Respiratory Parameters as Predictors of Balance and Gait Ability in Patients with Stroke at Discharge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
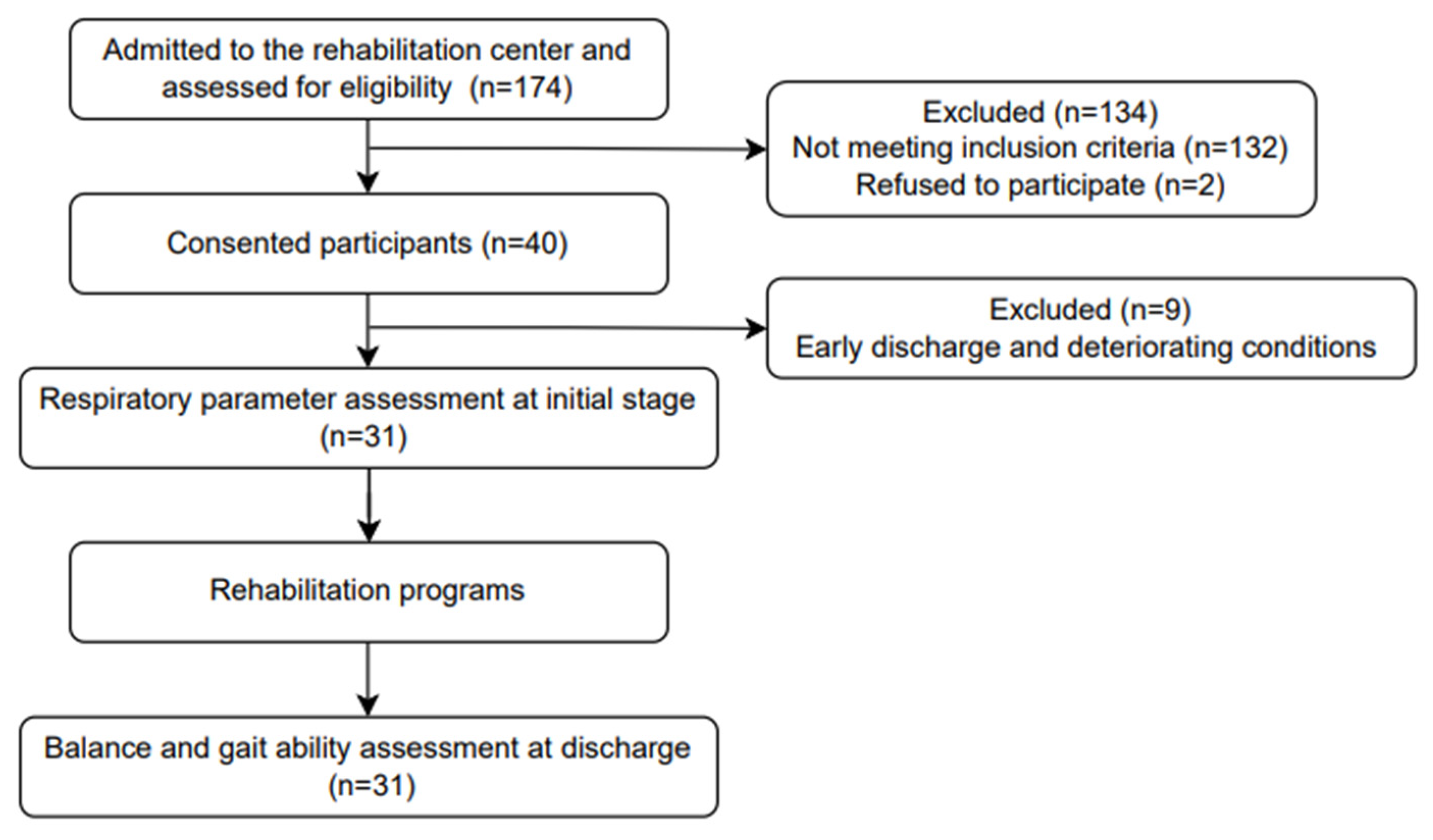
2.1. Study Design and Samples
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Respiratory Variable Assessments
2.3.2. Balance and Gait Variable Assessments
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Norrving, B.; Mensah, G.A. Global burden of stroke. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandt, S.R.; Caballero, R.M.; Junior, L.A.F.; Dias, A.S. Correlation between trunk control, respiratory muscle strength and spirometry in patients with stroke: An observational study. Physiother. Res. Int. 2011, 16, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, M.R.; Kim, N.S. Combined respiratory muscle training facilitates expiratory muscle activity in stroke patients. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 1970–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikbabu, S.; Chakrapani, M.; Ganeshan, S.; Rakshith, K.C.; Nafeez, S.; Prem, V. A review on assessment and treatment of the trunk in stroke: A need or luxury. Neural Regen. Res. 2012, 7, 1974–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes-Neto, M.; Saquetto, M.B.; Silva, C.M.; Carvalho, V.O.; Ribeiro, N.; Conceição, C.S. Effects of respiratory muscle training on respiratory function, respiratory muscle strength, and exercise tolerance in patients poststroke: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 1994–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Chuchalin, A.; Gusev, E.; Martynov, M.; Shogenova, L.; Panin, A. The syndrome of respiratory failure in acute stroke patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-H. Brain and lung: Lung injury in patients with brain injury. J. Neurocrit. Care 2017, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinotti, R.; Dordonnat-Moynard, A.; Feuillet, F.; Roquilly, A.; Rondeau, N.; Lepelletier, D.; Caillon, J.; Asseray, N.; Blanloeil, Y.; Rozec, B.; et al. Risk factors and pathogens involved in early ventilator-acquired pneumonia in patients with severe subarachnoid hemorrhage. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmer, J.; Hou, P.; Wilcox, S.R.; Chang, Y.; Schreiber, H.; Okechukwu, I.; Pontes-Neto, O.; Bajwa, E.; Hess, D.R.; Avery, L.; et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage*. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 1992–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon, F.; Maltenfort, M.; Dey, S.; Ghosh, S.; Vibbert, M.; Urtecho, J.; Jallo, J.; Ratliff, J.K.; McBride, J.W.; Bell, R. The prevalence and impact of mortality of the acute respiratory distress syndrome on admissions of patients with ischemic stroke in the United States. J. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 29, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, H.; Yamakawa, Y.; Kubota, E. Deformation of the ventrolateral medulla oblongata by subarachnoid hemorrhage from ruptured vertebral artery aneurysms causes neurogenic pulmonary edema. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2001, 41, 529–534; discussion 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossmann, I.; Rodriguez, K.; Soni, M.; Joshi, P.K.; Patel, S.C.; Shreya, D.; Zamora, D.I.; Patel, G.S.; Sange, I. Stroke and pneumonia: Mechanisms, risk factors, management, and prevention. Cureus 2021, 13, e19912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeugwu, V.E.; Olaogun, M.; Mbada, C.E.; Adedoyin, R. Comparative Lung function performance of stroke survivors and age-matched and sex-matched controls. Physiother. Res. Int. 2013, 18, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira-Salmela, L.F.; Parreira, V.F.; Britto, R.R.; Brant, T.C.; Inácio, E.P.; Alcântara, T.O.; Carvalho, I.F. Respiratory pressures and thoracoabdominal motion in community-dwelling chronic stroke survivors. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1974–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptaszkowska, L.; Ptaszkowski, K.; Halski, T.; Taradaj, J.; Dymarek, R.; Paprocka-Borowicz, M. Immediate effects of the respiratory stimulation on ventilation parameters in ischemic stroke survivors: A randomized interventional study (CONSORT). Medicine 2019, 98, e17128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandevia, S.C.; Butler, J.E.; Hodges, P.W.; Taylor, J.L. Balancing acts: Respiratory sensations, motor control and human posture. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, P.W.; Gandevia, S.C. Activation of the human diaphragm during a repetitive postural task. J. Physiol. 2000, 522, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Kim, G.S.; Jeong, Y.G.; Moon, H.I. Can pulmonary function testing predict the functional outcomes of poststroke patients? An observational study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 99, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.L.; Steenbruggen, I.; Miller, M.R.; Barjaktarevic, I.Z.; Cooper, B.G.; Hall, G.L.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; McCarthy, K.; McCormack, M.C.; et al. Standardization of spirometry 2019 update. An official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society technical statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e70–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolliger, C.T.; Mathur, P.N.; Beamis, J.F.; Becker, H.D.; Cavaliere, S.; Colt, H.; Diaz-Jimenez, J.P.; Dumon, J.F.; Edell, E.; Kovitz, K.L.; et al. ERS/ATS statement on interventional pulmonology. European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 19, 356–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS Statement on respiratory muscle testing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 518–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Cha, Y.J.; You, J.S.H. Effects of dynamic core-postural chain stabilization on diaphragm movement, abdominal muscle thickness, and postural control in patients with subacute stroke: A randomized control trial. NeuroRehabilitation 2020, 46, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydoğan Arslan, S.; Yakut, H.; Demirci, C.S.; Sertel, M.; Kutluhan, S. The reliability and validity of the Turkish version of brunel balance assessment (BBA-T). Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2020, 27, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentiplay, B.F.; Clark, R.A.; Bower, K.J.; Williams, G.; Pua, Y.H. Five times sit-to-stand following stroke: Relationship with strength and balance. Gait Posture 2020, 78, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.K.; Nelson, M.; Brooks, D.; Salbach, N.M. Validation of stroke-specific protocols for the 10-meter walk test and 6-minute walk test conducted using 15-meter and 30-meter walkways. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2020, 27, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.S.; Hui-Chan, C.W. The timed up & go test: Its reliability and association with lower-limb impairments and locomotor capacities in people with chronic stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, H.; Nozoe, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Kamo, A.; Noguchi, M.; Kanai, M.; Mase, K.; Shimada, S. Recovery process of respiratory muscle strength in patients following stroke: A pilot study. Phys. Ther. Res. 2020, 23, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terui, Y.; Iwasawa, S.; Kikuchi, K.; Furukawa, Y.; Suto, E.; Uemura, S.; Satake, M.; Shioya, T. The relationship between gait asymmetry and respiratory function in stroke patients: A pilot study. Open J. Ther. Rehabil. 2021, 9, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.S.D.; Dall’alba, S.C.F.; Forgiarini, S.G.I.; Rossato, D.; Dias, A.S.; Forgiarini Junior, L.A. Relationship between pulmonary function, functional independence, and trunk control in patients with stroke. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2019, 77, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Cho, S.H. Correlation between lung function and functional movement in healthy adults. Healthcare 2020, 8, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Seo, K.M.; Kim, D.K.; Kang, S.H. The relationship between initial trunk performances and functional prognosis in patients with stroke. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 39, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiwatari, M.; Tani, M.; Isayama, R.; Honaga, K.; Hayakawa, M.; Takakura, T.; Tanuma, A.; Kurosu, A.; Hatori, K.; Wada, F.; et al. Prediction of gait independence using the Trunk Impairment Scale in patients with acute stroke. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2022, 15, 17562864221140180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, Y. Predictive analyses for balance and gait based on trunk performance using clinical scales in persons with stroke. Phys. Ther. Rehabil. Sci. 2018, 7, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Jonkman, A.; de Vries, H.; Jansen, D.; Ottenheijm, C.; Girbes, A.; Spoelstra-de Man, A.; Zhou, J.X.; Brochard, L.; Heunks, L. Expiratory muscle dysfunction in critically ill patients: Towards improved understanding. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffler, L.R.; Chae, J. Hemiparetic gait. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 26, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.M.; Eng, J.J. Symmetry in vertical ground reaction force is accompanied by symmetry in temporal but not distance variables of gait in persons with stroke. Gait Posture 2003, 18, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terui, Y.; Suto, E.; Konno, Y.; Kubota, K.; Iwakura, M.; Satou, M.; Nitta, S.; Hasegawa, K.; Satake, M.; Shioya, T. Evaluation of gait symmetry using a tri-axial accelerometer in stroke patients. NeuroRehabilitation 2018, 42, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terui, Y.; Sutoh, E.; Iwasawa, S.; Kikuchi, K.; Furukawa, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Uemura, S.; Satake, M.; Shioya, T. Relationship between respiratory muscle strength and gait asymmetry in stroke patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, PA700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Stroke (n = 31) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 68.68 ± 5.85 |
| Height (cm) | 163.68 ± 7.89 |
| Weight (kg) | 63.42 ± 13.19 |
| Gender (male/female) | 25/6 (81/19) |
| Lesion type (infarction/hemorrhage) | 16/15 (52/48) |
| Time since stroke onset (days) | 43.10 ± 17.39 |
| Paretic side (left/right/bilateral) | 19/8/4 (61/26/13) |
| K-MMSE | 22.23 ± 4.60 |
| Variables | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| FVC (L) | 2.84 ± 0.77 |
| FVC (% predicted) | 82.52 ± 18.61 |
| PEF (L/s) | 5.87 ± 2.14 |
| PEF (% predicted) | 86.32 ± 28.90 |
| MIP (cmH2O) | 66.81 ± 22.42 |
| MIP (%) | 79.81 ± 26.96 |
| MEP (cmH2O) | 95.84 ± 36.23 |
| MEP (%) | 91.19 ± 38.57 |
| TIS | 17.48 ± 4.55 |
| BBS | 34.68 ± 17.90 |
| BBA | 8.45 ± 3.26 |
| 5STS (s) | 11.39 ± 9.91 |
| 10MWT (m/s) | 0.54 ± 0.46 |
| TUG (s) | 19.93 ± 20.04 |
| 6MWT (m) | 185.71 ± 156.62 |
| FVC | PEF | MIP | MEP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIS | 0.625 * | 0.648 * | 0.378 | 0.502 * |
| BBS | 0.232 | 0.470 * | 0.188 | 0.426 |
| BBA | 0.321 | 0.516 * | 0.173 | 0.447 * |
| 5STS | 0.208 | 0.206 | 0.217 | 0.060 |
| 10MWT | 0.262 | 0.489 * | 0.228 | 0.566 * |
| TUG | 0.133 | 0.079 | 0.143 | −0.043 |
| 6MWT | 0.245 | 0.435 | 0.221 | 0.497 * |
| Dependent Variable | Model | Independent Variable | R2 | Adjusted R2 | F | p | Durbin–Watson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIS | 1 | PEF | 0.420 | 0.401 | 21.043 | <0.001 | 2.159 |
| BBS | 1 | PEF | 0.221 | 0.194 | 8.239 | 0.008 | 1.770 |
| BBA | 1 | PEF | 0.266 | 0.241 | 10.510 | 0.003 | 1.753 |
| 10MWT | 1 | MEP | 0.320 | 0.297 | 13.674 | 0.001 | 2.093 |
| 6MWT | 1 | MEP | 0.247 | 0.221 | 9.495 | 0.004 | 2.014 |
| Dependent Variable | Model | Independent Variable | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | p | 95% Confidence Interval for B | Collinearity Statistics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Standard Error | β | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Tolerance | VIF | |||||
| TIS | 1 | PEF | 1.377 | 0.300 | 0.648 | 4.587 | <0.001 | 0.763 | 1.992 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| BBS | 1 | PEF | 3.928 | 1.368 | 0.470 | 2.870 | 0.008 | 1.129 | 6.727 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| BBA | 1 | PEF | 0.786 | 0.242 | 0.516 | 3.242 | 0.003 | 0.290 | 1.281 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 10MWT | 1 | MEP | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.566 | 3.698 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 6MWT | 1 | MEP | 2.147 | 0.697 | 0.497 | 3.081 | 0.004 | 0.722 | 3.572 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.-Y.; Kwon, O.-Y.; Yi, C.-H.; Jeon, H.-S.; Choi, W.J.; Ahn, S.-Y.; Hwang, U.-J. Respiratory Parameters as Predictors of Balance and Gait Ability in Patients with Stroke at Discharge. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 7098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20237098
Park H-Y, Kwon O-Y, Yi C-H, Jeon H-S, Choi WJ, Ahn S-Y, Hwang U-J. Respiratory Parameters as Predictors of Balance and Gait Ability in Patients with Stroke at Discharge. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(23):7098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20237098
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hee-Yong, Oh-Yun Kwon, Chung-Hwi Yi, Hye-Seon Jeon, Woochol Joseph Choi, So-Young Ahn, and Ui-Jae Hwang. 2023. "Respiratory Parameters as Predictors of Balance and Gait Ability in Patients with Stroke at Discharge" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 23: 7098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20237098
APA StylePark, H.-Y., Kwon, O.-Y., Yi, C.-H., Jeon, H.-S., Choi, W. J., Ahn, S.-Y., & Hwang, U.-J. (2023). Respiratory Parameters as Predictors of Balance and Gait Ability in Patients with Stroke at Discharge. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(23), 7098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20237098








