Environmental Monitoring of Legionella in Hospitals in the Campania Region: A 5-Year Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Hospital Characteristics
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Microbiological Analysis and Identification
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Positivity of Analyzed Samples
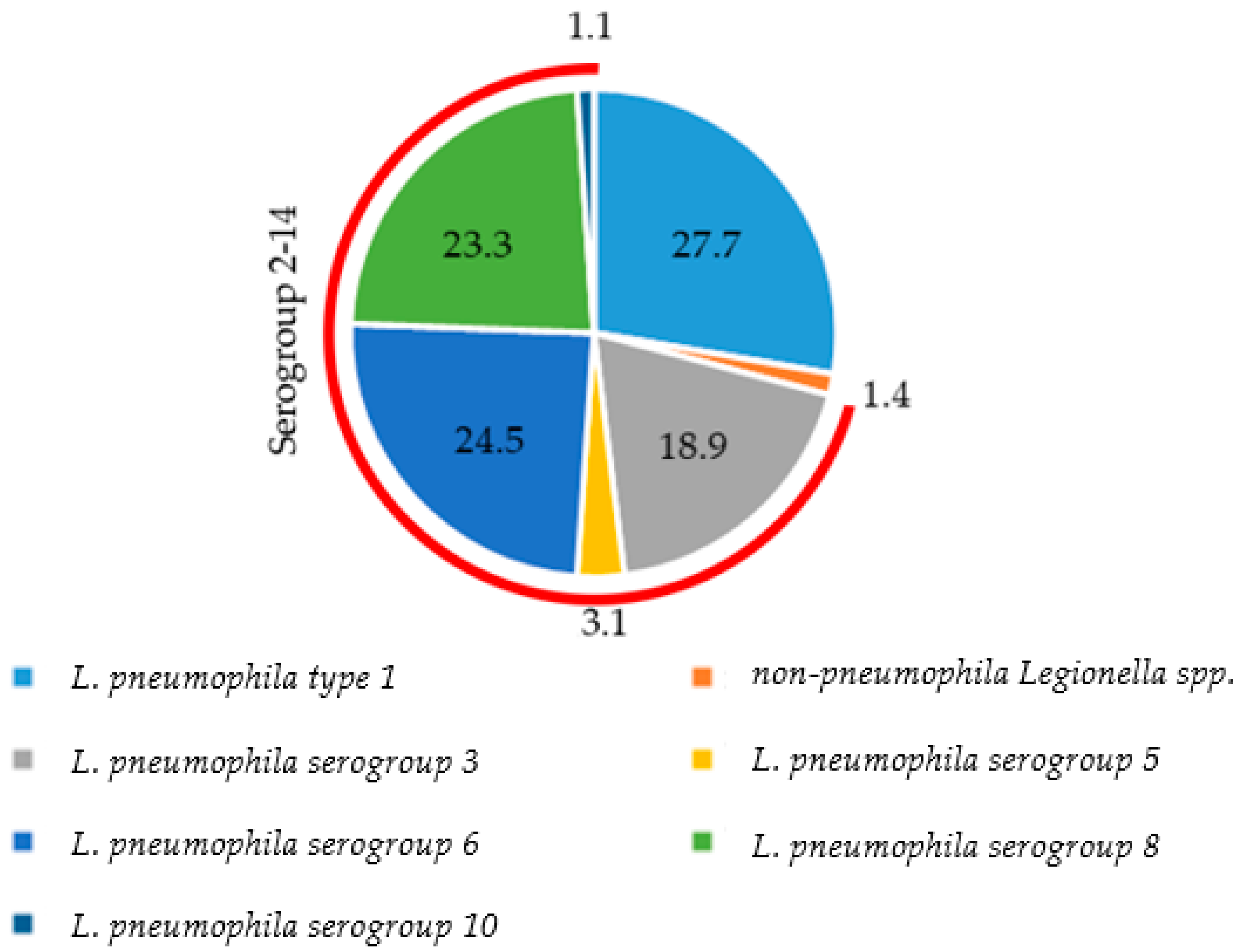
3.2. Distribution of Species and Serogroups among Positive Samples
3.3. Water Temperature and Residual Chlorine
3.4. Statistical Analysis
| Year | Pos./Tot. (%) | Mean (±SD 1) | Min | 25th Percentile | Median | 75th Percentile | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 164/479 (34.2) | 3.02 ± 0.72 | 1.70 | 2.54 | 3.12 | 3.63 | 4.28 |
| 2019 | 147/625 (23.5) | 2.71 ± 0.80 | 1.70 | 2.00 | 2.60 | 3.35 | 4.36 |
| 2020 | 142/840 (16.9) | 2.82 ± 0.74 | 1.70 | 2.18 | 2.81 | 3.38 | 4.30 |
| 2021 | 144/667 (21.6) | 2.96 ± 0.73 | 1.70 | 2.40 | 3.02 | 3.62 | 4.23 |
| 2022 | 111/754 (14.7) | 3.14 ± 0.58 | 1.70 | 2.78 | 3.20 | 3.62 | 4.04 |
4. Discussions
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younas, F.; Soltanmohammadi, N.; Knapp, O.; Benz, R. The major outer membrane protein of Legionella pneumophila Lpg1974 shows pore-forming characteristics similar to the human mitochondrial outer membrane pore, hVDAC1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, I.G.; Fernandes, H.S.; Melo, A.; Sousa, S.F.; Simões, L.C.; Simões, M. LegionellaDB—A database on Legionella outbreaks. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondino, S.; Schmidt, S.; Rolando, M.; Escoll, P.; Gomez-Valero, L.; Buchrieser, C. Legionnaires’ disease: State of the art knowledge of pathogenesis mechanisms of Legionella. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 439–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caicedo, C.; Rosenwinkel, K.H.; Exner, M.; Verstraete, W.; Suchenwirth, R.; Hartemann, P.; Nogueira, R. Legionella occurrence in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants and risks of reclaimed wastewater reuse. Water Res. 2019, 149, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herpers, B.L.; Bossink, A.W.; Cohen Stuart, J.W.; Hustinx, W.N.; Thijsen, S.F. A patient with Legionella pneumophila serogroup-3 pneumonia, detected by PCR. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 2005, 149, 2009–2012. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16171114 (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Khanna, N.; Meikle, A.; Gillespie, L.; Edwards, G.; Lindsay, D. Legionella pneumophila serogroup 3 infection: Importance of serology. Scott. Med. J. 2012, 57, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Ishida, T.; Washio, Y.; Yamazaki, A.; Tachibana, H. Legionella pneumonia due to non-Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1: Usefulness of the six-point scoring system. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Ishida, T.; Tachibana, H.; Ito, Y.; Takaiwa, T.; Fujii, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Nakajima, H.; Amemura-Maekawa, J. A case of community-acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila serogroup 9 wherein initial treatment with single-dose oral azithromycin appeared useful. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 70, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Hsueh, P.R.; Yang, P.C. Severe community-acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila serogroup 6. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2006, 105, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giglio, O.; Fasano, F.; Diella, G.; Lopuzzo, M.; Napoli, C.; Apollonio, F.; Brigida, S.; Calia, C.; Campanale, C.; Marzella, A.; et al. Legionella and legionellosis in touristic-recreational facilities: Influence of climate factors and geostatistical analysis in Southern Italy (2001–2017). Environ. Res. 2019, 178, 108721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, J.A.; Cohn, P.D. A review of legionnaires’ disease and public water systems–Scientific considerations, uncertainties and recommendations. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 240, 113906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, B.A.; Burillo, A.; Bouza, E. Legionnaires’ disease. Lancet 2016, 387, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciuto, E.L.; Laganà, P.; Filice, S.; Scalese, S.; Libertino, S.; Corso, D.; Faro, G.; Coniglio, M.A. Environmental Management of Legionella in Domestic Water Systems: Consolidated and Innovative Approaches for Disinfection Methods and Risk Assessment. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laganà, P.; Facciolà, A.; Palermo, R.; Delia, S. Environmental surveillance of legionellosis within an italian university hospital—Results of 15 years of analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzolo, C.; Maffongelli, G.; D’Abramo, A.; Lepore, L.; Mariano, A.; Vulcano, A.; Ascoli Bartoli, T.; Bevilacqua, N.; Giancola, M.L.; Di Rosa, E.; et al. Legionella pneumonia: Increased risk after COVID-19 lockdown? Italy, May to June 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paranjape, K.; Bédard, É.; Whyte, L.G.; Ronholm, J.; Prévost, M.; Faucher, S.P. Presence of Legionella spp. in cooling towers: The role of microbial diversity, Pseudomonas, and continuous chlorine application. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, M.; Rončević, D.; Vukić Lušić, D.; Mihelčić, M.; Kogoj, R.; Keše, D.; Glad, M.; Cenov, A.; Ožanič, M.; Glažar Ivče, D.; et al. Decreasing Pasteurization Treatment Efficiency against Amoeba-Grown Legionella pneumophila—Recognized Public Health Risk Factor. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh Azhar, A.; Bhangale, P.P. Disaster Management for Cooling Tower-Case Study. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2016, 6, 09–14. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, J.T. The influence of climate change on waterborne disease and Legionella: A review. Perspect. Public Health 2018, 138, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, M.M.; Gordon, J.L.; McCoy, W.F.; Cain, M.F. Water management for construction: Evidence for risk characterization in community and healthcare settings: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, M.M.; Gordon, J.L.; Tonozzi, A.A.; Griffin, S.C. Reducing the Risk of Healthcare Associated Infections from Legionella and Other Waterborne Pathogens Using a Water Management for Construction (WMC) Infection Control Risk Assessment (ICRA) Tool. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartram, J.; Corrales, L.; Davison, A.; Deere, D.; Drury, D.; Gordon, B.; Howard, G.; Rinehold, A.; Stevens, M. Water Safety Plan Manual: Step-by-Step Risk Management for Drinking-Water Suppliers; World Heart Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241562638 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Coniglio, M.A.; Ferrante, M.; Yassin, M.H. Preventing healthcare-associated legionellosis: Results after 3 years of continuous disinfection of hot water with monochloramine and an effective water safety plan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, B.S. Minimizing the Risk of Legionellosis Associated with Building Water Systems. Ashrae Guidline. 2000. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1570291225346474368 (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Muzzi, A.; Cutti, S.; Bonadeo, E.; Lodola, L.; Monzillo, V.; Corbella, M.; Scudeller, L.; Novelli, V.; Marena, C. Prevention of nosocomial legionellosis by best water management: Comparison of three decontamination methods. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 105, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Management of Legionella in Water Systems; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32200596/ (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Van Heijnsbergen, E.; Schalk, J.A.; Euser, S.M.; Brandsema, P.S.; den Boer, J.W.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Confirmed and potential sources of Legionella reviewed. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4797–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Suárez, A.; Dellundé, J.; Salvadó, H.; Cervero-Aragó, S.; Méndez, J.; Canals, O.; Blanco, S.; Arcas, A.; Araujo, R. Microbial and physicochemical parameters associated with Legionella contamination in hot water recirculation systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5534–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Liu, Y.C.; Lee, S.S.J.; Tsai, H.C.; Wann, S.R.; Kao, C.H.; Chang, C.L.; Huang, W.K.; Huang, T.S.; Chao, H.I.; et al. Abbreviated duration of superheat-and-flush and disinfection of taps for Legionella disinfection: Lessons learned from failure. Am. J. Infect. Control 2005, 33, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditommaso, S.; Giacomuzzi, M.; Memoli, G.; Garlasco, J.; Zotti, C.M. Persistence of Legionella in routinely disinfected heater-cooler units and heater units assessed by propidium monoazide qPCR. Pathogens 2020, 9, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus, W.L.; Plouffe, J.F.; File, T.M.; Lipman, H.B.; Hackman, B.H.; Salstrom, S.J.; Benson, R.F.; Breiman, R.F. Risk factors for domestic acquisition of Legionnaires disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1996, 156, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viasus, D.; Di Yacovo, S.; Garcia-Vidal, C.; Verdaguer, R.; Manresa, F.; Dorca, J.; Gudiol, F.; Carratala, J. Community-acquired Legionella pneumophila pneumonia: A single-center experience with 214 hospitalized sporadic cases over 15 years. Medicine 2013, 92, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campese, C.; Bitar, D.; Jarraud, S.; Maine, C.; Forey, F.; Etienne, J.; Desenclos, J.C.; Saura, C.; Che, D. Progress in the surveillance and control of Legionella infection in France, 1998–2008. Int. J. Infect. Dis 2011, 15, e30–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, B.J.; Lipman, H.B.; Breiman, R.F. Surveillance for Legionnaires’ disease: Risk factors for morbidity and mortality. Arch. Intern. Med. 1994, 154, 2417–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Boer, J.W.; Nijhof, J.; Friesema, I. Risk factors for sporadic community-acquired Legionnaires’ disease. A 3-year national case–control study. Public Health 2006, 120, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borella, P.; Bargellini, A.; Marchegiano, P.; Vecchi, E.; Marchesi, I. Hospital-acquired Legionella infections: An update on the procedures for controlling environmental contamination. Ann. Ig. 2016, 28, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, I.; Amemura-Maekawa, J.; Kura, F.; Kobayashi, T.; Sato, A.; Watanabe, H.; Matsumoto, T. Persistent Legionella contamination of water faucets in a tertiary hospital in Japan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili, M.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Zandi, H.; Ebrahimi, A.A.; Mokhtari, M.; Samaei, M.R.; Abbasi, F. Risk assessment and disease burden of Legionella presence in cooling towers of Iran’s central hospitals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 65945–65951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, I.; Diana, M.V.; Iervolino, C.; Borriello, T.; Imperato, O.C.; Maccarino, S.; Pennino, F. Legionella contamination in hospitals of the Campania region: Five years of environmental surveillance results. Ann. Ig. 2014, 26, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiana, G.; Arghittu, A.; Dettori, M.; Masia, M.D.; Deriu, M.G.; Piana, A.; Muroni, M.R.; Castiglia, P.; Azara, A. Environmental Surveillance of Legionella spp. In an Italian University Hospital Results of 10 Years of Analysis. Water 2021, 13, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italian Health Ministry Guidelines for Prevention and Control of Legionellosis. 2015. Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_2362_allegato.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Diederen, B.M.W. Legionella spp. And Legionnaires’ disease. J. Infect. 2008, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartram, J.; Chartier, Y.; Lee, J.V.; Pond, K.; Surman-Lee, S. Legionella and the Prevention of Legionellosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43233 (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Decker, B.K.; Palmore, T.N. The role of water in healthcare-associated infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 26, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viasus, D.; Gaia, V.; Manzur-Barbur, C.; Carratalà, J. Legionnaires’ disease: Update on diagnosis and treatment. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, D.; Baron, J.L.; Ma, X.; Sidari, F.P.; Wagener, M.M.; Stout, J.E. Water quality as a predictor of Legionella positivity of building water systems. Pathogens 2019, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.S.; Li, G.J.; Xing, Y.H.; Chen, T.; Li, W.J.; Ni, W.; Deng, K.; Gao, R.Q.; Chen, C.Z.; Gao, Y.; et al. Precautions are needed for COVID-19 patients with coinfection of common respiratory pathogens. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunello, A.; Civilini, M.; De Martin, S.; Felice, A.; Franchi, M.; Iacumin, L.; Saccomanno, N.; Vitacolonna, N. Machine learning-assisted environmental surveillance of Legionella: A retrospective observational study in Friuli-Venezia Giulia region of Italy in the period 2002–2019. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2022, 28, 100803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, M.C.; Caporali, M.G.; Bella, A.; Scaturro, M.; Giannitelli, S.; Ricci, M.L. I risultati del sistema di sorveglianza della legionellosi nel 2021. Boll. Epidemiol. Naz. 2022, 3, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.; Shames, S.R. Pathogenicity and Virulence of Legionella: Intracellular replication and host response. Virulence 2021, 12, 1122–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, B.S.; Benson, R.F.; Besser, R.E. Legionella and Legionnaires’ disease: 25 years of investigation. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 506–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditommaso, S.; Giacomuzzi, M.; Rivera, S.R.A.; Raso, R.; Ferrero, P.; Zotti, C.M. Virulence of Legionella pneumophila strains isolated from hospital water system and healthcare-associated Legionnaires’ disease in Northern Italy between 2004 and 2009. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenti, S.; de Waure, C.; Raponi, M.; Teleman, A.A.; Boninti, F.; Bruno, S.; Boccia, S.; Damiani, G.; Laurenti, P. Environmental surveillance of Legionella spp. colonization in the water system of a large academic hospital: Analysis of the four–year results on the effectiveness of the chlorine dioxide disinfection method. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giglio, O.; Napoli, C.; Lovero, G.; Diella, G.; Rutigliano, S.; Caggiano, G.; Montagna, M.T. Antibiotic susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila strains isolated from hospital water systems in Southern Italy. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, I.; Galia, E.; Fasciana, T.; Diquattro, O.; Tricoli, M.R.; Serra, N.; Palermo, M.; Giammanco, A. Four-Year Environmental Surveillance Program of Legionella spp. in One of Palermo’s Largest Hospitals. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquarella, C.; Veronesi, L.; Napoli, C.; Castiglia, P.; Liguori, G.; Rizzetto, R.; Torre, I.; Righi, E.; Farruggia, P.; Tesauro, M.; et al. Microbial environmental contamination in Italian dental clinics: A multicenter study yielding recommendations for standardized sampling methods and threshold values. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 420, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, I.; Alfano, R.; Borriello, T.; De Giglio, O.; Iervolino, C.; Montagna, M.T.; Scamardo, M.S.; Pennino, F. Environmental surveillance and in vitro activity of antimicrobial agents against Legionella pneumophila isolated from hospital water systems in Campania, South Italy: A 5-year study. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totaro, M.; Valentini, P.; Costa, A.L.; Frendo, L.; Cappello, A.; Casini, B.; Miccoli, M.; Privitera, G.; Baggiani, A. Presence of Legionella spp. in hot water networks of different Italian residential buildings: A three-year survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totaro, M.; Costa, A.L.; Frendo, L.; Profeti, S.; Casini, B.; Gallo, A.; Privitera, G.; Baggiani, A. Evaluation of Legionella spp. colonization in residential buildings having solar thermal system for hot water production. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatini, L.; Sisti, M.; Campana, R. Isolation and identification of Legionella spp. from non-hospital facilities: A preliminary one-year surveillance study in the urban area of Pesaro-Urbino (Central Italy). Ann. Ig. 2022, 34, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, P.; Mozzetti, C.; Messina, A.; D’Alò, G.L. Prevalence of Legionella in retirement homes and group homes water distribution systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, A.; Franchi, M.; De Martin, S.; Vitacolonna, N.; Iacumin, L.; Civilini, M. Environmental surveillance and spatio-temporal analysis of Legionella spp. in a region of northeastern Italy (2002–2017). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, E.; De Luca, G.; Legnani, P.P.; Sacchetti, R.; Stampi, S.; Zanetti, F. Legionella waterline colonization: Detection of Legionella species in domestic, hotel and hospital hot water systems. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, M.; Salaris, S.; Pascale, M.R.; Girolamini, L.; Cristino, S. Occurrence of Legionella spp. in man-made water sources: Isolates distribution and phylogenetic characterization in the Emilia-Romagna region. Pathogens 2021, 10, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, M.T.; De Giglio, O.; Napoli, C.; Cannova, L.; Cristina, M.L.; Deriu, M.G.; Delia, S.A.; Giuliano, A.; Guida, M.; Laganà, P.; et al. Legionella spp. contamination in indoor air: Preliminary results of an Italian multicenter study. Epidemiol. Prev. 2014, 38 (Suppl. 2), 62–65. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25759346/ (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Montagna, M.T.; Cristina, M.L.; De Giglio, O.; Spagnolo, A.M.; Napoli, C.; Cannova, L.; Deriu, M.G.; Delia, S.A.; Giuliano, A.; Guida, M.; et al. Serological and molecular identification of Legionella spp. isolated from water and surrounding air samples in Italian healthcare facilities. Environ. Res. 2016, 146, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, M.T.; De Giglio, O.; Cristina, M.L.; Napoli, C.; Pacifico, C.; Agodi, A.; Baldovin, T.; Casini, B.; Coniglio, M.A.; D’Errico, M.M.; et al. Evaluation of Legionella air contamination in healthcare facilities by different sampling methods: An Italian multicenter study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakić, A.; Perić, J.; Foglar, L. Influence of temperature, chlorine residual and heavy metals on the presence of Legionella pneumophila in hot water distribution systems. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 431–436. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23020035/ (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Weekly Epidemiological Updates and Monthly Operational Updates. Situation Report-25. 14 February 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports# (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Proctor, C.R.; Rhoads, W.J.; Keane, T.; Salehi, M.; Hamilton, K.; Pieper, K.J.; Cwiertny, D.M.; Prévost, M.; Whelton, A.J. Considerations for large building water quality after extended stagnation. AWWA Water Sci. 2020, 2, e1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federigi, I.; De Giglio, O.; Diella, G.; Triggiano, F.; Apollonio, F.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Cioni, L.; Verani, M.; Montagna, M.T.; Carducci, A. Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment Applied to Legionella Contamination on Long-Distance Public Transport. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvand, M.; Jungkind, K.; Hack, A. Contamination of the cold water distribution system of health care facilities by Legionella pneumophila: Do we know the true dimension? Eurosurveillance 2011, 16, 19844. Available online: http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=19844 (accessed on 24 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Orhan, F. Investigation of the presence of Legionella pneumophila in water samples from Erzurum and surrounding provinces in Turkey. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2021, 28, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojek, N.M.; Dutkiewicz, J. Co-existence of Legionella and other Gram-negative bacteria in potable water from various 676 rural and urban sources. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2011, 18, 330–334. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22216808/ (accessed on 24 November 2022).
- Fontana, S.; Scaturro, M.; Rota, M.C.; Caporali, M.G.; Ricci, M.L. Molecular typing of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 clinical strains isolated in Italy. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaturro, M.; Rota, M.C.; Caporali, M.G.; Girolamo, A.; Magoni, M.; Barberis, D.; Romano, C.; Cereda, D.; Gramegna, M.; Piro, A.; et al. A community-acquired Legionnaires’ disease outbreak caused by Legionella pneumophila serogroup 2: An uncommon event, Italy, August to October 2018. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2001961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amemura-Maekawa, J.; Kura, F.; Helbig, J.H.; Chang, B.; Kaneko, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Isobe, J.; Nukina, M.; Nakajima, H.; Kawano, K.; et al. Characterization of Legionella pneumophila isolates from patients in Japan according to serogroups, monoclonal antibody subgroups and sequence types. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Legionellosi. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/legionellosi/documentazione-italia (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Perola, O.; Kauppinen, J.; Kusnetsov, J.; Heikkinen, J.; Jokinen, C.; Katila, M.L. Nosocomial Legionella pneumophila serogroup 5 outbreak associated with persistent colonization of a hospital water system. APMIS 2002, 110, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borella, P.; Montagna, M.T.; Stampi, S.; Stancanelli, G.; Romano-Spica, V.; Triassi, M.; Marchesi, I.; Bargellini, A.; Tatò, D.; Napoli, C.; et al. Legionella contamination in hot water of Italian hotels. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5805–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girolamini, L.; Mazzotta, M.; Lizzadro, J.; Pascale, M.R.; Dormi, A.; Salaris, S.; Cristino, S. Sit bath systems: A new source of Legionella infection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiaflaka, A.; Pournaras, S.; Kristo, I.; Mouchtouri, V.A.; Kyritsi, M.; Velonakis, E.; Vatopoulos, A.C.; Hadjichristodoulou, C. Epidemiological investigation of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 2 to 14 isolates from water samples by amplified fragment length polymorphism and sequence-based typing and detection of virulence traits. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6102–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakis, A.; Chochlakis, D.; Sandalakis, V.; Keramarou, M.; Tselentis, Y.; Psaroulaki, A. Legionella spp. risk assessment in recreational and garden areas of hotels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhaee, F.; Mafi, S.; Zargar, M.; Vaziri, F.; Hajiesmaeili, M.; Siadat, S.D.; Fateh, A. Correlation between Legionella pneumophila serogroups isolated from patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia and water resources: A study of four hospitals in Tehran, Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 41368–41374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignato, S.; Coniglio, M.A.; Faro, G.; Cantaro, P.; Carini, S.A.; Mangano, G.; Cunsolo, R.; Coco, G.; Giammanco, G. Legionella contamination in the hospital environment: Monitoring of the hot water distribution systems of three hospitals in Catania (Italy). Ig. Sanita Pubbl. 2006, 62, 635–652. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17256019/ (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Ito, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Okazaki, A.; Ishiura, Y.; Kawagishi, Y.; Takiguchi, Y.; Kishi, K.; Taguchi, Y.; Shinzato, T.; et al. Evaluation of a novel urinary antigen test kit for diagnosing Legionella pneumonia. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 103, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojek, N.M.; Wójcik-Fatla, A.; Dutkiewicz, J. Efficacy of the detection of Legionella in hot and cold water samples by culture and PCR. II. Examination of native samples from various sources. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 295–298. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22742805/ (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Boppe, I.; Bedard, E.; Taillandier, C.; Lecellier, D.; Nantel-Gauvin, M.A.; Villion, M.; Laferrière, C.; Prévost, M. Investigative approach to improve hot water system hydraulics through temperature monitoring to reduce building environmental quality hazard associated to Legionella. Build. Environ. 2016, 108, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolamini, L.; Dormi, A.; Pellati, T.; Somaroli, P.; Montanari, D.; Costa, A.; Savelli, F.; Martelli, A.; Grottola, A.; Fregni Serpini, G.; et al. Advances in Legionella control by a new formulation of hydrogen peroxide and silver salts in a hospital hot water network. Pathogens 2019, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, D.; Fabiani, M.; Cerquetani, F.; Orsi, G.B. Trend of Legionella colonization in hospital water supply. Ann. Ig. 2015, 27, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaka, E.; Reed, S.; Davidson, M.; Oosthuizen, J. Opportunistic premise plumbing pathogens. A potential health risk in water mist systems used as a cooling intervention. Pathogens 2021, 10, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Struewing, I.; Mistry, J.H.; Wahman, D.G.; Pressman, J.; Lu, J. Legionella and other opportunistic pathogens in full-scale chloraminated municipal drinking water distribution systems. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiee, M.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Hajjaran, H.; Hajaghazadeh, M.; Miahipour, A.; Jahangiri-Rad, M. The efficacy of residual chlorine content on the control of Legionella spp. in hospital water systems. Iran. J. Public Health 2014, 43, 637–644. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26060765 (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Carlson, K.M.; Boczek, L.A.; Chae, S.; Ryu, H. Legionellosis and recent advances in technologies for Legionella control in premise plumbing systems: A review. Water 2020, 12, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giglio, O.; Napoli, C.; Apollonio, F.; Brigida, S.; Marzella, A.; Diella, G.; Calia, C.; Scrascia, M.; Pacifico, C.; Pazzani, C.; et al. Occurrence of Legionella in groundwater used for sprinkler irrigation in Southern Italy. Environ. Res. 2019, 170, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, G.B.; Vitali, M.; Marinelli, L.; Ciorba, V.; Tufi, D.; Del Cimmuto, A.; Ursillo, P.; Fabiani, M.; De Santis, S.; Protano, C.; et al. Legionella control in the water system of antiquated hospital buildings by shock and continuous hyperchlorination: 5 years experience. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, B.; Baggiani, A.; Totaro, M.; Mansi, A.; Costa, A.L.; Aquino, F.; Miccoli, M.; Valentini, P.; Bruschi, F.; Lopalco, P.L.; et al. Detection of viable but non-culturable Legionella in hospital water network following monochloramine disinfection. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 98, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sampling Year | Total Number of Samples | Number of Positive Samples (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 479 | 164 (34.2) |
| 2019 | 625 | 147 (23.5) |
| 2020 | 840 | 142 (16.9) |
| 2021 | 667 | 144 (21.6) |
| 2022 | 754 | 111 (14.7) |
| Tank Bottoms | Taps and Showers | ATUs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold | Hot | Cold | Hot | |
| N. (%) | N. (%) | N. (%) | N. (%) | N. (%) |
| 11/260 (4.2%) | 143/520 (27.5%) | 26/580 (4.5%) | 509/1485 (34.3%) | 19/520 (3.7%) |
| Legionella Concentration (Log10 CFU/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Analyzed Samples | Positive Samples (%) | Min | Max | Geometric Mean | |
| Cold-water samples (n. 840) | ≤20.9 | 382 | 19 (5.0%) | 1.70 | 3.81 | 2.81 |
| 21.0–25.9 | 458 | 18 (3.9%) | 1.70 | 4.00 | 2.83 | |
| Hot-water samples (n. 2005) | 26.0–30.9 | 54 | 31 (57.4%) | 1.70 | 4.18 | 3.10 |
| 31.0–35.9 | 179 | 84 (46.9%) | 1.70 | 4.23 | 2.98 | |
| 36.0–40.9 | 240 | 117 (48.8%) | 1.70 | 4.30 | 3.00 | |
| 41.0–45.9 | 558 | 170 (30.5%) | 1.70 | 4.30 | 2.96 | |
| 46.0–50.9 | 549 | 153 (27.9%) | 1.70 | 4.36 | 2.87 | |
| 51.0–55.9 | 296 | 72 (24.3%) | 1.70 | 3.96 | 2.67 | |
| ≥56.0 | 129 | 25 (19.4%) | 1.70 | 3.97 | 2.73 | |
| Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | Standard Error | t | p-Value | |
| Dependent Variable: Bacterial Concentration (CFU/L) | ||||
| Water Temperature (°C) | 0.0005 | 0.0008 | 0.63 | 0.526 |
| Residual Chlorine (mg/L) | −0.4844 | 0.0782 | −6.19 | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lombardi, A.; Borriello, T.; De Rosa, E.; Di Duca, F.; Sorrentino, M.; Torre, I.; Montuori, P.; Trama, U.; Pennino, F. Environmental Monitoring of Legionella in Hospitals in the Campania Region: A 5-Year Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20085526
Lombardi A, Borriello T, De Rosa E, Di Duca F, Sorrentino M, Torre I, Montuori P, Trama U, Pennino F. Environmental Monitoring of Legionella in Hospitals in the Campania Region: A 5-Year Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(8):5526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20085526
Chicago/Turabian StyleLombardi, Annalisa, Tonia Borriello, Elvira De Rosa, Fabiana Di Duca, Michele Sorrentino, Ida Torre, Paolo Montuori, Ugo Trama, and Francesca Pennino. 2023. "Environmental Monitoring of Legionella in Hospitals in the Campania Region: A 5-Year Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 8: 5526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20085526
APA StyleLombardi, A., Borriello, T., De Rosa, E., Di Duca, F., Sorrentino, M., Torre, I., Montuori, P., Trama, U., & Pennino, F. (2023). Environmental Monitoring of Legionella in Hospitals in the Campania Region: A 5-Year Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(8), 5526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20085526








