Examining the Effects of Gestational Physical Activity and Hofbauer Cell Polarization on Angiogenic Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Recruitment and Ethical Approval
2.2. Accelerometry Data Capture
2.3. Collection of Term Placenta Samples
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Hofbauer Cell Culture
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6.1. In Vitro Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6.2. In Vivo Immunofluorescence Staining
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Demographics
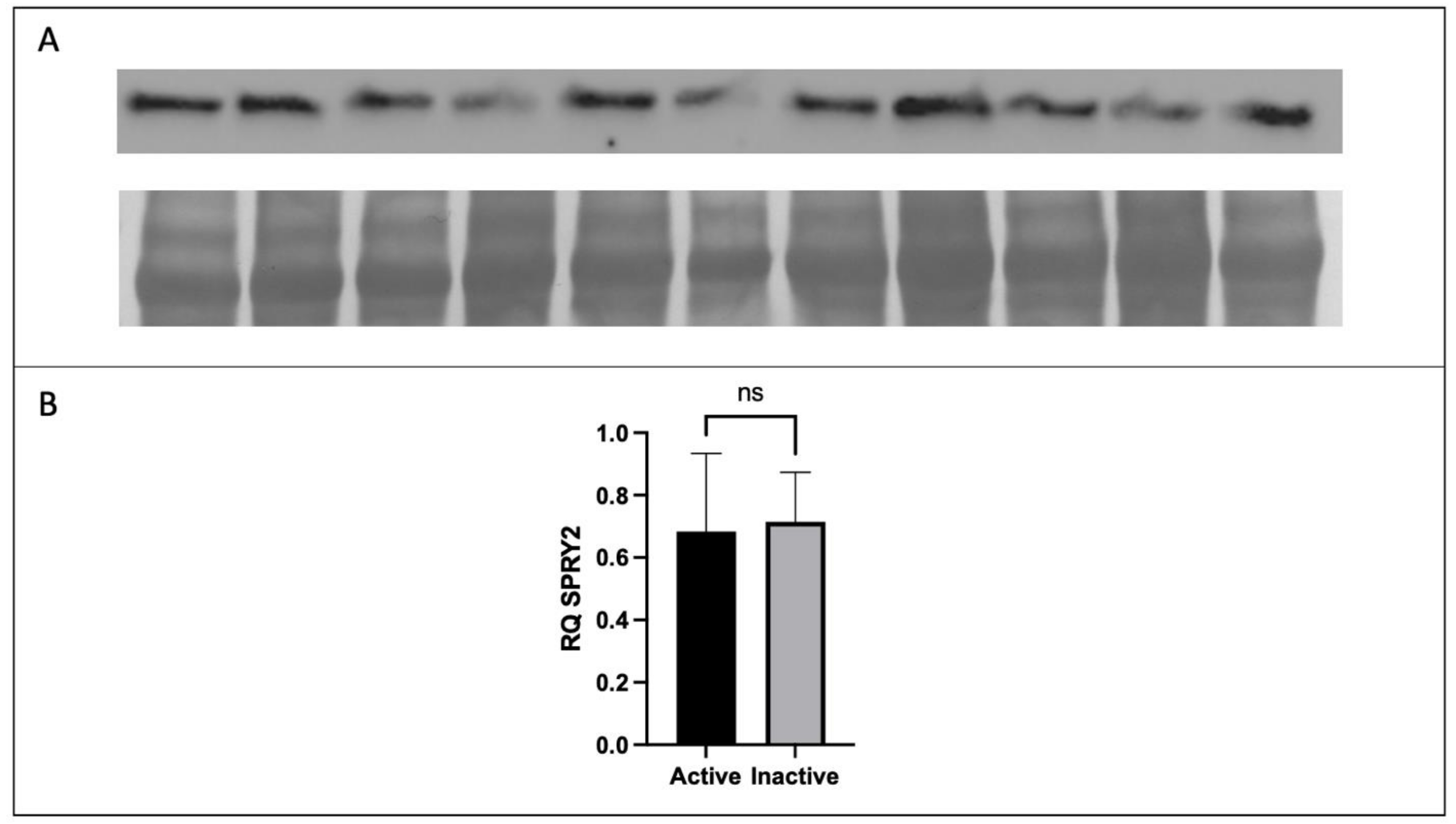
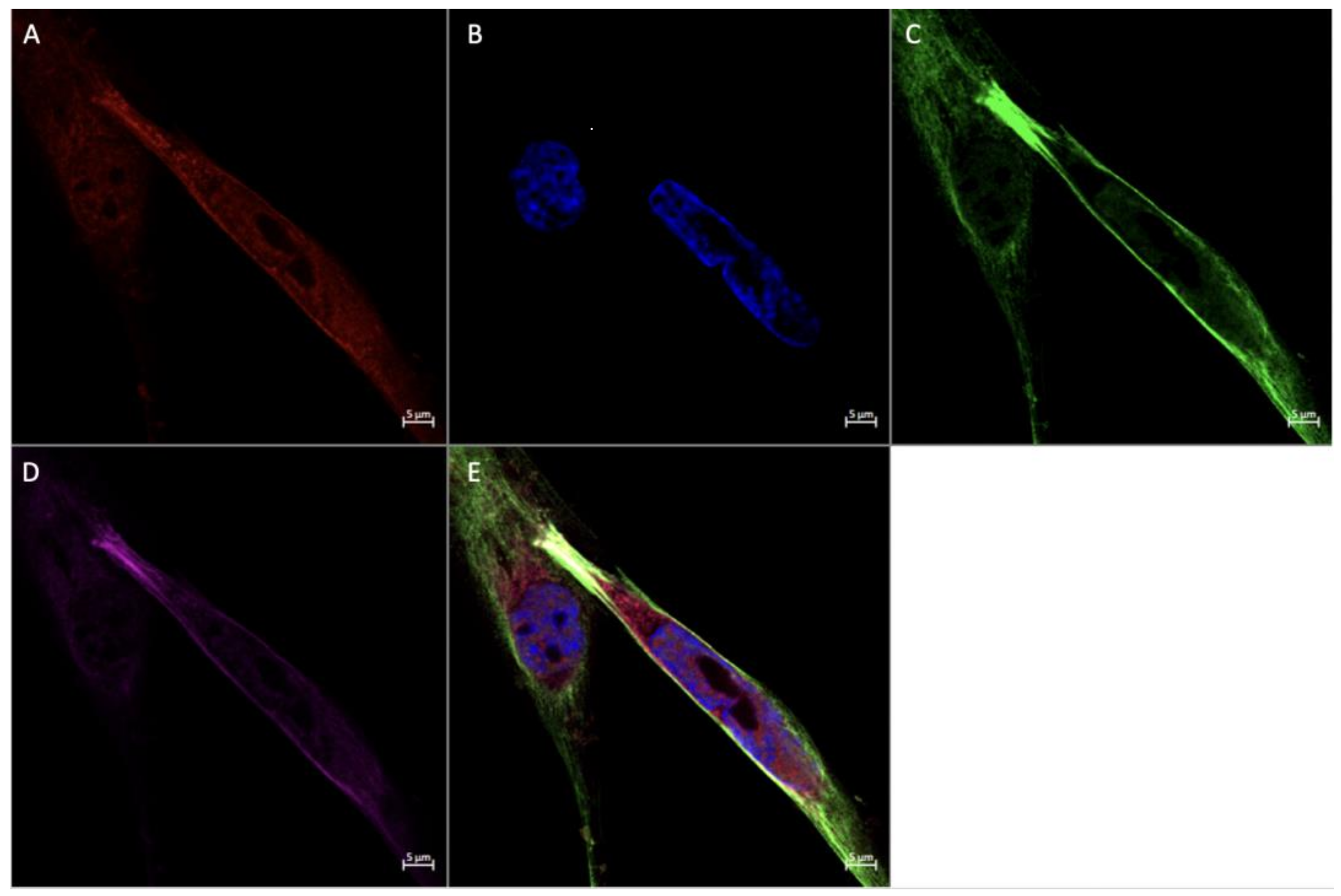
3.2. Expression of FGF2 and SPRY2 in Term Placenta
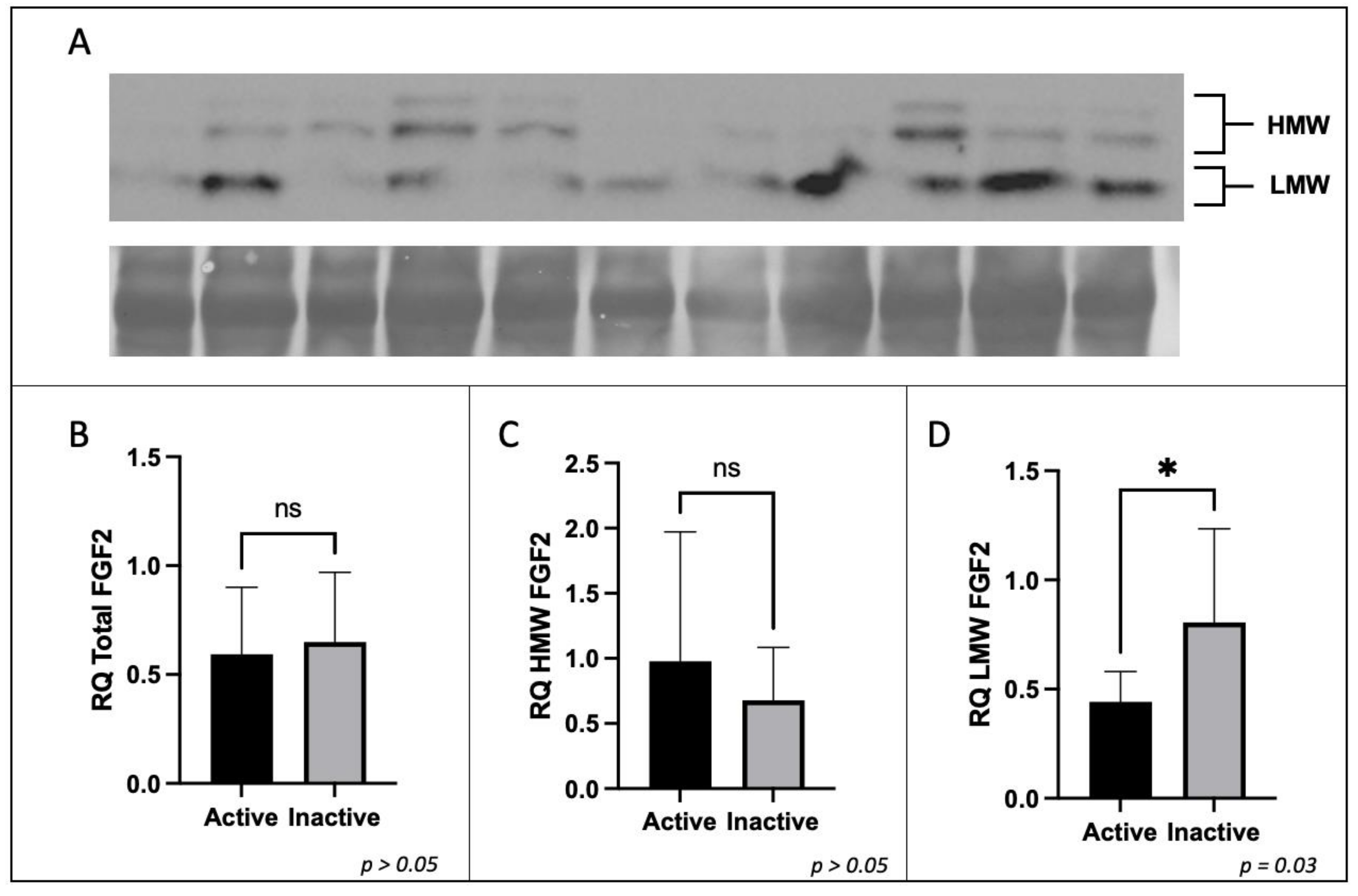
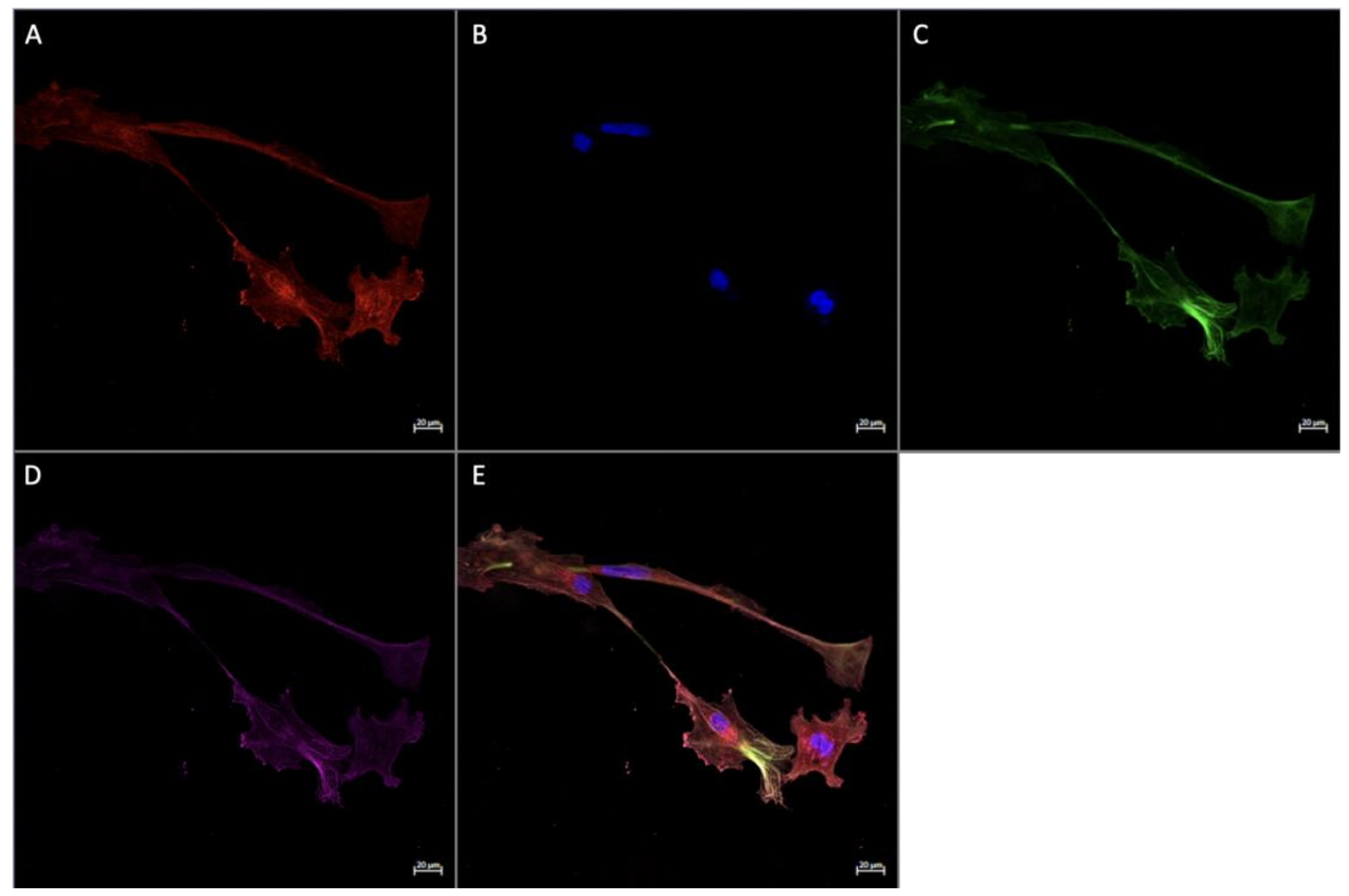
3.3. Expression of FGF2 in Term Placenta
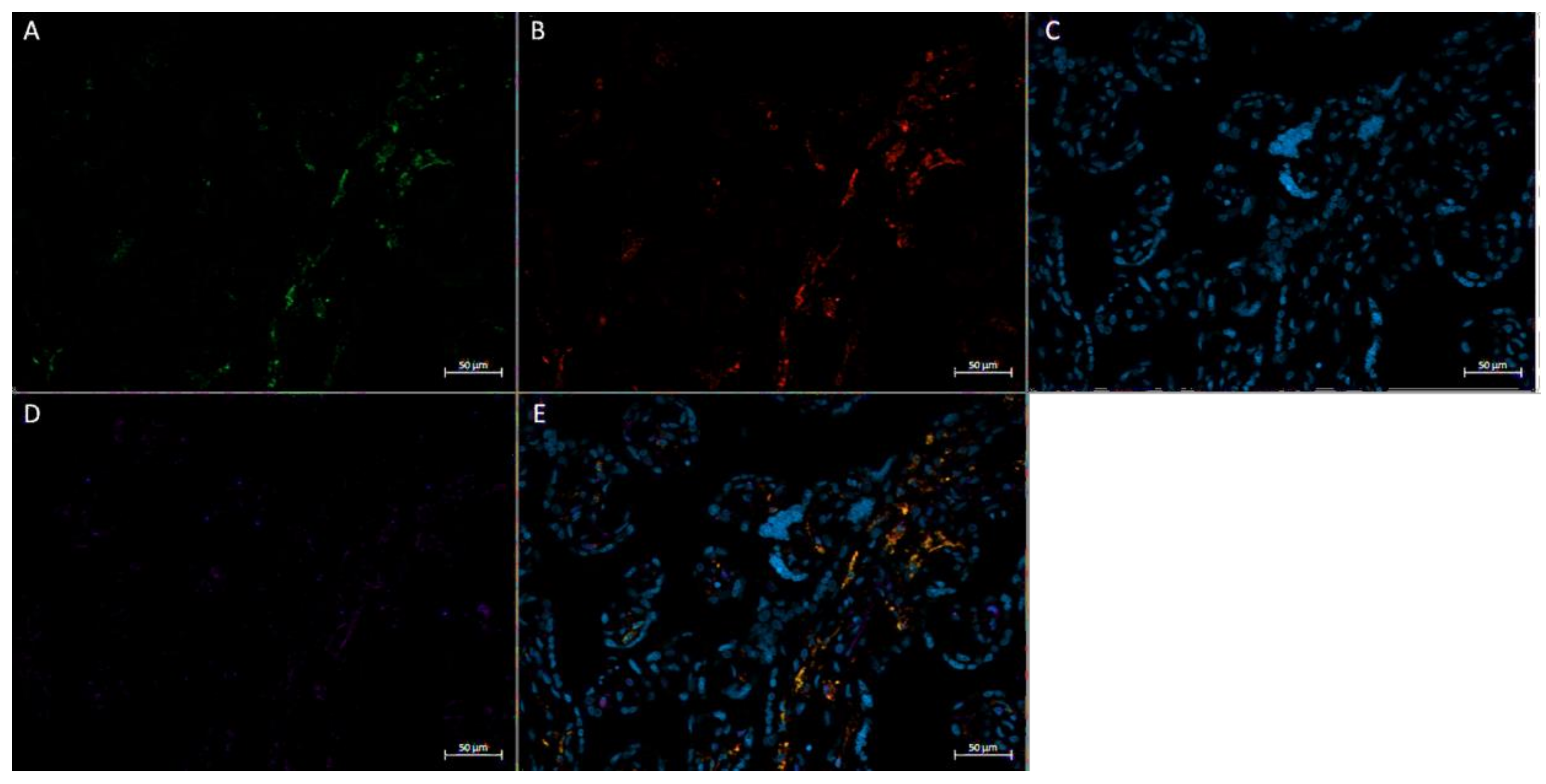
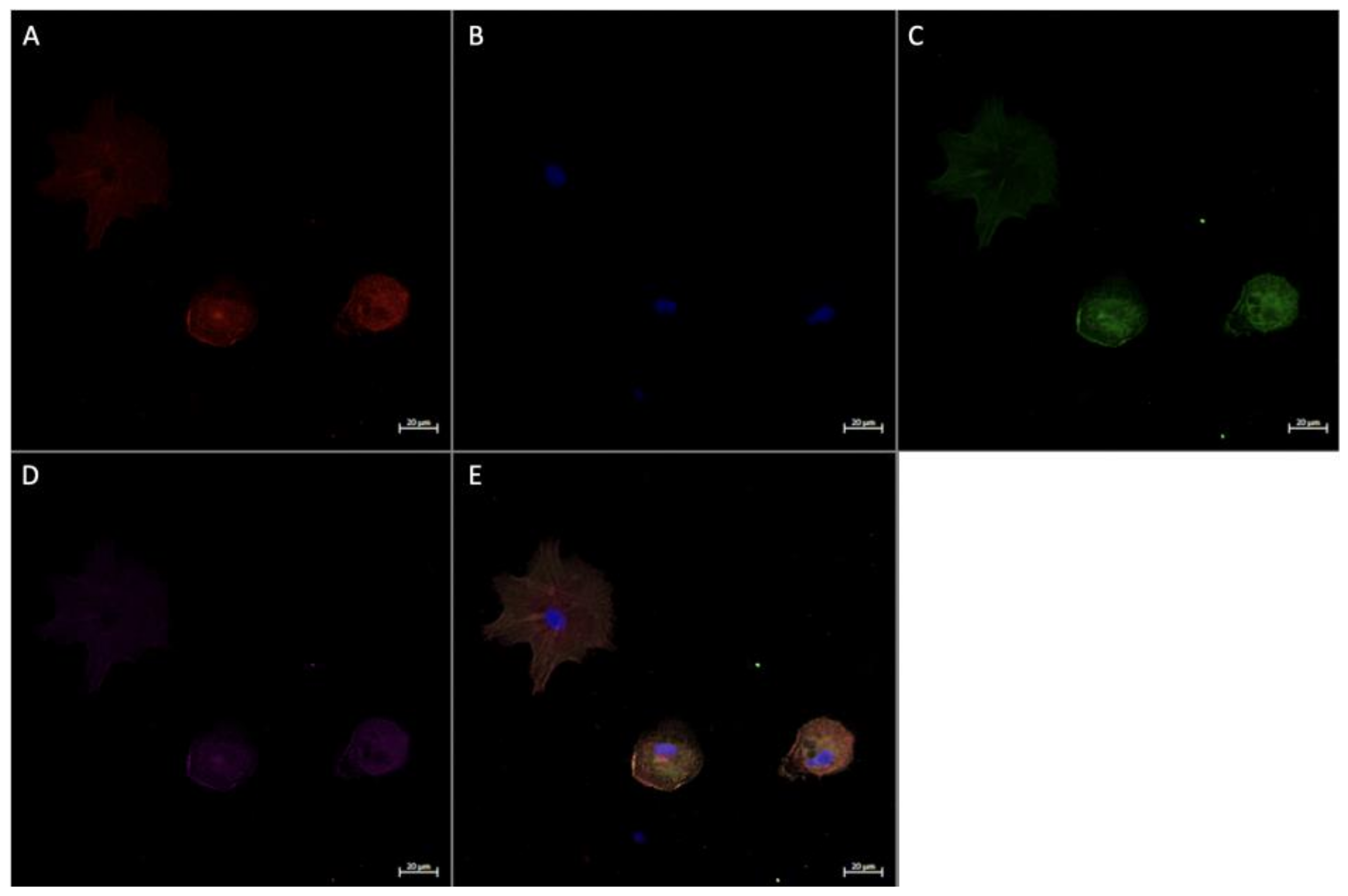
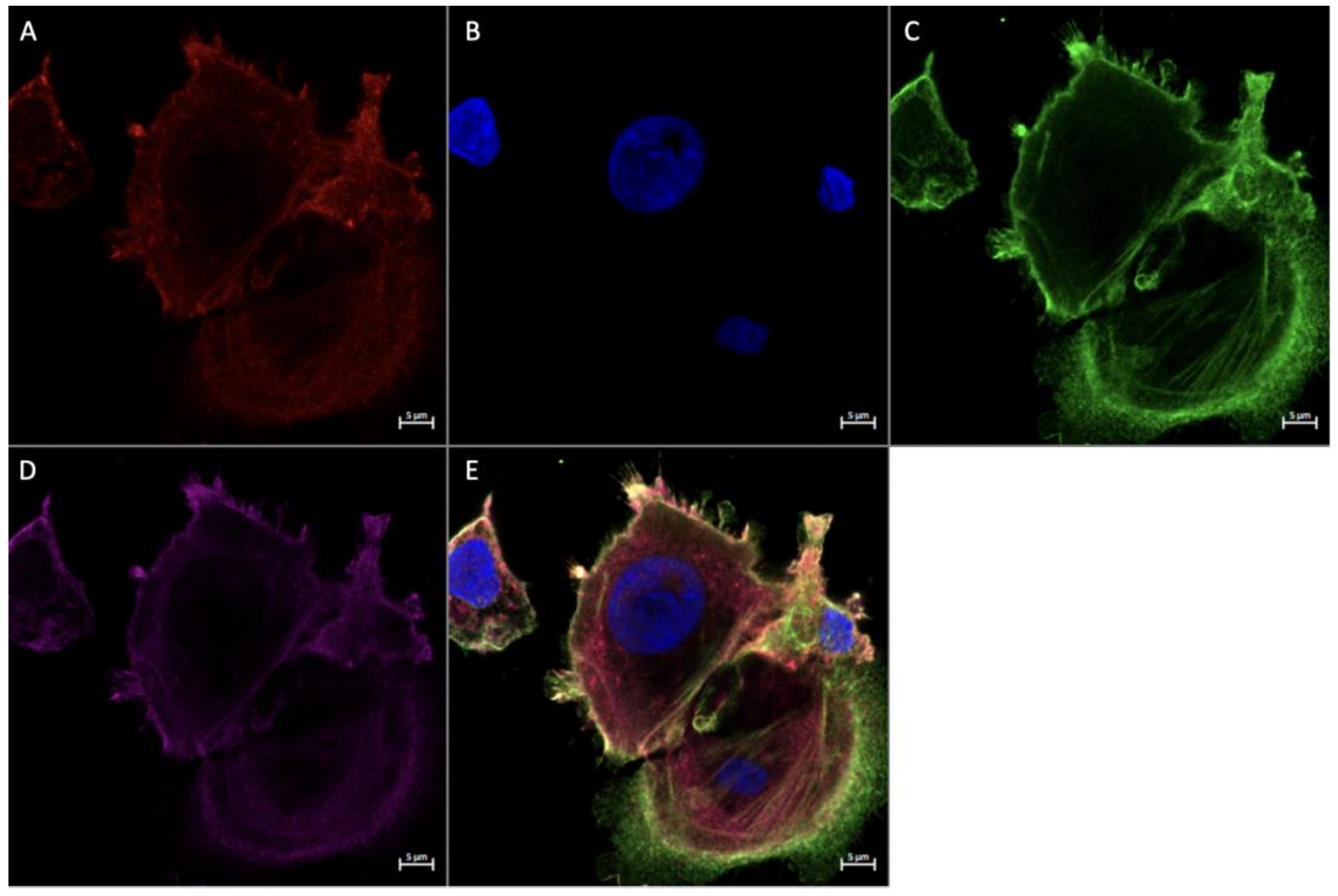
3.4. Expression of Angiogenic Markers in Cultured Hofbauer Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mottola, M.F.; Davenport, M.H.; Ruchat, S.M.; Davies, G.A.; Poitras, V.J.; Gray, C.E.; Garcia, A.J.; Barrowman, N.; Adamo, K.B.; Duggan, M.; et al. 2019 Canadian guideline for physical activity throughout pregnancy. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zulu, M.Z.; Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S.; Gray, C.M. The Elusive Role of Placental Macrophages: The Hofbauer Cell. J. Innate Immun. 2019, 11, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.R.; Appios, A.; Zhao, X.; Dutkiewicz, R.; Donde, M.; Lee, C.Y.C.; Naidu, P.; Lee, C.; Cerveira, J.; Liu, B.; et al. Phenotypic and functional characterization of first-trimester human placental macrophages, Hofbauer cells. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20200891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakonti, G.; Pantazi, P.; Bokun, V.; Holder, B. Placental Macrophage (Hofbauer Cell) Responses to Infection During Pregnancy: A Systematic Scoping Review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 756035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loegl, J.; Hiden, U.; Nussbaumer, E.; Schliefsteiner, C.; Cvitic, S.; Lang, I.; Wadsack, C.; Huppertz, B.; Desoye, G. Hofbauer cells of M2a, M2b and M2c polarization may regulate feto-placental angiogenesis. Reproduction 2016, 152, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schliefsteiner, C.; Peinhaupt, M.; Kopp, S.; Lögl, J.; Lang-Olip, I.; Hiden, U.; Heinemann, A.; Desoye, G.; Wadsack, C. Human Placental Hofbauer Cells Maintain an Anti-inflammatory M2 Phenotype despite the Presence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degner, K.; Magness, R.R.; Shah, D.M. Establishment of the Human Uteroplacental Circulation: A Historical Perspective. Reprod. Sci. 2017, 24, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vailhé, B.; Vittet, D.; Feige, J.-J. In Vitro Models of Vasculogenesis and Angiogenesis. Lab. Investig. 2001, 81, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reyes, L.; Golos, T.G. Hofbauer Cells: Their Role in Healthy and Complicated Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anteby, E.; Natanson-Yaron, S.; Greenfield, C.; Goldman-Wohl, D.; Haimov-Kochman, R.; Holzer, H.; Yagel, S. Human Placental Hofbauer Cells Express Sprouty Proteins: A Possible Modulating Mechanism of Villous Branching. Placenta 2005, 26, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.-J.; Ferrari, G.; Galloway, A.C.; Mignatti, P.; Pintucci, G. Basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2): The high molecular weight forms come of age. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 100, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Tian, X.Y. The Role of Macrophages in Vascular Repair and Regeneration after Ischemic Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, J.; Mohammad, S.; Goudreau, A.D.; Adamo, K.B. Physical activity differentially regulates VEGF, PlGF, and their receptors in the human placenta. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudreau, A.D.; Everest, C.; Tanara, L.; Tzaneva, V.; Adamo, K.B. Characterization of Hofbauer cell polarization and VEGF localization in human term placenta from active and inactive pregnant individuals. Physiol. Rep. 2023, 11, e15741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.F.; Mohammad, S.; Nagpal, T.S.; Souza, S.C.S.; Colley, R.C.; Adamo, K.B. How Many Valid Days Are Necessary to Assess Physical Activity Data from Accelerometry During Pregnancy? J. Phys. Act. Health. 2021, 18, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Gorber, S.C. Canadian Health Measures Survey: Brief Overview. Can. J. Public. Health. 2007, 98, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuuli, M.; Longtine, M.; Nelson, D. Review: Oxygen and trophoblast biology—A source of controversy. Placenta 2011, 32, S109–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.K.; Dick, A.D.; Bates, D.O.; Nicholson, L.B. VEGF Production in Macrophages Is Enhanced by Anti-Inflammatory Stimuli. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3758. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, S.K.; Campbell, J.P. Placental structure, function and drug transfer. Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain. 2015, 15, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burton, G.J.; Fowden, A.L. The placenta: A multifaceted, transient organ. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cackowski, F.C.; Anderson, J.L.; Patrene, K.D.; Choksi, R.J.; Shapiro, S.D.; Windle, J.J.; Blair, H.C.; Roodman, G.D. Osteoclasts are important for bone angiogenesis. Blood 2010, 115, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almatroodi, S.A.; McDonald, C.F.; Pouniotis, D.S. Alveolar Macrophage Polarisation in Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer Int. 2014, 2014, 721087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasko, R.; Bridges, K.; Pannone, R.; Sidhu, I.; Xing, Y.; Naik, S.; Miller-Jensen, K.; Horsley, V. Langerhans cells are essential components of the angiogenic niche during murine skin repair. Dev. Cell. 2022, 57, 2699–2713.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Gu, R.; Zhang, M.; Ren, H.; Shu, Q.; Xu, G.; Wu, H. Microglia enhanced the angiogenesis, migration and proliferation of co-cultured RMECs. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018, 18, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, R.; Eriksson, A.; Kubo, H.; Alitalo, K.; Cao, Y.; Thyberg, J. Comparative Evaluation of FGF-2–, VEGF-A–, and VEGF-C–Induced Angiogenesis, Lymphangiogenesis, Vascular Fenestrations, and Permeability. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, H.; He, L.; Zhou, L.; Wu, W. Effect of VEGF on Inflammatory Regulation, Neural Survival, and Functional Improvement in Rats following a Complete Spinal Cord Transection. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goudreau, A.D.; Everest, C.; Nagpal, T.S.; Puranda, J.L.; Bhattacharjee, J.; Vasanthan, T.; Adamo, K.B. Elucidating the interaction between maternal physical activity and circulating myokines throughout gestation: A scoping review. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2021, 86, e13488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y.; Tran, T.; Tan, K.S.; Wang, D.-Y.; Yan, Y. FGF2, an Immunomodulatory Factor in Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanafusa, H.; Torii, S.; Yasunaga, T.; Nishida, E. Sprouty1 and Sprouty2 provide a control mechanism for the Ras/MAPK signalling pathway. Nature 2002, 4, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Patel, R.; Ahmad, I.; Fleming, J.; Edwards, J.; McCracken, S.; Sahadevan, K.; Seywright, M.; Norman, J.; Sansom, O.; et al. SPRY2 loss enhances ErbB trafficking and PI3K/AKT signalling to drive human and mouse prostate carcinogenesis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, S.; Reddi, A.L.; Aggarwal, P.; Ambardekar, C.; Canciani, B.; Kim, M.K.; Hix, L.; Vilimas, T.; Mason, J.M.; Basson, M.A.; et al. Sprouty Proteins Inhibit Receptor-mediated Activation of Phosphatidylinositol-specific Phospholipase C. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2010, 21, 3487–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadeau, R.J.; Toher, J.L.; Yang, X.; Kovalenko, D.; Friesel, R. Regulation of Sprouty2 stability by mammalian Seven-in-Absentia homolog 2. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 100, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsavachidou, D.; Coleman, M.L.; Athanasiadis, G.; Li, S.; Licht, J.D.; Olson, M.F.; Weber, B.L. SPRY2 Is an Inhibitor of the Ras/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Pathway in Melanocytes and Melanoma Cells with Wild-Type BRAF but Not with the V599E Mutant. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5556–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.-L.; Boon, L.M.; Vikkula, M. Vascular Anomalies Caused by Abnormal Signaling within Endothelial Cells: Targets for Novel Therapies. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 34, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Olabi, L.; Polubothu, S.; Dowsett, K.; Andrews, K.A.; Stadnik, P.; Joseph, A.P.; Knox, R.; Pittman, A.; Clark, G.; Baird, W. Mosaic RAS/MAPK variants cause sporadic vascular malformations which respond to targeted therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1496–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Y.; Yang, Z.; Han, B. Switch of macrophage fusion competency by 3D matrices. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, N.; Verbruggen, S.; Gijbels, M.J.; Post, M.J.; De Winther, M.P.J.; Donners, M.M.P.C. Anti-inflammatory M2, but not pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote angiogenesis in vivo. Angiogenesis 2013, 17, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesson, A.M.; Fear, W.R.; Kazazi, F.; Mathijs, J.-M.; Chang, J.; King, N.J.C.; Cunningham, A.L. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection of Human Placental Macrophages In Vitro. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 168, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Bosshardt, D.D. Multinucleated Giant Cells: Good Guys or Bad Guys? Tissue Eng. Part. B Rev. 2018, 24, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Inclusion Criteria | Inactive |
|---|---|
|
|
| Active (n = 10) | Inactive (n = 7) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal demographics | |||
| Maternal age (years) | 32.50 ± 3.14 | 32.29 ± 2.69 | 0.8854 |
| Height (cm) | 165.80 ± 6.77 | 167.19 ± 8.68 | 0.7163 |
| Pre-pregnancy weight (kg) | 64.44 ± 10.87 | 67.64 ± 15.87 | 0.6271 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | 23.39 ± 2.80 | 23.94 ± 3.48 | 0.7219 |
| Gestational age at birth (weeks) | 40.47 ± 0.90 | 41.02 ± 0.49 | 0.1658 |
| Mid gestation MVPA (min/day) | 46.79 ± 10.23 | 6.44 ± 4.01 | <0.0001 |
| Late gestation MVPA (min/day) | 34.65 ± 9.50 | 3.34 ± 3.43 | <0.0001 |
| Newborn outcomes | |||
| Birth weight (kg) | 3.31 ± 0.38 | 3.75 ± 0.23 | 0.0169 |
| Birth length (cm) | 50.13 ± 2.46 | 52.69 ± 1.39 | 0.0260 |
| Sex, n | |||
| Male | 6 | 3 | |
| Female | 4 | 4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goudreau, A.D.; Tanara, L.; Tzaneva, V.; Adamo, K.B. Examining the Effects of Gestational Physical Activity and Hofbauer Cell Polarization on Angiogenic Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20136298
Goudreau AD, Tanara L, Tzaneva V, Adamo KB. Examining the Effects of Gestational Physical Activity and Hofbauer Cell Polarization on Angiogenic Factors. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(13):6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20136298
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoudreau, Alexandra D., Layli Tanara, Velislava Tzaneva, and Kristi B. Adamo. 2023. "Examining the Effects of Gestational Physical Activity and Hofbauer Cell Polarization on Angiogenic Factors" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 13: 6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20136298
APA StyleGoudreau, A. D., Tanara, L., Tzaneva, V., & Adamo, K. B. (2023). Examining the Effects of Gestational Physical Activity and Hofbauer Cell Polarization on Angiogenic Factors. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(13), 6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20136298









