Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Academic Stress and Perceived Classroom Climate in Spanish University Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Academic Stress
1.2. The Moderating Effects of Sex and the Year of Study on Academic Stress
1.3. Perceived Classroom Climate
1.4. The Impact of COVID-19 on University Context
1.5. Aims of the Study
2. Materials and Methods
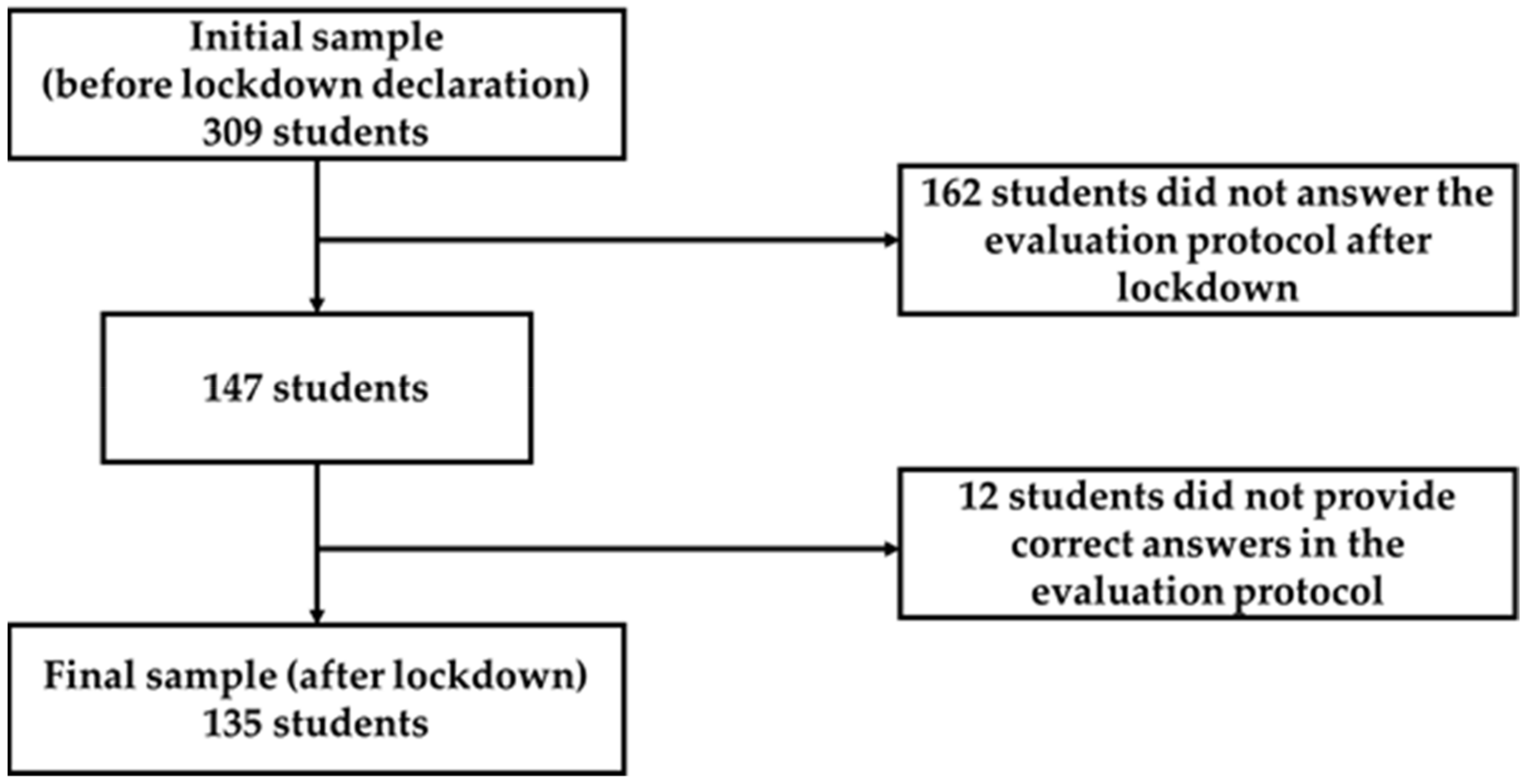
2.1. Research Method and Design
2.2. Research Context and Participants
2.3. Instruments
2.3.1. Sociodemographic and Educational Data
2.3.2. Academic Stress
2.3.3. Classroom Climate
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Scores in Academic Stress and Perceived Classroom Climate in Time 1 (before Lockdown Declaration) and Time 2 (after Lockdown)
3.2. Differences in Academic Stress and Perceived Classroom Climate in Time 1 (before Lockdown Declaration) and Time 2 (after Lockdown)
3.3. Differences in Academic Stress in Time 1 before Lockdown Declaration) and Time 2 (after Lockdown) by Sex and Year of Study
3.4. Differences in Perceived Classroom Climate in Time 1 before Lockdown Declaration) and Time 2 (after Lockdown) by Sex and Year of Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnsten, A.F.T. Prefrontal Cortical Network Connections: Key Site of Vulnerability in Stress and Schizophrenia. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 29, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupien, S.J.; McEwen, B.S.; Gunnar, M.R.; Heim, C. Effects of Stress throughout the Lifespan on the Brain, Behaviour and Cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casuso-Holgado, M.J.; Moreno-Morales, N.; Labajos-Manzanares, M.T.; Montero-Bancalero, F.J. The Association between Perceived Health Symptoms and Academic Stress in Spanish Higher Education Students. Eur. J. Educ. Psychol. 2019, 12, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Cabanach, R.; Souto-Gestal, A.; Franco, V. Escala de Estresores Académicos para la evaluación de los estresores académicos en estudiantes universitarios. Rev. Iberoam. Psicol. Salud 2016, 7, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevethan, M.; Jain, A.T.; Shatiyaseelan, A.; Luebbe, A.M.; Raval, V.V. A Longitudinal Examination of the Relation between Academic Stress and Anxiety Symptoms among Adolescents in India: The Role of Physiological Hyperarousal and Social Acceptance. Int. J. Psychol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, F.J.M. El Estrés Académico: Problemas y Soluciones Desde Una Perspectiva Psicosocial; Universidad de Huelva: Huelva, Spain, 2004; ISBN 978-84-95699-13-8. [Google Scholar]
- Pozos-Radillo, B.E.; de Lourdes Preciado-Serrano, M.; Acosta-Fernández, M.; de los Ángeles Aguilera-Velasco, M.; Delgado-García, D.D. Academic Stress as a Predictor of Chronic Stress in University Students. Psicol. Educ. 2014, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dunne, M.P.; Hou, X.-Y. Academic Stress among Adolescents in China. Australas. Epidemiol. 2012, 19, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Duan, H.; Qin, S.; Buchanan, T.W.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L. Long-Term Academic Stress Increases the Late Component of Error Processing: An ERP Study. Biol. Psychol. 2014, 99, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cabrera, J.; Fernández-Prada, M.; Iribar-Ibabe, C.; Peinado, J.M. Acute and Chronic Stress Increase Salivary Cortisol: A Study in the Real-Life Setting of a National Examination Undertaken by Medical Graduates. Stress 2014, 17, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kember, D.; Leung, Y.P. Characterising a Teaching and Learning Environment Conducive to Making Demands on Students While Not Making Their Workload Excessive. Stud. High. Educ. 2006, 31, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.D.; Menezes, D.A.B.; McDermott, H.E.; Hibbert, L.J.; Brennan, S.-L.; Ross, E.E.; Jones, L.A. A Comparison of Course-Related Stressors in Undergraduate Problem-Based Learning (PBL) versus Non-PBL Medical Programmes. BMC Med. Educ. 2009, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laranjeira, C.; Dixe, M.A.; Valentim, O.; Charepe, Z.; Querido, A. Mental Health and Psychological Impact during COVID-19 Pandemic: An Online Survey of Portuguese Higher Education Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Gallardo, J.-R.; Castaño, S.; Gómez-Alday, J.J.; Valdés, A. Assessing Student Workload in Problem Based Learning: Relationships among Teaching Method, Student Workload and Achievement. A Case Study in Natural Sciences. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2011, 27, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, Y.G.; Carrera, I.d.C.; Caeiro, E.M.L.; González, M.S. Comparación entre síntomas de estrés según el curso. In Proceedings of the IV Congreso Virtual Internacional sobre Innovación Pedagógica y Praxis Educativa INNOVAGOGÍA 2018: Libro de Actas, Sevilla, Spain, 20–22 March 2018; pp. 201–203, ISBN 978-84-09-00794-3. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal Conti, J.; Muntaner-Mas, A.; Palou Sampol, P. Diferencias de estrés y afrontamiento del mismo según el género y cómo afecta al rendimiento académico en estudiantes universitarios. Contextos Educ. 2018, 22, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Cabanach, R.; Rivera, F.; Freire, C.; González, P.; del Mar Ferradás, M. Diferencias en el afrontamiento del estrés en estudiantes universitarios hombres y mujeres. Eur. J. Educ. Psychol. 2013, 6, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutinho, I.L.D.; Maddalena, N.D.C.P.; Roland, R.K.; Lucchetti, A.L.G.; Tibiriçá, S.H.C.; Ezequiel, O.D.S.; Lucchetti, G. Depression, Stress and Anxiety in Medical Students: A Cross-Sectional Comparison between Students from Different Semesters. Rev. Assoc. Méd. Bras. 2017, 63, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, T.M. Stress, Coping and Health: Enhancing Well-Being during Medical School. Med. Educ. 1994, 28, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.C.; Zeldow, P.B. Vicissitudes of Depressed Mood during Four Years of Medical School. JAMA 1988, 260, 2521–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, D.; Bozzo, N.; Marchant, J.; Fernández, P. Factores que inciden en el clima de aula universitario. Rev. Latinoam. Estud. Educ. 2010, 40, 105–126. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, J.; Biggs, J.B. Calidad Del Aprendizaje Universitario; Narcea Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2004; ISBN 978-84-277-1398-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hannan, A.; Silver, H. La innovación en la Enseñanza Superior. Enseñanza, aprendizaje y culturas institucionales. Educ. Siglo XXI 2005, 23, 215–217. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, M. COVID-19 y educación superior: De los efectos inmediatos al día después. Análisis de impactos, respuestas políticas y recomendaciones. Rev. Argent. Educ. Super. 2020, 20, 156–158. [Google Scholar]
- Velázquez, L.G. Estrés académico en estudiantes universitarios asociado a la pandemia por COVID-19. Espac. I+D Innovación Más Desarro. 2020, 9, 158–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajarianto, H.; Kadir, A.; Galugu, N.; Sari, P.; Februanti, S. Study from Home in the Middle of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Analysis of Religiosity, Teacher, and Parents Support against Academic Stress. J. Talent. Dev. Excell. 2020, 12, 1791–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Dussel, I.; Ferrante, P.; Pulfer, D. Pensar la Educación en Tiempos de Pandemia: Entre la Emergencia, el Compromiso y la Espera; UNIPE Editorial Universitaria: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, J.; Alcántara, A.; Álvarez, F.; Amador, R.; Barrón, C.; Bravo, M.T.; Carbajosa, D.; Casanova, H.; Castañeda, R.; Cejudo, D.; et al. Educación y Pandemia una Visión Académica; IISUE: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, Y. Online Education during COVID-19: Perception of Academic Stress and Emotional Intelligence Coping Strategies among College Students. Asian Educ. Dev. Stud. 2020, 10, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldager, J.D.; Jervelund, S.S.; Berg-Beckhoff, G. Academic Stress in Danish Medical and Health Science Students during the COVID-19 Lock-Down. Dan. Med. J. 2021, 68, A11200805. [Google Scholar]
- Clabaugh, A.; Duque, J.F.; Fields, L.J. Academic Stress and Emotional Well-Being in United States College Students Following Onset of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 628787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohls, E.; Baldofski, S.; Moeller, R.; Klemm, S.-L.; Rummel-Kluge, C. Mental Health, Social and Emotional Well-Being, and Perceived Burdens of University Students during COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown in Germany. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos Fialho, P.M.; Spatafora, F.; Kühne, L.; Busse, H.; Helmer, S.M.; Zeeb, H.; Stock, C.; Wendt, C.; Pischke, C.R. Perceptions of Study Conditions and Depressive Symptoms during the COVID-19 Pandemic among University Students in Germany: Results of the International COVID-19 Student Well-Being Study. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 674665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Río, J.; Cecchini, J.A.; Merino-Barrero, J.A.; Valero-Valenzuela, A. Perceived Classroom Responsibility Climate Questionnaire: A New Scale. Psicothema 2019, 31, 475–481. [Google Scholar]
- Padrón, I.; Fraga, I.; Vieitez, L.; Montes, C.; Romero, E. A Study on the Psychological Wound of COVID-19 in University Students. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigaiani, Y.; Zoccante, L.; Zocca, A.; Arzenton, A.; Menegolli, M.; Fadel, S.; Ruggeri, M.; Colizzi, M. Adolescent Lifestyle Behaviors, Coping Strategies and Subjective Wellbeing during the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Online Student Survey. Healthcare 2020, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Fuente, J.; Pachón-Basallo, M.; Santos, F.H.; Peralta-Sánchez, F.J.; González-Torres, M.C.; Artuch-Garde, R.; Paoloni, P.V.; Gaetha, M.L. How Has the COVID-19 Crisis Affected the Academic Stress of University Students? The Role of Teachers and Students. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 626340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, M.L.A.; Martínez, F.T. Variables involucradas con el estrés académico y el afrontamiento en universitarios durante el confinamiento por COVID-19. Psicol. Iberoam. 2021, 29, e293331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Cabanach, R.; Fernández Cervantes, R.; González Doniz, L.; Freire Rodríguez, C. Estresores académicos percibidos por estudiantes universitarios de ciencias de la salud. Fisioterapia 2010, 32, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockinger, K.; Rinas, R.; Daumiller, M. Student Adaptability, Emotions, and Achievement: Navigating New Academic Terrains in a Global Crisis. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2021, 90, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besser, A.; Flett, G.L.; Zeigler-Hill, V. Adaptability to a Sudden Transition to Online Learning during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Understanding the Challenges for Students. Scholarsh. Teach. Learn. Psychol. 2020. Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, L.T.; Cohen, A.K.; Dull, B.; Maker Castro, E.; Yazdani, N. “Constant Stress Has Become the New Normal”: Stress and Anxiety Inequalities Among U.S. College Students in the Time of COVID-19. J. Adolesc. Health 2021, 68, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco-Ahulló, A.; Villarrasa-Sapiña, I.; Monfort-Torres, G. Estudio descriptivo sobre las diferencias de género en el estrés académico derivado del contexto COVID-19 en población universitaria española (Descriptive study on gender differences in academic stress derived from the COVID-19 context in a Spanish unive. Retos 2022, 43, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, H. The Impact of COVID-19 on Anxiety in Chinese University Students. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, N.; Shahid, A.; Abbas, N.; Shaheen, A.; Munir, N. Anxiety and Depression in Medical Students of a Private Medical College. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2017, 29, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Bedoya-Lau, F.N.; Matos, L.J.; Zelaya, E.C. Niveles de estrés académico, manifestaciones psicosomáticas y estrategias de afrontamiento en alumnos de la facultad de medicina de una universidad privada de Lima en el año 2012. Rev. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2014, 77, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Piko, B. Gender Differences and Similarities in Adolescents’ Ways of Coping. Psychol. Rec. 2001, 51, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Vigouroux, S.; Goncalves, A.; Charbonnier, E. The Psychological Vulnerability of French University Students to the COVID-19 Confinement. Health Educ. Behav. 2021, 48, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, F.M.M.; Rodríguez, A.M.M. Diferencias en ansiedad en función del curso en universitarios. Rev. INFAD Psicol. Int. J. Dev. Educ. Psychol. 2021, 1, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, D.P.L.; Cortés, A.O.; Nava, A.G.R.; Sánchez, G.R.; Lobato, D.E.T.; Palma, S.Z.; Pérez, V.R.; Villada, C. Regulación emocional cognitiva y estrategias de afrontamiento en estudiantes universitarios ante el COVID-19. Jóvenes Cienc. 2021, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pulido-Martos, M.; Augusto-Landa, J.M.; Lopez-Zafra, E. Sources of Stress in Nursing Students: A Systematic Review of Quantitative Studies. Int. Nurs. Rev. 2012, 59, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundín, O.A.; Gómez, C.M.V. Causas del estrés académico en estudiantes universitarios. In Psicología y Educación: Presente y Futuro; ACIPE: Alicante, Spain, 2016; pp. 2832–2839. ISBN 978-84-608-8714-0. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez-Montes, N.; Díaz-Subieta, L.B. Estrés académico, deserción y estrategias de retención de estudiantes en la educación superior. Rev. Salud Pública 2015, 17, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denovan, A.; Macaskill, A. Stress and Subjective Well-Being among First Year UK Undergraduate Students. J. Happiness Stud. Interdiscip. Forum Subj. Well-Being 2017, 18, 505–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornés-Vives, J.; Garcia-Banda, G.; Frias-Navarro, D.; Rosales-Viladrich, G. Coping, Stress, and Personality in Spanish Nursing Students: A Longitudinal Study. Nurse Educ. Today 2016, 36, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Paredes, E.; Mendoza, L.I.B.; Cabañas, R.P.; Avila, L.R.; Sales, K.G.G. Estrés y estrategias de afrontamiento en Estudiantes de Nivel Superior de la Universidad Autónoma de Guerrero. NURE Investig. Rev. Cient. Enferm. 2018, 15, 1. [Google Scholar]
- González Cabanach, R.; Souto-Gestal, A.; González-Doniz, L.; Franco Taboada, V. Perfiles de afrontamiento y estrés académico en estudiantes universitarios. Rev. Investig. Educ. 2018, 36, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales Rodríguez, F.M. Estrategias de afrontamiento en una muestra de estudiantes universitarios. Rev. INFAD Psicol. 2018, 2, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Categories | Total Sample N = 135 |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 21.7 ± 4.39 | |
| Sex | Male | 38 (28.1%) |
| Female | 97 (71.9%) | |
| Relationship status | Single | 91 (67.4%) |
| In a relationship | 44 (32.6%) | |
| Employment status | Employed | 30 (22.2%) |
| Non-employed | 105 (77.8%) | |
| Income (monthly) | EUR < 500 | 115 (87.1%) |
| EUR > 500 | 17 (12.9%) | |
| Current studies | Gastronomy | 31 (23%) |
| Criminology | 104 (77%) | |
| Current year of study | 1stcourse | 33 (24.4%) |
| 3rd course | 65 (48.1%) | |
| 4th course | 37 (27.4%) |
| Time 1 | Time 2 | Percentage Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Academic Stress | |||
| TMD | 38.4 ± 11.6 | 41.4 ± 11.9 | 7.81% |
| AOB | 25.2 ± 8.81 | 27.3 ± 8.37 | 8.33% |
| BAP | 22.31 ± 8.79 | 24 ± 8.62 | 7.58% |
| PI | 16.48 ± 6.35 | 16.38 ± 5.87 | -0.61% |
| NSE | 11 ± 3.84 | 11.59 ± 4.31 | 5.36% |
| EX | 11.28 ± 4.28 | 11.30 ± 4.23 | 0.18% |
| CW | 9.57 ± 3.34 | 10.02 ± 3.70 | 4.7% |
| PD | 6.30 ± 2.59 | 6.68 ± 2.72 | 6.03% |
| TAS | 140.50 ± 36.48 | 148.57 ± 35.37 | 5.74% |
| Classroom Climate | |||
| RCC | 26.64 ± 5.28 | 27.01 ± 4.78 | 1.39% |
| RCT | 28.05 ± 6.31 | 28.42 ± 5.50 | 1.32% |
| t | df | p | Mean Difference | SE Difference | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Academic Stress | ||||||
| TMD | −3.6431 | 134 | <0.001 | −2.9704 | 0.815 | −0.31355 |
| AOB | −3.3791 | 134 | <0.001 | −2.1407 | 0.634 | −0.29083 |
| BAP | −3.0833 | 134 | 0.002 | −1.6222 | 0.526 | −0.26536 |
| PI | 0.2659 | 134 | 0.791 | 0.0963 | 0.362 | 0.02289 |
| NSE | −1.8800 | 134 | 0.062 | −0.5852 | 0.311 | −0.16180 |
| EX | −0.0923 | 134 | 0.927 | −0.0222 | 0.241 | −0.00794 |
| CW | −1.5187 | 134 | 0.131 | −0.4519 | 0.298 | −0.13071 |
| PD | −1.6646 | 134 | 0.098 | −0.3778 | 0.227 | −0.14327 |
| TAS | −3.8514 | 134 | <0.001 | −8.0741 | 2.096 | −0.33147 |
| Classroom Climate | ||||||
| RCC | −0.751 | 134 | 0.454 | −0.370 | 0.493 | −0.0646 |
| RCT | −0.680 | 134 | 0.498 | −0.370 | 0.545 | −0.0585 |
| Time 1 | Time 2 | Percentage Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Academic Stress | ||||
| TMD | Females | 40.2 ± 10.9 | 43.7 ± 11.1 | 8.71% |
| Males | 33.9 ± 12.2 | 35.4 ± 12 | 4.42% | |
| AOB | Females | 26.6 ± 8.22 | 29 ± 7.23 | 9.02% |
| Males | 21.4 ± 9.25 | 23 ± 9.56 | 7.48% | |
| BAP | Females | 23.5 ± 8.15 | 25.5 ± 7.93 | 8.51% |
| Males | 19.3 ± 9.78 | 20.1 ± 9.19 | 4.15% | |
| PI | Females | 17.4 ± 6.14 | 17.7 ± 5.70 | 1.72% |
| Males | 14.2 ± 6.39 | 13.1 ± 5.08 | −7.75% | |
| NSE | Females | 11.5 ± 3.91 | 12.1 ± 4.49 | 5.22% |
| Males | 9.87 ± 3.46 | 10.4 ± 3.64 | 5.37% | |
| EX | Females | 12.4 ± 3.92 | 12.5 ± 3.82 | 0.81% |
| Males | 8.42 ± 3.85 | 8.34 ± 3.82 | −0.95% | |
| CW | Females | 9.57 ± 2.90 | 9.96 ± 3.33 | 4.08% |
| Males | 9.61 ± 4.33 | 10.2 ± 4.58 | 6.14% | |
| PD | Females | 6.56 ± 2.58 | 7.09 ± 2.83 | 8.08% |
| Males | 5.66 ± 2.56 | 5.63 ± 2.15 | −0.53% | |
| TAS | Females | 148 ± 32.1 | 157 ± 29.9 | 6.08% |
| Males | 122 ± 40.8 | 126 ± 38.7 | 3.28% | |
| Time 1 | Time 2 | Percentage Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Academic Stress | ||||
| TMD | 1 year | 36.1 ± 12 | 40.5 ± 12 | 12.19% |
| 3 year | 38.3 ± 11 | 41.7 ± 12.5 | 8.88% | |
| 4 year | 40.6 ± 12.1 | 41.6 ± 10.8 | 2.46% | |
| AOB | 1 year | 21.5 ± 7.8 | 23.5 ± 7.46 | 9.3% |
| 3 year | 25.8 ± 8.67 | 27.3 ± 7.62 | 5.81% | |
| 4 year | 27.2 ± 9.16 | 30.6 ± 9.15 | 12.5% | |
| BAP | 1 year | 21.6 ± 10.2 | 22.9 ± 8.81 | 6.02% |
| 3 year | 22.4 ± 7.99 | 23.6 ± 7.75 | 5.36% | |
| 4 year | 22.7 ± 9.06 | 25.4 ± 9.88 | 11.89% | |
| PI | 1 year | 15 ± 5.8 | 14.7 ± 5.43 | −2% |
| 3 year | 17.4 ± 6.88 | 17.1 ± 6.35 | −1.72% | |
| 4 year | 16.2 ± 5.75 | 16.7 ± 5.22 | 3.09% | |
| NSE | 1 year | 8.88 ± 2.32 | 9.27 ± 3.05 | 4.39% |
| 3 year | 10.7 ± 3.79 | 11.7 ± 4.20 | 9.35% | |
| 4 year | 13.5 ± 3.72 | 13.5 ± 4.60 | 0% | |
| EX | 1 year | 10.5 ± 4.53 | 11.1 ± 4.64 | 5.71% |
| 3 year | 11.4 ± 3.93 | 11.4 ± 4.19 | 0% | |
| 4 year | 11.8 ± 4.65 | 11.3 ± 4.06 | −4.24% | |
| CW | 1 year | 8.06 ± 3.34 | 8.82 ± 3.85 | 9.43% |
| 3 year | 10.3 ± 3.53 | 10.7 ± 3.97 | 3.88% | |
| 4 year | 9.68 ± 2.58 | 10 ± 2.82 | 3.31% | |
| PD | 1 year | 5.58 ± 2.45 | 5.64 ± 2.12 | 1.08% |
| 3 year | 6.17 ± 2.42 | 6.71 ± 2.69 | 8.75% | |
| 4 year | 7.19 ± 2.83 | 7.57 ± 3.01 | 5.29% | |
| TAS | 1 year | 127 ± 36.8 | 136 ± 33.3 | 7.09% |
| 3 year | 142 ± 35 | 150 ± 35.2 | 5.63% | |
| 4 year | 149 ± 36.3 | 157 ± 35.5 | 5.37% | |
| Time 1 | Time 2 | Percentage Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perceived Classroom Climate | ||||
| RCC | Females | 26.7 ± 5.24 | 26.8 ± 4.96 | 0.37% |
| Males | 26.5 ± 5.49 | 27.5 ± 4.31 | 3.77% | |
| RCT | Females | 27.8 ± 6.67 | 28.4 ± 5.47 | 2.16% |
| Males | 28.8 ± 5.33 | 28.5 ± 5.66 | −1.04% | |
| Time 1 | Time 2 | Percentage Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perceived Classroom Climate | ||||
| RCC | 1 year | 29.6 ± 3.81 | 28 ± 4.62 | −5.41% |
| 3 year | 26.5 ± 4.65 | 26.8 ± 4.42 | 1.13% | |
| 4 year | 24.2 ± 6.19 | 26.4 ± 5.47 | 9.09% | |
| RCT | 1 year | 30.2 ± 4.49 | 29.6 ± 5.36 | −1.99% |
| 3 year | 28 ± 6.11 | 27.5 ± 5.52 | −1.79% | |
| 4 year | 26.4 ± 7.58 | 29.1 ± 5.45 | 10.23% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-Robledillo, N.; Vela-Bermejo, J.; Clement-Carbonell, V.; Ferrer-Cascales, R.; Alcocer-Bruno, C.; Albaladejo-Blázquez, N. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Academic Stress and Perceived Classroom Climate in Spanish University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074398
Ruiz-Robledillo N, Vela-Bermejo J, Clement-Carbonell V, Ferrer-Cascales R, Alcocer-Bruno C, Albaladejo-Blázquez N. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Academic Stress and Perceived Classroom Climate in Spanish University Students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(7):4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074398
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-Robledillo, Nicolás, Juan Vela-Bermejo, Violeta Clement-Carbonell, Rosario Ferrer-Cascales, Cristian Alcocer-Bruno, and Natalia Albaladejo-Blázquez. 2022. "Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Academic Stress and Perceived Classroom Climate in Spanish University Students" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 7: 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074398
APA StyleRuiz-Robledillo, N., Vela-Bermejo, J., Clement-Carbonell, V., Ferrer-Cascales, R., Alcocer-Bruno, C., & Albaladejo-Blázquez, N. (2022). Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Academic Stress and Perceived Classroom Climate in Spanish University Students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(7), 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074398







