Waste-Based Ceramsite for the Efficient Removal of Ciprofloxacin in Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Batch Experiments
2.4. Desorption and Reusability of the Waste-Based Ceramsite
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Waste-Based Ceramsite
3.2. Batch experiments
3.2.1. Effect of the Waste-Based Ceramsite Dosage
3.2.2. Effect of Initial pH
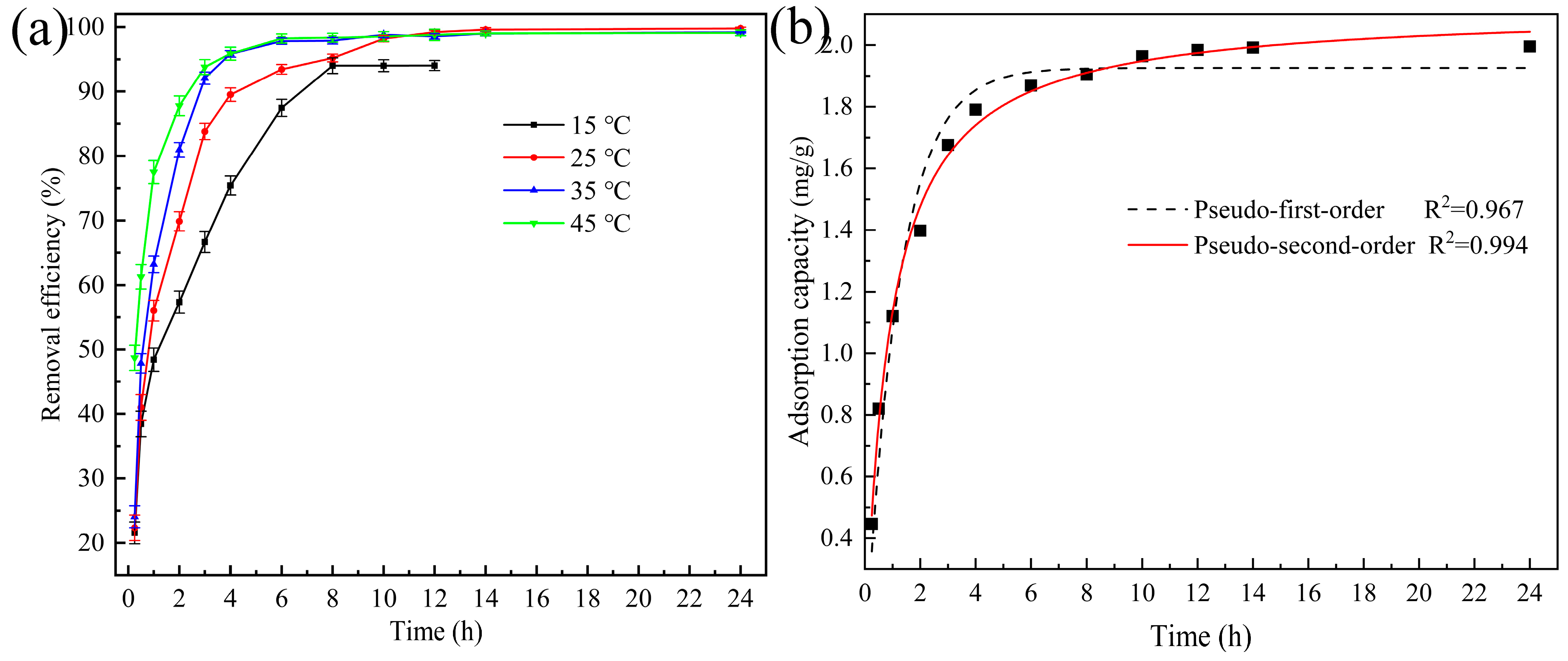
3.2.3. Effect of Contact Time and Adsorption Kinetics
3.2.4. Effect of Initial CIP Concentration and Isotherm Analysis Kinetics
3.2.5. Effect of Temperature
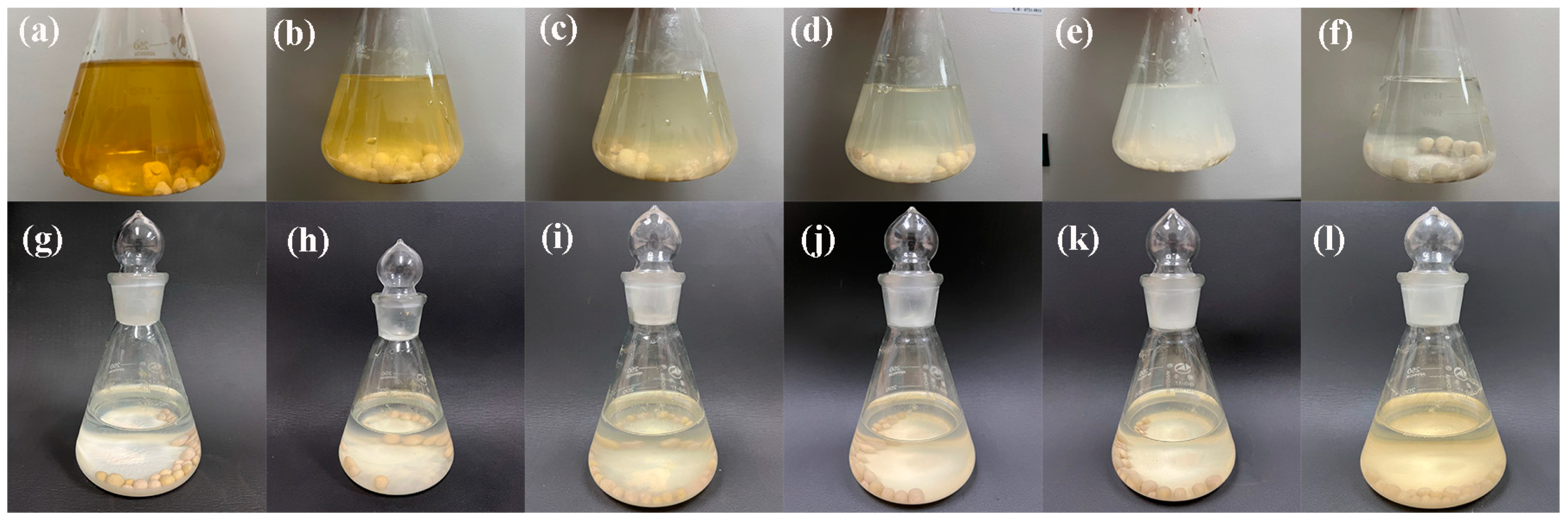
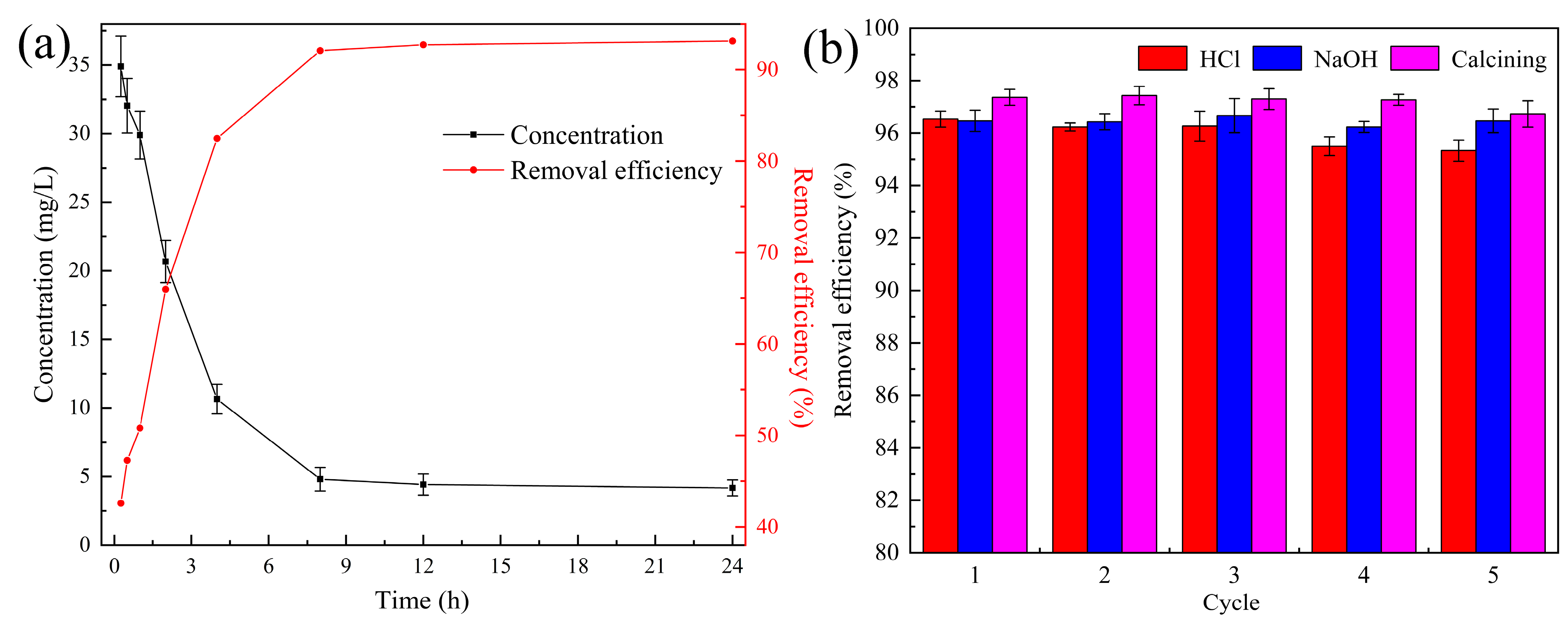
3.2.6. Treatment of Actual Wastewater
3.2.7. Regeneration and Reusability
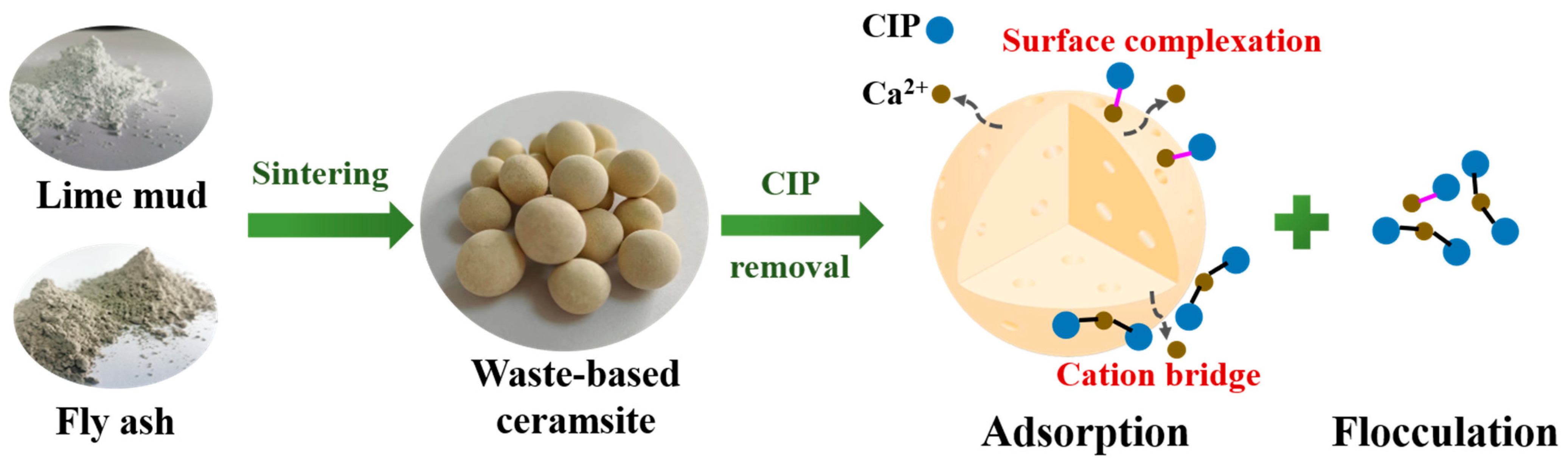
3.3. Mechanisms of CIP Removal by the Waste-Based Ceramsite
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, P.C.; Jain, A.; Jain, S.; Pahwa, R.; Yar, M.S. Ciprofloxacin: Review on developments in synthetic, analytical, and medicinal aspects. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2010, 25, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, H.T.; Oberoi, A.S.; He, Z.Q.; Khanal, S.K.; Lu, H. Ciprofloxacin-degrading Paraclostridium sp. isolated from sulfate-reducing bacteria-enriched sludge: Optimization and mechanism. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falyouna, O.; Maamoun, I.; Bensaida, K.; Tahara, A.; Sugihara, Y.; Eljamal, O. Encapsulation of iron nanoparticles with magnesium hydroxide shell for remarkable removal of ciprofloxacin from contaminated water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 605, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Gupta, A.K. Photocatalytic performance of 3D engineered chitosan hydrogels embedded with sulfur-doped C3N4/ZnO nanoparticles for Ciprofloxacin removal: Degradation and mechanistic pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 198, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.P.; Wang, S.; Tai, Y.P.; Tam, N.F.; Su, L.H.; Shi, Y.M.; Luo, B.K.; Tao, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.M. Evaluation of factors influencing annual occurrence, bioaccumulation, and biomagnification of antibiotics in planktonic food webs of a large subtropical river in South China. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, R.; Bashir, S.; Nabi, D.; Arshad, M. Occurrence and quantification of prevalent antibiotics in wastewater samples from Rawalpindi and Islamabad, Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; de Pedro, C.; Paxeus, N. Effluent from drug manufactures contains extremely high levels of pharmaceuticals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Najam, T.; Shah, S.S.A.; Hussain, E.; Ali, H.; Hussain, S.; Shaheen, A.; Ahmad, K.; Ashfaq, M. Development of Mn-PBA on GO sheets for adsorptive removal of ciprofloxacin from water: Kinetics, isothermal, thermodynamic and mechanistic studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 245, 122737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, E.; Sheikhmohammadi, A.; Nourmoradi, H.; Nazari, S.; Aghanaghad, M. Degradation of ciprofloxacin by ozonation process under irradiation with UVA: Comparative study, performance and mechanism. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2021, 147, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Dai, Z.; Xie, X.D.; Wen, Z.P.; Chen, R. Promotion of peroxydisulfate activation over Cu0.84Bi2.08O4 for visible light induced photodegradation of ciprofloxacin in water matrix. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobial resistance: Tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. In The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; Wellcome Trust: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kummerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, A.; Trivedi, J.S.; Kumar, S.B.; Chandel, A.K.S.; Haldar, S.; Jewrajka, S.K. Anti-organic fouling and anti-biofouling poly(piperazineamide) thin film nanocomposite membranes for low pressure removal of heavy metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalani, D.V.; Chandel, A.K.S.; Trivedi, J.S.; Roy, S.; Jewrajka, S.K. High molecular weight poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) induces hierarchical surface morphology in poly (vinylidene fluoride) membrane and facilitates separation of oil-water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 566, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidulu, D.; Majumder, A.; Gupta, A.K. A systematic review of moving bed biofilm reactor, membrane bioreactor, and moving bed membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment: Comparison of research trends, removal mechanisms, and performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.T.; Li, W.Q.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.S.; Gao, Y.Z. Removal of ciprofloxacin by persulfate activation with CuO: A pH-dependent mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Osagie, C.; Rahdar, S.; Khan, N.A.; Ahmed, S.; Hajini, H. Efficacy of persulfate-based advanced oxidation process (US/PS/Fe3O4) for ciprofloxacin removal from aqueous solutions. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.X.; An, Y.Y.; Yang, L.W.; Sun, Q.; Ma, J.Y.; Zheng, H.L. Chitin-biocalcium as a novel superior composite for ciprofloxacin removal: Synergism of adsorption and flocculation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de llurdoz, M.S.; Sadhwani, J.J.; Reboso, J.V. Antibiotic removal processes from water & wastewater for the protection of the aquatic environment-a review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosefian, M.; Ahmadzadeh, S.; Aghasi, M.; Dolatabadi, M. Optimization of electrocoagulation process for efficient removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotic using iron electrode; kinetic and isotherm studies of adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 225, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.J.; Dai, S.W.; Li, S.X.; Xu, J.; Qin, J. Adsorption performance and mechanism investigation of Mn2+ by facile synthesized ceramsites from lime mud and coal fly ash. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 38, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.A.; Bafico, J.G.; Villanueva, M.E.; Giorgieri, S.A.; Copello, G.J. Continuous flow adsorption of ciprofloxacin by using a nanostructured chitin/graphene oxide hybrid material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 188, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nazraz, M.; Yamini, Y.; Asiabi, H. Chitosan-based sorbent for efficient removal and extraction of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin from aqueous solutions. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Privar, Y.; Shashura, D.; Pestov, A.; Modin, E.; Baklykov, A.; Marinin, D.; Bratskaya, S. Metal-chelate sorbents based on carboxyalkylchitosans: Ciprofloxacin uptake by Cu(II) and Al(III)-chelated cryogels of N-(2-carboxyethyl)chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarmand, M.; Naeimi, A.; Rezakhani, M.S.; Chaji, M.A. Ni/NiO doped chitosan-cellulose based on the wastes of barley and shrimp for degradation of ciprofloxacin antibiotic. J. Mater. Res. Technol.-JMRT 2022, 18, 4060–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hou, T.Y.; Ma, J.Y.; Yuan, B.; Tian, Z.Q.; Yang, W.B.; Graham, N.J.D. Role of moderately hydrophobic chitosan flocculants in the removal of trace antibiotics from water and membrane fouling control. Water Res. 2020, 177, 115775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falyouna, O.; Bensaida, K.; Maamoun, I.; Ashik, U.P.M.; Tahara, A.; Tanaka, K.; Aoyagi, N.; Sugihara, Y.; Eljamal, O. Synthesis of hybrid magnesium hydroxide/magnesium oxide nanorods [Mg(OH)2/MgO] for prompt and efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 342, 130949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Gubitosa, J.; Signorile, R.; Fini, P.; Cecone, C.; Matencio, A.; Trotta, F.; Cosma, P. Cyclodextrin nanosponges as adsorbent material to remove hazardous pollutants from water: The case of ciprofloxacin. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YilimulGati, M.; Wang, L.F.; Ma, X.L.; Yang, C.W.; Habibul, N. Adsorption of ciprofloxacin to functionalized nano-sized polystyrene plastic: Kinetics, thermochemistry and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 142370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ma, L.Q.; Gao, B.; Gu, C. Influence of Cu and Ca cations on ciprofloxacin transport in saturated porous media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Cui, C.; Cui, X.Y.; Hussain, A.; Yang, C.M. Preparation and characterization of ceramsites from lime mud and coal fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 95, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.W.; Wen, Q.; Huang, F.; Bao, Y.Q.; Xi, X.D.; Liao, Z.P.; Shi, J.; Ou, C.J.; Qin, J. Preparation and application of MgO-loaded tobermorite to simultaneously remove nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Yang, C.M.; Cui, C.; Huang, J.T.; Hussain, A.; Ma, H.L. Ca2+ and OH− release of the ceramsites containing anorthite and gehlenite prepared from waste lime mud. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 47, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Karthikeyan, K.G. Sorption of the antimicrobial ciprofloxacin to aluminum and iron hydrous oxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9166–9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Che, R.B.; Zhou, Q.F. Analysis of the factors affecting the color of ciprofloxacin lactate injection. Chin. J. Vet. Drug 2004, 38, 14 + 41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, M.M.; Dai, L.C. Interaction between chlortetracycline and calcium-rich biochar: Enhanced removal by adsorption coupled with flocculation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.L.; Zhang, H.; Shahab, A.; Zeng, H.H.; Zeng, H.T.; Bacha, A.U.R.; Nabi, I.; Siddique, J.; Ullah, H. Efficient performance of magnesium oxide loaded biochar for the significant removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2021, 221, 112426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worch, E. Adsorption Technology in Water Treatment: Fundamentals, Processes, and Modeling; De Gruyter: Boston, MA, USA; Berlin, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wei, Y.F.; Yang, W.J.; Liu, C.B. Highly efficient As(III) removal in water using millimeter-sized porous granular MgO-biochar with high adsorption capacity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Khanal, S.K.; Jia, Y.Y.; Song, S.L.; Lu, H. Fundamental insights into ciprofloxacin adsorption by sulfate-reducing bacteria sludge: Mechanisms and thermodynamics. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, J.; Fang, Y.; Shi, J.; Tokoro, C.; Córdova-Udaeta, M.; Oyama, K.; Zhang, J. Waste-Based Ceramsite for the Efficient Removal of Ciprofloxacin in Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20065042
Qin J, Fang Y, Shi J, Tokoro C, Córdova-Udaeta M, Oyama K, Zhang J. Waste-Based Ceramsite for the Efficient Removal of Ciprofloxacin in Aqueous Solutions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(6):5042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20065042
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Juan, Yeting Fang, Jian Shi, Chiharu Tokoro, Mauricio Córdova-Udaeta, Keishi Oyama, and Juncheng Zhang. 2023. "Waste-Based Ceramsite for the Efficient Removal of Ciprofloxacin in Aqueous Solutions" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 6: 5042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20065042
APA StyleQin, J., Fang, Y., Shi, J., Tokoro, C., Córdova-Udaeta, M., Oyama, K., & Zhang, J. (2023). Waste-Based Ceramsite for the Efficient Removal of Ciprofloxacin in Aqueous Solutions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(6), 5042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20065042






