Interplay between Networking Capability and Hospital Performance in Indonesia’s Medical Tourism Sector
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Networking Capability
2.2. Stakeholder Theory
2.3. Digital Transformation and Hospital Performance
2.4. Digital Transformation and Networking Capability
2.5. Networking Capability and Hospital Performance
2.6. Resource Integration and Hospital Performance
2.7. Resource Integration and Networking Capability
2.8. Medical Tourism Ecosystem, Networking Capability, and Hospital Performance
2.9. Digital Transformation, Hospital Performance, and Networking Capability
2.10. Resource Integration, Hospital Performance, and Networking Capability
3. Methods
3.1. Sample
3.2. Operational Variables
3.3. Survey Development
4. Results
4.1. Profile of the Respondents
4.2. Description of Variables
4.3. Measurements Model Analysis
4.3.1. Testing the Validity and Reliability of the Research Variables Construct (Model of Second Confirmatory Factor Analysis)
4.3.2. Overall Model Fit
4.3.3. Manifest Variables Analysis
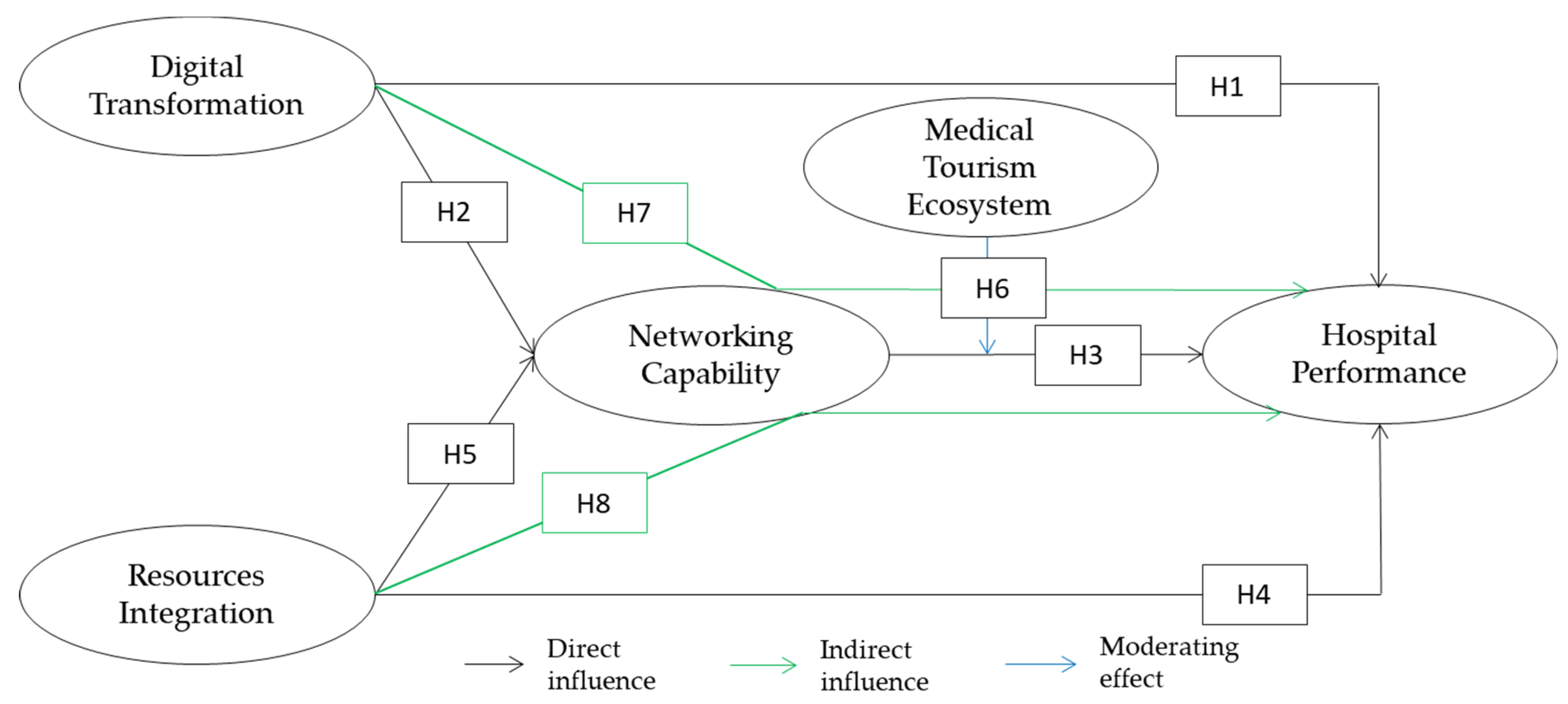
4.4. Hypothesis Testing and Discussion
4.4.1. Hypothesis Test
4.4.2. Hypothesis 1: Digital Transformation has a Positive Effect on Hospital Performance
- H0: There is no positive effect of digital transformation on hospital performance;
- Ha:There is a positive influence of digital transformation on hospital performance.
4.4.3. Hypothesis 2: Digital Transformation has a Positive Effect on Networking Capability
- H0: There is no positive effect of digital transformation on networking capability;
- Ha: There is a positive influence of digital transformation on networking capability.
4.4.4. Hypothesis 3: Networking Capability has a Positive Effect on Hospital Performance
- H0:There is no positive effect of networking capability on hospital performance;
- Ha: There is a positive influence of networking capability on hospital performance.
4.4.5. Hypothesis 4: Resource Integration has a Positive Effect on Hospital Performance
- H0: There is no positive effect of resource integration and hospital performance;
- Ha: There is a positive influence of resource integration and hospital performance.
4.4.6. Hypothesis 5: Resource Integration has a Positive Effect on Networking Capability
- H0: There is no positive effect of resource integration on networking ability;
- Ha: There is a positive influence of resource integration on networking ability.
4.4.7. Hypothesis 6: The Medical Tourism Ecosystem Strengthens the Relationship between Networking Capability and Hospital Performance
- H0: The medical tourism ecosystem cannot strengthen the relationship between networking capability and hospital performance;
- Ha: The medical tourism ecosystem can strengthen the relationship between networking capability and hospital performance.
4.4.8. Hypothesis 7: Digital Transformation has a Positive Effect on Hospital Performance Mediated by Networking Capability
- H0: Digital transformation has no positive effect on hospital performance mediated by networking capability;
- Ha: Digital transformation has a positive effect on hospital performance mediated by networking capability.
4.4.9. Hypothesis 8: Resource Integration has a Positive Effect on Hospital Performance Mediated by Networking Capabilities
- H0: Resource integration has no positive effect on hospital performance, which is mediated by networking skills;
- Ha: Resource integration has a positive effect on hospital performance, which is mediated by networking capabilities.
4.5. Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heung, V.C.S.; Kucukusta, D.; Song, H. Medical Tourism Development in Hong Kong: An Assessment of the Barriers. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, S.; Li, X.R. A Neglected Dimension of Medical Tourism Research Domestic Medical Tourism. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2012, 21, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, A. Sand, Surgery and Stakeholders: A Multi-Stakeholder Involvement Model of Domestic Medical Tourism for Australia’s Sunshine Coast. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2018, 25, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IHRC Medical Tourism Index 2020–2021 Global Destination. Available online: https://assets.website-files.com/5d8aac42c851d2d6528d50d4/5f0df13e57906e9f895e3767_2020-2021MedicalTourismIndexOverallRanking.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Oğuz, B.; Gordon, G.; Cruz, H.H.; Oğuz, B.; Gordon, G.; Cruz, H.H. Medical Tourism in the Time of COVID-19. Available online: https://knowledgecenter.ubt-uni.net/conference/2020/2020booksofproceedings/10?utm_source=knowledgecenter.ubt-uni.net%2Fconference%2F2020%2F2020booksofproceedings%2F10&utm_medium=PDF&utm_campaign=PDFCoverPages (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Kemenkes. Strategi Penguatan Sistem Kesehatan Nasional; Ministry of Health Republic of Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021.
- Berger, R. Medical and Wellness Tourism Strategy Post; Ministry of Tourism and Creative Economy of the Republic of Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2020.
- KARS. Daftar Rumah Sakit Terakreditasi Versi 2012. Available online: http://akreditasi.kars.or.id/accreditation/report/report_accredited.php (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- JCI. JCI-Accredited Organizations. Available online: https://www.jointcommissioninternational.org/about-jci/accredited-organizations/ (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- Bulatovic, I.; Iankova, K. Barriers to Medical Tourism Development in the United Arab Emirates (Uae). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human, G.; Naudé, P. Exploring the Relationship between Network Competence, Network Capability, and Firm Performance: A Resource Based Perspective in an Emerging Economy. Manag. Dyn. 2009, 18, 2–14. [Google Scholar]
- Majid, A.; Yasir, M.; Yousaf, Z.; Qudratullah, H. Role of Network Capability, Structural Flexibility and Management Commitment in Defining Strategic Performance in Hospitality Industry. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 31, 3077–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, D.; Santini, F.D.O.; Toigo, T. Network Capabilities and Firm Performance: A Meta-Analytical Study. In Proceedings of the XLV Encontro da ANPAD 2021, Online, 4–8 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Medhekar, A.; Wong, H.Y.; Hall, J.E. Health-Care Providers Perspective on Value in Medical Travel to India. Tour. Rev. 2020, 75, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morakanyane, R.; Grace, A.A.; Reilly, P.O. Conceptualizing Digital Transformation in Business Organizations: A Systematic Review of Literature. In Proceedings of the BLED Proceedings, Bled, Slovenia, 18–21 June 2017; pp. 427–444. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef, P.C.; Broekhuizen, T.; Bart, Y.; Bhattacharya, A.; Qi Dong, J.; Fabian, N.; Haenlein, M. Digital Transformation: A Multidisciplinary Reflection and Research Agenda. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 122, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, H.; Brochado, A.; Troilo, M.; Mohsin, A. Mirror, Mirror on the Wall, Who’s the Fairest of Them All? A Critical Content Analysis on Medical Tourism. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2017, 24, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Humbatova, G.; Xie, Y.; Yang, X.; Zolotarev, O.; Zhang, G. Different Roles of Telehealth and Telemedicine on Medical Tourism: An Empirical Study from Azerbaijan. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Dey, A.K.; Sahay, A. Exploring Sustainable Competitive Advantage of Multispecialty Hospitals in Dynamic Environment. Compet. Rev. 2020, 30, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, A.; Adegboye, O.; Adekunle, A.; Rahman, K.; McBryde, E.; Eisen, D. Economic Consequences of the COVID-19 Outbreak: The Need for Epidemic Preparedness. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkes, F.; Colding, J.; Folke, C. Navigating Social-Ecological Systems: Building Resilience for Complexity and Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lengnick-Hall, C.; Beck, T.; Lengnick-Hall, M. Developing a Capacity for Organizational Resilience through Strategic Human Resource Management. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2011, 21, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, A.; Steinhauser, K.; Kamal, A.; Jackson, V. Building Resilience for Palliative Care Clinicians: An Approach to Burnout Prevention Based on Individual Skills and Workplace Factors. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2016, 52, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, R.J.; Ranjan, K.R.; Verreynne, M.L.; Jiang, Y.; Previte, J. Coronavirus Crisis and Health Care: Learning from a Service Ecosystem Perspective. J. Serv. Theory Pract. 2021, 31, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemenparekraf. International Wellness Tourism Conference & Festival (IWTCF) 2022 Membawa Misi Jadikan Indonesia Sebagai Destinasi Wellness Tourism Dunia. Available online: https://kemenparekraf.go.id/ragam-ekonomi-kreatif/international-wellness-tourism-conference-festival-iwtcf-2022-membawa-misi-jadikan-indonesia-sebagai-destinasi-wellness-tourism-dunia (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Dyer, J.H.; Singh, H. Cooperative the Relational and Sources of Strategy Competitive Advantage. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2011, 23, 660–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, R. Alliances and Networks. Strateg. Manag. J. 1998, 19, 293–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzoni, G.; Lipparini, A. The Leveraging of Interfirm Relationships as a Distinctive Organizational Capability: A Longitudinal Study. Strateg. Manag. J. 1999, 20, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Thomas, E.; Peng, G.; Di Benedetto, A. Strategic Orientation and New Product Development Performance: The Role of Networking Capability and Networking Ability. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2016, 64, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Di Benedetto, A. Networking Capability and New Product Development. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2012, 59, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasti, M.; Garousi Mokhtarzadeh, N.; Jafarpanah, I. Networking Capability: A Systematic Review of Literature and Future Research Agenda. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2021, 37, 160–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, A.S.; Rydback, M.; Borg, E.; Osarenkhoe, A. Medical Tourism in Emerging Markets: The Role of Trust, Networks, and Word-of-Mouth. Health Mark. Q. 2019, 36, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, R.D.; Hoskisson, R.E.; Hitt, M.A. The Management of Strategy: Concepts and Cases, 13th ed.; South Western Cengage-Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-0-538-75319-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnafous-Boucher, M.; Rendtroff, J.D. Stakeholder Theory: A Model for Strategic Management; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 23, ISBN 9783319443553. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobides, M.G.; Cennamo, C.; Gawer, A. Towards a Theory of Ecosystems. Strateg. Manag. J. 2018, 39, 2255–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, S.L.; Lusch, R.F. Institutions and Axioms: An Extension and Update of Service-Dominant Logic. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2016, 44, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewkitipong, L. The Thai Medical Tourism Supply Chain: Its Stakeholders, Their Collaboration and Information Exchange. Thammasat Rev. 2018, 21, 60–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kamassi, A.; Abd Manaf, N.H.; Omar, A. The Identity and Role of Stakeholders in the Medical Tourism Industry: State of the Art. Tour. Rev. 2020, 75, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwankpa, J.; Roumani, Y. IT Capability and Digital Transformation: A Firm Performance Perspective. In Proceedings of the Thirty Seventh International Conference on Information Systems, Dublin, Ireland, 11–14 December 2016; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bharadwaj, A.S.; Bharadwaj, S.G.; Konsynski, B.R. Information Technology Effects on Firm Performance as Measured by Tobin’s Q. Manag. Sci. 1999, 45, 1008–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Krogstie, J.; Pappas, I.; Pavlou, P. Exploring the Relationship between Big Data Analytics Capability and Competitive Performance: The Mediating Roles of Dynamic and Operational Capabilities. Inf. Manag. 2020, 57, 103169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Yang, M.; Yang, R. Investigating the Effects of IT Capability on Hotel Performance Based on DEA Approach: An Empirical Example of International Hotels in Hong Kong. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunis, M.; Tarhini, A.; Kassar, A. The Role of ICT and Innovation in Enhancing Organizational Performance: The Catalysing Effect of Corporate Entrepreneurship. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 88, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Boura, M.; Lekakos, G.; Krogstie, J. Big Data Analytics and Firm Performance: Findings from a Mixed-Method Approach. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 98, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, P.; Kumar, A. The Intermediating Role of Organizational Culture and Internal Analytical Knowledge between the Capability of Big Data Analytics and a Firm’s Performance. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Chang, C.-H.; Lee, Z.C.R. Business-to-Business Platform Ecosystem Practices and Their Impacts on Firm Performance: Evidence from High-Tech Manufacturing Firms. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2022; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesalainen, J.; Hakala, H. Strategic Capability Architecture: The Role of Network Capability. Entrep. Reg. Dev. 2014, 43, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Ma, X.; Ren, L.; Zhou, Q. Antecedents of Network Capability and Their Effects on Innovation Performance: An Empirical Test of Hi-Tech Firms in China. Creat. Innov. Manag. 2014, 23, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenamor, J.; Parida, V.; Wincent, J. How Entrepreneurial SMEs Compete through Digital Platforms: The Roles of Digital Platform Capability, Network Capability and Ambidexterity. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 100, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, E.; Aknar, A.; Başar, Ö. Absorptive Capacity and Firm Performance: The Mediating Role of Strategic Agility. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 78, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wang, F.; Feng, C. The Double-Edged Sword of Networking: Complementary and Substitutive Effects of Networking Capability in China. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2018, 68, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, R.; Budiastuti, D.; Hamsal, M.; Kosasih, W. Networking Capability and Firm Performance: The Mediating Role of Market Orientation and Business Process Agility. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2020, 36, 1646–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, G.; Wensley, R. Assessing Advantage: A Framework for Diagnosing Competitive Superiority. J. Mark. 1988, 52, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahalad, C.K.; Hamel, G. The Core Competence of the Corporation. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1990, 68, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J.B.; Clark, D.N. Resource-Based Theory: Creating and Sustaining Competitive Advantage, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, E.; Palmatier, R.; Grewal, R. Effects of Customer and Innovation Asset Configuration Strategies on Firm Performance. J. Mark. Res. 2011, 48, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, K.; Pennings, J.M. Internal Capabilities, External Networks, and Performance: A Study on Technology-Based Ventures. Strateg. Manag. J. 2001, 22, 615–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Yang, W. An Empirical Study on the Relationship among Resources Integration in Alliance Portfolio, Ambidextrous Cooperation and Focal Firm Performance. Available online: https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-KXXG201802009.htm (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- Dosi, G.; Teece, D. Organizational Competencies and the Boundaries of the Firm; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bengesi, K.M.; Le Roux, I. The Influence of Dimensions of Networking Capability in Small and Medium Enterprise Performance. Int. J. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2014, 5, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Dickson, P.; Weaver, K. Institutional Readiness and Small to Medium-Sized Enterprise Alliance Formation. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2011, 49, 126–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welter, F.; Smallbone, D. Institutional Perspectives on Entrepreneurship. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2011, 49, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skountridaki, L. Barriers to Business Relations between Medical Tourism Facilitators and Medical Professionals. Tour. Manag. 2017, 59, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, E.Y.T.; Onggo, S. Service Collaboration between Healthcare Service Providers and Tourism Agencies. Adv. Cult. Tour. Hosp. Res. 2016, 12, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Z. The Influence of Corporate Networks on the Competitive Advantage of High Technology Enterprises in China: The Mediating Effects of Dynamic Capacities and Ambidextrous Combination. Int. J. Financ. Stud. 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratono, A.H. From Social Network to Firm Performance: The Mediating Effect of Trust, Selling Capability and Pricing Capability. Manag. Res. Rev. 2018, 41, 680–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, W.P.; Luo, X. Internationalization and the Performance of Born-Global SMEs: The Mediating Role of Social Networks. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2007, 38, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Beamish, P. The Internationalization and Performance of SMES. Strateg. Manag. J. 2001, 22, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Martín, O.; Chetty, S.; Bai, W. Foreign Market Entry Knowledge and International Performance: The Mediating Role of International Market Selection and Network Capability. J. World Bus. 2022, 57, 101266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaran, U.; Bougie, R. Research Methods for Business: A Skill-Building Approach, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Behrouzi, F.; Ma’aram, A. Identification and Ranking of Specific Balanced Scorecard Performance Measures for Hospitals: A Case Study of Private Hospitals in the Klang Valley Area, Malaysia. Int. J. Health Plann. Manag. 2019, 34, 1364–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostino, D.; Costantini, C. A Measurement Framework for Assessing the Digital Transformation of Cultural Institutions: The Italian Case. Meditari Account. Res. 2021, 30, 1141–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hilali, W.; Manouar, A. El Reaching Sustainability during a Digital Transformation: A PLS Approach. Int. J. Innov. Sci. 2020, 12, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loehlin, J.; Beaujean, A. Latent Variable Models: An Introduction to Factor, Path, and Structural Equation Analysis, 5th ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Manurung, A. Model Dan Estimasi Dalam Riset Manajemen Dan Keuangan; PT Adler Manurung Press: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2019; ISBN 978-979-3439-19-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Arcodia, C.; Kim, I. Critical Success Factors of Medical Tourism: The Case of South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppelletto, A.; Orlandi, L.B.; Rossignoli, C. Adopting a Digital Transformation Strategy to Enhance Business Network Commons Regeneration: An Explorative Case Study. TQM J. 2020, 32, 561–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, S.; Jones, P.; Kailer, N.; Weinmann, A.; Chaparro-Banegas, N.; Roig-Tierno, N. Digital Transformation: An Overview of the Current State of the Art of Research. SAGE Open 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, S.; Schiavone, F.; Pluzhnikova, A.; Invernizzi, A.C. Digital Transformation in Healthcare: Analyzing the Current State-of-Research. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 123, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, P.; Abadie, F.; Lupiañez, F.V.; Maghiros, I.; Mora, E.V.; Talaya, M.B.Z. Market Developments—Remote Patient Monitoring and Treatment, Telecare, Fitness/Wellness and MHealth; European Union: Luxembourg, 2013; ISBN 9789279257087. [Google Scholar]
- Manaf, N.H.A.; Hussin, H.; Kassim, P.N.J.; Alavi, R.; Dahari, Z. Medical Tourism Service Quality: Finally Some Empirical Findings. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2015, 26, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, S.; Guo, L.; Edvardsson, B. Role of Resource Integration in Adoption of Medical Tourism Service. Int. J. Qual. Serv. Sci. 2013, 5, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeh, E.; Garkaz, M. Interpretive Structural Modeling of Quality Factors in Both Medical and Hospitality Services in the Medical Tourism Industry. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2019, 36, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Hua, H. Research on the Tourism Resource Development from the Perspective of Network Capability—Taking Wuxi Huishan Ancient Town as an Example. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1820, 090022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vovk, V.; Beztelesna, L.; Pliashko, O. Identification of Factors for the Development of Medical Tourism in the World. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Tran, H.; Mai, P.; Amendah, E.R.; Kim, D. A Look at Collaborative Service Provision: Case for Cosmetic Surgery Medical Tourism at Korea for Chinese Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallmo, D.R.; Williams, C. Digital Transformation now!: Guiding the Successful Digitalization of Your Business Model; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-72844-5. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, M.; Boehme, P.; Mondritzki, T.; Ehlers, J.P.; Kavadias, S.; Truebel, H. Digital Transformation and Disruption of the Health Care Sector: Internet-Based Observational Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2018, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No | Hospital Class | Number of Hospitals | Sample | Subtotal | Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hospital Class A | 50 | 50 (200/374) | 26.7 | 27 |
| 2 | Hospital Class B | 324 | 324 (200/374) | 173.2 | 173 |
| Total | 374 | 200 | |||
| Hospital Performance | Definition | Ability to achieve hospital goals | ||
| Dimension | Code | Indicator | Scale | |
| Financial | F_1 | Increase in hospital income | Interval | |
| F_2 | Increased net profit/residual operating results of the hospital | Interval | ||
| F_3 | Hospital shows management improvement | Interval | ||
| Non- Financial | NF_1 | Increased patient satisfaction rate | Interval | |
| NF_2 | Decreased medical procedure error rate | Interval | ||
| NF_3 | Hospital reputation nationally | Interval | ||
| NF_4 | Regional Reputation of Hospital | Interval | ||
| NF_5 | Increased medical tourism patient visits | Interval | ||
| NF_6 | Hospital growth | Interval | ||
| Networking Capability | Definition | Ability to locate, manage, and leverage networks to create value | ||
| Dimension | Code | Indicator | Scale | |
| Looking for partners | MM_1 | Systems and mechanisms for identifying partners | Interval | |
| MM_2 | Systems and mechanisms for selecting partners | Interval | ||
| MM_3 | Systems and mechanisms to find partners under certain conditions | Interval | ||
| Manage network | MJ_1 | Relationship analysis with partners | Interval | |
| MJ_2 | Partnership relationship adjustment | Interval | ||
| MJ_3 | Integration of network activities into business operational processes | Interval | ||
| Take advantage of the network | MFJ_1 | Accurately receive help from partners | Interval | |
| MFJ_2 | Receive help from partners at the right time | Interval | ||
| MFJ_3 | Partners refer to third parties if they cannot provide direct assistance | Interval | ||
| MFJ_4 | Professional inter-collaboration with other hospitals | Interval | ||
| Resource Integration | Definition | The process of integrating resources to create value | ||
| Dimension | Code | Indicator | Scale | |
| Tangible | TN_1 | The hospital’s location is easily accessible | Interval | |
| TN_2 | Attractive hospital structures and designs | Interval | ||
| TN_3 | Medical equipment with cutting-edge technology is readily available. | Interval | ||
| Intangible | ITN_1 | In the view of patients, the hospital’s reputation is excellent. | Interval | |
| ITN_2 | Medical personnel who are skilled in their specialty are available. | Interval | ||
| ITN_3 | Availability of employees with good communication skills. | Interval | ||
| ITN_4 | The ability of the hospital to integrate resources to improve performance. | Interval | ||
| Digital Transformation | Definition | Using technology to improve performance and create value | ||
| Dimension | Code | Indicator | Scale | |
| Technology | T_1 | Complete adoption of digital technology | Interval | |
| T_2 | Use of digital technology to improve service activities | Interval | ||
| T_3 | Digital technology updates in accordance with the latest developments in the health sector | Interval | ||
| Non Technology | NT_1 | Staff support for changes according to digital transformation needs | Interval | |
| NT_2 | Patient involvement in service processes that use digital technology | Interval | ||
| NT_3 | Adjustment of business processes to the development of digital technology | Interval | ||
| Medical Tourism Ecosystem | Definition | Stakeholders involved in medical tourism | ||
| Code | Indicator | Scale | ||
| EWM_1 | The establishment of the Indonesia Health Tourism Board | Interval | ||
| EWM_2 | Government support in the advancement of medical tourism | Interval | ||
| EWM_3 | Support of tourism stakeholders in the medical tourism industry | Interval | ||
| EWM_4 | Support of medical stakeholders in the medical tourism industry | Interval | ||
| EWM_5 | Ecosystem benefits to stakeholders in the medical tourism industry | Interval | ||
| EWM_6 | The rules of the medical tourism ecosystem | Interval | ||
| Respondent Position | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| President Director/Hospital Director | 208 | 86.3% |
| Director of Medical Services/Deputy Director of Medical Services | 23 | 9.5% |
| Medical Support Director/Deputy Medical Support Director | 10 | 4.1% |
| Total | 241 | 100% |
| Hospital Performance | Dimension | Code | Indicator | Mean |
| Financial | F_1 | Increase in hospital income | 4 | |
| F_2 | Increased net profit/residual operating results Hospital | 3.93 | ||
| F_3 | Hospital shows management improvement | 4.06 | ||
| Means of financial dimension | 4 | |||
| Non- Financial | NF_1 | Increased patient satisfaction rate | 4.14 | |
| NF_2 | Decreased medical procedure error rate | 3.73 | ||
| NF_3 | Hospital reputation nationally | 4.03 | ||
| NF_4 | Regional Reputation of Hospital | 2.9 | ||
| NF_5 | Increased medical tourism patient visits | 4.13 | ||
| NF_6 | Hospital Growth | 4.17 | ||
| Means of non-financial dimension | 3.85 | |||
| Means of hospital performance | 3.9 | |||
| Networking Capability | Dimension | Code | Indicator | Mean |
| Looking for partners | MM_1 | Systems and mechanisms for identifying partners | 3.75 | |
| MM_2 | Systems and mechanisms for selecting partners | 3.78 | ||
| MM_3 | Systems and mechanisms to find partners under certain conditions | 3.79 | ||
| Means of looking for partners dimension | 3.77 | |||
| Manage network | MJ_1 | Relationship analysis with partners | 3.89 | |
| MJ_2 | Partnership relationship adjustment | 3.99 | ||
| MJ_3 | Integration of network activities into business operational processes | 3.92 | ||
| Means of management network dimension | 3.93 | |||
| Take advantage of the network | MFJ_1 | Accurately receive help from partners | 3.78 | |
| MFJ_2 | Receives help from partners at the right time | 3.81 | ||
| MFJ_3 | Partners refer to third parties if they cannot provide direct assistance | 3.89 | ||
| MFJ_4 | Professional inter-collaboration with other hospitals | 4.04 | ||
| Means of take advantage of the network dimension | 3.88 | |||
| Means of networking capability | 3.86 | |||
| Resource Integration | Dimension | Code | Indicator | Mean |
| Tangible | TN_1 | The hospital’s location is easily accessible | 4.57 | |
| TN_2 | Attractive hospital structures and designs | 4.04 | ||
| TN_3 | Medical equipment with cutting-edge technology is readily available. | 3.97 | ||
| Mean of tangible dimension | 4.19 | |||
| Intangible | ITN_1 | In the view of patients, the hospital’s reputation is excellent. | 4.20 | |
| ITN_2 | Medical personnel who are skilled in their specialty are available. | 4.38 | ||
| ITN_3 | Availability of employees with good communication skills. | 3.90 | ||
| ITN_4 | The ability of the hospital to integrate resources to improve performance. | 4.01 | ||
| Means of intangible dimension | 4.12 | |||
| Means of resources integration | 4.16 | |||
| Digital Transformation | Dimension | Code | Indicator | Mean |
| Technology | T_1 | Complete adoption of digital technology | 3.39 | |
| T_2 | Use of digital technology to improve service activities | 3.45 | ||
| T_3 | Digital technology updates in accordance with the latest developments in the health sector | 3.95 | ||
| Means of technology dimension | 3.6 | |||
| Non- Technology | NT_1 | Staff support for changes according to digital transformation needs | 4.1 | |
| NT_2 | Patient involvement in service processes that use digital technology | 3.78 | ||
| NT_3 | Adjustment of business processes to the development of digital technology | 4.03 | ||
| Means of non-technology dimension | 3.97 | |||
| Means of digital transformation | 3.78 | |||
| Medical Tourism Ecosystem | Code | Indicator | Mean | |
| EWM_1 | The establishment of the Indonesia Health Tourism Board | 4.12 | ||
| EWM_2 | Government support in the advancement of medical tourism | 3.83 | ||
| EWM_3 | Support of tourism stakeholders in the medical tourism industry | 3.81 | ||
| EWM_4 | Support of medical stakeholders in the medical tourism industry | 3.76 | ||
| EWM_5 | Ecosystem benefits to stakeholders in the medical tourism industry | 3.73 | ||
| EWM_6 | The rules of the medical tourism ecosystem | 3.04 | ||
| Means of medical tourism ecosystem | 3.71 | |||
| Indicators | Compute GoFI Value | Standard Value for Good Fit | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| p-value | 0.0 | >0.05 | Marginal value |
| RMSEA | 0.07 | <0.08 | Good Fit |
| NFI | 0.92 | >0.9 | Good Fit |
| NNFI | 0.93 | >0.9 | Good Fit |
| CFI | 0.94 | >0.9 | Good Fit |
| IFI | 0.94 | >0.9 | Good Fit |
| GFI | 0.93 | >0.9 | Good Fit |
| Variables | Manifest Variables | t-Value | Standardize Loading Factors | Composite Reliability (CR) | Variance Extracted (VE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital transformation | Technology | 15.85 | 0.83 | 0.8 | 0.67 |
| Non Technology | 15.78 | 0.83 | |||
| Resources integration | Tangible | 11.23 | 0.68 | 0.7 | 0.52 |
| Intangible | 12.84 | 0.75 | |||
| Networking capability | Looking for partners | *** | 0.76 | 0.83 | 0.62 |
| Manage network | 15.14 | 0.8 | |||
| Take advantage of the network | 15.13 | 0.8 | |||
| Hospital performance | Financial | *** | 1.3 | 0.78 | 0.65 |
| Non-financial | 7.4 | 1.43 | |||
| Medical Tourism ecosystem | EWM _1 | 13.11 | 0.75 | 0.91 | 0.64 |
| EWM _2 | 15.40 | 0.81 | |||
| EWM _3 | 17.30 | 0.83 | |||
| EWM _4 | 16.50 | 0.81 | |||
| EWM _5 | 16.35 | 0.81 | |||
| EWM _6 | 9.63 | 0.78 |
| No | Hypothesis | t-Value | Standardize Coefficient | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Digital transformation has a positive effect on hospital performance | 0.863 | 0.195 | Hypothesis rejected |
| H2 | Digital transformation has a positive effect on networking capabilities | 2.094 | 0.326 | Hypothesis accepted |
| H3 | Networking capabilities has a positive effect on hospital performance | 3.877 | 0.312 | Hypothesis accepted |
| H4 | Resources integration has a positive effect on hospital performance | 2.164 | 4.156 | Hypothesis accepted |
| H5 | Resources integration has a positive effect on networking capabilities | 6.045 | 1.018 | Hypothesis accepted |
| H6 | Medical tourism ecosystem strengthens the relationship between networking capability and hospital performance | 2.082 | 0.132 | Hypothesis accepted |
| H7 | Digital transformation has a positive effect on hospital performance mediated by networking capabilities | 1.693 | 0.102 | Hypothesis rejected |
| H8 | Resources integration has a positive effect on hospital performance mediated by networking capabilities | 2.988 | 0.318 | Hypothesis accepted |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ediansyah; Arief, M.; Hamsal, M.; Abdinagoro, S.B. Interplay between Networking Capability and Hospital Performance in Indonesia’s Medical Tourism Sector. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010374
Ediansyah, Arief M, Hamsal M, Abdinagoro SB. Interplay between Networking Capability and Hospital Performance in Indonesia’s Medical Tourism Sector. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(1):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010374
Chicago/Turabian StyleEdiansyah, Muhtosim Arief, Mohammad Hamsal, and Sri Bramantoro Abdinagoro. 2023. "Interplay between Networking Capability and Hospital Performance in Indonesia’s Medical Tourism Sector" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 1: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010374
APA StyleEdiansyah, Arief, M., Hamsal, M., & Abdinagoro, S. B. (2023). Interplay between Networking Capability and Hospital Performance in Indonesia’s Medical Tourism Sector. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(1), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010374





