Effect of Microplastic Particles on the Rheological Properties of Human Saliva and Mucus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Saliva
2.2. Mucus
2.3. Microplastics
2.4. Methodology
- Choice of the initial coefficient values;
- Calculation of the fitted curve for the current set of coefficients. The fitted response value ŷ is given by ŷ = f(X,β) and is calculated using the Jacobian of f(X,β). The Jacobian of f(X,β) is defined as a matrix of partial derivatives taken concerning the coefficients in β;
- Updating the values of the coefficients using a Trust-region algorithm [27].
3. Results and Discussion
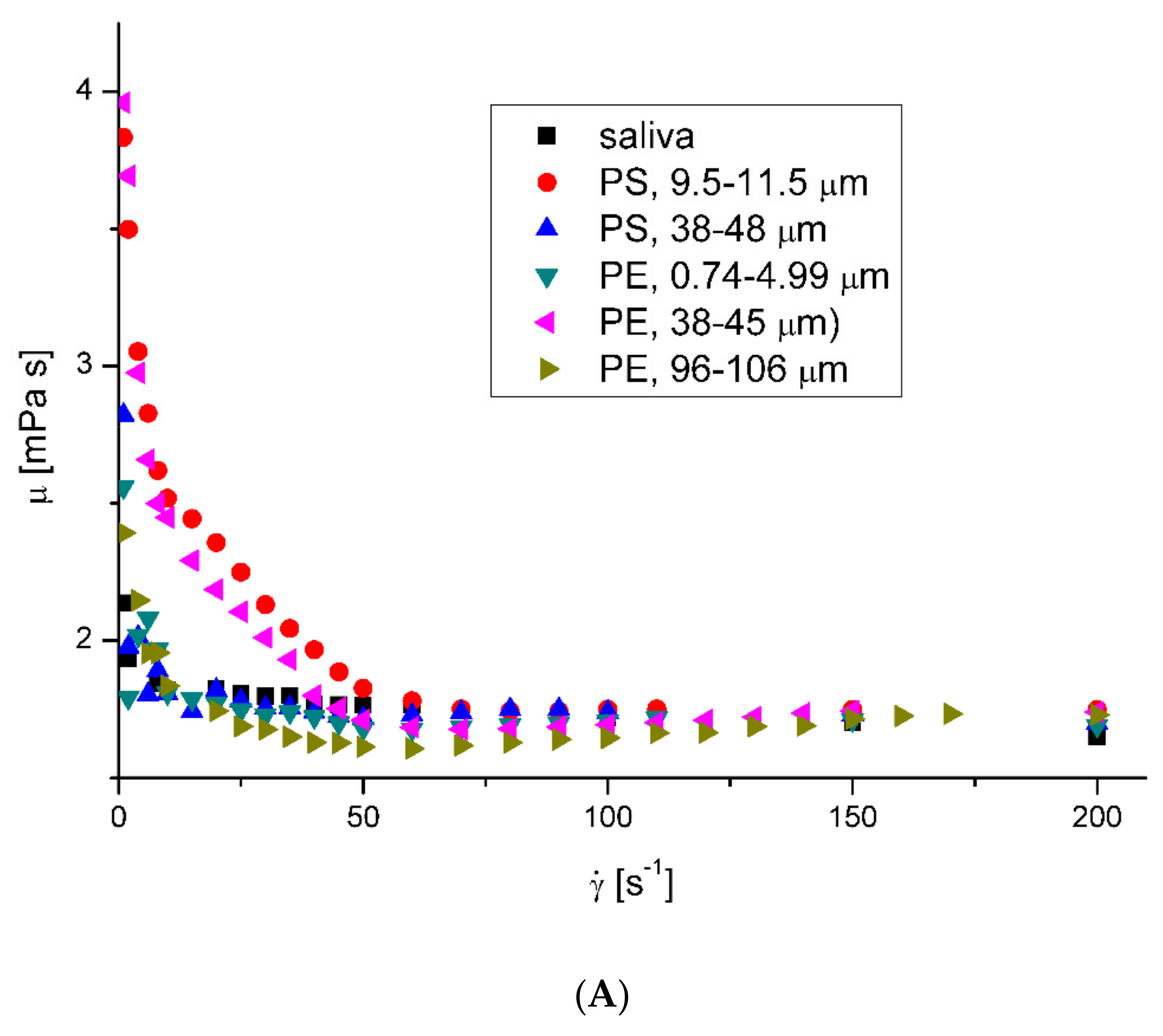
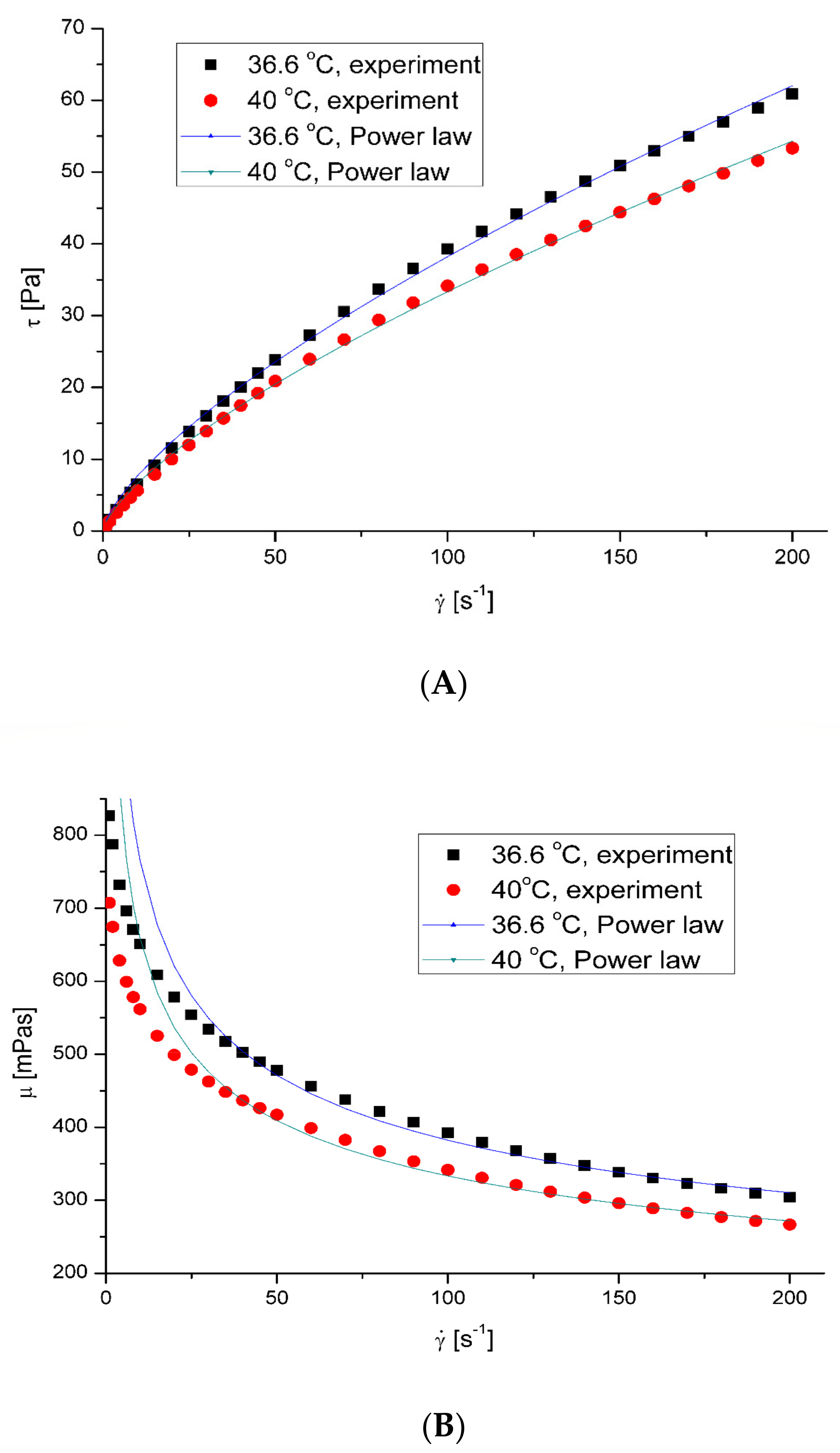
3.1. Rheological Properties of Saliva
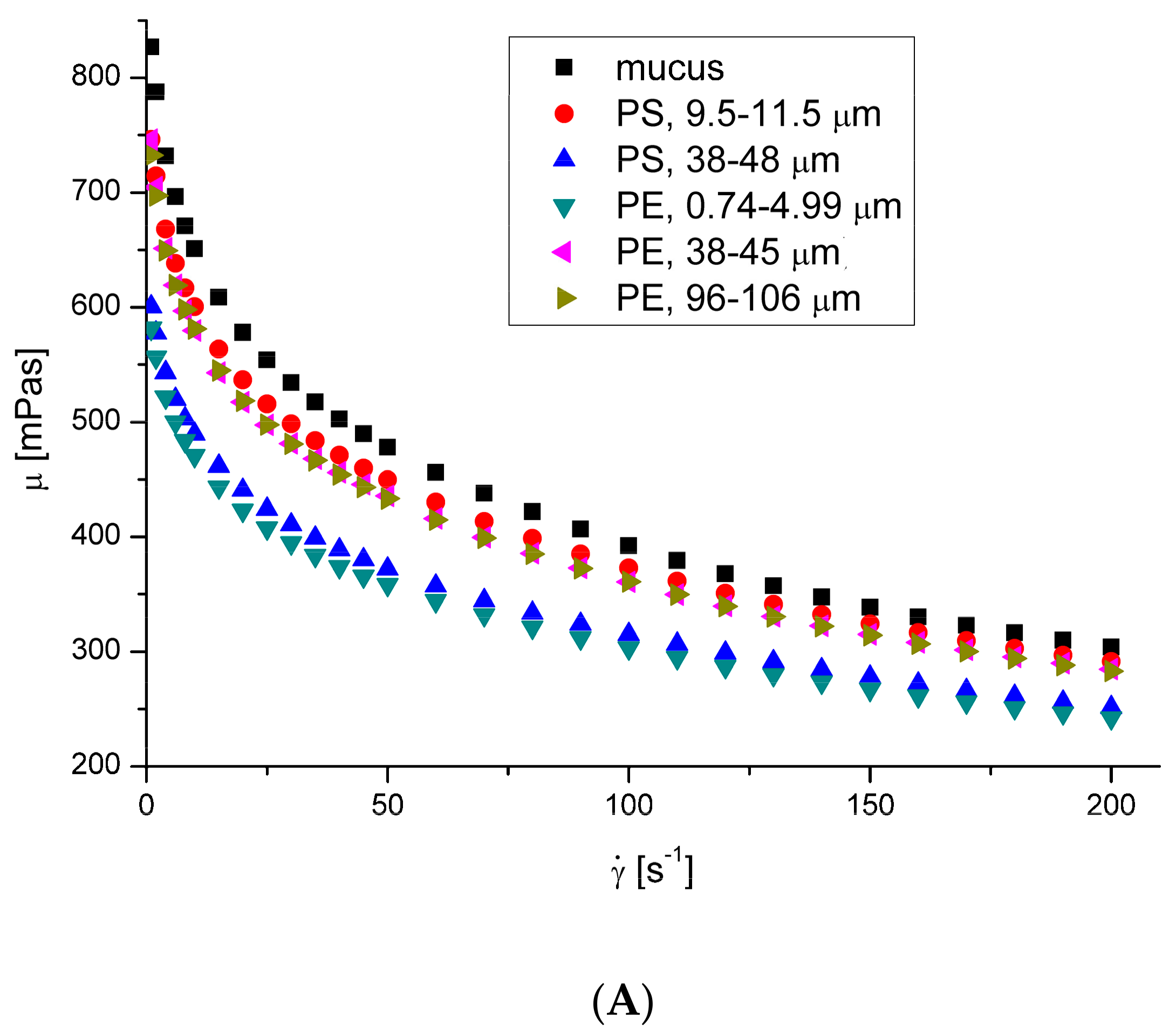
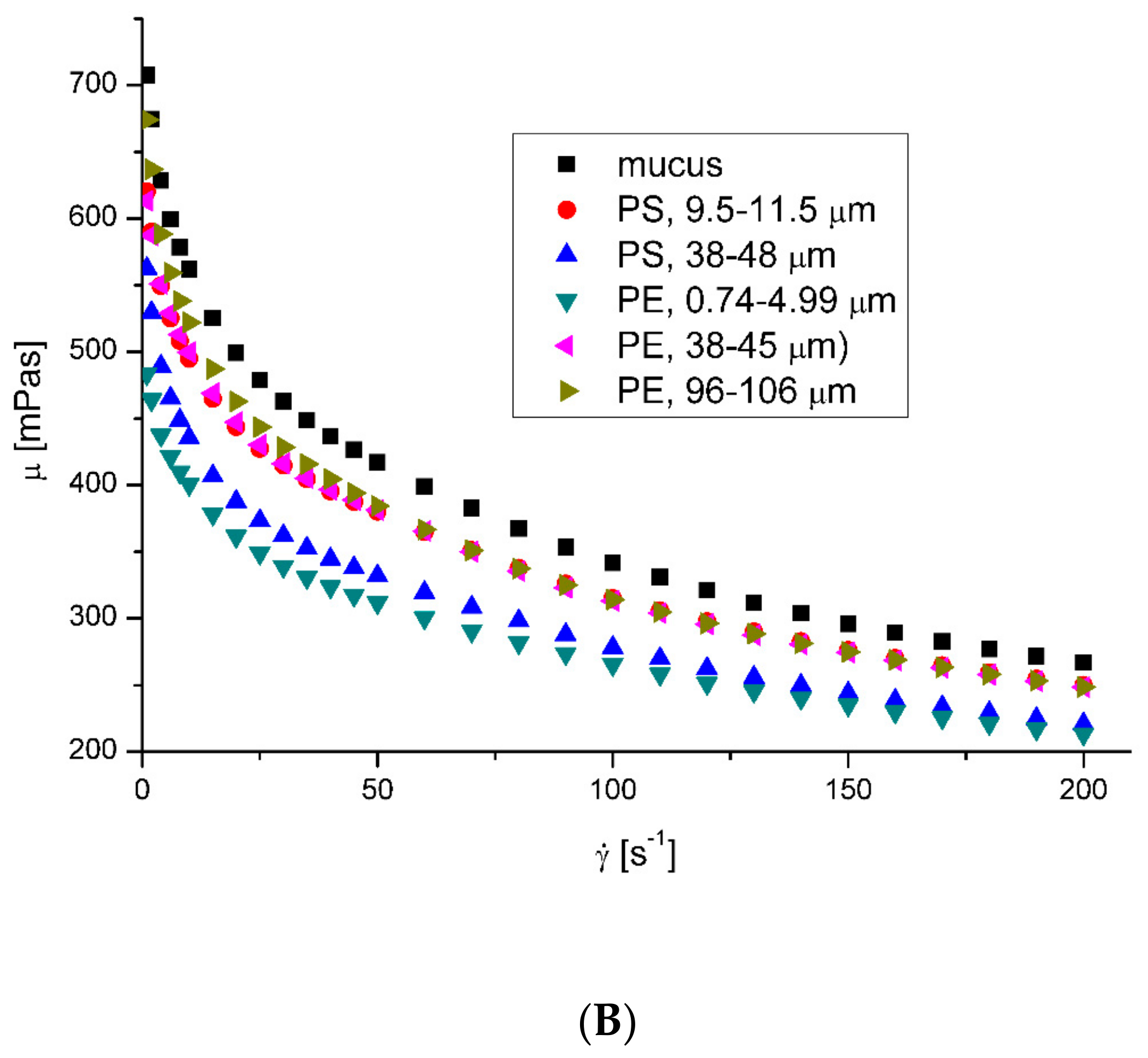
3.2. Rheological Properties of Mucus
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naseer, B.; Srivastava, G.; Qadri, O.; Faridi, S.; Ul Islam, R.; Younis, K. Importance and health hazards of nanoparticles used in the food industry. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2018, 7, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiede, K.; Foss Hansen, S.; Westerhoff, P.; Fren, G.; Hankin, S.; Aitken, R.; Chaudhry, Q.; Boxall, A. How important is drinking water exposure for the risks of engineered nanoparticles to consumers? Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaiman, L.; Aljomah, A.; Bineid, M.; Aljeldah, F.M.; Aldawsari, F.; Liebmann, B.; Lomako, I.; Sexlinger, K.; Alarfaj, R. The occurance nd dietary intake related to the presence of microplastics in drinking water in Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, L.C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Bennett, R.T.; Cowen, M.; Tentzeris, V.; Sadofsky, L.R. Detection of microplastics in human lung tissue using μFTIR spectroscopy. Sci. Total Enviorn. 2022, 831, 154907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador Cesa, F.; Turra, A.; Baruque-Ramos, J. Synthetic fibers as microplastics in the marine environment: A review from textile perspective with a focus on domestic washings. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Ji, X.; Ma, Y.; Lu, B.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X.; Fang, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Dahlgren, R.; et al. Airborne microplastics in indoor and outdoor environments of a coastal city in Eastern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, L.; Scibetta, L.; Makuszewski, P.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Drozdowska, V.; Makuch, P.; Jutrzenka-Trzebiatowska, P.; Zaleska-Medynska, K.; Ando, S.; Saliu, F.; et al. Airborne and marine microplastics from an oceanographic survey at the Baltic Sea: An emerging role of air-sea interaction? Sci. Total Eviorn. 2022, 824, 153709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tena, A.F.; Clarà, P.C. Deposition of inhaled particles in the lungs. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2012, 48, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.C.; Peters, J.I.; Williams, R.O., III. Influence of particle size on regional lung deposition–what evidence is there? Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 406, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Dick Vethaak, A.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Eniorn. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.V.; Bansod, G.; Mahajan, M.; Dietrich, P.; Singh, S.P.; Rav, K.; Thissen, A.; Bharde, A.M.; Rothenstein, D.; Kulkarni, S.; et al. Digital Transformation in Toxicology: Improving Communication and Efficiency in Risk Assessment. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 21377–21390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciola, A.; Visalli, G.; Pruiti Ciarello, M.; Di Pietro, A. Newly Emerging Airborne Pollutants: Current Knowledge of Health Impact of Micro and Nanoplastics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato-Lourenco, L.F.; dos Santos Galvao, L.; de Weger, L.A.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Vijver, M.G.; Mauad, T. An emerging class of air pollutants: Potential effects of microplastics to respiratory human health? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Chou, E.L.; Baecker, A.; You, N.-C.Y.; Song, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, S. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals, risk of type 2 diabetes, and diabetes-related metabolic traits: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes 2016, 8, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Transade, L.; Liu, B.; Bao, W. Phthalates and attributable mortality: A population-based longitudinal cohort study and cost analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118021. [Google Scholar]
- Hirt, N.; Bod-Malapel, M. Immunotoxicity and intestinal effects of nano- and microplastics: A review of the literature. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastics Europe. Plastics—The Facts; Plastics Europe: Brusseles, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mosca, A.C.; Chen, J. Food-saliva interactions: Mechanisms and implications. Trends Food Sci. Techn. 2017, 66, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christersson, C.E.; Lindh, L.; Arnebrant, T. Film-forming properties and viscosities of saliva substitutes and human whole saliva. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2000, 108, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, I.; Casciaro, B.; Miro, A.; Quaglia, F.; Mangoni, M.L.; Ungaro, F. Overcoming barriers in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections: Engineered nanoparticles for local delivery of a cationic antimicrobial peptide. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 717–725. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, M.; Krauland, E.; Wirtz, D.; Henes, J. Transport of polymeric nanoparticle gene carriers in gastric mucus. Biotechnol. Prog. 2004, 20, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, S.L.; Smith, H.D.C. Disruption of the mucus barrier by topically applied exogenous particles. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oßmann, B.E.; Sarau, G.; Holtmannspötter, H.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Christiansen, S.H.; Dicke, W. Small-sized microplastics and pigmented particles in bottled mineral water. Water Res. 2018, 141, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Bi, R.; Guo, Q.; Yu, X.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, Z.; Liu, T.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Detection and analysis of microplastics in human sputum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2476–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gittings, S.; Turnbull, N.; Henry, B.; Roberts, C.J.; Gershkovich, P. Characterisation of human saliva as a platform for oral dissolution medium development. Euro. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 91, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Cai, M.; Shi, Y.; Luo, Z.; Wang, T. Influence of cough airflow characteristics on respiratory mucus clearance. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 041911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C. Nonlinear Least Squares: Trust Region Methods. In Encyclopedia of Optimization, 2nd ed.; Floudas, C.A., Pardalos, P.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 2630–2637. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, R. Effect of particle size distribution and shear rate on relative viscosity of concentrated suspensions. Rheol. Acta 2021, 60, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesbrock, A.R.; Dirksen, T.; Schuster, G. Effects of tung oil on salivary viscosity and extent and incidence of dental caries in rats. Caries Res. 1992, 26, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yas, B.A.; Radhi, N.J. Salivary viscosity in relation to oral health status among a group of 20–22 years old dental students. Iraqi J. Comm. Med. 2013, 3, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Kitada, K.; Oho, T. Effect of saliva viscosity on the co-aggregation between oral streptococci and Actinomyces naeslundii. Gerodontology 2011, 29, e981–e987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalczuk, U.; Przekop, R.; Moskal, A. The effect of selected nanoparticles on rheological properties of human blood. Bull. Polish Acad. Sci. Techn. Sci. 2022, 70, e140437. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, W. How to decrease the viscosity of suspension with the second fluid and nanoparticles? Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvaramia, M.; Mangiapia, G.; Pipich, V.; Appavou, M.-S.; Jaksch, S.; Holderer, O.; Rukhadze, M.D.; Frielinghaus, H. Tunable viscosity modification with diluted particles: When particles decrease the viscosity of complex fluids. Colloid Polymer Sci. 2019, 297, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, E.A.; Habibi, M.; Haddad, E.; Sammar, M.; Angel, D.L.; Dror, H.; Lahovitski, H.; Booth, A.M.; Sabbah, I. Mechanism of nanoplastics capture by jellyfish mucin and its potential as a sustainable water treatment technology. Sci. Total Enviorn. 2023, 869, 161824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poling, B.E.; Prausnitz, J.M.; O’Connel, J.P. The Properties of Gases and Liquids, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 11.1–11.55. [Google Scholar]
- Penconek, A.; Michalczuk, U.; Moskal, A. The effect of airborne particles on human body fluids. In Practical Aspects of Chemical Engineering, 1st ed.; Ochowiak, M., Woziwodzki, S., Mitkowski, P.T., Doligalski, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 305–313. [Google Scholar]



| Particles | Number of Particles in 1 g |
|---|---|
| PE 0.74–4.99 μm | 7.762 × 108 |
| PE 38–45 μm | 2.672 × 107 |
| PE 96–106 μm | 2.029 × 106 |
| PS 9.5–11.5 μm | 4.182 × 108 |
| PE 38–48 μm | 2.378 × 107 |
| Model | Formula | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Prandtl | A (Pa), C (s−1) | |
| Powell–Eyring | A (s−1), B (Pa), C (Pas) | |
| Williamson | A (Pa), B (s−1), m∞ (Pas) | |
| Sisko | A (Pas), B (Pasn), n (-) |
| Case | k (mPasn) | n (-) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saliva, 36.6 °C | 2.052 | 0.9598 | 0.8647 |
| Saliva, 40 °C | 1.813 | 0.9797 | 0.9911 |
| PS, 9.5–11.5 μm, 36.6 °C | 3.904 | 0.8169 | 0.9918 |
| PS, 9.5–11.5 μm, 40 °C | 3.619 | 0.8041 | 0.9889 |
| PS, 38–48 μm, 36.6 °C | 2.645 | 0.8782 | 0.8816 |
| PS, 38–48 μm, 40 °C | 2.759 | 0.8482 | 0.8891 |
| PE, 0.74–4.99 μm, 36.6 °C | 2.514 | 0.8924 | 0.9681 |
| PE, 0.74–4.99 μm, 40 °C | 3.323 | 0.8198 | 0.9809 |
| PE, 38–45 μm, 36.6 °C | 4.038 | 0.7874 | 0.9876 |
| PE, 38–45 μm, 40 °C | 3.980 | 0.7685 | 0.9863 |
| PE, 96–106 μm, 36.6 °C | 2.407 | 0.8954 | 0.9835 |
| PE, 96–106 μm, 40 °C | 2.911 | 0.8551 | 0.8708 |
| Case | k (mPasn) | n (-) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mucus, 36.6 °C | 1531 | 0.6987 | 0.9983 |
| Mucus, 40 °C | 1301 | 0.7043 | 0.9984 |
| PS, 9.5–11.5 μm, 36.6 °C | 1367 | 0.7122 | 0.9984 |
| PS, 9.5–11.5 μm,40 °C | 1097 | 0.7244 | 0.9985 |
| PS, 38–48 μm, 36.6 °C | 1032 | 0.7372 | 0.9989 |
| PS, 38–48 μm, 40 °C | 944 | 0.7294 | 0.9987 |
| PE, 0.74–4.99 μm, 36.6 °C | 992 | 0.7374 | 0.9985 |
| PE, 0.74–4.99 μm, 40 °C | 831 | 0.7470 | 0.9988 |
| PE, 38–45 μm, 36.6 °C | 1305 | 0.7874 | 0.9876 |
| PE, 38–45 μm, 40 °C | 1173 | 0.7102 | 0.9988 |
| PE, 96–106 μm, 36.6 °C | 944 | 0.7484 | 0.9988 |
| PE, 96–106 μm, 40 °C | 1113 | 0.7205 | 0.9986 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Przekop, R.; Michalczuk, U.; Penconek, A.; Moskal, A. Effect of Microplastic Particles on the Rheological Properties of Human Saliva and Mucus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20227037
Przekop R, Michalczuk U, Penconek A, Moskal A. Effect of Microplastic Particles on the Rheological Properties of Human Saliva and Mucus. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(22):7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20227037
Chicago/Turabian StylePrzekop, Rafał, Urszula Michalczuk, Agata Penconek, and Arkadiusz Moskal. 2023. "Effect of Microplastic Particles on the Rheological Properties of Human Saliva and Mucus" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 22: 7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20227037
APA StylePrzekop, R., Michalczuk, U., Penconek, A., & Moskal, A. (2023). Effect of Microplastic Particles on the Rheological Properties of Human Saliva and Mucus. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(22), 7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20227037









