Research on Coal Dust Wettability Identification Based on GA–BP Model
Abstract
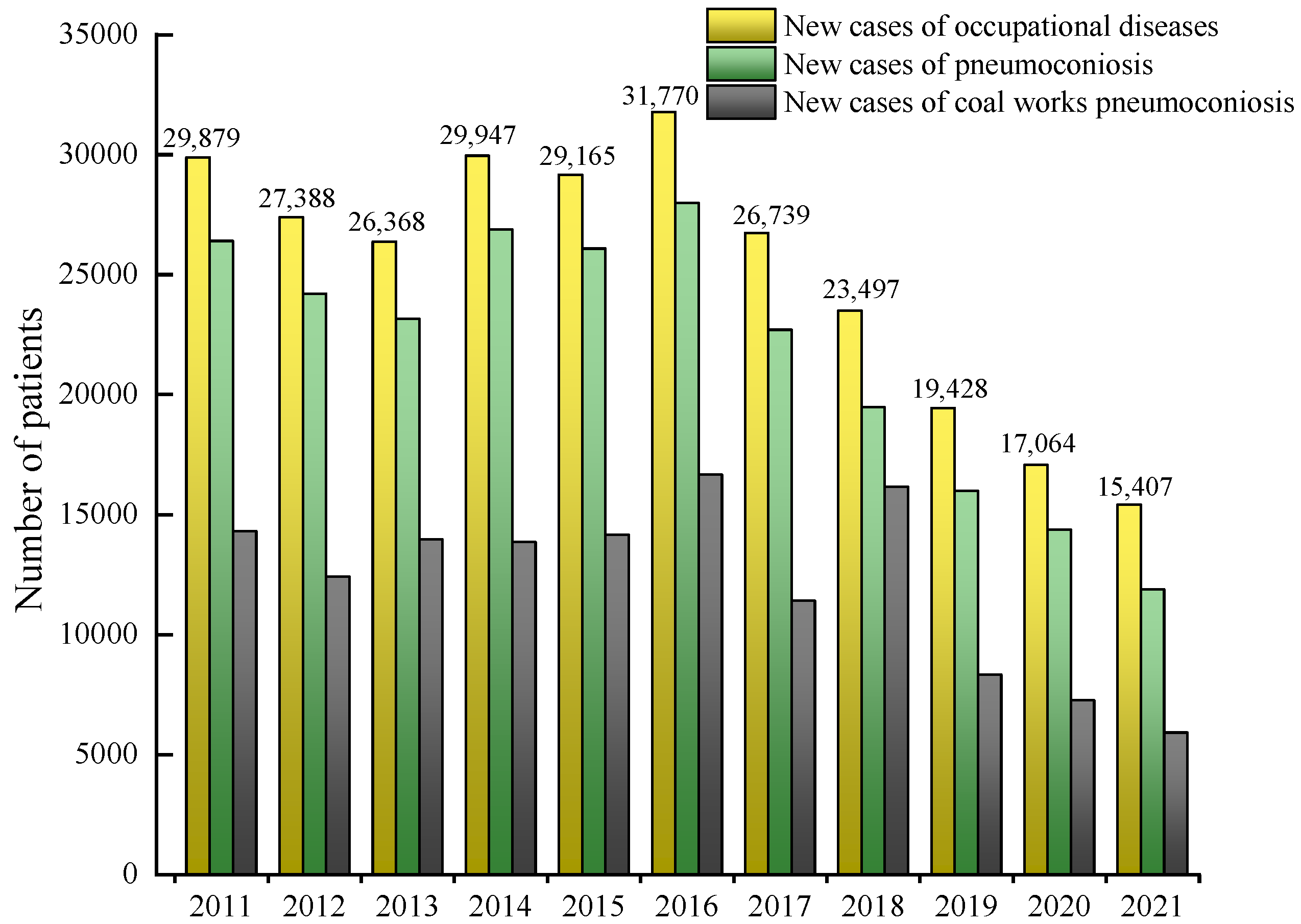
:1. Introduction
2. Influencing Factors and Data Acquisition of Coal Dust Wettability
2.1. Physical and Chemical Properties of Coal Dust Wettability
2.2. Methods for Measuring Wettability of Coal Dust
2.3. Data Acquisition
3. Coal Dust Wettability Prediction Model Based on GA–BP
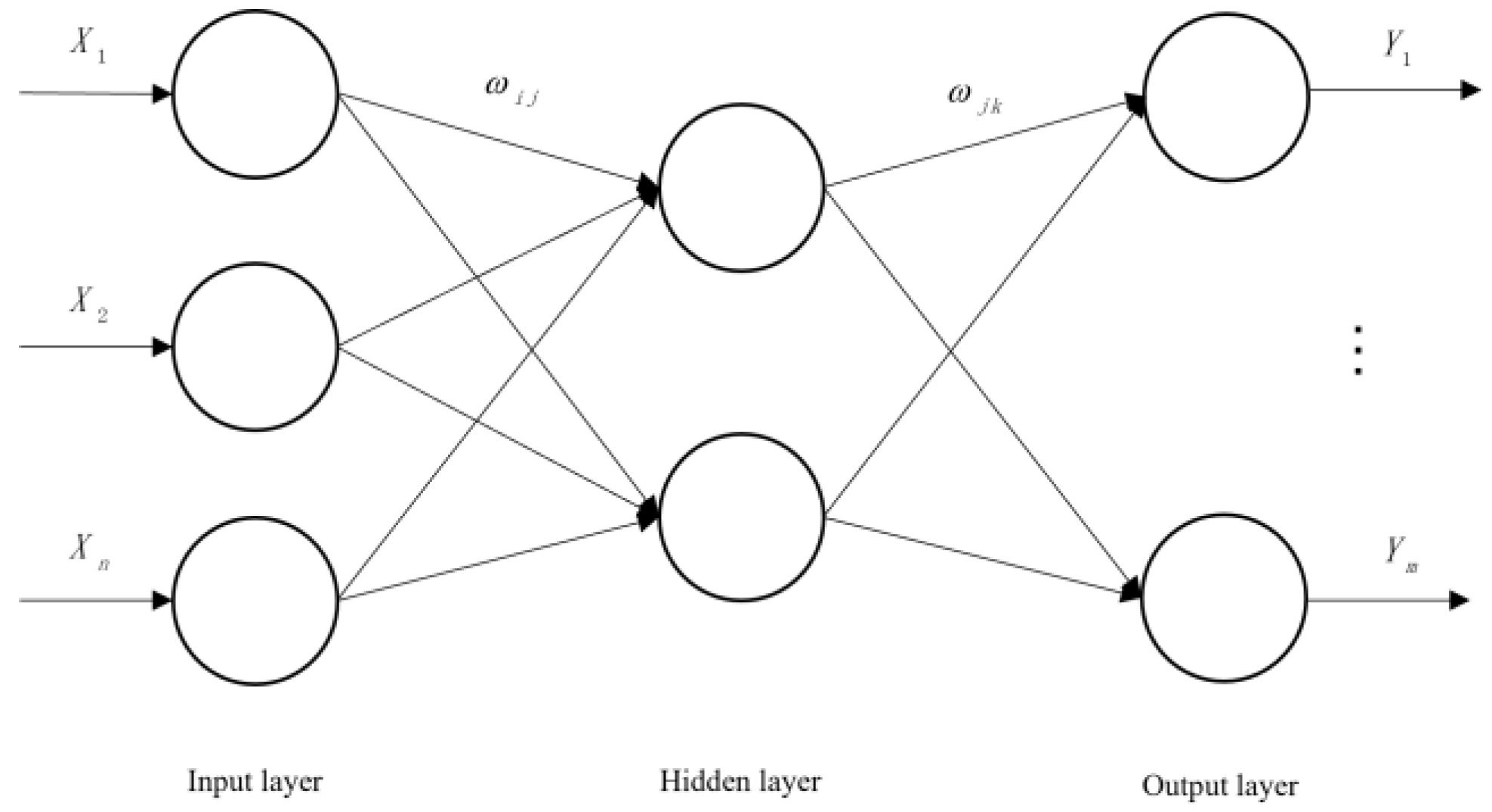
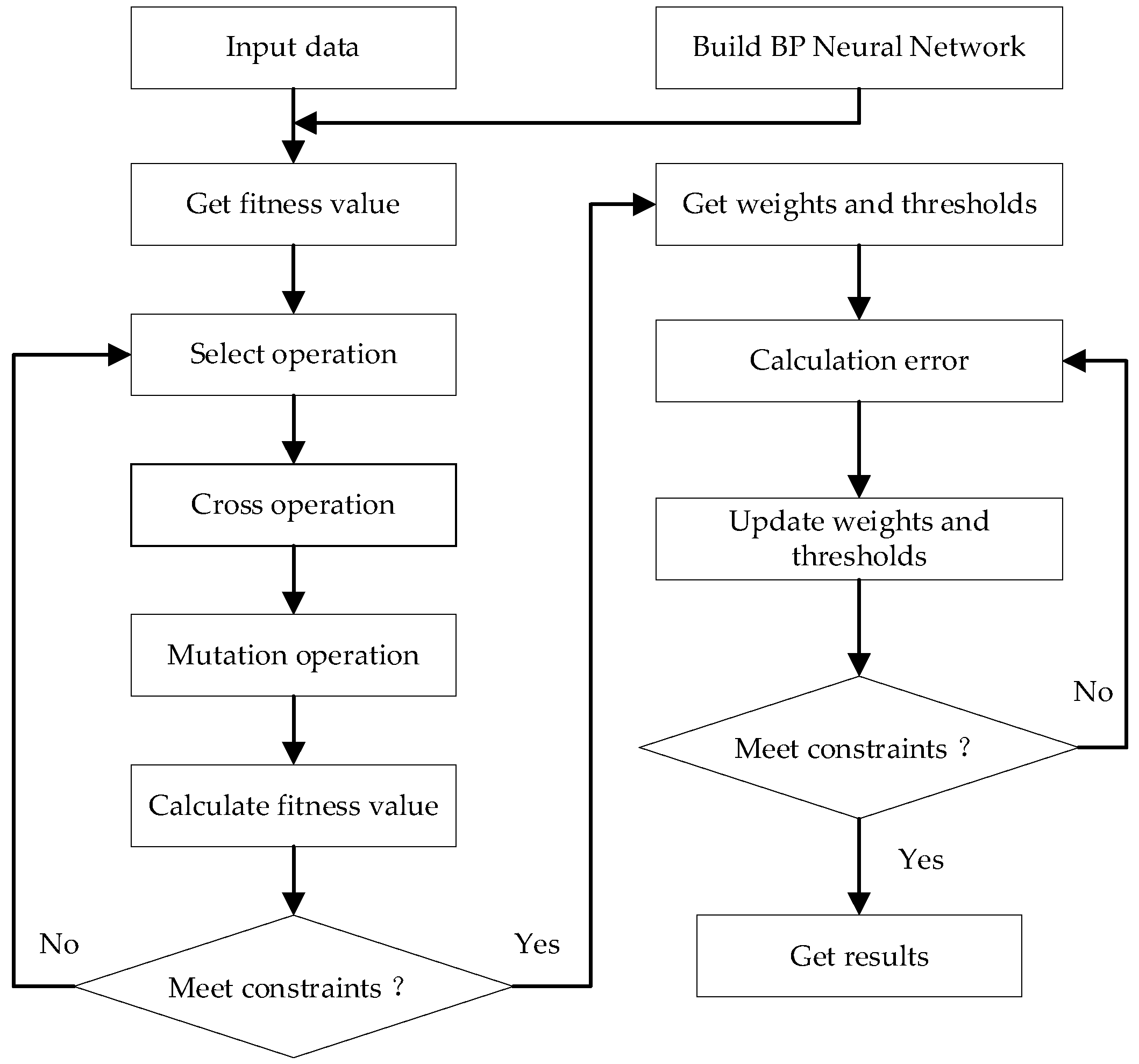
3.1. GA–BP Algorithm
3.2. Establishment of Model
3.2.1. GA–BP Hidden Layer Number Selection
3.2.2. Parameter Setting of GA–BP Model
4. Simulation Results and Performance Analysis
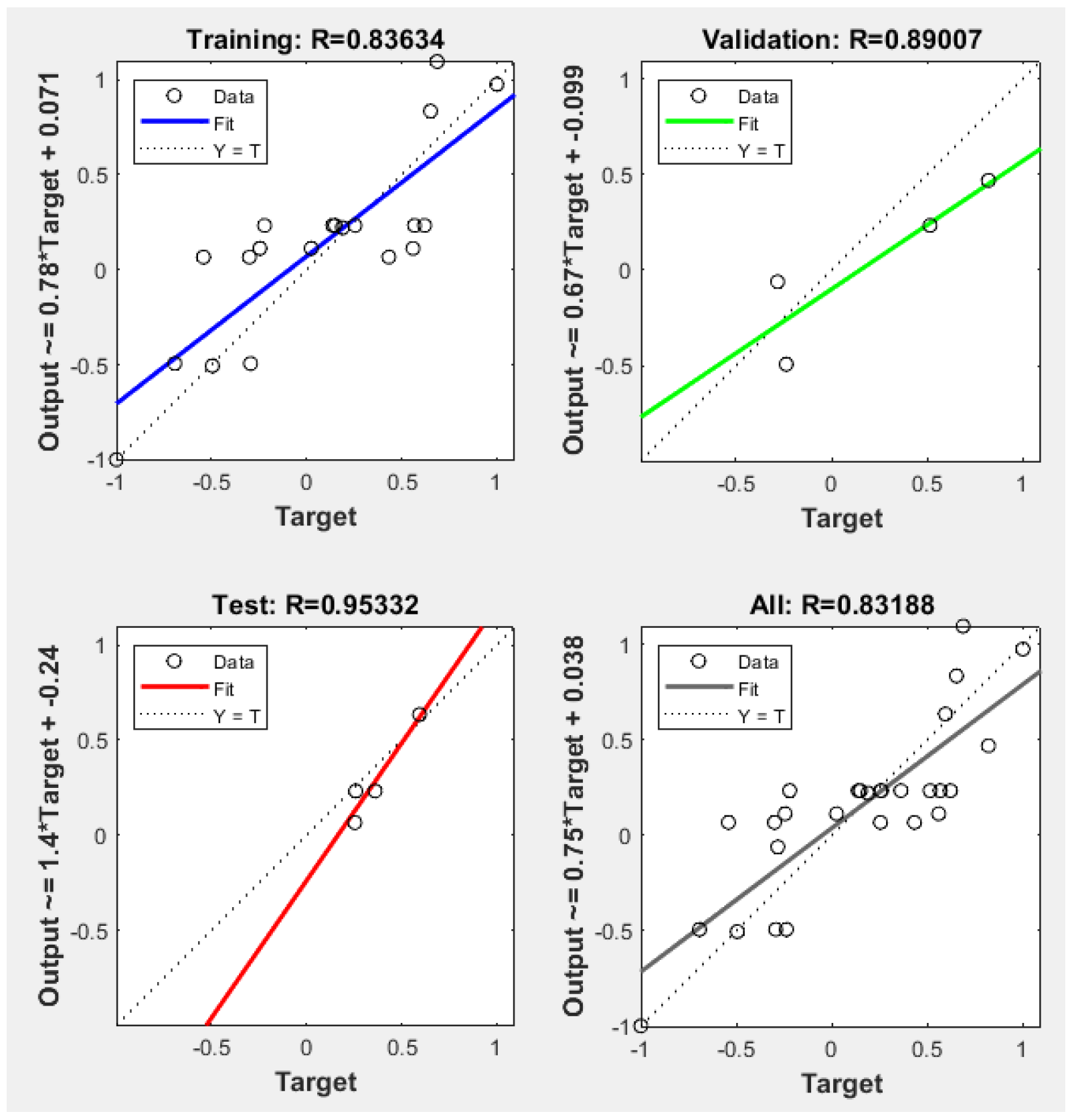
4.1. Simulation Results
4.2. Performance Analysis of Prediction Results of Different Algorithms
5. Conclusions and Discussion
6. Contributions and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sui, J.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Z. Status quo and development direction of coal mine dust hazard control technology in China. Min. Saf. Environ. Pro. 2019, 46, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.M.; Zhou, G.; Chen, L.J.; Wang, G.; Nie, W.; Zhang, Q.T. Research progress and prospect of dust control Theory and Technology in Coal mine in 20 years. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 48, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Ray, S.; Mohalik, N.; Mishra, D.; Mandal, S.; Pandey, J. Experimental and CFD Simulation Techniques for Coal Dust Explosibility: A Review. Min. Met. Explor. 2022, 39, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xie, S.; Huang, Q.; Wang, E.; Wang, S. Study on the performances of fluorescent tracers for the wetting area detection of coal seam water injection. Energy 2022, 263, 126091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Huang, T.; Yan, S.; Liu, X. Experimental study of the fracturing-wetting effect of VES fracturing fluid for the coal seam water injection. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 295, 111715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Jiang, W.; Si, L.; Xu, X.; Wen, Z. Experimental research of the surfactant effect on seepage law in coal seam water injection. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 103, 104612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Nie, W.; Liu, X.; Zhou, C.; Wei, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, Q.; Yin, S. Optimization of dust removal performance of ventilation system in tunnel constructed using shield tunneling machine. Build. Environ. 2020, 173, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Nie, W.; Liu, Q.; Peng, H.; Wei, W.; Cai, P. The development and application of a novel multi-radial-vortex-based ventilation system for dust removal in a fully mechanized tunnelling face. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 98, 103253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J. Study on air curtain cooperative spray dust removal in heading face based on swirl theory. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Han, F.; Yang, F.; Sheng, Y. Study and application on foam-water mist integrated dust control technology in fully mechanized excavation face. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 133, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Liang, W.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, S. A novel water-free cleaning robot for dust removal from distributed photovoltaic (PV) in water-scarce areas. Sol. Energy 2022, 241, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cheng, W.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Study on spray dust removal law for cleaner production at fully mechanized mining face with large mining height. Powder Technol. 2021, 389, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Gao, D.; Wang, S.; Sun, B. Dust removal effect of negatively-pressured spraying collector for advancing support in fully mechanized coal mining face: Numerical simulation and engineering application. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 95, 103149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Z.; Nie, W.; Cai, P.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X. Partially enclosed air curtain dust control technology to prevent pollution in a fully mechanized mining face. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, C.; Du, S.; Jin, W.; Fan, D. Dust dispersion law and high-pressure air curtain control technology of crossheading during the process of ore unloading. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2022, 230, 105179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Nie, W.; Hua, Y.; Peng, H.; Ma, H.; Yin, S.; Guo, L. Long-duct forced and short-duct exhaust ventilation system in tunnels: Formation and dust control analysis of pressure ventilation air curtain. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 132, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Cao, J.; Xiao, Q.; Yang, K.; Shi, L. Explosion propagation in a dust removal pipeline under dust collector explosion. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2022, 74, 104662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, R. Research on law and mechanism of dust explosion in bag type dust collector. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhou, G.; Yang, Y.; Duan, J.; Kong, Y.; Meng, Q. Design of pulse cleaning device for single-filter cartridge dust collector by multi-factor orthogonal method based numerical simulation. Powder Technol. 2021, 391, 494–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Li, B.; Ding, Y. Study on influence of coal dust wettability by chemical composition and structure parameters. Dalian Jiaotong Univ. 2016, 37, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F. Study on influence of coal composition upon hydrophilicity of coal dust. Min. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2014, 41, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Lin, B.; Li, Q. Effects of oxygen containing functional groups on coal dust wettability. Saf. Coal Mines 2014, 45, 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, G.; Qin, F.; Yan, B. The study on the water-wetting properties of coal from mines in China. J. Fuxin Min. Inst. 1997, 16, 666–669. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Xue, J.; Zhou, G. Study of coal dust wettability based on FTIR. J. China Coal Soc. 2014, 39, 2256–2262. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Xu, C.; Zhou, G. Evolution lawof carbon and oxygen groups on coal surface with increasing metamorphic grade and its effect on wettability. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2016, 44, 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Yang, J. Study of coal dust wettability based on multiple stepwise regression analysis. Saf. Coal Mines 2012, 43, 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Gosiewska, A.; Drelich, J.; Laskowski, J.S.; Pawlik, M. Mineral matter distribution on coal surface and its effect on coal wettability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 247, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Xue, J.; Zhou, G.; Nie, W.; Wen, J. Research on the relationship between bituminous coal dust wettability and inorganic mineral content. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2016, 45, 462–468. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, C.; Sun, C. Experimental study of coal dust wettability. J. China Coal Soc. 2011, 36, 442–446. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Yang, H.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, K. Study on the influence of new compound reagents on the functional groups and wettability of coal. Fuel 2021, 302, 121113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tan, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, R. Influence of particle diameter on the wettability of coal dust and the dust suppression efficiency via spraying. Process Saf. Environ. 2019, 132, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Gu, M.; Li, S.; Fang, X. Risk Assessment of Deep Coal and Gas Outbursts Based on IQPSO-SVM. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, J.M.K.; Bechtel, A.; Christanis, K. On the fundamental difference between coal rank and coal type. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2013, 118, 58–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Xin, H.; Ma, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. Effects of chemical properties of coal dust on its wettability. Powder Technol. 2017, 318, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Qin, B.; Huang, H. Research on the formation mechanism of magnetized water used to wet coal dust based on experiment and simulation investigation on its molecular structures. Powder Technol. 2021, 391, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Nie, B.; Wu, W.; Wang, R. Methane sorption behavior on tectonic coal under the influence of moisture. Fuel 2022, 327, 125150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Cen, K. Coal mill model considering heat transfer effect on mass equations with estimation of moisture. J. Process Control 2021, 104, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, B.; Liao, Q.; Wang, H.; Gao, R. Thermodynamic characteristics of methane adsorption about coking coal molecular with different sulfur components: Considering the influence of moisture contents. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 94, 104053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Xu, C.; Finkelman, R.; Engle, M.; Li, Q.; Peng, M.; He, L.; Huang, B.; Yang, Y. Coal elemental (compositional) data analysis with hierarchical clustering algorithms. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2022, 249, 103892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Feng, J.; Qin, Y.; Li, W. Prediction of elemental composition of coal using proximate analysis. Fuel 2017, 193, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, J.; Lin, Z.; Gong, S.; Xie, C.; Chang, L. Effects of experimental parameters on elemental analysis of coal by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2009, 41, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanger, R.; Xie, W.; Wall, T.; Lucas, J.; Mahoney, M. Dynamic Elemental Thermal Analysis: A technique for continuous measurement of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen chemistry of tar species evolved during coal pyrolysis. Fuel 2013, 103, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Han, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Experimental study on synergistic wetting of a coal dust with dust suppressant compounded with noncationic surfactants and its mechanism analysis. Powder Technol. 2019, 356, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, Z.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, S.; Song, C.; Zhu, F. Improvement of wettability of coal seams in water injection via co-deposition of polydopamine and polyacrylamide. Colloid Surf. A 2022, 636, 128112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Qin, B. Coal dust suppression based on water mediums: A review of technologies and influencing factors. Fuel 2021, 302, 121196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nie, W.; Yan, J.; Bao, Q.; Wang, H.; Jin, H.; Peng, H.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q. Preparation and performance study of a novel polymeric spraying dust suppression agent with enhanced wetting and coagulation properties for coal mine. Powder Technol. 2020, 364, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; He, X. Experimental investigation on the wettability of respirable coal dust based on infrared spectroscopy and contact angle analysis. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 3130–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Che, B.; Xia, S. Characteristics of self–ignition and smoldering of coal dust layer under inclination conditions. Process Saf. Environ. 2021, 156, 105475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zheng, H.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Sun, L.; Geng, J. Evaluation of deep coal and gas outburst based on RS-GA-BP. Nat. Hazards 2022, 06, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G. Research on coal dust wettability discrimination and difficult-to-wet coal dust control technology. Liaoning Technol. Univ. 2016, 15, 94–103. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, J. The investigation into the failure criteria of concrete based on the BP neural network. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 275, 108835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xie, N.; Wang, Y. An elite genetic algorithm for flexible job shop scheduling problem with extracted grey processing time. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 131, 109783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Optimal selection of control parameters for automatic machining based on BP neural network. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 7016–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhao, G.; Wu, B. Real-time prediction of the mechanical behavior of suction caisson during installation process using GA-BP neural network. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 116, 105475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Number | Data | Dust Explosion Accident Place | Death Toll |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 27 February 1950 | Yiluo Mine of Xinyu Company, Henan Province | 174 |
| 2 | 9 May 1960 | Laobaidong Mine of Datong Company, Shannxi Province | 684 |
| 3 | 28 November 1960 | Longshanmiao Mine of Pingdingshan Company, Henan Province | 187 |
| 4 | 24 December 1981 | Minmetals of Pingdingshan Mining Company, Henan Province | 133 |
| 5 | 21 April 1991 | Sanjiaohe Mine of Hongdong Company, Shanxi Province | 147 |
| 6 | 27 September 2000 | Muchonggou Mine of Shuicheng Company, Guizhou Province | 162 |
| 7 | 27 November 2005 | Dongfeng Mine of Qitaihe Company, Heilongjiang Province | 171 |
| Number | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32.74 | 13.73 | 12.42 | 41.11 | 76.39 | 5.25 | 13.52 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 347.20 | 48.69 |
| 2 | 18.14 | 11.59 | 0.69 | 69.58 | 88.38 | 3.80 | 3.46 | 3.13 | 1.24 | 0.52 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 298.60 | 81.46 |
| 3 | 6.34 | 34.82 | 4.24 | 54.60 | 78.83 | 5.28 | 13.57 | 0.95 | 1.37 | 0.80 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 434.40 | 78.50 |
| 4 | 19.62 | 13.05 | 2.35 | 64.98 | 89.41 | 3.28 | 5.37 | 1.01 | 0.93 | 0.44 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 296.00 | 73.77 |
| 5 | 17.32 | 29.50 | 2.86 | 50.32 | 81.35 | 5.13 | 11.37 | 1.27 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 402.40 | 63.87 |
| 6 | 20.58 | 7.12 | 3.76 | 68.54 | 86.23 | 3.62 | 7.19 | 1.78 | 1.18 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 269.40 | 82.68 |
| 7 | 6.75 | 31.27 | 8.46 | 53.52 | 77.39 | 5.11 | 15.78 | 0.67 | 1.05 | 0.79 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 300.80 | 50.87 |
| 8 | 34.71 | 21.91 | 3.58 | 39.80 | 72.03 | 7.73 | 17.63 | 1.68 | 0.93 | 1.29 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 358.40 | 48.31 |
| 9 | 16.93 | 12.55 | 1.63 | 68.89 | 88.01 | 4.36 | 3.65 | 2.85 | 1.13 | 0.59 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 253.00 | 93.66 |
| 10 | 24.75 | 25.73 | 7.42 | 42.10 | 75.56 | 5.08 | 16.91 | 0.93 | 1.52 | 0.81 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 236.80 | 67.54 |
| 11 | 2.47 | 39.71 | 4.08 | 53.74 | 81.84 | 5.38 | 10.56 | 0.54 | 1.68 | 0.79 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 356.60 | 76.64 |
| 12 | 23.45 | 24.51 | 3.87 | 48.17 | 84.75 | 4.25 | 8.70 | 1.10 | 1.20 | 0.60 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 148.40 | 65.24 |
| 13 | 6.49 | 35.83 | 4.99 | 53.69 | 79.96 | 5.02 | 13.28 | 0.66 | 1.08 | 0.75 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 134.40 | 63.45 |
| 14 | 20.08 | 18.48 | 8.35 | 53.09 | 77.02 | 5.73 | 14.37 | 0.81 | 2.07 | 0.89 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 218.40 | 59.47 |
| 15 | 13.99 | 35.71 | 2.67 | 47.63 | 81.63 | 5.54 | 9.75 | 1.13 | 1.95 | 0.81 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 176.70 | 67.70 |
| 16 | 64.38 | 17.47 | 5.62 | 12.53 | 44.55 | 5.07 | 47.22 | 1.83 | 1.33 | 1.37 | 0.79 | 0.03 | 134.60 | 23.57 |
| 17 | 28.33 | 28.12 | 10.37 | 33.18 | 71.15 | 4.83 | 21.73 | 1.24 | 1.05 | 0.81 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 148.40 | 39.64 |
| 18 | 37.41 | 17.87 | 6.51 | 38.22 | 78.32 | 6.62 | 12.81 | 1.22 | 1.03 | 1.01 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 305.60 | 50.28 |
| 19 | 15.88 | 21.56 | 2.58 | 59.98 | 81.73 | 4.16 | 10.08 | 2.42 | 1.61 | 0.61 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 221.80 | 79.45 |
| 20 | 10.52 | 32.64 | 4.27 | 52.57 | 81.28 | 5.38 | 11.36 | 0.74 | 1.24 | 0.79 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 353.60 | 71.26 |
| 21 | 15.39 | 28.55 | 15.74 | 40.32 | 73.34 | 3.04 | 21.08 | 1.05 | 1.49 | 0.50 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 420.80 | 50.02 |
| 22 | 40.60 | 20.04 | 9.47 | 29.89 | 66.87 | 7.59 | 20.75 | 1.84 | 0.95 | 1.36 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 136.80 | 34.33 |
| 23 | 16.04 | 10.13 | 3.98 | 69.85 | 82.67 | 4.23 | 9.52 | 2.04 | 1.54 | 0.61 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 277.00 | 87.34 |
| 24 | 24.24 | 30.42 | 4.39 | 40.95 | 77.54 | 5.26 | 15.32 | 0.69 | 1.19 | 0.81 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 157.00 | 41.28 |
| 25 | 14.63 | 16.58 | 8.56 | 60.23 | 80.09 | 4.46 | 13.63 | 0.95 | 1.87 | 0.67 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 356.20 | 78.21 |
| 26 | 8.42 | 38.06 | 2.57 | 50.95 | 84.93 | 4.92 | 6.83 | 2.09 | 1.23 | 0.70 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 375.80 | 80.35 |
| 27 | 25.85 | 18.58 | 12.52 | 43.05 | 72.14 | 4.55 | 21.42 | 0.83 | 1.06 | 0.76 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 241.20 | 48.10 |
| 28 | 30.76 | 12.34 | 1.57 | 55.33 | 89.75 | 4.77 | 3.27 | 0.82 | 1.39 | 0.64 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 252.60 | 67.53 |
| 29 | 27.32 | 17.64 | 9.09 | 45.95 | 88.32 | 4.94 | 4.67 | 0.94 | 1.13 | 0.67 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 216.80 | 76.04 |
| 30 | 32.96 | 18.29 | 5.83 | 42.92 | 78.78 | 4.86 | 13.35 | 1.28 | 0.73 | 0.74 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 188.60 | 60.56 |
| 31 | 8.44 | 33.52 | 5.36 | 52.68 | 79.13 | 4.91 | 14.21 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.74 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 155.20 | 62.46 |
| 32 | 34.06 | 19.25 | 6.68 | 40.00 | 78.95 | 5.96 | 12.94 | 1.65 | 1.50 | 0.91 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 364.40 | 50.87 |
| 33 | 28.37 | 26.74 | 2.84 | 42.05 | 80.85 | 5.37 | 10.46 | 2.04 | 1.28 | 0.80 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 249.60 | 81.03 |
| 34 | 17.87 | 20.52 | 17.77 | 43.84 | 72.80 | 5.14 | 18.68 | 1.75 | 1.63 | 0.85 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 306.60 | 53.60 |
| 35 | 28.39 | 20.32 | 10.56 | 40.73 | 68.37 | 5.02 | 23.58 | 1.77 | 1.26 | 0.88 | 0.26 | 0.01 | 345.80 | 49.40 |
| Layer | RRMSE |
|---|---|
| 3 | 0.016256 |
| 4 | 0.047823 |
| 5 | 0.28504 |
| 6 | 0.067797 |
| 7 | 0.26669 |
| 8 | 0.18253 |
| 9 | 0.1357 |
| 10 | 0.0.1968 |
| 11 | 0.12199 |
| 12 | 0.028462 |
| 13 | 0.134831 |
| 14 | 0.0884 |
| 15 | 0.034375 |
| Parameter Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Training goal minimum error (goal) | 0.00001 |
| Training times (epochs) | 1000 |
| Learning rate (lr) | 0.01 |
| Momentum factor (mc) | 0.01 |
| Minimum performance gradient (min_grad) | 10−6 |
| Maximum number of failures (max_fail) | 6 |
| Training iteration display frequency (show) | 25 |
| Activation function | Sigmoid |
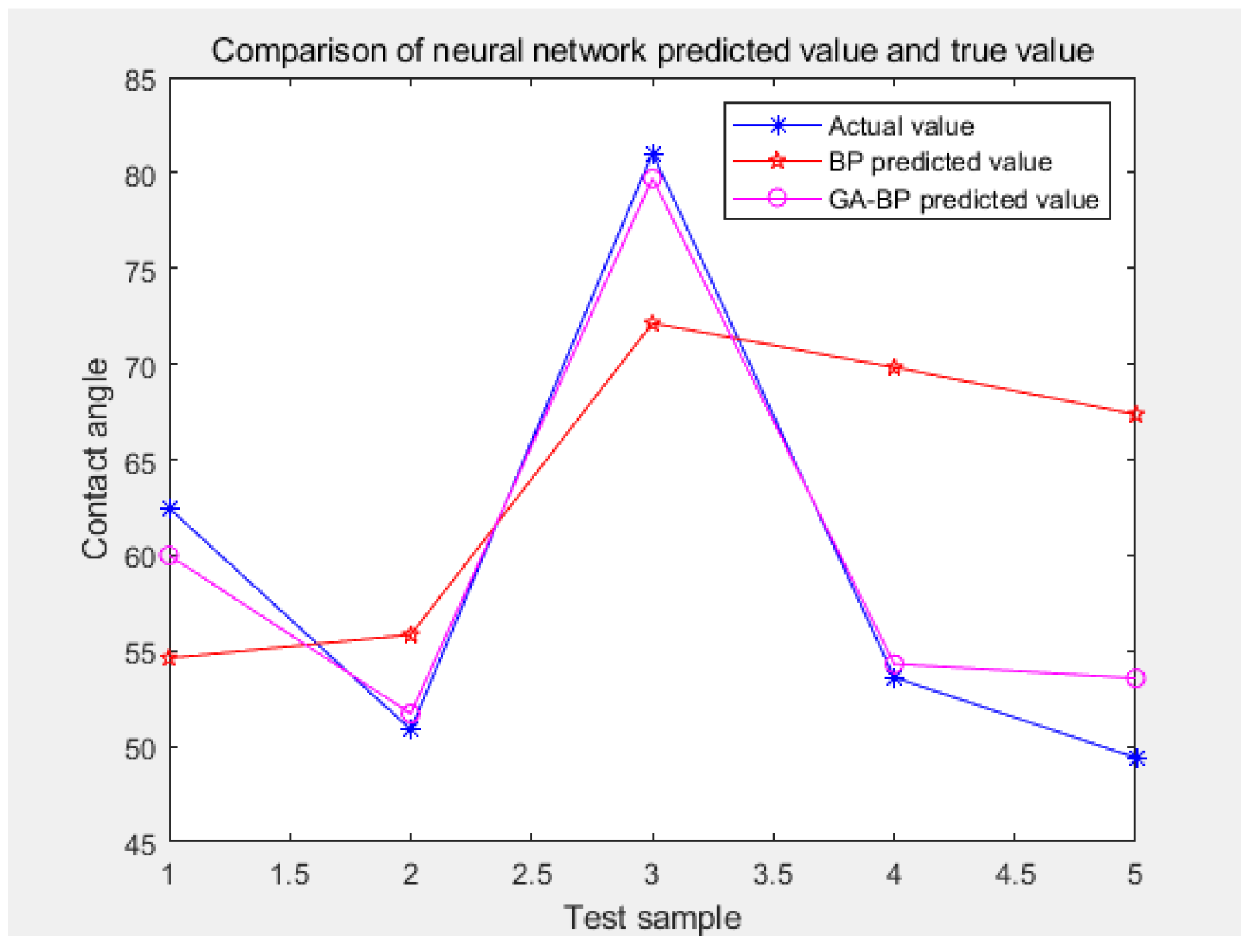
| Test Set | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact angle measurement | 62.462° | 50.87° | 81.031° | 53.6° | 49.4° |
| BP predicted value | 54.61974° | 55.83009° | 72.13396° | 69.82025° | 67.35999° |
| GA–BP predicted value | 59.9874° | 51.70715° | 79.70484° | 54.31024° | 53.56109° |
| Model | BP | ELM | PSO–ELM | GA–BP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE/% | 12.2549 | 8.4900 | 6.5839 | 2.2979 |
| MAE/% | 11.1759 | 7.3872 | 4.9410 | 1.9018 |
| MAPE/% | 0.1998 | 0.1188 | 0.0838 | 0.034 |
| Time/s | 0.886169 | 0.066717 | 3.090464 | 25.102379 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, H.; Shi, S.; Jiang, B.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, H. Research on Coal Dust Wettability Identification Based on GA–BP Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010624
Zheng H, Shi S, Jiang B, Zheng Y, Li S, Wang H. Research on Coal Dust Wettability Identification Based on GA–BP Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(1):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010624
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Haotian, Shulei Shi, Bingyou Jiang, Yuannan Zheng, Shanshan Li, and Haoyu Wang. 2023. "Research on Coal Dust Wettability Identification Based on GA–BP Model" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 1: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010624
APA StyleZheng, H., Shi, S., Jiang, B., Zheng, Y., Li, S., & Wang, H. (2023). Research on Coal Dust Wettability Identification Based on GA–BP Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(1), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010624








