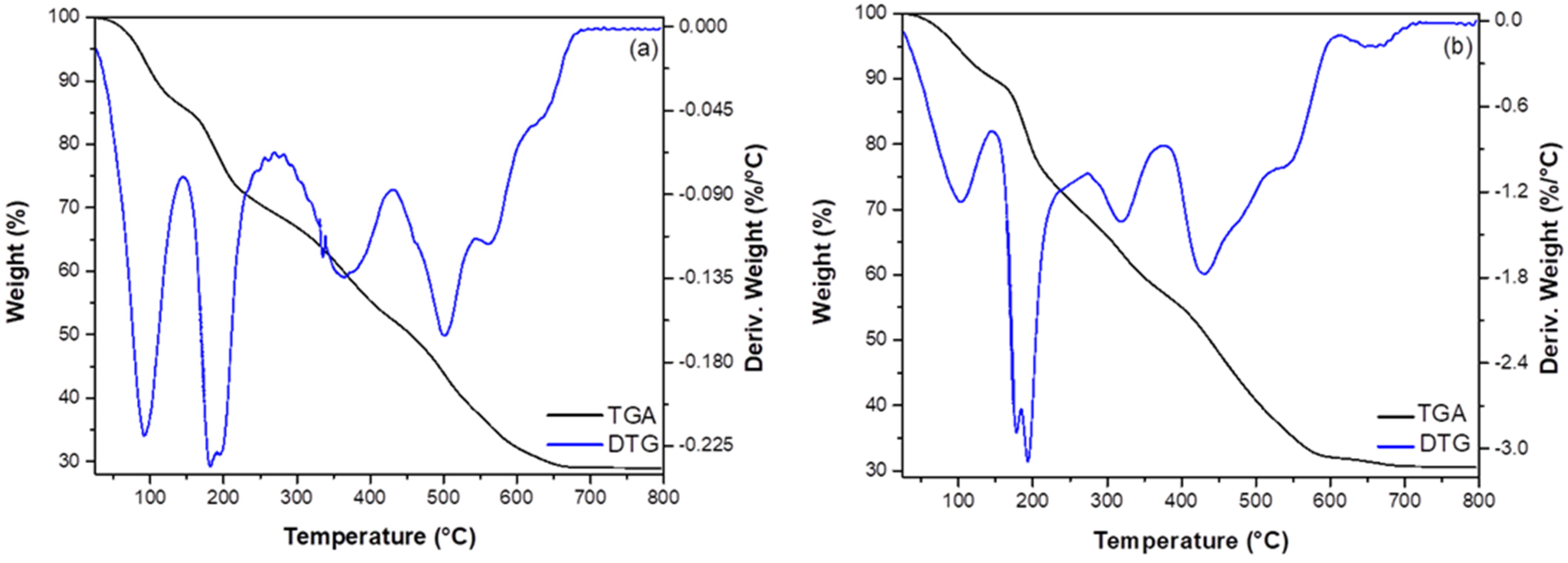
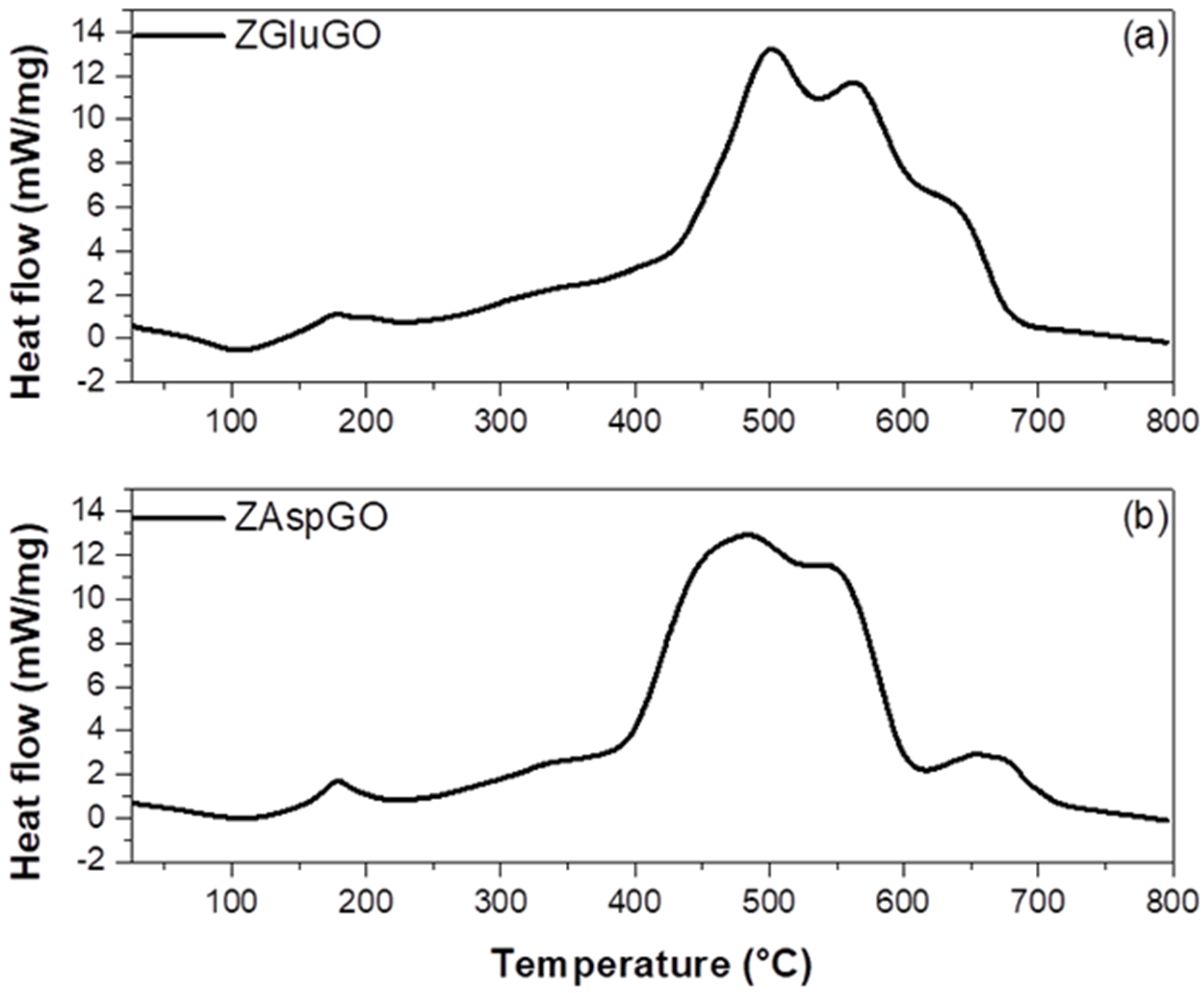
3.1. Characterization of Adsorbents
3.2. Adsorption Studies
3.2.1. Effect of pH
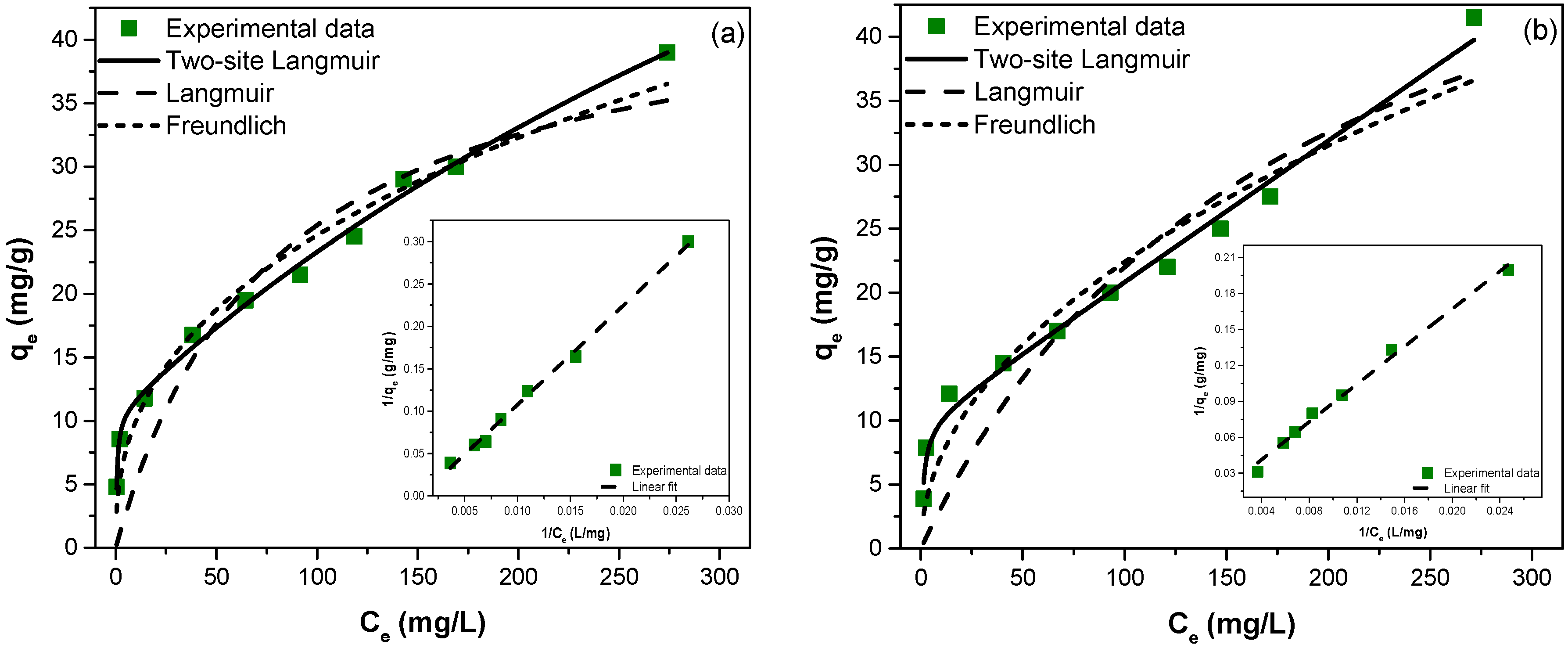
3.2.2. Adsorption Isotherms
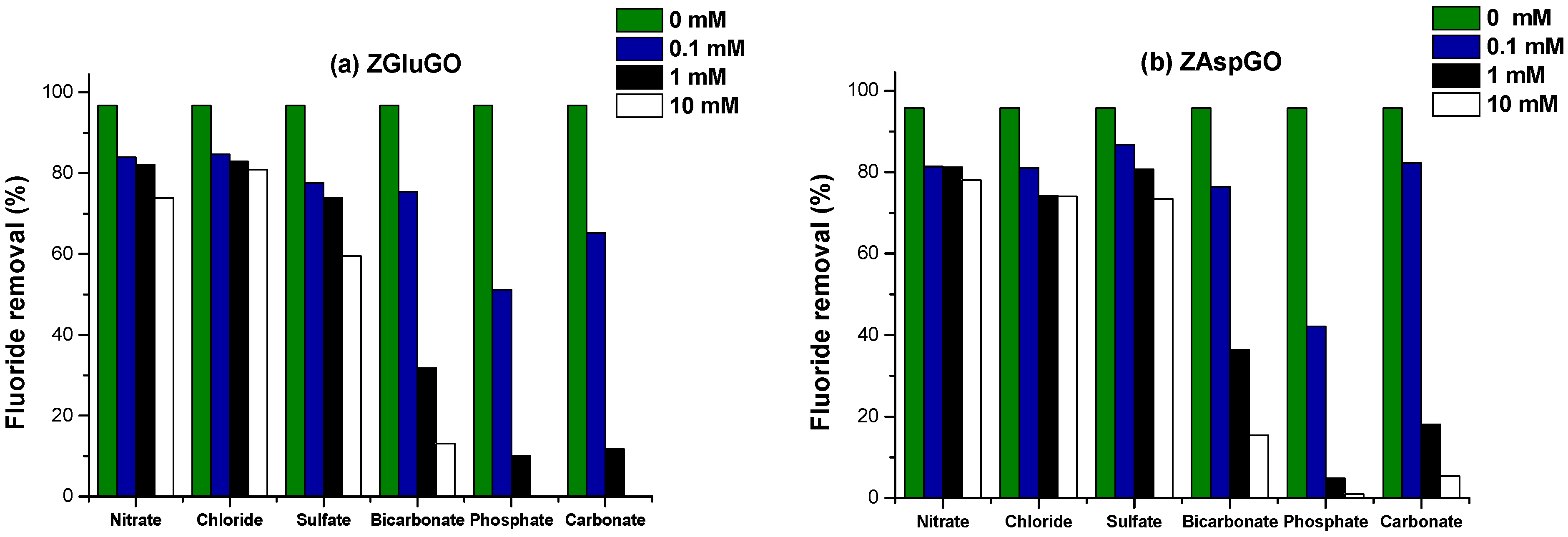
3.2.3. Interfering Ions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goncharuk, V. Role of Water in Human Life. In Drinking Water; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosborg, I.; Ferrante, M.; Soni, V. Microminerals at optimum concentrations: Protection against diseases. In Drinking Water Minerals and Mineral Balance; Rosborg, I., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 53–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubisa, S.L.; Choubisa, D. Status of Industrial Fluoride Pollution and Its Diverse Adverse Health Effects in Man and Domestic Animals in India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7244–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, W.M.; Smedley, P.L. Fluoride in natural waters. In Essentials of Medical Geology, 2nd ed.; Selinus, O., Alloway, B., Centeno, J.A., Finkelman, R.B., Fuge, R., Lindh, U., Smedley, P.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 311–336. [Google Scholar]
- Hurtado-Jiménez, R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J. Estimation of exposure to fluoride in “Los Altos de Jalisco”, México. Salud. Publica. Mex. 2005, 47, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sairam Sundaram, C.; Meenakshi, S. Fluoride sorption using organic–inorganic hybrid type ion exchangers. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2009, 333, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.F.; Atwa, S.M.; El-Giar, E.M. 6—Development of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Fluoride and Organic Matter Removal from Drinking Water. In Water Purification; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 209–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crittenden, J.C.; Trussell, R.R.; Hand, D.W.; Howe, K.J.; Tchobanoglous, G. Introduction. In MWH’s Water Treatment: Principles and Design, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Mao, L.; Wang, H. Adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution by using hybrid adsorbent fabricated with Mg/Fe composite oxide and alginate via a facile method. J. Fluor. Chem. 2017, 200, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Montoya, V.; Ramírez-Montoya, L.A.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Montes-Morán, M.A. Optimizing the removal of fluoride from water using new carbons obtained by modification of nut shell with a calcium solution from egg shell. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 62, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Singh, K.P.; Singh, V.K. Wastewater treatment using low cost activated carbons derived from agricultural byproducts-A case study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.S.; Raichur, A.M. Abatement of fluoride from water using manganese dioxide-coated activated alumina. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliyekkal, S.M.; Shukla, S.; Philip, L.; Nambi, I.M. Enhanced fluoride removal from drinking water by magnesia-amended activated alumina granules. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 140, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Guo, H. Fluoride adsorption on modified natural siderite: Optimization and performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutli-Sequeira, A.; Solache-Ríos, M.; Balderas-Hernández, P. Modification effects of hematite with aluminum hydroxide on the removal of fluoride ions from water. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Parker, D.J.; Smith, M.D. Adsorption kinetics of fluoride on low cost materials. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4929–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sujana, M.G.; Mishra, A.; Acharya, B.C. Hydrous ferric oxide doped alginate beads for fluoride removal: Adsorption kinetics and equilibrium studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 270, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila-Rodriguez, J.L.; Escobar-Barrios, V.A.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Removal of fluoride from drinking water by a chitin-based biocomposite in fixed-bed columns. J. Fluor. Chem. 2012, 140, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.K.; Mishra, S.; Patnaik, T.; Patel, R.K.; Jha, U.; Dey, R.K. Fluoride removal performance of a new hybrid sorbent of Zr(IV)-ethylenediamine. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, F.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Hadizadeh, Z. Modification of Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanoparticles with zirconium oxide; preparation, characterization and its application toward fluoride removal. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 72058–72068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, M.; Wu, Z.; Wei, L.; Mitra, S. Water defluoridation using a nanostructured diatom–ZrO2 composite synthesized from algal Biomass. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Xu, J.; Wu, B.; Li, Z.; Liu, X. Enhanced removal of fluoride by polystyrene anion exchanger supported hydrous zirconium oxide nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9347–9354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, P.C.; Swain, S.K.; Patel, S.B.; Patnaik, T.; Muller, F.; Delpeux-Ouldriane, S.; Das, S.; Dey, R.K. Kinetics and thermodynamics of defluoridation of drinking water using high performance hybrid zirconium (IV)-hexamethylenediamine: A comparative aspect with ion-exchanger amorphous zirconium (IV) phosphate. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 13, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Nasir, M. Development of Zr(IV)—doped polypyrrole/zirconium (IV) iodate composite for efficient removal of fluoride from water environment. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 19, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, I.; Ghosh, A.; Nandi, D.; Gupta, K.; Chatterjee, D.; Ghosh, U.C. β-cyclodextrin modified hydrous zirconium oxide: Synthesis, characterization and defluoridation performance from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.; Bandhoyapadhyay, D.; Ghosh, U.C. Adsorption kinetics of fluoride on iron(III)-zirconium(IV) hybrid oxide. Adsorption 2007, 13, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geleta, W.S.; Alemayehu, E.; Lennartz, B. Enhanced Defluoridation of Water Using Zirconium—Coated Pumice in Fixed-Bed Adsorption Columns. Materials 2021, 14, 6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Lan, G.; Xu, Q. Synthesizing a Novel Zr/Fe/Al-Incorporated Cross-linked Chitosan as Absorbent for Effective Removal of Fluoride from Aqueous Solution. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, T.; Chan, T.S.A.; Jande, Y.A.C.; Shen, J. Removal of fluoride from water using activated carbon fibres modified with zirconium by a drop-coating method. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.M.; Meenakshi, S. Chemistry of defluoridation by one-pot synthesized dicarboxylic acids mediated polyacrylamide-zirconium complex. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.M.; Elanchezhiyan, S.S.; Lee, G.; Meenakshi, S. Defluoridation of water by graphene oxide supported needle-like complex adsorbents. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2016, 26, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathibha, C.; Biswas, A.; Avinash Chunduri, L.A.; Reddy, S.K.; Loganathan, P.; Kalaruban, M.; Venkatarmaniah, K. Zr(IV) functionalized graphene oxide anchored sand as potential and economic adsorbent for fluoride removal from water. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 109, 108081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Bandosz, T.J. New Approaches in the Detoxification of CWAs. In Detoxification of Chemical Warfare Agents; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 37–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Joshua, K.; Mitchella, J.K.; Teresa, J.; Bandosz, T.J. Reactive adsorption of mustard gas surrogate on zirconium (hydr)oxide/graphite oxide composites: The role of surface and chemical features. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, P.; Nouruzi, N.; Doustkhah, E.; Mohtasham, H.; Ahadi, A.; Ghiasi-Moaser, A.; Rostamnia, S.; Mahmoudi, G.; Khataee, A. Zirconium based porous coordination polymer (PCP) bearing organocatalytic ligand: A promising dual catalytic center for ultrasonic heterocycle synthesis. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 58, 104653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Ren, J.; El Hankari, S.; Huo, J. Aqueous Synthesis of a Mesoporous Zr-Based Coordination Polymer for Removal of Organic Dyes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Li, B.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Shi, J.; Gu, J. Effective Adsorption and Enhanced Removal of Organophosphorus Pesticides from Aqueous Solution by Zr-Based MOFs of UiO-67. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyaseelan, A.; Viswanathan, N. Facile Fabrication of Zirconium–Organic Framework–Embedded Chitosan Hybrid Spheres for Efficient Fluoride Adsorption. ACS EST Water 2022, 2, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Jimenez, L.H.; Hurt, R.H.; Matos, J.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Zirconium–carbon hybrid sorbent for removal of fluoride from water: Oxalic acid mediated Zr(IV) assembly and adsorption mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcano, D.C.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Berlin, J.M.; Sinitskii, A.; Sun, Z.; Slesarev, A.; Alemany, L.B.; Lu, W.; Tour, J.M. Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4806–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Huang, X.; Yu, C. Fast capture of fluoride by anion-exchange zirconium–graphene hybrid adsorbent. Langmuir 2019, 35, 6861–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.-P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivanna, M.; Nagappa, N.; Siddalingappa, D.M. Structural, Morphological and Photoluminescence Studies of Pure ZrO2 and ZrO2: Eu+3 Nanophosphors Synthesised by Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Technique. Plasmonics 2020, 15, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, G.V.; Petrov, A.I.; Staloverova, N.A.; Shubin, A.A.; Dergachev, I.D. Complex formation of Sn(II) with l-cysteine: An IR, DTA/TGA and DFT Investigation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 122, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudorachi, N.; Chiriac, A.P. TGA/FTIR/MS study on thermal decomposition of poly(succinimide) and sodium poly(aspartate). Polym. Test. 2011, 30, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W. Graphite Oxide. In Springer Handbook of Nanomaterials; Vajtai, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 571–604. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, M.; Ojha, P.K.; Jayasingh, E.M.; Prasad, C.D. Synthesis of nanocrystalline yttria stabilized zirconia for SOFC. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2011, 1, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, L.; Guo, D.; Duan, J.; Sang, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Terbium–aspartic acid nanocrystals with chirality-dependent tunable fluorescent properties. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, B.; Nema, A.; Shetake, N.G.; Gupta, J.; Barick, K.C.; Lawande, M.A.; Pandey, B.N.; Priyadarsini, I.K.; Hassan, P.A. Glutamic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles for tumor-targeted imaging and therapeutics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.E.; Mohammed, A.M.A. Experimental and computational vibration study of amino acids. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2013, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, M. Preparation, characterization of L-aspartic acid chelated calcium from oyster shell source and its calcium supplementation effect in rats. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullick, A.; Neogi, S. Acoustic cavitation induced synthesis of zirconium impregnated activated carbon for effective fluoride scavenging from water by adsorption. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2008, 45, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hashemi, R.; Safari, N.; Amani, S.; Amani, V.; Khavasi, H.R. Monomer and cyclic tetramer of copper(II) complexes: Synthesis, characterization and crystal structure determination of [Cu(dm4bt)Cl(Hipht)] and [{Cu(dm4bt)(H2O)(ipht)}4·2H2O]. Polyhedron 2010, 29, 2409–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, G.B.; Huber, F.; Phillips, R.J. Diagnosis of the nature of carboxylate coordination from the direction of shifts of carbon-oxygen stretching frequencies. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1985, 104, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Applications in Inorganic Chemistry. In Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, 6th ed.; Nakamoto, K., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 149–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.; Bushiri, M.J.; Jayakumar, K.; Vaidyan, V.K. Infrared and Raman spectral studies of zirconium hydrated nitrate. AIP Conf. Proc. 2008, 1075, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jere, G.V.; Santhamma, M.T. IR and laser raman studies on peroxo fluoro species of zirconium. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1977, 24, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, C.K.; Ahern, K.G.; Van Holde, K.E. Bioquímica, 3rd ed.; Pearson Eduación, S.A.: Madrid, Spain, 2002; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- Király, Z.; Dékány, I. Interpretation of adsorption excess quantities: The absolute surface excess concentration. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1990, 268, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakre, D.; Jagtap, S.; Sakhare, N.; Labhsetwar, N.; Meshram, S.; Rayalu, S. Chitosan based mesoporous Ti–Al binary metal oxide supported beads for defluoridation of water. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 158, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z. Bioinspired synthesis of mesoporous ZrO2 nanomaterials with elevated defluoridation performance in agarose gels. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 49811–49818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, C.; Yuan, K.; Gan, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. Characterization and adsorption mechanism of ZrO2 mesoporous fibers for health-hazardous fluoride removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 346, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ouyang, G.; Han, R. Enhanced fluoride adsorption from aqueous solution by zirconium (IV)-impregnated magnetic chitosan graphene oxide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Puri, A. A review of permissible limits of drinking water. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 16, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perosa, A.; Zecchini, F. Methods and Reagents for Green Chemistry: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
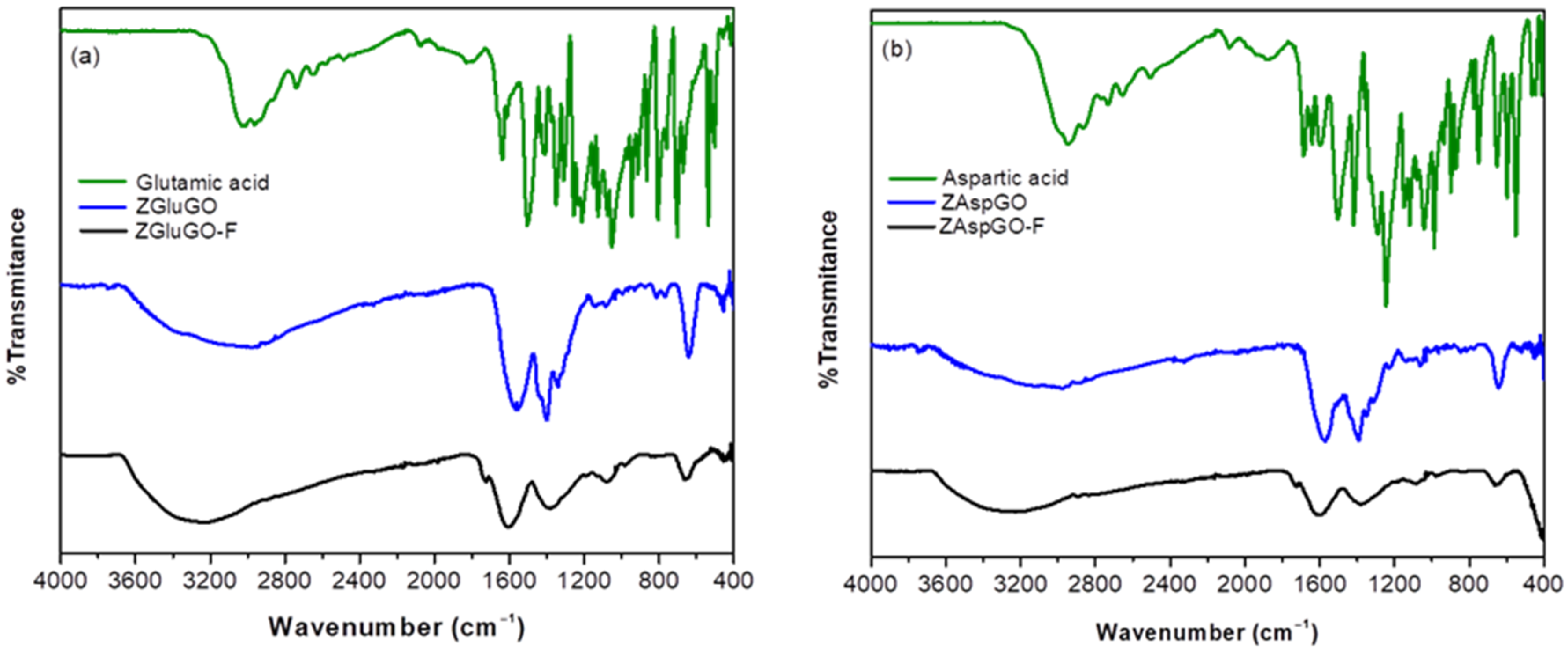


| Compound | ∆ (νas − νs) | Bond Type |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium glutamate | 78 | Ionic |
| ZGluGO | 231 | Monodentate |
| 130 | Bridge | |
| Sodium aspartate | 108 | Ionic |
| ZAspGO | 260 | Monodentate |
| 158 | Bridge |
| Material | Isotherm Model | Parameters | Statistics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | χ2 | |||||||
| Langmuir | KL | RL | ||||||
| (mg/g) | (L/mg) | |||||||
| ZGluGO | Nonlinear | 45.28 | 0.013 | 0.204–0.939 | 0.8492 | 16.81 | ||
| Linear | 38.76 | 0.025 | 0.116–0.88 | 0.9070 | – | |||
| ZAspGO | Nonlinear | 62.46 | 0.005 | 0.400–0.976 | 0.8154 | 21.51 | ||
| Linear | 39.37 | 0.018 | 0.153–0.915 | 0.8243 | – | |||
| Freundlich | KF | n | ||||||
| (mg/g) | ||||||||
| ZGluGO | Nonlinear | 4.044 | 0.392 | – | 0.9653 | 3.865 | ||
| Linear | 6.112 | 0.299 | – | 0.9728 | - | |||
| ZAspGO | Nonlinear | 2.333 | 0.491 | – | 0.9205 | 9.260 | ||
| Linear | 4.218 | 0.363 | – | 0.9448 | – | |||
| Two-site Langmuir | q1 | b1 | q2 | b2 | ||||
| (mg/g) | (L/mg) | (mg/g) | (L/mg) | |||||
| ZGluGO | Nonlinear | 97.32 | 0.0015 | 10.64 | 1.8547 | – | 0.9937 | 0.705 |
| ZAspGO | – | – | 9.924 | 0.7663 | – | 0.9830 | 1.976 | |
| q1 + q2 | b1 + b2 | |||||||
| ZGluGO | Linear | 105.3 | 0.0008 | – | 0.9959 | – | ||
| ZAspGO | 101.0 | 0.0013 | – | 0.9927 | – | |||
| Adsorbent | AC (mg/g) | pH | CT (min) | Interfering Ions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxalic acid-mediated polyacrylamide-zirconium complex | 9.6 | 3–7 | 20 | HCO3− | [30] |
| Oxalic acid-graphene oxide-zirconium complex | 9.7 | 3–7 | 18 | HCO3− | [31] |
| Zirconium-oxalic acid-activated carbon | 7.4 | 7 | 50 | Mixture of Cl−, SO42−, PO43−, NO3− and HCO3− | [39] |
| Zirconium-impregnated magnetic chitosan-graphene oxide | 8.84 | 4–8 | 180 | HCO3- | [64] |
| Zirconium-modified activated carbon fibers | 28.5 | 3.2–5.6 | 360 | - | [29] |
| ZGluGO | 105.3 | 3–7 | 180 | HCO3−, CO32− and PO43− | Present work |
| ZAspGO | 101.0 | 3–7 | 180 | HCO3−, CO32− and PO43− | Present work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Aguiñaga, E.; Pérez-Tavares, J.A.; Patakfalvi, R.; Szabó, T.; Illés, E.; Pérez Ladrón de Guevara, H.; Cardoso-Avila, P.E.; Castañeda-Contreras, J.; Saavedra Arroyo, Q.E. Amino Acid Complexes of Zirconium in a Carbon Composite for the Efficient Removal of Fluoride Ions from Water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063640
González-Aguiñaga E, Pérez-Tavares JA, Patakfalvi R, Szabó T, Illés E, Pérez Ladrón de Guevara H, Cardoso-Avila PE, Castañeda-Contreras J, Saavedra Arroyo QE. Amino Acid Complexes of Zirconium in a Carbon Composite for the Efficient Removal of Fluoride Ions from Water. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(6):3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063640
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Aguiñaga, Efrén, José Antonio Pérez-Tavares, Rita Patakfalvi, Tamás Szabó, Erzsébet Illés, Héctor Pérez Ladrón de Guevara, Pablo Eduardo Cardoso-Avila, Jesús Castañeda-Contreras, and Quetzalcoatl Enrique Saavedra Arroyo. 2022. "Amino Acid Complexes of Zirconium in a Carbon Composite for the Efficient Removal of Fluoride Ions from Water" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 6: 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063640
APA StyleGonzález-Aguiñaga, E., Pérez-Tavares, J. A., Patakfalvi, R., Szabó, T., Illés, E., Pérez Ladrón de Guevara, H., Cardoso-Avila, P. E., Castañeda-Contreras, J., & Saavedra Arroyo, Q. E. (2022). Amino Acid Complexes of Zirconium in a Carbon Composite for the Efficient Removal of Fluoride Ions from Water. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(6), 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063640








