Bacterial Community Characteristics Shaped by Artificial Environmental PM2.5 Control in Intensive Broiler Houses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Broiler House Structure and Daily Management
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.4. Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.5. Processing of Sequencing Data
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Variation in Environmental Control Variables and PM2.5 Concentrations
3.2. Variation in Airborne Bacterial Community Structure of PM2.5 throughout the Rearing Cycle
3.3. Effects of Environmental Control Variables on the Bacterial Community Structure in PM2.5 Samples
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Bacterial Community in Feces and PM2.5
3.5. Potential Pathogens in Airborne PM2.5
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, P.; Shen, D.; Tang, Q.; Huang, K.; Li, C. PM2.5 from a broiler breeding production system: The characteristics and microbial community analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Oh, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Min, K.H.; Hur, G.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kang, K.H.; Shim, J.J. Harmful impact of air pollution on severe acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Particulate matter is hazardous. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2018, 13, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arphorn, S.; Ishimaru, T.; Hara, K.; Mahasandana, S. Considering the effects of ambient particulate matter on the lung function of motorcycle taxi drivers in Bangkok, Thailand. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2018, 68, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skora, J.; Matusiak, K.; Wojewodzki, P.; Nowak, A.; Sulyok, M.; Ligocka, A.; Okrasa, M.; Hermann, J.; Gutarowska, B. Evaluation of Microbiological and Chemical Contaminants in Poultry Farms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.M.; Chimenti, M.S.; Farnell, M.; Tabler, T.; Bair, T.; Bray, J.L.; Nonnenmann, M.W. High throughput genomic sequencing of bioaerosols in broiler chicken production facilities. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Guo, M.; Liu, G.; Yu, G.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Chai, T. Detection and analysis of fine particulate matter and microbial aerosol in chicken houses in Shandong Province, China. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbal, C.; Gautam, S.; Trivedi, U. A review on recent progress in observations, and health effects of bioaerosols. Environ. Int. 2018, 118, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, T.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, H.; Yu, X.; Tang, J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; et al. PM2.5 in poultry houses synergizes with Pseudomonas aeruginosa to aggravate lung inflammation in mice through the NF-kappaB pathway. J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 21, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Gates, R.S.; Green, A.R.; Mitloehner, F.M.; Moore, P.A., Jr.; Wathes, C.M. Environmental impacts and sustainability of egg production systems. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Wang, W.; Ye, X.; Isa, A.M.; Khan, M.T.; Sa, R.; Liu, L.; Ma, T.; Zhang, H. Comparison of Bacterial Community Structure in PM2.5 within Broiler Houses under Different Rearing Systems in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodka, K.; Kozajda, A.; Buczynska, A.; Szadkowska-Stanczyk, I. The variability of bacterial aerosol in poultry houses depending on selected factors. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2012, 25, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Qin, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, T.; Dong, Y.; Chai, T. The composition of microbial aerosols, PM2.5, and PM10 in a duck house in Shandong province, China. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5913–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Li, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, H.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, T.; Zhang, X. Analyses of Aerosol Concentrations and Bacterial Community Structures for Closed Cage Broiler Houses at Different Broiler Growth Stages in Winter. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Li, M.; Tang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, T.; Zhang, X. Effect of Different Disinfectants on Bacterial Aerosol Diversity in Poultry Houses. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.Q. Research and demonstration to improve air quality for the U.S. animal feeding operations in the 21st century—A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungan, R.S. BOARD-INVITED REVIEW: Fate and transport of bioaerosols associated with livestock operations and manures. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 3693–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.T.; Nieuwland, M.G.; Aarnink, A.J.; Kemp, B.; Parmentier, H.K. Effects of 2 size classes of intratracheally administered airborne dust particles on primary and secondary specific antibody responses and body weight gain of broilers: A pilot study on the effects of naturally occurring dust. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, R.V.; Garcia, B.C.; Vital, P.G. Assessment of airborne bacteria in selected occupational environments in Quezon City, Philippines. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2017, 72, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, N.; Kirychuk, S.; Gilbert, Y.; Letourneau, V.; Veillette, M.; Singh, B.; Duchaine, C. Bacterial diversity characterization of bioaerosols from cage-housed and floor-housed poultry operations. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixao, A.C.; Ferreira, A.C.; Fontes, M.; Themudo, P.; Albuquerque, T.; Soares, M.C.; Fevereiro, M.; Martins, L.; de Sa, M.I.C. Detection of virulence-associated genes in pathogenic and commensal avian Escherichia coli isolates. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1646–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, L.L.; Bisgaard, M.; Son, N.T.; Trung, N.V.; An, H.M.; Dalsgaard, A. Enterococcus faecalis clones in poultry and in humans with urinary tract infections, Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, X.; Dai, X.; Dong, X.; Song, W. Endophytic bacterial diversity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots estimated by 16S rDNA sequence analysis. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namdari, S.; Nicholson, T.; Abboud, J.; Lazarus, M.; Ramsey, M.L.; Williams, G.; Parvizi, J. Comparative study of cultures and next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of shoulder prosthetic joint infections. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams Ischer, S.; Farnell, M.B.; Tabler, G.T.; Moreira, M.; O’Shaughnessy, P.T.; Nonnenmann, M.W. Evaluation of a sprinkler cooling system on inhalable dust and ammonia concentrations in broiler chicken production. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2017, 14, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Cao, G. Quick Estimation Model for the Concentration of Indoor Airborne Culturable Bacteria: An Application of Machine Learning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Shepherd, T.A.; Li, H.; Xin, H. Environmental assessment of three egg production systems--Part I: Monitoring system and indoor air quality. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Ferrari, S.; Guarino, M. Yearly emission factors of ammonia and particulate matter from three laying-hen housing systems. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2012, 52, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, B.; Mejdell, C.; Michel, V.; Lund, V.; Moe, R.O. Air Quality in Alternative Housing Systems may have an Impact on Laying Hen Welfare. Part II-Ammonia. Animals 2015, 5, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, T.; Schmucker, S.S.; Bessei, W.; Grashorn, M.; Stefanski, V. Impact of Housing Environment on the Immune System in Chickens: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wei, K.; Wu, Y.; Shen, F.; Chen, Q.; Li, M.; Yao, M. Enhancing bioaerosol sampling by Andersen impactors using mineral-oil-spread agar plate. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bowers, R.M.; Clements, N.; Emerson, J.B.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Hannigan, M.P.; Fierer, N. Seasonal variability in bacterial and fungal diversity of the near-surface atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12097–12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, B.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. A review on airborne microorganisms in particulate matters: Composition, characteristics and influence factors. Environ. Int. 2018, 113, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Mariman, R.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Boere, J.F.; Folkerts, G.; Cassee, F.R.; Pinelli, E. Microbiome composition of airborne particulate matter from livestock farms and their effect on innate immune receptors and cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, R.; Ali, Z.; Afzal, N.; Safdar, S.; Nasir, Z.A. Characterization of Bioaerosols in Controlled Environment Broiler Houses at Different Stages of Growth. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2020, 30, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smets, W.; Moretti, S.; Denys, S.; Lebeer, S. Airborne bacteria in the atmosphere: Presence, purpose, and potential. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 139, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Qiu, T.; Sun, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, M. Diversity of tetracycline- and erythromycin-resistant bacteria in aerosols and manures from four types of animal farms in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 24213–24222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Huang, K.; Liu, J.; Shen, D.; Dai, P.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Seasonal variations of microbial assemblage in fine particulate matter from a nursery pig house. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Jin, G.D.; Park, J.; Choi, Y.H.; Kang, S.K.; Chae, B.J.; Kim, E.B.; Choi, Y.J. Tracing of the fecal microbiota of commercial pigs at five growth stages from birth to shipment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alain, B.P.E.; Chae, J.P.; Balolong, M.P.; Bum Kim, H.; Kang, D.K. Assessment of fecal bacterial diversity among healthy piglets during the weaning transition. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 60, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubasova, T.; Davidova-Gerzova, L.; Babak, V.; Cejkova, D.; Montagne, L.; Le-Floc’h, N.; Rychlik, I. Effects of host genetics and environmental conditions on fecal microbiota composition of pigs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tsai, T.; Deng, F.; Wei, X.; Chai, J.; Knapp, J.; Apple, J.; Maxwell, C.V.; Lee, J.A.; Li, Y.; et al. Longitudinal investigation of the swine gut microbiome from birth to market reveals stage and growth performance associated bacteria. Microbiome 2019, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morotomi, M.; Nagai, F.; Watanabe, Y. Description of Christensenella minuta gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human faeces, which forms a distinct branch in the order Clostridiales, and proposal of Christensenellaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolka, B.; Czopowicz, M.; Chrobak-Chmiel, D.; Ledwon, A.; Szeleszczuk, P. Prevalence, antibiotic susceptibility and virulence factors of Enterococcus species in racing pigeons (Columba livia f. domestica). BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayappan, S.; Manneras-Holm, L.; Chaplin-Scott, A.; Belzer, C.; Herrema, H.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Duncan, S.H.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Groen, A.K.; Flint, H.J.; et al. Oral treatment with Eubacterium hallii improves insulin sensitivity in db/db mice. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2016, 2, 16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazhar, S.; Altermann, E.; Hill, C.; McAuliffe, O. Draft Genome Sequences of the Type Strains of Six Macrococcus Species. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e00344-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savin, K.W.; Zawadzki, J.; Auldist, M.J.; Wang, J.; Ram, D.; Rochfort, S.; Cocks, B.G. Faecalibacterium diversity in dairy cow milk. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miquel, S.; Martin, R.; Rossi, O.; Bermudez-Humaran, L.G.; Chatel, J.M.; Sokol, H.; Thomas, M.; Wells, J.M.; Langella, P. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and human intestinal health. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.C.; Chen, C.J.; Lin, T.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chien, Y.C. Characteristics of microbial aerosols released from chicken and swine feces. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal variations in the association between particulate matter and airborne bacteria based on the size-resolved respiratory tract deposition in concentrated layer feeding operations. Environ. Int. 2021, 150, 106413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain-Jones, N.M.; Packer, C.; Jacquot, M.; Blanchet, F.G.; Terio, K.; Craft, M.E. Endemic infection can shape exposure to novel pathogens: Pathogen co-occurrence networks in the Serengeti lions. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narciso-Schiavon, J.L.; Borgonovo, A.; Marques, P.C.; Tonon, D.; Bansho, E.T.O.; Maggi, D.C.; Dantas-Corrêa, E.B.; Schiavon, L.d.L. Enterococcus casseliflavus and Enterococcus gallinarum as causative agents of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Ann. Hepatol. 2015, 14, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangal, V.; Hoskisson, P.A. Evolution, epidemiology and diversity of Corynebacterium diphtheriae: New perspectives on an old foe. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 43, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noto, M.J.; Boyd, K.L.; Burns, W.J.; Varga, M.G.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Skaar, E.P. Toll-Like Receptor 9 Contributes to Defense against Acinetobacter baumannii Infection. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 4134–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.; Kolenda, R.; Khan, M.M.; Weinreich, J.; Li, G.; Wieler, L.H.; Tedin, K.; Roggenbuck, D.; Schierack, P. Novel Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Genes Responsible for Adhesion to Chicken and Human Cell Lines. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01068-01020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Woo, C.; Yamamoto, N.; Choi, H.-L. Variations in abundance, diversity and community composition of airborne fungi in swine houses across seasons. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

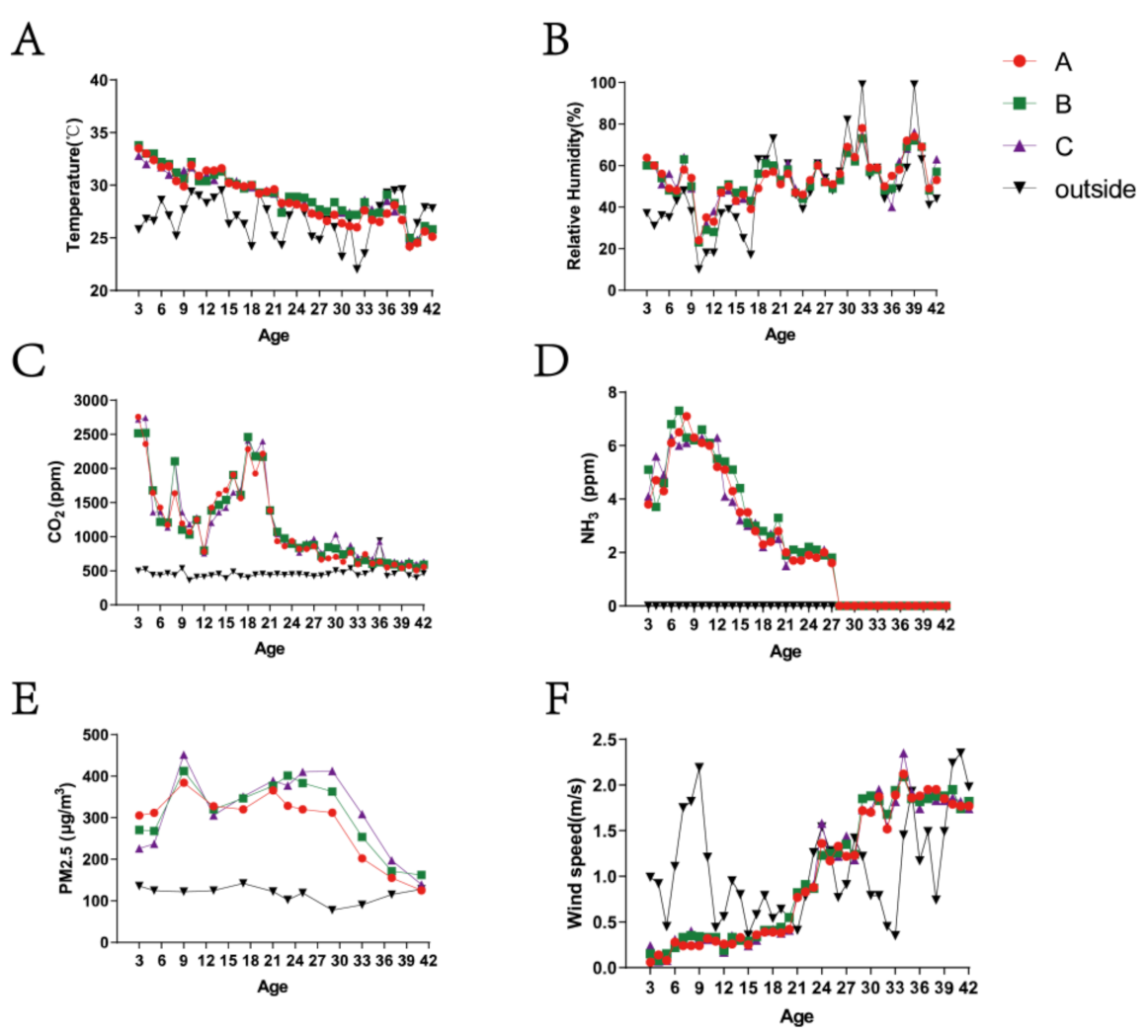


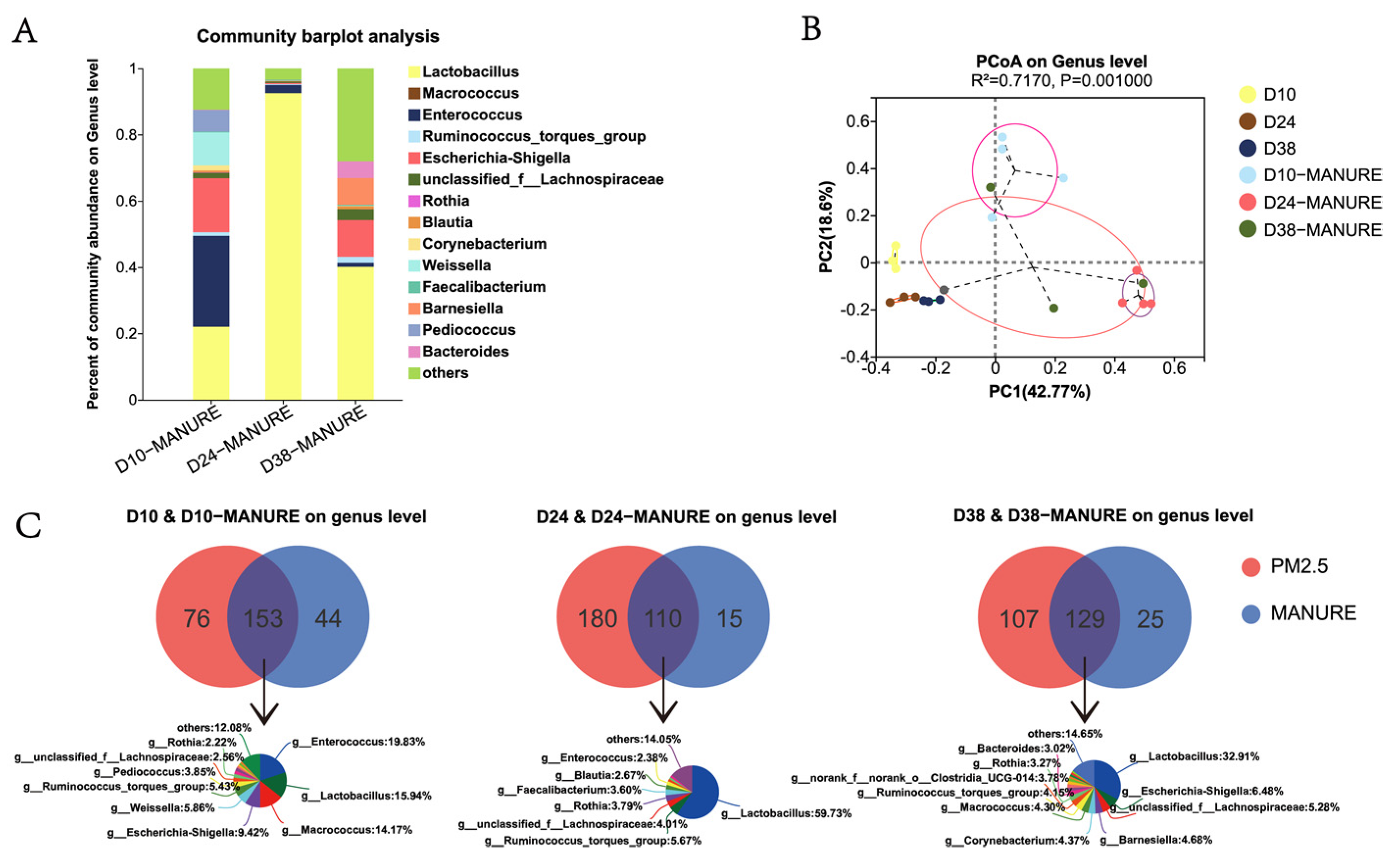
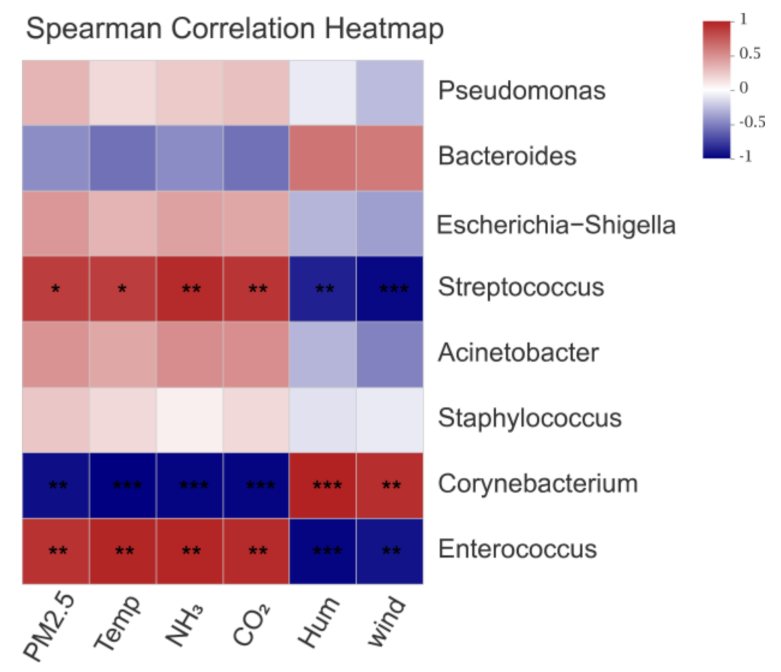
| PM2.5 | Temperature | Humidity | NH3 | CO2 | Wind | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao | R2 | 0.0048 | 0.1759 | 0.0080 | 0.1078 | 0.0960 | 0.0964 |
| p-value | 0.8595 | 0.2611 | 0.8190 | 0.3882 | 0.4173 | 0.4161 | |
| Shannon | R2 | 0.1105 | 0.4878 | 0.2299 | 0.3592 | 0.4019 | 0.3729 |
| p-value | 0.3821 | 0.0364 * | 0.1916 | 0.0881 | 0.0667 | 0.0807 |
| D10 | D24 | D38 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterococcus | 9.56 ± 1.94 a | 2.17 ± 0.11 b | 1.02 ± 0.08 b | 0.003 |
| Corynebacterium | 0.67 ± 0.27 b | 0.87 ± 0.02 b | 9.94 ± 2.56 a | 0.007 |
| Staphylococcus | 1.23 ± 0.01 | 1.51 ± 0.14 | 1.00 ± 0.28 | 0.221 |
| Streptococcus | 2.30 ± 0.79 a | 0.34 ± 0.10 b | 0.31 ± 0.07 b | 0.035 |
| Acinetobacter | 1.60 ± 0.62 | 0.82 ± 0.31 | 0.41 ± 0.05 | 0.188 |
| Escherichia-Shigella | 0.18 ± 0.04 a | 0.26 ± 0.02 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 b | 0.007 |
| Bacteroides | - b | 0.30 ± 0.10 a | 0.14 ± 0.06 a | 0.052 |
| Pseudomonas | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0 | 0.208 |
| Total | 15.68 ± 0.68 a | 6.37 ± 0.49 b | 12.92 ± 2.76 a | 0.019 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Dang, G.; Khan, I.; Ye, X.; Liu, L.; Zhong, R.; Chen, L.; Ma, T.; Zhang, H. Bacterial Community Characteristics Shaped by Artificial Environmental PM2.5 Control in Intensive Broiler Houses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010723
Wang W, Dang G, Khan I, Ye X, Liu L, Zhong R, Chen L, Ma T, Zhang H. Bacterial Community Characteristics Shaped by Artificial Environmental PM2.5 Control in Intensive Broiler Houses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(1):723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010723
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenxing, Guoqi Dang, Imran Khan, Xiaobin Ye, Lei Liu, Ruqing Zhong, Liang Chen, Teng Ma, and Hongfu Zhang. 2023. "Bacterial Community Characteristics Shaped by Artificial Environmental PM2.5 Control in Intensive Broiler Houses" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 1: 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010723
APA StyleWang, W., Dang, G., Khan, I., Ye, X., Liu, L., Zhong, R., Chen, L., Ma, T., & Zhang, H. (2023). Bacterial Community Characteristics Shaped by Artificial Environmental PM2.5 Control in Intensive Broiler Houses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(1), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010723








