Research on the Development of Urban Parks Based on the Perception of Tourists: A Case Study of Taihu Park in Beijing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Method
2.3. Research Hypothesis
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overall Test of Structural Equation Model
3.2. Discussion of Environmental Perception
3.3. Discussion of Service and Quality Perception
3.4. Discussion of Accessibility
3.5. Discussion of Tourist Loyalty
3.6. Discussion of Tourist Complaint
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
- (1)
- Tourist satisfaction plays an important decisive role in the sustainable development of the park. In order to improve the urban status of the park, it is necessary to improve tourist satisfaction.
- (2)
- Environmental perception, service and quality perception, accessibility, and tourist loyalty all have a significantly positive impact on tourist satisfaction. Therefore, to improve the tourist satisfaction, environmental perception, service and quality perception, accessibility, and tourist loyalty must be enhanced.
- (3)
- Tourist complaint is in the opposite direction as the change of tourist satisfaction, whose rise will reduce tourist satisfaction.
- (1)
- At the park manager level, Taihu Park can add self-service vending machines in the park to improve service and quality perception, increase the accessibility by increasing the number of parking spaces, and improve its software and hardware service quality to reduce tourists’ complaints.
- (2)
- From the government’s perspective, it is still up to the government to make efforts to enhance the status of urban parks. Therefore, the government should rely on its own influence to increase publicity for Taihu Park, expand its influence, attract foreign investment, and form a development model in which the market promotes the park. In addition, the government should adopt the necessary financial means to encourage Taihu Park to maintain the trees and infrastructures greatly and to improve the tourist satisfaction by giving more financial support and improving the standard of management subsidy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qian, Y. Research on Recreation Satisfaction and Behavioral Intention of Xi’an Urban Parks Based on Tourists’ Perception. Master’s Thesis, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, C.; Francis, C. PEOPLE PLACES: Design Guidelines for Urban Open Space, 2nd ed.; John Willey & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Madanipour, A. WHOSE PUBLIC SPACE? International Case Studies in Urban Design and Development; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kongphunphin, C.; Iamtrakul, P. The Transition of Roles of Public Spaces in Thailand. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1j060450m15y0p809v0m0gg0rf082328&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- Carmona, M.; Tiesdell, S.; Heath, T.; Oc, T. Public Places-Urban Spaces: The Dimensions of Urban Design, 2nd ed.; Architectural Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kongphunphin, C.; Srivanit, M. A Multi-Dimensional Clustering Applied to Classify the Typology of Urban Public Parks in Bangkok Metropolitan Area, Thailand. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.; Zaval, L.; Orlove, B.; Moraga, V.; Culligan, P. More than nature: Linkages between well-being and greenspace influenced by a combination of elements of nature and non-nature in a New York City urban park. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021. pre-publish. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäntymaa, E.; Jokinen, M.; Juutinen, A.; Lankia, T.; Louhi, P. Providing ecological, cultural and commercial services in an urban park: A travel cost–contingent behavior application in Finland. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 209, 104042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, W.; Dove, M.R.; Felson, A.J. Engaging the unengaged: Understanding residents’ perceptions of social access to urban public space. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 59, 126991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Gobster, P.H. Leisure preferences and open space needs in an urban Chinese American community. J. Archit. Plan. Res. 1998, 15, 338–355. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson, B.; Knez, L.; Hedblom, M.; Sang, A.O. Effects of biodiversity and environment-related attitude on the perception of urban green space. Urban Ecosyst. 2017, 20, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Sun, Z.; Bao, Z. Landscape perception and recreation needs in urban green space in Fuyang, Hangzhou, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Che, S.; Xie, C.; Tian, S. Understanding Shanghai Residents’ Perception of Leisure Impact and Experience Satisfaction of Urban Community Parks: An Integrated and IPA Method. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z.; Fan, J. Big Data-Based Evaluation of Urban Parks: A Chinese Case Study. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolund, P.; Hunhammar, S. Ecosystem services in urban areas. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, P.; Kinzig, A. Nature in the metropolis. Sci. Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci. 2005, 308, 1225–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Gaston, K.J.; Warren, P.H.; Thompson, K.; Smith, R.M. Urban domestic gardens (IV): The Extent of the Resource and its Associated Features. Biodivers. Conserv. 2005, 14, 3327–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.M.; Gaston, K.J.; Warren, P.H.; Thompson, K. Urban domestic gardens (V): Relationships between landcover composition, housing, and landscape. Landsc. Ecol. 2005, 20, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, T. Using Microclimatic Landscape Design to Create Thermal Comfort and Energy Efficiency. Actas Da Conf. Sobre Edif. Efic. Univ. Do Algarve 2008, 25, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, Y.; Kim, S. A study of event quality, destination image, perceived value, tourist satisfaction, and destination loyalty among sport tourists. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2020, 32, 940–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hsu, M.K. The relationships of destination image, satisfaction, and behavioral intentions: An integrated model. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2020, 27, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Han, H. Tourist experience quality and loyalty to an island destination: The moderating impact of destination image. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2019, 36, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliedan, M.M.; Sobaih, A.E.E.; Elshaer, I.A. Influence of Cities-Based Entertainment on Tourist Satisfaction: Mediating Roles of Destination Image and Experience Quality. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, W.; Bai, Y. Analysis of the relationship between urban park types and functions: A case study of Beijing Urban park. Geogr. Res. 2013, 10, 1964–1976. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Li, X.; Han, D. Research on accessibility of urban parks: Methods and key issues. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 19, 5381–5390. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Zhai, H. Post-use evaluation (POE) of urban forest parks: A case study of Taibao Park in Baoshan city, Yunnan Province. Urban Archit. 2021, 2, 164–167. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, C.S. Discussion on ecological construction and management of urban park. Low-Carbon World 2021, 2, 253–254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, J.; Song, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Research on the status value and development path of Parks in Beijing. Beijing Society of Landscape Architecture. 2012 Landscape greening and Livable City construction in Beijing. Beijing Soc. Landsc. Archit. 2012, 10, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.; Yao, H.; Xia, J.; Fu, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Accessibility-Based Equity Assessment of Urban Parks in Beijing. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2021, 147, 05021018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Song, H. Understanding Visitors at an Urban Park by Profiling of Destination Attributes. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talal, M.L.; Santelmann, M.V. Visitor access, use, and desired improvements in urban parks. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 63, 127216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, R.; Jia, T. Research on member satisfaction of farmers’ professional cooperatives and its influencing factors: Taking Huairou District, Beijing as an example. China Agric. Sci. Bull. 2022, 38, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Pizam, A. Tourism’s impacts: The social costs to the destination community as perceived by its residents. J. Travel Res. 1978, 16, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.B.; Ragheb, M.G. Measuring leisure satisfaction. J. Leis. Res. 1980, 12, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.W.; Sullivan, M.W. The antecedents and consequences of customer satisfaction for firms. Mark. Sci. 1993, 12, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, G.H.G.; Levesque, T. Customer satisfaction with services: Putting perceived value into the equation. J. Serv. Mark. 2000, 2014, 392–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Uysal, M. An examination of the effects of motivation and satisfaction on destination loyalty: A structural model. Tour. Manag. 2005, 26, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J. Voice, exit, and negative word of mouth behaviors: An investigation across three service categories. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1990, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Review and Prospect of Tourist Satisfaction Research. J. Beijing Int. Stud. Univ. 2010, 1, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, D.A.; Crompton, J.L. Quality, satisfaction and behavioral intentiongs. Ann. Tour. Res. 2000, 27, 785–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscue, I.R.; Martin, H.S.; Collado, J. The role of expectations in the consumer satisfaction formation process: Empirical evidence in the travel agency sector. Tour. Manag. 2006, 27, 410–419. [Google Scholar]
- Gallarza, M.G.; Saura, I.G. Value dimensions, perceived value, satisfaction and loyalty: An investigation of university students’ travel behavior. Tour. Manag. 2006, 27, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.G.-Q.; Qu, H. Examining the structural relationships of destination image, tourist satisfaction and destination loyalty: An integrated approach. Tour. Manag. 2008, 29, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jeon, S.; Kim, D. The impact of tour quality and tourist satisfaction on tourist loyalty: The case of Chinese tourists in Korea. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y. Research on the influencing factors of tourist eco-tourism satisfaction. Bus. Res. 2016, 11, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Q.; Gao, Q. Analysis on influencing factors and mechanism of tourist satisfaction in garden expo park: An empirical study based on structural equation model. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2016, 8, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Albayrak, T.; Caber, M. Examining the relationship between tourist motivation and satisfaction by two competing methods. Tour. Manag. 2018, 69, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L. Study on urbanization process and status quo of Beijing suburbs: A case study of Olympic Village and Taihu Town. Beijing Plan. Constr. 2014, 2, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Claes, F.L.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Bai, Y. American Customer Satisfaction Index. Chin. J. Manag. 2005, 4, 495–504. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Research on measurement Method of Customer satisfaction. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2001, 2, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Woodard, M.D. Leisure among African-Americans: Toward an indigenous frame of reference. In Managing Urban and High-Use Recreation Settings; Gobster, P., Ed.; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, North Central Forest Experiment Station: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1993; pp. 129–131. [Google Scholar]
- Pietila, M.; Neuvonen, M.; Borodulin, K.; Korpela, K.; Sievanen, T.; Tyrvainen, L. Relationships between exposure to urban green spaces, physical activity and self-rated health. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2015, 10, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, S. How to Improve the Public Trust of the Intelligent Aging Community: An Empirical Study Based on the ACSI Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazi, K.M. Veterans’ voices: Use of the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) Survey to identify My HealtheVet personal health record users’ characteristics, needs, and preferences. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2010, 2, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, L.J.; Gillaspy, J.A., Jr.; Rebecca, P.S. Reporting Practices in Confirmatory Factor Analysis: An Overview and Some Recommendations. Psychol. Methods 2009, 14, 6–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, R.H.; Ji, A. Digital ITEMS Module 2: Scale Reliability in Structural Equation Modeling. Educ. Meas. Issues Pract. 2018, 37, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H. Research on Regional Economic Vitality based on Factor Analysis. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2019, 4, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Doll, W.J.; Xia, W.; Torkzadeh, G. A Confirmatory Factor Analysis of the End-User Computing Satisfaction Instrument. MIS Q. 1994, 18, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K. Characteristics and application of structural equation model. Stat. Decis. Mak. 2006, 10, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, S. Measuring the accessibility and equity of public parks: A case study using GIS. Manag. Leis. 2001, 6, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, P.; Kundi, M.; Arnberger, A.; Eder, R.; Allex, B.; Weitensfelder, L.; Hutter, H.-P. Reloading Pupils’ Batteries: Impact of Green Spaces on Cognition and Wellbeing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-T.; Li, D.; Chang, P.-J. Effects of Urban Park Quality, Environmental Perception, and Leisure Activity on Well-Being among the Older Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekkel, E.D.; de Vries, S. Nearby green space and human health: Evaluating accessibility metrics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 157, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, P.; Zhevelev, H.M. Effect of visitors’ pressure on soil and vegetation in several different micro-environments in urban parks in Tel Aviv. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jim, C.; Song, H. Assessing Structural Connectivity of Urban Green Spaces in Metropolitan Hong Kong. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.; Zhang, D. Analyzing the Level of Accessibility of Public Urban Green Spaces to Different Socially Vulnerable Groups of People. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, D.; He, J. Exploring Differentiated Conservation Priorities of Urban Green Space Based on Tradeoffs of Ecological Functions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
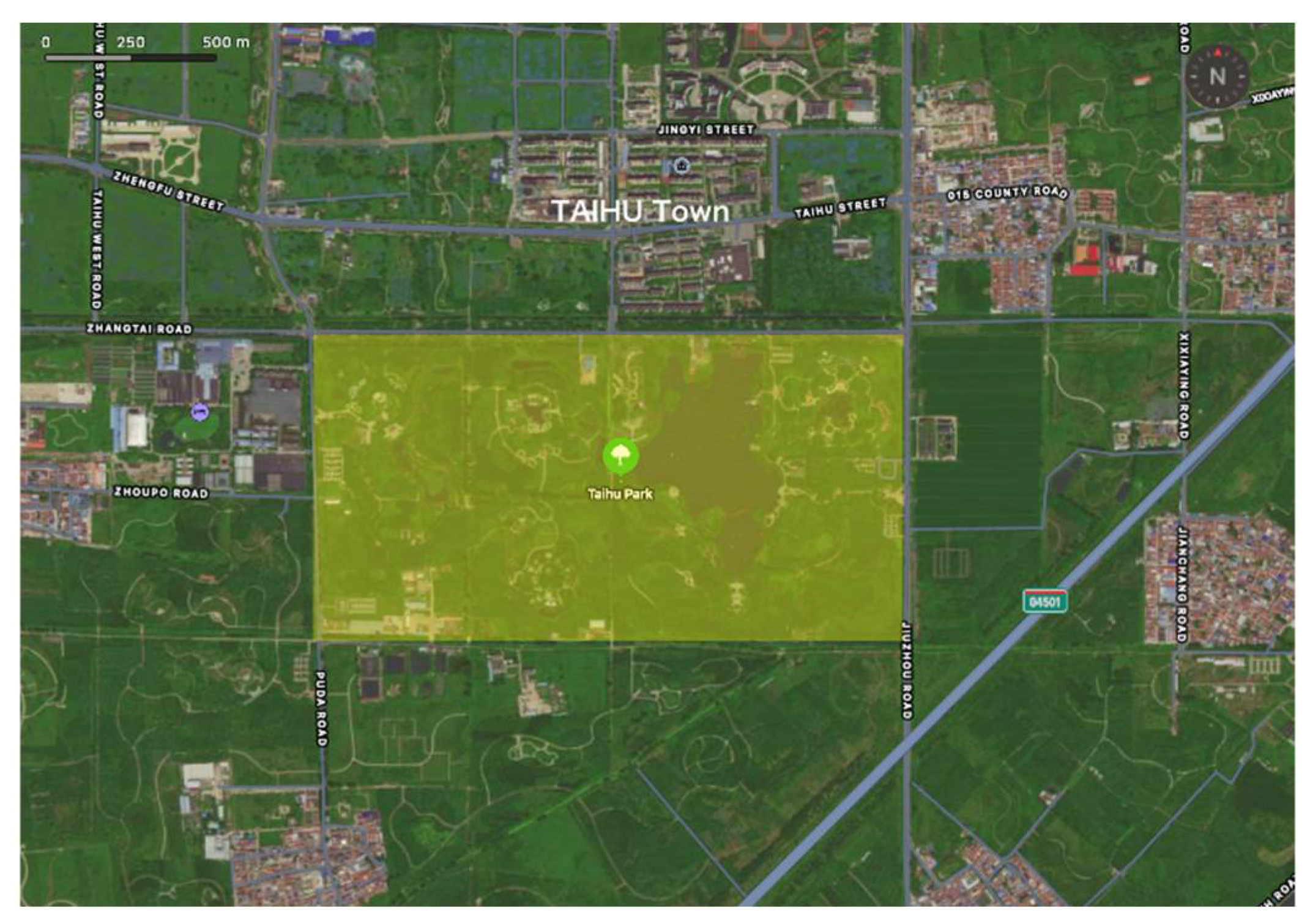





| Natural Environment | General Situation |
|---|---|
| Location | Located in the south of Tongzhou District of Beijing, adjacent to Zhangjiawan Town in the east, across the Liangshui River with Majuqiao Town in the south, Beijing Economic and Technological Development Zone in the west, and Liyuan Town in the north |
| Area | 81.3 km2 |
| Climate | Temperate monsoon climate |
| River system | The starting point of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal |
| Latent Variables | Observational Variable | Codes | Questions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Travel time | X1 | How do you feel about the time it takes to get to the park? | |
| Distribution of entrances and exits | X2 | How do you feel about the distribution of entrances and exits in the park? | ||
| Distance | X3 | How do you feel about the distance between the park and your neighborhood? | ||
| Tourist perception | Quality and service perception | Infrastructure | X4 | How do you feel about the infrastructure of the park? |
| Greening | X5 | How do you feel about greening the park? | ||
| Natural scenery | X6 | How do you feel about the natural scenery of the park? | ||
| Recreational activities | X7 | How do you feel about the entertainment activities in the park? | ||
| Service quality | X8 | How do you feel about the service quality of the park? | ||
| Environmental awareness | Environmental sanitation facilities | X9 | How do you feel about the location and number of environmental sanitation facilities in the park? | |
| Signage | X10 | How do you feel about the signage in the park? | ||
| Sanitary conditions | X11 | How do you feel about the cleanliness and sanitation in the park? | ||
| Tourist loyalty | Revisit | X12 | Would you like to visit again? | |
| Recommend to others | X13 | Would you recommend this place to your relatives and friends? | ||
| Revisit at a lower price | X14 | Would you visit the park again if you were charged a lower entrance fee? | ||
| Tourist complaint | Negative publicity | X15 | Do you think the park is worth coming back to? | |
| Complaints or suggestions | X16 | Do you have some suggestions that you would like to share with the relevant authorities? | ||
| Tourist satisfaction | The whole park | X17 | How do you feel about the park as a whole? | |
| Fulfillment of expectations | X18 | Does this trip meet your travel expectations? | ||
| Characteristics | Category | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 98 | 53.1% |
| Female | 111 | 46.9% | |
| Below 18 years old | 12 | 5.7% | |
| 18–25 years old | 29 | 13.9% | |
| 26–30 years old | 22 | 10.5% | |
| Age | 31–40 years old | 69 | 33.0% |
| 41–50 years old | 28 | 13.4% | |
| 51–60 years old | 19 | 9.1% | |
| Over 60 years old | 30 | 14.4% | |
| Education | High school and below | 50 | 23.9% |
| Junior college | 52 | 24.9% | |
| Undergraduate degree | 84 | 40.2% | |
| Postgraduate and above | 23 | 11.0% | |
| Trips | First time | 76 | 36.4% |
| Second time | 18 | 8.6% | |
| Third time or more | 115 | 55.0% | |
| Way to travel | Private car | 132 | 63.2% |
| Bus | 26 | 12.4% | |
| Electric bicycle | 7 | 3.3% | |
| Bicycle | 13 | 6.2% | |
| Walking | 31 | 14.8% |
| Travel Motivation | Level | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical exercise | Totally disagree | 9 | 4.3% |
| Disagree | 5 | 2.4% | |
| General | 40 | 19.1% | |
| Agree | 70 | 33.5% | |
| Totally agree | 85 | 40.7% | |
| Totally disagree | 8 | 3.8% | |
| Disagree | 2 | 1.0% | |
| Outing entertainment | General | 27 | 12.9% |
| Agree | 75 | 35.9% | |
| Totally agree | 97 | 46.4% | |
| Emotional relaxation | Totally disagree | 5 | 2.4% |
| Disagree | 9 | 4.3% | |
| General | 59 | 28.2% | |
| Agree | 89 | 42.6% | |
| Totally agree | 47 | 22.5% |
| Fitness Index | CMIN/DF | GFI | AGFI | TLI | IFI | CFI | RMSEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Report Values | 2.530 | 0.846 | 0.861 | 0.775 | 0.924 | 0.912 | 0.103 |
| Recommended Value 1 | <3 | >0.8 | >0.8 | >0.8 | >0.9 | >0.9 | <0.08 |
| Fitness Index | CMIN/DF | GFI | AGFI | TLI | IFI | CFI | RMSEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Report Values | 2.216 | 0.879 | 0.887 | 0.802 | 0.931 | 0.925 | 0.075 |
| Recommended Value 1 | <3 | >0.8 | >0.8 | >0.8 | >0.9 | >0.9 | <0.08 |
| Path | Standardized Estimates | Nonstandardized Estimates | S.E. | C.R. | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tourist satisfaction | <--- | Environmental perception | 0.594 | 0.630 | 0.158 | 3.980 | *** 1 |
| Tourist satisfaction | <--- | Accessibility | 0.134 | 0.132 | 0.094 | 1.403 | 0.011 |
| Tourist satisfaction | <--- | Tourist loyalty | 0.124 | 0.114 | 0.058 | 1.956 | 0.049 |
| Tourist satisfaction | <--- | Tourist complaint | −0.133 | −0.106 | 0.057 | −1.851 | *** 1 |
| Tourist satisfaction | <--- | Service and quality perception | 0.237 | 0.262 | 0.197 | 1.331 | *** 1 |
| Number | Content | Verification Results |
|---|---|---|
| H1 | Accessibility has a significant positive impact on tourist satisfaction (β = 0.132, p < 0.05) | Supported |
| H2 | The environmental perception has a significant positive impact on tourist satisfaction (β = 0.630, p < 0.01) | Supported |
| H3 | Tourist loyalty has a significant positive impact on tourist satisfaction (β = 0.114, p < 0.05) | Supported |
| H4 | Service and quality perception has a significant positive impact on tourist satisfaction (β = 0.262, p < 0.01) | Supported |
| H5 | Tourist complaint has a significant positive impact on tourist satisfaction (β = −0.106, p < 0.01) | Supported |
| Path | Standardized Estimates | Nonstandardized Estimates | C.R. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X4 | <--- | Environmental perception | 0.765 | 0.986 | 11.985 |
| X5 | <--- | Environmental perception | 0.770 | 0.878 | 11.629 |
| X7 | <--- | Environmental perception | 0.826 | 1.125 | 12.636 |
| X1 | <--- | Accessibility | 0.825 | 0.900 | 11.097 |
| X2 | <--- | Accessibility | 0.737 | 0.947 | 11.466 |
| X12 | <--- | Tourist loyalty | 0.880 | 0.923 | 11.213 |
| X13 | <--- | Tourist loyalty | 0.775 | 0.770 | 10.105 |
| X14 | <--- | Tourist loyalty | 0.491 | 0.713 | 6.704 |
| X15 | <--- | Tourist complaint | 0.765 | 0.885 | 10.899 |
| X16 | <--- | Tourist complaint | 0.613 | 0.489 | 1.978 |
| X17 | <--- | Tourist satisfaction | 0.862 | 0.966 | 11.576 |
| X18 | <--- | Tourist satisfaction | −0.086 | −0.547 | −1.207 |
| X3 | <--- | Accessibility | 0.874 | 0.956 | 13.948 |
| X8 | <--- | Environmental perception | 0.895 | 1.174 | 13.881 |
| X9 | <--- | Service and quality perception | 0.792 | 1.023 | 13.683 |
| X10 | <--- | Service and quality perception | 0.769 | 0.902 | 11.900 |
| X11 | <--- | Service and quality perception | 0.861 | 1.098 | 13.706 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Zhao, R. Research on the Development of Urban Parks Based on the Perception of Tourists: A Case Study of Taihu Park in Beijing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095287
Du Y, Zhao R. Research on the Development of Urban Parks Based on the Perception of Tourists: A Case Study of Taihu Park in Beijing. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(9):5287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095287
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yaqi, and Rong Zhao. 2022. "Research on the Development of Urban Parks Based on the Perception of Tourists: A Case Study of Taihu Park in Beijing" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 9: 5287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095287
APA StyleDu, Y., & Zhao, R. (2022). Research on the Development of Urban Parks Based on the Perception of Tourists: A Case Study of Taihu Park in Beijing. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(9), 5287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095287





