Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of a Localized Food System and Food Waste Reduction in a Water-Scarce Region Using Diet Optimization Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
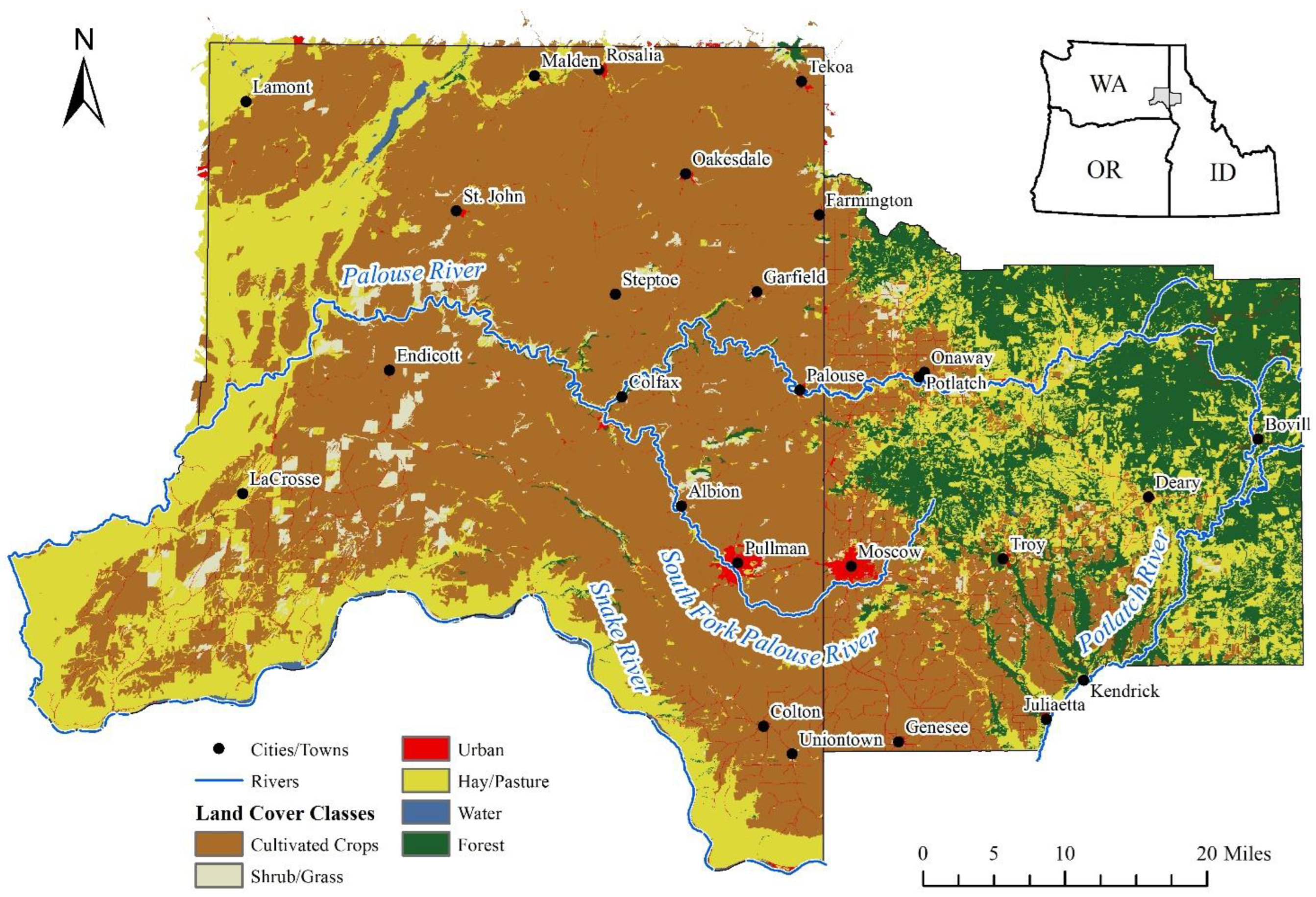
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Environmental Footprints of Local Foods
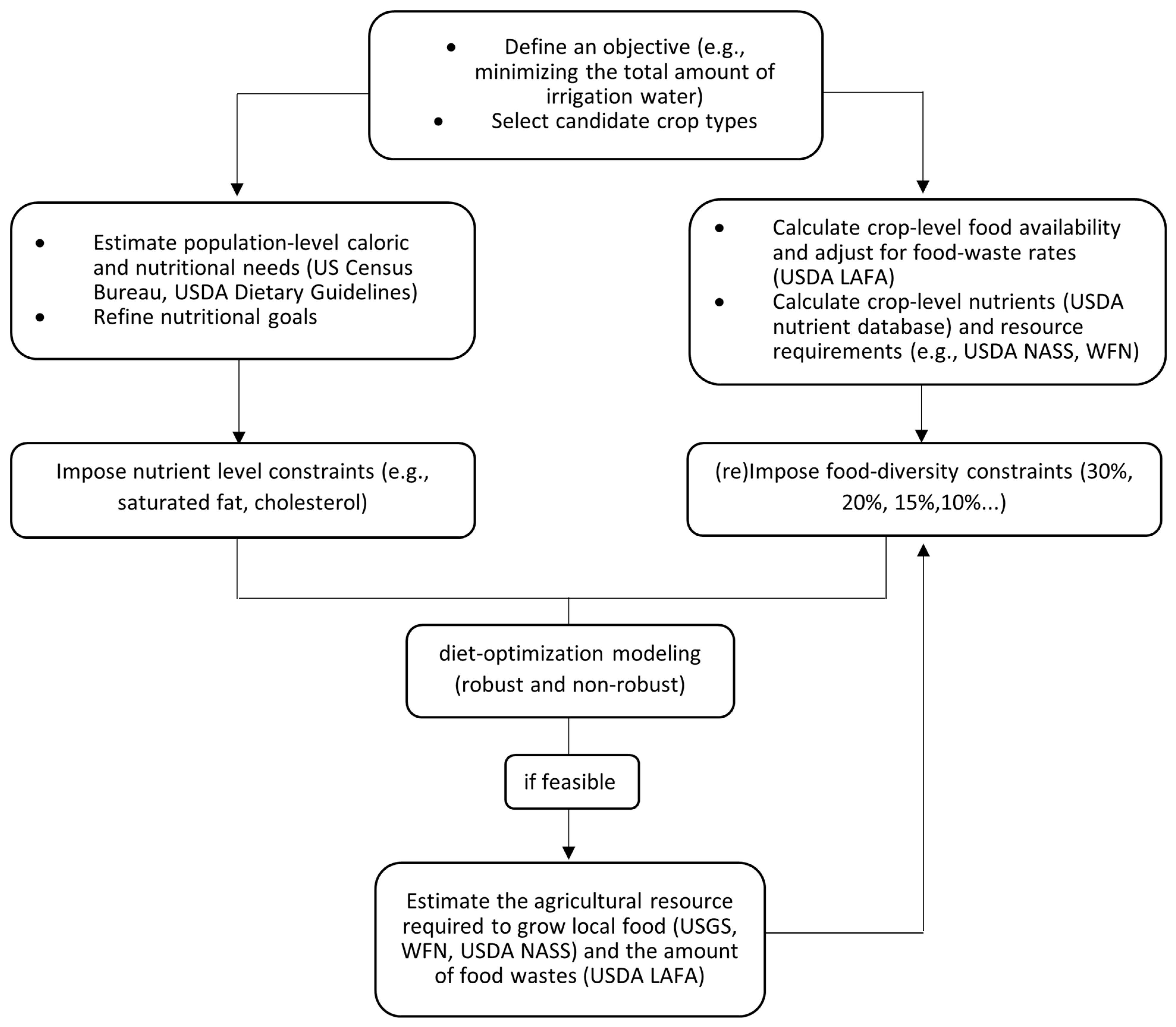
2.3. Objectives, Constraints, and Uncertainty
2.4. Alternative Scenario on Food Waste Reduction
3. Results
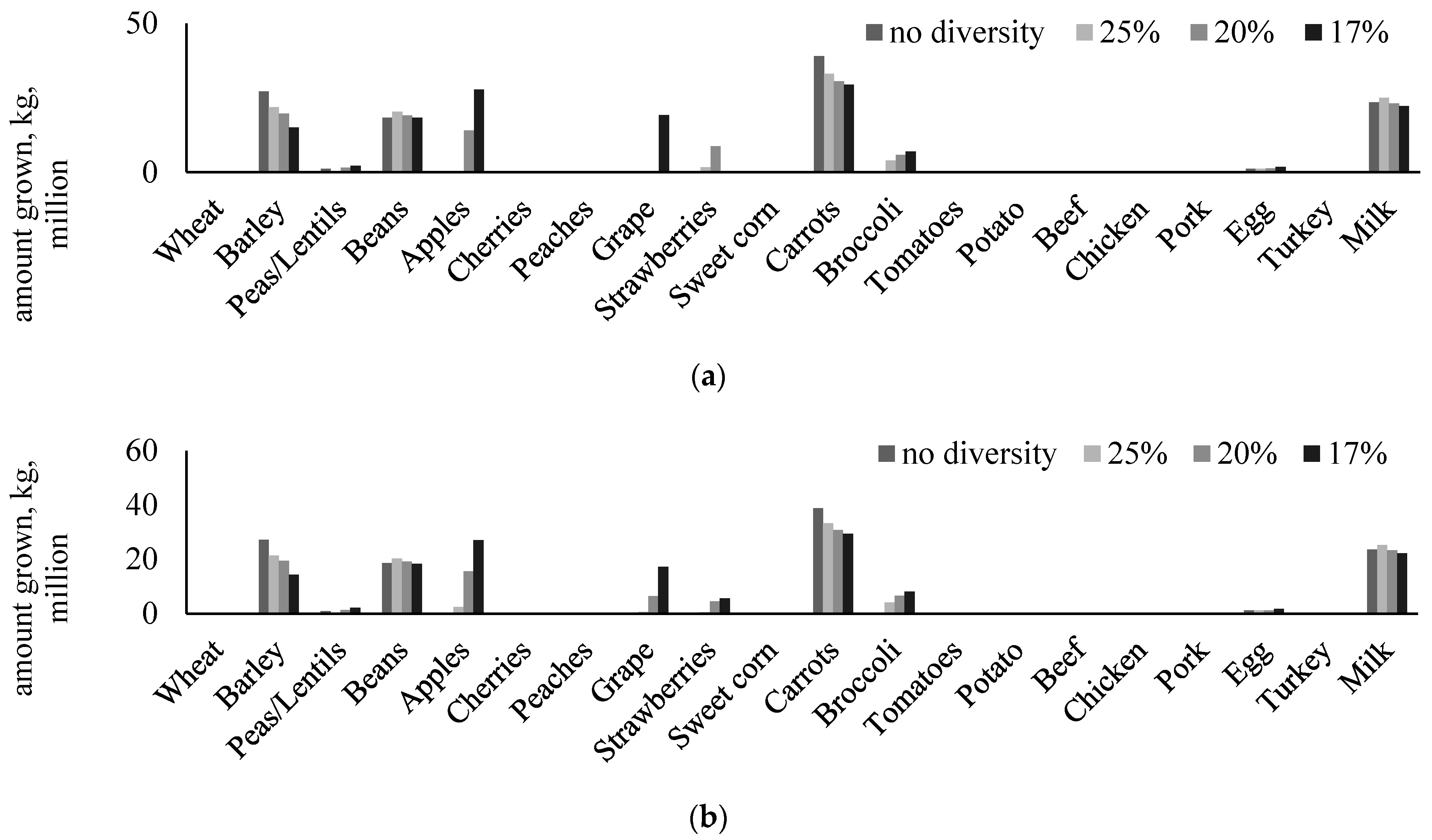
3.1. Estimated Amount of Food to Be Grown Locally and Its Resource Requirements
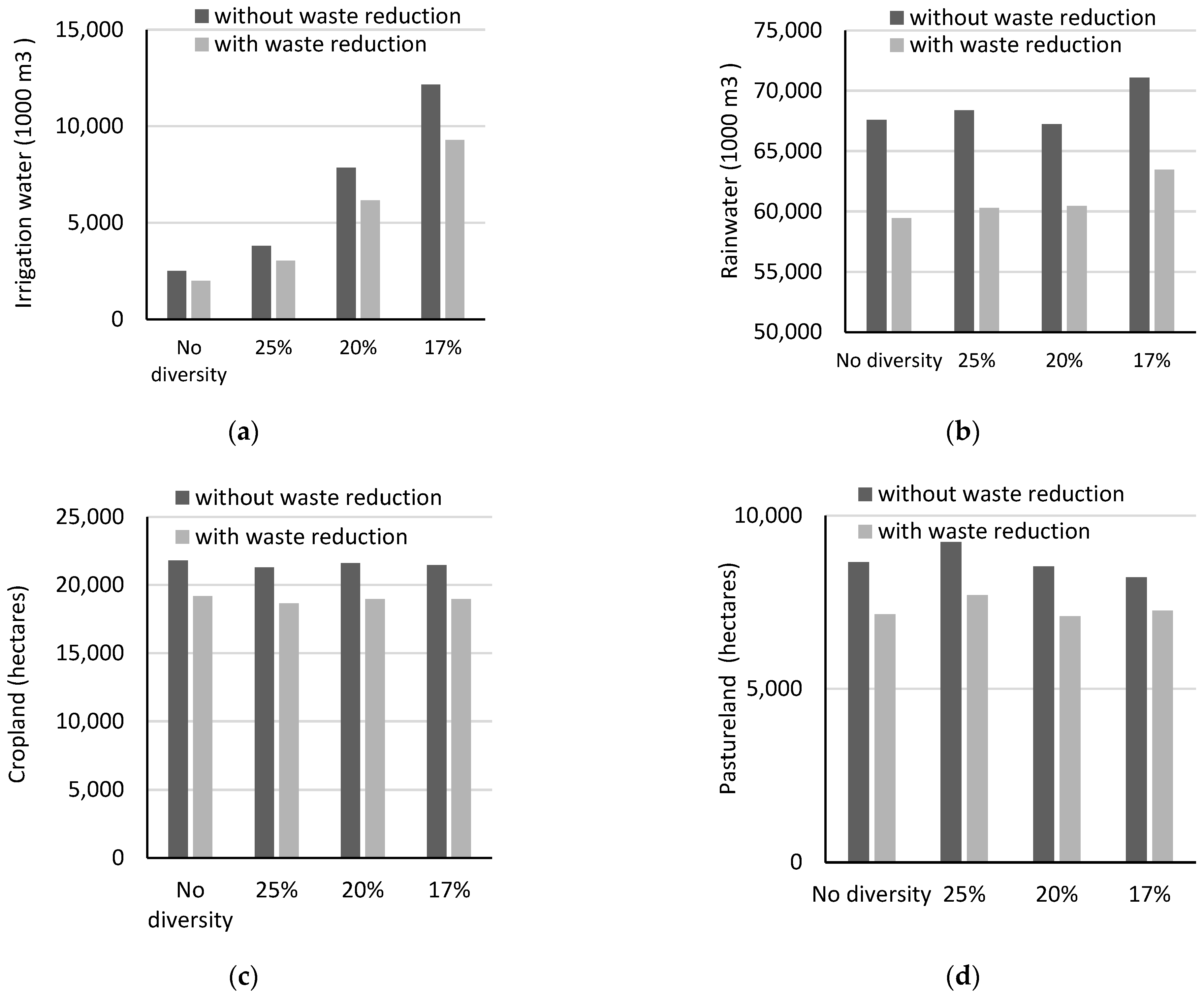
3.2. Environmental Impacts of Food Waste Reduction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USDA. USDA Releases Local Food Marketing Practices. Available online: https://www.nass.usda.gov/Newsroom/2022/04-28-2022.php (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- Michel-Villarreal, R.; Hingley, M.; Canavari, M.; Bregoli, I. Sustainability in Alternative Food Networks: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, T.A.; Wertheim-Heck, S.C.O. Retailing Local Food through Supermarkets: Cases from Belgium and the Netherlands. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 300, 126948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.K.; Inwood, S.M. Scaling-up Regional Fruit and Vegetable Distribution: Potential for Adaptive Change in the Food System. Agric. Hum. Values 2016, 33, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsetoohy, O.; Ayoun, B.; Abou-Kamar, M. COVID-19 Pandemic Is a Wake-Up Call for Sustainable Local Food Supply Chains: Evidence from Green Restaurants in the USA. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuPuis, E.M.; Ransom, E.; Worosz, M.R. Food Supply Chain Shocks and the Pivot Toward Local: Lessons From the Global Pandemic. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, Z.S.; Barton, D.N.; Gundersen, V.; Figari, H.; Nowell, M. Urban Nature in a Time of Crisis: Recreational Use of Green Space Increases during the COVID-19 Outbreak in Oslo, Norway. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 104075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brislen, L. Meeting in the Middle: Scaling-up and Scaling-over in Alternative Food Networks. Cult. Agric. Food Environ. 2018, 40, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saul, D.; Newman, S.; DePhelps, C.; Liao, F. Exploration of Values and Agency in Place-Based Food Systems. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 89, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Ai, N. Evaluating the Sustainability of Urban Food Recovery Programs: A Quantitative Assessment in Chicago. Transp. Res. Rec. 2022, 2676, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.J.; Bills, N.L.; Lembo, A.J.; Wilkins, J.L.; Fick, G.W. Mapping Potential Foodsheds in New York State by Food Group: An Approach for Prioritizing Which Foods to Grow Locally. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2012, 27, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkley, C. Visualizing the Social and Geographical Embeddedness of Local Food Systems. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 54, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duram, L.; Oberholtzer, L. A Geographic Approach to Place and Natural Resource Use in Local Food Systems. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2010, 25, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Burnett, K.; Ghimire, J. Assessing the Potential for Food and Energy Self-Sufficiency on the Island of Kauai, Hawaii. Food Policy 2015, 54, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.H.; Gordon, B.; DePhelps, C.; Saul, D.; Fan, C.; Feng, W. A Land-Based and Spatial Assessment of Local Food Capacity in Northern Idaho, USA. Land 2019, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschitz, H.; Frick, R. City Food Flow Analysis. A New Method to Study Local Consumption. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.J.; Bills, N.L.; Wilkins, J.L.; Fick, G.W. Foodshed Analysis and Its Relevance to Sustainability. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2009, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Vicente, J.L.; Sanz-Sanz, E.; Napoleone, C.; Moulery, M.; Piorr, A. Foodshed, Agricultural Diversification and Self-Sufficiency Assessment: Beyond the Isotropic Circle Foodshed—A Case-Study From Avignon (France). Agriculture 2021, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, D.A.; Radka, C.N.; Müller, N.M.; Watson, T.D.; Rekstein, N.J.; Van, M. Wright, H.; Hollingshead, S.E. Effect of Localizing Fruit and Vegetable Consumption on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Nutrition, Santa Barbara County. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4555–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, Z.; Blackstone, N.T.; Roy, E.D. Healthy Diets Can Create Environmental Trade-Offs, Depending on How Diet Quality Is Measured. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, M.; Sussmann, C.; Dorward, C.; Mullinix, K. Local or Global: A Biophysical Analysis of a Regional Food System. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2019, 34, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanham, D.; Comero, S.; Gawlik, B.M.; Bidoglio, G. The Water Footprint of Different Diets within European Sub-National Geographical Entities. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.; Oveysi, Z.; Dundar, B.; McGarvey, R. Assessment of the Effect of Urban Agriculture on Achieving a Localized Food System Centered on Chicago, IL Using Robust Optimization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2684–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgroi, F. The Circular Economy for Resilience of the Agricultural Landscape and Promotion of the Sustainable Agriculture and Food Systems. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 8, 100307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Campbell, J.E. Improving Attributional Life Cycle Assessment for Decision Support: The Case of Local Food in Sustainable Design. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 145, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Mekonnen, M.M. The Water Footprint of Humanity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desa, U.N. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Woolston, C. Healthy People, Healthy Planet: The Search for a Sustainable Global Diet. Nature 2020, 588, S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, Z.; Niles, M.T.; Neher, D.A.; Roy, E.D.; Tichenor, N.E.; Jahns, L. Relationship between Food Waste, Diet Quality, and Environmental Sustainability. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, M.C.; Willits-Smith, A.; Mahon, T.; Keoleian, G.A.; Rose, D. Individual US Diets Show Wide Variation in Water Scarcity Footprints. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Fulton, J. The Effect of Diet Changes and Food Loss Reduction in Reducing the Water Footprint of an Average American. Water Int. 2018, 43, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, Q.D.; Brown, S.; Cuéllar, A.D.; Finn, S.M.; Gephart, J.A.; Marston, L.T.; Meyer, E.; Weitz, K.A.; Muth, M.K. Assessing the Environmental Impacts of Halving Food Loss and Waste along the Food Supply Chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, Q.D.; Hondula, K.L.; Muth, M.K. Biodiversity Effects of Food System Sustainability Actions from Farm to Fork. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113884119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, C.J.; Wilkins, J.L.; Fick, G.W. Testing a Complete-Diet Model for Estimating the Land Resource Requirements of Food Consumption and Agricultural Carrying Capacity: The New York State Example. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2007, 22, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.C.; Griffin, T.S.; Srinivasan, S.; Peters, C.J. Regional Variability in Land and Water Use in Fruit and Vegetable Production in the United States. Urban Agric. Reg. Food Syst. 2021, 6, e20020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.M. Alongside the Grain: Conceptualizing Scale and the Upper Threshold of Local in the Agro-Industrial Palouse. Cult. Agric. Food Environ. 2018, 40, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Consus Bureau. QuickFacts: Latah County, Idaho; United States Consus Bureau: Suitland, MD, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/latahcountyidaho,US/PST045221 (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- USDA. 2017 Census of Agriculture; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- USDA. National Agricultural Statistics Service Quick Stats; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- Bauman, A.; DePhelps, C.; McFadden, D.T. Assessing a Local Food System: The Palouse-Clearwater Food Coalition Assessment Process. J. Agric. Food Syst. Community Dev. 2019, 8, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePhelps, C.; Peterson, S. Estimating the Economic Contributions of the Moscow Farmers Market. In Western Economics Forum; Western Agricultural Economics Association: Westminster, CO, USA, 2020; Volume 18, pp. 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Beall, A.; Fiedler, F.; Boll, J.; Cosens, B. Sustainable Water Resource Management and Participatory System Dynamics. Case Study: Developing the Palouse Basin Participatory Model. Sustainability 2011, 3, 720–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- City of Moscow. Moscow Comprehensive Plan; City of Moscow: Moscow, ID, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dieter, C.A.; Maupin, M.A.; Caldwell, R.R.; Harris, M.A.; Ivahnenko, T.I.; Lovelace, J.K.; Barber, N.L.; Linsey, K.S. Estimated Use of Water in the United States in 2015; Circular; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018; 1441, p. 76.
- Medici, G.; Engdahl, N.B.; Langman, J.B. A Basin-Scale Groundwater Flow Model of the Columbia Plateau Regional Aquifer System in the Palouse (USA): Insights for Aquifer Vulnerability Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2021, 15, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhungel, R.; Fiedler, F. Water Balance to Recharge Calculation: Implications for Watershed Management Using Systems Dynamics Approach. Hydrology 2016, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galzki, J.C.; Mulla, D.J.; Meier, E. Mapping Potential Foodsheds Using Regionalized Consumer Expenditure Data for Southeastern Minnesota. J. Agric. Food Syst. Community Dev. 2017, 7, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, L.; Ao, Y.; Konar, M.; Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. High-Resolution Water Footprints of Production of the United States. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 2288–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The Green, Blue and Grey Water Footprint of Crops and Derived Crop Products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1577–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.; Xue, X.; Howarth, R.W. Comparison of Production-Phase Environmental Impact Metrics Derived at the Farm- and National-Scale for United States Agricultural Commodities. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 114004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, B.; Costello, C.; McGarvey, R.G. Robust Optimization Evaluation of Reliance on Locally Produced Foods. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2017, 37, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. CNPP USDA Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion (CNPP); Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. In Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015–2020; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Conner, D.S.; Knudson, W.A.; Hamm, M.W.; Peterson, H.C. The Food System as an Economic Driver: Strategies and Applications for Michigan. J. Hunger Environ. Nutr. 2008, 3, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haytowitz, D.; Lemar, L.; Pehrsson, P.; Exler, J.; Patterson, K.; Thomas, R.; Nickle, M.; Williams, J.; Showell, B.; Khan, M. USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 24; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Chen, Z.; Sim, M.; Xiong, P. Robust Stochastic Optimization Made Easy with RSOME. Manag. Sci. 2020, 66, 3329–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Federal Interagency Collaboration to Reduce Food Loss and Waste. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sustainable-management-food/federal-interagency-collaboration-reduce-food-loss-and-waste (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- USDA USDA ERS—Food Availability (Per Capita) Data System. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/food-availability-per-capita-data-system/ (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Conrad, Z. Daily Cost of Consumer Food Wasted, Inedible, and Consumed in the United States, 2001–2016. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, Q.D.; Muth, M.K. Cost-Effectiveness of Four Food Waste Interventions: Is Food Waste Reduction a “Win–Win?”. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.G.M.; Karsten, H.D.; Veith, T.L.; Beegle, D.B.; Kleinman, P.J. Conservation Dairy Farming Impact on Water Quality in a Karst Watershed in Northeastern US. Agric. Syst. 2018, 165, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.W. Beyond ‘Local’ Food: How Supermarkets and Consumer Choice Affect the Economic Viability of Small-Scale Family Farms in Sydney, Australia. Area 2016, 48, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraeni, E.W.; Handayati, Y.; Novani, S. Improving Local Food Systems through the Coordination of Agriculture Supply Chain Actors. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, M.; Canavari, M.; Castellini, A. Exploring the Economic, Social, and Environmental Dimensions of Community-Supported Agriculture in Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Whitman, WA | Washington | Latah, ID | Idaho | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All farms | ||||
| # of farms | 1039 | 35,793 | 1041 | 15,028 |
| Average farm size (acre) | 1240 | 410 | 336 | 305 |
| Average size of farms with irrigation | 56 | 113 | 3 | 217 |
| Average sales per farm ($) | $268,309 | $269,172 | $74,901 | $213,657 |
| Vegetables and fruits | ||||
| # of farms | 19 | 6850 | 41 | 1552 |
| Average farm size (acre) | 3.31 | 59.33 | 1.51 | 135.14 |
| Average sales per farm ($) | $5737 | $586,130 | $5533 | $276,753 |
| Animals and livestock | ||||
| # of farms | 240 | 14,405 | 325 | 12,305 |
| Average farm size (acre) | 612.03 | 256.86 | 55.47 | 351.72 |
| Average sales per farm ($) | $79,721 | $184,039 | $13,606 | $354,052 |
| Farms with directly marketed retail sales | ||||
| # of farms | 53 | 4503 | 72 | 1765 |
| Average sales per farm ($) | $6302 | $15,229 | $3028 | $15,865 |
| Land use | ||||
| % of cropland irrigated | 0.49 | 22.56 | 0.06 | 57.65 |
| % farms with irrigated ag. land | 9.80 | 61.43 | 5.99 | 89.96 |
| Water Use (1000 m3/Day) | Whitman, WA | Latah, ID | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groundwater | Surface Water | Groundwater | Surface Water | |
| Irrigation crops | 3.75 | 5.75 | 6.93 | 3.07 |
| Livestock | 0.83 | 0.08 | 0.26 | 0.19 |
| Irrigation golf | 0.64 | N/A | 1.48 | N/A |
| Public supply | 21.27 | N/A | 21.46 | N/A |
| Total freshwater withdrawal | 27.90 | 5.83 | 36.11 | 3.63 |
| Food | Blue WF or Irrigation Water Requirement | Green WF | Cropland | Pasture | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| County /State | Minimum | Maximum | County /State | County /State | National | |
| m3/1000 kg | m3/1000 kg | m3/1000 kg | m3/1000 kg | m2/1000 kg | m2/1000 kg | |
| Wheat | - | - | - | 802 | 2642 | - |
| Barley | - | - | - | 533 | 2655 | - |
| Lentils/peas | - | - | - | 948 | 4546 | - |
| Beans | - | - | - | 1679 | 5217 | - |
| Apples | 127 | 92 | 171 | 97 | 280 | - |
| Cherries | 1016 | 711 | 1320 | 278 | 1001 | - |
| Peaches | 381 | 267 | 496 | 278 | 718 | - |
| Grapes | 195 | 137 | 254 | 321 | 661 | - |
| Strawberries | 209 | 146 | 271 | 97 | 895 | - |
| Sweet corn | 232 | 162 | 302 | 112 | 569 | - |
| Carrots | 22 | 15 | 28 | 22 | 166 | - |
| Broccoli | 175 | 123 | 228 | 63 | 491 | - |
| Tomatoes | 139 | 97 | 181 | 55 | 288 | - |
| Potato | 109 | 76 | 142 | 24 | 159 | - |
| Beef | 589 | 401 | 548 | 14,751 | 8890 | 30,000 |
| Chicken | 205 | 159 | 217 | 1896 | 9300 | - |
| Pork | 568 | 385 | 526 | 3811 | 21,890 | - |
| Egg | 198 | 129 | 172 | 1836 | 7300 | - |
| Turkey | 221 | 156 | 205 | 2043 | 10,400 | - |
| Milk | 72 | 45 | 62 | 783 | 1290 | 3700 |
| Unit | No Diversity | 25% | 20% | 17% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-RO model | |||||
| Irrigation | 1000 m3 | 2476 | 3566 | 7181 | 10,936 |
| Green water | 1000 m3 | 67,592 | 68,383 | 67,236 | 71,094 |
| Cropland | Hectare | 21,798 | 21,287 | 21,597 | 21,447 |
| Pastureland | Hectare | 8658 | 9242 | 8534 | 8215 |
| Irrigation | m3/1000 kg | 22 | 33 | 58 | 77 |
| Green water | m3/1000 kg | 612 | 641 | 546 | 499 |
| Cropland | m2/1000 kg | 1974 | 1994 | 1753 | 1507 |
| Pastureland | m2/1000 kg | 784 | 866 | 693 | 577 |
| RO model | |||||
| Irrigation | 1000 m3 | 2502 | 3801 | 7851 | 12,151 |
| Green water | 1000 m3 | 67,835 | 68,679 | 69,197 | 74,898 |
| Cropland | Hectare | 21,833 | 21,219 | 21,673 | 21,913 |
| Pastureland | Hectare | 8688 | 9326 | 8614 | 9082 |
| Irrigation | m3/1000 kg | 23 | 35 | 61 | 83 |
| Green water | m3/1000 kg | 614 | 629 | 541 | 513 |
| Cropland | m2/1000 kg | 1977 | 1944 | 1694 | 1501 |
| Pastureland | m2/1000 kg | 787 | 855 | 673 | 622 |
| Food Group | Amount of Food Needed | Amount of Food Wasted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Million kg | Retail Level | Consumer Level | |||
| Million kg | % of Loss | Million kg | % of Loss | ||
| Grains | 14.24 | 1.71 | 12.00 | 3.88 | 27.23 |
| Fruits | 49.74 | 10.72 | 21.56 | 10.22 | 20.55 |
| Vegetables | 37.42 | 3.79 | 10.12 | 13.81 | 36.90 |
| Meats, poultry, eggs, and dairy | 24.19 | 2.92 | 12.07 | 4.48 | 18.53 |
| Legumes (beans and peas) | 20.37 | 1.22 | 6.00 | 1.87 | 9.20 |
| Total | 145.96 | 20.36 | 13.95 | 34.26 | 23.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, F.H.; Heinse, R.; Saul, D.; Newman, S.; Huang, L.; DePhelps, C.; Peterson, S. Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of a Localized Food System and Food Waste Reduction in a Water-Scarce Region Using Diet Optimization Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105890
Liao FH, Heinse R, Saul D, Newman S, Huang L, DePhelps C, Peterson S. Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of a Localized Food System and Food Waste Reduction in a Water-Scarce Region Using Diet Optimization Models. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(10):5890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105890
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Felix Haifeng, Robert Heinse, Darin Saul, Soren Newman, Li Huang, Colette DePhelps, and Steven Peterson. 2023. "Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of a Localized Food System and Food Waste Reduction in a Water-Scarce Region Using Diet Optimization Models" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 10: 5890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105890
APA StyleLiao, F. H., Heinse, R., Saul, D., Newman, S., Huang, L., DePhelps, C., & Peterson, S. (2023). Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of a Localized Food System and Food Waste Reduction in a Water-Scarce Region Using Diet Optimization Models. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(10), 5890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105890






