Risk Behaviors, Family Support, and Emotional Health among Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Israel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Participants and Procedure
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Outcome Measures
2.3.2. Outcomes Assessing Risky Behavior
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants’ Characteristics
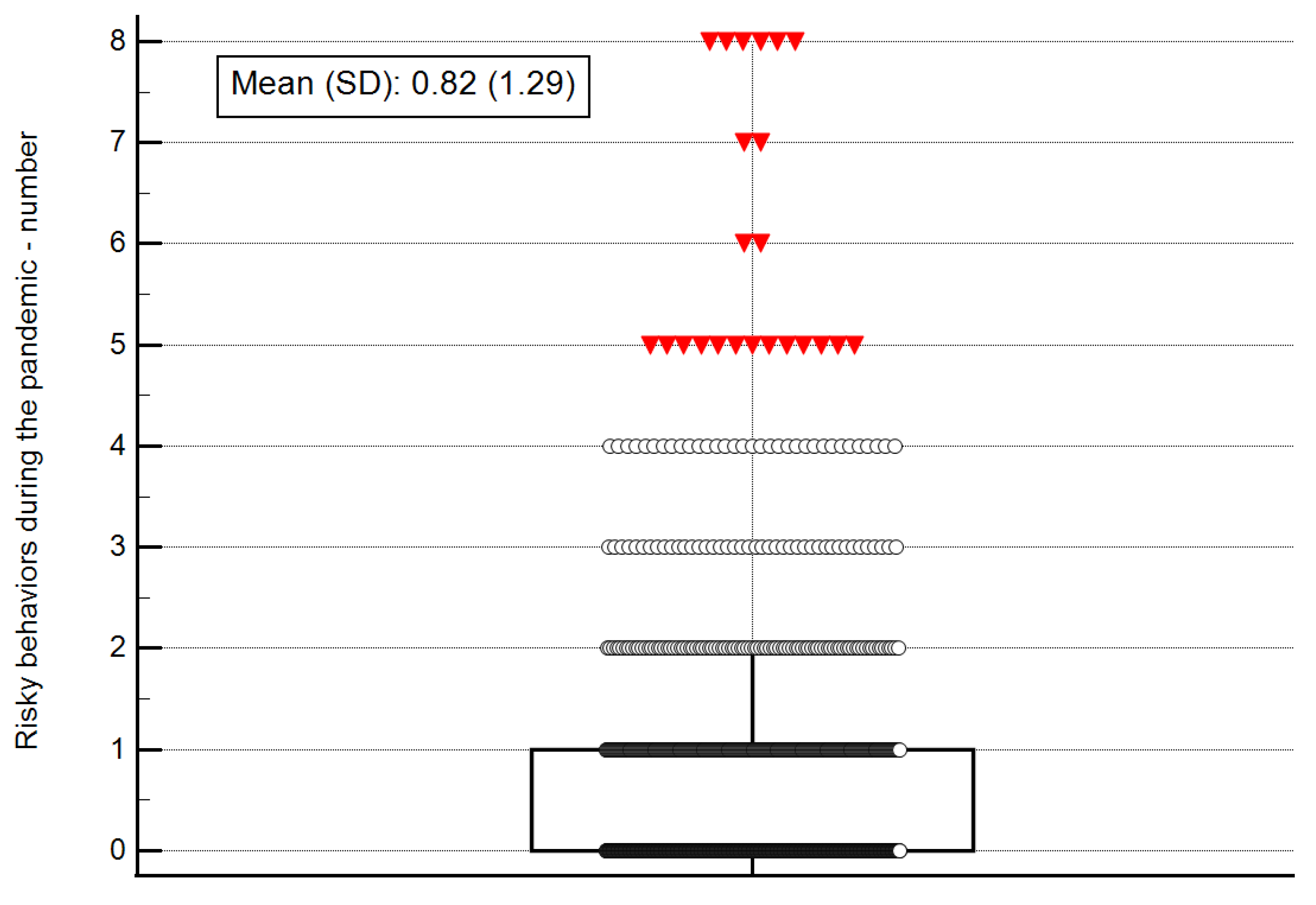
3.2. Risky Behavior Characteristics
3.3. Factors Related to and Predicting Risky Behavior
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uddin, R.; Lee, E.Y.; Khan, S.R.; Tremblay, M.S.; Khan, A. Clustering of lifestyle risk factors for non-communicable diseases in 304,779 adolescents from 89 countries: A global perspective. Prev. Med. 2020, 131, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- COVID-19 and Children—UNICEF DATA. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/covid-19-and-children/ (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Azevedo, J.P.; Hasan, A.; Goldemberg, D.; Iqbal, S.A.; Geven, K. Simulating the Potential Impacts of COVID-19 School Closures on Schooling and Learning Outcomes: A Set of Global Estimates. World Bank Res. Obs. 2021, 36, lkab003. [Google Scholar]
- Manzar, M.D.; Albougami, A.; Usman, N.; Mamun, M.A. Suicide among adolescents and youths during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdowns: A press media reports-based exploratory study. J. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2021, 34, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mental and Social Well-Being and Risk Behavior Trends 1994–2019 in Israeli Youth; Findings from the 8th International HBSC Survey (2019); Bar Ilan University: Ramat Gan, Israel, 2020; Available online: https://hbsc.biu.ac.il/books.html (accessed on 7 March 2022).
- Rabinowicz, S.; Leshem, E.; Pessach, I.M. COVID-19 in the pediatric population—Review and current evidence. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2020, 22, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoshani, A.; Kor, A. The mental health effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on children and adolescents: Risk and protective factors. Psychol. Trauma Theory Res. Pract. Policy 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesler, R.; Barak, S.; Reges, O.; Moreno-Maldonado, C.; Maor, R.; Gaspar, T.; Ercan, O.; Sela, Y.; Green, G.; Zigdon, A.; et al. Identifying Cardiovascular Risk Profiles Clusters among Mediterranean Adolescents across Seven Countries. Healthcare 2022, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesler, R.; Kolobov, T.; Korn, L.; Shuval, K.; Levin-Zamir, D.; Marques, A.; Harel Fisch, Y. Trends in tobacco use among children and adolescents in Israel, 1998–2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clay, J.M.; Parker, M.O. Alcohol use and misuse during the COVID-19 pandemic: A potential public health crisis? Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, E259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzman, E.T.; Greene, J. Is adversity in childhood linked to marijuana use in adulthood? Findings from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. Subst. Use Misuse 2022, 57, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ryzin, M.J.; Fosco, G.M.; Dishion, T.J. Family and peer predictors of substance use from early adolescence to early adulthood: An 11-year prospective analysis. Addict. Behav. 2012, 37, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonny-Noach, H.; Cohen-Louck, K.; Levy, I. Substances use between early and later stages of the COVID-19 pandemic in Israel. Isr. J. Health Policy Res. 2021, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, S.; Stevens, G.W.; Maes, M.; Boer, M.; Delaruelle, K.; Eriksson, C.; Brooks, F.M.; Tesler, R.; van der Schuur, W.A.; Finkenauer, C. Perceived social support from different sources and adolescent life satisfaction across 42 countries/regions: The moderating role of national-level generalized trust. J. Youth Adolesc. 2021, 50, 1384–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronfenbrenner, U.; Evans, G.W. Developmental Science in the 21st Century: Emerging Questions, Theoretical Models, Research Designs and Empirical Findings. Soc. Dev. 2000, 9, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpfer, K.L.; Alvarado, R. Family-Strengthening Approaches for the Prevention of Youth Problem Behaviors. Am. Psychol. 2003, 58, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaborskis, A.; Grincaitė, M.; Kavaliauskienė, A.; Tesler, R. Family structure and affluence in adolescent eating behavior: A cross-national study in forty-one countries. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumrind, D. The Influence of Parenting Style on Adolescent Competence and Substance Use. J. Early Adolesc. 2016, 11, 56–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becoña, E.; Martínez, Ú.; Calafat, A.; Juan, M.; Fernández-Hermida, J.R.; Secades-Villa, R. Parental styles and drug use: A review. Drugs Educ. Prev. Policy 2011, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, B.; McCrae, N.; Grealish, A. A systematic review: The influence of social media on depression, anxiety, and psychological distress in adolescents. Int. J. Adolesc. Youth 2019, 25, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, W.E.; Dumas, T.M.; Forbes, L.M. Physically isolated but socially connected: Psychological adjustment and stress among adolescents during the initial COVID-19 crisis. Can. J. Behav. Sci. Rev. Can. Sci. Comport. 2020, 52, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiha, S.M.; Cheng, J.; Halpern-Felsher, B. Association between Youth Smoking, Electronic Cigarette Use, and COVID-19. J. Adolesc. Health 2020, 67, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, T.M.; Ellis, W.; Litt, D.M. What Does Adolescent Substance Use Look Like During the COVID-19 Pandemic? Examining Changes in Frequency, Social Contexts, and Pandemic-Related Predictors. J. Adolesc. Health 2020, 67, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapetanovic, S.; Gurdal, S.; Ander, B.; Sorbring, E. Reported Changes in Adolescent Psychosocial Functioning during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Adolescents 2021, 1, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodas, M.; Peleg, K. Self-isolation compliance in the COVID-19 era influenced by compensation: Findings from a recent survey in Israel. Health Aff. 2020, 39, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bodas, M.; Siman-Tov, M.; Kreitler, S.; Peleg, K. Psychological Correlates of Civilian Preparedness for Conflicts. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2017, 11, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, C.; Molcho, M.; Boyce, W.; Holstein, B.; Torsheim, T.; Richter, M. Researching health inequalities in adolescents: The development of the Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children (HBSC) Family Affluence Scale. Soc. Sci. Med. 2008, 66, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, W.; Torsheim, T.; Currie, C.; Zambon, A. The Family Affluence Scale as a Measure of National Wealth: Validation of an Adolescent Self-Report Measure. Soc. Indic. Res. 2006, 78, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchley, J.; Currie, D.; Budisavljevic, S.; Torsheim, T.; Jåstad, A.; Cosma, A.; Kelly, C.; Arnarsson, M.A.; Samdal, O. (Eds.) Spotlight on Adolescent Health and Well-Being: Findings from the 2017/2018 Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children (HBSC) Survey in Europe and Canada; International Report; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020; Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/en/publications/abstracts/spotlight-on-adolescent-health-and-well-being.-findings-from-the-20172018-health-behaviour-in-school-aged-children-hbsc-survey-in-europe-and-canada.-international-report.-volume-2.-key-data (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Ng, C.G.; Amer Siddiq, A.N.; Aida, S.A.; Zainal, N.Z.; Koh, O.H. Validation of the Malay version of the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support (MSPSS-M) among a group of medical students in Faculty of Medicine, University Malaya. Asian J. Psychiatry 2010, 3, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravens-Sieberer, U.; Erhart, M.; Torsheim, T.; Hetland, J.; Freeman, J.; Danielson, M.; Thomas, C.; The HBSC Positive Health Group. An international scoring system for self-reported health complaints in adolescents. Eur. J. Public Health 2008, 18, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hetland, J.; Torsheim, T.; Aarø, L.E. Subjective health complaints in adolescence: Dimensional structure and variation across gender and age. Scand. J. Public Health 2002, 30, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugland, S.; Wold, B.; Stevenson, J.; Aaroe, L.E.; Woynarowska, B. Subjective health complaints in adolescence: A cross-national comparison of prevalence and dimensionality. Eur. J. Public Health 2001, 11, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.D.; Molcho, M.; Craig, W.; Harel-Fisch, Y.; Huynh, Q.; Kukaswadia, A.; Aasvee, K.; Várnai, D.; Ottova, V.; Ravens-Sieberer, U.; et al. Physical and Emotional Health Problems Experienced by Youth Engaged in Physical Fighting and Weapon Carrying. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, M.; Nixon, S.; Haines, J.; McPherson, A.C. Examining risk factors for overweight and obesity in children with disabilities: A commentary on Bronfenbrenner’s ecological systems framework. Dev. Neurorehabil. 2018, 22, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.; Ng, K.; Rintala, P.O.; Tynjälä, J.; Välimaa, R.; Villberg, J. Physical Activity Trends of Finnish Adolescents with Long-Term Illnesses or Disabilities from 2002–2014. J. Phys. Act. Health 2016, 13, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charrier, L.; Berchialla, P.; Galeone, D.; Spizzichino, L.; Borraccino, A.; Lemma, P.; Dalmasso, P.; Cavallo, F. Smoking habits among Italian adolescents: What has changed in the last decade? BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 287139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntsche, E.; Kuntsche, S.; Knibbe, R.; Simons-Morton, B.; Farhat, T.; Hublet, A.; Bendtsend, P.; Godeau, E.; Demetrovics, Z. Cultural and Gender Convergence in Adolescent Drunkenness: Evidence from 23 European and North American Countries. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2011, 165, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wexler, M. “Adolescent drug use and psychological health: A longitudinal inquiry”: Comment. Am. Psychol. 1991, 46, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sznitman, S.R.; Kolobov, T.; ter Bogt, T.; Kuntsche, E.; Walsh, S.D.; Harel-Fisch, Y. Investigating Cannabis Use Normalization by Distinguishing Between Experimental and Regular Use: A Multilevel Study in 31 Countries. J. Stud. Alcohol Drugs 2015, 76, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadi, N.; Schroeder, R.; Jensen, J.W.; Levy, S. Association between Electronic Cigarette Use and Marijuana Use among Adolescents and Young Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, e192574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuRant, R.H.; Smith, J.A.; Kreiter, S.R.; Krowchuk, D.P. The Relationship between Early Age of Onset of Initial Substance Use and Engaging in Multiple Health Risk Behaviors among Young Adolescents. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1999, 153, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehra, V.M.; Keethakumar, A.; Bohr, Y.M.; Abdullah, P.; Tamim, H. The association between alcohol, marijuana, illegal drug use and current use of E-cigarette among youth and young adults in Canada: Results from Canadian Tobacco, Alcohol and Drugs Survey 2017. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grigsby, T.J.; Howard, J.T.; Deason, R.G.; Haskard-Zolnierek, K.B.; Howard, K. Correlates of COVID-19 pandemic-related increases in sleep aid and anti-anxiety medication use. J. Subst. Use 2021, 27, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodkiewicz, J.; Talarowska, M.; Miniszewska, J.; Nawrocka, N.; Bilinski, P. Alcohol consumption reported during the COVID-19 pandemic: The initial stage. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, M.; Biglan, A.; Ary, D.; Li, F. Replication of a problem behavior model with American Indian, Hispanic, and Caucasian youth. J. Early Adolesc. 2001, 21, 133–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihić, J.; Skinner, M.; Novak, M.; Ferić, M.; Kranželić, V. The importance of family and school protective factors in preventing the risk behaviors of youth. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 31, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumpfer, K.L.; Magalhães, C. Strengthening families program: An evidence-based family intervention for parents of high-risk children and adolescents. J. Child Adolesc. Subst. Abus. 2018, 27, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, H.W.; Iacovou, M. Dimensions of the Parent-Child Relationship: Effects on Substance Use in Adolescence and Adulthood. Subst. Use Misuse 2019, 54, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Gera, T.; Behmani, R.K. Parenting Styles and Mental Health of Adolescents. J. Psychol. Behav. Stud. 2021, 1, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- álvarez-García, D.; Núñez, J.C.; González-Castro, P.; Rodríguez, C.; Cerezo, R. The effect of parental control on cyber-victimization in adolescence: The mediating role of impulsivity and high-risk behaviors. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashraf, M.U.; Asif, M.; Iqbal, M.M.A.; Warraich, I.A. Role of Socioeconomic Status and Parenting Practices in construction of Violent Behavior among Youth: A Study from South Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. J. Soc. Sci. 2019, 39, 639–651. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, M.D.; Chen, E. Socioeconomic status, and health behaviors in adolescence: A review of the literature. J. Behav. Med. 2007, 30, 263–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills, T.A.; Resko, J.A.; Ainette, M.G.; Mendoza, D. Role of parent support and peer support in adolescent substance use: A test of mediated effects. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2004, 18, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Figueiredo, C.S.; Sandre, P.C.; Portugal, L.C.L.; Mázala-de-Oliveira, T.; da Silva Chagas, L.; Raony, Í.; Ferreira, E.S.; Giestal-de-Araujo, E.; dos Santos, A.A.; Bomfim, P.O.-S. COVID-19 pandemic impact on children and adolescents’ mental health: Biological, environmental, and social factors. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 106, 110171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuine, T.A.; Biese, K.M.; Petrovska, L.; Hetzel, S.J.; Reardon, C.; Kliethermes, S.; Bell, D.R.; Brooks, A.; Watson, A.M. Mental Health, Physical Activity, and Quality of Life of US Adolescent Athletes During COVID-19-Related School Closures and Sport Cancellations: A Study of 13,000 Athletes. J. Athl. Train. 2021, 56, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meherali, S.; Punjani, N.; Louie-Poon, S.; Abdul Rahim, K.; Das, J.K.; Salam, R.A.; Lassi, Z.S. Mental Health of Children and Adolescents Amidst COVID-19 and Past Pandemics: A Rapid Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutzler, Y.; Tesler, R.; Ng, K.; Barak, S.; Kazula, H.; Harel-Fisch, Y. Physical activity, sedentary screen time and bullying behaviors: Exploring differences between adolescents with and without disabilities. Int. J. Adolesc. Youth 2021, 26, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesler, R.; Plaut, P.; Endvelt, R. The Effects of an Urban Forest Health Intervention Program on Physical Activity, Substance Abuse, Psychosomatic Symptoms, and Life Satisfaction among Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda-Babarro, A.; Coca, A.; Arbillaga-Etxarri, A.; Gutiérrez-Santamaría, B. Physical Activity Change during COVID-19 Confinement. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Mean (SD) [Range] OR n (%) | Chi-Squared (p Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years: mean (SD) [range] | 16.73 (0.99) | - | |
| [15.00–18.00] | |||
| Sex: n (%) | Females | 584 (57.3) | 21.47 (<0.0001) |
| Males | 436 (42.7) | ||
| Socio-economic status, score: mean (SD) [range] † | 13.80 (2.20) | - | |
| [7.00–19.00] | |||
| Living area: n (%) | North of the country | 188 (18.4) c,e | 130.48 (<0.0001) |
| South and coastal plain | 211 (20.7) c,e | ||
| Center of the country | 328 (32.2) a,b,d,e | ||
| East of the country | 193 (18.9) c,e | ||
| Central coastal plain | 100 (9.8) a,b,c,d | ||
| Risky Behavior | n (%) | Chi-Squared (p-Value) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tobacco smoking | In last 30 days | Yes | 93 (9.1) | 681.91 |
| No | 927 (90.9) | (<0.0001) | ||
| Drinking | Binge drinking | Yes | 345 (33.8) | 106.76 |
| No | 675 (66.2) | (<0.0001) | ||
| Cannabis | Abstinence | 952 (93.3) | 766.13 | |
| Experimental or regular | 68 (6.7) | (<0.0001) | ||
| Risky behavior during the pandemic | No risky behavior | 922 (90.4) | 665.66 | |
| One or more risk behavior | 98 (9.6) | (<0.0001) | ||
| Tobacco Smoking in Last 30 Days: r (p Value) | Cannabis Use in Last 30 Days: r (p Value) | Binge Drinking in Last 30 Days: r (p-Value) | Risky Behavior during the Pandemic: r (p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tobacco smoking in last 30 days | - | 0.33 (<0.0001) | 0.40 (<0.0001) | 0.47 (<0.0001) |
| Cannabis use in last 30 days | - | - | 0.41 (<0.0001) | 0.32 (<0.0001) |
| Binge drinking in last 30 days | - | - | - | 0.41 (<0.0001) |
| Risky behavior during the pandemic | - | - | - | - |
| Risky Behavior | Stopped Using during the Pandemic: n (%) | Started Using during the Pandemic: n (%) | Decreased the Amount of Use during the Pandemic: n (%) | Increased the Amount of Use during the Pandemic: n (%) | No Change during the Pandemic: n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smoking cigarettes (n = 106) | 9 (8.5) | 12 (11.3) | 20 (18.9) | 10 (9.4) | 55 (51.9) |
| Smoking electronic cigarettes (n = 73) | 10 (13.7) | 18 (24.7) | 7 (9.6) | 2 (2.7) | 36 (49.3) |
| Drinking alcohol (n = 359) | 52 (14.5) | 17 (4.7) | 57 (15.9) | 35 (9.7) | 198 (55.20) |
| Anti-anxiety medications (n = 86) | 8 (9.3) | 11 (12.8) | 8 (9.3) | 16 (18.6) | 43 (50.0) |
| Smoking cannabis (n = 62) | 9 (14.5) | 9 (14.5) | 3 (4.8) | 10 (16.1) | 31 (50.0) |
| Other illegal drugs (n = 15) | 4 (26.7) | 0 (0.00) | 3 (20.0) | 1 (6.7) | 7 (46.7) |
| New psychoactive substances (n = 16) | 3 (18.8) | 1 (6.2) | 1 (6.2) | 3 (18.8) | 8 (50.0) |
| Ritalin (n = 124) | 48 (38.7) | 9 (7.3) | 20 (16.1) | 4 (3.2) | 43 (34.7) |
| Variables | Tobacco Smoking in the Last 30 Days | Binge Drinking | Cannabis Use | Risky Behavior during the Pandemic | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n = 93) | No (n = 927) | Yes (n = 345) | No (n = 675) | Abstinence (n = 952) | Experimental or Regular (n = 68) | No Risky Behavior (n = 922) | One or More Risky Behaviors (n = 98) | ||
| Sex | Females, n (%) | 46 (49.50) | 538 (58.0) | 177 (51.3) | 407 (60.3) | 546 (57.4) | 38 (55.9) | 533 (57.8) | 51 (52.0) |
| Males, n (%) | 47 (50.5) | 389 (42.0) | 168 (48.7) | 268 (39.7) † | 406 (42.6) † | 30 (44.1) | 389 (42.2) | 47 (48.0) | |
| Age, years: mean (SD) | 17.11 (0.88) | 16.69 (0.99) * | 16.90 (1.00) | 16.64 (0.97) * | 16.70 (0.98) | 17.04 (0.94) | 16.71 (0.99) | 16.95 (0.91) * | |
| Family support, total score: mean (SD) | 17.32 (3.77) | 18.21 (3.77) * | 17.69 (3.76) | 18.35 (3.77) * | 18.21 (3.76) | 16.41 (4.18) * | 18.25 (3.76) | 16.94 (3.74) * | |
| Socio-economic status, score: mean (SD) | 13.55 (2.21) | 13.82 (2.19) | 13.98 (2.27) | 13.70 (2.15) | 13.80 (2.19) | 13.88 (2.40) | 13.79 (2.19) | 13.85 (2.27) * | |
| Friends support, score: mean (SD) | 20.55 (5.50) | 21.17 (5.13) | 21.47 (5.29) | 20.94 (5.10) | 21.16 (5.11) | 19.80 (6.33) | 21.18 (5.08) | 20.47 (5.90) | |
| Physical activity volume, days/week: mean (SD) | 1.75 (1.89) | 1.76 (1.90) | 1.77 (1.91) | 1.75 (1.89) | 1.77 (1.90) | 1.36 (1.62) | 1.77 (1.90) | 1.62 (1.89) | |
| Corona restrictions, number: mean (SD) | 2.32 (1.30) | 2.16 (1.06) | 2.21 (1.15) | 2.15 (1.05) | 2.16 (1.08) | 2.38 (1.29) | 2.16 (1.08) | 2.30 (1.19) | |
| Health during the pandemic, score: mean (SD) | 3.32 (0.75) | 3.50 (0.67) * | 3.46 (0.69) | 3.49 (0.68) | 3.49 (0.68) | 3.24 (0.77) * | 3.50 (0.66) | 3.29 (0.80) * | |
| Emotional health, score: mean (SD) | 21.37 (7.81) | 18.84 (7.05) * | 19.86 (7.29) | 18.67 (7.06) * | 18.91 (7.15) | 21.52 (6.84) * | 18.74 (7.09) | 22.20 (7.10) * | |
| Dependent Variable | Predictors | Coefficient | Standard Error | Odds Ratio | Wald | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tobacco smoking in the last 30 days | Constant | −10.21 | 2.29 | 19.77 | <0.0001 | ||
| Age, years | 0.47 | 0.12 | 1.61 | 15.85 | 1.27–2.04 | 0.0001 | |
| Family support, score | −0.03 | 0.02 | 0.96 | 1.40 | 0.91–1.02 | 0.23 | |
| Health during the pandemic, score | −0.12 | 0.16 | 0.88 | 0.57 | 0.63–1.21 | 0.44 | |
| Emotional health, score | 0.04 | 0.01 | 1.04 | 6.46 | 1.00–1.07 | 0.01 | |
| Model summary | Chi-squared = 30.16, p < 0.001, Nagelkerke R2 = 0.07. | ||||||
| Binge drinking | Constant | −5.34 | 1.25 | 18.10 | <0.0001 | ||
| Sex (reference—males) | −0.51 | 0.14 | 0.59 | 13.44 | 0.45–0.78 | 0.0002 | |
| Age, years | 0.29 | 0.06 | 1.34 | 18.28 | 1.17–1.54 | <0.0001 | |
| Family support, total score | −0.03 | 0.01 | 0.96 | 3.46 | 0.93–1.00 | 0.06 | |
| Emotional health, score | 0.03 | 0.01 | 1.03 | 9.03 | 1.01–1.05 | 0.002 | |
| Model summary | Chi-squared = 40.98, p < 0.001, Nagelkerke R2 = 0.06. | ||||||
| Cannabis use | Constant | −0.09 | 1.13 | 0.76 | 0.04 | ||
| Family support, total score | −0.09 | 0.03 | 0.91 | 5.97 | 0.84–0.98 | 0.01 | |
| Health during the pandemic, score | −0.25 | 0.20 | 0.77 | 1.55 | 0.51–1.15 | 0.21 | |
| Emotional health, score | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.02 | 1.39 | 0.98–1.07 | 0.23 | |
| Model summary | Chi-squared = 14.47, p = 0.01, Nagelkerke R2 = 0.05. | ||||||
| Risky behavior during the pandemic | Constant | −7.53 | 2.27 | 10.98 | 0.0009 | ||
| Age, years | 0.29 | 0.11 | 1.34 | 6.79 | 1.07–1.67 | 0.0009 | |
| Family support, total score | −0.06 | 0.02 | 0.94 | 4.43 | 0.88–0.99 | 0.03 | |
| Socioeconomic status, score | 0.04 | 0.05 | 1.04 | 0.82 | 0.94–1.15 | 0.36 | |
| Health during the pandemic, score | −0.11 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 0.49 | 0.65–1.22 | 0.48 | |
| Emotional health, score | 0.05 | 0.01 | 1.05 | 11.48 | 1.02–1.09 | 0.0007 | |
| Model summary | Chi-squared = 32.88, p < 0.0001, Nagelkerke R2 = 0.07. | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shapiro, O.; Gannot, R.N.; Green, G.; Zigdon, A.; Zwilling, M.; Giladi, A.; Ben-Meir, L.; Adilson, M.; Barak, S.; Harel-Fisch, Y.; et al. Risk Behaviors, Family Support, and Emotional Health among Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Israel. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19073850
Shapiro O, Gannot RN, Green G, Zigdon A, Zwilling M, Giladi A, Ben-Meir L, Adilson M, Barak S, Harel-Fisch Y, et al. Risk Behaviors, Family Support, and Emotional Health among Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Israel. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(7):3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19073850
Chicago/Turabian StyleShapiro, Orit, Rachel Nissanholtz Gannot, Gizell Green, Avi Zigdon, Moti Zwilling, Ariela Giladi, Lilach Ben-Meir, Marques Adilson, Sharon Barak, Yossi Harel-Fisch, and et al. 2022. "Risk Behaviors, Family Support, and Emotional Health among Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Israel" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 7: 3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19073850
APA StyleShapiro, O., Gannot, R. N., Green, G., Zigdon, A., Zwilling, M., Giladi, A., Ben-Meir, L., Adilson, M., Barak, S., Harel-Fisch, Y., & Tesler, R. (2022). Risk Behaviors, Family Support, and Emotional Health among Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Israel. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(7), 3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19073850










