Immersive Experience and Climate Change Monitoring in Digital Landscapes: Evidence from Somatosensory Sense and Comfort
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
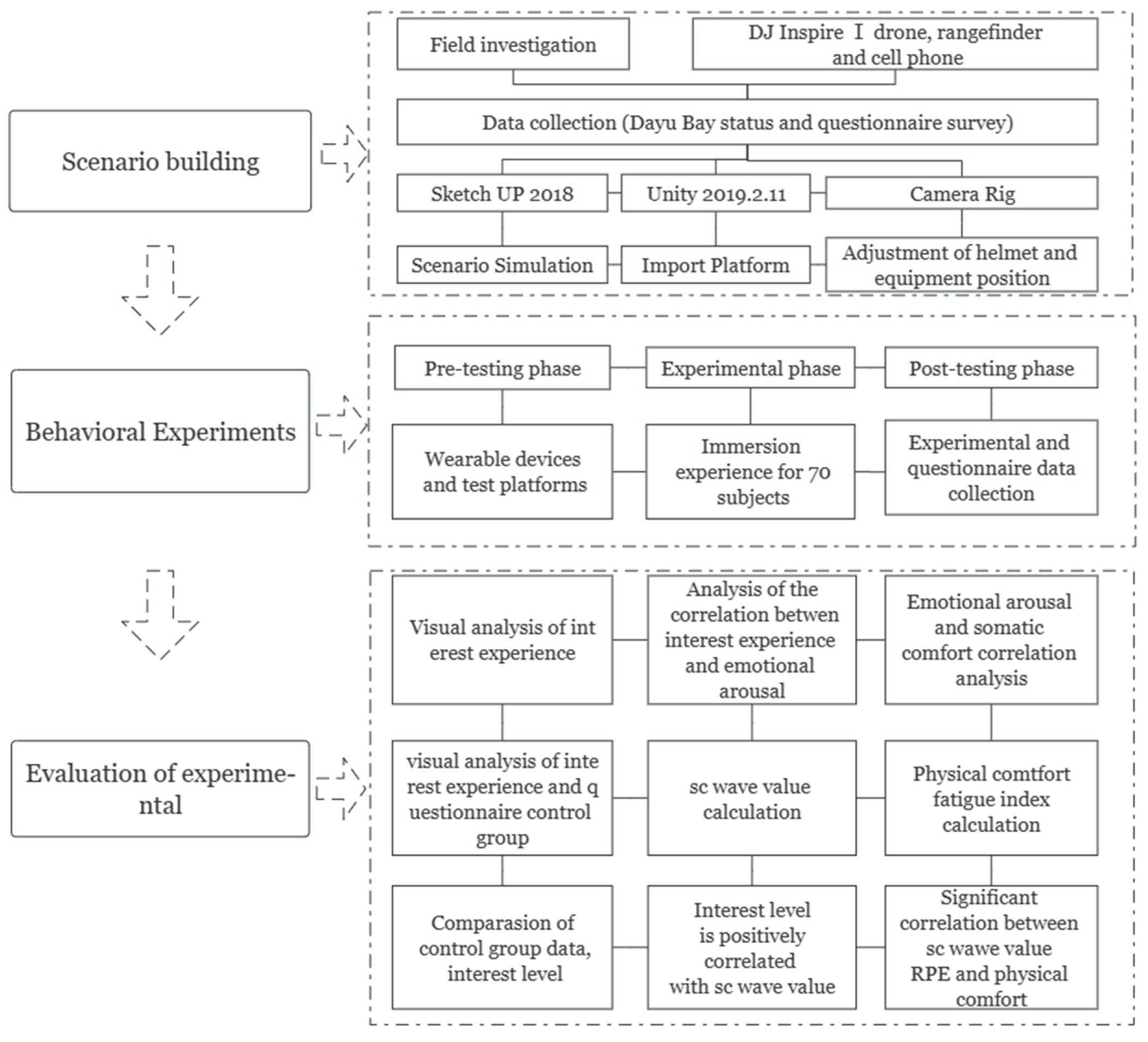
3. Data Sources and Methods
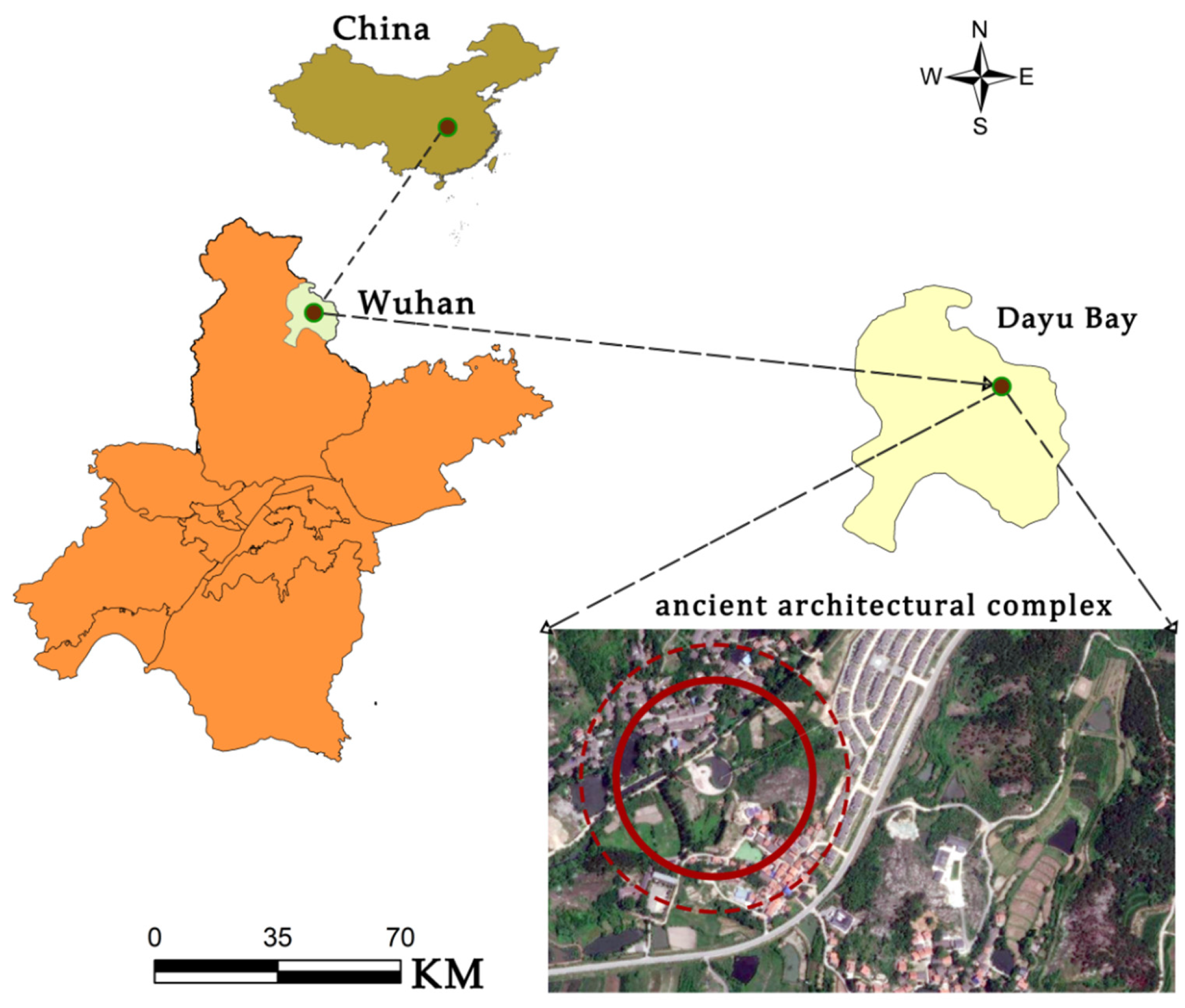
3.1. Location Overview
3.2. Field Investigation
3.3. Construction of Virtual Scenes
3.4. VR Eye Movement and Skin Electrical Experiments
3.4.1. Experimental Hypothesis
3.4.2. Experimental Design
3.4.3. Experimental Materials
3.4.4. Experimental Process
3.4.5. Experimental Results
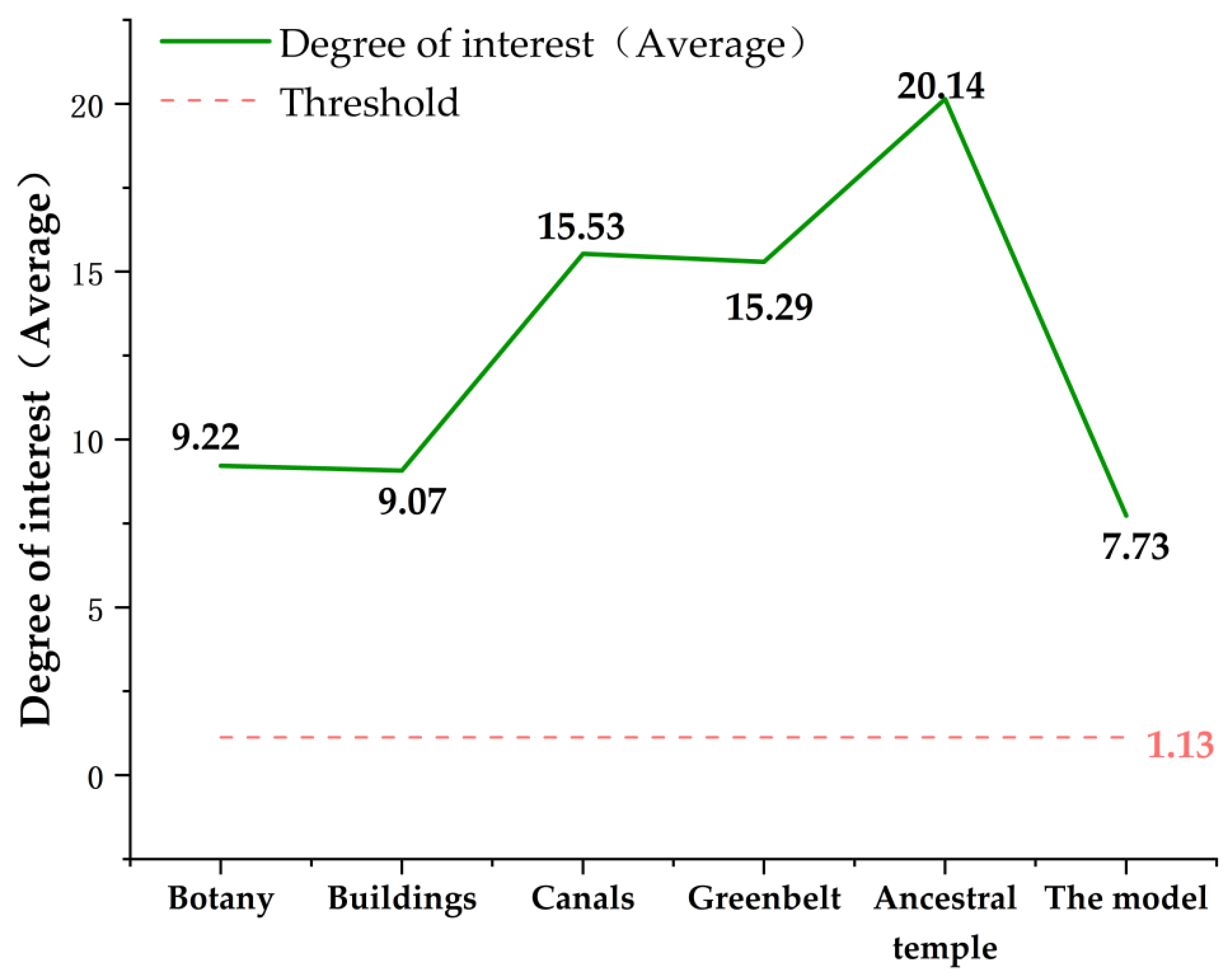
- Visual analysis of interest experience.
- 2.
- Correlation analysis between virtual immersive experience and emotional arousal
- 3.
- Correlation analysis between emotional arousal and somatosensory comfort level
3.4.6. Logical Structure Visualization
4. Research Results
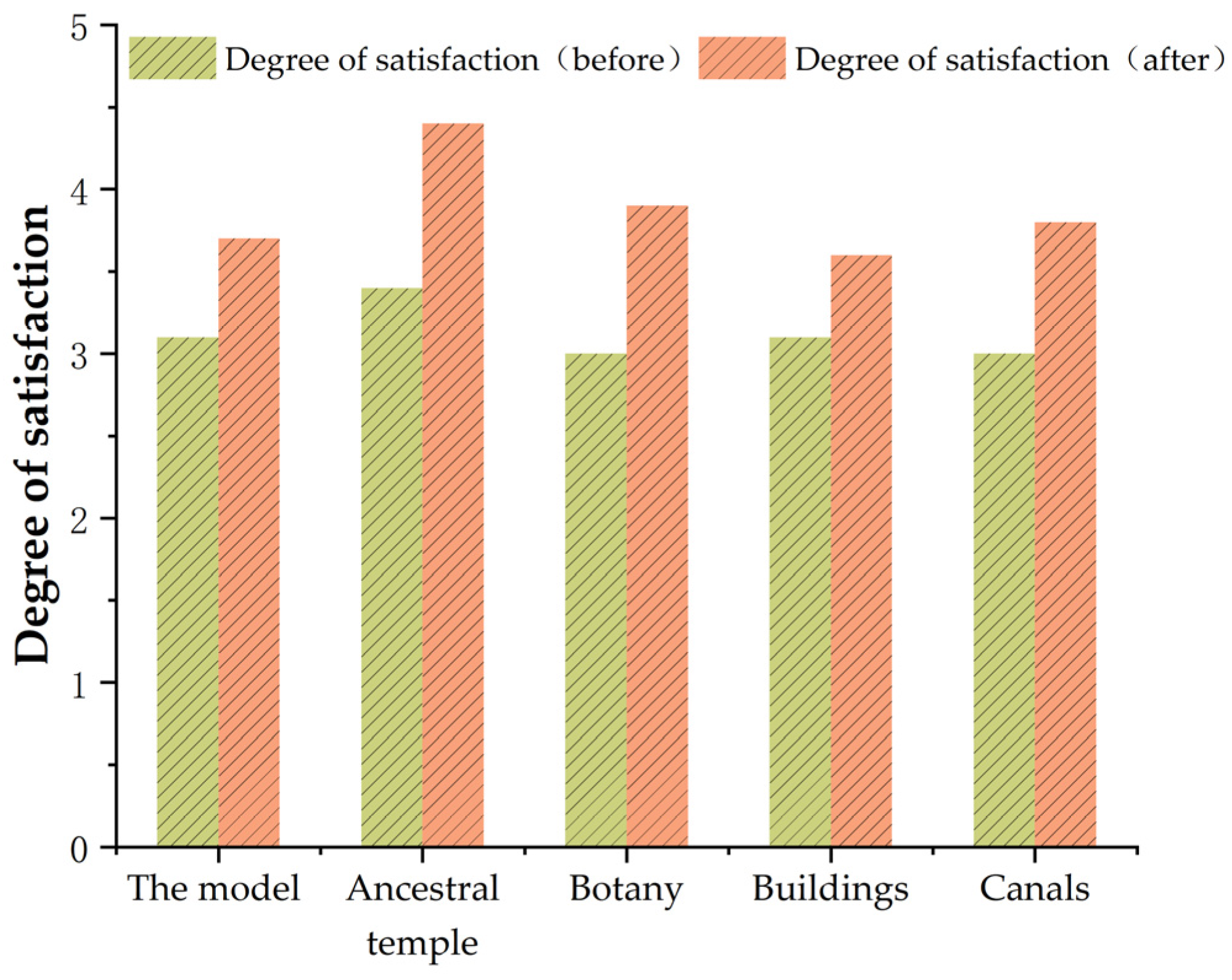
4.1. Subjects Showed the Highest Interest in the Ancient Tree Ecological Area after the Digital Roaming Landscape Immersive Experience
4.2. Subjects’ High Interest after Immersive Experience Is Significantly Correlated with Emotional Arousal
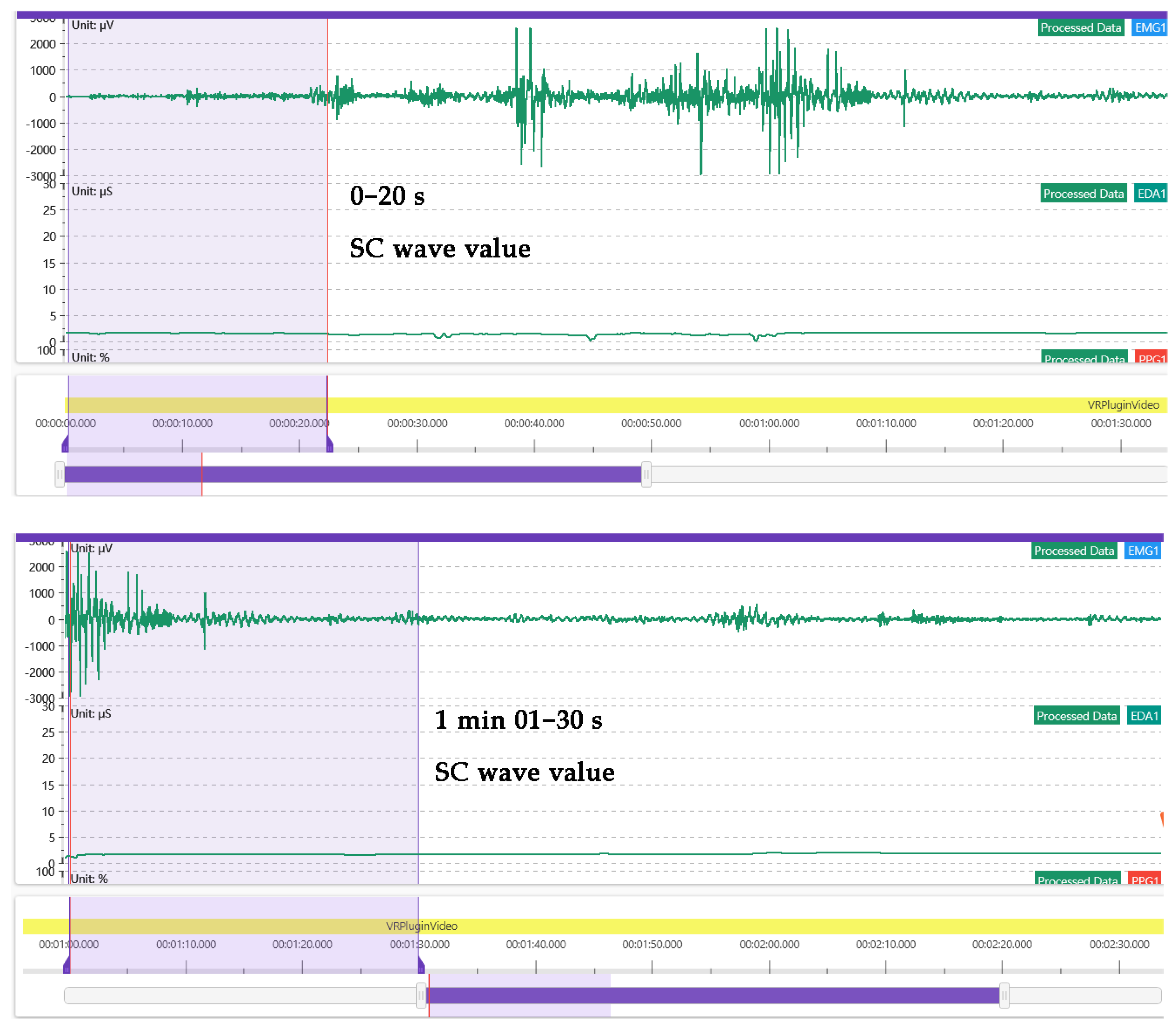
4.3. The Subjects’ Low Emotional Arousal, Low Fatigue Level and High Somatosensory Sense Comfort Were Significantly Correlated
4.4. Somatosensory Comfort Can Effectively Distinguish the Optimal Comfort Level between the Ancient Tree Ecological Area and the Sunlight-Exposed Area
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farooq, M.U.; Shahzad, U.; Sarwar, S.; ZaiJun, L. The impact of carbon emission and forest activities on health outcomes: Empirical evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12894–12906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, E.; Zainab, K.; Muhammad, Z.T.; Hongxia, Z.; Xing, L.R. Extreme weather events risk to crop-production and the adaptation of innovative management strategies to mitigate the risk: A retrospective survey of rural Punjab, Pakistan. Technovation 2022, 117, 102255. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsan, E.; Zainab, K. Estimating smart energy inputs packages using hybrid optimisation technique to mitigate envir-onmental emissions of commercial fish farms. Appl. Energy 2022, 326, 119602. [Google Scholar]
- Spracklen, D. China’s contribution to climate change. Nature 2016, 531, 310–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-J.; Midgley, G.F.; Archer, E.R.M.; Arneth, A.; Barnes, D.K.A.; Chan, L.; Hashimoto, S.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Insarov, G.; Leadley, P.; et al. Actions to halt biodiversity loss generally benefit the climate. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 2846–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.U. On the thought of ecological ethics and its contemporary significance in the chinese multinational proverbs. Inn. Mong. Soc. Sci. 2018, 4, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, G. Materialist Value Orientations as Correlates of the New Ecological Paradigm among University Students in China. Psychol. Rep. 2015, 116, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YuChieh, C.; MinFu, H.; ChunMing, H. An Example of Ecological Wisdom in Historical Settlement: The Wind Environment of Huazhai Village in Taiwan. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2017, 16, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Wang, R.; Gasser, T. Delayed use of bioenergy crops might threaten climate and food security. Nature 2022, 609, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.S.; Church, S.P.; Dang, L. Does climate change framing matter? Evidence from an experiment of crop advisors in the Midwestern United States. Clim. Change 2017, 162, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadalavada, K.; Kumari, B.D.R.; Kumar, T.S. Sorghum mitigates climate variability and change on crop yield and quality. Planta 2021, 253, 113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Laurance, W.F. The ecology, distribution, conservation and management of large old trees. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1434–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depardieu, C.; Girardin, M.P.; Nadeau, S.; Lenz, P.; Bousquet, J.; Isabel, N. Adaptive genetic variation to drought in a widely distributed conifer suggests a potential for increasing forest resilience in a drying climate. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Fabbri, M.; Zhang, C. Reciprocity in Quarantine: Observations from Wuhan’s COVID-19 Digital Landscapes. Asian Bioeth. Rev. 2020, 12, 435–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Hu, K.; Lysenko, V. A scientometric analysis of agricultural pollution by using bibliometric software VoSViewer and Histcite™. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 37882–37893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L. Retracted Article: Application of heterogeneous execution body scheduling and VR technology for mimic cloud services in urban landscape design. Pers Ubiquit Comput. 2021, 25 (Suppl. S1), 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, P.; Sun, W. Auxiliary use and detail optimization of computer VR technology in landscape design. Arab J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Narumi, T.; Tanikawa, T.; Hirose, M. Basic Study on Connecting AR and VR for Digital Exhibition with Mobile Devices. In Human Interface and the Management of Information: Supporting Learning, Decision-Making and Collaboration; Yamamoto, S., Ed.; HIMI. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 10274. [Google Scholar]
- Wellsby, M.; Pexman, P.M. Developing embodied cognition: Insights from children’s concepts and language processing. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danish, J.A.; Enyedy, N.; Saleh, A. Learning in embodied activity framework: A sociocultural framework for embodied cognition. Intern. J. Comput.-Support. Collab. Learn 2020, 15, 49–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, N.; Grimstead, I.J.; Avis, N.J. Accessible haptic technology for drug design applications. J. Mol. Model. 2009, 15, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xianzheng, F.; Dengyang, X. Not only for Watching, but also for Touching: How does the Haptic Mental Imagery of Applications Icon Influence Consumer’s Preference. Manag. World 2020, 7, 153–170. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Gao, C.; Cui, L. The role of emotion arousal in the retrieval practice effect. Exp. Brain Res. 2019, 237, 3241–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.P. Vagal Control of the Heart: Experimental Basis and Clinical Implications. Crit. Care Med. Oct. 1995, 23, 1795–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, J.; Balogun, M.-S.; Wang, P.; Tong, Y.; Huang, Y. Charge Relays via Dual Carbon-Actions on Nanostructured BiVO4 for High Performance Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Edward, A.; Huizenga, C.; Taeyoung, H. Thermal sensation and comfort models for non-uniform and transient environments, part Ⅱ: Local comfort of individual body parts. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiman, M.M. Seasonal depression of fertility in hot climates as influenced by production level and temperature humidity stress. Genet. Sel. Evol. 1982, 14, 103a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigo, N. Teaching and Learning About Unconventional Food Plants in an Edible Urban Landscape: A Brief Report. In Local Food Plants of Brazil. Ethnobiology; Jacob, M.C.M., Albuquerque, U.P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 413–417. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Schwarz, P.; Yang, H. Adjusting energy consumption structure to achieve China’s CO2 emissions peak. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 122, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Guo, B.; Fan, S.; Tan, J. Analysis of the change in the original Metasequoia glyptostroboides population and its environment in Lichuan, Hubei from 1948 to 2003. Front. For. China 2003, 1, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.F.; Gao, Y.K. Appreciating the beauty and history of the ancient trees—Discussion on the sustainable utilization of the landscape of ancient trees of fragrant hills park in beijing. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2014, 30, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hammami, F.; Uzer, E. Heritage and Resistance: Theoretical Insights. In Theorizing Heritage through Non-Violent Resistance. Palgrave Studies in Cultural Heritage and Conflict; Hammami, F., Uzer, E., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 257–279. [Google Scholar]
- Gangyi, T. Research of Dayuwan Village Dwellings in Huangpi County, Hubei Province. Huazhong Archit. 1999, 4, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Duanya, Z.; Xingyu, Z. Identification and Protection of Traditional Geomagnetic Pattern of Historical Villages Based on GIS Spatial Model: Taking Dayu Bay of Wuhan City, Hubei Province as an Example. Dev. Small Cities Towns 2022, 40, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Fangting, W.; Zheng, L.; Renwen, W. Research on the Development of Chinese Traditional Ancient Villages Tourism Based on Tourist Satisfaction. Qual. Explor. 2017, 14, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhiyi, Y.; Jingqi, L. Identification and mapping of landscape gene in historic and cutural villages and towns:a case study of Dayuwan village, Huangpi district. City Planning Review 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Xu, J.; Yang, Z. Preliminary Research on Planning of Decentralizing Ancient Towns in Small-Scale Famous Historic and Cultural Cities with a Case Study of Tingchow County, Fujian Province. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Weijun, Y. A Preliminary Study on the Development of Farming and Reading Culture in the Traditional Villages—A Case Study of Da Yuwan Village In Huangpi. Agric. Hist. China 2017, 36, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, G.; Shi, X.; He, D. Designing a spatial pattern to rebalance the orientation of development and protection in Wuhan. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, M.G.; Ştefan, L.D.; Ionescu, B. Visual Interestingness Prediction: A Benchmark Framework and Literature Review. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1526–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, R.; Shekar, B. Interestingness of association rules in data mining: Issues relevant to e-commerce. Sadhana 2005, 30, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fager, S.K.; Sorenson, T.; Jakobs, E.; Koester, H.; Jakobs, T.; Beukelman, D.R. Multi-modal access method (eye-tracking + switch-scanning) for individuals with severe motor impairment: A preliminary investigation. Assist. Technol. 2022, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, J.D.; Rizzo, A.; Geng, J.J.; Schweitzer, J.B. Measuring Attentional Distraction in Children With ADHD Using Virtual Reality Technology With Eye-Tracking. Front. Virtual Real. 2022, 3, 855895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulbright, R. Cognitive Augmentation Metrics Using Representational Information Theory. In Augmented Cognition. Enhancing Cognition and Behavior in Complex Human Environments; Schmorrow, D., Fidopiastis, C., Eds.; AC. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; p. 10285. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, R.D.; Marsden, P. Physiological responses to different WEB page designs. Int. J. Hum. -Comput. Stud. 2003, 59, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Research and Design of Digital Display of Ancient and Famous Trees in Beijing. Comput. Softw. Comput. Appl. 2019, 4, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Perini, K.; Magliocco, A. Effects of vegetation, urban density, building height, and atmospheric conditions on local temperatures and thermal comfort. Urban For. Urban Green. 2014, 13, 459–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Chen, B.; Liu, K. Quantification of the influence of thermal comfort and life patterns on outdoor space activities. Build. Simul. 2020, 13, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, J.; Cleyndert, G.; Newman, R.; Brugere, C.; Cuni-Sanchez, A.; Marchant, R. Adaptation of Seaweed Farmers in Zanzibar to the Impacts of Climate Change. In African Handbook of Climate Change Adaptation; Oguge, N., Ayal, D., Adeleke, L., da Silva, I., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Addas, A. Exploring the pattern of use and accessibility of urban green spaces: Evidence from a coastal desert megacity in Saudi Arabia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 55757–55774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuze, J.; Xindi, Z.; Xiaohu, J.; Zixuan, W.; Jianyu, C. A study on climate comfort of public space in traditional villages in hot summer and cold winter zones: A case study of Dayuwan village in Wuhan. Urban. Archit. 2018, 23, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Seijo, M.; Larumbe, E.; Alkhatib, A. Effectiveness of multi-ingredient supplement on substrate utilisation, perception of hunger, mood state and rate of perceived exertion (RPE) at rest and during exercise. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12 (Suppl. S1), 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crewe, H.; Tucker, R.; Noakes, T.D. The rate of increase in rating of perceived exertion predicts the duration of exercise to fatigue at a fixed power output in different environmental conditions. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 103, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, A. Use of rating of perceived exertion for determining plyometric exercises intensity in physically active men. Sport Sci. Health 2014, 10, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.; Vance, S.; Lomax, M. Measurement frequency influences the rating of perceived exertion during sub-maximal treadmill running. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, Y.H.; Toh, H.S.; Chew, B.T. A review of human thermal comfort model in predicting human–environment interaction in non-uniform environmental conditions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 14739–14763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanos, J.K.; Warland, J.S.; Gillespie, T.J. Thermal comfort modelling of body temperature and psychological variations of a human exercising in an outdoor environment. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2022, 56, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.H.; Chen, C.L.; Ma, J.P. Eye Tracking Analysis of Readers’ Psychological Interaction with Marketing Copy Referencing Life Values. In HCI International 2015—Posters’ Extended Abstracts. HCI 2015. Communications in Computer and Information Science; Stephanidis, C., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 528. [Google Scholar]
- Machała, E.; Redynk, M.; Gruchała, A.; Kołomecki, K. Analysis of exercise tolerance on the basis of six-minute walk test—6MWT and Borg RPE scale in men with inguinal hernia before and after Lichtenstein repair. Pol. Prz. Chir. 2020, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessels, R.S.; Kemner, C.; van den Boomen, C.; Hooge, I.T.C. The area-of-interest problem in eyetracking research: A noise-robust solution for face and sparse stimuli. Behav. Res. 2016, 48, 1694–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongerius, C.; Callemein, T.; Goedemé, T. Eye-tracking glasses in face-to-face interactions: Manual versus automated assessment of areas-of-interest. Behav. Res. 2021, 53, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorigo, L.; Haridasan, M.; Brynjarsdóttir, H.; Xia, L.; Joachims, T.; Gay, G.; Granka, L.; Pellacini, F.; Pan, B. Eye tracking and online search: Lessons learned and challenges ahead. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 2008, 59, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtel, E.; Lau, N.; Park, J. Eye tracking in surgical education: Gaze-based dynamic area of interest can discriminate adverse events and expertise. Surg. Endosc. 2019, 33, 2249–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhou, S.; Chen, X.; Lin, Z.; Gan, F. Colour Preference and Healing in Digital Roaming Landscape: A Case Study of Mental Subhealth Populations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Huang, T.; Gan, F.; Ye, X. Research on Ecological Landscape Design and Healing Effect Based on 3D Roaming Technology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briefer, E.; Maigrot, A.L.; Mandel, R. Erratum: Segregation of information about emotional arousal and valence in horse whinnies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 46956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G. The Qingdao Preschooler Facial Expression Set: Acquisition and Validation of Chinese Children’s Facial Emotion Stimuli. Front. Psychol. 2021, 11, 554821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kron, A.; Schul, Y.; Cohen, A.; Hassin, R.R. Feelings don’t come easy: Studies on the effortful nature of feelings. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2010, 139, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.L. Study on the microclimatic characteristics and human comfort of park plant communities in summer. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2021, 13, 755–765. [Google Scholar]
- Atake, T. New developments in calorimetry and thermal analysis on thermodynamic studies of ceramics. Ceram. Jpn. 2007, 42, 839–846. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Ren, C.; Edward, N.G. Analysis of urban design strategies based on the outdoor wind environment and thermal comfort—A case study of beijing xidan commercial district. Urban Plan. Forum 2012, 5, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, L.I.; Zhang, K.B.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, B.T.; Yang, X.H. Plant community spatial distribution pattern of wetland ecosystem in a semi-arid region of northwestern China. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2008, 30, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K. Research on virtual landscape platform based on gis and vr. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2017, 42, 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L. A Full-body Motion Sensor Based Immersive Forest Landscape Display. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2013, 10, 24. [Google Scholar]
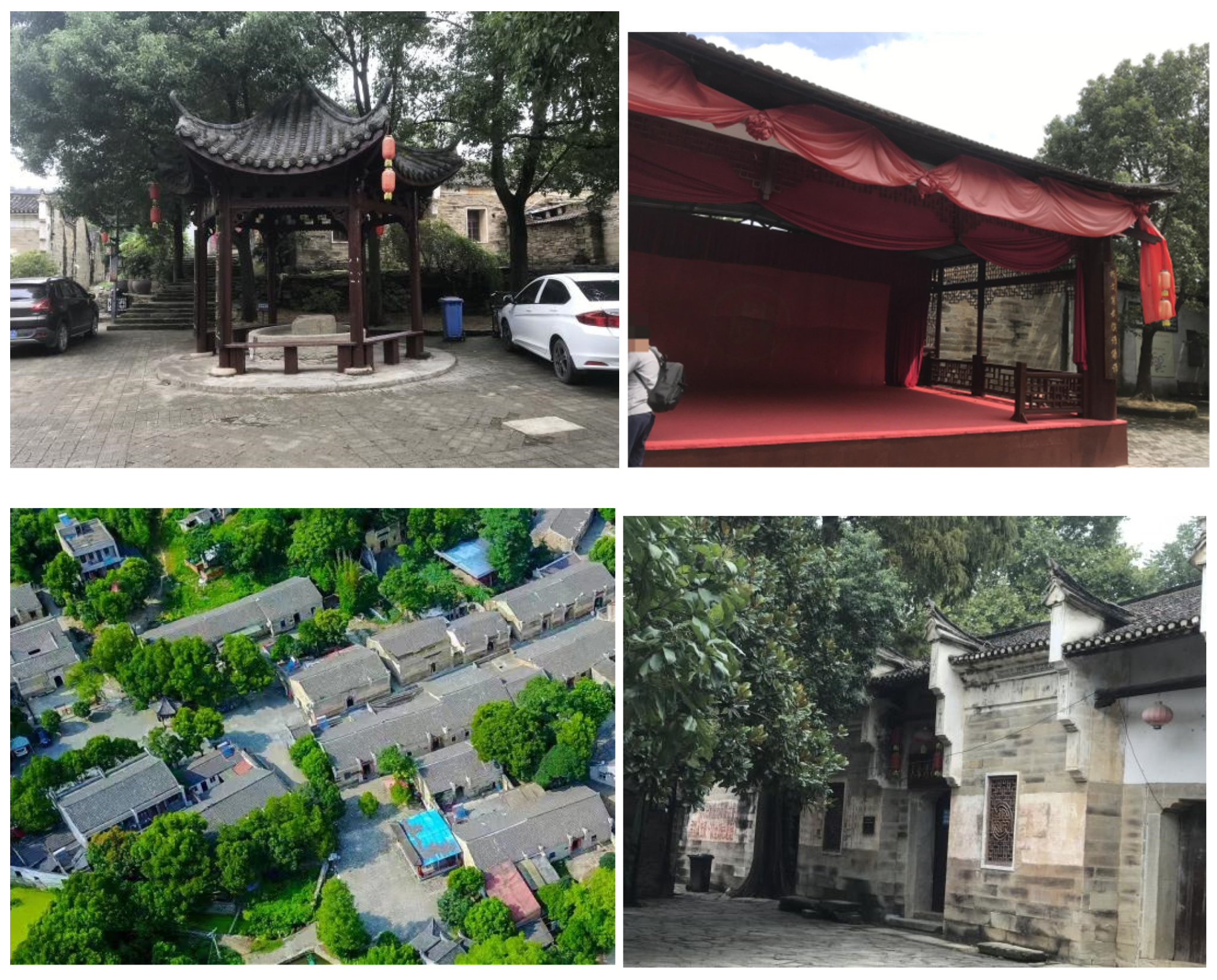




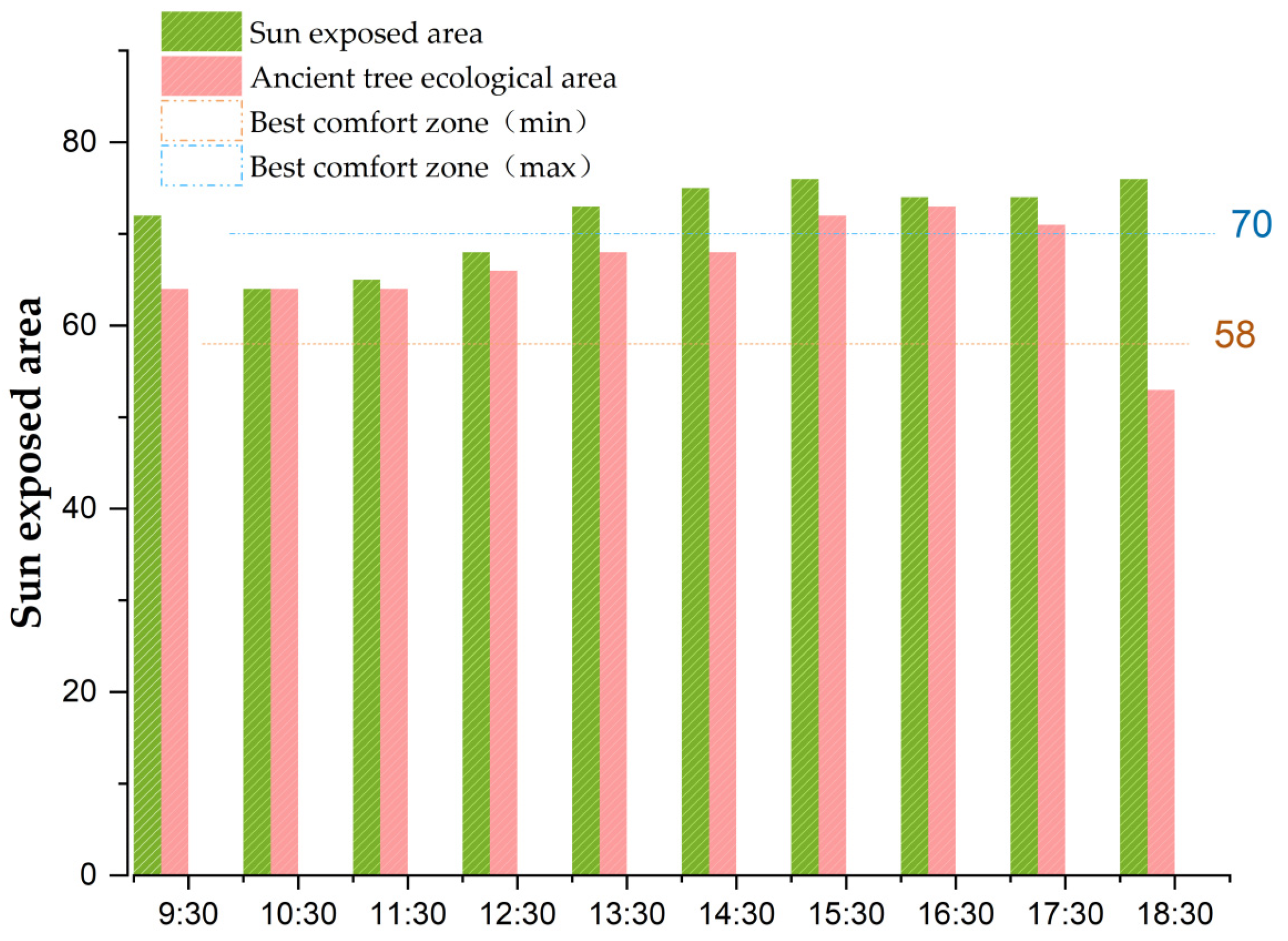

| Ancient Tree Ecological Area | Sunlight-Exposed Area | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | t (°C) | RH (%) | V (m/s) | t (℃) | RH (%) | V (m/s) |
| 9:30 | 26.1 | 84.50 | 17.50 | 29.2 | 56.30 | 18.30 |
| 10:30 | 27.2 | 82.30 | 18.60 | 29.1 | 60.40 | 20.80 |
| 11:30 | 27.1 | 75.40 | 17 | 30.2 | 55.20 | 17.50 |
| 12:30 | 28.3 | 70 | 13.20 | 31.1 | 57.20 | 15.20 |
| 13:30 | 28.3 | 68.10 | 9.80 | 32.4 | 60.10 | 8.70 |
| 14:30 | 29.3 | 57.20 | 8.60 | 33.5 | 60.20 | 7.30 |
| 15:30 | 30.3 | 59.50 | 5.20 | 33.2 | 60.10 | 6.50 |
| 16:30 | 30.2 | 57.40 | 4 | 33.1 | 65.30 | 10 |
| 17:30 | 29.1 | 63.20 | 6.30 | 32.2 | 70.40 | 9.20 |
| 18:30 | 27.4 | 92 | 8.50 | 31.1 | 75.20 | 5.60 |
| AOI | Plant Landscape | Architecture Landscape | The Ditch Landscape | The Street Landscape | Landscape of Ancient Tree Ecological Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The maximum | 9.22 | 9.02 | 15.53 | 15.29 | 20.14 |
| The minimum | 1.52 | 1.60 | 1.15 | 1.15 | 1.15 |
| Interest in the Category | Sig | p | N |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant landscape | 0.00 | <0.01 | 64 |
| Landscape architecture | 0.00 | <0.01 | 64 |
| Water landscape | 0.037 | <0.05 | 64 |
| Landscape of ancient tree ecological area | 0.00 | <0.01 | 64 |
| The street landscape | 0.99 | >0.05 | 64 |
| RPE | ICHB | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SC value | The correlation coefficient | 0.583 ** | 0.257 * |
| p values | 0.000 | 0.040 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ye, X. Immersive Experience and Climate Change Monitoring in Digital Landscapes: Evidence from Somatosensory Sense and Comfort. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043332
Lin Z, Yang Z, Ye X. Immersive Experience and Climate Change Monitoring in Digital Landscapes: Evidence from Somatosensory Sense and Comfort. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):3332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043332
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Zhengsong, Ziqian Yang, and Xinyue Ye. 2023. "Immersive Experience and Climate Change Monitoring in Digital Landscapes: Evidence from Somatosensory Sense and Comfort" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043332
APA StyleLin, Z., Yang, Z., & Ye, X. (2023). Immersive Experience and Climate Change Monitoring in Digital Landscapes: Evidence from Somatosensory Sense and Comfort. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043332







