Parents’ Perceptions of Changes in Sleep Duration, Physical Activity, and Sedentary Behavior in Arab Israeli Children during the COVID-19 Outbreak
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (i)
- Were there alterations in physical activity, sedentary behaviors, and sleep duration among Arab Israeli children during the COVID-19 outbreak, according to the perception of their parents?;
- (ii)
- What is the prevalence of children who met the 24 h movement guidelines, in general and during the COVID-19 outbreak?;
- (iii)
- Were there differences between boys and girls or between 3–4-year-old children and 5–13-year-old children in physical activity, sedentary behavior, sleep duration, and meeting the 24 h movement guidelines before and during the COVID-19 outbreak?
- (i)
- We hypothesized that Arab Israeli parents would report negative changes in their children’s physical activity, sedentary behaviors, and sleep duration during the COVID-19 outbreak;
- (ii)
- We hypothesized that the prevalence of children who met the 24 h movement guidelines in general was greater than during the COVID-19 outbreak;
- (iii)
- We hypothesized that boys and 5–13 years old were, negatively, more affected than girls and 3–4-year-old children during the COVID-19 outbreak in terms of physical activity, sedentary behaviors, and sleep duration.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Setting
2.2. Data Collection Procedure
2.2.1. Physical Activity Measure
2.2.2. Sedentary Behavior Measure
2.2.3. Sleep Duration Measure
2.3. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Sleep Duration Pre- and during COVID-19 Outbreak
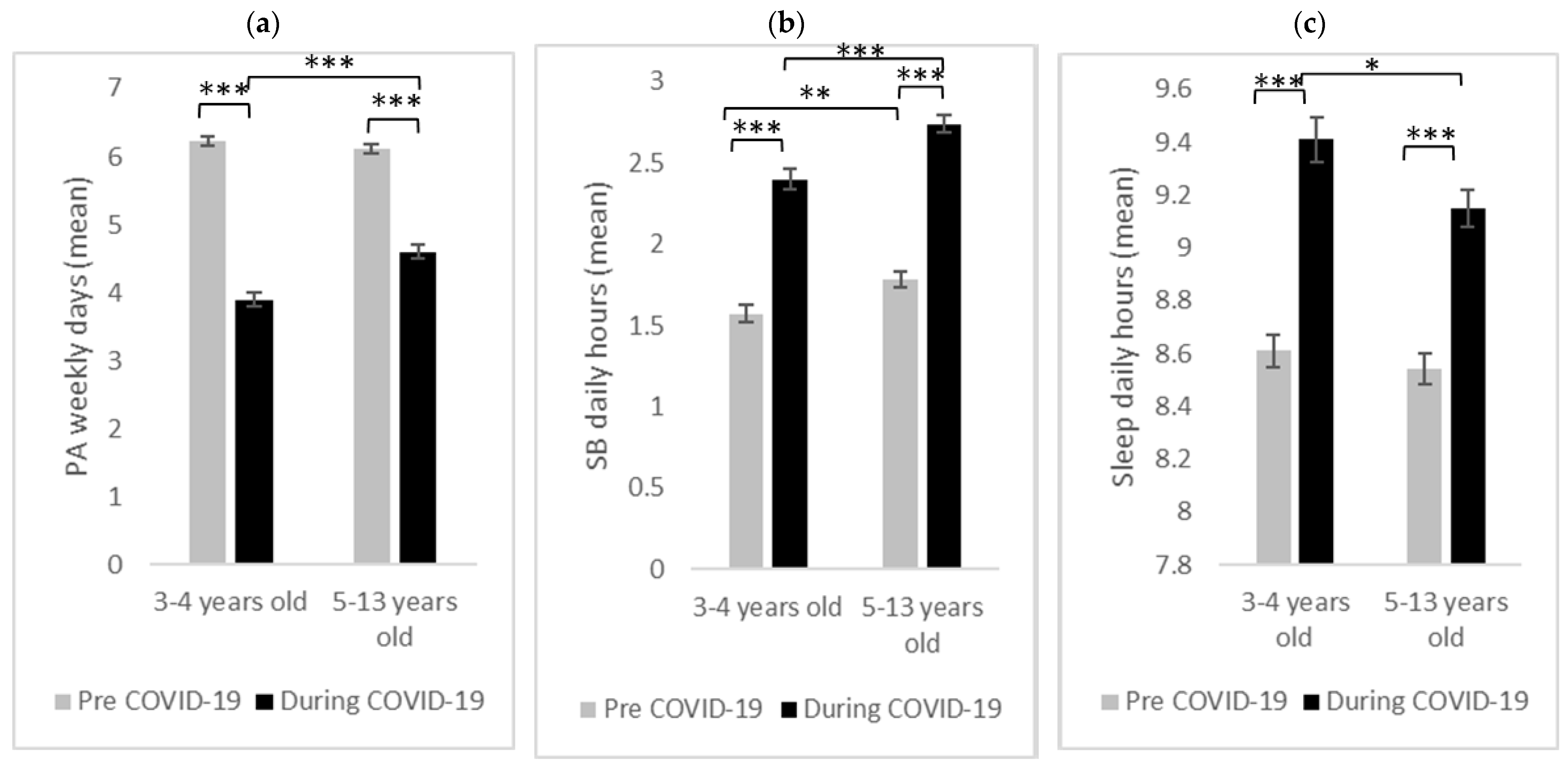
3.2. Age Group Differences
3.2.1. Physical Activity
3.2.2. Sedentary Behavior
3.2.3. Sleep Duration
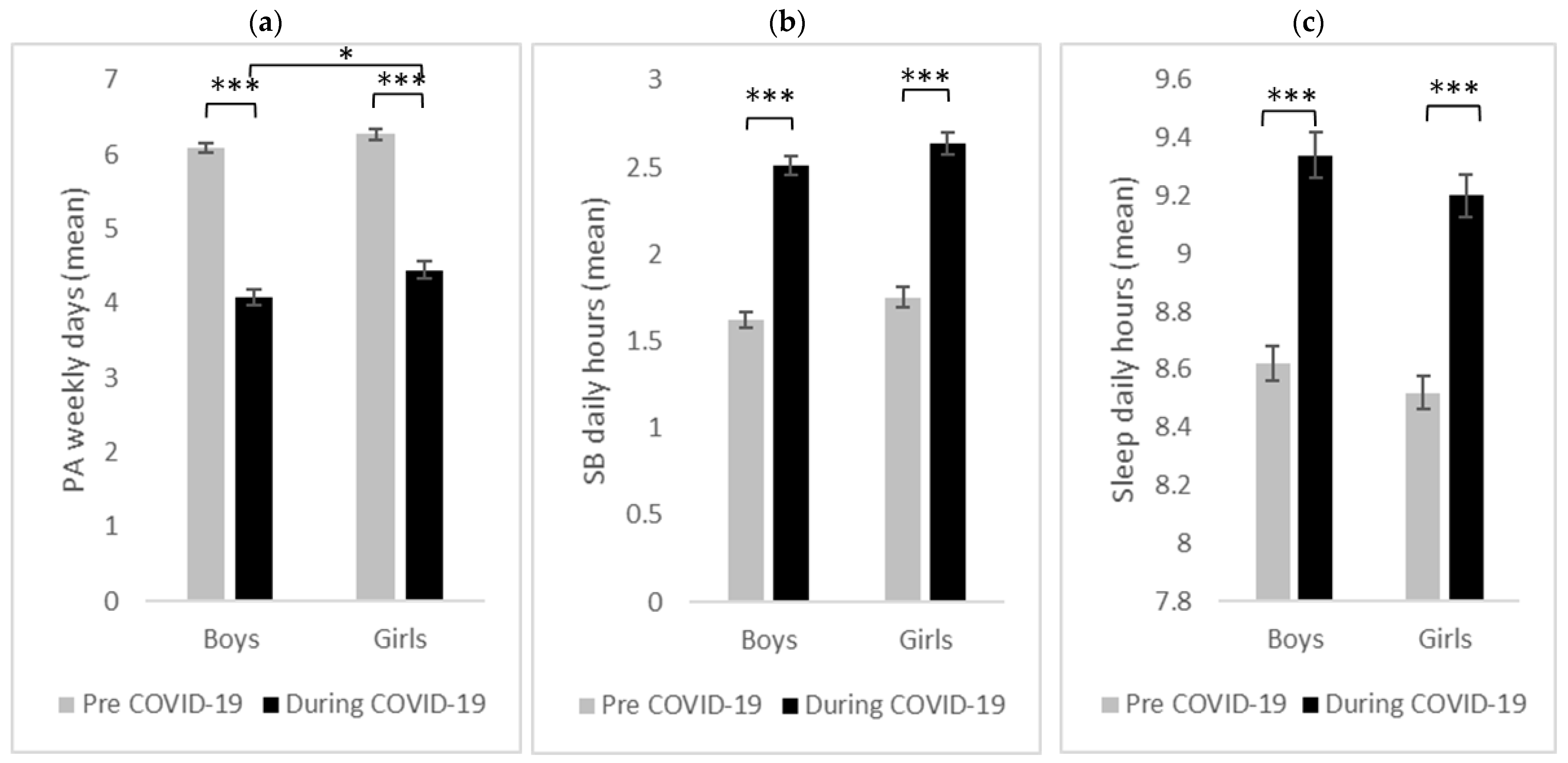
3.3. Gender Differences
3.3.1. Physical Activity
3.3.2. Sedentary Behavior
3.3.3. Sleep Duration
3.4. Proportions Meeting the 24 h Movement Guidelines
3.4.1. Age Group Comparison
3.4.2. Gender Comparison
4. Discussion
4.1. Physical Activity
4.2. Sedentary Behavior
4.3. Sleep Duration
4.4. Limitations and Implications for Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, N.; Zhang, F.; Wei, C.; Jia, Y.; Shang, Z.; Sun, L.; Wu, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Prevalence and predictors of PTSS during COVID-19 outbreak in China hardest-hit areas: Gender differences matter. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 287, 112921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israel Ministry of Health. 2021. Available online: https://www.gov.il/en/departments/topics/corona-main-sub (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Ghanamah, R.; Eghbaria-Ghanamah, H. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Behavioral and Emotional Aspects and Daily Routines of Arab Israeli Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanamah, R.; Eghbaria-Ghanamah, H. The Psychological Effects of Coronavirus on Children in the Perception of Arab Israeli Parents Sample. Child Youth Serv. 2023; 1–21, epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.Y.; Wang, L.N.; Liu, J.; Fang, S.F.; Jiao, F.Y.; Pettoello-Mantovani, M.; Somekh, E. Behavioral and Emotional Disorders in Children during the COVID-19 Epidemic. J. Pediatr. 2020, 221, 264–266.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.A.; Faulkner, G.; Rhodes, R.E.; Brussoni, M.; Chulak-Bozzer, T.; Ferguson, L.J.; Mitra, R.; O’reilly, N.; Spence, J.C.; Vanderloo, L.M.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 virus outbreak on movement and play behaviours of Canadian children and youth: A national survey. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klar, Y.; Mar’i, A.A.-R.; Halabi, S.; Basheer, A.; Basheer, B. Reactions of Arab-Palestinians in Israel Toward an In-group Member Mixing Hebrew or English with Arabic. J. Lang. Soc. Psychol. 2020, 39, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.M.; Doom, J.; Lechuga-Peña, S.; Watamura, S.E.; Koppels, T. Stress and parenting during the global COVID-19 pandemic. Child Abus. Negl. 2020, 110, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, A. COVID-19: Medical conferences around the world are cancelled after US cases are linked to Massachusetts meeting. BMJ 2020, 368, m1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yancy, C.W. COVID-19 and African Americans. JAMA 2020, 323, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katz, C.; Cohen, N. Invisible children and non-essential workers: Child protection during COVID-19 in Israel according to policy documents and media coverage. Child Abus. Negl. 2021, 116, 104770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saban, M.; Myers, V.; Shachar, T.; Miron, O.; Wilf-Miron, R.R. Effect of Socioeconomic and Ethnic Characteristics on COVID-19 Infection: The Case of the Ultra-Orthodox and the Arab Communities in Israel. J. Racial Ethn. Health Disparities 2020, 9, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.M.; Sadeh, A. Annual Research Review: Sleep problems in childhood psychiatric disorders—A review of the latest science. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2016, 57, 296–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Percze, A.R.; Nagy, A.; Polivka, L.; Barczi, E.; Czaller, I.; Kovats, Z.; Varga, J.T.; Ballai, J.H.; Muller, V.; Horvath, G. Fatigue, sleepiness and sleep quality are SARS-CoV-2 variant independent in patients with long COVID symptoms. Inflammopharmacology, 2023; 1–7, epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Song, Q.; Duan, J.; Liu, C.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, A.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. The impact of impaired sleep quality on symptom change and future exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altena, E.; Baglioni, C.; Espie, C.A.; Ellis, J.; Gavriloff, D.; Holzinger, B.; Schlarb, A.; Frase, L.; Jernelöv, S.; Riemann, D. Dealing with sleep problems during home confinement due to the COVID-19 outbreak: Practical recommendations from a task force of the European CBT-I Academy. J. Sleep Res. 2020, 29, e13052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, S.H.; Williams, J.S.; Hassani, F. Physical activity during COVID-19 quarantine. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 2147–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, V.; Chaput, J.-P.; Janssen, I.; Tremblay, M.S. Health associations with meeting new 24-hour movement guidelines for Canadian children and youth. Prev. Med. 2017, 95, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Carson, V.; Chaput, J.-P.; Gorber, S.C.; Dinh, T.; Duggan, M.; Faulkner, G.; Gray, C.E.; Gruber, R.; Janson, K.; et al. Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for Children and Youth: An Integration of Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour, and Sleep. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, S311–S327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzik, N.; Poitras, V.J.; Tremblay, M.S.; Lee, E.-Y.; Hunter, S.; Carson, V. Systematic review of the relationships between combinations of movement behaviours and health indicators in the early years (0–4 years). BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rollo, S.; Antsygina, O.; Tremblay, M.S. The whole day matters: Understanding 24-hour movement guideline adherence and relationships with health indicators across the lifespan. J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, T.J.; Gray, C.E.; Poitras, V.J.; Chaput, J.-P.; Janssen, I.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Olds, T.; Gorber, S.C.; Kho, M.E.; Sampson, M.; et al. Combinations of physical activity, sedentary behaviour and sleep: Relationships with health indicators in school-aged children and youth. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, S283–S293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallè, F.; Sabella, E.A.; Ferracuti, S.; De Giglio, O.; Caggiano, G.; Protano, C.; Valeriani, F.; Parisi, E.A.; Valerio, G.; Liguori, G.; et al. Sedentary Behaviors and Physical Activity of Italian Undergraduate Students during Lockdown at the Time of COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, L.; Tully, M.A.; Barnett, Y.; Lopez-Sanchez, G.F.; Butler, L.; Schuch, F.; López-Bueno, R.; McDermott, D.; Firth, J.; Grabovac, I.; et al. The relationship between physical activity and mental health in a sample of the UK public: A cross-sectional study during the implementation of COVID-19 social distancing measures. Ment. Health Phys. Act. 2020, 19, 100345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.; Herring, M.; McDowell, C.; Lansing, J.; Brower, C.; Schuch, F.; Smith, L.; Tully, M.; Martin, J.; Caswell, S.; et al. Joint prevalence of physical activity and sitting time during COVID-19 among US adults in April 2020. Prev. Med. Rep. 2020, 20, 101256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gil, J.F.; Tremblay, M.S.; Brazo-Sayavera, J. Changes in Healthy Behaviors and Meeting 24-h Movement Guidelines in Spanish and Brazilian Preschoolers, Children and Adolescents during the COVID-19 Lockdown. Children 2021, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonza, A.; Sá-Caputo, D.D.C.D.; Bachur, J.A.; Araújo, M.D.G.R.D.; Trippo, K.V.T.V.; Gama, D.R.N.d.G.R.N.d.; Borges, D.L.; Mendonça, V.A.; Bernardo-Filho, M. Brazil before and during COVID-19 pandemic: Impact on the practice and habits of physical exercise. Acta Bio Med. Atenei Parm. 2020, 92, e2021027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Kuwahara, K. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on children and adolescents’ lifestyle behavior larger than expected. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 63, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrobelli, A.; Pecoraro, L.; Ferruzzi, A.; Heo, M.; Faith, M.; Zoller, T.; Antoniazzi, F.; Piacentini, G.; Fearnbach, S.N.; Heymsfield, S.B. Effects of COVID-19 Lockdown on Lifestyle Behaviors in Children with Obesity Living in Verona, Italy: A Longitudinal Study. Obesity 2020, 28, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenic, N.; Taiar, R.; Gilic, B.; Blazevic, M.; Maric, D.; Pojskic, H.; Sekulic, D. Levels and Changes of Physical Activity in Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Contextualizing Urban vs. Rural Living Environment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bueno, R.; López-Sánchez, G.F.; Casajús, J.A.; Calatayud, J.; Gil-Salmerón, A.; Grabovac, I.; Tully, M.A.; Smith, L. Health-related behaviors among school-aged children and adolescents during the Spanish COVID-19 confinement. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, R.; Ammar, A.; Maaloul, R.; Souissi, N.; Hammouda, O. Effect of COVID-19-Related Home Confinement on Sleep Quality, Screen Time and Physical Activity in Tunisian Boys and Girls: A Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, F.C.; Yűksel, D.; de Zambotti, M. Sex Differences in Sleep. In Sleep Disorders in Women; Humana: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, M.; Mishra, S.K. Screen time and adiposity among children and adolescents: A systematic review. J. Public Health 2020, 28, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, J.E.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Adair, L.S.; Popkin, B.M. Screen Time and Physical Activity during Adolescence: Longitudinal Effects on Obesity in Young Adulthood. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2007, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boone, J.E.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Adair, L.S.; Popkin, B.M. Cross-sectional Associations between the Screen-time of Parents and Young Children: Differences by Parent and Child Gender and Day of the Week. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnett, T.A.; O’Loughlin, J.; Sabiston, C.M.; Karp, I.; Bélanger, M.; Van Hulst, A.; Lambert, M. Teens and Screens: The Influence of Screen Time on Adiposity in Adolescents. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 172, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dana, A.; Nodeh, H.; Salehian, M.H.; Mokari Saei, S.; Sarvari, S. Smartphone usage status, sleep pattern, health-related quality of life, and physical activity among adolescents from before to during the COVID-19 confinement: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Sch. Health 2022, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dallolio, L.; Marini, S.; Masini, A.; Toselli, S.; Stagni, R.; Bisi, M.C.; Gori, D.; Tessari, A.; Sansavini, A.; Lanari, M.; et al. The impact of COVID-19 on physical activity behaviour in Italian primary school children: A comparison before and during pandemic considering gender differences. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Education. Transparency in Education. 2023. Available online: https://shkifut.education.gov.il/national (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- Prochaska, J.J.; Sallis, J.F.; Long, B. A physical activity screening measure for use with adolescents in primary care. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2001, 155, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour and Sleep for Children under 5 Years of Age; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Chambonniere, C.; Lambert, C.; Fearnbach, N.; Tardieu, M.; Fillon, A.; Genin, P.; Larras, B.; Melsens, P.; Bois, J.; Pereira, B.; et al. Effect of the COVID-19 lockdown on physical activity and sedentary behaviors in French children and adolescents: New results from the ONAPS national survey. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 43, 101308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, R.; Pedro, M.; Delvecchio, E.; Espada, J.P.; Morales, A.; Mazzeschi, C.; Orgilés, M. Psychological Symptoms and Behavioral Changes in Children and Adolescents During the Early Phase of COVID-19 Quarantine in Three European Countries. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 570164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano, M.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Oses, M.; Arenaza, L.; Amasene, M.; Labayen, I. Changes in lifestyle behaviours during the COVID -19 confinement in Spanish children: A longitudinal analysis from the MUGI project. Pediatr. Obes. 2021, 16, e12731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, M.D.; Vanderloo, L.M.; Rhodes, R.E.; Faulkner, G.; Moore, S.A.; Tremblay, M.S. Canadian children’s and youth’s adherence to the 24-h movement guidelines during the COVID-19 pandemic: A decision tree analysis. J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, L.C.; Zieff, G.; Stanford, K.; Moore, J.B.; Kerr, Z.Y.; Hanson, E.D.; Barone Gibbs, B.; Kline, C.E.; Stoner, L. COVID-19 Impact on Behaviors across the 24-Hour Day in Children and Adolescents: Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Sleep. Children 2020, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Farias, N.; Toledo-Vargas, M.; Miranda-Marquez, S.; Cortinez-O’Ryan, A.; Cristi-Montero, C.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, F.; Martino-Fuentealba, P.; Okely, A.B.; Del Pozo Cruz, B. Sociodemographic Predictors of Changes in Physical Activity, Screen Time, and Sleep among Toddlers and Preschoolers in Chile during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hands, B.P.; Chivers, P.; Parker, H.E.; Beilin, L.; Kendall, G.; Larkin, D. The associations between physical activity, screen time and weight from 6 to 14 yrs: The Raine Study. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2011, 14, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, P.; Elshaug, C.; Leslie, E.; Toumbourou, J.W.; Patton, G.C.; Williams, J. Physical activity, leisure-time screen use and depression among children and young adolescents. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2014, 17, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twenge, J.M.; Campbell, W.K. Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Prev. Med. Rep. 2018, 12, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deslandes, S.F.; Coutinho, T. The intensive use of the internet by children and adolescents in the context of COVID-19 and the risks for self-inflicted violence. Ciência Saúde Coletiva 2020, 25, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zreik, G.; Asraf, K.; Haimov, I.; Tikotzky, L. Maternal perceptions of sleep problems among children and mothers during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic in Israel. J. Sleep Res. 2021, 30, 13201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedrone, F.; Buomprisco, G.; Nicola, M.; La Torre, G.; Nieto, H.; Perri, R.; Montagna, V.; Greco, E.; De Sio, S. Alcohol Use during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Survey among Healthcare and Office Workers in Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgilés, M.; Morales, A.; Delvecchio, E.; Mazzeschi, C.; Espada, J.P. Immediate Psychological Effects of the COVID-19 Quarantine in Youth from Italy and Spain. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 579038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-F.; Liao, M.-Q.; Cai, W.-L.; Yu, X.-X.; Li, S.-N.; Ke, X.-Y.; Tan, S.-X.; Luo, Z.-Y.; Cui, Y.-F.; Wang, Q.; et al. Physical activity, screen exposure and sleep among students during the pandemic of COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, A.; George, P.; Ng, M.; Wenden, E.; Bai, P.; Phiri, Z.; Christian, H. Impact of COVID-19 Restrictions on Western Australian Children’s Physical Activity and Screen Time. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 490) | 3–4 Years Old (n = 246) | 5–13 Years Old (n = 244) | Test a (Effect Size b) | Males (n = 273) | Females (n = 217) | Test a (Effect size b) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parents | |||||||
| Female [N(%)] | 418 (85.3) | 214 (87) | 204 (83.6) | 1.12 (0.05) | 229 (83.9) | 189 (87.1) | 0.99 (0.05) |
| Age [M] | 38.77 | 37.01 | 40.56 | 1.05 (0.13) | 38.60 | 38.98 | 1.01 (0.12) |
| Education [N(%)] | 20.55 (0.21) | 36.50 (0.27) | |||||
| ≤Secondary BA degree ≥MA degree | 181 (36.9) 174(35.5) 135 (27.6) | 111 (45.1) 87 (35.3) 48 (19.5) | 70 (28.6) 87 (35.7) 87 (35.7) | 126 (46.1) 99 (36.2) 48 (17.5) | 55 (25.3) 75 (34.6) 87 (40.1) | ||
| Working (yes) | 372 (75.9) | 182 (74) | 190 (77.9) | 1.01 (0.05) | 208 (76.2) | 164 (75.6) | 0.03(0) |
| Was a member of your family diagnosed with COVID-19? (yes) | 191 (39) | 99 (40.2) | 92 (37.7) | 1.50 (0.08) | 105 (38.5) | 86 (39.6) | 0.39 (0.04) |
| Was a member of your family in isolation? (yes) | 354 (72.2) | 180 (73.2) | 174 (71.3) | 0.15 (0.02) | 209 (76.6) | 154 (71) | 1.01 (0.06) |
| Children | |||||||
| Male [N(%)] | 273 (55.7) | 137 (55.7) | 136 (55.7) | 0.01 (0) | |||
| Age [M (SD)] | 3.18 (0.49) | 7.25 (0.84) | |||||
| Age Level | 0.64 (0.05) | ||||||
| 3–4 years old | 246 (50.2) | 116 (47.1) | 130 (52.8) | ||||
| Diagnosed with COVID-19 | 63 (12.9) | 35 (14.2) | 28 (11.5) | 0.44 (0.04) | 37 (13.5) | 26 (12) | 0.39 (0.04) |
| Asked to be in isolation | 243 (49.6) | 122 (49.5) | 121 (49.6) | 0.01 (0) | 136 (49.8) | 107 (49.3) | 0.02 (0.01) |
| Measure | Total (n = 490) | 3–4 Years Old (n = 246) | 5–13 Years Old (n = 244) | Boys (n = 273) | Girls (n = 217) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre M (SD) | During M (SD) | Pre M (SD) | During M (SD) | Pre M (SD) | During M (SD) | Pre M (SD) | During M (SD) | Pre M (SD) | During M (SD) | |
| Physical activity (days per week) | 6.17 (1.50) | 4.24 (1.71) | 6.23 (1.13) | 3.89 (1.65) | 6.11 (1.67) | 4.60 (1.71) | 6.09 (1.17) | 4.08 (1.67) | 6.27 (1.12) | 4.45 (1.74) |
| Sedentary behavior (hours per day) | 1.68 (0.82) | 2.57 (0.90) | 1.57 (0.85) | 2.40 (0.95) | 1.78 (0.78) | 2.74 (0.81) | 1.62 (0.79) | 2.51 (0.88) | 1.75 (0.87) | 2.64 (0.94) |
| Sleep duration (hours per day) | 8.57 (0.92) | 9.28 (1.21) | 8.61 (0.95) | 9.41 (1.30) | 8.54 (0.91) | 9.15 (1.11) | 8.62 (0.99) | 9.34 (1.32) | 8.52 (0.84) | 9.20 (1.07) |
| Total % (n = 490) | 3–4 Years Old % (n = 246) | 5–13 Years Old % (n = 244) | t (p, d) | Boys % (n = 273) | Girls % (n = 217) | t (p, d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before COVID-19 Outbreak | |||||||
| PA | 59.2 | 61.8 | 56.6 | 1.18 (0.240, 0.11) | 54.6 | 65 | −2.33 (0.020, 0.21) |
| SB | 60 | 53.2 | 66.8 | −3.09 (0.002, 0.28) | 61.5 | 58.1 | 0.78 (0.437, 0.07) |
| SD | 36.1 | 28 | 44.3 | −3.78 (<0.001, 0.34) | 39.9 | 31.3 | 1.97 (0.049, 0.18) |
| 24 h combined | 12 | 7.7 | 16.4 | −2.97 (0.003, 0.27) | 12.8 | 11.1 | 0.59 (0.533, 0.05) |
| During COVID-19 Outbreak | |||||||
| PA | 20.6 ↓ | 16.3 ↓ | 25 ↓ | −2.40 (0.017, 0.22) | 17.9 ↓ | 24 ↓ | 1.64 (0.102, 0.15) |
| SB | 20.8 ↓ | 21.5 ↓ | 20.1 ↓ | 0.40 (0.691, 0.04) | 19.4 ↓ | 22.6 ↓ | −0.86 (0.392, 0.08) |
| SD | 56.1 ↑ | 50.8 ↑ | 61.5 ↑ | −2.38 (0.017, 0.22) | 65.4 ↑ | 55.8 ↑ | 0.14 (0.886, 0.01) |
| 24 h combined | 3.1 ↓ | 2.4 ↓ | 3.7 ↓ | −0.80 (0.423, 0.07) | 2.2 ↓ | 4.1 ↓ | −1.24 (0.214, 0.11) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghanamah, R.; Eghbaria-Ghanamah, H.; Abu-Saleh, N.; Kitany, S. Parents’ Perceptions of Changes in Sleep Duration, Physical Activity, and Sedentary Behavior in Arab Israeli Children during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20116041
Ghanamah R, Eghbaria-Ghanamah H, Abu-Saleh N, Kitany S. Parents’ Perceptions of Changes in Sleep Duration, Physical Activity, and Sedentary Behavior in Arab Israeli Children during the COVID-19 Outbreak. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(11):6041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20116041
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhanamah, Rafat, Hazar Eghbaria-Ghanamah, Nabil Abu-Saleh, and Sujood Kitany. 2023. "Parents’ Perceptions of Changes in Sleep Duration, Physical Activity, and Sedentary Behavior in Arab Israeli Children during the COVID-19 Outbreak" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 11: 6041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20116041
APA StyleGhanamah, R., Eghbaria-Ghanamah, H., Abu-Saleh, N., & Kitany, S. (2023). Parents’ Perceptions of Changes in Sleep Duration, Physical Activity, and Sedentary Behavior in Arab Israeli Children during the COVID-19 Outbreak. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(11), 6041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20116041






