Water Quality Evaluation and Pollution Source Apportionment of Surface Water in a Major City in Southeast China Using Multi-Statistical Analyses and Machine Learning Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Preparation
2.3. Water Quality Index
2.4. Random Forests
2.5. Positive Matrix Factorisation
2.6. Contribution of Potential Pollution Sources to the Variation in WQI Values
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Water Quality Characteristics Based on Individual Parameters
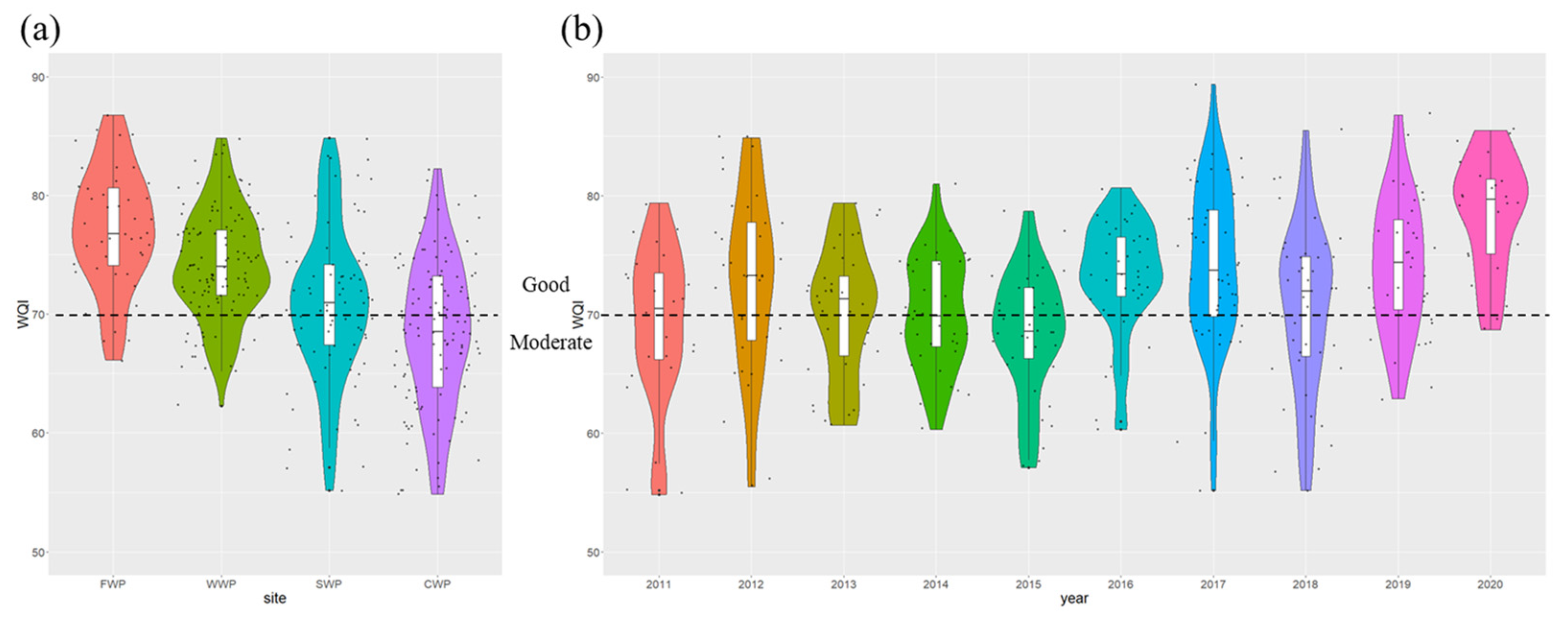
3.2. Water Quality Assessment Based on the WQI
3.3. Selection of Key Water Quality Parameters
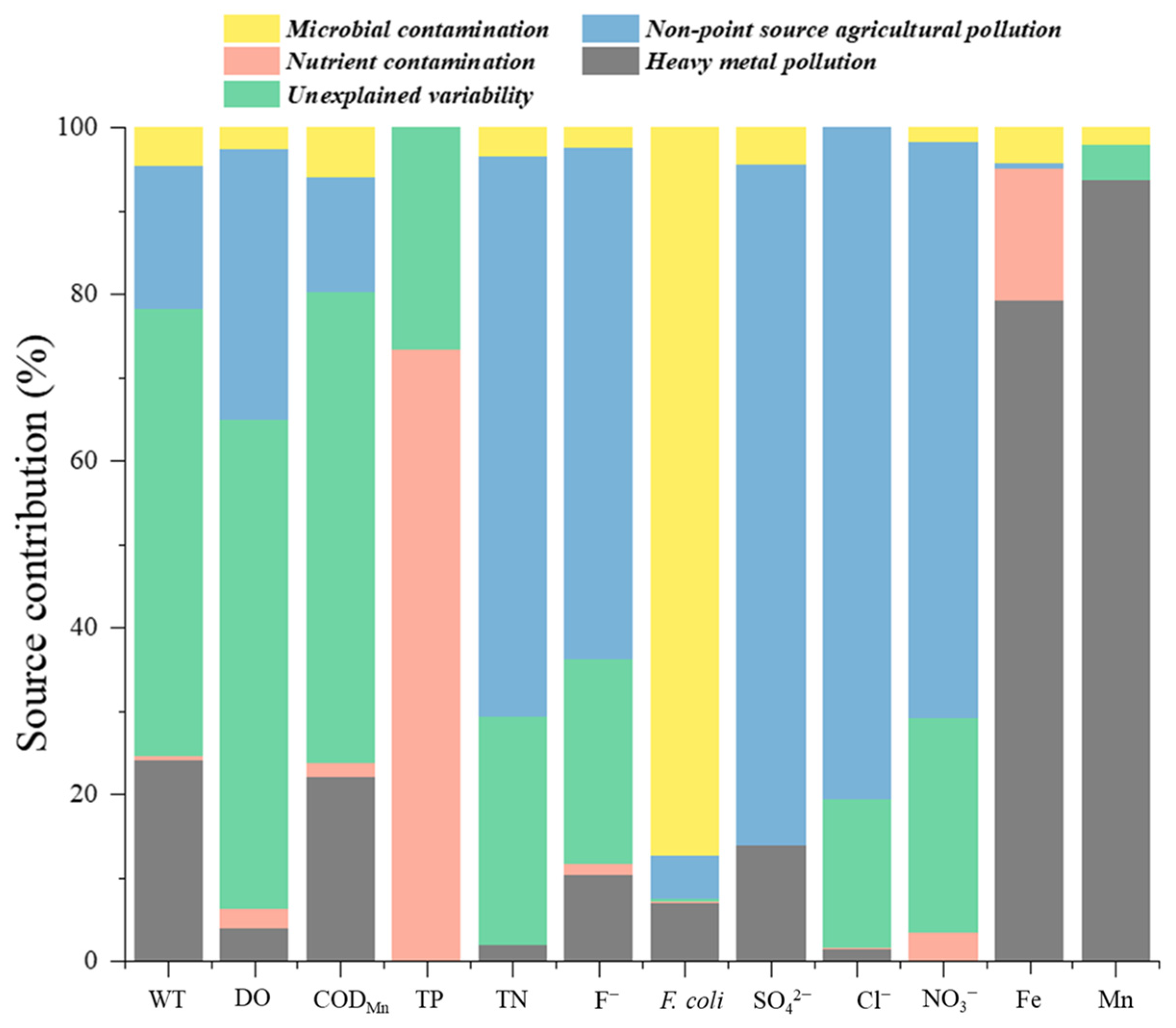
3.4. Pollution Source Apportionment Using the PMF Model
3.5. Contribution of Pollution Sources to Variation of WQI Value
4. Discussion
4.1. Quantitative Assessment of the Impact of Pollution Sources on Water Quality
4.2. Advantages and Innovation of RFs in the Construction of the WQImin Model
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
References
- Niu, A.P.; Song, L.Y.; Xiong, Y.H.; Lu, C.J.; Junaid, M.; Pei, D.S. Impact of water quality on the microbial diversity in the surface water along the Three Gorge Reservoir (TGR), China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 181, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Chen, Y.S.; Liu, H.; Xia, W.T.; Lu, Y.; Gang, D.D.; Lin, L.S. A holistic assessment of water quality condition and spatiotemporal patterns in impounded lakes along the eastern route of China's South-to-North water diversion project. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nong, X.Z.; Shao, D.G.; Zhong, H.; Liang, J.K. Evaluation of water quality in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China using the water quality index (WQI) method. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, K.; Dadheech, N.; Kumar, P.; Khare, M. Regression-based flexible models for photochemical air pollutants in the national capital territory of megacity Delhi. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; Dong, Y.C.; Kong, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, H.B.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.P. Insights into the long-term pollution trends and sources contributions in Lake Taihu, China using multi-statistic analyses models. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodell, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Wiese, D.N.; Reager, J.T.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Landerer, F.W.; Lo, M.H. Emerging trends in global freshwater availability. Nature 2018, 557, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillen, C. Water and the death of ambition in global health, c.1970–1990. Hist. Cienc. Saude-Manguinhos 2020, 27, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Q.Y.; Yu, M.X.; Hu, B.; Wang, Z.G.; Yu, Z.Q. Analysis and assessment of the nutrients, biochemical indexes and heavy metals in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, from 2008 to 2013. Water Res. 2016, 92, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, T.; Sadiq, R.; Mazumder, A. Adaptation and evaluation of the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Water Quality Index (CCME WQI) for use as an effective tool to characterize drinking source water quality. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3544–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.S.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Cai, Y.J.; Deng, J.C. Assessing river water quality using water quality index in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Berndtsson, R.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Adamowski, J.F.; Abyaneh, M.R. A critical review on the application of the National Sanitation Foundation Water Quality Index. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nong, X.Z.; Shao, D.G.; Xiao, Y.; Zhong, H. Spatio-Temporal Characterization Analysis and Water Quality Assessment of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocer, M.; Sevgili, H. Parameters selection for water quality index in the assessment of the environmental impacts of land-based trout farms. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, H.Y.; Chuah, C.J.; Tan, M.L.; Yong, E.L.; Snyder, S.A. A framework for assessing the adequacy of Water Quality Index—Quantifying parameter sensitivity and uncertainties in missing values distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesce, S.F.; Wunderlin, D.A. Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Cordoba City (Argentina) on Suquia River. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2915–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Y.; Chen, H.X.; Zhou, C.L.; Huang, Y.C.; Qi, X.Y.; Shen, R.Q.; Liu, F.R.; Zuo, M.; Zou, X.Y.; Wang, J.F.; et al. Comparative analysis of surface water quality prediction performance and identification of key water parameters using different machine learning models based on big data. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.F.; Ma, X. Hybrid decision tree-based machine learning models for short-term water quality prediction. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roguet, A.; Eren, A.M.; Newton, R.J.; McLellan, S.L. Fecal source identification using random forest. Microbiome 2018, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.W.; Li, W.Y.; Chen, X. Identification the source of fecal contamination for geographically unassociated samples with a statistical classification model based on support vector machine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, S.Q.; Li, H.F.; Fu, K.; Xu, Y. Groundwater pollution source identification and apportionment using PMF and PCA-APCA-MLR receptor models in a typical mixed land-use area in Southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive Matrix Factorization—A Nonnegative Factor Model with Optimal Utilization of Error-Estimates of Data Values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.P.; Mei, K.; Liu, X.M.; Wu, L.S.; Zhang, M.H.; Xu, J.M.; Wang, F. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of water pollution in different administrative zones of Wen-Rui-Tang (WRT) river watershed, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5341–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, I.; Sajjad, R.U.; Paule-Mercado, M.C.; Memon, S.A.; Lee, B.Y.; Sukhbaatar, C.; Lee, C.H. Comparison of two receptor models PCA-MLR and PMF for source identification and apportionment of pollution carried by runoff from catchment and sub-watershed areas with mixed land cover in South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.; Reddi, L. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; Zhang, C.; Qu, L.Y.; Song, Q.J.; Ji, X.L.; Mei, K.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.H. A comprehensive analysis and source apportionment of metals in riverine sediments of a rural-urban watershed. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 121230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S.Y.; Kao, S.J. Climate-Dependent Sediment Composition and Transport of Mountainous Rivers in Tectonically Stable, Subtropical East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.S.; Lai, X.J.; Li, K.Y. Water quality assessment of rivers in Lake Chaohu Basin (China) using water quality index. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random Forests for land cover classification. Pattern. Recogn. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, C.; Boulesteix, A.L.; Kneib, T.; Augustin, T.; Zeileis, A. Conditional variable importance for random forests. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parkhurst, D.F.; Brenner, K.P.; Dufour, A.P.; Wymer, L.J. Indicator bacteria at five swimming beaches—Analysis using random forests. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindal, S.; Singh, C.K. Predicting groundwater arsenic contamination: Regions at risk in highest populated state of India. Water Res. 2019, 159, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.W.; Wang, F.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.L. Variability of Phosphorus Concentration in Large, Shallow and Eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Water Environ. Res. 2008, 80, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milojkovic, J.V.; Popovic-Djordjevic, J.B.; Pezo, L.L.; Brceski, I.D.; Kostic, A.Z.; Milosevic, V.D.; Stojanovic, M.D. Applying multi-criteria analysis for preliminary assessment of the properties of alginate immobilized Myriophyllum spicatum in lake water samples. Water Res. 2018, 141, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotti, C.; Rotiroti, M.; Fumagalli, L.; Stefania, G.A.; Canonaco, F.; Stefenelli, G.; Prevot, A.; Leoni, B.; Bonomi, T. Groundwater and surface water quality characterization through positive matrix factorization combined with GIS approach. Water Res. 2019, 159, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarabadi, A.R.; Raudonyte-Svirbutaviciene, E.; Toosi, A.S.; Bakhtiari, A.R. Positive matrix factorization receptor model and dynamics in fingerprinting of potentially toxic metals in coastal ecosystem sediments at a large scale (Persian Gulf, Iran). Water Res. 2021, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.S.; Xu, J.; Tian, Y.Z.; Shi, G.L.; Feng, Y.C. Potential source contributions and risk assessment of PAHs in sediments from Taihu Lake, China: Comparison of three receptor models. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3065–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variables | Abbreviation | Units | Testing Base |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | pH | GB6920-1986 | |
| Water temperature | WT | °C | GB/T13195-1991 |
| Dissolved oxygen | DO | mg/L | HJ506-2009 |
| Total nitrogen | TN | mg/L | HJ636-2012 |
| Ammonia | NH3-N | mg/L | HJ665-2013 |
| Nitrate | NO3-N | mg/L | HJ/T84-2001 |
| Total phosphorus | TP | mg/L | GB/T11893-1989 |
| Permanganate index | CODMn | mg/L | GB 11892-1989 |
| Chloride | Cl− | mg/L | HJ/T84-2001 |
| Sulphate | SO42− | mg/L | HJ/T84-2001 |
| Iron | Fe | mg/L | HJ700-2014 |
| Manganese | Mn | mg/L | HJ700-2014 |
| Fecal coliform | F. coli | colonies/L | GB/T5750.12-2006 |
| Fluoride | F- | mg/L | HJ/T84-2001 |
| WQI value | 91–100 | 71–90 | 51–70 | 26–50 | 0–25 |
| Water quality | Excellent | Good | Moderate | Poor | Very poor |
| Parameters | Feature Importance | R2 | MSE | MAE | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | 0.35 | — | — | — | — |
| Mn + Fe | 0.58 | 0.73 | 20.01 | 3.66 | 5.09 |
| Mn + Fe + F. coli | 0.76 | 0.84 | 11.26 | 2.76 | 3.88 |
| Mn + Fe + F. coli + DO | 0.84 | 0.93 | 2.99 | 1.41 | 1.98 |
| Mn + Fe + F. coli + DO + TN | 0.88 | 0.96 | 1.77 | 1.06 | 1.47 |
| All water quality parameters | 1 | 0.97 | 1.60 | .0.95 | 1.35 |
| Pollution Sources | Microbial Contamination | Non-Point Source Agricultural Pollution | Unexplained Variability | Nutrient Contamination | Heavy Metal Pollution | Model Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contribution (%) | 18.15 | 9.64 | 10.95 | 6.73 | 53.18 | 1.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, L. Water Quality Evaluation and Pollution Source Apportionment of Surface Water in a Major City in Southeast China Using Multi-Statistical Analyses and Machine Learning Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010881
Zhou Y, Wang X, Li W, Zhou S, Jiang L. Water Quality Evaluation and Pollution Source Apportionment of Surface Water in a Major City in Southeast China Using Multi-Statistical Analyses and Machine Learning Models. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(1):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010881
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yu, Xinmin Wang, Weiying Li, Shuyun Zhou, and Laizhu Jiang. 2023. "Water Quality Evaluation and Pollution Source Apportionment of Surface Water in a Major City in Southeast China Using Multi-Statistical Analyses and Machine Learning Models" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 1: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010881
APA StyleZhou, Y., Wang, X., Li, W., Zhou, S., & Jiang, L. (2023). Water Quality Evaluation and Pollution Source Apportionment of Surface Water in a Major City in Southeast China Using Multi-Statistical Analyses and Machine Learning Models. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(1), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010881









