Leaching of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from the Coal Tar in Sewage Wastewater, Acidic and Alkaline Mine Drainage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Phase Partition Equilibrium (Raoult’s Law) and Dissolution of Kinetics
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Methodology
Determination of PAHs from GC–MS
3. Results and Discussion
Influence of Ageing of Coal Tar/Various Water Sources Interphase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norouzi, N.; Fani, M. Environmental sustainability and coal: The role of financial development and globalization in South Africa. Iran. (Iran.) J. Energy Environ. 2021, 12, 68–80. [Google Scholar]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Awosusi, A.A.; Bekun, F.V.; Altuntaş, M. Coal energy consumption beat renewable energy consumption in South Africa: Developing policy framework for sustainable development. Renew. Energy 2021, 175, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulangé, M.; Lorgeoux, C.; Biache, C.; Michel, J.; Michels, R.; Faure, P. Aging as the main factor controlling PAH and polar-PAC (polycyclic aromatic compound) release mechanisms in historically coal-tar-contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamvura, T.; Govha, J.; Danha, G.; Muzenda, E.; Kamotoa, N. Production of modified bitumen from used engine oil, coal tar and waste tyre for construction applications. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 33, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Mojiri, A.; Zhou, J.L.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Kindaichi, T. Comprehensive review of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water sources, their effects and treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munyengabe, A. Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Water, Soils and Surface Sediments of the Msunduzi River, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Master’s Thesis, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wlodarczyk-Makula, M. The loads of PAHs in wastewater and sewage sludge of municipal treatment plant. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2005, 25, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świetlik, R.; Kowalczyk, D.; Dojlido, J. Influence of selected physicochemical factors on the degradation of PAHs in water. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2002, 11, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Urbano, I.; Villen-Guzman, M.; Perez-Recuerda, R.; Rodriguez-Maroto, J.M. Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in conventional drinking water treatment processes. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 243, 103888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-H.; Thi, L.-A.P.; Van Le, Q.; Singh, P.; Raizada, P.; Kajitvichyanukul, P. Tailored photocatalysts and revealed reaction pathways for photodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water, soil and other sources. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeola, A.O.; Forbes, P.B. Advances in water treatment technologies for removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Existing concepts, emerging trends, and future prospects. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Atrazine in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- Cai, T.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Ren, Y.; Dong, Y. Effects of total organic carbon content and leaching water volume on migration behavior of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils by column leaching tests. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, W.F.; Loehr, R.C. Estimating the equilibrium aqueous concentrations of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in complex mixtures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Endo, S.; Eberhardt, C.; Grathwohl, P.; Schmidt, T.C. Partition behavior of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons between aged coal tar and water. Environ. Toxicol.Chem. Int. J. 2009, 28, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.T.; Poirier-McNeil, M.M.; Mayer, A.S. Dissolution of trapped nonaqueous phase liquids: Mass transfer characteristics. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2783–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthy, R.G.; Dzombak, D.A.; Peters, C.A.; Roy, S.B.; Ramaswami, A.; Nakles, D.V.; Nott, B.R. Remediating tar-contaminated soils at manufactured gas plant sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 266A–276A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, S.A.; Poster, D.L.; Leigh, S.D.; Rimmer, C.A.; Mössner, S.; Schubert, P.; Sander, L.C.; Schantz, M.M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a coal tar standard reference material—SRM 1597a updated. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Lee, B.-K. Adsorptive/photo-catalytic process for naphthalene removal from aqueous media using in-situ nickel doped titanium nanocomposite. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 155, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makelane, H.; Waryo, T.; Feleni, U.; Iwuoha, E. Dendritic copolymer electrode for second harmonic alternating current voltammetric signalling of pyrene in oil-polluted wastewater. Talanta 2019, 196, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, D.; Peterson, M.E.; Anderson, C.R. pH-dependence of organic matter solubility: Base type effects on dissolved organic C, N, P, and S in soils with contrasting mineralogy. Geoderma 2016, 271, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.B.; Shaikh, S.; Jain, K.R.; Desai, C.; Madamwar, D. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Sources, toxicity and remediation approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
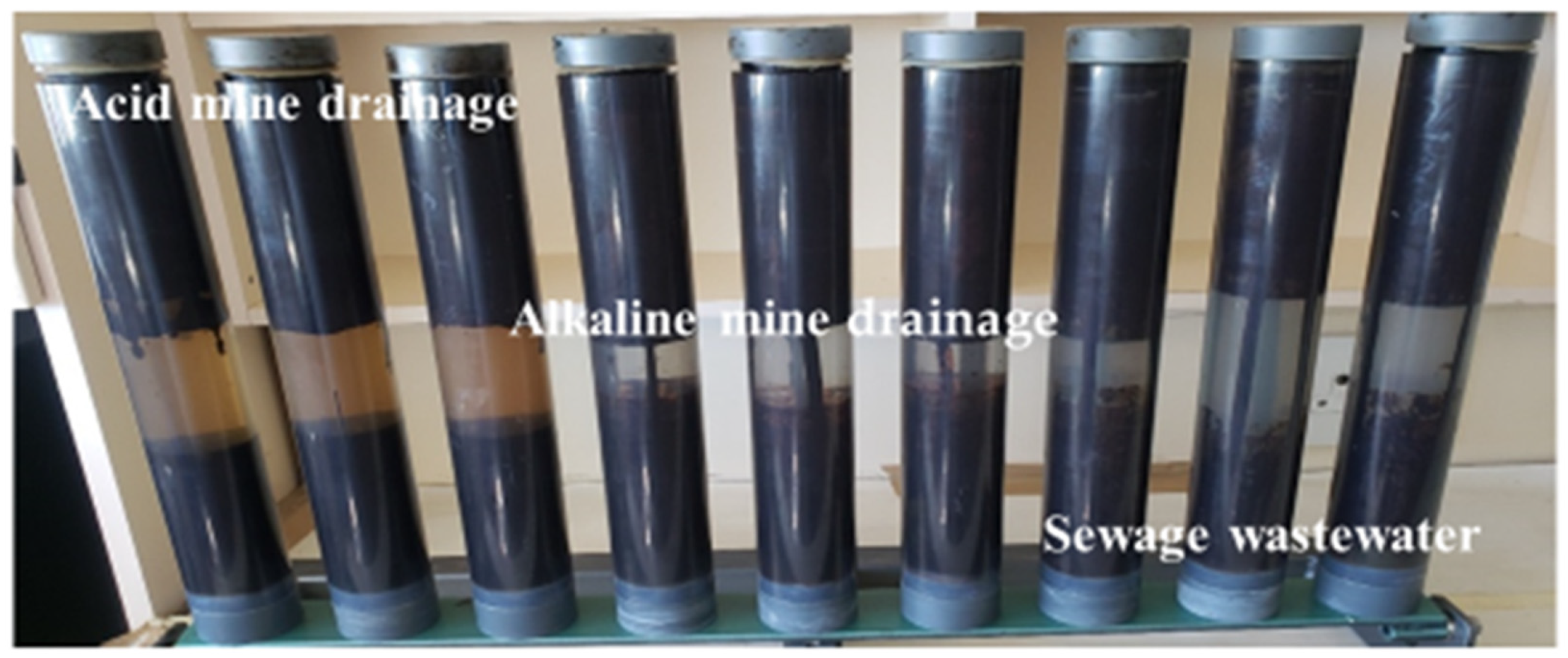
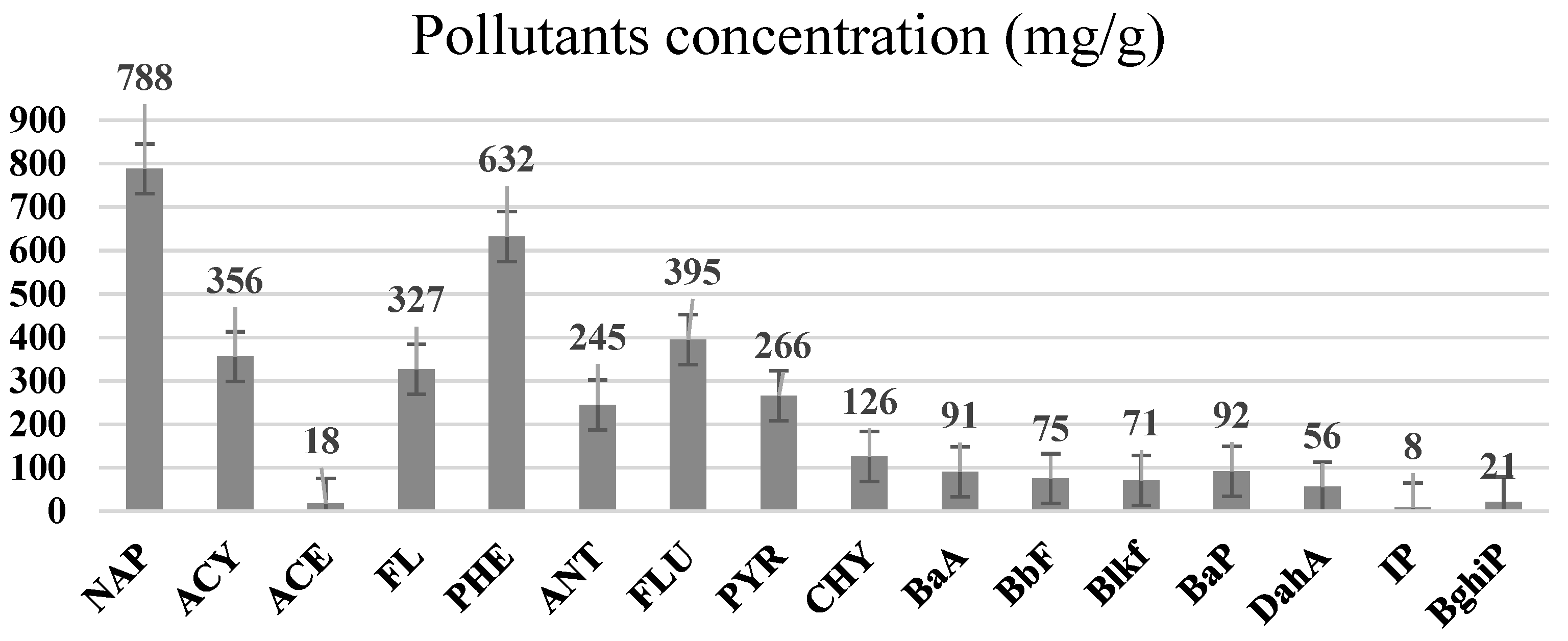

| Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) | Acronyms |
|---|---|
| Naphthalene | NAP |
| Acenaphthylene | ACY |
| Acenaphthene | ACE |
| Fluorene | FL |
| Phenanthrene | PHE |
| Anthracene | ANT |
| Fluoranthene | FLU |
| Pyrene | PYR |
| Chrysene | CHY |
| Benzo(a)anthracene | BaA |
| Benzo(b)fluoranthene | BbF |
| Benzo(k)fluoranthene | Blkf |
| Benzo(a)pyrene | BaP |
| Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene | DahA |
| Indeno(1,2,3,c-,d-)pyrene | IP |
| Benzo(g,h,i)pyrene | BghiP |
| PAHs | Formula | No. of Rings | Molar Weight (g/mol) | Geometry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAP | C10H8 | 2 | 128 |  |
| ANT | C14H10 | 3 | 178 |  |
| PHE | C14H10 | 3 | 178 | 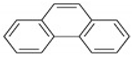 |
| CHY | C18H12 | 4 | 228 |  |
| CHY | C16H10 | 4 | 202 | 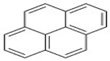 |
| BaP | C20H12 | 5 | 252 | 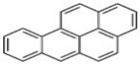 |
| BghiP | C22H12 | 6 | 276 | 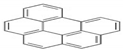 |
| ACY | C12H8 | 3 | 152 | 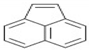 |
| FL | C13H10 | 3 | 166 | 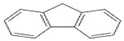 |
| FLU | C16H10 | 4 | 202 | 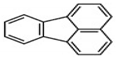 |
| BaA | C18H12 | 4 | 228 | 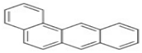 |
| BbF | C20H12 | 5 | 252 | 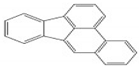 |
| Blkf | C20H12 | 5 | 252 |  |
| DahA | C22H14 | 5 | 278 | 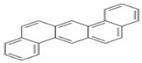 |
| BaP | C22H12 | 6 | 276.33 | 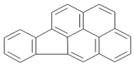 |
| ACE | C12H10 | 5 | 154.21 |  |
| PAHs (×10−6) mg/L | ACE | ACY | ANT | BaA | BaP | BbF | Blkf | BghiP | CHY | DahA | FL | FLU | IP | NAP | PHE | PYR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drinking Water | 3.8 to 478 | 1.8 to 1210 | 1.4 to 71 | 2.29 to 10 | 1.3 to 8 | 2.1 to 24 | 4.6 to 24 | 2.0 to 8 | 1.8 to 27 | 2.0 to 9 | 4.0 to 41,000 | 6.5 to 1,430,000 | 1.6 to 3 | 4.6 to 14,000 | 13.1 to 139,000 | 4.2 to 92,000 | |
| Rivers and Lakes | 2.6 to 579,000 | 2.7 to 537,000 | 1.0 to 256,000 | 0.6 to 3200 | 0.5 to 1,239,000 | 1.2 to 7,800,000 | 0.8 to 3100 | 0 to 11,700 | 1.8 to 4300 | 4.0 to 11,400 | 5.6 to 2,480,000 | 4.2 to 2,498,000 | 1.0 to 7200.0 | 52.5 to 6900 | 13.3 to 126,000 | 2.9 to 1,138,000 | |
| Groundwater | 0.4 to 149 | 0.8 to 13 | 0.1 to 196 | 0.1 to 6 | 3.0 to 123 | 1.9 to 39 | 5.1 to 30 | 0.4 to 9 | 0.1 to 71 | 0.1 to 4 | 0.4 to 168 | 2.0 to 51 | 3.6 to 12 | 2.1 to 281 | 2.0 to 179 | 0.3 to 42 | |
| Wastewater | 28.8 to 100 | 16.6 to 66 | 42.0 to 295 | 46 | 71.6 to 1,447,000 | 82.0 to 8,310,000 | 100.0 to 204 | 92 | 20.7 to 112 | 0 | 20.0 to 234,000 | 14.0 to 2,340,000 | 21 | 40.0 to 47,000 | 33.0 to 6,495,000 | 19.1 to 1,186,600 | |
| Seawater | 2.6 to 4200 | 4.5 to 4100 | 0.1 to 3350.0 | 0.0 to 17,490 | 0.0 to 17,490 | 0.2 to 28,490 | 0.0 to 32,050 | 0.2 to 14,790 | 0.1 to 42,710 | 0.0 to 32,340 | 0.2 to 1520 | 0.0 to 6610 | 0.0 to 46,600 | 75.9 to 7800 | 0.2 to 1080 | 0.0 to 987 | |
| Sediments | 0.6 to 1821 | 1.7 to 13 | 2.0 to 658 | 0.2 to 152 | 0.0 to 739 | <1 to 932 | 3.8 to 17,486 | 8.9 to 5153 | 0.9 to 193 | 1.8 to 999 | 0< to 52 | <1 to 24,857 | 0.4 to 552 | <1 to 69 | 5.7 to 410 | 2.8 to 27 | |
| Water Samples | Physical/Aesthetic Parameters | Unit Result | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acid mine drainage | Acidity as CaCO3 | mg/L | 672 |
| Alkalinity-Total as CaCO3 | mg/L | <10.0 | |
| Dissolved Oxygen | mg/L | 8.00 | |
| Electrical Conductivity @ 25 °C | mS/m | 214 | |
| pH @ 25 °C | pH units | 2.77 | |
| Organic Parameters | |||
| Dissolved organic carbon | mg/L | 2.25 | |
| Alkaline mine drainage | Acidity as CaCO3 | mg/L | 12.0 |
| Alkalinity-Total as CaCO3 | mg/L | 402 | |
| Dissolved Oxygen | mg/L | 8.30 | |
| Electrical Conductivity @ 25 °C | mS/m | 352 | |
| pH @ 25 °C | pH units | 7.95 | |
| Organic Parameters | |||
| Dissolved organic carbon | mg/L | 4.35 | |
| Sewage wastewater | Acidity as CaCO3 | mg/L | 216 |
| Alkalinity-Total as CaCO3 | mg/L | 438 | |
| Dissolved Oxygen | mg/L | 0.50 | |
| Electrical Conductivity @ 25 °C | mS/m | 154 | |
| pH @ 25 °C | pH units | 6.70 | |
| Organic Parameters | |||
| Dissolved organic carbon | mg/L | 113 | |
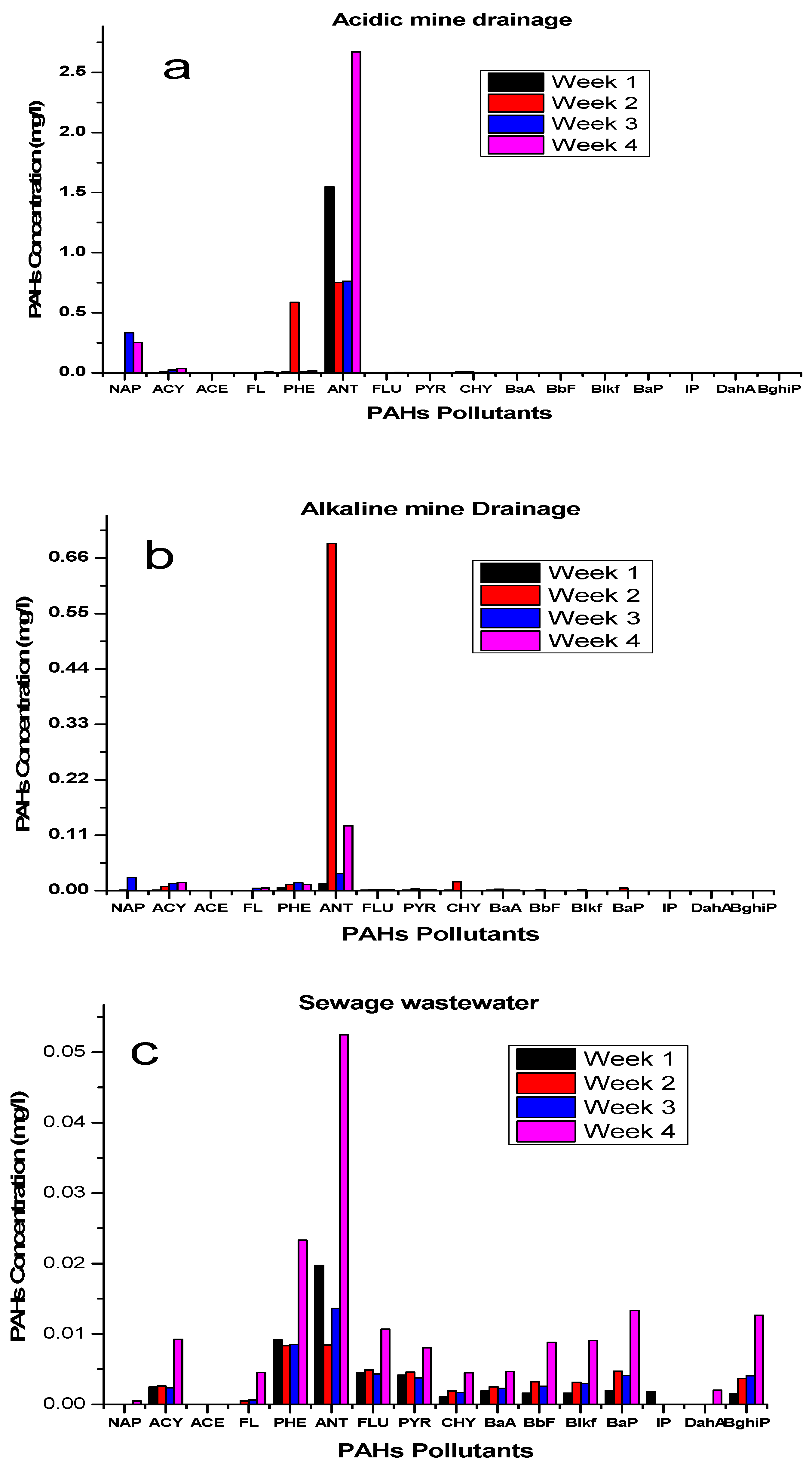
| PAHs Content | Week 1 (mg/L) | Week 2 (mg/L) | Week 3 (mg/L) | Week 4 (mg/L) | PAHs Concentration (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid Mine Drainage | NAP | 0 | 0 | 0.332402 | 0.254163 | 0.5877 |
| ACY | 0.00232 | 0.006527 | 0.023753 | 0.03721 | 0.0707 | |
| ACE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| FL | 0 | 0 | 0.005651 | 0.009247 | 0.0155 | |
| PHE | 0.0074534 | 0.585888 | 0.0095059 | 0.0173442 | 0.620 | |
| ANT | 1.548783 | 0.753182 | 0.763863 | 2.669656 | 5.7355 | |
| FLU | 0.0015533 | 0.001267 | 0.00161 | 0.00473 | 0.0092 | |
| PYR | 0.001593 | 0.001553 | 0.001507 | 0.003643 | 0.0083 | |
| CHY | 0.013611 | 0.013096 | 0 | 0.001075 | 0.0288 | |
| BaA | 0.0012033 | 0.0011733 | 0.0012 | 0.0018733 | 0.0054 | |
| BbF | 0.000393 | 0.000347 | 0.00037 | 0.002063 | 0.0032 | |
| Blkf | 0.0001967 | 0.0001367 | 0.0001643 | 0.0019023 | 0.0024 | |
| BaP | 0.00331 | 0.002507 | 0.000253 | 0.002853 | 0.0098 | |
| IP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| DahA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| BghiP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.002315 | 0.0023 | |
| PAHs Total | 7.0944 | |||||
| PAHs Content | Week 1 (mg/L) | Week 2 (mg/L) | Week 3 (mg/L) | Week 4 (mg/L) | PAHs Concentration (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaline mine drainage | NAP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.000483 | 0.0005 |
| ACY | 0.002493 | 0.00264 | 0.002393 | 0.009223 | 0.0167 | |
| ACE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| FL | 0 | 0.000506 | 0.000633 | 0.004562 | 0.0057 | |
| PHE | 0.0091672 | 0.0083211 | 0.00851 | 0.0233266 | 0.0493 | |
| ANT | 0.019723 | 0.008446 | 0.013635 | 0.052464 | 0.0943 | |
| FLU | 0.004533 | 0.004873 | 0.004317 | 0.010687 | 0.0244 | |
| PYR | 0.004137 | 0.00459 | 0.00377 | 0.008077 | 0.0206 | |
| CHY | 0.001077 | 0.00192 | 0.001702 | 0.004518 | 0.0092 | |
| BaA | 0.0019267 | 0.00252 | 0.0022933 | 0.0046833 | 0.0114 | |
| BbF | 0.001637 | 0.00322 | 0.002577 | 0.00884 | 0.0163 | |
| Blkf | 0.00163 | 0.003142 | 0.002957 | 0.0090683 | 0.0168 | |
| BaP | 0.001993 | 0.004723 | 0.004103 | 0.013353 | 0.0242 | |
| IP | 0.001769 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0018 | |
| DahA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.002039 | 0.0020 | |
| BghiP | 0.001521 | 0.003682 | 0.00409 | 0.012656 | 0.0219 | |
| Total PAHs | 0.3152 | |||||
| PAHs Content | Week 1 (mg/L) | Week 2 (mg/L) | Week 3 (mg/L) | Week 4 (mg/L) | PAHs Concentration | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg/L) | ||||||
| Sewage Wastewater | NAP | 0 | 0.00096 | 0.02564 | 0.02579 | 0.0524 |
| ACY | 0.001167 | 0.008353 | 0.014387 | 0.016147 | 0.0401 | |
| ACE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| FL | 0 | 0 | 0.004661 | 0.005021 | 0.0097 | |
| PHE | 0.005983 | 0.012669 | 0.015708 | 0.012209 | 0.0466 | |
| ANT | 0.013944 | 0.688642 | 0.033595 | 0.128699 | 0.8649 | |
| FLU | 0.001 | 0.00263 | 0.002653 | 0.002507 | 0.0088 | |
| PYR | 0.001223 | 0.00338 | 0.001847 | 0.00194 | 0.0084 | |
| CHY | 0.001336 | 0.01732 | 0 | 0.000317 | 0.0190 | |
| BaA | 0.001 | 0.00318 | 0.001023 | 0.001303 | 0.0066 | |
| BbF | 0.000343 | 0.00235 | 0.00035 | 0.00064 | 0.0037 | |
| Blkf | 0.0001347 | 0.002133 | 0.0001453 | 0.0004623 | 0.0029 | |
| BaP | 0.00024 | 0.00511 | 0.000257 | 0.0006 | 0.0063 | |
| IP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| DahA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| BghiP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total PAHs | 1.0690 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batchamen Mougnol, J.B.; Waanders, F.; Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Al Alili, A.R. Leaching of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from the Coal Tar in Sewage Wastewater, Acidic and Alkaline Mine Drainage. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084791
Batchamen Mougnol JB, Waanders F, Fosso-Kankeu E, Al Alili AR. Leaching of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from the Coal Tar in Sewage Wastewater, Acidic and Alkaline Mine Drainage. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(8):4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084791
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatchamen Mougnol, Jean Bedel, Frans Waanders, Elvis Fosso-Kankeu, and Ali Rashed Al Alili. 2022. "Leaching of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from the Coal Tar in Sewage Wastewater, Acidic and Alkaline Mine Drainage" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 8: 4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084791
APA StyleBatchamen Mougnol, J. B., Waanders, F., Fosso-Kankeu, E., & Al Alili, A. R. (2022). Leaching of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from the Coal Tar in Sewage Wastewater, Acidic and Alkaline Mine Drainage. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(8), 4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084791






