Influence of Hand Tracking in Immersive Virtual Reality for Memory Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
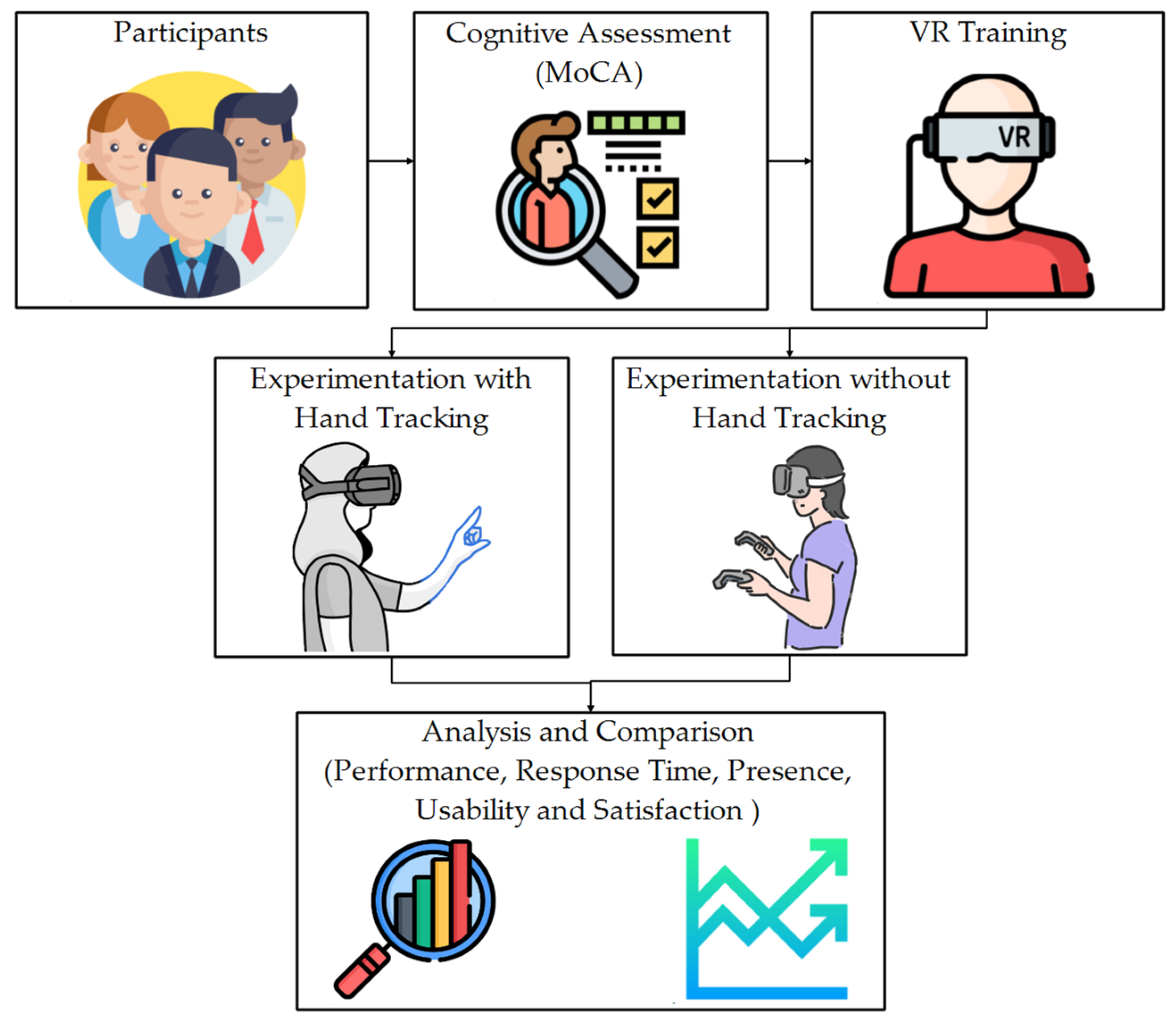
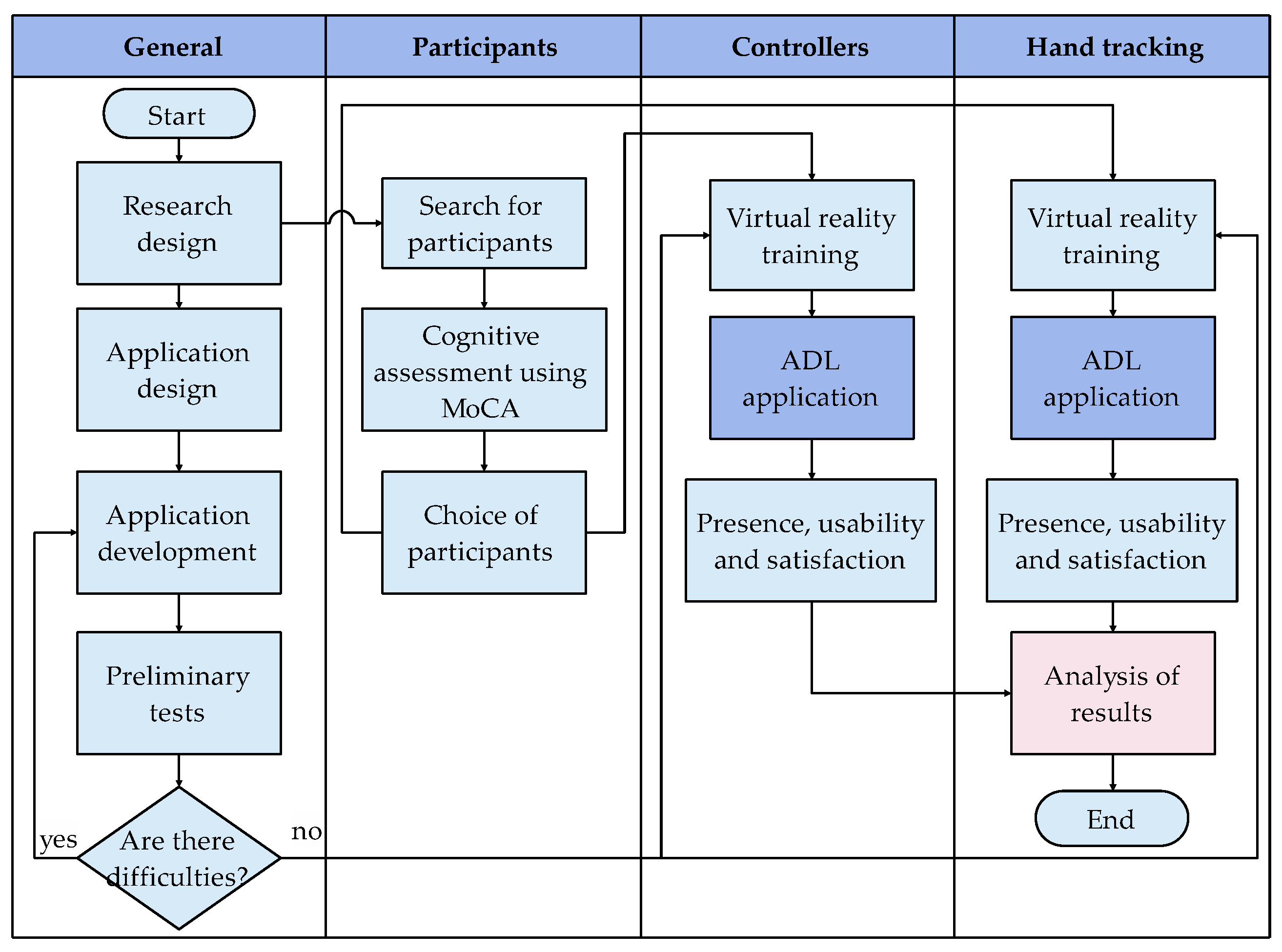
3. Materials and Methods
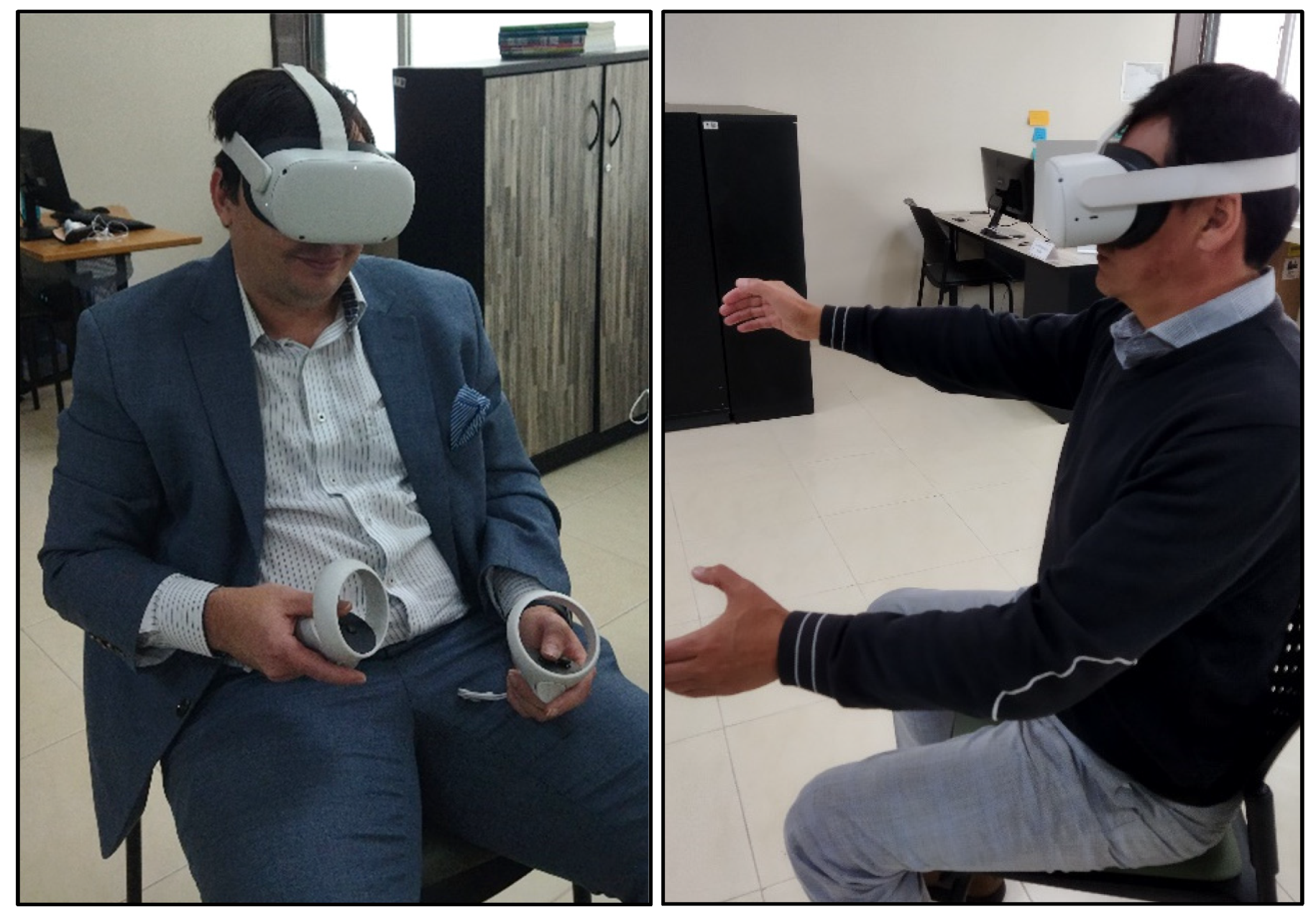
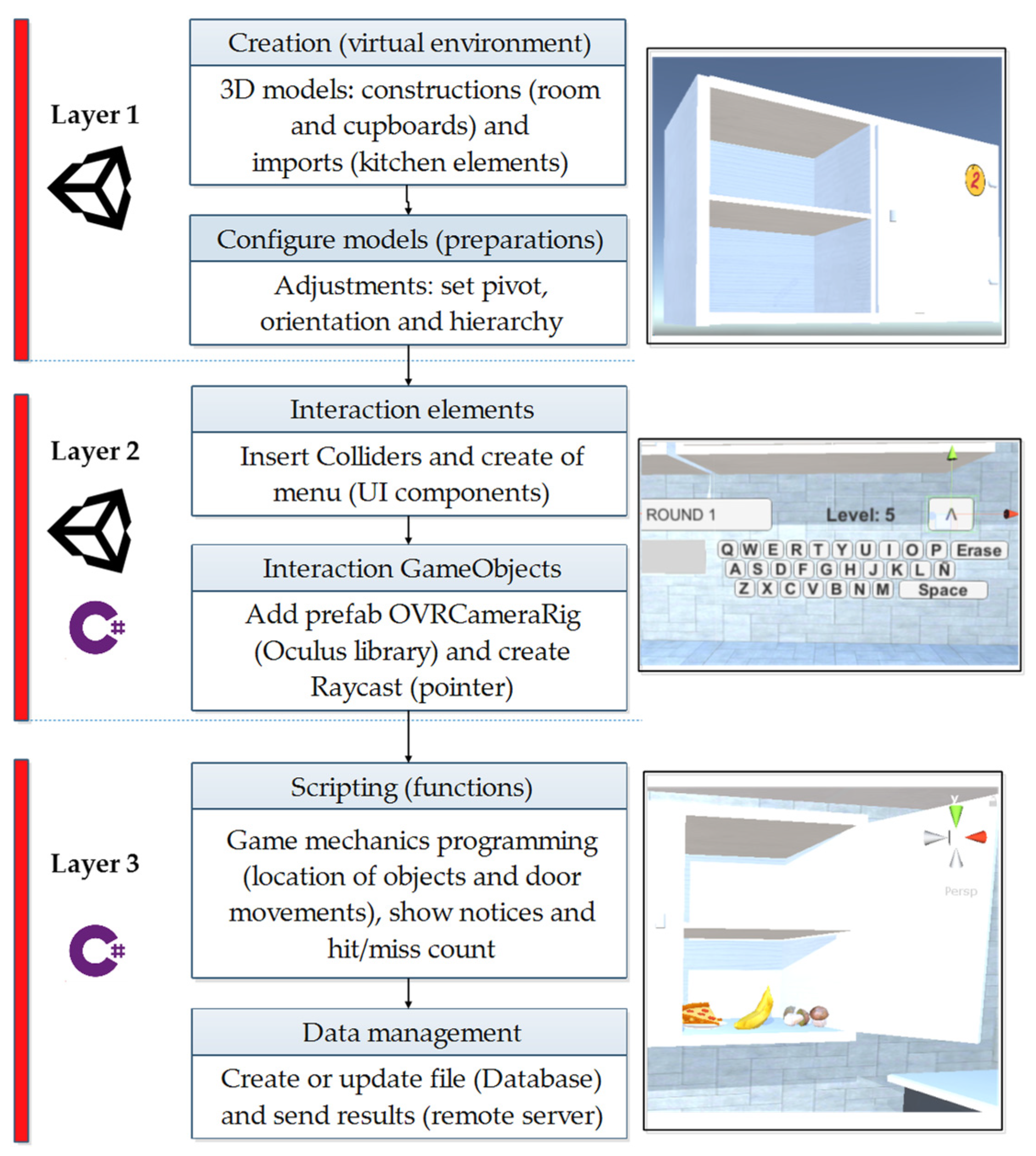
3.1. Application
3.2. Participants
3.3. Procedures
3.4. Instruments
4. Results
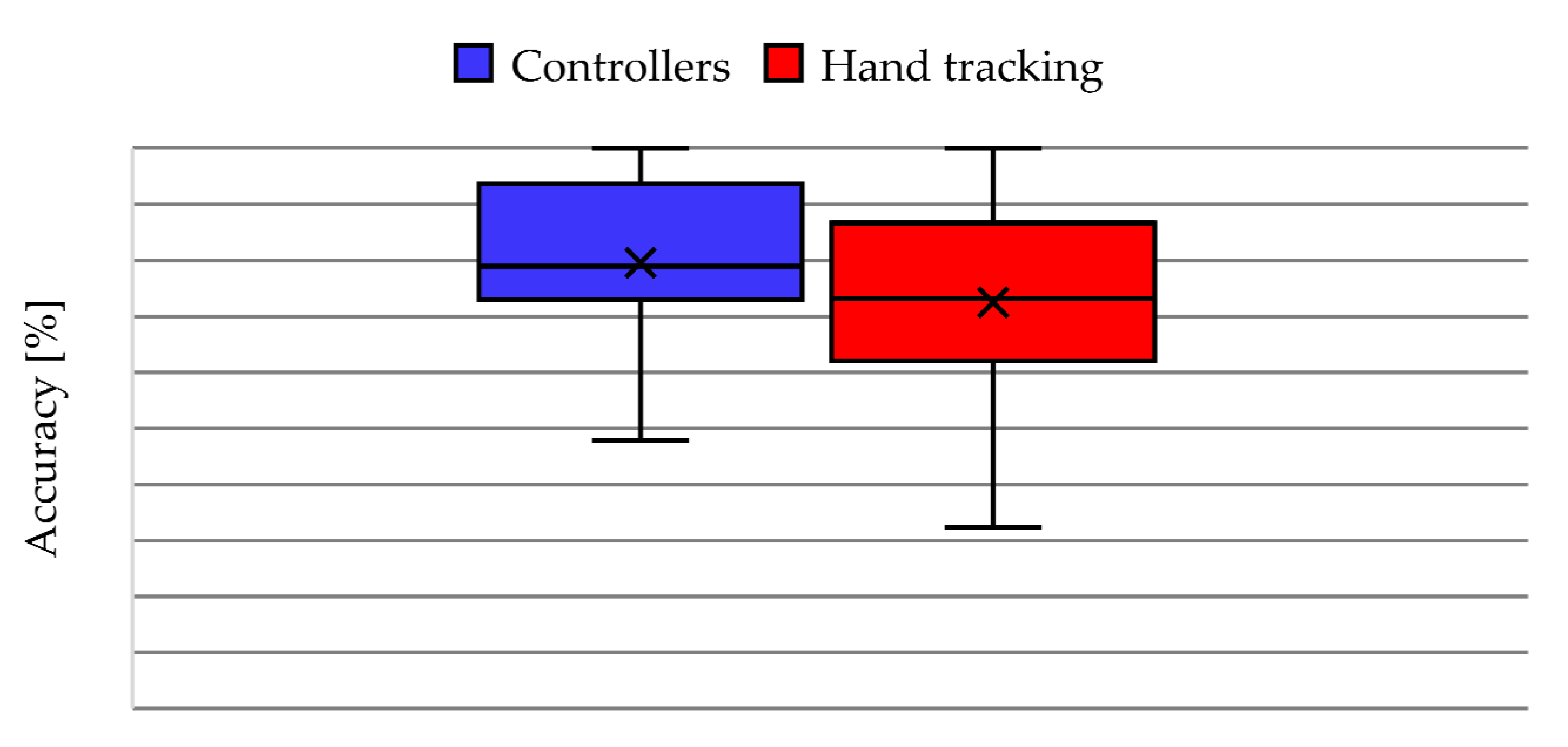
4.1. Accuracy
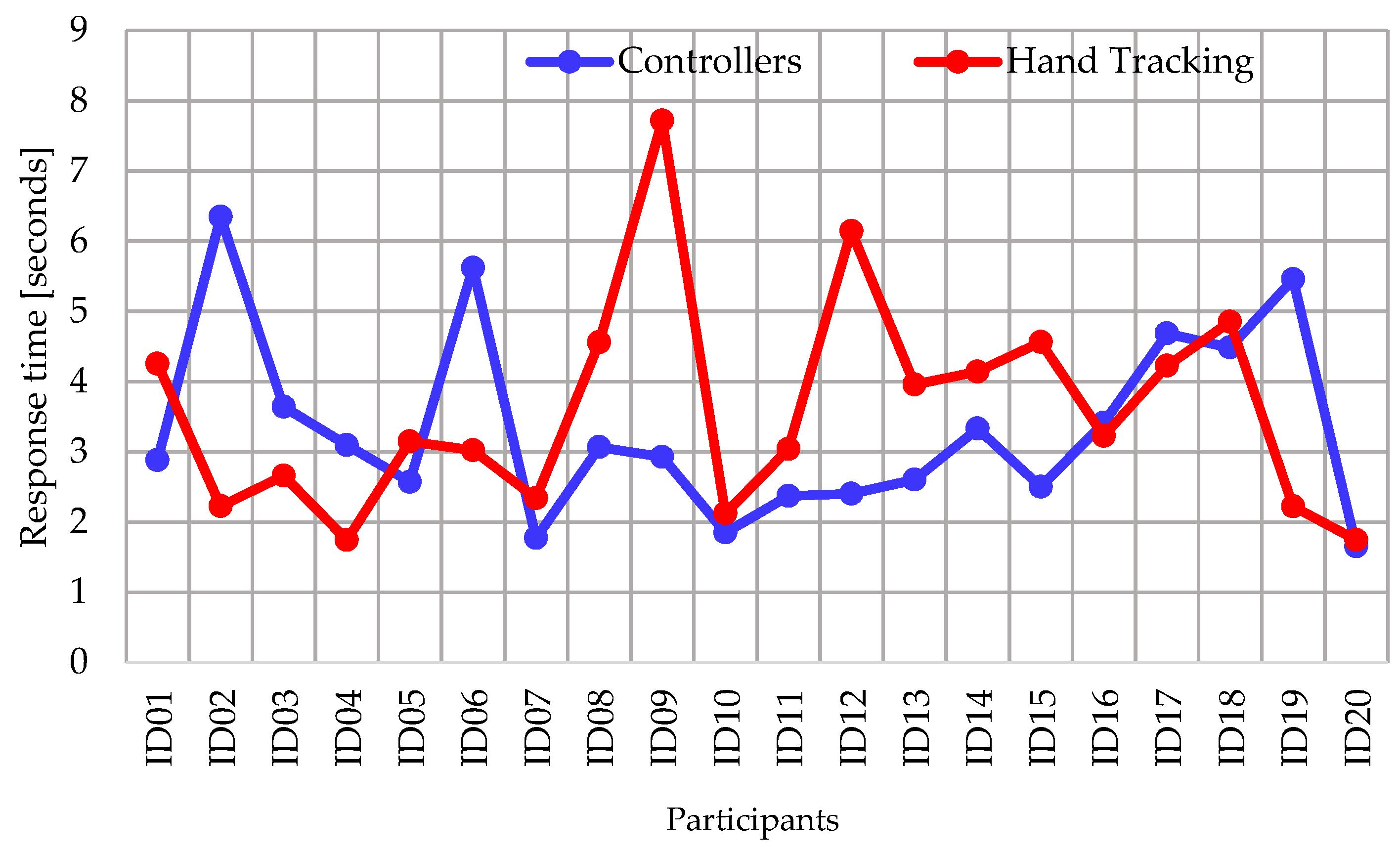
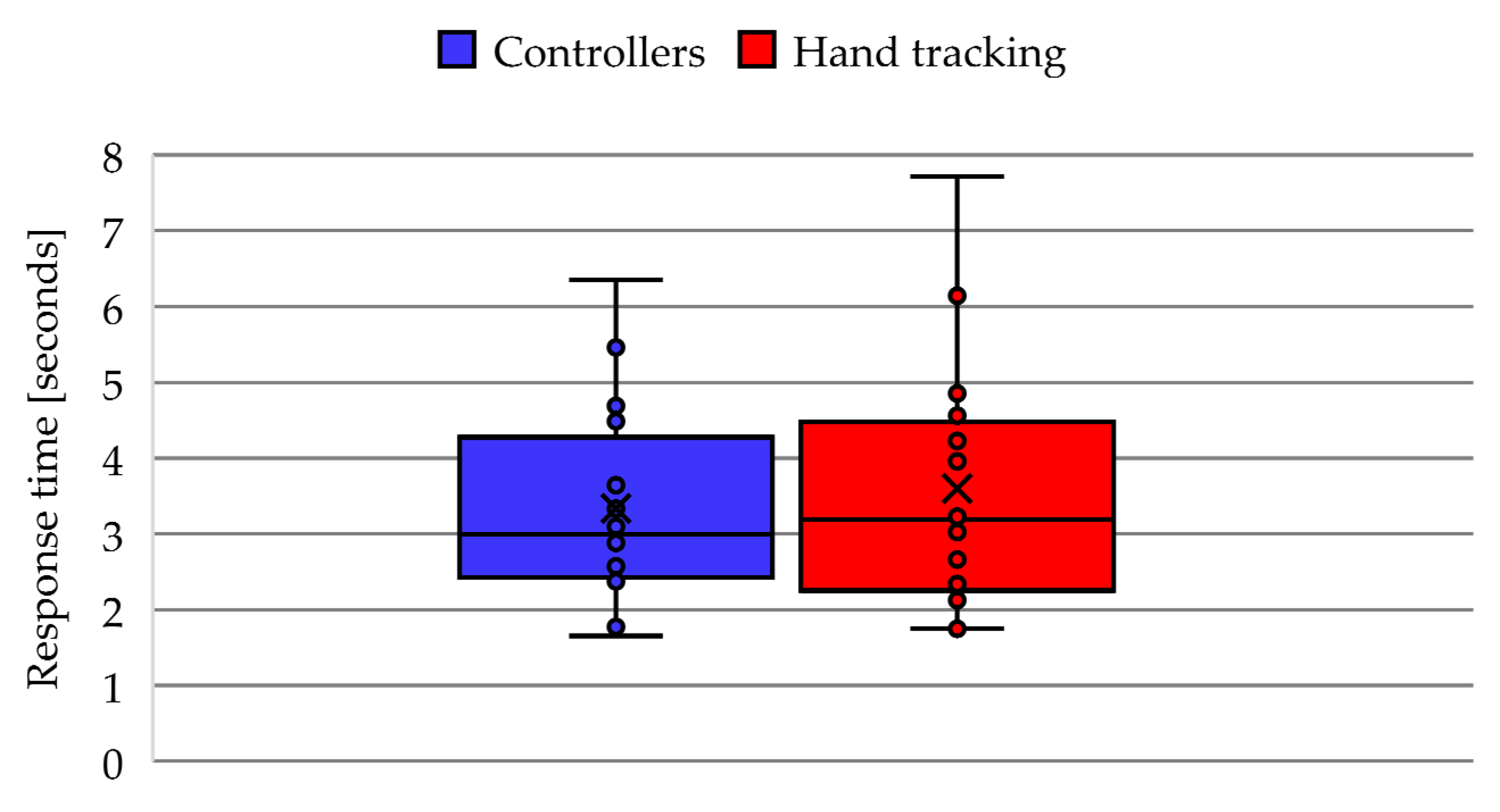
4.2. Response Time
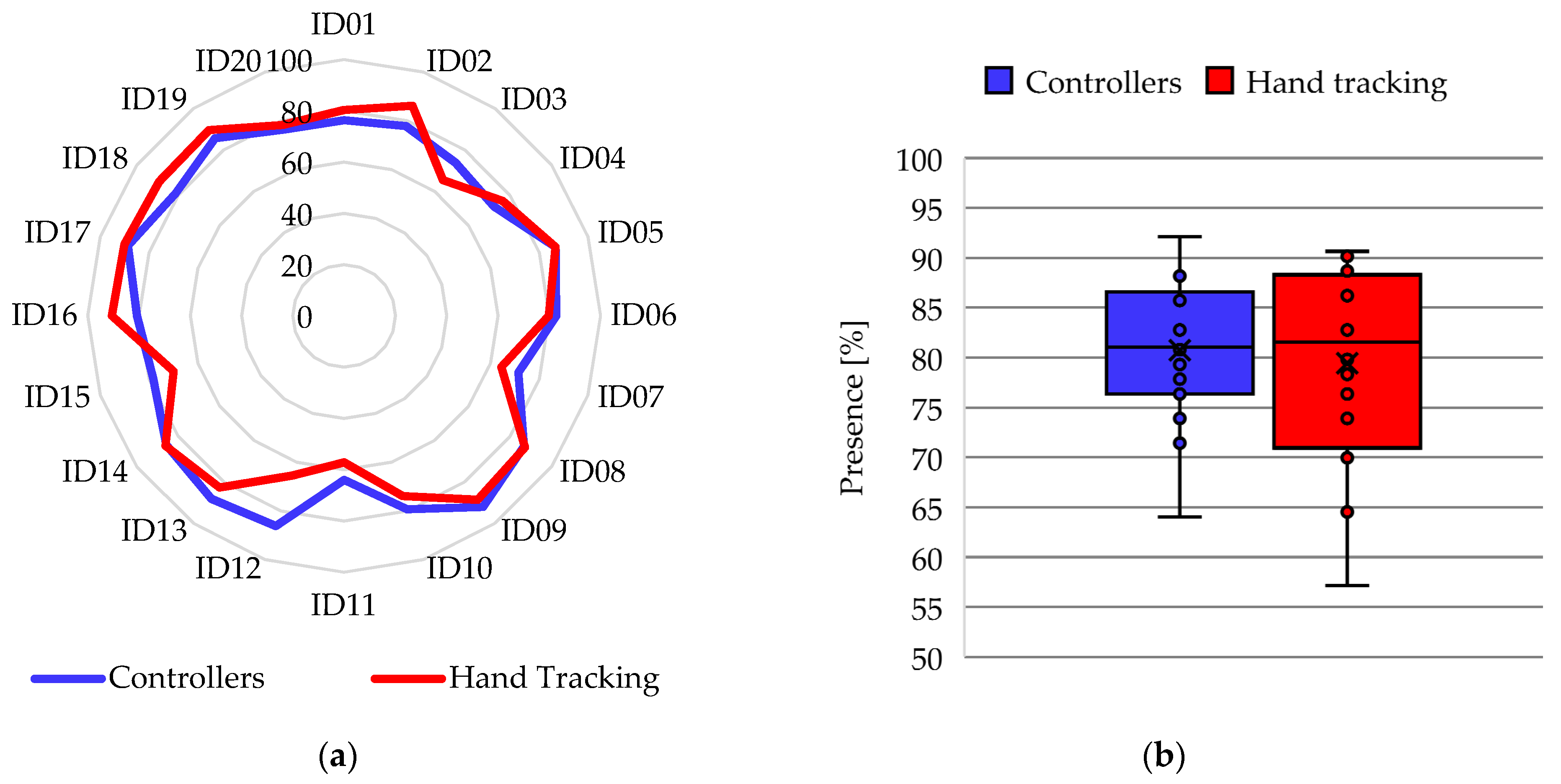
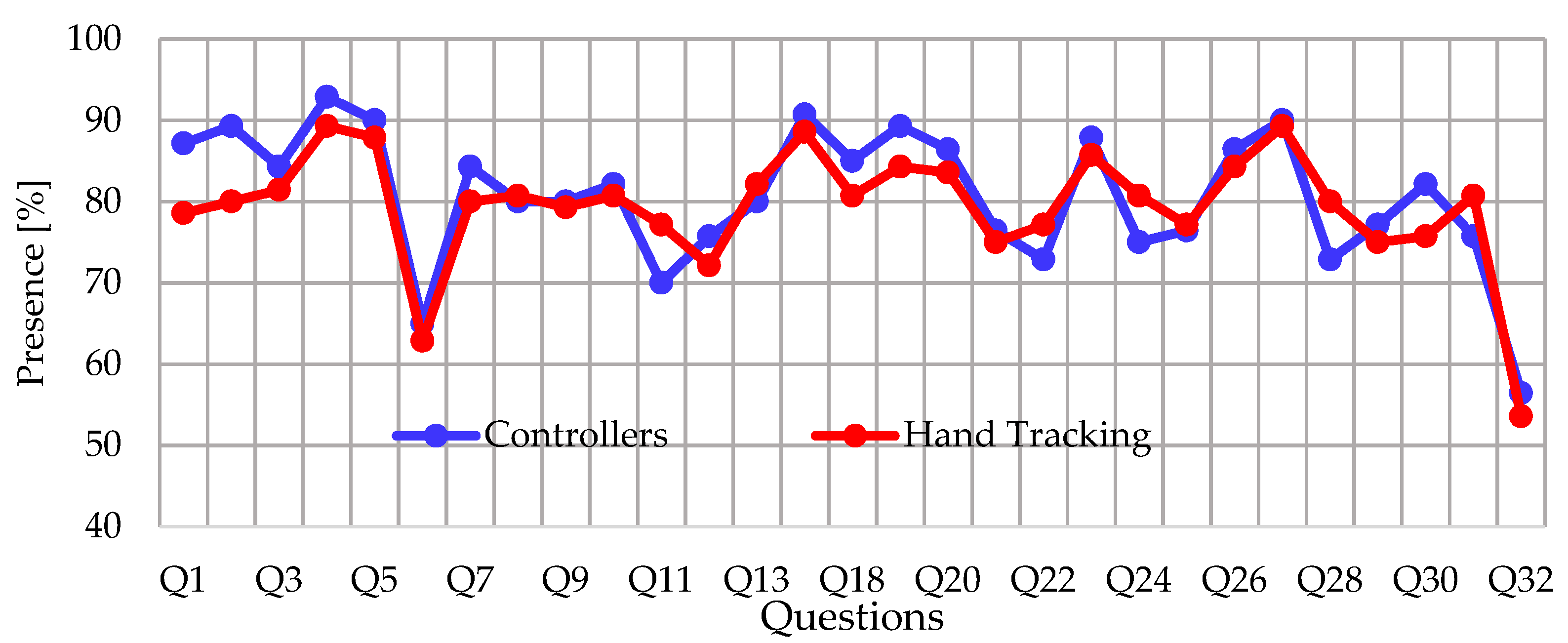
4.3. Presence
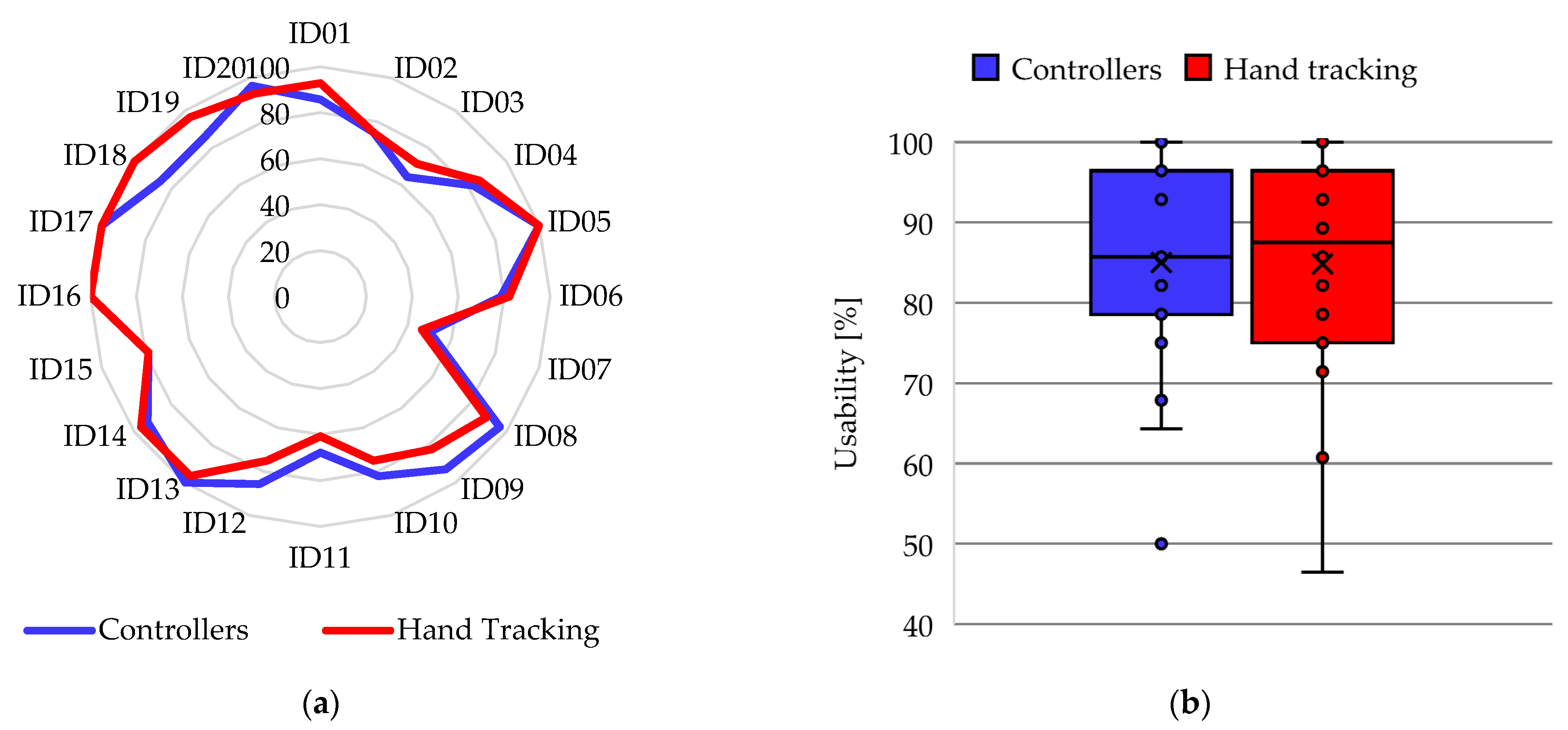
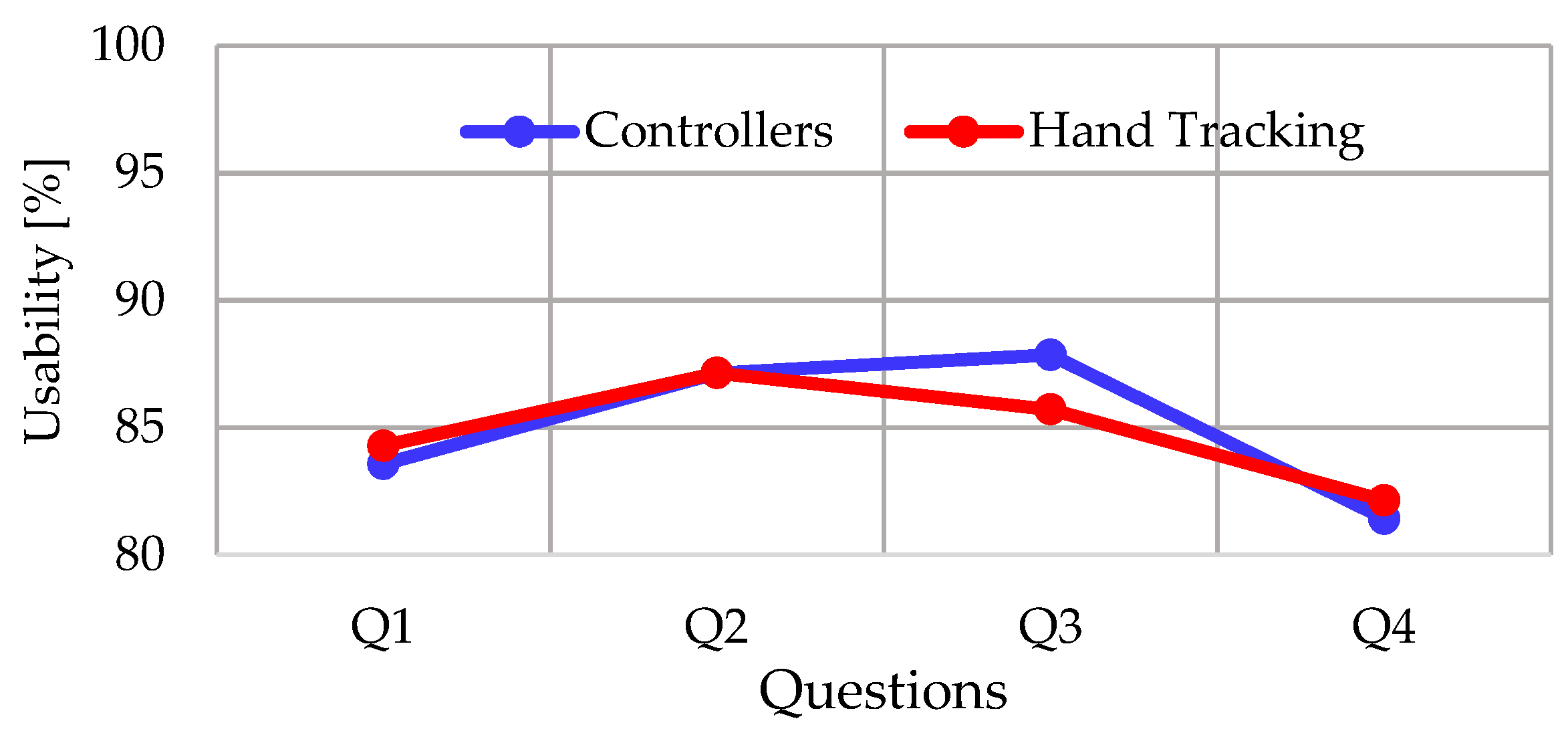
4.4. Usability
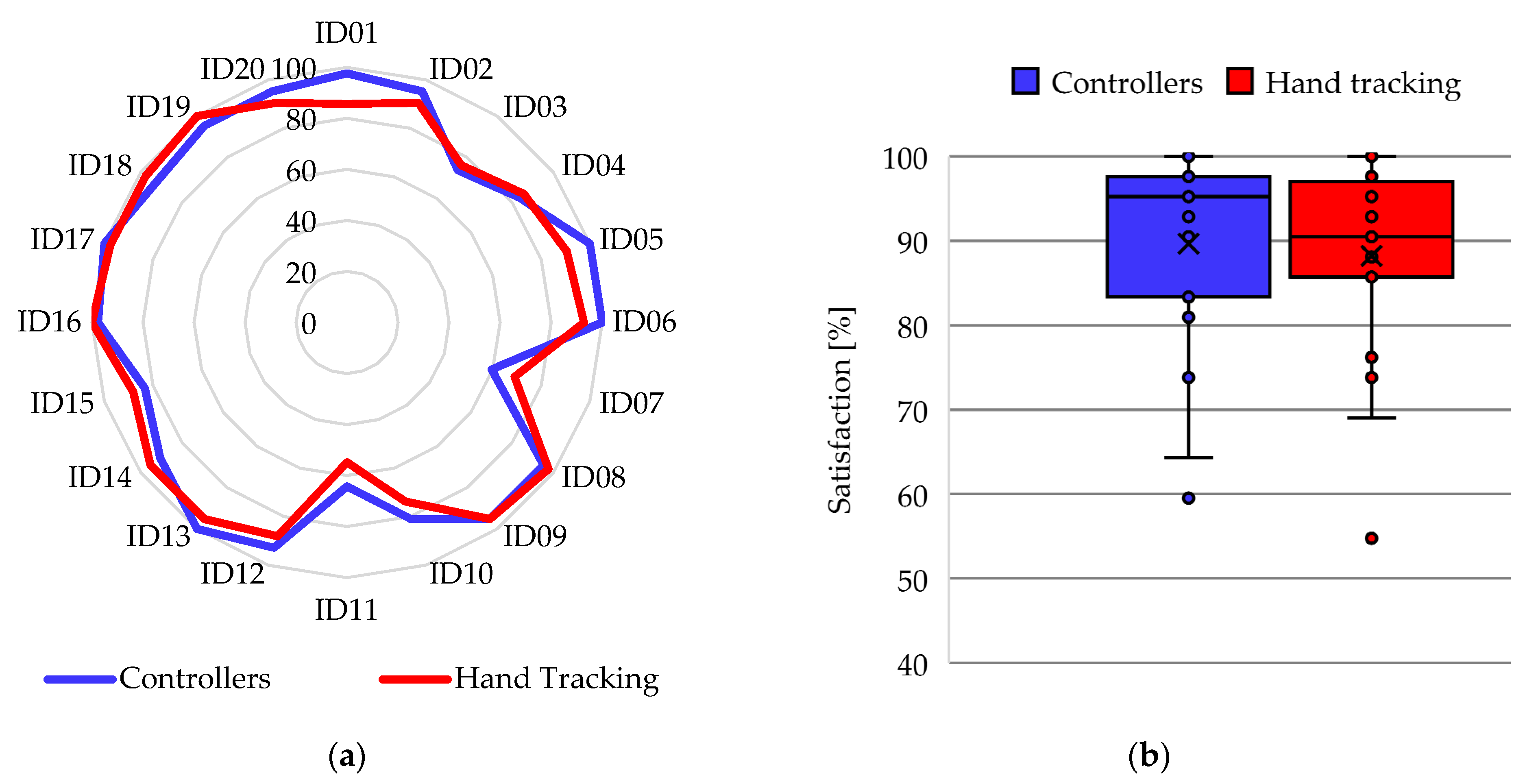
4.5. Satisfaction
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lange, B.; Koenig, S.; Chang, C.Y.; McConnell, E.; Suma, E.; Bolas, M.; Rizzo, A. Designing Informed Game-Based Rehabilitation Tasks Leveraging Advances in Virtual Reality. Disabil. Rehabil. 2012, 34, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furht, B. Desktop Virtual Reality. In Encyclopedia of Multimedia; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 150–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcañiz, M.; Bigné, E.; Guixeres, J. Virtual Reality in Marketing: A Framework, Review, and Research Agenda. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Georgiev, D.D.; Georgieva, I.; Gong, Z.; Nanjappan, V.; Georgiev, G.V. Virtual Reality for Neurorehabilitation and Cognitive Enhancement. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Betances, R.I.; Jiménez-Mixco, V.; Arredondo, M.T.; Cabrera-Umpiérrez, M.F. Using Virtual Reality for Cognitive Training of the Elderly. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 2015, 30, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, W.R.; Craig, A.B. Understanding Virtual Reality: Interface, Application, and Design. Presence 2003, 12, 441–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crosbie, J.; McDonough, S.; Lennon, S.; McNeill, M. Development of a Virtual Reality System for the Rehabilitation of the Upper Limb after Stroke. In Personalised Health Management Systems; Nugent, C.D., McCullagh, P.J., McAdams, E.T., Eds.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 117, pp. 218–222. ISBN 1586035657. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, M. Immersion and the Illusion of Presence in Virtual Reality. Br. J. Psychol. 2018, 109, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.A.; Schultheis, M.; Kerns, K.A.; Mateer, C. Analysis of Assets for Virtual Reality Applications in Neuropsychology. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2004, 14, 207–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeter, C. Being There: The Subjective Experience of Presence. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 1992, 1, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ortega, D.; Díaz-Pernas, F.J.; Martínez-Zarzuela, M.; Antón-Rodríguez, M.; Díez-Higuera, J.F.; Boto-Giralda, D. Real-Time Hands, Face and Facial Features Detection and Tracking: Application to Cognitive Rehabilitation Tests Monitoring. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2010, 33, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayma, M.; Tuijt, R.; Cooper, C.; Walters, K.; Heyn, P.C. Are We There Yet? Immersive Virtual Reality to Improve Cognitive Function in Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Gerontologist 2020, 60, E502–E512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, E.; Zucchella, C.; Bottiroli, S.; Federico, A.; Giugno, R.; Sandrini, G.; Chiamulera, C.; Tamburin, S. Telemedicine and Virtual Reality for Cognitive Rehabilitation: A Roadmap for the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isernia, S.; Di Tella, S.; Pagliari, C.; Jonsdottir, J.; Castiglioni, C.; Gindri, P.; Salza, M.; Gramigna, C.; Palumbo, G.; Molteni, F.; et al. Effects of an Innovative Telerehabilitation Intervention for People with Parkinson’s Disease on Quality of Life, Motor, and Non-Motor Abilities. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.D.; Courtney, C.G.; Arizmendi, B.; Dawson, M. Virtual Reality Stroop Task for Neurocognitive Assessment. In Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 18; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 163, pp. 433–439. ISBN 9781607507055. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, T.D.; Courtney, C.G. Neurocognitive and Psychophysiological Interfaces for Adaptive Virtual Environments. In Human-Centered Design of E-Health Technologies: Concepts, Methods and Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 208–233. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, B.; Marion, S.; Rizzo, A.; Turnbull, J.; Nolty, A. Virtual Reality Assessment of Classroom—Related Attention: An Ecologically Relevant Approach to Evaluating the Effectiveness of Working Memory Training. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faria, A.L.; Cameirão, M.S.; Couras, J.F.; Aguiar, J.R.O.; Costa, G.M.; Bermúdez i Badia, S. Combined Cognitive-Motor Rehabilitation in Virtual Reality Improves Motor Outcomes in Chronic Stroke—A Pilot Study. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maggio, M.G.; Maresca, G.; De Luca, R.; Stagnitti, M.C.; Porcari, B.; Ferrera, M.C.; Galletti, F.; Casella, C.; Manuli, A.; Calabrò, R.S. The Growing Use of Virtual Reality in Cognitive Rehabilitation: Fact, Fake or Vision? A Scoping Review. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2019, 111, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alashram, A.R.; Annino, G.; Padua, E.; Romagnoli, C.; Mercuri, N.B. Cognitive Rehabilitation Post Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review for Emerging Use of Virtual Reality Technology. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 66, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamito, P.; Oliveira, J.; Morais, D.; Coelho, C.; Santos, N.; Alves, C.; Galamba, A.; Soeiro, M.; Yerra, M.; French, H.; et al. Cognitive Stimulation of Elderly Individuals with Instrumental Virtual Reality-Based Activities of Daily Life: Pre-Post Treatment Study. Cyberpsychology, Behav. Soc. Netw. 2019, 22, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela-Aldás, J.; Palacios-Navarro, G.; Amariglio, R.; García-Magariño, I. Head-Mounted Display-Based Application for Cognitive Training. Sensors 2020, 20, 6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, N.; Park, H.J.; Yang, J.-G.; Son, H.; Jang, M.; Lee, J.; Kang, S.W.; Park, K.W.; Park, H. The Effect of a Virtual Reality-Based Intervention Program on Cognition in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Control Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caglio, M.; Latini-Corazzini, L.; D’Agata, F.; Cauda, F.; Sacco, K.; Monteverdi, S.; Zettin, M.; Duca, S.; Geminiani, G. Virtual Navigation for Memory Rehabilitation in a Traumatic Brain Injured Patient. Neurocase 2012, 18, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Helvoort, D.; Stobbe, E.; Benning, R.; Otgaar, H.; van de Ven, V. Physical Exploration of a Virtual Reality Environment: Effects on Spatiotemporal Associative Recognition of Episodic Memory. Mem. Cogn. 2020, 48, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tummon, H.M.; Allen, J.; Bindemann, M. Facial Identification at a Virtual Reality Airport. Iperception. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plancher, G.; Gyselinck, V.; Piolino, P. The Integration of Realistic Episodic Memories Relies on Different Working Memory Processes: Evidence from Virtual Navigation. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tascón, L.; García-Moreno, L.M.; Cimadevilla, J.M. Almeria Spatial Memory Recognition Test (ASMRT): Gender Differences Emerged in a New Passive Spatial Task. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 651, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriveau Lecavalier, N.; Ouellet, É.; Boller, B.; Belleville, S. Use of Immersive Virtual Reality to Assess Episodic Memory: A Validation Study in Older Adults. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2020, 30, 462–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecouvey, G.; Morand, A.; Gonneaud, J.; Piolino, P.; Orriols, E.; Pélerin, A.; Da Silva, L.F.; de La Sayette, V.; Eustache, F.; Desgranges, B. An Impairment of Prospective Memory in Mild Alzheimer’s Disease: A Ride in a Virtual Town. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallejo, V.; Wyss, P.; Rampa, L.; Mitache, A.V.; Müri, R.M.; Mosimann, U.P.; Nef, T. Evaluation of a Novel Serious Game Based Assessment Tool for Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iliadou, P.; Paliokas, I.; Zygouris, S.; Lazarou, E.; Votis, K.; Tzovaras, D.; Tsolaki, M. A Comparison of Traditional and Serious Game-Based Digital Markers of Cognition in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Healthy Controls. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 79, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.L.; Andrade, A.; Soares, L.; Bermúdez I Badia, S. Benefits of Virtual Reality Based Cognitive Rehabilitation through Simulated Activities of Daily Living: A Randomized Controlled Trial with Stroke Patients. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2016, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foloppe, D.A.; Richard, P.; Yamaguchi, T.; Etcharry-Bouyx, F.; Allain, P. The Potential of Virtual Reality-Based Training to Enhance the Functional Autonomy of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients in Cooking Activities: A Single Case Study. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2018, 28, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.-Y.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Wang, C.-J.; Hsu, W.-C. Using Virtual Reality-Based Training to Improve Cognitive Function, Instrumental Activities of Daily Living and Neural Efficiency in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Betances, R.I.; Arredondo Waldmeyer, M.T.; Fico, G.; Cabrera-Umpiérrez, M.F. A Succinct Overview of Virtual Reality Technology Use in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krohn, S.; Tromp, J.; Quinque, E.M.; Belger, J.; Klotzsche, F.; Rekers, S.; Chojecki, P.; Mooij, J.d.; Akbal, M.; McCall, C.; et al. Multidimensional Evaluation of Virtual Reality Paradigms in Clinical Neuropsychology: Application of the VR-Check Framework. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e16724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brade, J.; Lorenz, M.; Busch, M.; Hammer, N.; Tscheligi, M.; Klimant, P. Being There Again—Presence in Real and Virtual Environments and Its Relation to Usability and User Experience Using a Mobile Navigation Task. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2017, 101, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechatá, A.; Nekovářová, T.; Fajnerová, I. What Is the Future for Immersive Virtual Reality in Memory Rehabilitation? A Systematic Review. NeuroRehabilitation 2021, 48, 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, S.; Brivio, E.; Riva, G.; Baños, R.M. Immersive Versus Non-Immersive Experience: Exploring the Feasibility of Memory Assessment Through 360° Technology. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinescu, A.; David, D. The Effect of Learning in a Virtual Environment on Explicit and Implicit Memory by Applying a Process Dissociation Procedure. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2019, 35, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, K.A.; Oiknine, A.H.; Files, B.T.; Sinatra, A.M.; Patton, D.; Ericson, M.; Thomas, J.; Khooshabeh, P. Level of Immersion Affects Spatial Learning in Virtual Environments: Results of a Three-Condition within-Subjects Study with Long Intersession Intervals. Virtual Real. 2020, 24, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krokos, E.; Plaisant, C.; Varshney, A. Virtual Memory Palaces: Immersion Aids Recall. Virtual Real. 2019, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plechatá, A.; Sahula, V.; Fayette, D.; Fajnerová, I. Age-Related Differences with Immersive and Non-Immersive Virtual Reality in Memory Assessment. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuena, C.; Serino, S.; Dutriaux, L.; Riva, G.; Piolino, P. Virtual Enactment Effect on Memory in Young and Aged Populations: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelkamp, J.; Zimmer, H.D.; Mohr, G.; Sellen, O. Memory of Self-Performed Tasks: Self-Performing during Recognition. Mem. Cogn. 1994, 22, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.; Attree, E.; Rose, F.; Clifford, B.; Leadbetter, A. The Specificity of Memory Enhancement during Interaction with a Virtual Environment. Memory 1999, 7, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebara, N.; Orriols, E.; Zaoui, M.; Berthoz, A.; Piolino, P. Effects of Enactment in Episodic Memory: A Pilot Virtual Reality Study with Young and Elderly Adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhorst-Cates, E.M.; Rand, K.M.; Creem-Regehr, S.H. Does Active Learning Benefit Spatial Memory during Navigation with Restricted Peripheral Field? Attention Perception Psychophys. 2020, 82, 3033–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouellet, É.; Boller, B.; Corriveau-Lecavalier, N.; Cloutier, S.; Belleville, S. The Virtual Shop: A New Immersive Virtual Reality Environment and Scenario for the Assessment of Everyday Memory. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 303, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamalian, N.; Gillies, M.; Leymarie, F.F.; Pan, X. The Effects of Hand Tracking on User Performance: An Experimental Study of an Object Selection Based Memory Game. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Singapore, Singapore, 17–21 October 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 768–776. [Google Scholar]
- Khundam, C.; Sukkriang, N.; Noël, F. No Difference in Learning Outcomes and Usability between Using Controllers and Hand Tracking during a Virtual Reality Endotracheal Intubation Training for Medical Students in Thailand. J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 2021, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela-Aldás, J.; Buele, J.; Amariglio, R.; García-Magariño, I.; Palacios-Navarro, G. The Cupboard Task: An Immersive Virtual Reality-Based System for Everyday Memory Assessment. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2022, 167, 102885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Liu, B.; Cabezas, R.; Twigg, C.D.; Zhang, P.; Petkau, J.; Yu, T.-H.; Tai, C.-J.; Akbay, M.; Wang, Z.; et al. MEgATrack. ACM Trans. Graph. 2020, 39, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masurovsky, A.; Chojecki, P.; Runde, D.; Lafci, M.; Przewozny, D.; Gaebler, M. Controller-Free Hand Tracking for Grab-and-Place Tasks in Immersive Virtual Reality: Design Elements and Their Empirical Study. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2020, 4, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facebook Technologies, LLC. First Steps with Hand Tracking. Available online: https://sidequestvr.com/app/3358/first-steps-with-hand-tracking (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- González-Landero, F.; García-Magariño, I.; Amariglio, R.; Lacuesta, R. Smart Cupboard for Assessing Memory in Home Environment. Sensors 2019, 19, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Julayanont, P.; Nasreddine, Z.S. Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA): Concept and Clinical Review. In Cognitive Screening Instruments; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 139–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MoCA Test Inc. In MoCA Test; MoCA Test Inc.: Quebec, QC, Canada.
- Witmer, B.G.; Singer, M.J. Measuring Presence in Virtual Environments: A Presence Questionnaire. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 1998, 7, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paolis, L.T.; De Luca, V. The Effects of Touchless Interaction on Usability and Sense of Presence in a Virtual Environment. Virtual Real. 2022, 26, 1551–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finstad, K. The Usability Metric for User Experience. Interact. Comput. 2010, 22, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Gómez, J.A.; Manzano-Hernández, P.; Albiol-Pérez, S.; Aula-Valero, C.; Gil-Gómez, H.; Lozano-Quilis, J.A. USEQ: A Short Questionnaire for Satisfaction Evaluation of Virtual Rehabilitation Systems. Sensors 2017, 17, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rantamaa, H.-R.; Kangas, J.; Kumar, S.K.; Mehtonen, H.; Järnstedt, J.; Raisamo, R. Comparison of a VR Stylus with a Controller, Hand Tracking, and a Mouse for Object Manipulation and Medical Marking Tasks in Virtual Reality. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Normoyle, A.; Adkins, A.; Sun, Y.; Robb, A.; Ye, Y.; Di Luca, M.; Jorg, S. The Effect of Hand Size and Interaction Modality on the Virtual Hand Illusion. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), Osaka, Japan, 23–27 March 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 510–518. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.A. The Magical Number Seven, plus or Minus Two: Some Limits on Our Capacity for Processing Information. Psychol. Rev. 1956, 63, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, C.I.; Whitmer, D.E.; Entinger, J.; Peterson, E.K.; Sobel, B.M. Interacting with Virtual Reality with a Controller Instead of the Body Benefits Performance and Perceptions. Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 2022, 66, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggente, N.; Essoe, J.K.Y.; Baek, H.Y.; Rissman, J. The Method of Loci in Virtual Reality: Explicit Binding of Objects to Spatial Contexts Enhances Subsequent Memory Recall. J. Cogn. Enhanc. 2020, 4, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A. Virtual Reality in Episodic Memory Research: A Review. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2019, 26, 1213–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, M. Measuring Presence: A Response to the Witmer and Singer Presence Questionnaire. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 1999, 8, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoh, M.; Catena, E.; Arman, S.; Slater, M. Using Presence Questionnaires in Reality. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 2000, 9, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessiter, J.; Freeman, J.; Keogh, E.; Davidoff, J. A Cross-Media Presence Questionnaire: The ITC-Sense of Presence Inventory. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 2001, 10, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khundam, C.; Vorachart, V.; Preeyawongsakul, P.; Hosap, W.; Noël, F. A Comparative Study of Interaction Time and Usability of Using Controllers and Hand Tracking in Virtual Reality Training. Informatics 2021, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavedoni, S.; Chirico, A.; Pedroli, E.; Cipresso, P.; Riva, G. Digital Biomarkers for the Early Detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment: Artificial Intelligence Meets Virtual Reality. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruet, A.; Brochet, B. Cognitive Assessment in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: From Neuropsychological Batteries to Ecological Tools. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 63, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Demographics | Value | Demographics | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||
| Gender: | Mean | 36.05 | |
| Male | 10 | SD | 9.69 |
| Female | 10 | Min | 20 |
| Max | 56 | ||
| MoCA | Education years | ||
| Mean | 27.75 | Mean | 19.4 |
| SD | 1.37 | SD | 2.85 |
| Min | 26 | Min | 15 |
| Max | 30 | Max | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varela-Aldás, J.; Buele, J.; López, I.; Palacios-Navarro, G. Influence of Hand Tracking in Immersive Virtual Reality for Memory Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054609
Varela-Aldás J, Buele J, López I, Palacios-Navarro G. Influence of Hand Tracking in Immersive Virtual Reality for Memory Assessment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(5):4609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054609
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarela-Aldás, José, Jorge Buele, Irene López, and Guillermo Palacios-Navarro. 2023. "Influence of Hand Tracking in Immersive Virtual Reality for Memory Assessment" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 5: 4609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054609
APA StyleVarela-Aldás, J., Buele, J., López, I., & Palacios-Navarro, G. (2023). Influence of Hand Tracking in Immersive Virtual Reality for Memory Assessment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(5), 4609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054609









