A Crossed Pure Agraphia by Graphemic Buffer Impairment following Right Orbito-Frontal Glioma Resection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Report
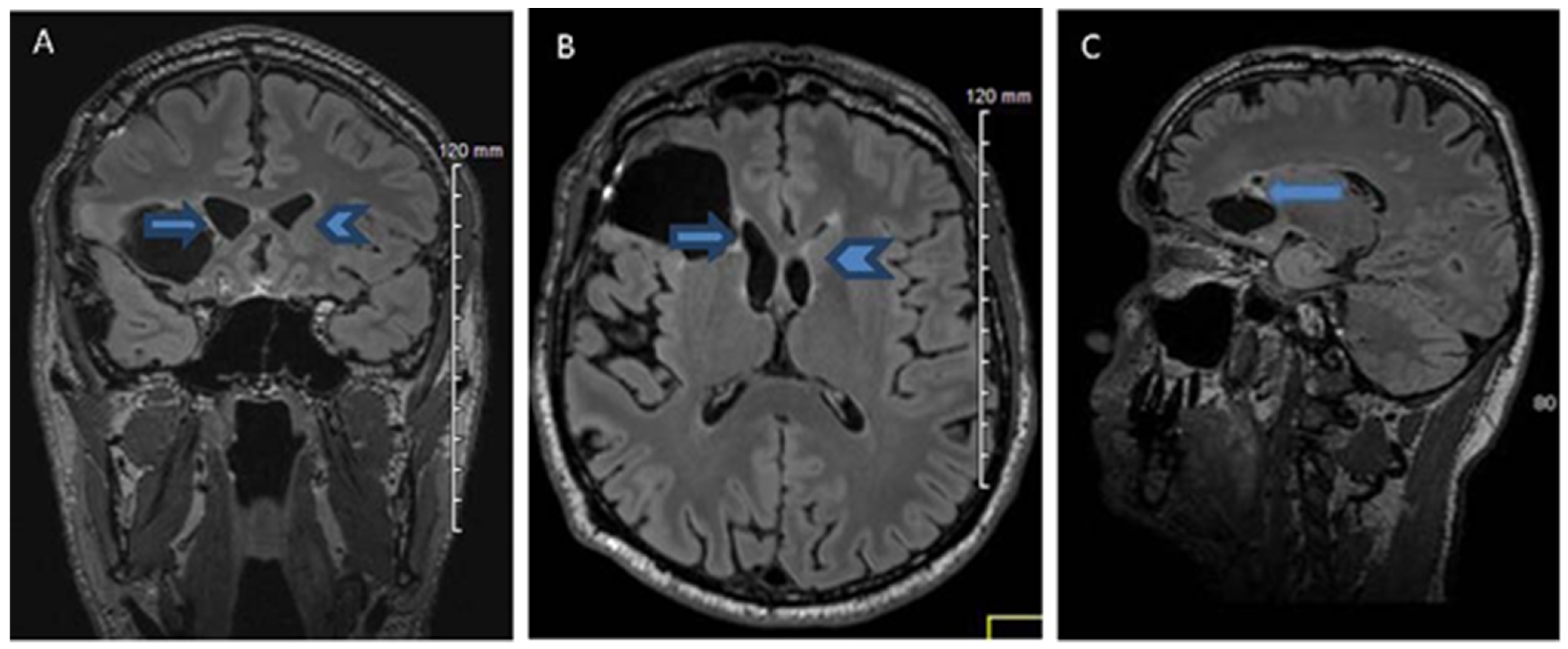
2.1. History, Neuro-Imaging and Surgical Treatment
2.2. Neuropsychological Evaluation: Pre-Operative and Post-Operative Neuropsychological Assessments
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Written Transcription of Dictated Words Test during the Assessments in March, May, and October 2014 (Errors in Italic Letter Format)
| Words Length | Written Transcription (Errors in Parentheses) | ||
| March 2014 | 3 to 6 letters | 3 letters | bol |
| 4 letters | gelé, rôti | ||
| 5 letters | fruit, radis, album | ||
| 6 letters | volcan, canari, abbaye | ||
| 7 to 9 letters | 7 letters | cratère, progrès, rivière, sportif | |
| 8 letters | éruption | ||
| 9 letters | transport, marmelade, chirurgie (chirugie), accordéon (acordéon, accordéon), cavalcade (calvalque, calvalde), spectacle (septacle, secpta, sceptacle) | ||
| 10 to 13 letters | 10 letters | pharmacien, stratagème (scartagène, stratagéne) | |
| 11 letters | sarcastique, caricatural (cariccatural) | ||
| 12 letters | distribution, bibliothèque, encombrement, intelligence, construction (constrution, construction), perspicacité (pertiscasité) | ||
| 13 letters | fréquentation, chevaleresque (chevallerestec) | ||
| May 2014 | 3 to 6 letters | 3 letters | bol |
| 4 letters | gelé, soif | ||
| 5 letters | force, fruit, melon, oncle, radis, soupe | ||
| 6 letters | garçon, gâteau, jasmin, pirate, volcan | ||
| 7 to 9 letters | 7 letters | cratère, cravate, liberté, lorsque, poltron, progrès, rivière, sportif, vermeil, théâtre (théârtre) | |
| 8 letters | acrobate (ocrobate), carnaval, éruption, servante, tabouret | ||
| 9 letters | accordéon, attention, cascadeur, clocheton, carnivore, fermeture, clandestin, platitude, transport, servitude chirurgie (chrirugie, chirurgie), physicien (phisitien, physitien), marmelade (marnelade) | ||
| 10 to 13 letters | 10 letters | exactement, pharmacien, stratagème, volontaire, psalmodier (salmodier, salemdier, phasmodier, slasmodier), borborygme (borborigleme), conscience (conthience, conscience) | |
| 11 letters | flagornerie, particulier, caricatural (caritatural) | ||
| 12 letters | encombrement, intelligence (intelitgence, intellit), perspicacité (perpiscasité, perpisas, perspicati, perspicacité) | ||
| 13 letters | chevaleresque, transcription, fréquentation (ferquentation, fréquentation), introspection (introstecp, introstecsion, introspection) | ||
| October 2014 | 3 to 6 letters | 3 letters | bol |
| 4 letters | gelé, soif | ||
| 5 letters | force, fruit, laver, melon, oncle, radis, soupe | ||
| 6 letters | farine, garçon, gâteau, gloire, stable, tulipe, valise | ||
| 7 to 9 letters | 7 letters | abricot, adjoint, crapaud, surpris, théâtre, verglas, drapeau, ergoter, exploit, glouton, hospice, liberté, marteau, piscine, poltron, progrès, rivière, silence, cratère (grati, gratère, cratère), sportif (sorptif) | |
| 8 letters | acrobate, alchimie, bordeaux, carnaval, englouti, escargot, myrtille, tabouret, perplexe, sabotier, sclérose, scabreux (scabru, scar, scabreux), scrupule (scurpugle, scurpule, scrupule), espiègle (espièsgle, espiègle), mélomane (mélomgne, mélomagne, mélomane) | ||
| 9 letters | antiquité, spirituel, splendide, sulfatage, vermifuge, astrolabe, attention, chirurgie, dictateur, infirmier, monarchie, obscurité, marmelade, servitude, astigmate (asthismate, astitmate, asticmate), cavalcade (calvaque, cavalcade), grotesque (grodesque, grosdesque, grostesque), organisme (orgamisne, orgamisme, organisme), physicien (physite, physitien), spectacle (septacle, sepctacle, secptacle), turpitude (turtitude, turpitude) | ||
| 10 to 13 letters | 10 letters | aspirateur, difficulté, distribuer, indulgence, pharmacien, particulier, proportion, jardinage, stratagème, conscience (constience, consthience), scarlatine (scarlatigne), strapontin sprapontin, strapontin) | |
| 11 letters | caricatural, chirurgical, circonscrit, description | ||
| 12 letters | déflagration, fermentation, intelligence, préservation, soustraction, circonscrire (circonscrice, circoncrire, circonscrire), circonstance (circontanse, circonstance), encombrement (ecombrement, encombrement), exceptionnel (expletionnel, exthionnel, exexthionnel), introduction (introdution, intrduction), perspicacité (perpicascité, perspicacité) | ||
| 13 letters | accordéoniste, agglomération, chevaleresque, fréquentation, spectaculaire (sepctaculaire, secptaculaire), transcription (transgrition, transcrition, transcriction) | ||
References
- Dubois, J.; Hécaen, H.; Marcie, P. L’agraphie “pure”. Neuropsychologia 1969, 7, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bub, D.; Kertesz, A. Deep agraphia. Brain Lang. 1982, 17, 146–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeltgen, D.P.; Heilman, K.M. Lexical agraphia: Further support for the two-system hypothesis of linguistic agraphia. Brain 1984, 107, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gvion, A.; Friedmann, N. Dyscravia: Voicing substitution dysgraphia. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 1935–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramazza, A.; Miceli, G.; Silveri, M.C.; Laudanna, A. Reading mechanisms and the organization of the lexicon: Evidence from acquired dyslexia. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 1985, 2, 81–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramazza, A.; Miceli, G.; Villa, G.; Romani, C. The role of the Graphemic Buffer in spelling: Evidence from a case of acquired dysgraphia. Cognition 1987, 26, 59–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramazza, A.; Miceli, G. The structure of graphemic representations. Cognition 1990, 37, 243–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Baum, S.; McCloskey, M.; Rapp, B. Representation of Letter Position in Spelling: Evidence from Acquired Dysgraphia. Cognition 2010, 115, 466–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, S.; Poli, R.; Piccirilli, M. Neurolinguistic analysis of a case of pure agraphia. Riv. Neurol. 1990, 60, 219–220. [Google Scholar]
- Piccirilli, M.; Petrillo, S.; Poli, R. Dysgraphia and selective impairment of the graphemic buffer. Ital. J. Neuro. Sci. 1992, 13, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yamadori, A.; Satou, K. Pure Kana agraphia as a manifestation of graphemic buffer impairment. Cortex 2001, 37, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiller, N.O.; Greenhall, J.A.; Shelton, J.R.; Caramazza, A. Serial order effects in spelling errors: Evidence from two dysgraphic patients. Neurocase 2001, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Alaoui Faris, M.; Benbelaid, F.; Ettahiri, L.; Jiddane, M.; Chkili, T. Agraphie pure en arabe: Dissociation entre voyelles et consonnes. Syndrome du buffer graphémique. Rev. Neurol. 2004, 160, 956–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exner, S. Untersuchungen über die Lokalization der Funktionen in der Grosshimrinde des Menschen; Braumuller: Vienna, Austria, 1881. [Google Scholar]
- Young, J.S.; Lee, A.T.; Changm, E.F. A Review of Cortical and Subcortical Stimulation Mapping for Language. Neurosurgery 2021, 89, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, G.; De Bastiani, P. Pure agraphia: A discrete form of aphasia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 1979, 42, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, T.; Marttila, R.J. Pure agraphia: A case study. Neuropsychologia 1981, 19, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, F.E.; Djidjeli, I.; Nicolau, J.; Darcourt, J.; Le Lann, F.; Demonet, J.F. Pure Agraphia Associated with a Frontal Meningioma on Left Superior Frontal Gyrus. Clin. Neurol. Neurosci. 2021, 5, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billeri, L.; Naro, A.; Manulin, A.; Calabrò, R.S. Could pure agraphia be the only sign of stroke? Lessons from two case reports. J. Postgrad. Med. 2021, 67, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, K.; Yokoyama, R.; Yanagihara, A. A crossed kana agraphia. Behav. Neurol. 1995, 8, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hécaen, H.; Ajuriaguerra, J. Les Gauchers; Presses Universitaires de France: Paris, France, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Yordana, Y.N.; Moritz-Gasser, S.; Duffau, H. Awake surgery for WHO Grade II gliomas within “non-eloquent” areas in the left dominant hemisphere: Toward a “supratotal” resection. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, R.; Toullat, G.; Pluchon, C.; Micheneau, D.; Cariou, B.; Rivault, L.; Sicot, I.; Boissonnot, L.; Neau, J.P. Une méthode d’évaluation rapide des fonctions cognitives (ERFC). Son application à la démence sénile de type Alzheimer. Sem. Hôp. Paris 1986, 62, 2127–3213. [Google Scholar]
- Deloche, G.; Hannequin, D. DO 80: Épreuve de Dénomination Orale d’images; Éditions du Centre de Psychologie Appliquée: Paris, France, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, C.J. Stroop color and word test. In A Manual for Clinical and Experimental Uses; Stoelting Company: Chicago, IL, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Slachevsky, A.; Villalpando, J.; Sarazin, M.; Hahn-Barma, V.; Pillon, B.; Dubois, B. Frontal assessment battery and differential diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2004, 61, 1104–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, H.E. A modified Card Sorting Test sensitive to frontal lobe defects. Cortex 1976, 12, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilkki, J.; Holst, P. Speed and flexibility on word fluency tasks after focal brain lesions. Neuropsychologia 1994, 32, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.; Joanette, Y.; Puel, M. Démences et syndromes démentiels. In Approche Neuropsychologique; Masson: Paris, France, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, 4th ed.; Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, A. Manuel du Test de Copie et de Reproduction de Mémoire de Figures Géométriques Complexes; Éditions Centre de Psychologie appliqué: Paris, France, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Mazaux, J.M.; Orgogozo, J.M. BDAE-F: Boston Diagnostic Aphasia Examination; Éditions Scientifiques et Psychologiques: Issy les Moulineaux, France, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Content, A.; Mousty, P.H.; Radeau, M. Une base de connées lexicales informatisée pour le français écrit et parlé (BRULEX). L’Année Psychol. 1990, 90, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, D. Echelle Clinique de Mémoire, 3rd ed.; Éditions Centre de Psychologie appliquée: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ierschot, F.; Bastiaanse, R.; Miceli, G. Evaluating Spelling in Glioma Patients Undergoing Awake Surgery: A Systematic Review. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2018, 28, 470–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, K.; Ellis, A.W. Lexical influences in graphemic buffer disorder. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 2004, 21, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.; Fischer-Baum, S.; Capasso, R.; Miceli, G.; Rapp, B. Temporal stability and representational distinctiveness: Key functions of orthographic working memory. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 2011, 28, 338–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, A.M.; Baddeley, A.D. Spelling errors in handwriting: A corpus and a distributional analysis. In Cognitive Processes in Spelling; Frith, U., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Planton, S.; Jucla, M.; Roux, F.E.; Démonet, J.F. The “handwriting brain”: A meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies of motor versus orthographic processes. Cortex 2013, 49, 2772–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufor, O.; Rapp, B. Letter representations in writing: An fMRI adaptation approach. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeltgen, D. Agraphia. In Clinical Neuropsychology, 2nd ed.; Heilman, K.M., Valenstein, E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Rapp, B.; Purcell, J.J.; Hillis, A.E.; Capasso, R.; Miceli, G. Neural bases of orthographic long-term memory and working memory in dysgraphia. Brain 2015, 139, 588–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutman, L.; Gingis, L.; Newhart, M.; Davis, C.; Heidler-Gary, J.; Crinion, J.; Hillis, A.E. A neural network critical for spelling. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motomura, K.; Fujii, M.; Maesawa, S.; Kuramitsu, S.; Natsume, A.; Wakabayashi, T. Association of dorsal inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus fibers in the deep parietal lobe with both reading and writing processes: A brain mapping study. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, J.J.; Napoliello, E.M.; Eden, G.F. A combined fMRI study of typed spelling and reading. Neuroimage 2011, 55, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deldar, Z.; Gevers-Montoro, C.; Khatibi, A.; Ghazi-Saidi, L. The interaction between language and working memory: A systematic review of fMRI studies in the past two decades. AIMS Neurosci. 2020, 8, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Test | June 2012 Pre-Operative Evaluation | October 2012 Post-Operative Evaluation | March 2014 Post-Operative Evaluation | May 2014 Post-Operative Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RECF | 47/50 (NP) | 46.5/50 (NP) | 46.5/50 (NP) | 46.5/50 (NP) |
| RECF digit span | 1.5/2 (NP) | 1.5/2 (NP) | 2/2 (NP) | 1.5/2 (NP) |
| WAIS-III digit span | 7/19 (NP) | 9/19 (NP) | 9/19 (NP) | |
| DO80 | 79/80 (NP) | 80/80 (NP) | 79/80 (NP) | 79/80 (NP) |
| FAST | 18/18 (NP) | 17/18 (NP) | 15/18 (NP) | 17/18 (NP) |
| WCST categories | 6 (NP) | 6 (NP) | 6 (NP) | |
| WCST errors (%) | 40% (NP) | 0% (NP) | 14.28% (NP) | |
| Stroop test (RS–PS) | 0.08 (NP) | 9.29 (NP) | 4.85 (NP) | |
| Category fluency | 15 (NP) | 18 (NP) | 17 (NP) | |
| Letter fluency | 11 (NP) | 14 (NP) | 7 (NP) | |
| WAIS-III block design | 11/19 (NP) | 12/19 (NP) | 9/19 (NP) | 8/19 (NP) |
| ROCF copy type | IV (NP) | IV (NP) | IV (NP) | |
| ROCF copy time | 169 (NP) | 146 (NP) | 163 (NP) | |
| ROCF copy total score | 36 (NP) | 33 (NP) | 29 | |
| ROCF recall type | II (NP) | IV (NP) | ||
| ROCF recall total score | 18 (NP) | 17 (NP) |
| BDAE Subtests | Score | BDAE Subtests | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spontaneous oral expression | Aphasic transformations of oral language | ||
| 7/7 |
| 0 |
| 0 | ||
| Repetition |
| 0 | |
| 10/10 | ||
| 8/8 | Written language comprehension | |
| 8/8 |
| 10/10 |
| 8/8 | ||
| Denomination |
| 8/8 | |
| 30/30 |
| 10/10 |
| 105/105 |
| 10/10 |
| 30/30 | ||
| Writing | |||
| Reading aloud |
| 3/3 | |
| 30/30 |
| 36/36 |
| 10/10 |
| 8/8 |
| Stimulus Length | March 2014 | May 2014 | October 2014 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Word Errors | Non-Word Errors | Word Errors | Non-word Errors | Word Errors | Non-Word Errors | |
| 3–6 letters | 0/9 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/14 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/17 (0%) | 0/4 (0%) |
| 7–9 letters | 4/11 (36.36%) | 2/2 (100%) | 7/29 (24.13%) | 3/3 (100%) | 13/54 (24.07%) | 2/4 (50%) |
| 10–13 letters | 5/12 (41.66%) | 8/17 (47.05%) | 11/33 (33.33%) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arroyo-Anlló, E.M.; Pluchon, C.; Bouyer, C.; Baudiffier, V.; Stal, V.; Du Boisgueheneuc, F.; Wager, M.; Gil, R. A Crossed Pure Agraphia by Graphemic Buffer Impairment following Right Orbito-Frontal Glioma Resection. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021346
Arroyo-Anlló EM, Pluchon C, Bouyer C, Baudiffier V, Stal V, Du Boisgueheneuc F, Wager M, Gil R. A Crossed Pure Agraphia by Graphemic Buffer Impairment following Right Orbito-Frontal Glioma Resection. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(2):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021346
Chicago/Turabian StyleArroyo-Anlló, Eva M., Claudette Pluchon, Coline Bouyer, Vanessa Baudiffier, Veronique Stal, Foucaud Du Boisgueheneuc, Michel Wager, and Roger Gil. 2023. "A Crossed Pure Agraphia by Graphemic Buffer Impairment following Right Orbito-Frontal Glioma Resection" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 2: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021346
APA StyleArroyo-Anlló, E. M., Pluchon, C., Bouyer, C., Baudiffier, V., Stal, V., Du Boisgueheneuc, F., Wager, M., & Gil, R. (2023). A Crossed Pure Agraphia by Graphemic Buffer Impairment following Right Orbito-Frontal Glioma Resection. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021346






