Assessment of Electrical Brain Activity of Healthy Volunteers Exposed to 3.5 GHz of 5G Signals within Environmental Levels: A Controlled–Randomised Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Volunteers
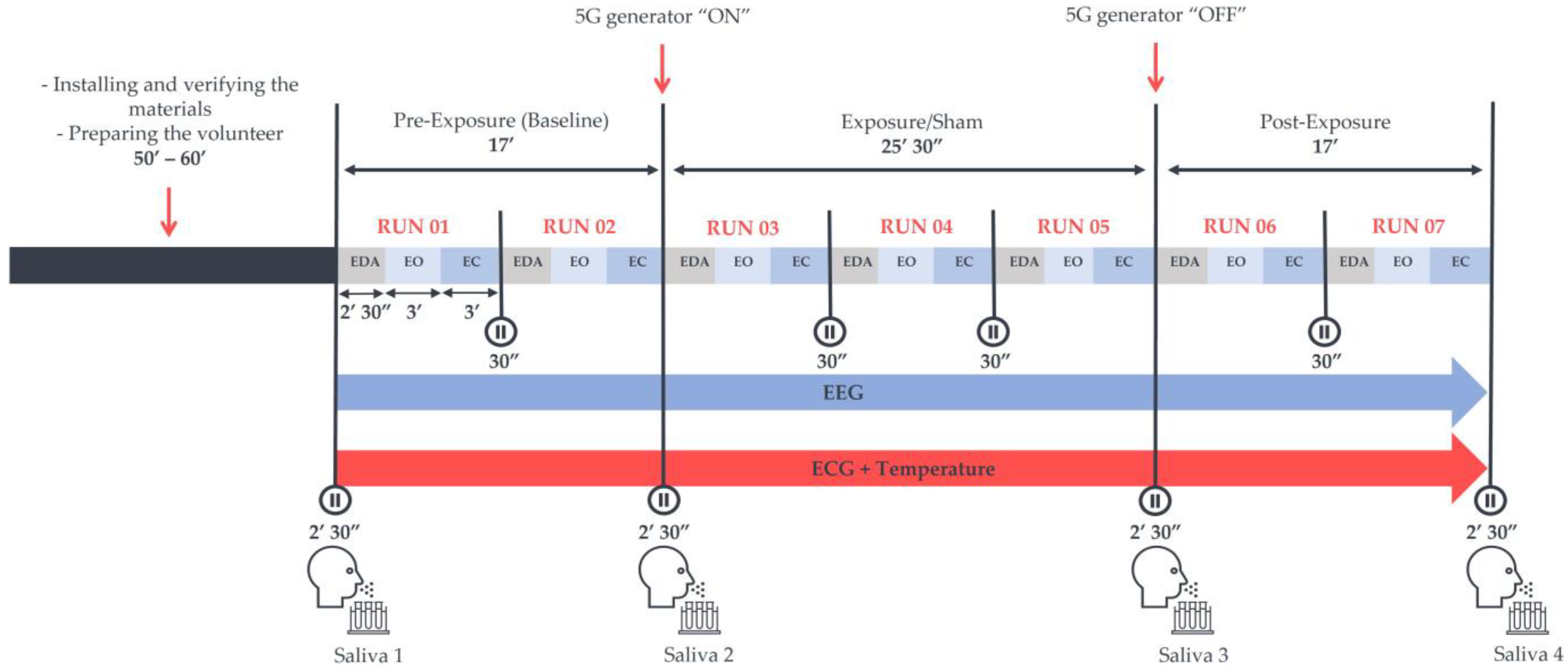
2.2. Study Design and Experimental Protocol
2.3. Exposure System
2.4. Signal Acquisition and Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
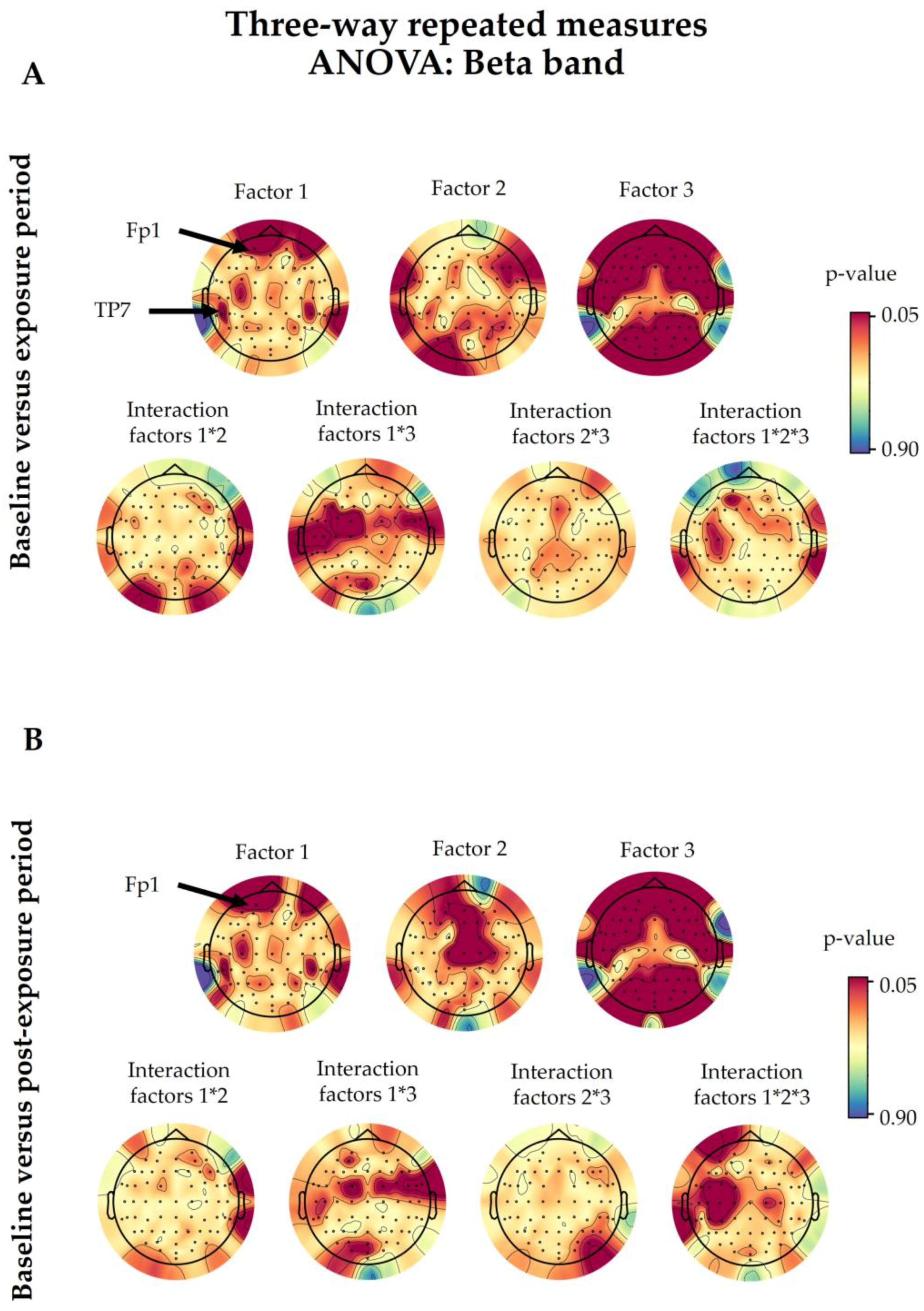
3.1. Beta Spectral Power
3.1.1. 5G Exposure (Factor 1)
3.1.2. Time Period (Factor 2)
3.1.3. Eye Condition (Factor 3)
3.1.4. Interaction among Factors
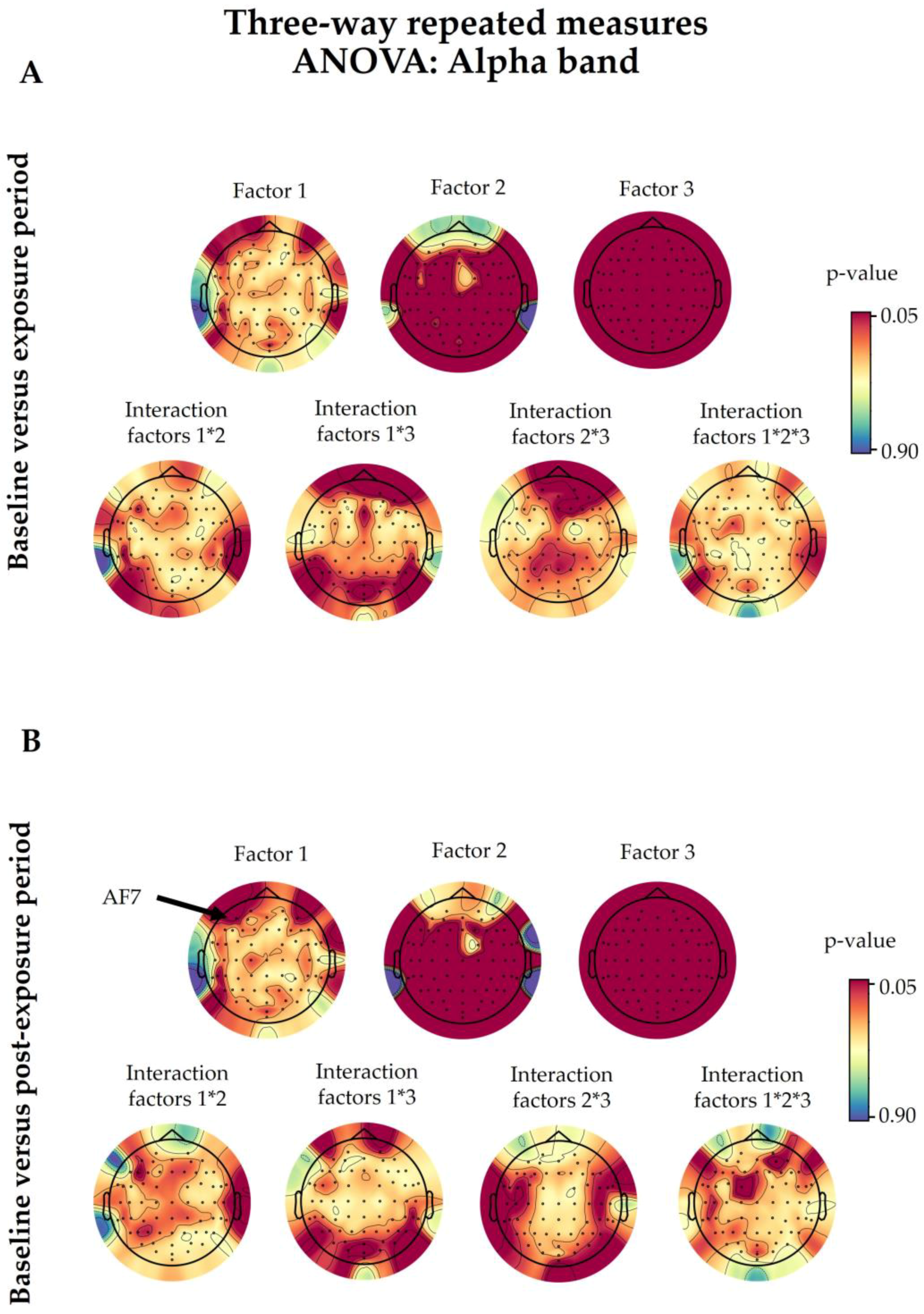
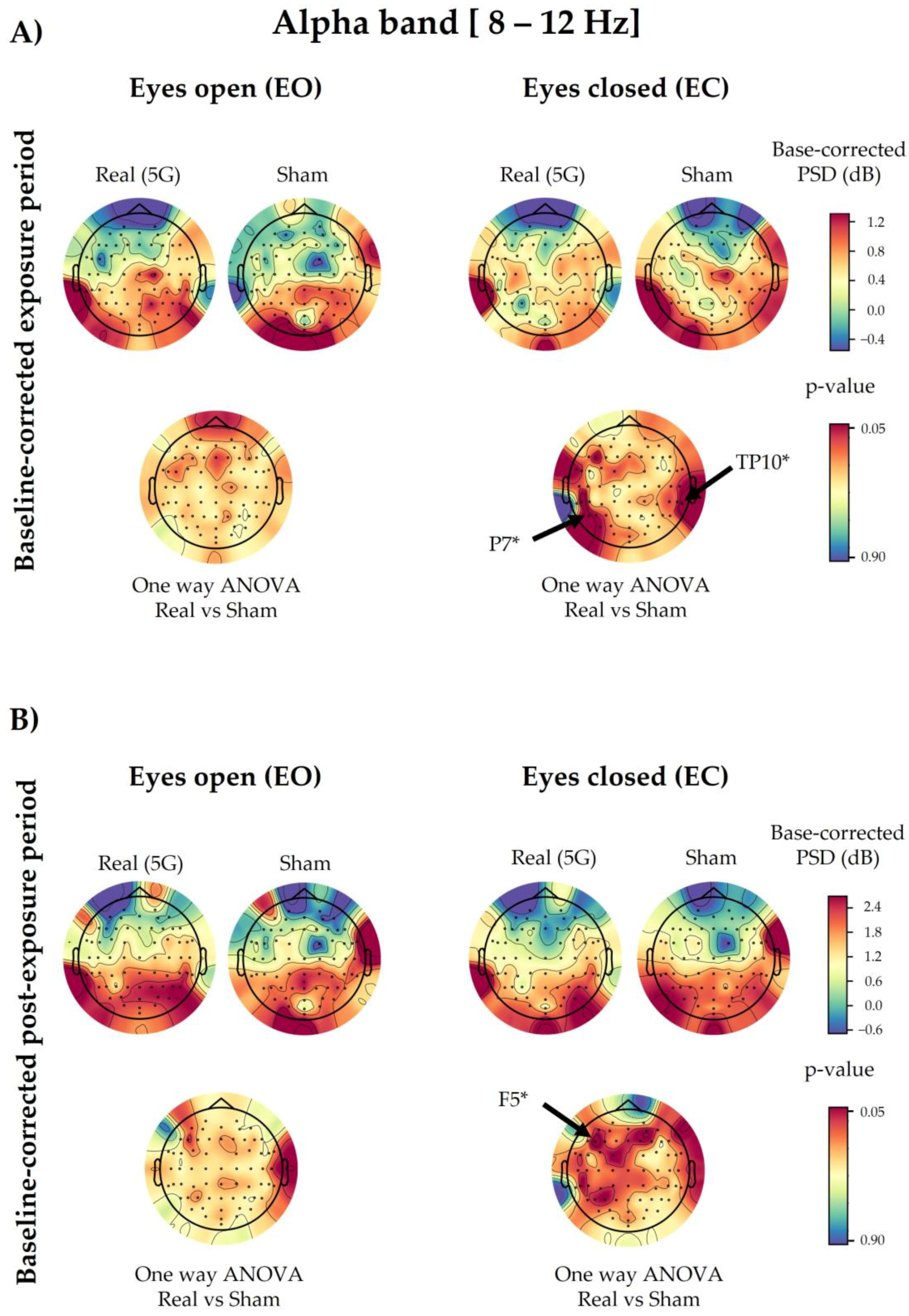
3.2. Alpha Spectral Power
3.2.1. 5G Exposure (Factor 1)
3.2.2. Time Period (Factor 2)
3.2.3. Eye Condition (Factor 3)
3.2.4. Interaction among Factors
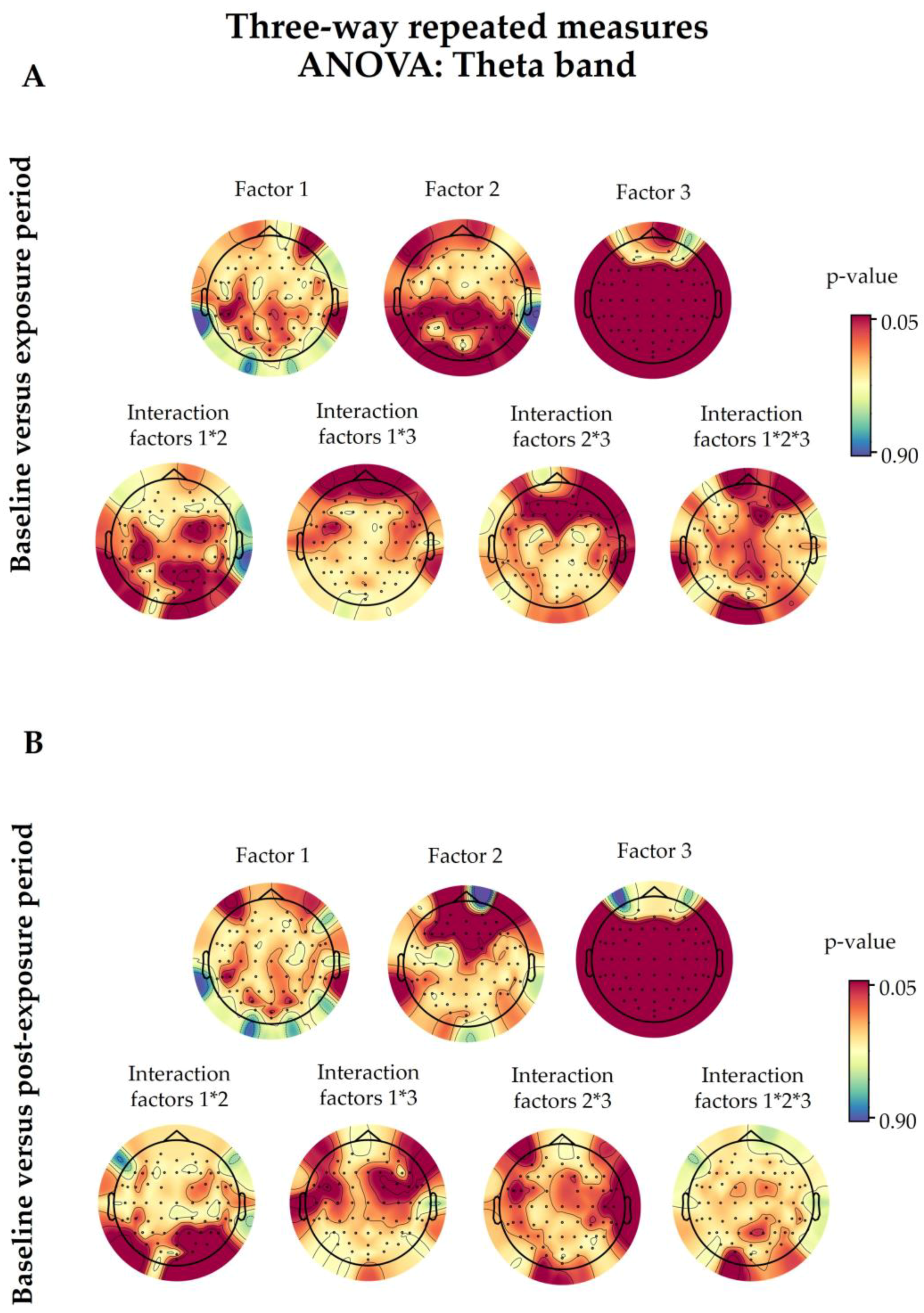
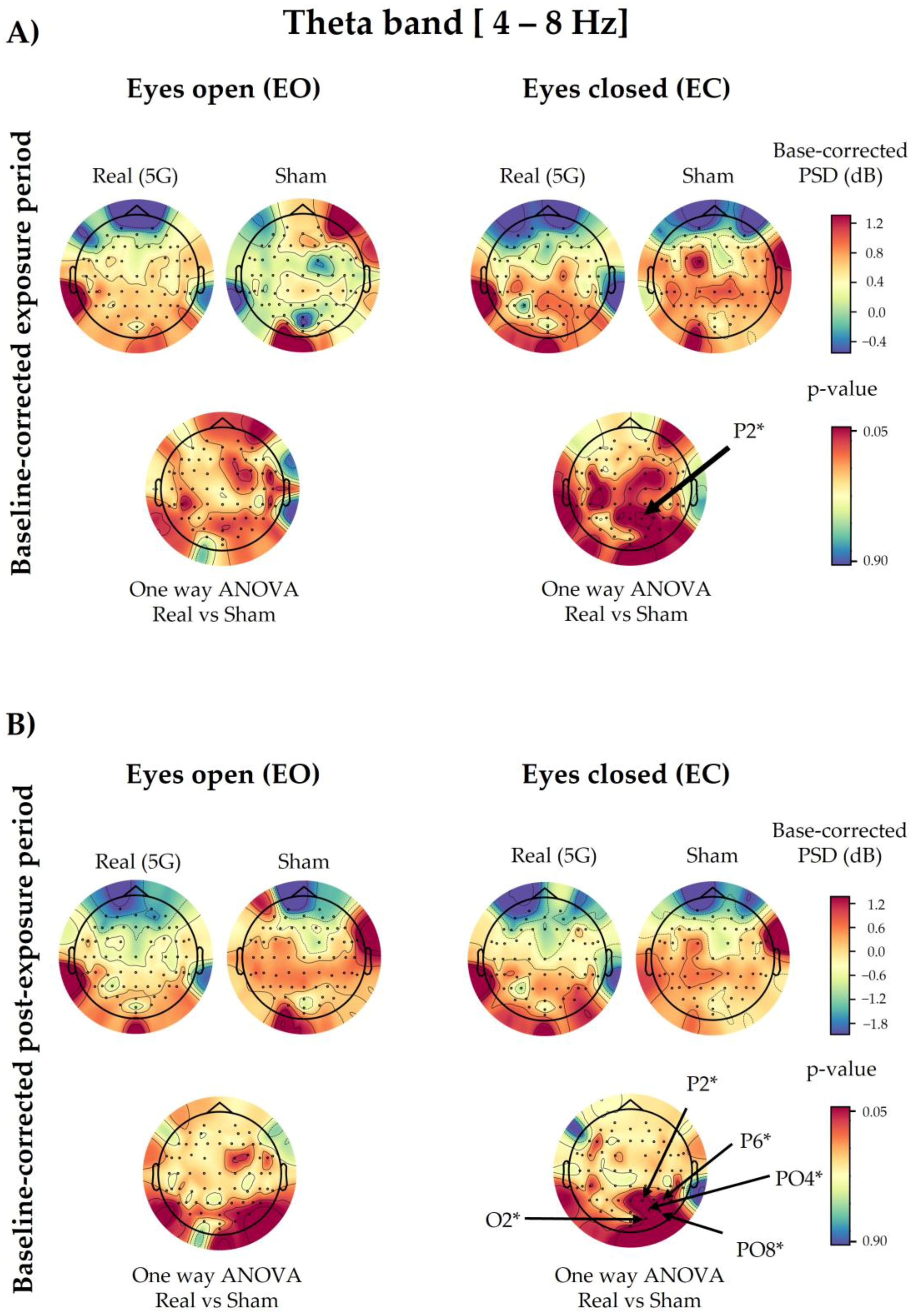
3.3. Theta Spectral Power
3.3.1. 5G Exposure (Factor 1)
3.3.2. Time Period (Factor 2)
3.3.3. Eye Condition (Factor 3)
3.3.4. Interaction among Factors
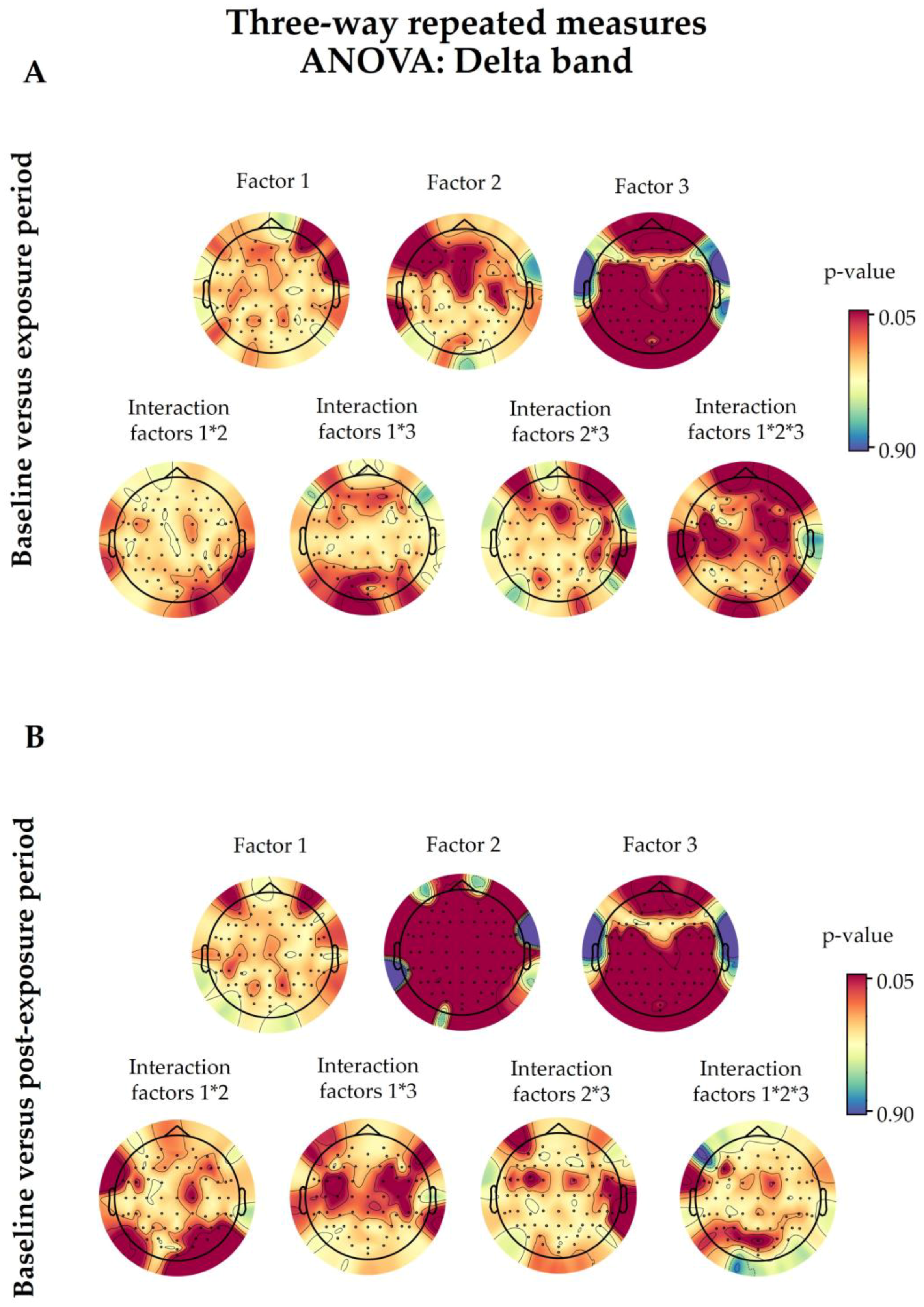
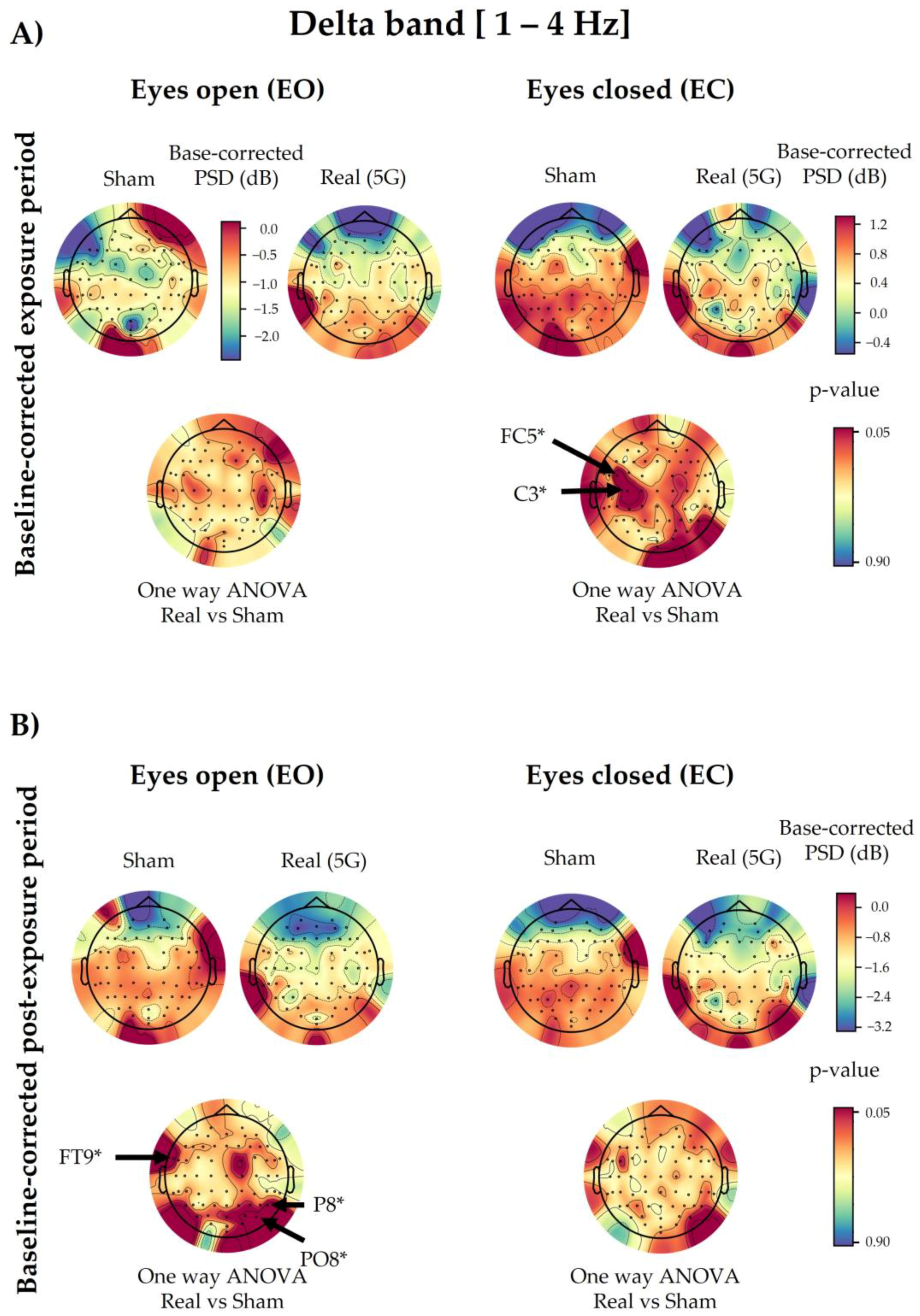
3.4. Delta Spectral Power
3.4.1. 5G Exposure (Factor 1)
3.4.2. Time Period (Factor 2)
3.4.3. Eye Condition (Factor 3)
3.4.4. Interaction with 5G
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- IARC. IARC Classifies Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields as Possibly Carcinogenic to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cacioppo, J.; Tassinary, L.; Berntson, G. Handbook of Psychophysiology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhang, P.A.; Gawali, B.W.; Mehrotra, S.C. Chapter 2—Technological Basics of EEG Recording and Operation of Apparatus. In Introduction to EEG- and Speech-Based Emotion Recognition; Abhang, P.A., Gawali, B.W., Mehrotra, S.C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danker-Hopfe, H.; Eggert, T.; Dorn, H.; Sauter, C. Effects of RF-EMF on the Human Resting-State EEG—The Inconsistencies in the Consistency. Part 1: Non-Exposure-Related Limitations of Comparability Between Studies. Bioelectromagnetics 2019, 40, 291–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, R.; Treyer, V.; Borbely, A.A.; Schuderer, J.; Gottselig, J.M.; Landolt, H.P.; Werth, E.; Berthold, T.; Kuster, N.; Buck, A.; et al. Electromagnetic Fields, Such as Those from Mobile Phones, Alter Regional Cerebral Blood Flow and Sleep and Waking EEG. J. Sleep Res. 2002, 11, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, G.; Ferrara, M.; Moroni, F.; D’Inzeo, G.; Bertini, M.; De Gennaro, L. Is the Brain Influenced by a Phone Call? An EEG Study of Resting Wakefulness. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 53, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, F.; Babiloni, C.; Ferreri, F.; Curcio, G.; Fini, R.; Del Percio, C.; Rossini, P.M. Mobile Phone Emission Modulates Interhemispheric Functional Coupling of EEG Alpha Rhythms. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 1908–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regel, S.J.; Gottselig, J.M.; Schuderer, J.; Tinguely, G.; Retey, J.V.; Kuster, N.; Landolt, H.P.; Achermann, P. Pulsed Radio Frequency Radiation Affects Cognitive Performance and the Waking Electroencephalogram. NeuroReport 2007, 18, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardasano, J.L.; Alvarez-Ude, J.; Gutierrez, I.; Raposo, M.; Goya, R. EEG Bioeffects on Cochlear Deaf from Cellular Phones. Environmentalist 2007, 27, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, R.J.; Hamblin, D.L.; Spong, J.; Wood, A.W.; McKenzie, R.J.; Stough, C. The Effect of Mobile Phone Electromagnetic Fields on the Alpha Rhythm of Human Electroencephalogram. Bioelectromagnetics 2008, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinrikus, H.; Bachmann, M.; Lass, J.; Tomson, R.; Tuulik, V. Effect of 7, 14 and 21 Hz Modulated 450 MHz Microwave Radiation on Human Electroencephalographic Rhythms. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2008, 84, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, R.J.; Leung, S.; McKenzie, R.J.; Loughran, S.P.; Iskra, S.; Hamblin, D.L.; Cooper, N.R. Effects of 2G and 3G Mobile Phones on Human Alpha Rhythms: Resting EEG in Adolescents, Young Adults, and the Elderly. Bioelectromagnetics 2010, 31, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, F.; Tombini, M.; Buffo, P.; Assenza, G.; Pellegrino, G.; Benvenga, A.; Babiloni, C.; Rossini, P.M. Mobile Phone Emission Increases Inter-Hemispheric Functional Coupling of Electroencephalographic Alpha Rhythms in Epileptic Patients. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2012, 84, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggeveen, S.; van Os, J.; Viechtbauer, W.; Lousberg, R. EEG Changes Due to Experimentally Induced 3G Mobile Phone Radiation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrikus, H.; Bachmann, M.; Karai, D.; Lass, J. Mechanism of Low-Level Microwave Radiation Effect on Nervous System. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2017, 36, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loughran, S.P.; Verrender, A.; Dalecki, A.; Burdon, C.A.; Tagami, K.; Park, J.; Taylor, N.A.S.; Croft, R.J. Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure and the Resting EEG: Exploring the Thermal Mechanism Hypothesis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, F.; Buffo, P.; Sergio, S.; Iacoviello, D.; Rossini, P.M.; Babiloni, C. Mobile Phone Emission Modulates Event-Related Desynchronization of Alpha Rhythms and Cognitive-Motor Performance in Healthy Humans. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perentos, N.; Croft, R.J.; McKenzie, R.J.; Cosic, I. The Alpha Band of the Resting Electroencephalogram under Pulsed and Continuous Radio Frequency Exposures. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosn, R.; Yahia-Cherif, L.; Hugueville, L.; Ducorps, A.; Lemaréchal, J.-D.; Thuróczy, G.; de Seze, R.; Selmaoui, B. Radiofrequency Signal Affects Alpha Band in Resting Electroencephalogram. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 113, 2753–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Q.; Lv, B.; Wu, T. Long-Term Evolution Electromagnetic Fields Exposure Modulates the Resting State EEG on Alpha and Beta Bands. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2017, 48, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecsei, Z.; Knakker, B.; Juhász, P.; Thuróczy, G.; Trunk, A.; Hernádi, I. Short-Term Radiofrequency Exposure from New Generation Mobile Phones Reduces EEG Alpha Power with No Effects on Cognitive Performance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 18010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roschke, J.; Mann, K. No Short-Term Effects of Digital Mobile Radio Telephone on the Awake Human Electroencephalogram. Bioelectromagnetics 1997, 18, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietanen, M.; Kovala, T.; Hämäläinen, A.M. Human Brain Activity during Exposure to Radiofrequency Fields Emitted by Cellular Phones. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2000, 26, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perentos, N.; Croft, R.J.; McKenzie, R.J.; Cvetkovic, D.; Cosic, I. Comparison of the Effects of Continuous and Pulsed Mobile Phone like RF Exposure on the Human EEG. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2007, 30, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinlogel, H.; Dierks, T.; Koenig, T.; Lehmann, H.; Minder, A.; Berz, R. Effects of Weak Mobile Phone—Electromagnetic Fields (GSM, UMTS) on Event Related Potentials and Cognitive Functions. Bioelectromagnetics 2008, 29, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinlogel, H.; Dierks, T.; Koenig, T.; Lehmann, H.; Minder, A.; Berz, R. Effects of Weak Mobile Phone—Electromagnetic Fields (GSM, UMTS) on Well-Being and Resting EEG. Bioelectromagnetics 2008, 29, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, S.; Croft, R.J.; McKenzie, R.J.; Iskra, S.; Silber, B.; Cooper, N.R.; O’Neill, B.; Cropley, V.; Diaz-Trujillo, A.; Hamblin, D.; et al. Effects of 2G and 3G Mobile Phones on Performance and Electrophysiology in Adolescents, Young Adults and Older Adults. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 2203–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trunk, A.; Stefanics, G.; Zentai, N.; Kovács-Bálint, Z.; Thuróczy, G.; Hernádi, I. No Effects of a Single 3G UMTS Mobile Phone Exposure on Spontaneous EEG Activity, ERP Correlates, and Automatic Deviance Detection. Bioelectromagnetics 2013, 34, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughran, S.P.; Benz, D.C.; Schmid, M.R.; Murbach, M.; Kuster, N.; Achermann, P. No Increased Sensitivity in Brain Activity of Adolescents Exposed to Mobile Phone-like Emissions. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 124, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trunk, A.; Stefanics, G.; Zentai, N.; Bacskay, I.; Felinger, A.; Thuroczy, G.; Hernadi, I. Effects of Concurrent Caffeine and Mobile Phone Exposure on Local Target Probability Processing in the Human Brain. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, T.; Dorn, H.; Sauter, C.; Marasanov, A.; Hansen, M.L.; Peter, A.; Schmid, G.; Bolz, T.; Danker-Hopfe, H. Terrestrial Trunked Radio (TETRA) Exposure and Its Impact on Slow Cortical Potentials. Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentai, N.; Csathó, Á.; Trunk, A.; Fiocchi, S.; Parazzini, M.; Ravazzani, P.; Thuróczy, G.; Hernádi, I. No Effects of Acute Exposure to Wi-Fi Electromagnetic Fields on Spontaneous EEG Activity and Psychomotor Vigilance in Healthy Human Volunteers. Radiat. Res. 2015, 184, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani-Enomoto, S.; Yamazaki, M.; Nishiura, K.; Enomoto, H.; Ugawa, Y. Effects of Electromagnetic Fields from Long-Term Evolution on Awake Electroencephalogram in Healthy Humans. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 156, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICNIRP. Guidelines for Limiting Exposure to Time-Varying Electric and Magnetic Fields (1 Hz to 100 KHz). Health Phys. 2010, 99, 818–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICNIRP. Guidelines for Limiting Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields (100 KHz to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 2020, 118, 483–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simkó, M.; Mattsson, M.-O. 5G Wireless Communication and Health Effects—A Pragmatic Review Based on Available Studies Regarding 6 to 100 GHz. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ANSES. Exposition de La Population Aux Champs Électromagnétiques Liée Au Déploiement de La Technologie de Communication « 5G » et Effets Sanitaires Associés; ANSES: Maisons-Alfort, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bushberg, J.T.; Chou, C.K.; Foster, K.R.; Kavet, R.; Maxson, D.P.; Tell, R.A.; Ziskin, M.C. IEEE Committee on Man and Radiation—COMAR Technical Information Statement: Health and Safety Issues Concerning Exposure of the General Public to Electromagnetic Energy from 5G Wireless Communications Networks. Health Phys. 2020, 119, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. Health Impact of 5G: Current State of Knowledge of 5G Related Carcinogenic and Reproductive/Developmental Hazards as They Emerge from Epidemiological Studies and In Vivo Experimental Studies; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2021.
- ANSES. Exposition Aux Champs Électromagnétiques Liée Au Déploiement de La Technologie « 5G » Connaître, Evaluer, Protéger Avis Actualisé de l’Anses Rapport D’expertise Collective; ANSES: Maisons-Alfort, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Selmaoui, B.; Mazet, P.; Petit, P.-B.; Kim, K.; Choi, D.; de Seze, R. Exposure of South Korean Population to 5G Mobile Phone Networks (3.4–3.8 GHz). Bioelectromagnetics 2021, 42, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrikus, H.; Koppel, T.; Lass, J.; Roosipuu, P.; Bachmann, M. Limiting Exposure to Radiofrequency Radiation: The Principles and Possible Criteria for Health Protection. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 99, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leveque, P.; Reineix, A.; Jecko, B. Modelling of Dielectric Losses in Microstrip Patch Antennas—Application of FDTD Method. Electron. Lett. 1992, 28, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveque, P.; Dale, C.; Veyret, B.; Wiart, J. Dosimetric Analysis of a 900-MHz Rat Head Exposure System. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2004, 52, 2076–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taflove, A.; Hagness, S.C.; Piket-May, M. Computational Electromagnetics: The Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method. In The Electrical Engineering Handbook; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 629–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, M.J. The Visible Human Project. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- «Dielectric Properties» IT’IS Foundation. Available online: https://itis.swiss/virtual-population/tissue-properties/database/dielectric-properties/ (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Gabriel, C. Compilation of the Dielectric Properties of Body Tissues at RF and Microwave Frequencies; Defense Technical Information Center: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The Dielectric Properties of Biological Tissues: III. Parametric Models for the Dielectric Spectrum of Tissues. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, J.N.; Hani, A.; Cheek, J.; Thirumala, P.; Tsuchida, T.N. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Guideline 2: Guidelines for Standard Electrode Position Nomenclature. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 33, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramfort, A.; Luessi, M.; Larson, E.; Engemann, D.; Strohmeier, D.; Brodbeck, C.; Goj, R.; Jas, M.; Brooks, T.; Parkkonen, L.; et al. MEG and EEG Data Analysis with MNE-Python. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlens, J. A Tutorial on Independent Component Analysis. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1404.2986. [Google Scholar]
- Yahia-Cherif, L. Mega-Stats: A Toolbox for Advanced Statistical Analysis of MEG-EEG Data. 2022. Available online: https://gitlab.com/lydia.yahia/mega_stats_package (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Maris, E.; Oostenveld, R. Nonparametric Statistical Testing of EEG- and MEG-Data. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 164, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.; Yahia-Cherif, L.; Gitton, C.; Hugueville, L.; Lemaréchal, J.-D.; Selmaoui, B. Modulation of Magnetoencephalography Alpha Band Activity by Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Depicted in Sensor and Source Space. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.; Shang, W.; Gitton, C.; Hugueville, L.; Yahia-Cherif, L.; Selmaoui, B. Theta Band Brainwaves in Human Resting EEG Modulated by Mobile Phone Radiofrequency. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2023, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, A.; Souques, M. Champs Électromagnétiques, Environnement et Santé, 2nd ed.; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hinrikus, H.; Koppel, T.; Lass, J.; Orru, H.; Roosipuu, P.; Bachmann, M. Possible Health Effects on the Human Brain by Various Generations of Mobile Telecommunication: A Review Based Estimation of 5G Impact. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 1210–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, F.; Babiloni, C.; Ferreri, F.; Buffo, P.; Cibelli, G.; Curcio, G.; van Dijkman, S.; Melgari, J.-M.; Giambattistelli, F.; Rossini, P.M. Mobile Phone Emission Modulates Inter-Hemispheric Functional Coupling of EEG Alpha Rhythms in Elderly Compared to Young Subjects. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.; Selmaoui, B. Effect of Mobile Phone Radiofrequency Signal on the Alpha Rhythm of Human Waking EEG: A Review. Environ. Res. 2019, 175, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.; Clarke, A.; Johnstone, S.; Magee, C.; Rushby, J. EEG Differences between Eyes-Closed and Eyes-Open Resting Conditions. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2765–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.; Blasio, F.D. EEG Differences between Eyes-Closed and Eyes-Open Resting Remain in Healthy Ageing. Biol. Psychol. 2017, 129, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, L.; Dane, A.; Rhodes, J.; Lynch, P.; Hughes, A.M. Diurnal Variation in the Quantitative EEG in Healthy Adult Volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 50, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobert, M.; Wilson, F.J.; Ruigt, G.S.F.; Brunovsky, M.; Prichep, L.S.; Drinkenburg, W.H.I.M.; IPEG Pharmaco-EEG Guidelines Committee. Guidelines for the Recording and Evaluation of Pharmaco-EEG Data in Man: The International Pharmaco-EEG Society (IPEG). Neuropsychobiology 2012, 66, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobert, M.; Wilson, F.J. Advanced Analysis of Pharmaco-EEG Data in Humans. Neuropsychobiology 2016, 72, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.; Yahia-Cherif, L.; Gitton, C.; Hugueville, L.; Lemaréchal, J.-D.; Selmaoui, B. Human Resting-State EEG and Radiofrequency GSM Mobile Phone Exposure: The Impact of the Individual Alpha Frequency. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamal, L.; Yahia-Cherif, L.; Hugueville, L.; Mazet, P.; Lévêque, P.; Selmaoui, B. Assessment of Electrical Brain Activity of Healthy Volunteers Exposed to 3.5 GHz of 5G Signals within Environmental Levels: A Controlled–Randomised Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20186793
Jamal L, Yahia-Cherif L, Hugueville L, Mazet P, Lévêque P, Selmaoui B. Assessment of Electrical Brain Activity of Healthy Volunteers Exposed to 3.5 GHz of 5G Signals within Environmental Levels: A Controlled–Randomised Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(18):6793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20186793
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamal, Layla, Lydia Yahia-Cherif, Laurent Hugueville, Paul Mazet, Philippe Lévêque, and Brahim Selmaoui. 2023. "Assessment of Electrical Brain Activity of Healthy Volunteers Exposed to 3.5 GHz of 5G Signals within Environmental Levels: A Controlled–Randomised Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 18: 6793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20186793
APA StyleJamal, L., Yahia-Cherif, L., Hugueville, L., Mazet, P., Lévêque, P., & Selmaoui, B. (2023). Assessment of Electrical Brain Activity of Healthy Volunteers Exposed to 3.5 GHz of 5G Signals within Environmental Levels: A Controlled–Randomised Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(18), 6793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20186793





