Occurrence, Risk, and Source of Heavy Metals in Lake Water Columns and Sediment Cores in Jianghan Plain, Central China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
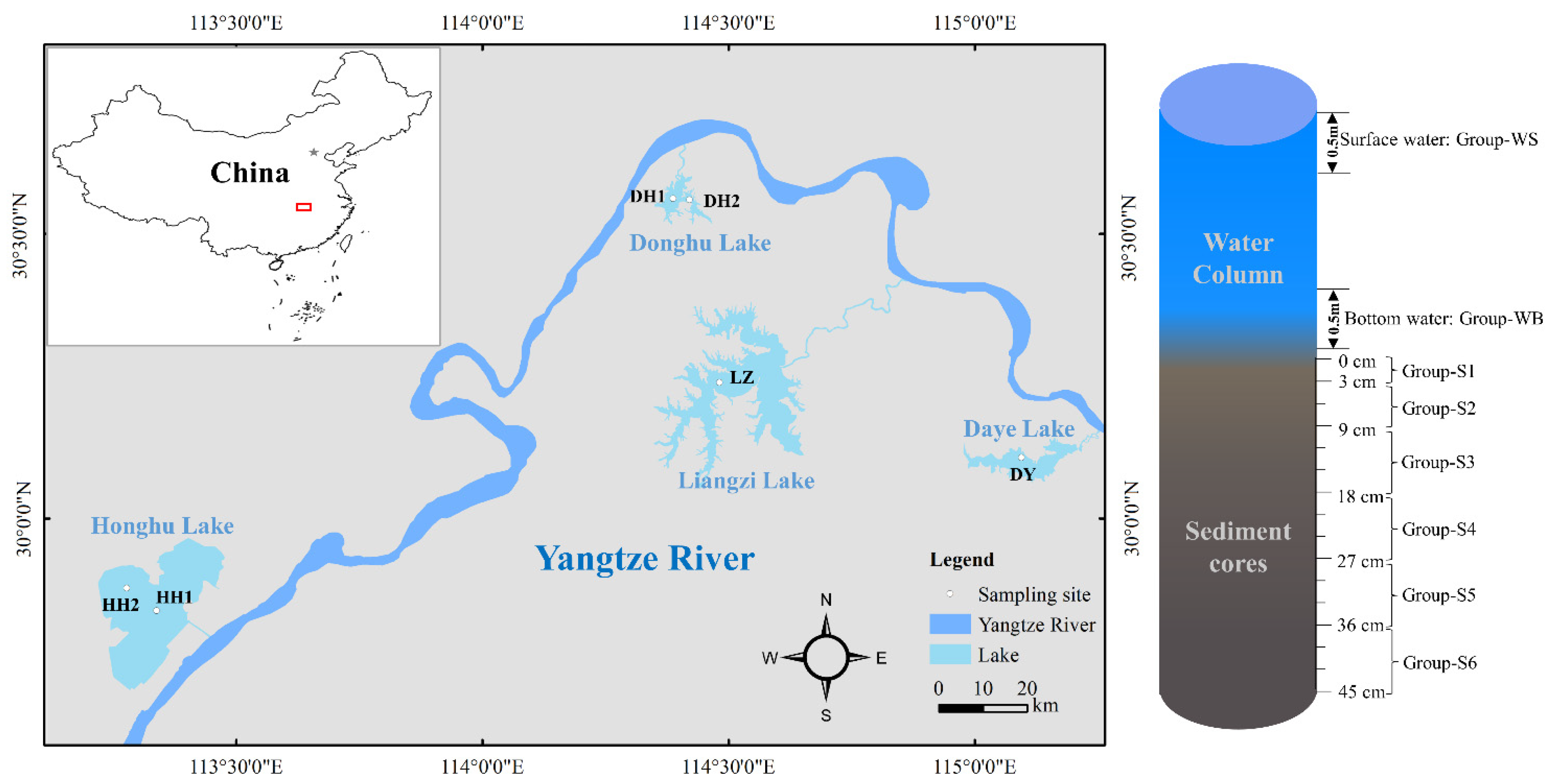
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Analysis
2.3. Pollution and Risk Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters in Water and Sediment
3.2. Concentration of Heavy Metals
3.2.1. Heavy Metals in Water Columns
3.2.2. Heavy Metals in Sediment Cores
3.3. Pollution Assessment of Heavy Metals
3.4. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals
3.5. Source Identification of Heavy Metals
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, V.; Parihar, R.D.; Sharma, A.; Bakshi, P.; Singh Sidhu, G.P.; Bali, A.S.; Karaouzas, I.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; et al. Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: A meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.W.; Ramamoorthy, S. Heavy Metals in Natural Waters: Applied Monitoring and Impact Assessment; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Yu, R.; Chen, J.; Leng, X.; Zhao, D.; Jia, H.; An, S. Ecological risk of heavy metals in lake sediments of China: A national-scale integrated analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. Ecological and health risk assessments and water quality criteria of heavy metals in the Haihe River. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 117971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Xu, C.; Kang, S.; Huo, A.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M.; Nover, D. Heavy metals in water and surface sediments of the Fenghe River Basin, China: Assessment and source analysis. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3072–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomons, W.; Förstner, U. Metals in the Hydrocycle; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wei, M.; Xiaona, H. Characterization of heavy metals in water and sediments in Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 4367–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, B.; Liu, X.; Guo, X.; Lu, S. Occurrence and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediment, and fish from Dongting Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34076–34090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Zhao, C.; Luo, Y.; Liu, C.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, D.; An, S.; Zhu, H. Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: Their relations to environmental factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 270, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, W. Dissolved trace elements and heavy metals from the shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River region, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Z.; Peng, S.-C.; Chen, T.-H.; Zhang, L. Occurrence, source identification and ecological risk evaluation of metal elements in surface sediment: Toward a comprehensive understanding of heavy metal pollution in Chaohu Lake, Eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Li, E.; Wang, Z. Heavy Metal Distribution and Bioaccumulation Combined With Ecological and Human Health Risk Evaluation in a Typical Urban Plateau Lake, Southwest China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 814678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSY. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Wang, Z.; Du, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, E.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Occurrence and ecological hazard assessment of selected antibiotics in the surface waters in and around Lake Honghu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tao, T.; Zuo, Y. Comparative characterisation of two fulvic acids from East Lake and Liangzi Lake in central China. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.H.; Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Tao, R.; Liu, D. Assessment of heavy metal contamination status in sediments and identification of pollution source in Daye Lake, Central China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xu, Y.; Peng, H. Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from Donghu Lake, Wuhan, China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2014, 23, 502–507. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wu, W.; Zhang, B.; Liao, Q. Distribution characteristic of heavy metals and nutrient in sediments of Liangzi Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 38, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Xiao, M.; Wu, Z. Distribution, bioavailability and probabilistic integrated ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from Honghu Lake, China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 116, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apha, A. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Quevauviller, P. Operationally defined extraction procedures for soil and sediment analysis I. Stand. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1998, 17, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEPA. GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water. China Environmental Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Nemerow, N.L. Stream, Lake, Estuary, and Ocean Pollution; Van Nostrand Reinhold Publishing Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Z. Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Ni, S.J.; Tuo, X.; Zhang, C.J. Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 31, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Human Health Evaluation Manual, Supplemental Guidance: Update of Standard Default Exposure FactorOffice of Emergency and Remedial Response; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Schaider, L.A.; Senn, D.B.; Estes, E.R.; Brabander, D.J.; Shine, J.P. Sources and fates of heavy metals in a mining-impacted stream: Temporal variability and the role of iron oxides. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Zhou, S.Q.; Wu, P.; Qu, K.J. Assessment of the distribution, bioavailability and ecological risks of heavy metals in the lake water and surface sediments of the Caohai plateau wetland, China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Tang, X.; Guo, W.; Lin, L.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, M. Spatiotemporal distribution dynamics of heavy metals in water, sediment, and zoobenthos in mainstream sections of the middle and lower Changjiang River. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, B.; Xiao, R.; Zhao, H. Heavy metals in water, soils and plants in riparian wetlands in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Bing, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, L.; Deng, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, L. Ecological risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments of a river–reservoir system. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, X.; Yang, X. Revealing anthropogenic effects on lakes and wetlands: Pollen-based environmental changes of Liangzi Lake, China over the last 150 years. CATENA 2021, 207, 105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yi, Z.; Xing, J.; Yang, T. A comparative study on recent sedimentation rates in Lake Donghu, Wuhan with 210Pb and 137Cs dating techniques. J. Cent. China Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2004, 38, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Min, F.; Shihua, Q.I.; Chengxi, W.U.; Lisong, H.U.; Qiuke, S.U. High Resolution Sedimentary Record of Organochlorine Pesticides in Sediments Core from Honghu Lake. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2006, 25, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Bolan, N.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Hou, D. Green immobilization of toxic metals using alkaline enhanced rice husk biochar: Effects of pyrolysis temperature and KOH concentration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.-M.; Wen, H.-H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.-S.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turap, Y.; Talifu, D.; Wang, X.; Abulizi, A.; Maihemuti, M.; Tursun, Y.; Ding, X.; Aierken, T.; Rekefu, S. Temporal distribution and source apportionment of PM2.5 chemical composition in Xinjiang, NW-China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 257–268. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Davy, P.K.; Huang, M.; Duan, J.; Wang, X.; Fan, Q.; Chang, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Xie, S. High-resolution sampling and analysis of ambient particulate matter in the Pearl River Delta region of southern China: Source apportionment and health risk implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2049–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheong, T.S.; Wu, Y. The impacts of structural transformation and industrial upgrading on regional inequality in China. China Econ. Rev. 2014, 31, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.-L.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Yang, Z. Inputting history of heavy metals into the inland lake recorded in sediment profiles: Poyang Lake in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onianwa, P.; Jaiyeola, O.; Egekenze, R. Heavy metals contamination of topsoil in the vicinities of auto-repair workshops, gas stations and motor-parks in a Nigerian city. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2003, 84, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, M.; Xie, Z. Level, source identification, and risk analysis of heavy metal in surface sediments from river-lake ecosystems in the Poyang Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21902–21916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Ye, S.; Yuan, H.; Ding, X.; Wang, J. Surface sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 2966–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Jiang, J.; Tan, L.; Du, S. Improved adaptive recursive even mirror Fourier nonlinear filter for nonlinear active noise control. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 146, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Liao, L. Spatio-temporal characteristics and source identification of water pollutants in Wenruitang River watershed. Huan Jing ke Xue= Huanjing Kexue 2015, 36, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.K.; Khandegar, V.; Saroha, A.K. Removal of chromium from electroplating industry effluent using electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2013, 17, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. Antibiotic and antibiotic resistance genes in freshwater aquaculture ponds in China: A meta-analysis and assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.M. Estimate of mercury emissions to the atmosphere from petroleum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4704–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, F.; Wang, A.; Dai, H.; Cheng, S.; Wang, J.; Tang, L. Atmospheric heavy metal deposition in agro-ecosystems in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 5822–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y.C.; Al-Obaidi, K.M.; Mahyuddin, N. Recycling of end-of-life vehicles (ELVs) for building products: Concept of processing framework from automotive to construction industries in Malaysia. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Leonard, B.M.; Zhou, Q.; DiSalvo, F.J. Pt alloy and intermetallic phases with V, Cr, Mn, Ni, and Cu: Synthesis as nanomaterials and possible applications as fuel cell catalysts. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 2190–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zheng, N.; Tang, L.; Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Hua, X. Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of human exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb pollution in urban street dust across China between 2009 and 2018. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anik, A.H.; Khan, R.; Hossain, S.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Tamim, U.; Islam, A.T.; Idris, A.M.; Tareq, S.M. Reconciling the geogenic and non-crustal origins of elements in an Indo-Bangla transboundary river, Atrai: Pollution status, sediment quality, and preliminary risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Class | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Pollution Rank | Scope | Pollution Rank | Scope | Pollution Rank | Scope | Risk Rank | Scope | Risk Rank | |
| 1 | ≤1 | Unpolluted | ≤0.7 | Unpolluted | ≤0 | Unpolluted | ≤40 | Low risk | ≤40 | Low risk |
| 2 | 1–2 | Slight pollution | 0.7–1 | Slight pollution | 0–1 | Slight pollution | 40–80 | Moderate risk | 40–80 | Moderate risk |
| 3 | 2–3 | Moderate pollution | 1–2 | Moderate pollution | 1–2 | Moderate pollution | 80–160 | Considerable risk | 80–160 | Considerable risk |
| 4 | ≥3 | Heavy pollution | ≥2 | Heavy pollution | 2–3 | Moderate to Heavy pollution | 160–320 | High risk | 160–320 | High risk |
| 5 | 3–4 | Heavy pollution | ≥320 | Extremely high risk | ≥320 | Extremely high risk | ||||
| 6 | 4–5 | Heavy to extreme pollution | ||||||||
| 7 | ≥5 | Extreme pollution | ||||||||
| Reference | [22] | [24] | [25] | [22] | [26] | |||||
| Dianchi Lake | Taihu Lake | Chaohu Lake | Dongting Lake | Caohai Lake | Yangtze River | Haihe River | Pearl River | Honghu Lake | Donghu Lake | Daye Lake | Liangzi Lake | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 2.78 a | 8.21 | 3.62 (1.77–6.91) b | (1.45–2.97) | 3.41 | 2.34 (nd–5.34) | 0.46–1.83 | 1.37–4.03 | 15.70–33.37 | 0.45–0.56 | ||
| Hg | nd | (0.03–0.14) | 0.14 | 0.14 (nd–0.47) | 0.06–0.10 | 0.08–0.14 | 0.12–0.14 | 0.11–0.13 | ||||
| Cr | 1.54 | 1.29 (0.27–3.81) | 0.50 | 0.62 (0.15–1.03) | (2.25–5.59) | 28.18 (1.22–47.04) | 8.5 | nd–1.29 | nd–0.35 | nd–0.26 | nd | |
| Ni | 2.05 | 2.44 (0.28–6.37) | 26.47 | 1.51 (0.29–5.11) | 20.33 (0.87–33.6) | 12.5 | 0.51–1.52 | nd–0.59 | 1.23–2.59 | 0.16–0.42 | ||
| Cu | 1.36 | 2.88 (0.96–6.24) | 2.56 | 2.50 (0.70–7.65) | (1.83–2.63) | 2.86 | 2.81 (1.37–8.35) | 1.6 | 1.15–1.56 | 1.23–1.93 | 2.16–3.01 | 1.10–1.12 |
| Zn | 20.64 | 8.78 (2.49–18.52) | 23.05 | 20.91 (2.81–71.24) | (28.92–55.78) | 5.40 | 26.17 (0.30–196.05) | 8.9 | 2.41–3.79 | 3.59–5.84 | 2.68–3.64 | 4.31–4.33 |
| Cd | 0.22 | 0.05 (0.03–0.08) | 0.58 | 0.05 (nd–0.15) | (0.25–3.53) | 0.97 | 0.06 (nd–0.63) | 2.9 | nd | nd | nd–0.06 | nd |
| Pb | 0.54 | 3.51 | 1.49 (nd–3.66) | (2.00–6.74) | 4.69 | 0.45 (nd–1.46) | 12.8 | 0.19–0.46 | 0.16–0.86 | 0.23–0.24 | 0.35–0.61 | |
| Mn | 4.32 | 1.73 (0.01–7.53) | 42.16 (4.14–188.67) | 0.53–3.71 | 0.33–3.73 | 0.63–1.50 | 3.04–3.42 | |||||
| Reference | [12] | [7] | [11] | [8] | [30] | [31] | [4] | [32] | This study | This study | This study | This study |
| Dianchi Lake | Taihu Lake | Chaohu Lake | Dongting Lake | Poyang Lake | Yangtze River | Haihe River | Pearl River | Honghu Lake | Donghu Lake | Daye Lake | Liangzi Lake | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 2.06 a | 29.22 (16.04–64.28) b | (2.2–30.3) | 20.1 (8.9–33.9) | 1.35 (nd–7.65) | 21.99 (3.34–37.11) | 14.5 (11.5–18.8) | 16.2 (11.7–24.0) | 51.5 (15.6–77.1) | 14.0 (9.79–17.4) | ||
| Hg | 0.18 (0.05–0.47) | 0.03 (0.01–0.09) | 0.07 (nd–0.84) | 0.13 (0.01–0.25) | 0.07 (0.06–0.08) | 0.12 (0.08–0.17) | 0.09 (0.06–0.13) | 0.05 (0.04–0.06) | ||||
| Fe | 50,720 | (6200–56,000) | 48,614 (24,510–59,358) | 55,335 (51,718–57,385) | 46,376 (44,295–48,420) | 40,891 (39,746–41,704) | ||||||
| Cr | 74.78 | 138.4 (9.35–464.9) | 61.0 (28.7–91.1) | 89.0 (53.5–116.0) | (5.8–88.4) | 28.35 (9.31–73.23) | 78.4 (12–130) | 100.3 (47.1–119) | 138.3 (103–200) | 82.6 (78.9–85.9) | 79.2 (78.2–80.2) | |
| Ni | 45.81 | 47.9 (11.5–114.9) | 36.0 (14.8–59.1) | 41.7 (23.0–54.9) | (2.7–50.2) | 31.5 (26.1–33.9) | 15.42 (4.73–23.96) | 49.5 (27.4–55.2) | 50.9 (46.1–54.8) | 47.8 (37.6–61.0) | 31.9 (29.7–34.1) | |
| Cu | 146.2 | 35.1 (11.8–134.6) | 26.9 (12.6–41.8) | 45.5 (34.9–73.4) | (2.7–245.9) | 28.5 (13.9–37.0) | 12.26 (2.52–26.20) | 46.8 (5.8–170.6) | 44.4 (24.0–50.9) | 44.7 (37.7–51.1) | 143.1 (53.1–224) | 29.4 (25.6–33.7) |
| Zn | 496.8 | 89.7 (16.7–295.9) | 341 (1.5–907) | 322.6 (227.0–463.4) | (13.3–311.8) | 104.1 (71.9–130.9) | 46.0 (10.1–82.9) | 143.1 (32–259) | 116.9 (69.3–130) | 127.1 (116–138) | 237.5 (151–319) | 76.2 (65.2–94.5) |
| Cd | 13.2 | 1.35 (0.03–4.09) | 17.5 (0.04–42.4) | 2.87 (0.66–7.89) | (0.04–6.3) | 0.67 (0.33–0.89) | 0.11 (0.02–0.35) | 0.46 (0.06–2.06) | 0.33 (0.26–0.49) | 0.30 (0.14–0.65) | 6.2 (0.40–11.9) | 0.23 (0.09–0.45) |
| Pb | 108.8 | 38.3 (0.01–93.6) | 47.5 (1.56–113) | 58.0 (39.0–102.9) | (15.5–71.8) | 27.3 (16.9–41.8) | 6.87 (1.4–34.8) | 49.6 (23–78) | 34.9 (28.6–37.5) | 41.7 (36.7–60.0) | 81.8 (67.7–96.5) | 31.4 (26.2–40.8) |
| Mn | 813 | 696.7 (116–1955) | 482 (168–887) | (177–1656) | 977 (725–1620) | 229.2 (55.9–346.5) | 934 (540–1318) | 988 (707–1523) | 1057 (537–1644) | 642 (583–721) | ||
| Co | 15.24 | 10.8 (4.4–16.7) | (2.0–24.8) | 5.56 (1.87–9.2) | 18.7 (9.4–21.9) | 20.4 (19.7–21.4) | 19.1 (17.9–21.0) | 15.5 (14.9–16.0) | ||||
| Reference | [12] | [7] | [11] | [8] | [44] | [31] | [4] | [45] | This study | This study | This study | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Zou, G.; Wang, Z. Occurrence, Risk, and Source of Heavy Metals in Lake Water Columns and Sediment Cores in Jianghan Plain, Central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043676
Wang C, Wang K, Zhou W, Li Y, Zou G, Wang Z. Occurrence, Risk, and Source of Heavy Metals in Lake Water Columns and Sediment Cores in Jianghan Plain, Central China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043676
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cong, Kan Wang, Wuquan Zhou, Yong Li, Guoqing Zou, and Zhi Wang. 2023. "Occurrence, Risk, and Source of Heavy Metals in Lake Water Columns and Sediment Cores in Jianghan Plain, Central China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043676
APA StyleWang, C., Wang, K., Zhou, W., Li, Y., Zou, G., & Wang, Z. (2023). Occurrence, Risk, and Source of Heavy Metals in Lake Water Columns and Sediment Cores in Jianghan Plain, Central China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043676







