Energy Logistic Regression and Survival Model: Case Study of Russian Exports
Abstract
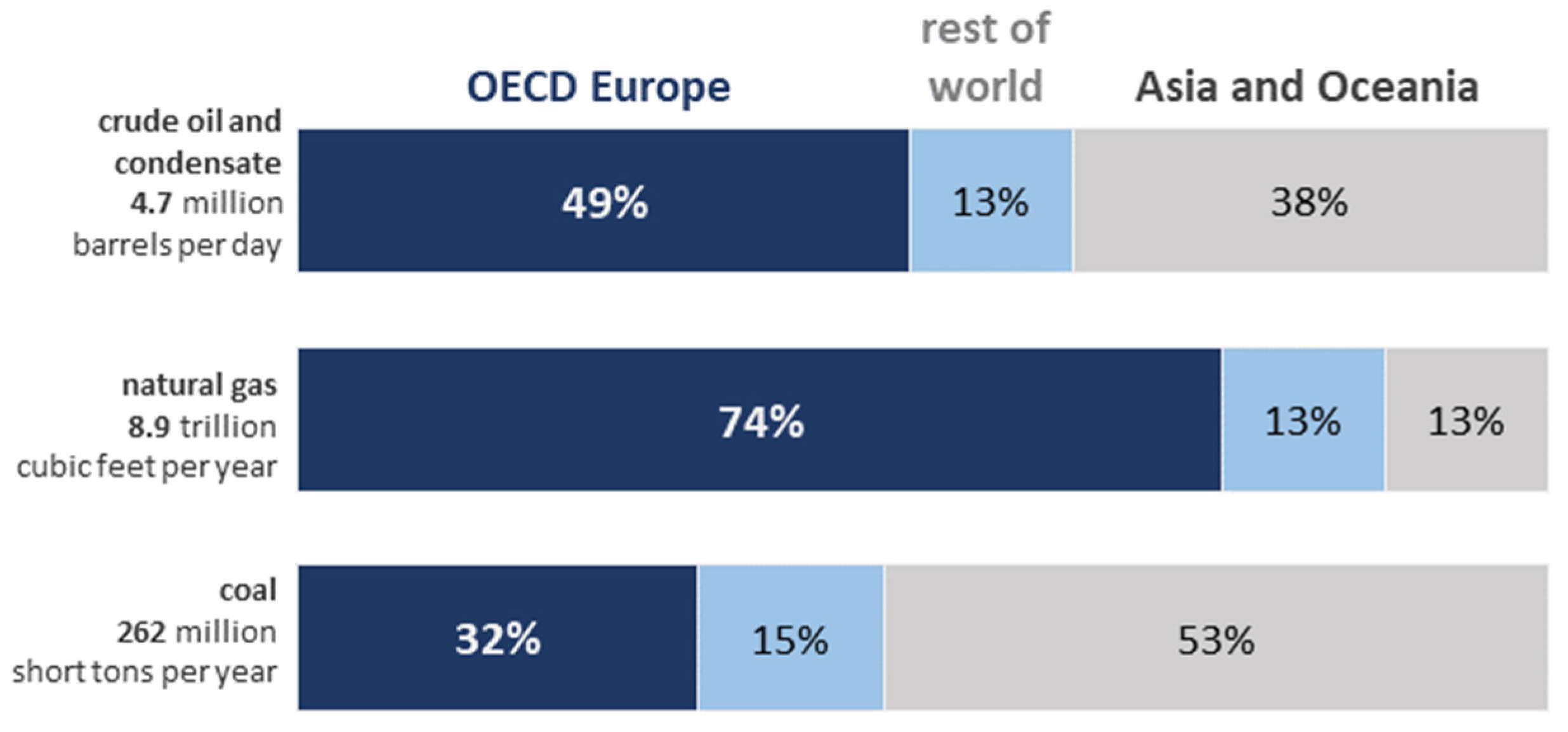
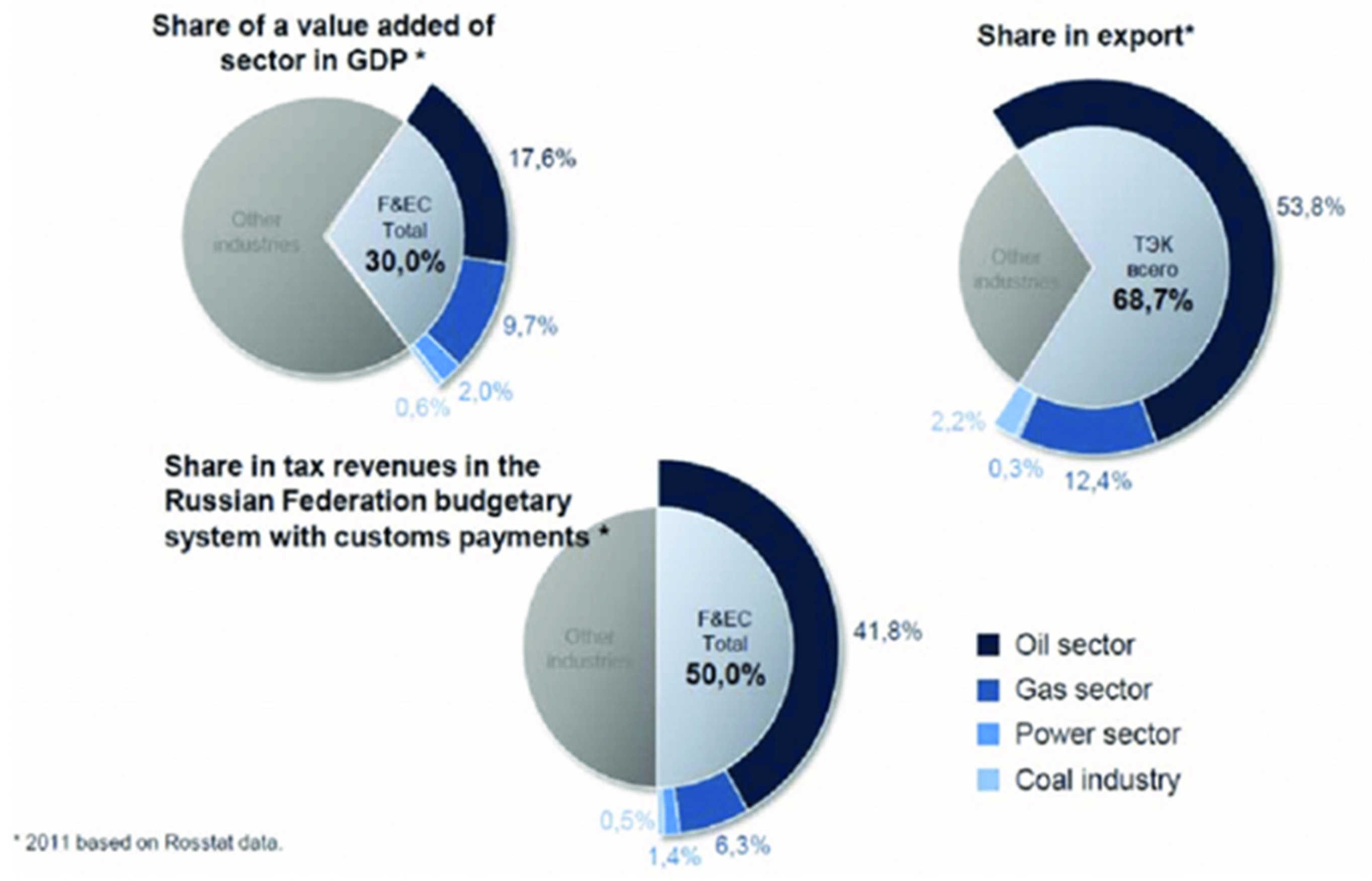
1. Introduction
- 1.
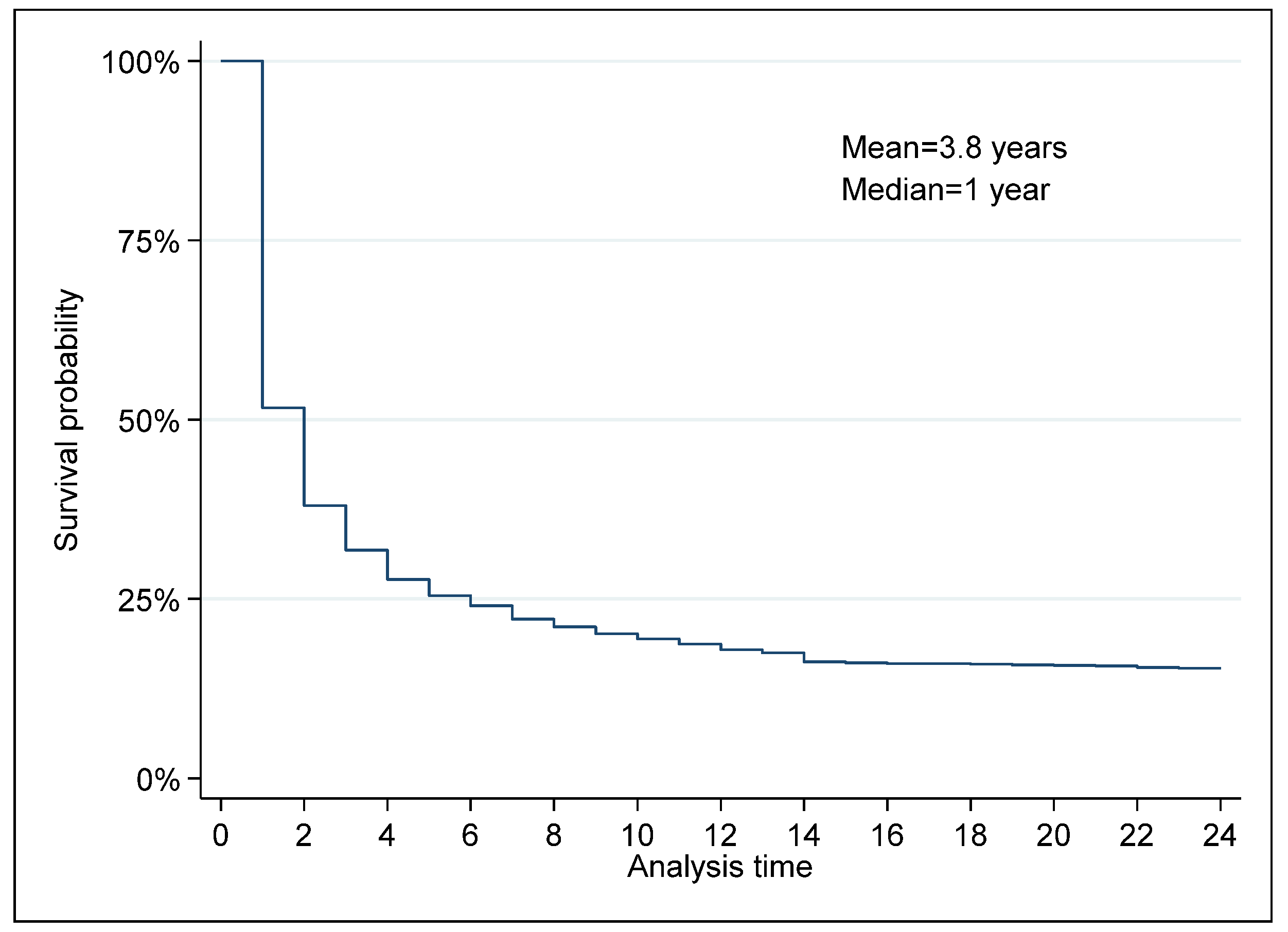
- The duration of exporting is short.
- 2.
- The hazard rate decreases with duration.
- 3.
- Varied factors determine export duration.
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
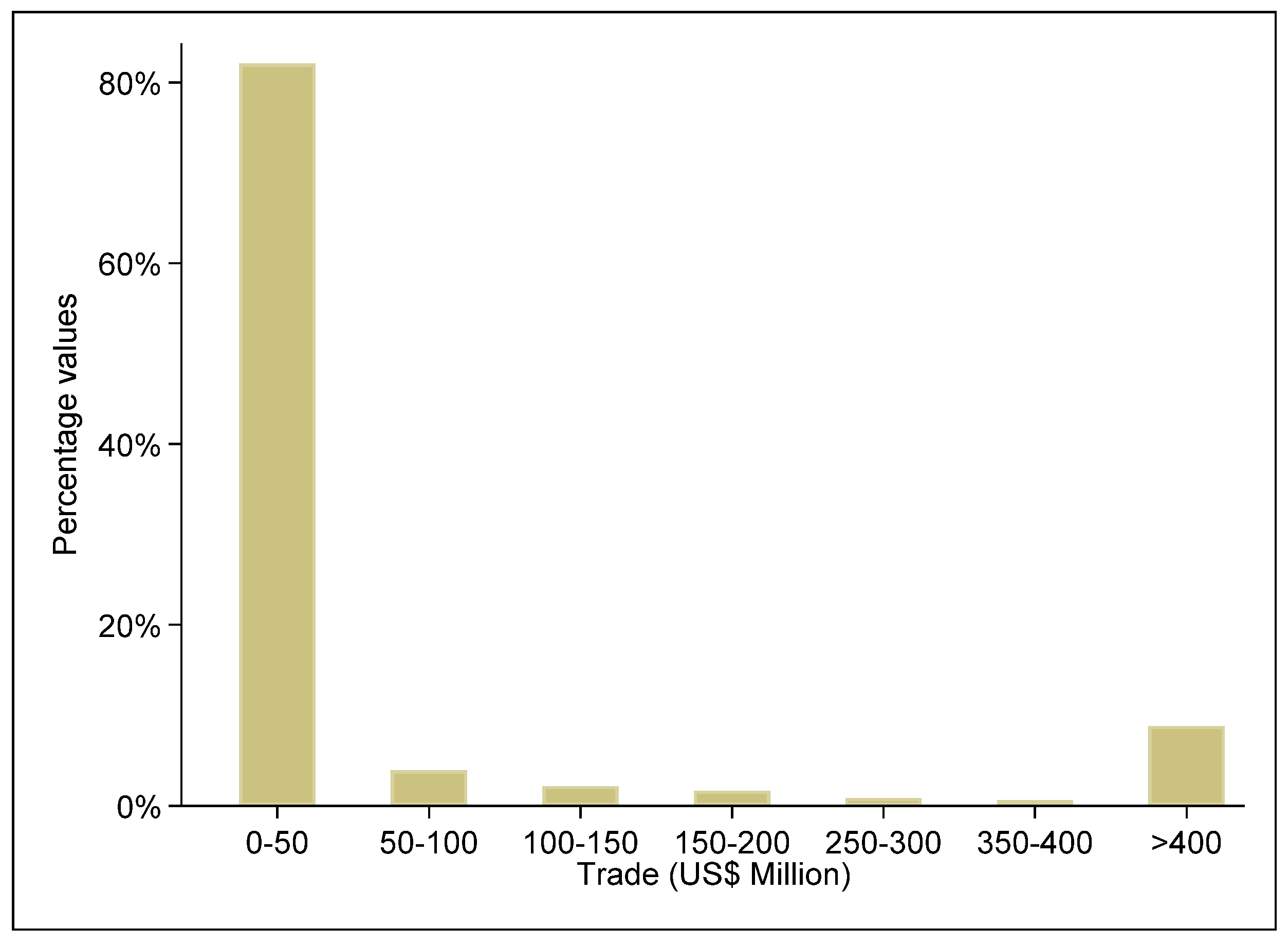
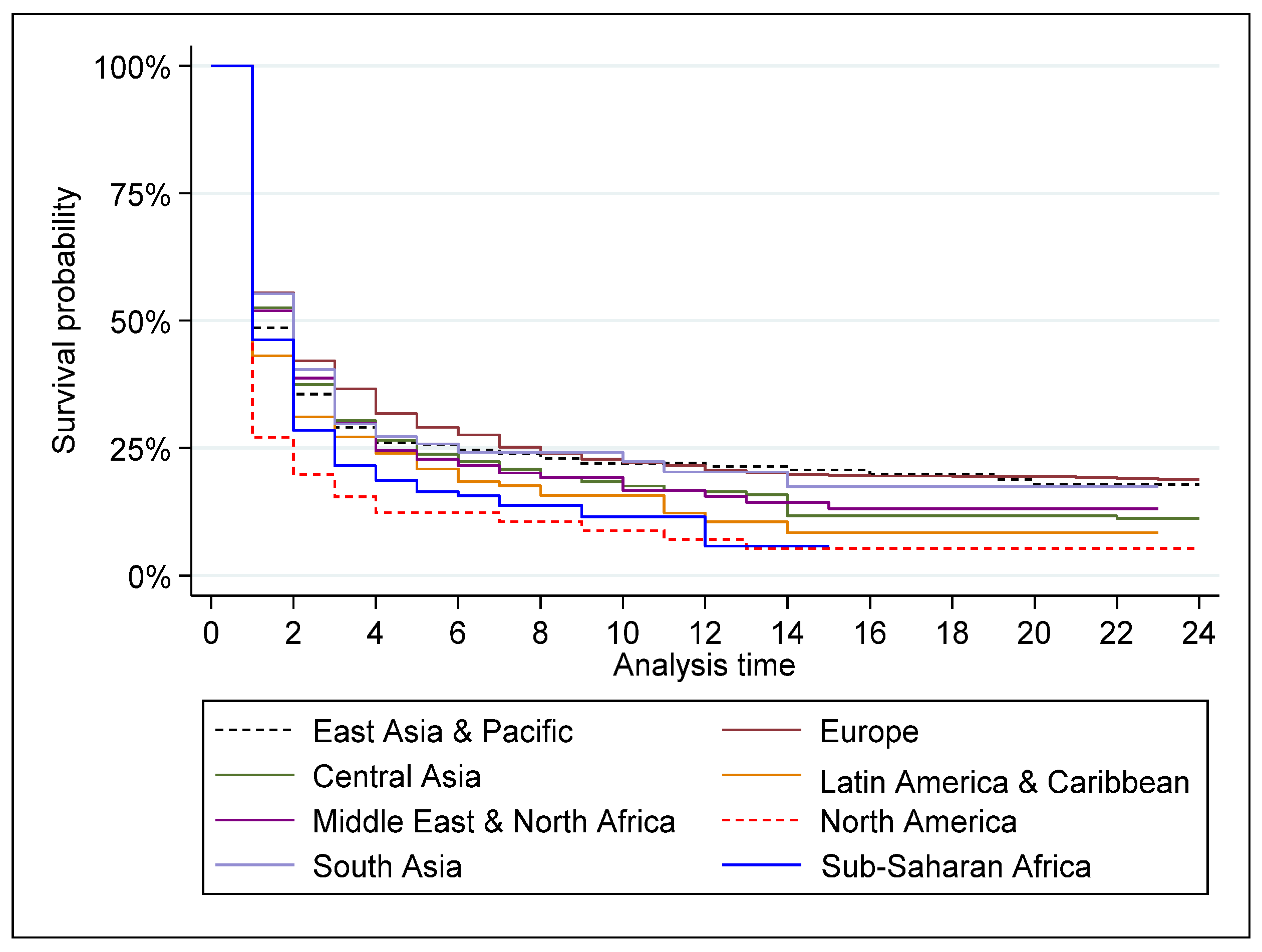
3.1. Data Analysis
3.2. Regression analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yarashynskaya, A.; Prus, P. Smart Energy for a Smart City: A Review of Polish Urban Development Plans. Energies 2022, 15, 8676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. Europe is a Key Destination for Russia’s Energy Exports. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=51618 (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- Eurostat. From Where Do We Import Energy? Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/cache/infographs/energy/bloc-2c.html (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- Mitrova, T. The Geopolitics of Russian Natural Gas. Available online: https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.25430.29768 (accessed on 27 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Besedeš, T.; Prusa, T.J. Ins, Outs and the Duration of Trade. Can. J. Econ. 2006, 39, 266–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Mora, C.; Córcoles, D.; Gandoy, R. Export Survival in Global Production Chains. World Econ. 2015, 38, 1526–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majune, S.K.; Moyi, E.; Kamau, G.J. Explaining Export Duration in Kenya. S. Afr. J. Econ. 2020, 88, 204–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugazza, M.; Molina, A.C. On the Determinants of Export Survival. In United Nations Conference on Trade and Development: Policy Issues in International Trade and Commodities Study Series No.46; United Nations: New York, NY, USA; Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Brenton, P.; Cadot, O.; Pierola, M.D. Pathways to African Export Sustainability; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Besedeš, T.; Prusa, T.J. Product differentiation and duration of US import trade. J. Int. Econ. 2006, 70, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitch, V. Die another day: Duration in German import trade. Rev. World Econ. 2009, 145, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkcan, K.; Saygili, H. Global Production Chains and Export Survival. East. Eur. Econ. 2018, 57, 103–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besedeš, T. A search cost perspective on formation and duration of trade. Rev. Int. Econ. 2008, 16, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, W.; Persson, M. The duration of trade revisited. Empir. Econ. 2012, 43, 1083–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenton, P.; Saborowski, C.; von Uexkull, E. What Explains the Low Survival Rate of Developing Country Export Flows? World Bank Econ. Rev. 2010, 24, 474–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuhoro, J.B.; Larue, B.; Gervais, Y. Factors Determining the Success or Failure of Canadian Establishents on Foreign Markets: A Survial Analysis Approach. Int. Trade J. 2006, 20, 33–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majune, S.K.; Moyi, E.; Türkcan, K. Export margins and survival: A firm-level analysis using Kenyan data. S. Afr. J. Econ. 2022, 90, 149–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, F.; Hallak, J.C.; Fanelli, S. Survival in Export Markets. J. Int. Econ. 2016, 102, 262–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirbat, L.; Record, R.; Nghardsaysone, K. Determinants of Export Survival in the Lao PDR (Policy Research Working Paper 6301); East Asia and Pacific Region; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Faruq, H.; Lopez, R.A.; Álvarez, R. Is Previous Export Experience Important for New Exports? J. Dev. Stud. 2013, 49, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, J.E.; Watson, J. Starting small in an unfamiliar environment. Int. J. Ind. Organ. 2003, 21, 1021–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, R. International investment and international trade in the product cycle. Q. J. Econ. 1966, 80, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.B.; Redding, S.J.; Schott, P.K. Multiple-Product Firms and Product Switching. Am. Econ. Rev. 2010, 100, 70–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.; Eslava, M.; Kugler, M.; Tybout, J. Export Dynamics in Columbia: Firm-Level Evidence (Working Paper 13531); National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER): Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kamuganga, D.N. Does inta-Africa regional trade cooperation enhance Africa’s export survival? Working Paper No.16/2012; Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Phiri, J.; Majune, S.K.; Malec, K.; Appiah-Kubi, S.N.; Gebeltová, Z.; Kotásková, S.K.; Naluwooza, P. Durability of Zambia’s Agricultural Exports. Agriculture 2021, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, H.; Anders, S. Experience matters—trade duration and survival of coffee exports. EAAE 2014 Congress. In Agri-Food and Rural Innovations for Healthier Societies; European Association of Agricultural Economists (EAAE): Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y. The effects of oil shocks on export duration of China. Energy 2017, 125, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltramello, A.; De Backer, K.; Moussiegt, L. The Export Performance of Countries within Global Value Chains (GVCs); OECD Science, Technology and Industry Working Papers: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.; Eslava, M.; Jinkins, D.; Krizan, C.J.; Tybout, J. A Search and Learning Model of Export Dynamics (Working Papers 21–17); Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau: Suitland-Silver Hill, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Besedeš, T.; Blyde, J. What Drives Export Survival? An Analysis of Export Duration in Latin America; SEMANTIC SCHOLAR: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Besedeš, T.; Moreno-Cruz, J.; Nitsch, V. Trade Integration and the Fragility of Trade Relationships: Theory and Empirics (Georgia Tech Working Paper). 2016. Available online: http://besedes.econ.gatech.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/322/2016/10/besedes-eia.pdf (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Jenkins, S. Survival Analysis, Unpublished Lecture Notes Manuscript; Institute for Social and Economic Research, University of Essex: Colchester, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, W.; Persson, M. Exploring the duration of EU imports. Rev. World Econ. 2012, 147, 665–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.R. Regression models and life-tables. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1972, 34, 187–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Wu, Y. Export survival pattern and its determinants: An empirical study of Chinese manufacturing firms. Asian-Pac. Econ. Lit. 2014, 28, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicek, P. Dancing with the devil: Explaining the European Union’s engagement with Ukraine under Viktor Yanukovych. J. Contemp. Eur. Stud. 2017, 25, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttke, M. To Whom the Crimea belongs? Putins Justified the Crimean-Annexation. Z. Slaw. 2015, 60, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miazhevich, G. International broadcasting and the conflict-related national media events: The framing of EuroMaidan by the BBC and RT. In Media Events: A Critical Contemporary Approach; Mitu, B., Poulakidakos, S., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK, 2016; pp. 53–70. [Google Scholar]
- Khorolskaya, M.; Cherkasova, E. Germany and Spain: Similarities and Differences in Approach to Ukrainian Crisis. World Economy Int. Relat. 2019, 63, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J. Panina-Burke, S. The reunification of Crimea and the city of Sevastopol with the Russian Federation. Russ. Law J. 2017, 5, 29–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloglog | Probit | Logit | |
| GDP Russia | −0.1579 ** | −0.1432 ** | −0.2352 ** |
| (0.080) | (0.069) | (0.116) | |
| GDP importer | −0.0288 ** | −0.0314 *** | −0.0480 ** |
| (0.013) | (0.011) | (0.019) | |
| Distance | 0.2063 *** | 0.2050 *** | 0.3423 *** |
| (0.062) | (0.056) | (0.093) | |
| Time Zone Difference | 0.0053 | 0.0037 | 0.0041 |
| (0.019) | (0.017) | (0.029) | |
| Common border | −0.1947 *** | −0.1600 *** | −0.2739 *** |
| (0.066) | (0.058) | (0.096) | |
| Financial Development | −0.0267 | −0.0317 | −0.0520 |
| (0.034) | (0.029) | (0.049) | |
| Exchange rate | −0.0296 *** | −0.0249 *** | −0.0432 *** |
| (0.010) | (0.009) | (0.015) | |
| RTA | −0.1711 ** | −0.1627 *** | −0.2671 *** |
| (0.066) | (0.058) | (0.097) | |
| Initial export value | −0.0861 *** | −0.0709 *** | −0.1214 *** |
| (0.008) | (0.007) | (0.011) | |
| Lagged duration | −0.0640 *** | −0.0287 *** | −0.0557 *** |
| (0.017) | (0.011) | (0.020) | |
| Total export value | −0.0463 *** | −0.0507 *** | −0.0820 *** |
| (0.008) | (0.007) | (0.013) | |
| Duration dummies | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Spell dummies | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year dummies | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 12,393 | 12,393 | 12,393 |
| Spells | 3652 | 3652 | 3652 |
| Trade relations | 1984 | 1984 | 1984 |
| Log-likelihood | −4766 | −4762 | −4759 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | East Asia and Pacific | Europe | Central Asia | Latin America and Caribbean | Middle East and North Africa | North America | South Asia | Sub-Saharan Africa | |
| GDP Russia | −0.0292 ** | −0.1011 ** | −0.0074 | 0.0530 | −0.1538 ** | −0.1835 | −0.8361 | 0.0833 | 0.0250 |
| (0.014) | (0.048) | (0.021) | (0.043) | (0.078) | (0.122) | (1.989) | (0.104) | (0.143) | |
| GDP importer | −0.0059 ** | −0.0087 | −0.0028 | −0.0020 | −0.0307 *** | −0.0178 | 1.3618 | 0.0138 | −0.0393 ** |
| (0.002) | (0.006) | (0.004) | (0.011) | (0.011) | (0.019) | (3.050) | (0.044) | (0.018) | |
| Distance | 0.0411 *** | 0.0476 | 0.0451 | 0.0737 | 0.0677 | −0.0632 | −35.2179 | 0.3125 | −0.0393 |
| (0.011) | (0.115) | (0.032) | (0.140) | (0.129) | (0.146) | (78.102) | (0.497) | (0.182) | |
| Time zone difference | 0.0006 | 0.0032 | 0.0285* | 0.0014 | −0.0082 | 0.0087 | −10.7320 | 0.0258 | −0.0301 |
| (0.004) | (0.020) | (0.017) | (0.030) | (0.016) | (0.038) | (24.637) | (0.271) | (0.023) | |
| Common border | −0.0343 *** | −0.0834 | −0.0098 | 0.0200 | - | - | - | - | - |
| (0.012) | (0.057) | (0.023) | (0.047) | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Financial development | −0.0054 | −0.0186 | 0.0329 * | 0.0405 ** | 0.0165 | 0.0973 | −0.0785 | 0.0300 | 0.0126 |
| (0.006) | (0.013) | (0.020) | (0.020) | (0.027) | (0.084) | (0.071) | (0.345) | (0.052) | |
| Exchange rate | −0.0046 ** | −0.0117 * | 0.0004 | −0.0114 * | 0.0026 | 0.0040 | 2.1269 | 0.0540 ** | −0.0084 |
| (0.002) | (0.006) | (0.004) | (0.006) | (0.009) | (0.009) | (6.040) | (0.026) | (0.013) | |
| RTA | −0.0335 *** | 0.0263 | −0.0117 | −0.0328 | −0.1249 | - | - | - | - |
| (0.012) | (0.141) | (0.021) | (0.056) | (0.144) | - | - | - | - | |
| Initial export value | −0.0150 *** | −0.0275 *** | −0.0130 *** | −0.0179 *** | −0.0145 *** | −0.0180 *** | −0.0086 | −0.0076 | −0.0085 |
| (0.001) | (0.005) | (0.002) | (0.004) | (0.006) | (0.007) | (0.009) | (0.009) | (0.008) | |
| Lagged duration | −0.0070 *** | −0.0018 | −0.0061 * | −0.0136 ** | −0.0139 | −0.0074 | −0.0740 | 0.0261 ** | −0.0225 |
| (0.002) | (0.009) | (0.003) | (0.006) | (0.015) | (0.021) | (0.059) | (0.011) | (0.028) | |
| Total export value | −0.0102 *** | −0.0104 * | −0.0116 *** | −0.0077 ** | −0.0159 ** | −0.0197 ** | −0.0278 * | 0.0191 * | −0.0265 *** |
| (0.002) | (0.006) | (0.002) | (0.004) | (0.007) | (0.008) | (0.015) | (0.011) | (0.009) | |
| Observations | 12,393 | 1132 | 6533 | 2101 | 478 | 630 | 160 | 259 | 369 |
| Spells | 3643 | 3643 | 3643 | 3643 | 3643 | 3643 | 3643 | 3643 | 3643 |
| Trade relations | 1978 | 1978 | 1978 | 1978 | 1978 | 1978 | 1978 | 1978 | 1978 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malec, K.; Majune, S.K.; Kuzmenko, E.; Phiri, J.; Nyamoita, R.L.M.; Appiah-Kubi, S.N.K.; Maitah, M.; Smutka, L.; Gebeltová, Z.; Tomšík, K.; et al. Energy Logistic Regression and Survival Model: Case Study of Russian Exports. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010885
Malec K, Majune SK, Kuzmenko E, Phiri J, Nyamoita RLM, Appiah-Kubi SNK, Maitah M, Smutka L, Gebeltová Z, Tomšík K, et al. Energy Logistic Regression and Survival Model: Case Study of Russian Exports. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(1):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010885
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalec, Karel, Socrates Kraido Majune, Elena Kuzmenko, Joseph Phiri, Rahab Liz Masese Nyamoita, Seth Nana Kwame Appiah-Kubi, Mansoor Maitah, Luboš Smutka, Zdeňka Gebeltová, Karel Tomšík, and et al. 2023. "Energy Logistic Regression and Survival Model: Case Study of Russian Exports" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 1: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010885
APA StyleMalec, K., Majune, S. K., Kuzmenko, E., Phiri, J., Nyamoita, R. L. M., Appiah-Kubi, S. N. K., Maitah, M., Smutka, L., Gebeltová, Z., Tomšík, K., Kobzev Kotásková, S., & Marušiak, J. (2023). Energy Logistic Regression and Survival Model: Case Study of Russian Exports. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(1), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010885











