A Precautionary Tale: Individual Decision Making in the Time of COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.2.1. Study 1
2.2.2. Study 2
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Precautionary Behaviors
2.3.2. Demographics
2.3.3. COVID-19 Knowledge and Beliefs Questionnaire [11]
2.3.4. Perceived Susceptibility
2.3.5. Information Seeking
2.3.6. Daily Behaviors
2.4. Analysis
2.4.1. Study 1
2.4.2. Study 2
3. Results
3.1. Study 1
3.2. Study 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. COVID-19—A Global Pandemic. What Do We know about SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19? June 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/risk-comms-updates/update-28-covid-19-what-we-know-may-2020.pdf?sfvrsn=ed6e286c_2 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. June 2020. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/data (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. How to Protect Yourself & Others. 18 August 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Rosenstock, I.M. The health belief model and preventive health behavior. Health Educ. Monogr. 1974, 2, 354–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.P.; Sam, I. Knowledge and attitudes in regard to pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in a multiethnic community of Malaysia. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2011, 18, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sabbagh, M.Q.; Al-Ani, A.; Mafrachi, B.; Siyam, A.; Isleem, U.; Massad, F.I.; Alsabbagh, Q.; Abufaraj, M. Predictors of adherence with home quarantine during COVID-19 crisis: The case of health belief model. Psychol. Health Med. 2022, 27, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, R.; Narendran, M.; Bindu, A.; Beevi, N.; Manju, L.; Benny, P.V. Public perception and preparedness for the pandemic COVID 19: A Health Belief Model approach. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 9, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, G.; Quah, S.R.; Ho, L.-M.; Ho, S.-Y.; Hedley, A.J.; Lee, H.-P.; Lam, T.-H. A tale of two cities: Community psychobehavioral surveillance and related impact on outbreak control in Hong Kong and Singapore during the severe acute respiratory syndrome epidemic. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2004, 25, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador Casara, B.G.; Suitner, C.; Bettinsoli, M.L. Viral suspicions: Vaccine hesitancy in the Web 20. J. Exp. Psychol. Appl. 2019, 25, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bish, A.; Michie, S. Demographic and attitudinal determinants of protective behaviours during a pandemic: A review. Br. J. Health Psychol. 2010, 15, 797–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearman, A.; Hughes, M.L.; Smith, E.L.; Neupert, S.D. Age Differences in Risk and Resilience Factors in COVID-19-Related Stress. J. Gerontology. Ser. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2020, 76, e38–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryhurst, S.; Schneider, C.R.; Kerr, J.; Freeman, A.L.J.; Recchia, G.; van der Bles, A.M.; Spiegelhalter, D.; van der Linden, S. Risk perceptions of COVID-19 around the world. J. Risk Res. 2020, 23, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruin, W.B.; Bennett, D. Relationships between initial COVID-19 risk perceptions and protective health behaviors: A national survey. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 59, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeze, M.; Baumgartner, M.; Bruno, P.; Gunderson, J.R.; Olin, J.; Ross, M.Q.; Szafran, J. Fake claims of fake news: Political misinformation, warnings, and the tainted truth effect. Political Behav. 2020, 43, 1433–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, L.; Steinhoff, A.; Bechtiger, L.; Murray, A.L.; Nivette, A.; Hepp, U.; Ribeaud, D.; Eisner, M. Emotional distress in young adults during the covid-19 pandemic: Evidence of risk and resilience from a longitudinal cohort study. Psychol. Med. 2020, 52, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.F.; Rodgers, M.; Miller, M.B.; McCrae, C.S. Impact of sex on COVID-19 media exposure, anxiety, perceived risk, and severity in middle-aged and older adults. J. Aging Health 2021, 34, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depoux, A.; Martin, S.; Karafillakis, E.; Preet, R.; Wilder-Smith, A.; Larson, H. The pandemic of social media panic travels faster than the COVID-19 outbreak. J. Travel Med. 2020, 27, taaa031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, D.P.; Casman, E.; Albert, S. Deriving behavior model parameters from survey data: Self-protective behavior adoption during the 2009–2010 influenza a (H1N1) pandemic. Risk Anal. Int. J. 2012, 32, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reintjes, R.; Das, E.; Klemm, C.; Richardus, J.H.; Keßler, V.; Ahmad, A. “Pandemic Public Health Paradox”: Time series analysis of the 2009/10 Influenza A/H1N1 epidemiology, media attention, risk perception and public reactions in 5 European countries. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscadelli, A.; Albora, G.; Biamonte, M.; Giorgetti, D.; Innocenzio, M.; Paoli, S.; Lorini, C.; Bonanni, P.; Bonaccorsi, G. Fake news and COVID-19 in Italy: Results of a quantitative observational study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Zheng, L.; Wen, J.; Jin, S.; Gan, Y. Coping with coronavirus disease 2019: Relationships between coping strategies, benefit finding and well-being. Stress Health 2021, 38, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Older Adults. 16 August 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/older-adults.html#:~:text=Risk%20for%20Severe%20Illness%20Increases%20with%20Age&text=Similarly%2C%20people%20in%20their%2060s,those%20aged%2085%20or%20older (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Running Essential Errands. 10 April 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/daily-life-coping/essential-goods-services.html (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Barr, M.; Raphael, B.; Taylor, M.; Stevens, G.; Jorm, L.; Giffin, M.; Lujic, S. Pandemic influenza in Australia: Using telephone surveys to measure perceptions of threat and willingness to comply. BMC Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearman, A.; Hughes, M.L.; Smith, E.L.; Neupert, S.D. Mental health challenges of U.S. healthcare professionals during COVID-19. Front. Psychol. Psychol. Clin. Settings 2020, 11, 2065. [Google Scholar]
- Raudenbush, S.W.; Bryk, A. Hierarchical Linear Models: Applications and Data Analysis Methods; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Grzywacz, J.G.; Almeida, D.M.; Neupert, S.D.; Ettner, S.L. Socioeconomic status and health: A micro-level analysis of exposure and vulnerability to daily stressors. J. Health Soc. Behav. 2004, 45, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupert, S.D.; Almeida, D.M.; Mroczek, D.K.; Spiro, A. Daily stressors and memory failures in a naturalistic setting: Findings from the VA Normative Aging Study. Psychol. Aging 2006, 21, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niepel, C.; Kranz, D.; Borgonovi, F.; Emslander, V.; Greiff, S. The coronavirus (COVID-19) fatality risk perception of us adult residents in March and April 2020. Br. J. Health Psychol. 2020, 25, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raifman, M.A.; Raifman, J. Disparities in the population at risk of severe illness from COVID-19 by race/ethnicity and income. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 59, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.L. COVID-19 information seeking on digital media and preventive behaviors: The mediation role of worry. Cyberpsychology Behav. Soc. Netw. 2020, 23, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasneh, R.; Al-Azzam, S.; Muflih, S.; Soudah, O.; Hawamdeh, S.; Khader, Y. Media’s effect on shaping knowledge, awareness risk perceptions and communication practices of pandemic COVID-19 among pharmacists. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1897–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfin, D.R.; Silver, R.C.; Holman, E.A. The novel coronavirus (COVID-2019) outbreak: Amplification of public health consequences by media exposure. Health Psychol. 2020, 39, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupinacci, L. ‘Absentmindedly scrolling through nothing’: Liveness and compulsory continuous connectedness in social media. Media Cult. Soc. 2020, 43, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagger, M.S.; Keech, J.; Hamilton, K. Managing stress during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and beyond: Reappraisal and mindset approaches. Stress Health 2020, 36, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, M.W.; Nápoles, A.M.; Pérez-Stable, E.J. COVID-19 and racial/ethnic disparities. JAMA 2020, 323, 2466–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, V.L.; Skinner, C. The Health Belief Model, in Health Behavior and Health Education: Theory, Research, and Practice; Glanz, K., Rimer, B., Viswanath, K., Eds.; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 45–65. [Google Scholar]
- Michie, S.; Van Stralen, M.M.; West, R. The behaviour change wheel: A new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement. Sci. 2011, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson Miller, J.; Hartman, T.K.; Levita, L.; Martinez, A.P.; Mason, L.; McBride, O.; McKay, R.; Murphy, J.; Shevlin, M.; Stocks, T.V.; et al. Capability, opportunity, and motivation to enact hygienic practices in the early stages of the COVID-19 outbreak in the United Kingdom. Br. J. Health Psychol. 2020, 25, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minow, M. Saving the News: Why the Constitution Calls for Government Action to Preserve Freedom of Speech; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Arden, M.A.; Byrne-Davis, L.; Chater, A.M.; Hart, J.; McBride, E.; Chilcot, J. The vital role of health psychology in the response to COVID-19. Br. J. Health Psychol. 2020, 25, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Mean (SD) | Range | Valid Percent | Mean (SD) | Range | Valid Percent |
| Age | 38.74 (11.51) | 20–79 | 64.29 (5.20) | 55–79 | ||
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 59.9 | 32.2 | ||||
| Female | 40.1 | 67.8 | ||||
| Race | ||||||
| American Indian | 0.3 | 0.4 | ||||
| Asian | 5.4 | 1.5 | ||||
| Black or African American | 8.0 | 2.3 | ||||
| White | 83.7 | 92.7 | ||||
| Other | 0.3 | 1.1 | ||||
| More than one race | 2.1 | 1.9 | ||||
| I do not wish to answer | 0.3 | |||||
| Income | ||||||
| $10,000 or less | 2.8 | 2.7 | ||||
| $10,000 to $25,000 | 11.3 | 16.5 | ||||
| $25,000 to $50,000 | 34.0 | 35.2 | ||||
| $50,000 to $100,000 | 39.3 | 33.3 | ||||
| $100,000 or more | 12.6 | 12.3 | ||||
| Percent | ||
|---|---|---|
| Precaution | Study 1 | Study 2 |
| Avoid people who cough and/or sneeze | 95 | 96 |
| Covering mouth and nose when coughing and sneezing | 95 | 97 |
| Avoid large gatherings of people | 96 | 95 |
| Avoid small gathers of people except family | 92 | 88 |
| Wash your hands more often | 94 | 92 |
| Use hand sanitizer more often | 83 | 67 |
| Avoid people who are in contact with infected people | 95 | 95 |
| Avoid public transportation | 93 | 96 |
| Avoid school and/or work | 79 | 76 |
| Avoid public spaces | 83 | 75 |
| Avoid travel to infected areas | 93 | 95 |
| Avoid any travel | 85 | 83 |
| Use disinfectant on surfaces | 88 | 79 |
| Wear a mask | 60 | 54 |
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
| Precautions | 87.89 | 16.57 | 8.33 | 100 | 84.84 | 18.14 | 0 | 100 |
| COVID-19 Knowledge | 18.57 | 4.51 | 3 | 23 | 19.85 | 2.80 | 5 | 23 |
| Degree | 6.64 | 1.55 | 2 | 10 | 6.56 | 1.86 | 2 | 10 |
| Age | 38.74 | 11.52 | 20 | 79 | 64.61 | 5.13 | 55 | 79 |
| Income | 3.48 | 0.95 | 1 | 5 | 3.37 | 0.94 | 1 | 5 |
| Information Seeking | 2.38 | 0.92 | 1 | 5 | 1.37 | 0.32 | 1 | 3.8 |
| In-Person Interactions | 3.79 | 29.43 | 0 | 800 | 4.62 | 18.30 | 0 | 500 |
| COVID-19 Fake News Beliefs | 1.13 | 1.58 | 0 | 6 | 0.86 | 1.35 | 0 | 6 |
| Ability to Avoid COVID-19 | 3.62 | 1.02 | 1 | 5 | 3.83 | 0.88 | 1 | 5 |
| Risk of Developing COVID-19 | 2.91 | 1.25 | 1 | 5 | 2.07 | 0.94 | 1 | 4 |
| Disruption to Daily Routine | 2.72 | 0.98 | 1 | 4 | 2.69 | 1.03 | 1 | 5 |
| Left Home | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0 | 1 |
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Precautions | -- | .16 *** | .07 | −.03 | .10 ** | .09 * | −.10 ** | −.13 *** | −.02 | .08 * | .19 *** | -- |
| 2. COVID-19 Knowledge | .31 *** | -- | −.17** | .10 ** | .03 | −.59 *** | −.08 * | −.53 *** | −.16 *** | −.04 | −.03 | -- |
| 3. Degree | −.08 | .04 | -- | −.03 | .25 *** | .28 *** | .01 | .19 *** | .05 | .06 | .06 *** | -- |
| 4. Age | −.02 | −.03 | .09 | -- | −.03 | −.07 | −.02 | .01 | .04 | .01 | −.05 | -- |
| 5. Income | .05 | .00 | .16 * | −.07 | -- | .02 | −.05 | −.08 * | .01 | .04 | .01 ** | -- |
| 6. Information Seeking | −.01 | −.29 *** | −.03 | −.10 | .14 * | -- | .08 * | .40 *** | .19 *** | .16 *** | .22 *** | -- |
| 7. In-Person Interactions | −.14 * | .02 | .04 | −.02 | −.05 | −.06 | -- | −.01 | .00 | −.05 | −.02 | -- |
| 8. COVID-19 Fake News Beliefs | −.47 *** | −.43 *** | −.04 | .04 | .00 | .10 | .10 | -- | .25 *** | −.08 * | −.05 | -- |
| 9. Ability to Avoid COVID-19 | −.12 | −.11 | −.08 | .08 | .15 * | −.04 | −.04 | −.17 ** | -- | −.32 *** | −.07 | -- |
| 10. Risk of Developing COVID-19 | .25 ** | .08 | .02 | −.06 | −.06 | .08 | .08 | .07 | −.31 *** | -- | .26 *** | -- |
| 11. Disruption to Daily Routine | .11 | .09 | .12 | −.08 | .17 ** | .22 ** | .22 ** | −.08 | −.16 * | −.30 *** | -- | -- |
| 12. Left Home | −.19 * | .02 | .05 | .07 | .17 * | −.20 ** | −.20 ** | .17 * | .11 | .10 | −.13 * | -- |
| Fixed Effects | Study 1 B (SE B) | Study 2—Concurrent B (SE B) | Study 2—Lagged B (SE B) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 88.40 (0.60) *** | 58.10 (17.25) ** | 45.43 (13.58) ** |
| Previous day’s Precautions | 23.19 (1.36) *** | ||
| COVID-19 Knowledge | 0.82 (0.17) *** | 1.18 (0.43) ** | 0.86 (0.34) * |
| Degree | 0.19 (0.40) | −1.12 (0.53) * | −0.92 (0.42) * |
| Age | −0.03 (0.05) | 0.10 (0.19) | 0.07 (0.15) |
| Income | 0.85 (0.62) | 1.10 (1.02) | 0.71 (0.81) |
| Individual Information Seeking | 4.16 (0.84) *** | −0.16 (0.68) | −1.02 (0.70) |
| Daily Information Seeking | 2.22 (2.59) | 2.76 (2.26) | |
| In-Person Interactions | −0.05 (0.02) ** | −0.05 (0.01) *** | −0.04 (0.01) *** |
| COVID-19 Fake News Beliefs | −0.64 (0.45) | −4.93 (0.84) *** | −3.85 (0.66) *** |
| Ability to Avoid COVID-19 | 0.50 (0.63) | 0.45 (0.32) | 0.81 (0.33) * |
| Risk of Developing COVID-19 | 0.57 (0.54) | 2.95 (1.42) * | 2.55 (1.25) * |
| Disruption to Daily Routine | 1.92 (0.62) ** | 0.41 (0.20) * | 0.39 (0.21) |
| Left Home | −3.07 (0.26) *** | −3.06 (0.26) *** | |
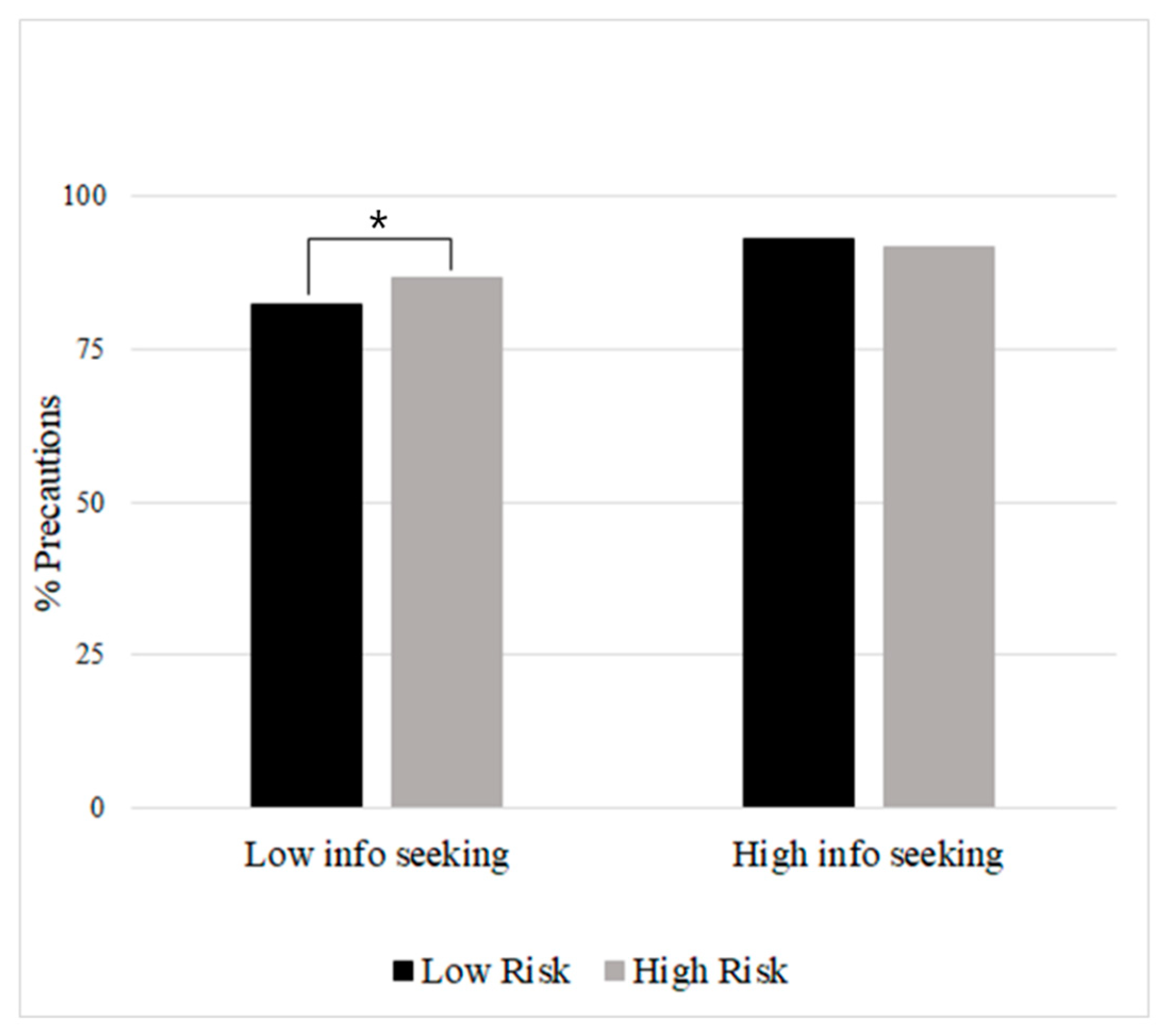
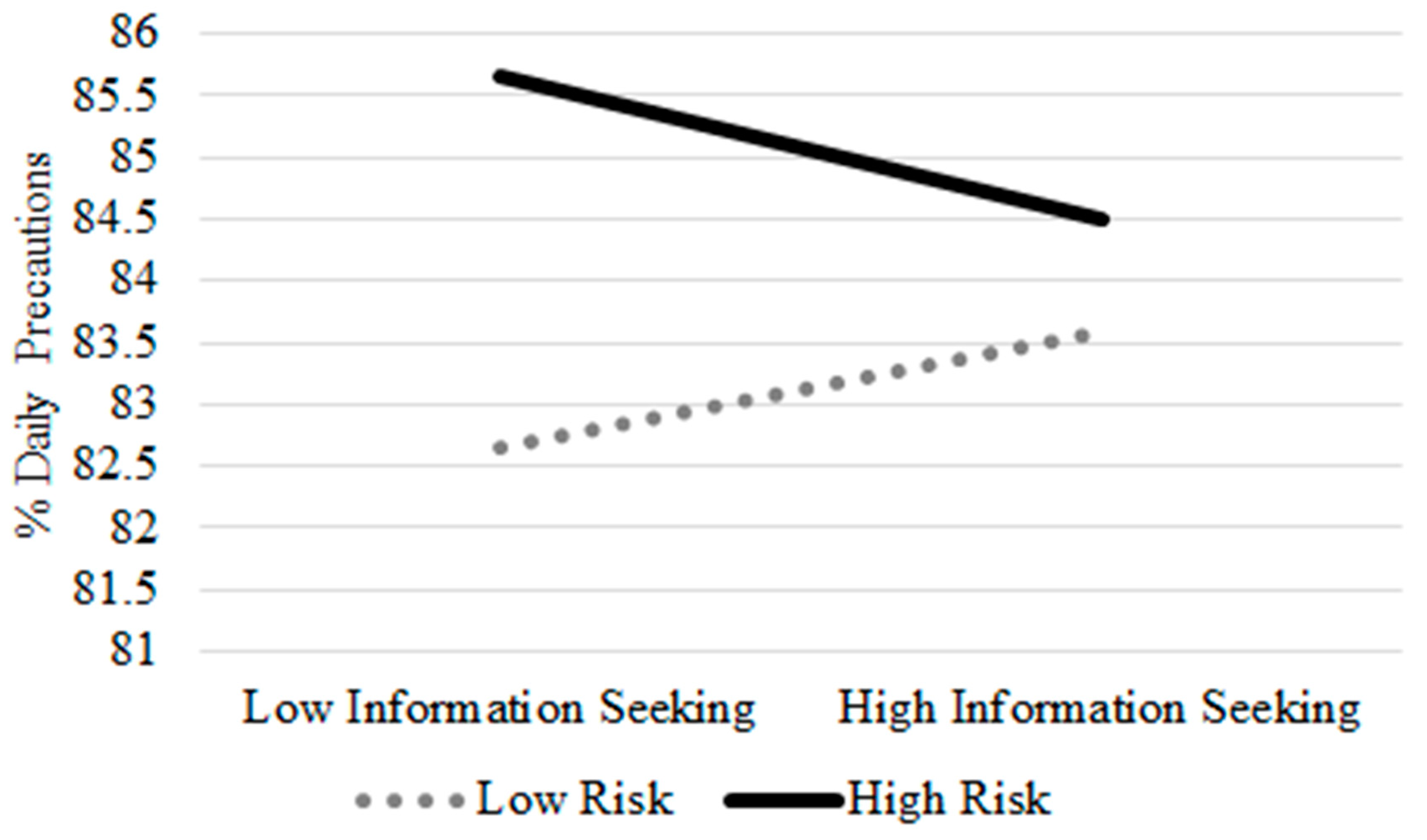
| Information Seeking*Perceived Risk | −1.25 (0.46) ** | −1.46 (0.66) * | −1.36 (0.66) * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pearman, A.; Hughes, M.L.; Coblenz, C.W.; Smith, E.L.; Neupert, S.D. A Precautionary Tale: Individual Decision Making in the Time of COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054597
Pearman A, Hughes ML, Coblenz CW, Smith EL, Neupert SD. A Precautionary Tale: Individual Decision Making in the Time of COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(5):4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054597
Chicago/Turabian StylePearman, Ann, MacKenzie L. Hughes, Clara W. Coblenz, Emily L. Smith, and Shevaun D. Neupert. 2023. "A Precautionary Tale: Individual Decision Making in the Time of COVID-19" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 5: 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054597
APA StylePearman, A., Hughes, M. L., Coblenz, C. W., Smith, E. L., & Neupert, S. D. (2023). A Precautionary Tale: Individual Decision Making in the Time of COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(5), 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054597






