Removal of Emerging Contaminants (Endocrine Disruptors) Using a Photocatalyst and Detection by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents, Solutions, and Equipment
2.2. Synthesis of Ag3AsO4
2.3. Characterization of Ag3AsO4
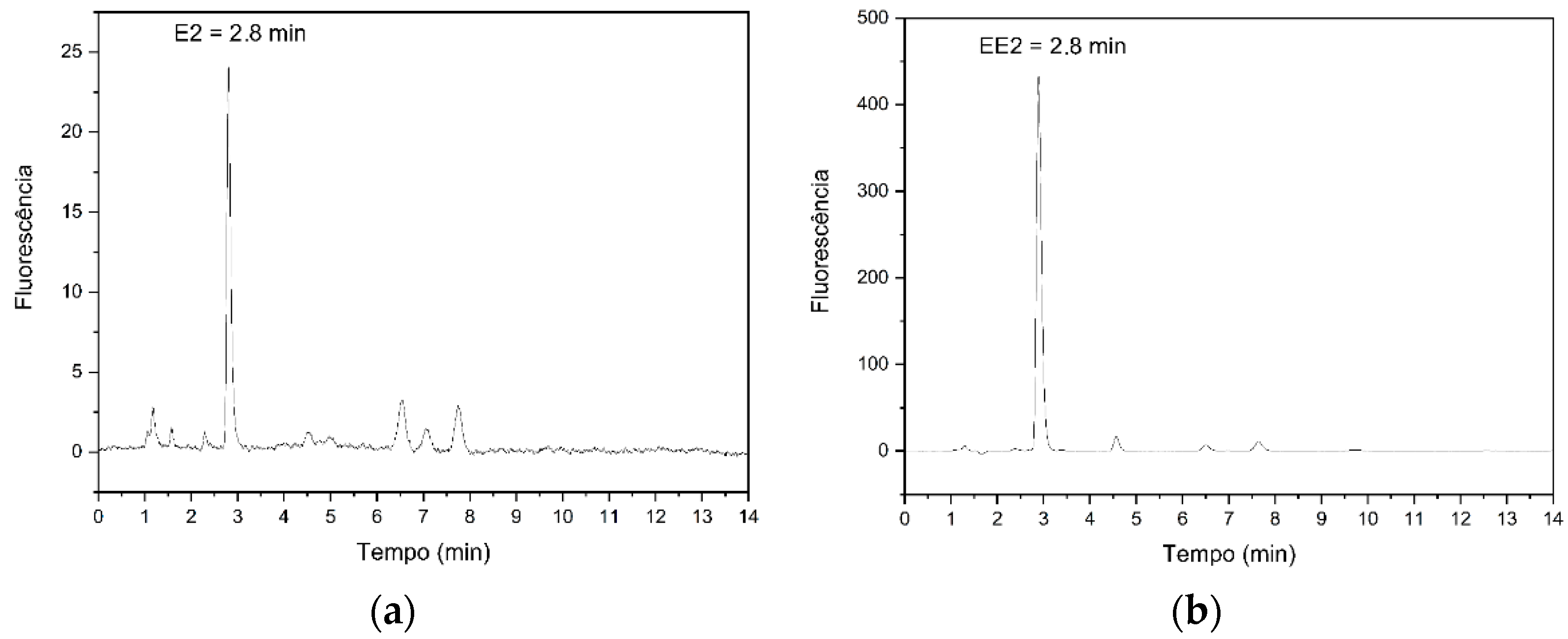
2.4. Chromatographic Conditions
2.5. Analytical Validation
2.6. Photocatalyst Study
3. Results and Discussion
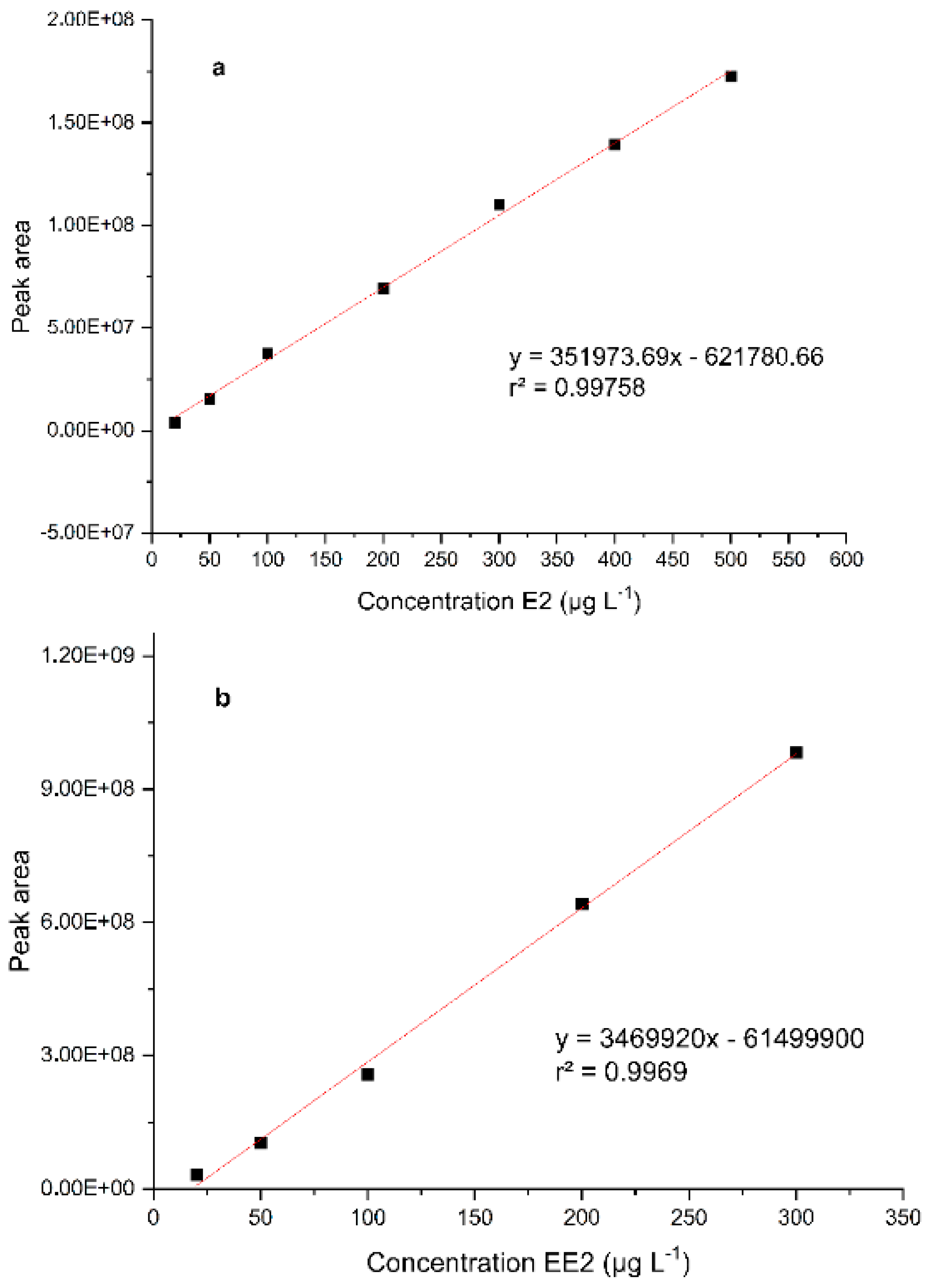
3.1. Analytical Validation
3.1.1. Linearity
3.1.2. Precision
3.1.3. Accuracy
3.1.4. Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantification
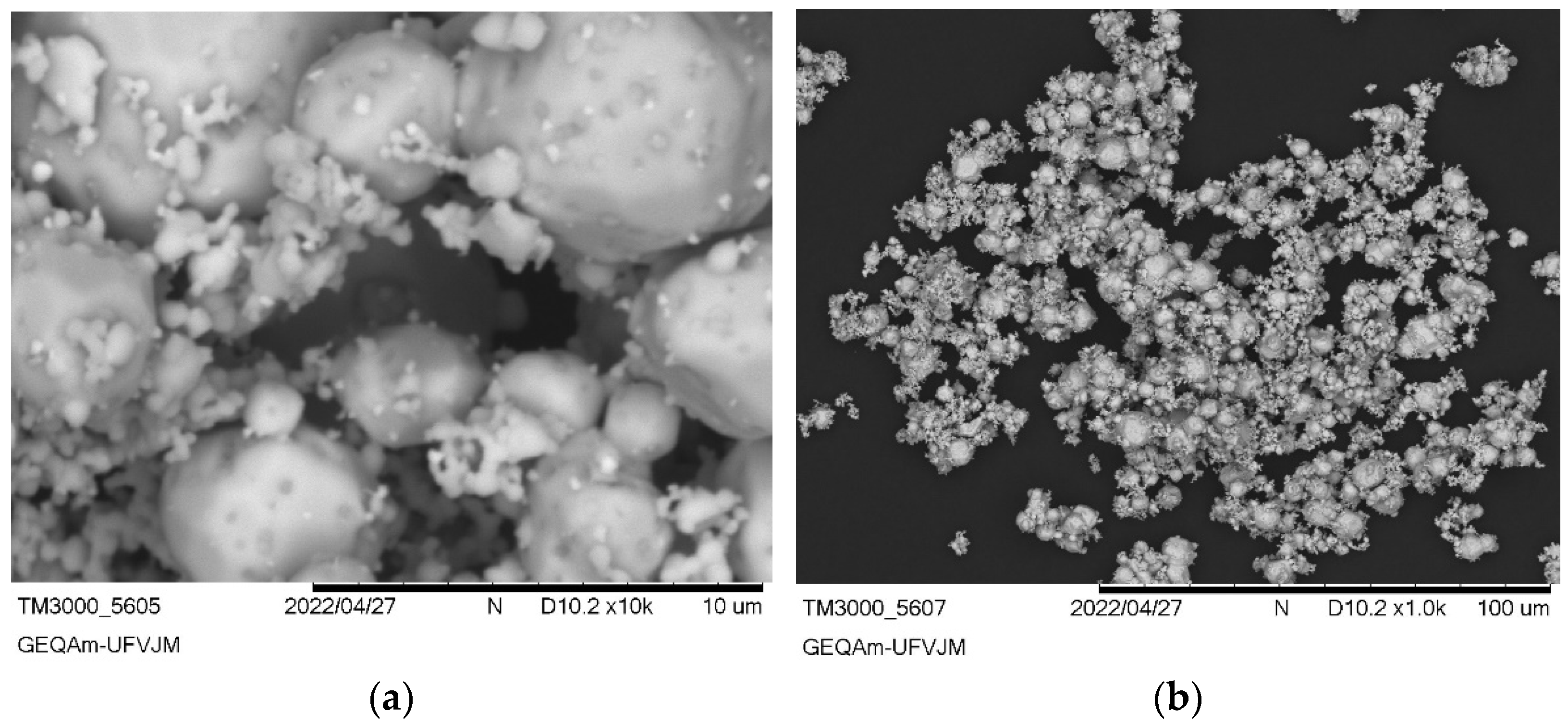
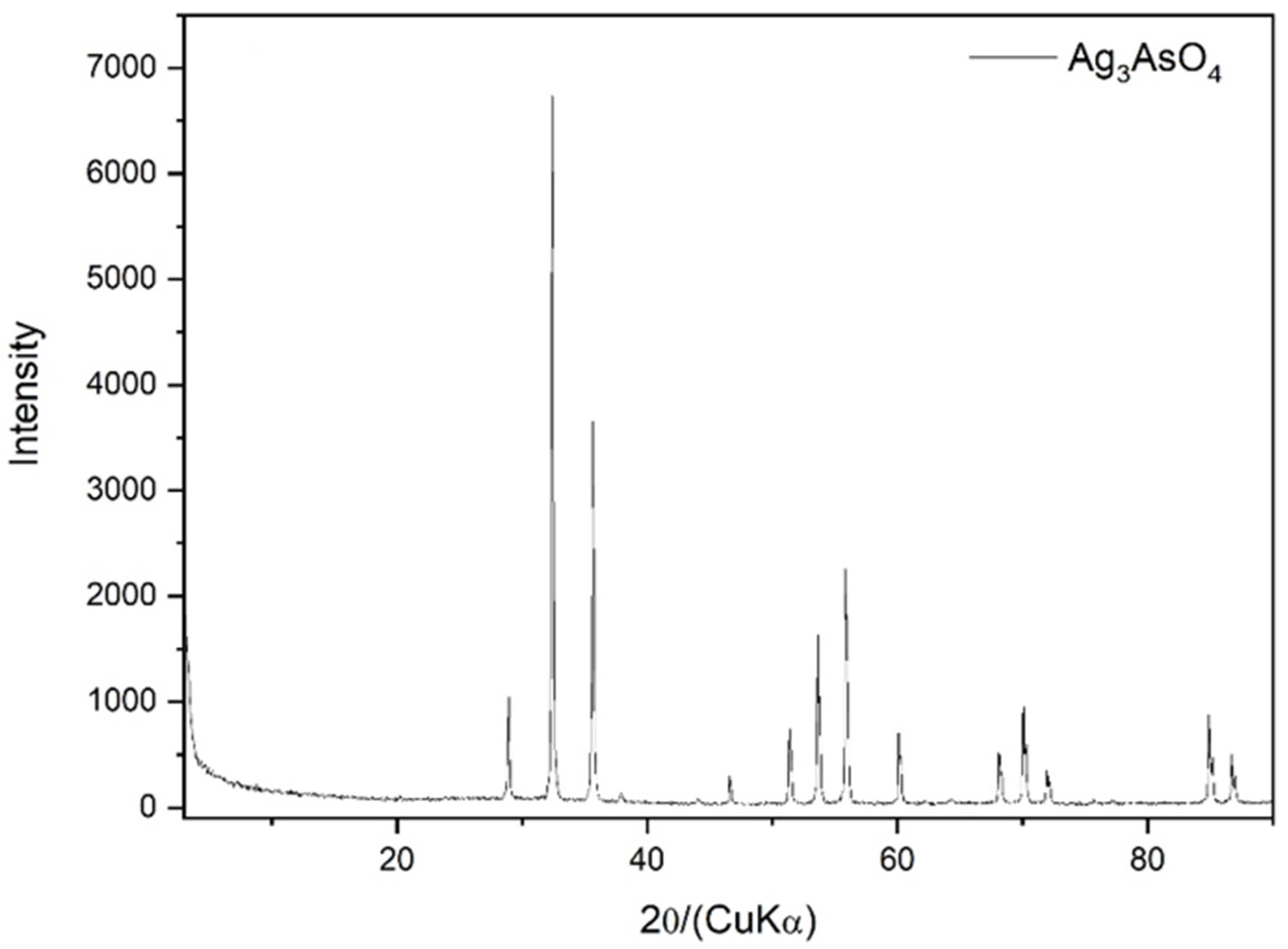
3.2. Ag3AsO4 Characterization
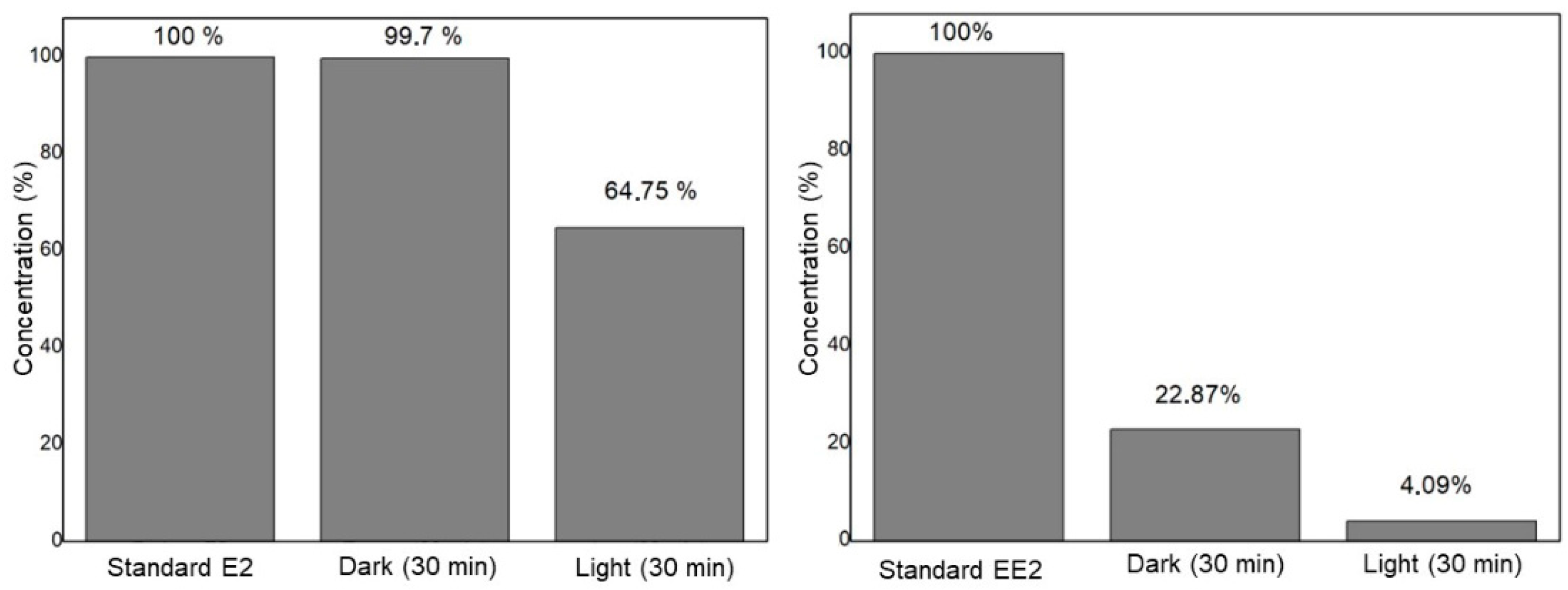
3.3. Hormone Degradation–Adsorption Process Using the Compound Ag3AsO4
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salazar, M. Sistemas integrales de tratamiento de aguas residuales, mediante el uso combinado de digestión anaerobia y micro algas. Contactos 2009, 73, 16–22. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Veronesi, M.L.S.; Rodriguez, M.V.R.; Marinho, G.; Bomfeti, C.A.; Rocha, B.A.; Barbosa, F.; Souza, M.C.O.; Faria, M.C.S.; Rodrigues, J.L. Degradation of Praguicide Disulfoton Using Nanocompost and Evaluation of Toxicological Effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.P.R.; Silva, L.Z.; Freire, B.M.; Faria, M.C.S.; Batista, B.L.; Rocha, B.A.; Barbosa, F.; Rodrigues, J.L. Artisanal Gem Mining in Brazil: A Source of Genotoxicity and Exposure to Toxic Elements. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, A.R.; Faria, M.C.S.; Freire, B.M.; Pereira, R.M.; Batista, B.L.; Rodrigues, J.L. Determination of 14 trace elements in blood, serum and urine after environmental disaster in the Doce River basin: Relationship between mining waste and metal concentration in the population. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 70, 126920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, A.O.; Santos, M.S.; Costa, A.S.V.; Silva, H.T.; Maia, L.F.O.; Faria, M.C.S.; Rodriguez, M.V.R.; Rodrigues, J.L. Assessment of Health Risk and Presence of Metals in Water and Fish Samples from Doce River, Brazil, After Fundão Dam Collapse. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 84, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yong, W.; Chu, X.; Lin, J.M. Simultaneous determination of 15 steroidal oral contraceptives in water using solid-phase disk extraction followed by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 5416–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, C.J.E. Contaminantes emergentes: A aspectos químicos microbiológicos y de salud. In Contaminantes Emergentes: Su Importancia, Retos y Perspectivas Sobre la Medición, el Tratamiento y la Reglamentación, 1st ed.; Gabriela, M., Gerardo, B., Eds.; Mexican Institute of Water Technology: Jiutepec, México, 2012; pp. 19–27. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. United State Environmental Protection Agency. Contaminants of Emerging Concern; 2014. Available online: http://water.epa.gov/scitech/cec/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Montagnera, C.C.; Vidal, C.; Acayaba, R.D. Contaminantes emergentes em matrizes aquáticas do brasil: Cenário atual e aspectos analíticos, ecotoxicológicos e regulatórios. Quim. Nova. 2017, 40, 1094–1110. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hileman, B. Environmental Estrogens Linked to Reproductive Abnormalities, Cancer. Chem. Eng. New 1994, 72, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobling, S.; Sumpter, J.P. Detergent components in sewage effluent are weakly oestrogenic to fish: An in vitro study using rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 27, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Deng, H.; Wu, F.; Deng, N. Microalgae-promoted photodegradation of two endocrine disrupters in aqueous solutions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 84, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbrow, C.; Routledge, E.J.; Brighty, G.C.; Sumpter, J.P.; Waldock, M. Identification of Estrogenic Chemicals in STW Effluent. 1. Chemical Fractionation and in Vitro Biological Screening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sorensen, B. Algal toxicity of antibacterial agents used in intensive farming. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleuvers, M. Initial risk assessment for three β-blockers found in the aquatic environment. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, R.; Blassengale, A.A.; Wang, Q. Degradation of estrogenic hormones in a silt loam soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9152–9158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Díaz, I.; Vela-Soria, F.; Rodríguez-Gómez, R.; Zafra-Gómez, A.; Ballesteros, O.; Navalón, A. Analytical methods for the assessment of endocrine disrupting chemical exposure during human fetal and lactation stages: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 892, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PEV. Prontuario de Especialidades Veterinaria (2014) PLM México. 2014. Available online: https://www.diccionarioveterinarioplm.com/ (accessed on 23 February 2023). (In Spanish).
- Koh, Y.K.K.; Chiu, T.Y.; Boobis, A.; Cartmell, E.; Lester, J.N.; Scrimshaw, M.D. Determination of steroid estrogens in wastewater by high performance liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1173, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caban, M.; Lis, E.; Kumirska, J.; Stepnowski, P. Determination of pharmaceutical residues in drinking water in Poland using a new SPE-GC-MS(SIM) method based on Speedisk extraction disks and DIMETRIS derivatization. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 538, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.O.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: An Endocrine Society 19 scientific statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scognamiglio, V.; Antonaccia, A.; Patrolecco, L.; Lambreva, M.D.; Litescu, S.C.; Ghuge, S.A.; Rea, G. Analytical tools monitoring endocrine disrupting chemicals. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.F.; Silva, G.L.; Silva, P.T.S.; Silva, V.L. Identificação e Quantificação de Contaminantes Emergentes em Estações de Tratamento de Esgoto. Rev. Virtual Química 2016, 8, 702–715. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.O.; Postigo, C.; Alda, M.L.; Daniel, L.A.; Barcelo, D. Removal of estrogens through water disinfection processes and formation of by-products. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. CCL 3 List Chemical Contaminants [on líne]. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2012. Available online: http://water.epa.gov/scitech/drinkingwater/dws/ccl/ccl3.cfm (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Gilbert, N. Drug-Pollution Law All Washed Up. Nature 2012, 491, 503–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, D.P.; Zhang, Z.L.; Readman, J.W.; Zhou, J.L. A comparison of three analytical techniques for the measurement of steroidal estrogens in environmental water samples. Talanta 2009, 78, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ying, G.G.; Zhao, J.L.; Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Zhou, L.J.; Tao, R.; Su, H.C. Assessing estrogenic activity in surface water and sediment of the Liao River system in northeast China using combined chemical and biological tools. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zha, J.; Xu, Y.; Lei, B.; Wang, Z. Occurrences of six steroid estrogens from different effluents in Beijing, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Deng, J.; Sun, P.; Liu, J.; Ji, Y.; Nakada, N.; Qiao, Z.; Tanaka, H.; Yang, Y. Nanomaterials for treating emerging contaminants in water by adsorption and photocatalysis: Systematic review and bibliometric analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuster, M.; Azevedo, D.A.; López, M.J.; Aquino, F.R.; Barceló, D. Analysis of phytoestrogens, progestogens and estrogens in environmental waters from Rio de Janeiro (Brazil). Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbinnen, R.T.; Nunes, G.S.; Vieirae, M. Determinação de hormônios estrógenos em água potável usando CLAE-DAD. Quimica Nova 2010, 33, 1837–1842. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohagheghian, A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Mesdghinia, A.; Rastkari, N.; Mahvi, A.H.; Alimohammadi, M.; Yunesian, M.; Ahmadkhaniha, R.; Nazmara, S. Distribution of Estrogenic Steroids in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants in Tehran, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, G.O.; Souza, N.C.; Vidal, C.B.; Alves, J.A.C.; Firmino, P.I.M.; Nascimento, R.F.; Santos, A.B. Occurrence and removal of estrogens in Brazilian wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.Y.; Praveena, S.M.; Burbure, C.; Ari, A.Z.; Ismail, S.N.S.; Rasdi, I. Analytical techniques for steroid estrogens in water samples—A review. Chemosphere 2016, 165, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caban, M.; Migowska, N.; Stepnowski, P.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Kumirska, J. Matrix effects and recovery calculations in analyses of pharmaceuticals based on the determination of β-blockers and β-agonists in environmental samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1258, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Kreckel, P.; Mueller, J. Behaviour and occurrence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants-II. Aerobic batch experiments with activated sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 225, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, T.G.; Santos, M.S.; Maia, L.F.O.; Aquino, T.E.O.; Silva, L.Z.; Silva, V.C.; Faria, M.C.S.; Batista, B.L.; Pedron, T.; Oliveira, L.C.A.; et al. Iron Oxide Nanomaterials for the Removal of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) from Contaminated River After Mariana Mining Disaster. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 21, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, L.F.O.; Lages, G.; Ladeira, P.C.C.; Batista, B.L.; Faria, M.C.S.; Oliveira, L.C.A.; Pereira, M.C.; Rodrigues, J.L. Development of hollow δ -FeOOH structures for mercury removal from water. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.P.O.; Santos, M.V.N.; Matos, R.S.; Van Der Maas, A.S.; Faria, M.C.S.; Batista, B.L.; Rodrigues, J.L.; Bomfeti, C.A. Pleurotus strains with remediation potential to remove toxic metals from Doce River contaminated by Samarco dam mine. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 19, 6625–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hott, R.C.; Magalhães, T.S.; Maia, L.F.O.; Santos, K.S.F.; Rodrigues, G.L.; Oliveira, L.C.A.; Pereira, M.C.; Faria, M.C.S.; Carli, A.P.; Alves, C.C.A.; et al. Purification of arsenic-contaminated water using iron molybdate filters and monitoring of their genotoxic, mutagenic, and cytotoxic effects through bioassays. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 5714–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.P. Desenvolvimento de Métodos Baseados em Cromatografia Líquida Acoplada à Espectrometria de Massas para Determinação de Micotoxinas e Agrotóxicos em Alimentos. 137 f. Tese; Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2021. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Hott, R.C.; Andrade, T.G.; Santos, M.S.; Lima, A.C.F.; Faria, M.C.S.; Bomfeti, C.A.; Barbosa, F.; Maia, L.F.O.; Oliveira, L.C.; Pereira, M.C.; et al. Adsorption of arsenic from water and its recovery as a highly active photocatalyst. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21969–21979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Zhu, N.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Sunlight-Assisted Degradation of Dye Pollutants in Ag3PO4 Suspension. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 5167–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.C.S.; Hott, R.C.; Santos, M.J.; Santos, M.S.; Andrade, T.G.; Bomfeti, C.A.; Rocha, B.A.; Barbosa, F.; Rodrigues, J.L. Arsenic in Mining Areas: Environmental Contamination Routes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, N.C.; Faria, M.C.S.; Pedron, T.; Batista, B.L.; Mesquita, J.P.; Bomfeti, C.A.; Rodrigues, J. LIsolation and characterization of bacteria from a brazilian gold mining area with a capacity of arsenic bioaccumulation. Chemosphere 2019, 240, 124871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhunia, S.K.; Jana, N.R. Reduced Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanoparticle Composite as Visible Light Photocatalyst for Degradation of Colorless Endocrine Disruptors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20085–20092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.V.; Isecke, B.G.; Carvalho, E.; Teran, F.J.C. Photocatalytic oxidation of 17 α-Ethinylestradiol by UVactivated TiO2 in batch and continuous-flow reactor. J. Chem. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2017, 8, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Metrologia, Normalização e Qualidade Industrial (INMETRO). Orientação sobre Validação de Métodos Analíticos: Documento de Caráter Orientativo (DOQ-CGCRE-008). Available online: http://www.inmetro.gov.br/Sidoq/Arquivos/Cgcre/DOQ/DOQ-Cgcre-8_05.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2023). (In Portuguese)
- Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária. Resolução RE No. 899: Guia para Validação de Métodos Analíticos e Bioanalíticos. 2017. Available online: http://redsang.ial.sp.gov.br/site/docs_leis/vm/vm1.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2022). (In Portuguese)
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, in Guidelines for Standard Method Performance Requirements (Appendix F). 2016. Available online: https://www.aoac.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/app_f.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Deki Makkliang, F.; Pianjing, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Thavarungkul, P.; Thammakhet-Buranachai, C. Natural Luffa cylindrica sponge sorbent for the solid phase extraction of estrone, 17-β-estradiol, and testosterone in aquaculture water. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.L.; Pires, B.C.; Teixeira, L.S.; Dinali, L.A.F.; Simões, N.S.; Borges, W.S.; Borges, K.B. Novel restricted access material combined to molecularly imprinted polymer for selective magnetic solid-phase extraction of estrogens from human urine. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 104043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merib, J.; Spudeit, D.A.; Corazza, G.; Carasek, E.; Anderson, J.L. Magnetic ionic liquids as versatile extraction phases for the rapid determination of estrogens in human urine by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4689–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Nogueira, J.M.F. Determination of steroid sex hormones in water and urine matrices by stir bar sorptive extraction and liquid chromatography with diode array detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Tan, Z.; Li, D. A novel Ag3AsO4 visible-light-responsive photocatalyst: Facile synthesis and exceptional photocatalytic performance. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5498–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, Z.W.; Chong, W.C.; Pang, Y.L.; Koo, C.H. An overview of the recent advances of carbon quantum dots/metal oxides in the application of heterogeneous photocatalysis in photodegradation of pollutants towards visible-light and solar energy exploitation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.V.; Krishnan, S.; Shriwastav, A. An overview of heterogeneous photocatalysis for the degradation of organic compounds: A special emphasis on photocorrosion and reusability. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Myung, Y.; Le, Q.V.; Kim, T.Y. Visible-light photocatalysis of Ag-doped graphitic carbon nitride for photodegradation of micropollutants in wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Meng, Q.; Li, S.; Chang, M.; Meng, F.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Qiu, Q.; Shao, J.; Huo, H. Mechanism of 17β-estradiol degradation by Rhodococcus equi via the 4,5-seco pathway and its key genes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 120021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, A.; Gupta, A.K. Kinetic modeling of the photocatalytic degradation of 17-β estradiol using polythiophene modified Al-doped ZnO: Influence of operating parameters, interfering ions, and estimation of the degradation pathways. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.G.; Ferreira, L.H.; Bertazzoli, R.; Longo, C. Remediation of 17-α-ethinylestradiol aqueous solution by photocatalysis and electrochemically-assisted photocatalysis using TiO2 and TiO2/WO3 electrodes irradiated by a solar simulator. Water Res. 2015, 72, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Meng, D.; He, L.; Wang, X.; Xia, L.; Pan, X.; Jiang, F.; Wang, H.; Dai, J. Photocatalytic activation of peroxydisulfate by a new porous g-C3N4/reduced graphene oxide/TiO2 nanobelts composite for efficient degradation of 17α-ethinylestradiol. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analytes | Linear Range (µg L−1) | LOD (µg L−1) | LOQ (µg L−1) | R | Precision (Intraday) | Precision (Interday) | Recovery | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (µg L−1) | % | (µg L−1) | % | (µg L−1) | % | |||||
| 17-β-estradiol (E2) | 20–500 | 5.01 | 15.19 | 0.9987 | 200 | 7.3127 | 200 | 11.3393 | 100 | 100.15 |
| 400 | 8.4965 | 400 | 3.3377 | 200 | 98.48 | |||||
| 500 | 7.4633 | 500 | 9.5608 | 400 | 99.12 | |||||
| 17-α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) | 20–300 | 0.51 | 1.54 | 0.9984 | 50 | 8.7034 | 50 | 5.2371 | 50 | 94.96 |
| 100 | 7.9037 | 100 | 5.5929 | 200 | 101.23 | |||||
| 200 | 10.9725 | 200 | 4.7280 | 300 | 100.31 | |||||
| Reference | Analytes | Linear Range (µg L−1) | LOQ (µg L−1) | Analytical Technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [52] | 17-β-estradiol (E2) | 15–1000 | 32.10 | HPLC-DAD |
| [53] | 17-β-estradiol (E2) | 80–1100 | 80.00 | HPLC-UV |
| 17-α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) | 80–1100 | 80.00 | ||
| [54] | 17-β-estradiol (E2) | 5–500 | 5.00 | HPLC-DAD |
| 17-α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) | 5–500 | 5.00 | ||
| [55] | 17-β-estradiol (E2) | 300–500 | 150.00 | HPLC-DAD |
| 17-α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) | 600–5000 | 300.00 | ||
| This study | 17-β-estradiol (E2) | 20–500 | 15.19 | HPLC-FLD |
| 17-α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) | 20–300 | 1.54 |
| Material | Analyte | Removal Rate | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhodococcus equi | 17 β-estradiol (E2) | 63.70% | [60] |
| Pth/Al-ZnO | 17 β-estradiol (E2) | 99.00% | [61] |
| Ag3AsO4 | 17β-estradiol (E2) | 35.00% | This study |
| TiO2/WO3 | 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) | 45.00% | [62] |
| C3N4/reduced graphene oxide/TiO2 | 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) | 100% | [63] |
| Ag3AsO4 | 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) | 96.00% | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, M.S.; Mourão, A.O.; Santos, T.S.X.; Rodriguez, M.d.V.R.; Faria, M.C.d.S.; Franco, E.S.; Aguilar, N.A.d.; Rodrigues, J.L. Removal of Emerging Contaminants (Endocrine Disruptors) Using a Photocatalyst and Detection by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22030334
Santos MS, Mourão AO, Santos TSX, Rodriguez MdVR, Faria MCdS, Franco ES, Aguilar NAd, Rodrigues JL. Removal of Emerging Contaminants (Endocrine Disruptors) Using a Photocatalyst and Detection by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(3):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22030334
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Mayra Soares, Amanda Oliveira Mourão, Thuanny Souza Xavier Santos, Mariandry del Valle Rodriguez Rodriguez, Márcia Cristina da Silva Faria, Elton Santos Franco, Núbia Aparecida de Aguilar, and Jairo Lisboa Rodrigues. 2025. "Removal of Emerging Contaminants (Endocrine Disruptors) Using a Photocatalyst and Detection by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 3: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22030334
APA StyleSantos, M. S., Mourão, A. O., Santos, T. S. X., Rodriguez, M. d. V. R., Faria, M. C. d. S., Franco, E. S., Aguilar, N. A. d., & Rodrigues, J. L. (2025). Removal of Emerging Contaminants (Endocrine Disruptors) Using a Photocatalyst and Detection by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(3), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22030334







