Root Canal Configuration and Its Relationship with Endodontic Technical Errors and Periapical Status in Premolar Teeth of a Saudi Sub-Population: A Cross-Sectional Observational CBCT Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Outcomes, Sample Size Calculation, Research Protocol
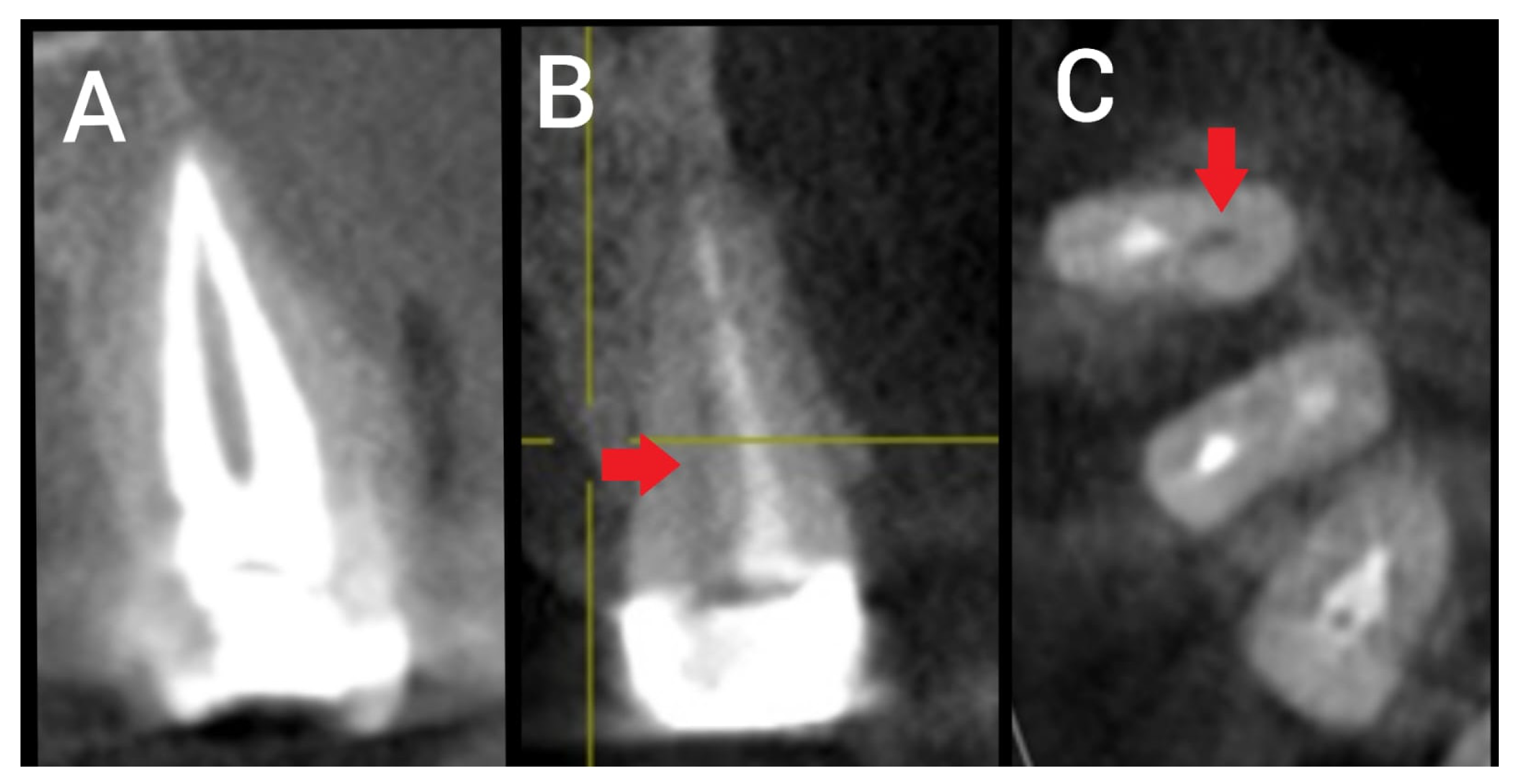
2.2. Sample Selection, Data Acquisition, and Screening Method
- Underfilling, obturation > 2mm short of the radiographic root apex.
- Overfilling, obturation extruded beyond the radiographic root apex.
- Non-homogenous obturation, canal obturation with apparent voids.
- Non-filled canals.
- Separated endodontic instruments in root canals.
- Deviation from the root canal’s anatomical path.
2.3. Evaluators’ Intra- and Inter-Reliability and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatti, U.A.; Muhammad, M.; Javed, M.Q.; Sajid, M. Frequency of middle mesial canal in mandibular first molars and its association with various anatomic variables. Aust. Endod. J. 2022, 48, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavo, R.; Lalis, R.M.; Zmener, O.; DiPietro, S.; Grana, D.; Pameijer, C.H. Frequency and distribution of teeth requiring endodontic therapy in an Argentine population attending a specialty clinic in endodontics. Int. Dent. J. 2011, 61, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.Q.; Khabeer, A.; Al Harbi, F.; Arrejaie, A.S.; Moheet, I.A.; Farooqi, F.A.; Majeed, A. Frequency of root canal treatment among patients attending a teaching dental hospital in Dammam, Saudi Arabia. Saudi. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Pedemonte, E.; Cabrera, C.; Torres, A.; Jacobs, R.; Harnisch, A.; Ramírez, V.; Concha, G.; Briner, A.; Brizuela, C. Root and canal morphology of mandibular premolars using cone-beam computed tomography in a Chilean and Belgian subpopulation: A cross-sectional study. Oral. Radiol. 2018, 34, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zubaidi, S.M.; Almansour, M.I.; Alshammari, A.S.; Al Mansour, N.N.; Alshammari, A.F.; Altamimi, Y.S.; Madfa, A.A. Root and canal morphology of mandibular premolars in a Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomography study. Int. J. Dent. 2022, 2022, 4038909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trope, M.; Elfenbein, L.; Tronstad, L. Mandibular premolars with more than one root canal in different race groups. J. Endod. 1986, 12, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.Y.; Yang, S.F.; Pai, S.F. Complicated root canal morphology of mandibular first premolar in a Chinese population using the cross section method. J. Endod. 2006, 32, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertucci, F.J. Root canal morphology and its relationship to endodontic procedures. Endod. Topics 2005, 10, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, A.; Bolla, N.; Vemuri, S.; Kurian, J. Endodontic retreatment-unusual anatomy of a maxillary second and mandibular first premolar: Report of two cases. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2013, 24, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, E.H.; Gaêta-Araujo, H.; Andrade, M.F.; Freitas, D.Q. Prevalence of technical errors and periapical lesions in a sample of endodontically treated teeth: A CBCT analysis. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2018, 22, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruwa, A.O.; Martins, J.N.; Meirinhos, J.; Pereira, B.; Gouveia, J.; Quaresma, S.A.; Monroe, A.; Ginjeira, A. The influence of missed canals on the prevalence of periapical lesions in endodontically treated teeth: A cross-sectional study. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, G.A.; Pullishery, F.; Attar, A.N.; Albalawi, M.A.; Alshareef, M.A.; Alsadeq, A.R.; Alraddadi, A.K. Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation of canal morphology of mesiobuccal root of maxillary molars in Saudi Subpopulation. J. Pharm. Bioallied. Sci. 2022, 14, S410–S414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulfat, H.; Ahmed, A.; Javed, M.Q.; Hanif, F. Mandibular second molars’ C-shaped canal frequency in the Pakistani subpopulation: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomography clinical study. Saudi. Endod. J. 2021, 11, 383–387. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, G.; Liang, R.; Zhou, G.; Wu, Y.; Sun, C.; Fan, W. Root and canal morphology of maxillary second molars by cone-beam computed tomography in a native Chinese population. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrazzi, V.; Oliveira-Neto, J.M.; Sequeira, P.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Nasser, M. Hand and ultrasonic instrumentation for orthograde root canal treatment of permanent teeth. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2010, 18, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popowicz, W.; Palatyńska-Ulatowska, A.; Kohli, M.R. Targeted endodontic microsurgery: Computed tomography–based guided stent approach with platelet-rich fibrin graft: A report of 2 cases. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.B. Applications of cone beam computed tomography in endodontics. Evid.-Based Endod. 2020, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, D.G.; Kose, E.; Ozcan, G.; Sekerci, A.E.; Canger, E.M.; Sisman, Y. Evaluation of root morphology and root canal configuration of premolars in the Turkish individuals using cone beam computed tomography. Eur. J. Dent. 2015, 9, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palkovics, D.; Mangano, F.G.; Nagy, K.; Windisch, P. Digital three-dimensional visualization of intrabony periodontal defects for regenerative surgical treatment planning. BMC Oral. Health 2020, 20, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S. New dimensions in endodontic imaging: Part 2. Cone beam computed tomography. Int. Endod. J. 2009, 42, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, E.G.; Tanomaru-Filho, M.; Gonçalves, M.; Tanomaru, J.M. Detection of periapical lesion development by conventional radiography or computed tomography. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2008, 106, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paula-Silva, F.W.; Wu, M.K.; Leonardo, M.R.; da Silva, L.A.; Wesselink, P.R. Accuracy of periapical radiography and cone-beam computed tomography scans in diagnosing apical periodontitis using histopathological findings as a gold standard. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaboodi, R.A.; Srivastava, S.; Javed, M.Q. Cone-beam computed tomographic analysis of root canal morphology of permanent mandibular incisors -Prevalence and related factors. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mheiri, E.; Chaudhry, J.; Abdo, S.; El Abed, R.; Khamis, A.H.; Jamal, M. Evaluation of root and canal morphology of maxillary permanent first molars in an Emirati population; a cone-beam computed tomography study. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzeng, L.T.; Chang, M.C.; Chang, S.H.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Jeng, J.H. Analysis of root canal system of maxillary first and second molars and their correlations by cone beam computed tomography. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2020, 119, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, X.; Jin, L.; Han, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qi, S. Comparison between periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for the diagnosis of anterior maxillary trauma in children and adolescents. Dent. Traumatol. 2022, 38, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, M.I.; Nair, M.; Levin, M.D.; Benavides, E.; Rubinstein, R.A.; Barghan, S.; Hirschberg, C.S.; Ruprecht, A. AAE and AAOMR joint position statement: Use of cone beam computed tomography in endodontics 2015 update. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 120, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, E.H.; Nascimento, M.C.; Gaêta-Araujo, H.; Fontenele, R.C.; Freitas, D.Q. Root canal configuration and its relation with endodontic technical errors in premolar teeth: A CBCT analysis. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, J.N.; Kishen, A.; Marques, D.; Silva, E.J.; Carames, J.; Mata, A.; Versiani, M.A. Preferred reporting items for epidemiologic cross-sectional studies on root and root canal anatomy using cone-beam computed tomographic technology: A systematized assessment. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 915–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertucci, F.J. Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1984, 58, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.C.; Nejaim, Y.; Silva, A.I.; Haiter-Neto, F.; Cohenca, N.; Zaia, A.A.; Silva, E.J. Influence of endodontic treatment and coronal restoration on status of periapical tissues: A cone-beam computed tomographic study. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1614–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchetti, D.V. Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychologica. Assess. 1994, 6, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zubaidi, S.M.; Almansour, M.I.; Al Mansour, N.N.; Alshammari, A.S.; Alshammari, A.F.; Altamimi, Y.S.; Madfa, A.A. Assessment of root morphology and canal configuration of maxillary premolars in a Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomographic study. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, F.; Ahmed, A.; Javed, M.Q.; Khan, Z.J.; Ulfa, H. Frequency of root canal configurations of maxillary premolars as assessed by cone-beam computerized tomography scans in the Pakistani subpopulation. Saudi Endod. J. 2022, 12, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, J.N.; Gu, Y.; Marques, D.; Francisco, H.; Caramês, J. Differences on the root and root canal morphologies between Asian and white ethnic groups analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ok, E.; Altunsoy, M.; Nur, B.G.; Aglarci, O.S.; Çolak, M.; Güngör, E. A cone-beam computed tomography study of root canal morphology of maxillary and mandibular premolars in a Turkish population. Acta. Odontol. Scand. 2014, 72, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.M.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Lin, J. Do procedural errors cause endodontic treatment failure? J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2005, 136, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamifar, K.; Tondari, A.; Saghiri, M.A. Endodontic periapical lesion: An overview on the etiology, diagnosis and current treatment Modalities. Eur. Endod. J. 2020, 5, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; de Uzeda, M. Disinfection by calcium hydroxide pastes of dentinal tubules infected with two obligate and one facultative anaerobic bacteria. J. Endod. 1996, 22, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, F.; Shakir, M. The influence of Enterococcus faecalis as a dental root canal pathogen on endodontic treatment: A systematic review. Cureus 2020, 12, 7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amlani, H.; Hegde, V. Microleakage: Apical seal vs coronal seal. World. J. Dent. 2013, 4, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, S.; Khan, F.R. Failure of endodontic treatment: The usual suspects. Eur. J. Dent. 2016, 10, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenhagen, S.; Skeie, H.; Bårdsen, A.; Laegreid, T. Influence of the coronal restoration on the outcome of endodontically treated teeth. Acta. Odontol. Scand. 2020, 78, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajerfar, M.; Nadizadeh, K.; Hooshmand, T.; Beyabanaki, E.; Neshandar Asli, H.; Sabour, S. Coronal microleakage of teeth restored with cast posts and cores cemented with four different luting agents after thermocycling. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atlas, A.; Grandini, S.; Martignoni, M. Evidence-based treatment planning for the restoration of endodontically treated single teeth: Importance of coronal seal, post vs no post, and indirect vs direct restoration. Quintessence Int. 2019, 50, 772–781. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, O.; Sathorn, C.; Parashos, P. A comparative investigation of cone-beam computed tomography and periapical radiography in the diagnosis of a healthy periapex. J. Endodon. 2014, 40, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieruzzi, M.; Pagano, S.; De Carolis, C.; Eramo, S.; Kenny, J.M. Scanning electron microscopy evaluation of dental root resorption associated with granuloma. Micros. Microanal. 2015, 21, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Premolars | Roots Number and Percentage | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| One Root | Double-Rooted | Total | |
| First Maxillary (n = 65) | 24 (36.9) | 41 (63.1) | 106 (41.5) |
| Second Maxillary (n = 56) | 53 (94.6) | 3 (5.4) | 59 (23.0) |
| First Mandibular (n = 32) | 32 (100) | 0 (0) | 32 (12.5) |
| Second Mandibular (n = 59) | 59 (100) | 0 (0) | 59 (23.0) |
| Total (n = 212) | 168 (79.2) | 44 (20.8) | 256 |
| Vertucci’s Classification * Error Type Cross Tabulation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertucci’s Classification of Root Canal Configuration | Error Type (Frequency and Percentage) | * Total | ||||||
| No Technical Endodontic Errors | Underfilling | Unfilled Canal | Non-Homogeneous Filling | Deviation | Overfilling | Association of Technical Errors | ||
| Type I (n = 199) | 124 (62.3) | 45 (22.6) | 2 (1) | 33 (16.5) | 1 (0.5) | 4 (2) | 10 (5) | 75 (37.6) |
| Type II (n = 26) | 13 (50) | 5 (19.2) | 4 (15.3) | 3 (11.5) | 0 (0) | 1 (3.8) | 0 (0) | 13 (50) |
| Type III (n = 4) | 2 (50) | 1 (25) | 1 (25) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (50) |
| Type IV (n = 22) | 10 (45.4) | 5 (22.7) | 1 (4.5) | 11 (50) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 (22.7) | 12 (54.5) |
| Type V (n = 4) | 1 (25) | 0 (0) | 2 (50) | 1 (25) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (75) |
| Type VI (n = 1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (100) |
| Total (n = 256) | 150 (58.5) | 56 (21.8) | 11 (4.2) | 48 (18.7) | 1 (0.4) | 5 (1.9) | 15 (5.8) | 106 (41.4) |
| Technical Error | Vertucci’s Classification | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type I (1-1) | Type II (2-1) | Type III (1-2-1) | Type IV (2-2) | Type V (1-2) | Type VI (2-1-2) | ||||
| Present | Apical Radioulency | Present | 58 (77.3) | 10 (76.9) | 2 (100) | 12 (100) | 2 (66) | 1 (100) | 85 (80.1) |
| Absent | 17 (22.6) | 2 (23) | 0 | 0 | 1 (33) | 0 | 20 (19.9) | ||
| Total | 75 | 13 | 2 | 12 | 3 | 1 | 106 | ||
| Absent | Apical Radioulency | Present | 26 (20.9) | 6 (46.1) | 1 (50) | 5 (50) | 1 (100) | 0 | 39 (26) |
| Absent | 98 (79) | 8 (53.8 | 1 (50) | 5 (50) | 0 | 0 | 112 (74) | ||
| Total | 124 | 13 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 150 | ||
| Total | Apical Radioulency | Present | 84 (42.2) | 16 (61.5) | 3 (75) | 17 (77.2) | 3 (75) | 1 (100) | 124 (48.4) |
| Absent | 115 (57.7) | 10 (38.4) | 1 (25) | 5 (22.7) | 1 (25) | 0 | 132 (51.5) | ||
| Total | 199 | 26 | 4 | 22 | 4 | 1 | 256 | ||
| Technical Error | Coronal Restoration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absent | Present | Total | |||
| Present | Apical Radioulency | Present | 4 (100) | 82 (80.3) | 86 (81.1) |
| Absent | 0 | 20 (19.6) | 20 (18.8) | ||
| Total | 4 | 102 | 106 | ||
| Absent | Apical Radioulency | Present | 14 (93.3) | 24 (17.7) | 38 (25.3) |
| Absent | 1 (6.6) | 111 (82.2) | 112 (74.6) | ||
| Total | 15 | 135 | 150 | ||
| Total | Apical Radioulency | Present | 18 (94.7) | 106 (44.7) | 124 (48.4) |
| Absent | 1 (5.2) | 131 (55.2) | 132 (51.5) | ||
| Total | 19 | 237 | 256 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Yahya, R.S.; Al Attas, M.H.; Javed, M.Q.; Khan, K.I.; Atique, S.; Abulhamael, A.M.; Bahammam, H.A. Root Canal Configuration and Its Relationship with Endodontic Technical Errors and Periapical Status in Premolar Teeth of a Saudi Sub-Population: A Cross-Sectional Observational CBCT Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021142
Al Yahya RS, Al Attas MH, Javed MQ, Khan KI, Atique S, Abulhamael AM, Bahammam HA. Root Canal Configuration and Its Relationship with Endodontic Technical Errors and Periapical Status in Premolar Teeth of a Saudi Sub-Population: A Cross-Sectional Observational CBCT Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(2):1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021142
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Yahya, Rayan Suliman, Mustafa Hussein Al Attas, Muhammad Qasim Javed, Kiran Imtiaz Khan, Sundus Atique, Ayman M. Abulhamael, and Hammam Ahmed Bahammam. 2023. "Root Canal Configuration and Its Relationship with Endodontic Technical Errors and Periapical Status in Premolar Teeth of a Saudi Sub-Population: A Cross-Sectional Observational CBCT Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 2: 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021142
APA StyleAl Yahya, R. S., Al Attas, M. H., Javed, M. Q., Khan, K. I., Atique, S., Abulhamael, A. M., & Bahammam, H. A. (2023). Root Canal Configuration and Its Relationship with Endodontic Technical Errors and Periapical Status in Premolar Teeth of a Saudi Sub-Population: A Cross-Sectional Observational CBCT Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021142







