Trends of Incidence, Mortality, and Risk Factors for Lower Respiratory Infections among Children under 5 Years in China from 2000 to 2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Estimation of LRI Incidence and Mortality
2.3. Correlation of Case Fatality Ratio with HDI and HRDI
2.4. Trend Analysis
2.5. Estimation of Risk Factors
3. Results
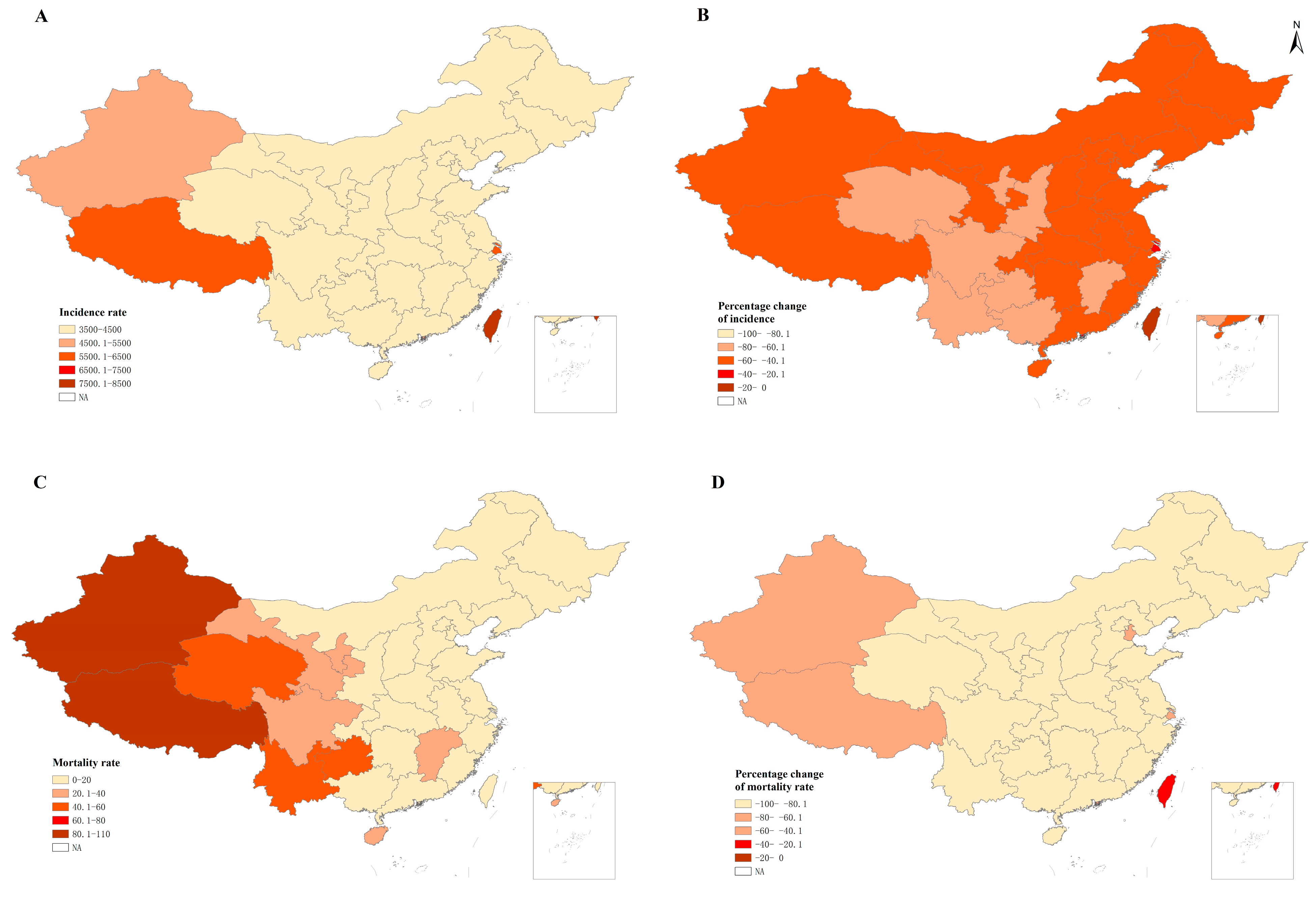
3.1. Trends of Incidence for LRI in China from 2000 to 2019
3.2. Trends of Mortality for LRI in China from 2000 to 2019
3.3. Correlation of CFR with HDI and HRDI in China, 2019
3.4. LRI Mortality Attribution to Risk Factors in China from 2000 to 2019
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 LRI Collaborators. Age-sex differences in the global burden of lower respiratory infections and risk factors, 1990–2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1626–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2016 Lower Respiratory Infections Collaborators. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory infections in 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1191–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safiri, S.; Mahmoodpoor, A.; Kolahi, A.A.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Mansournia, M.A.; Ansarin, K.; Collins, G.S.; Kaufman, J.S.; Abdollahi, M. Global burden of lower respiratory infections during the last three decades. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1028525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 LRI Collaborators. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory tract infections in 195 countries: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 1133–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhutta, Z.; Das, J.; Walker, N.; Rizvi, A.; Campbell, H.; Rudan, I.; Black, R. Childhood Pneumonia and Diarrhoea 2 Interventions to address deaths from childhood pneumonia and diarrhoea equitably: What works and at what cost? Lancet 2013, 381, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, S.; Aboubaker, S.; MacLean, R.; Fontaine, O.; Mantel, C.; Goodman, T.; Young, M.; Henderson, P.; Cherian, T. Ending preventable child deaths from pneumonia and diarrhoea by 2025. Development of the integrated Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Pneumonia and Diarrhoea. Arch. Dis. Child. 2015, 100, S23–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stop Pneumonia. The Stop Pneumonia Initiative. Available online: https://stoppneumonia.org/stop-pneumonia-initiative/ (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- WHO. IMCI Integrated Management of Childhood Illness. 2005. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42939 (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Vissing, N.H.; Larsen, J.M.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Chawes, B.L.; Thysen, A.H.; Bønnelykke, K.; Brix, S.; Bisgaard, H. Susceptibility to Lower Respiratory Infections in Childhood is Associated with Perturbation of the Cytokine Response to Pathogenic Airway Bacteria. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Kang, L.; Miao, L.; Li, Q.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. Pneumonia Mortality among Children under 5 in China from 1996 to 2013: An Analysis from National Surveillance System. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruan, Z.; Qi, J.; Qian, Z.M.; Zhou, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Vaughn, M.G.; LeBaige, M.H.; Yin, P.; Lin, H. Disease burden and attributable risk factors of respiratory infections in China from 1990 to 2019. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2021, 11, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Jing, W.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, M. The trends of mortality, aetiologies and risk factors of lower respiratory infections in China from 1990 to 2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. J. Infect. Public Health 2022, 15, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Zeng, X.; Yin, P.; Zhu, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 394, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, Q.; Ke, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, L.; Xue, D.; Bian, Y. Finding flaws in the spatial distribution of health workforce and its influential factors: An empirical analysis based on Chinese provincial panel data, 2010–2019. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 953695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Fay, M.P.; Feuer, E.J.; Midthune, D.N. Permutation tests for joinpoint regression with applications to cancer rates. Stat. Med. 2000, 19, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Ward, E.M.; Johnson, C.J.; Cronin, K.A.; Ma, J.; Ryerson, B.; Mariotto, A.; Lake, A.J.; Wilson, R.; Sherman, R.L.; et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, 1975–2014, Featuring Survival. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djx030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GBD 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1923–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2019 Demographics Collaborators. Global age-sex-specific fertility, mortality, healthy life expectancy (HALE), and population estimates in 204 countries and territories, 1950–2019: A comprehensive demographic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1160–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Lower Respiratory Infections Collaborators. Quantifying risks and interventions that have affected the burden of lower respiratory infections among children younger than 5 years: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van de Maat, J.S.; Peeters, D.; Nieboer, D.; van Wermeskerken, A.M.; Smit, F.J.; Noordzij, J.G.; Tramper-Stranders, G.; Driessen, G.J.A.; Obihara, C.C.; Punt, J.; et al. Evaluation of a clinical decision rule to guide antibiotic prescription in children with suspected lower respiratory tract infection in The Netherlands: A stepped-wedge cluster randomised trial. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, S.; Meng, Q.; Chen, L.; Bekedam, H.; Evans, T.; Whitehead, M. Tackling the challenges to health equity in China. Lancet 2008, 372, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Bai, J.; Na, H. The history of China’s maternal and child health care development. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 20, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2016 Healthcare Access and Quality Collaborators. Measuring performance on the Healthcare Access and Quality Index for 195 countries and territories and selected subnational locations: A systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2018, 391, 2236–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Silk, B.J.; Li, W.; Fleischauer, A.T.; Xing, X.; Jiang, X.; Yu, H.; Olsen, S.J.; Cohen, A.L. Pneumonia incidence and mortality in Mainland China: Systematic review of Chinese and English literature, 1985–2008. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, X.; Liu, X.; Shao, H. Healthy China 2030: A Vision for Health Care. Value Health Reg. Issues 2017, 12, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schraufnagel, D.E.; Balmes, J.R.; Cowl, C.T.; De Matteis, S.; Jung, S.H.; Mortimer, K.; Perez-Padilla, R.; Rice, M.; Riojas-Rodriguez, H.; Sood, A.; et al. Air Pollution and Noncommunicable Diseases: A Review by the Forum of International Respiratory Societies’ Environmental Committee, Part 1: The Damaging Effects of Air Pollution. Chest 2019, 155, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z. Spatial and dynamic effects of air pollution on under-five children’s lower respiratory infections: An evidence from China 2006 to 2017. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 25391–25407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pan, X.; Guo, X.; Li, G. Health impact of China’s Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan: An analysis of national air quality monitoring and mortality data. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, e313–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, M.; Luo, S.; Liang, J.; Liddell, C.A.; Coates, M.M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; He, C.; et al. Under-5 mortality in 2851 Chinese counties, 1996–2012: A subnational assessment of achieving MDG 4 goals in China. Lancet 2016, 387, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GBD 2019 Under-5 Mortality Collaborators. Global, regional, and national progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 3.2 for neonatal and child health: All-cause and cause-specific mortality findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2021, 398, 870–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, L.D. The global burden of vaccine-preventable infectious diseases in children less than 5 years of age: Implications for COVID-19 vaccination. How can we do better? Allergy Asthma Proc. 2021, 42, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Garcia, C.; Yu, W.; Knoll, M.D.; Lai, X.; Xu, T.; Jing, R.; Qin, Y.; Yin, Z.; Wahl, B.; et al. National and provincial impact and cost-effectiveness of Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine in China: A modeling analysis. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Incidence (95% UI) | Incidence Rate per 100,000 (95% UI) | AAPC of Incidence Rate (95% CI), 2000–2019 | Mortality (95% UI) | Mortality Rate Per 100,000 (95% UI) | AAPC of Mortality Rate (95% CI), 2000–2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early Neonatal | ||||||
| Male | 7316 (5632~9302) | 4774.7 (3675.6~6070.7) | −6.3 * (−6.8~−5.9) | 2598 (1085~1843) | 863.9 (707.9~1041.5) | −8.6 * (−8.8~−8.4) |
| Female | 6220 (4801~7901) | 4741.7 (3660.1~6023.4) | −6.8 * (−7.0~−6.7) | 874 (738~1017) | 666.0 (563.0~775.5) | −8.7 * (−9.0~−8.4) |
| Total | 13,536 (10,445~17,237) | 4759.4 (3672.8~6060.9) | −6.5 * (−6.8~−6.3) | 2197 (1843~2598) | 772.6 (648.1~913.4) | −8.7 * (−8.9~−8.5) |
| Late Neonatal | ||||||
| Male | 22,021 (17,060~27,748) | 4792.8 (3713~6039.4) | −6.3 * (−6.7~−5.9) | 2317 (876~1643) | 235.8 (190.7~285.2) | −9.1 * (−9.6~−8.5) |
| Female | 18,683 (14,520~23,556) | 4748.5 (3690.5~5987) | −6.8 * (−6.9~−6.7) | 878 (749~1019) | 223.1 (190.2~258.9) | −9.0 * (−9.3~−8.8) |
| Total | 40,704 (31,661~51,476) | 4772.4 (3712.2~6035.3) | −6.5 * (−6.7~−6.3) | 1961 (1643~2317) | 229.9 (192.6~271.6) | −9.1 * (−9.3~−8.8) |
| Post Neonatal | ||||||
| Male | 341,956 (266,547~434,088) | 4557.6 (3552.5~5785.5) | −5.5 * (−5.7~−5.2) | 10,103 (4002~6889) | 66.8 (53.3~81.6) | −11.0 * (−11.2~−10.7) |
| Female | 279,864 (219,471~357,519) | 4354.0 (3414.5~5562.2) | −5.9 * (−6.1~−5.8) | 3429 (2837~4096) | 53.3 (44.1~63.7) | −11.9 * (−12.1~−11.6) |
| Total | 621,820 (486,515~791,897) | 4463.7 (3492.4~5684.6) | −5.6 * (−5.7~−5.6) | 8438 (6889~10,103) | 60.6 (49.5~72.5) | −11.4 * (−11.6~−11.1) |
| 1~4 years | ||||||
| Male | 1,506,646 (1,102,615~1,946,495) | 4213.6 (3083.7~5443.7) | −3.5 * (−3.9~−3.0) | 2670 (897~1709) | 3.2 (2.5~4.2) | −11.3 * (−11.8~−10.7) |
| Female | 1,186,398 (864,892~1,539,284) | 3868.8 (2820.4~5019.5) | −3.6 * (−4.2~−3.1) | 992 (806~1205) | 3.2 (2.6~3.9) | −12.1 * (−12.6~−11.6) |
| Total | 2,693,044 (1,966,696~3,501,221) | 4054.4 (2960.9~5271.1) | −3.6 * (−4.1~−3.1) | 2152 (1709~2670) | 3.2 (2.6~4.0) | −11.7 * (−11.9~−11.4) |
| Under 5 years | ||||||
| Male | 1,877,939 (1,433,413~2,386,254) | 4280.4 (3267.2~5439.1) | −4.0 * (−4.3~−3.7) | 17,579 (6961~12,124) | 19.5 (15.9~23.7) | −10.7 * (−11.0~−10.3) |
| Female | 1,491,165 (1,142,972~1,901,960) | 3963.9 (3038.3~5055.9) | −4.3 * (−4.7~−4.0) | 6172 (5170~7282) | 16.4 (13.7~19.4) | −11.4 * (−12.0~−10.8) |
| Total | 3,369,103 (2,576,496~4,304,427) | 4134.3 (3161.7~5282.1) | −4.1 * (−4.4~−3.8) | 14,749 (12,124~17,579) | 18.1 (14.9~21.6) | −11.0 * (−11.6~−10.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, X.; Wu, M.; Jia, X.; Bao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yu, M.; Yang, Y. Trends of Incidence, Mortality, and Risk Factors for Lower Respiratory Infections among Children under 5 Years in China from 2000 to 2019. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043547
Shi X, Wu M, Jia X, Bao J, Wang Y, Yang C, Yu M, Yang Y. Trends of Incidence, Mortality, and Risk Factors for Lower Respiratory Infections among Children under 5 Years in China from 2000 to 2019. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043547
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Xuezhong, Meina Wu, Xiaocan Jia, Junzhe Bao, Yuping Wang, Chaojun Yang, Mengdie Yu, and Yongli Yang. 2023. "Trends of Incidence, Mortality, and Risk Factors for Lower Respiratory Infections among Children under 5 Years in China from 2000 to 2019" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043547
APA StyleShi, X., Wu, M., Jia, X., Bao, J., Wang, Y., Yang, C., Yu, M., & Yang, Y. (2023). Trends of Incidence, Mortality, and Risk Factors for Lower Respiratory Infections among Children under 5 Years in China from 2000 to 2019. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043547






