The Threat of Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate in Coastal and Marine Environments: Ecotoxicological Assays Using Tropical Species from Different Trophic Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
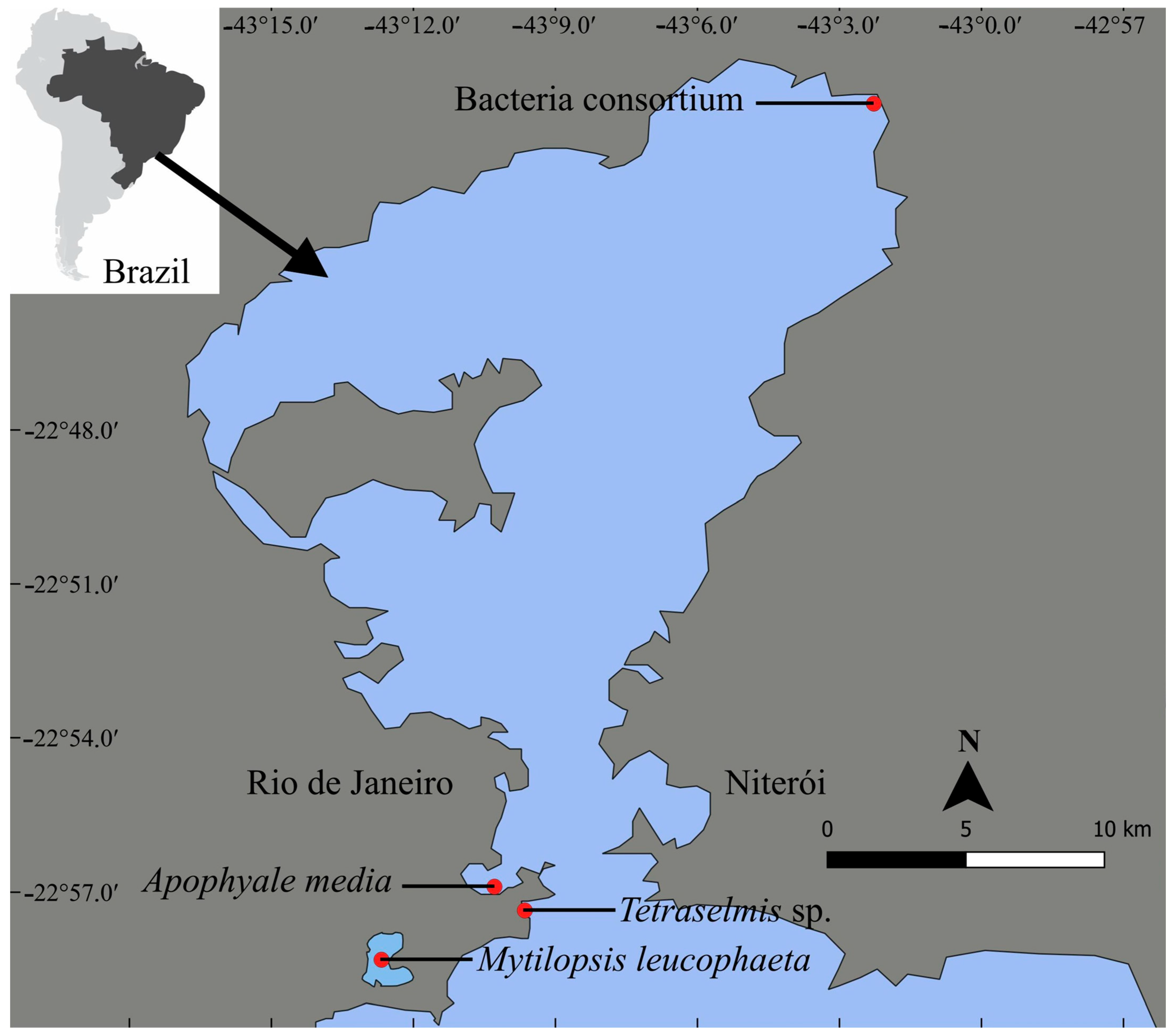
2.1. Organisms
2.2. Stock and Test Solution Preparation
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. Primary Producer Microalgae
2.3.2. Bacterial Consortium
2.3.3. Zooplanktonic Grazer
2.3.4. Benthic Omnivorous Crustacean
2.3.5. Suspensivorous Filter-Feeder
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
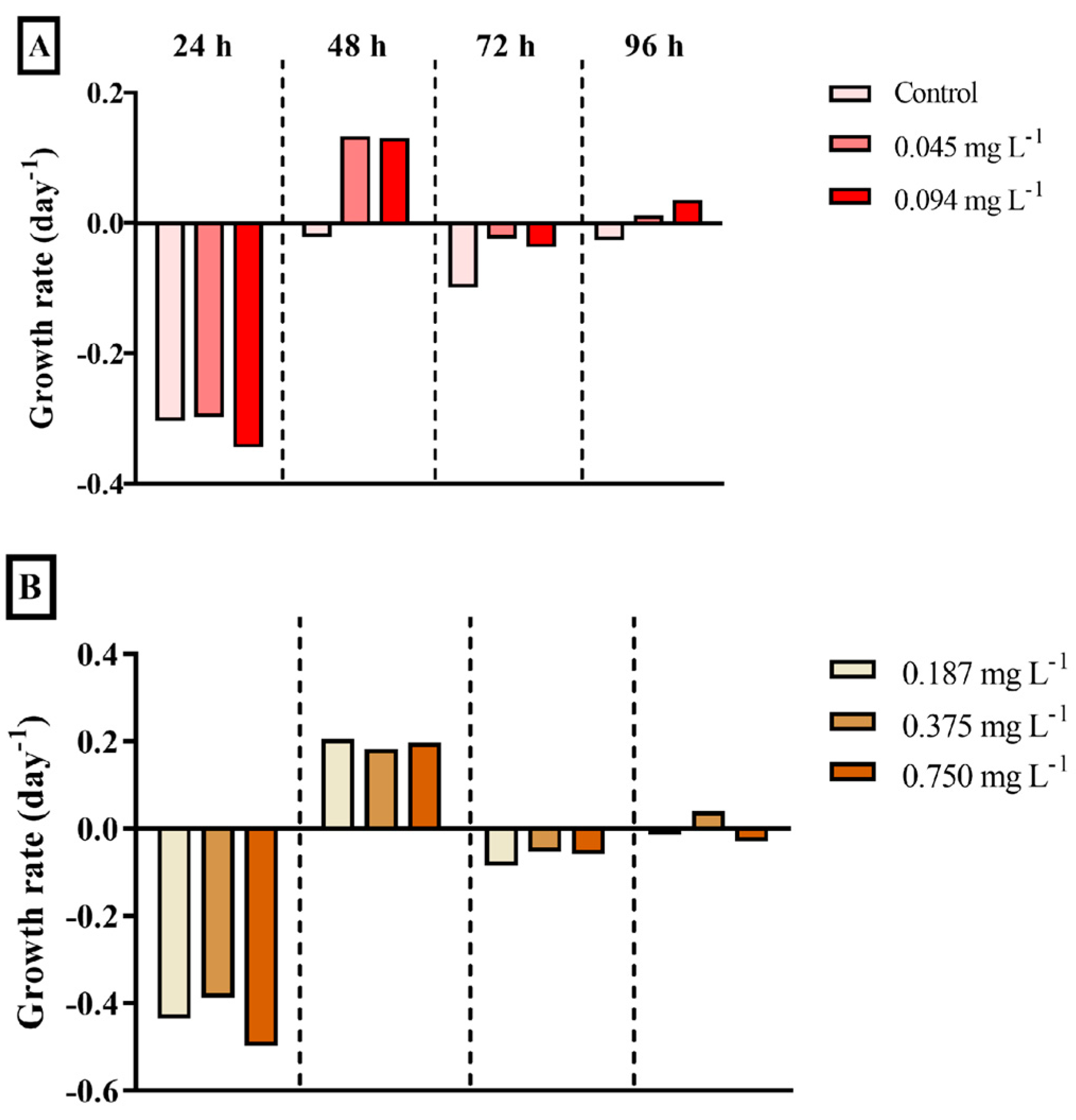
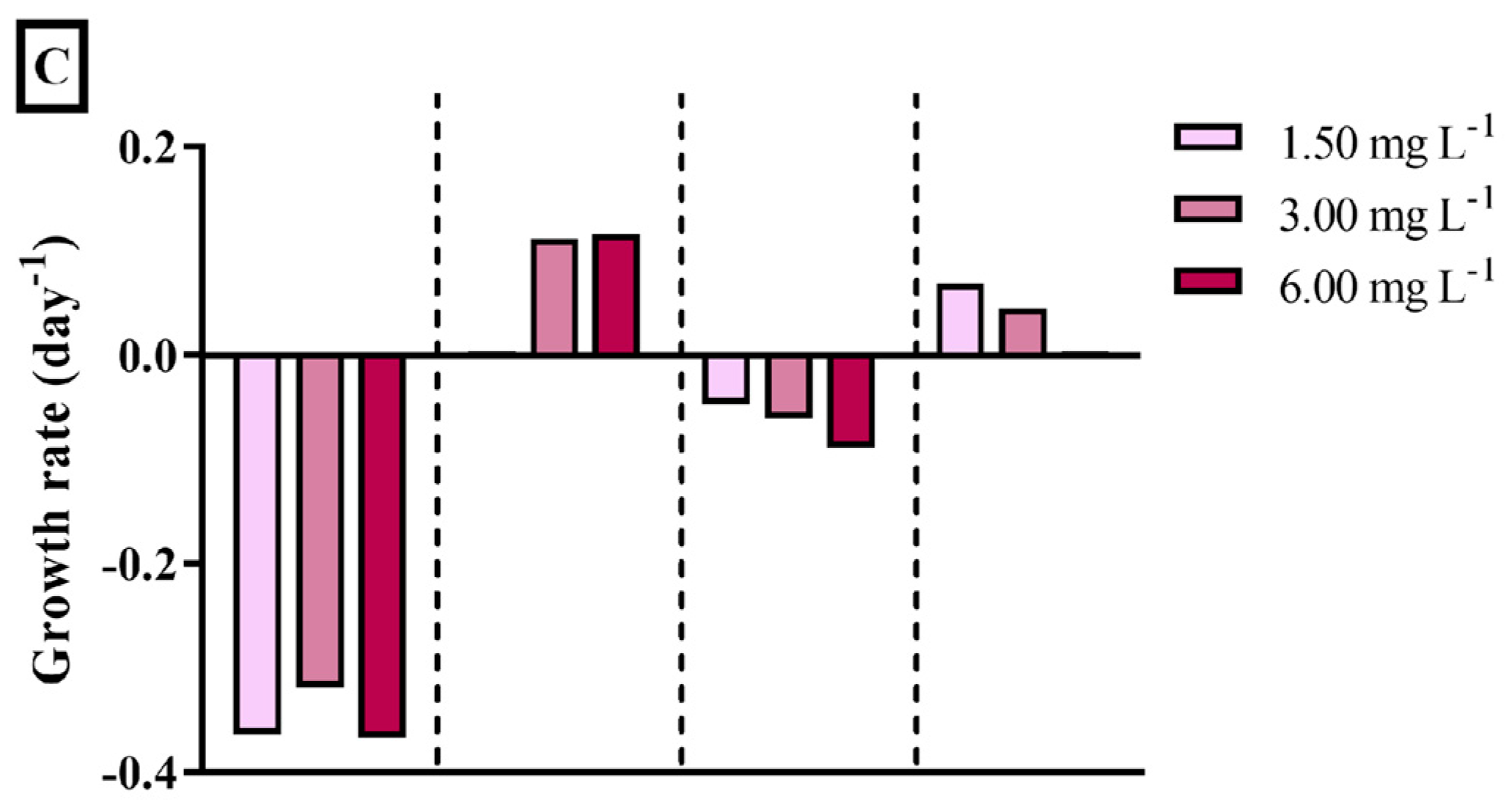
3.1. Primary Producer Microalgae
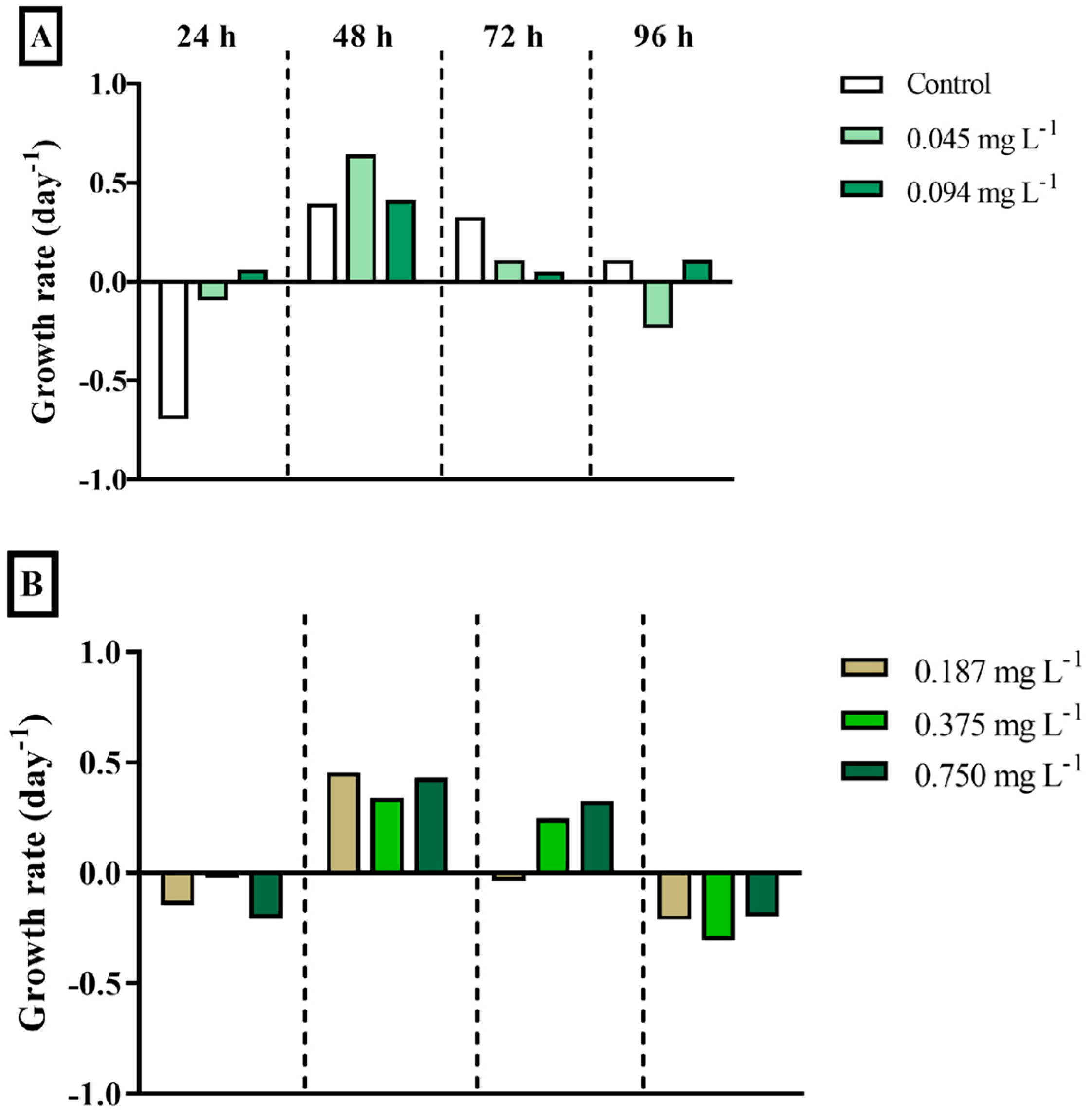
3.2. Bacterial Consortium
3.3. Zooplanktonic Grazer
3.4. Benthic Omnivorous Crustaceans
3.5. Suspensivorous Filter-Feeder
4. Discussion
4.1. Primary Producer Microalgae
4.2. Bacterial Consortium
4.3. Zooplanktonic Grazer
4.4. Benthic Omnivorous Crustaceans
4.5. Suspensivorous Filter-Feeder
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bank, M.S.; Hansson, S.V. The Plastic Cycle: A Novel and Holistic Paradigm for the Anthropocene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7177–7179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haram, L.E.; Carlton, J.T.; Ruiz, G.M.; Maximenko, N.A. A Plasticene Lexicon. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-la-Torre, G.E.; Dioses-Salinas, D.C.; Pizarro-Ortega, C.I.; Santillán, L. New plastic formations in the Anthropocene. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, A.; Jones, K.C.; Pereira, M.G.; Spurgeon, D.J. Emerging and legacy plasticisers in coastal and estuarine environments: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erythropel, H.C.; Maric, M.; Nicell, J.A.; Leask, R.L.; Yargeau, V. Leaching of the plasticizer di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) from plastic containers and the question of human exposure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9967–9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardon, T.; Huvet, A.; Paul-Pont, I.; Cassone, A.L.; Sham Koua, M.; Soyez, C.; Jezequel, R.; Receveur, J.; Le Moullac, G. Toxic effects of leachates from plastic pearl-farming gear on embryo-larval development in the pearl oyster Pinctada margaritifera. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Velis, C.A.; Weber, R.; Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P. An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheftel, V.O. Indirect Food Additives and Polymers: Migration and Toxicology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; ISBN 9781566704991. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yin, P.; Zhao, L. Phthalate esters in water and surface sediments of the Pearl River Estuary: Distribution, ecological, and human health risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 19341–19349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, X.; Vogt, R.D.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, B.; Song, Y.; Lu, X. Distributions, temporal trends and ecological risks of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) in sediments of Jiaozhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 165, 112176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cao, W.; Sun, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Jiang, S.; Zhong, C. Dose-Dependent Effects of Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) in Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 658361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluselli, A.; Aminot, Y.; Galgani, F.; Net, S.; Sempéré, R. Occurrence of phthalate acid esters (PAEs) in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea and the Rhone River. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 163, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.; Choi, M.J.; Park, J.; Nam, T.; Cho, J. Anthropogenic Occurrence of Phthalate Esters in Beach Seawater in the Southeast Coast Region, South Korea. Water 2018, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huysman, S.; Van Meulebroek, L.; Janssens, O.; Vanryckeghem, F.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K.; Vanhaecke, L. Targeted quantification and untargeted screening of alkylphenols, bisphenol A and phthalates in aquatic matrices using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to hybrid Q-Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1049, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malem, F.; Soonthondecha, P.; Khawmodjod, P.; Chunhakorn, V.; Whitlow, H.J.; Chienthavorn, O. Occurrence of phthalate esters in the eastern coast of Thailand. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 2019, 191, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.H.; Shi, X.Z.; Zou, Y.W.; Yang, G.P. Pollution characteristics, spatial variation, and potential risks of phthalate esters in the water–sediment system of the Yangtze River estuary and its adjacent East China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, N.; Alkan, A.; Castro-Jiménez, J.; Royer, F.; Papillon, L.; Ourgaud, M.; Sempéré, R. Environmental occurrence of phthalate and organophosphate esters in sediments across the Gulf of Lion (NW Mediterranean Sea). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebara, A.; Albergamo, A.; Rando, R.; Potortì, A.G.; Lo Turco, V.; Mansour, H.B.; Di Bella, G. Phthalates and non-phthalate plasticizers in Tunisian marine samples: Occurrence, spatial distribution and seasonal variation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, R.A.F.; Miralha, A.; Guimarães, T.B.; Sorrentino, R.; Marques Calderari, M.R.C.; Santos, L.N. Phthalates contamination in the coastal and marine sediments of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 114819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, C.; Lamprecht, J.; Hüffer, T.; Hofmann, T. Environmental factors strongly influence the leaching of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate from polyvinyl chloride microplastics. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baini, M.; Martellini, T.; Cincinelli, A.; Campani, T.; Minutoli, R.; Panti, C.; Finoia, M.G.; Fossi, M.C. First detection of seven phthalate esters (PAEs) as plastic tracers in superficial neustonic/planktonic samples and cetacean blubber. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochatzis, E.; Karayannakidis, P.; Kalogiannis, S. Determination of selected dichloroanilines and phthalates in lyophilised mussels samples with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry after QuEChERS clean-up. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Jiménez, J.; Ratola, N. An innovative approach for the simultaneous quantitative screening of organic plastic additives in complex matrices in marine coastal areas. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 11450–11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Mao, L.; Fang, S.; Xie, J.; Zhao, M.; Jin, H. Occurrence of phthalic acid esters in marine organisms from Hangzhou Bay, China: Implications for human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliu, F.; Montano, S.; Lasagni, M.; Galli, P. Biocompatible solid-phase microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography triple quadrupole mass spectrometry analysis for the determination of phthalates in marine invertebrate. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1618, 460852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo-Serrano, M.; Borrull, F.; Marcé, R.M.; Pocurull, E. Simple method for determining phthalate diesters and their metabolites in seafood species using QuEChERS extraction and liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Brutto, S.; Iaciofano, D.; Lo Turco, V.; Potortì, A.G.; Rando, R.; Arizza, V.; Di Stefano, V. First Assessment of Plasticizers in Marine Coastal Litter-Feeder Fauna in the Mediterranean Sea. Toxics 2021, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routti, H.; Harju, M.; Lühmann, K.; Aars, J.; Ask, A.; Goksøyr, A.; Kovacs, K.M.; Lydersen, C. Concentrations and endocrine disruptive potential of phthalates in marine mammals from the Norwegian Arctic. Environ. Int. 2021, 152, 106458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoca, D.; Arculeo, M.; Vecchioni, L.; Cambera, I.; Visconti, G.; Melfi, R.; Arizza, V.; Palumbo Piccionello, A.; Buscemi, S.; Pace, A. Can phthalates move into the eggs of the loggerhead sea turtle Caretta caretta? The case of the nests on the Linosa Island in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, L.; Zhao, S.; Guo, W.; Luo, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, J. Seasonal distribution and ecological risk of phthalate esters in surface water and marine organisms of the Bohai Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotelli, V.R.T.; Neuhauss, S.C.F.; Ehrengrubera, M.U. Long-term exposure to bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) inhibits growth of guppy fish (Poecilia reticulata). J. Appl. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Shen, G.; Pang, S.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Mu, X. Integrated toxicity assessment of DEHP and DBP toward aquatic ecosystem based on multiple trophic model assays. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 87402–87412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Lan, W.; Jiang, H.; Pan, K. Short-Term Exposure to MPs and DEHP Disrupted Gill Functions in Marine Bivalves. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreyeva, A.Y.; Lobko, V.V.; Gostyukhina, O.L.; Tkachuk, A.A.; Murashova, A.I.; Malakhova, L.V.; Kladchenko, E.S. Accumulation, functional and antioxidant responses to acute exposure to Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadeeswaran, I.; Harini, S. EU 1907/2006; Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals. In Medical Device Guidelines and Regulations Handbook; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 237–260. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation, E.C. Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 Concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH), Establishing a European Chemicals Agency, Amending Directive 1999/45/EC and Repealing Council Regulation (EEC) No 793/93 and Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 as Well as Council Directive 76/769/EEC and Commission Directives 91/155/EEC, 93/67/EEC, 93/105/EC and 2000/21/EC. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2006/1907/oj (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- OECD. Detailed Review Paper on Aquatic Testing Methods for Pesticides and Industrial Chemicals; OECD Series on Testing and Assessment. No. 11—Part 2: Annexes; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2002; Available online: https://one.oecd.org/document/env/mc/chem(98)19/part2/en/pdf (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- OECD. Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; Test No. 201; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botterell, Z.L.; Bergmann, M.; Hildebrandt, N.; Krumpen, T.; Steinke, M.; Thompson, R.C.; Lindeque, P.K. Microplastic ingestion in zooplankton from the Fram Strait in the Arctic. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, R.A.F.; Guimarães, T.B.; Santos, L.N. First Record of Microplastic Contamination in the Non-Native Dark False Mussel Mytilopsis leucophaeata (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae) in a Coastal Urban Lagoon. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, P.P. Produção de biossurfactante e biomassa por consórcios bacterianos ambientais submetidos a diferentes condições de crescimento; Monografia: Instituto de Biociências; Universidade Federal do Estado do Rio de Janeiro: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, P. M Integrating toxicology and ecology: Putting the “eco” into ecotoxicology. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluselli, A.; Kim, S. Horizontal and vertical distribution of phthalates acid ester (PAEs) in seawater and sediment of East China Sea and Korean South Sea: Traces of plastic debris? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lörz, A.N.; Myers, A.; Gordon, D. An inquiline deep-water bryozoan/amphipod association from New Zealand, including the description of a new genus and species of Chevaliidae. Eur. J. Taxon. 2014, 72, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marsden, I.D.; Rainbow, P.S. Does the accumulation of trace metals in crustaceans affect their ecology—The amphipod example? J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 300, 373–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, R.R.R. Culture methods. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae—IOC Manual and Guides; Hallegraef, G.G., Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, R.; Gutiérrez, J.L.; Aldridge, D.C. Non-indigenous invasive bivalves as ecosystem engineers. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 2367–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerco, C.F.; Noel, M.R. Monitoring, modeling, and management impacts of bivalve filter feeders in the oligohaline and tidal fresh regions of the Chesapeake Bay system. Ecol. Modell. 2010, 221, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, N.; Fayet, A.L.; Padget, O.; Syposz, M.; Wynn, J.; Bond, S.; Guilford, T. Short-term behavioural impact contrasts with long-term fitness consequences of biologging in a long-lived seabird. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopal, S.; Van Der Velde, G.; Van Der Gaag, M.; Jenner, H.A. Byssal detachment underestimates tolerance of mussels to toxic compounds. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengoni, N.G.; Klosowski, E.S.; Oliveira, K.P.D.; Chambo, A.P.S.; Gonçalves Junior, A.C. Bioacumulação de metais pesados e nutrientes no mexilhão dourado do reservatório da usina hidrelétrica de Itaipu binacional. Química Nova 2013, 36, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bac GroTM Culture Media. Instructions Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB). 2022; pp. 1–3. Available online: https://www.goldstandarddiagnostics.com/pub/media/productattachments/files/IFU_POW1200_Rev_02_Tryptic_Soy_Broth_1.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- EUR 23384 EN/2; European Union Risk Assessment Report bis (2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP). Pakalin, S., Aschberger, K., Cosgrove, O., Lund, B.-O., Paya-Perez, A., Vegro, S., Eds.; EUR—Scientific and Technical Research Series. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities—VIII: Luxembourg, 2008; Volume 80, p. 22.
- Cui, D.; Ricardo, M.; Quinete, N. A novel report on phthalates levels in Biscayne Bay surface waters and drinking water from South Florida. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Liang, H. An overview of phthalate acid ester pollution in China over the last decade: Environmental occurrence and human exposure. Sci.Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Methods for Acute Toxicity Tests with Fish, Macroinvertebrates, and Amphibians; Ecological Research Series; Report Number EPA-660/3-75-009; National Environmental Research Center, Office of Research and Development; U. S. Environmental Protection Agency: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1975. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/91013TCX.PDF?Dockey=91013TCX.PDF (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Standard Evaluation Procedure for Acute Toxicity Test for Freshwater Invertebrates; Ecological Research Series; Report Number EPA-540/9-85-005; National Environmental Research Center; Office of Pesticide Programs: Washington, DC, USA, 1985. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/P100WHV3.PDF?Dockey=P100WHV3.PDF (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Huang, Y.H.; Huang, X.J.; Chen, X.H.; Cai, Q.Y.; Chen, S.; Mo, C.H.; Lü, H.; Wong, M.H. Biodegradation of di-butyl phthalate (DBP) by a novel endophytic bacterium Bacillus subtilis and its bioaugmentation for removing DBP from vegetation slurry. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CETESB (Companhia Ambiental do Estado de São Paulo). Determination of Chlorophyll-a and Pheophytin-a: Specttrophotometric Method. Standard Method (Norma Técnica) n° L5, Vol. 306, 3rd edition, 14p. Available online: https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/DD_093_14_E.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Falcão, V.G.O.; Carneiro, D.d.C.; Pereira, S.A.; da Silva, M.R.D.; Candé, A.A.; da Cunha Lima, S.T. Analyzing the toxicity of bisphenol-A to microalgae for ecotoxicological applications. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveira, C.; Rodrigues, N.; Santos, F.S.; Santos, L.N.; Neves, R.A.F. Acute toxicity of Bisphenol A (BPA) to tropical marine and estuarine species from different trophic groups. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xu, W.; Luan, T.; Pan, T.; Yang, L.; Lin, L. Comparative responses of cell growth and related extracellular polymeric substances in Tetraselmis sp. to nonylphenol, bisphenol A and 17α-ethinylestradiol. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, M.; Cid, Á.; Esperanza, M. Toxicity of bisphenol A on marine microalgae: Single- and multispecies bioassays based on equivalent initial cell biovolume. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendra, M.; Moreno-Garrido, I.; Blasco, J. Single and multispecies microalgae toxicological tests assessing the impact of several BPA analogues used by industry. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattullo, C.E.; Bährs, H.; Steinberg, C.E.W.; Loffredo, E. Removal of bisphenol A by the freshwater green alga Monoraphidium braunii and the role of natural organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 416, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, R.; Ma, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, G.; Ruan, R.; Lu, Y.; Yan, X.; Cheng, P. Improved growth of bait microalgae Isochrysis and aquacultural wastewater treatment with mixotrophic culture. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; He, Y.; Song, L.; Ding, J.; Ren, S.; Lv, M.; Chen, L. Methylparaben toxicity and its removal by microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.A.; Salgado, E.M.; Gonçalves, A.L.; Esteves, A.F.; Pires, J.C.M. Microalgae-Based Remediation of Real Textile Wastewater: Assessing Pollutant Removal and Biomass Valorisation. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, T.; Fernandes, I.; Andrade, C.A.P.; Cordeiro, N. Marine microalgae growth and carbon partitioning as a function of nutrient availability. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’Rabet, C.; Kéfi-Daly Yahia, O.N.; Zentz, F.; Bilien, G.; Pringault, O. Transient effect of bisphenol A (BPA) and di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) on the cosmopolitan marine diatom Chaetoceros decipiens-lorenzianus. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Othman, H.; Pick, F.R.; Sakka Hlaili, A.; Leboulanger, C. Effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on marine and freshwater microalgae—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Rabet, C.; Pringault, O.; Zmerli-Triki, H.; Ben Gharbia, H.; Couet, D.; Kéfi-Daly Yahia, O. Impact of two plastic-derived chemicals, the Bisphenol A and the di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate, exposure on the marine toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, J. Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate induced the growth inhibition and oxidative damage in the microalga Chlorella vulgaris. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 227, p. 052054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Rabet, C.; Kéfi-Daly Yahia, O.; Couet, D.; Gueroun, S.K.M.; Pringault, O. Consequences of a contaminant mixture of bisphenol A (BPA) and di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), two plastic-derived chemicals, on the diversity of coastal phytoplankton. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit; Chandra, R.; Ghosh, U.K.; Nayak, J.K. Phycoremediation potential of marine microalga Tetraselmis indica on secondary treated domestic sewage for nutrient removal and biodiesel production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20868–20875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, H.; Mata, M.T.; Riquelme, C. The effect of heavy metals on the viability of Tetraselmis marina AC16-MESO and an evaluation of the potential use of this microalga in bioremediation. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, B.; Beuchel, C.; Liers, C.; Reisser, W.; Harms, H.; Schlosser, D. Laccase-like enzyme activities from chlorophycean green algae with potential for bioconversion of phenolic pollutants. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y. Biodegradation of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate by a halotolerant consortium LF. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Doyle, E.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, D.; Gu, C.; Gao, J. Metagenomic analysis exploring microbial assemblages and functional genes potentially involved in di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate degradation in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 137037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.J.; Bosch, R.; Gibson, M.I.; Christie-Oleza, J.A. Plasticizer Degradation by Marine Bacterial Isolates: A Proteogenomic and Metabolomic Characterization. Environ. Sci Technol. 2020, 54, 2244–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.T.S.; Chen, Y.L.; Wu, Y.W.; Wu, T.Y.; Lai, Y.L.; Wang, P.H.; Ismail, W.; Lee, T.H.; Chiang, Y.R. Integrated Multi-omics Investigations Reveal the Key Role of Synergistic Microbial Networks in Removing Plasticizer Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate from Estuarine Sediments. MSystems 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, H. Biodegradation of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate by a new bacterial consortium. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningthoujam, R.; Satiraphan, M.; Sompongchaiyakul, P.; Bureekul, S.; Luadnakrob, P.; Pinyakong, O. Bacterial community shifts in a di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-degrading enriched consortium and the isolation and characterization of degraders predicted through network analyses. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Wei, J.L.; Tang, G.X.; Chen, Y.S.; Huang, Y.H.; Hu, R.; Mo, C.H.; Zhao, H.M.; Xiang, L.; Li, Y.W.; et al. Microbial consortium degrading of organic pollutants: Source, degradation efficiency, pathway, mechanism and application. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 451, 141913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Park, B.J. Removal of bisphenol A from wastewater by physical, chemical and biological remediation techniques. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1801–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolvenbach, B.A.; Helbling, D.E.; Kohler, H.P.E.; Corvini, P.F.X. Emerging chemicals and the evolution of biodegradation capacities and pathways in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltoukhy, A.; Jia, Y.; Nahurira, R.; Abo-Kadoum, M.A.; Khokhar, I.; Wang, J. Biodegradation of endocrine disruptor Bisphenol A by Pseudomonas putida strain YC-AE1 isolated from polluted soil, Guangdong, China. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Morais Farias, J.; Krepsky, N. Bacterial degradation of bisphenol analogues: An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 76543–76564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.N.; Liu, Y.S.; Hu, L.X.; Chen, X.W. Microbial transformation of progesterone and dydrogesterone by bacteria from swine wastewater: Degradation kinetics and products identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peressutti, S.R.; Olivera, N.L.; Babay, P.A.; Costagliola, M.; Alvarez, H.M. Degradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate by a bacterial consortium isolated from the aquatic environment of Argentina. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Weng, L.; Chen, D.; Hu, H.; Jia, Y.; Zhou, J.L. Bioremediation of PAEs-contaminated saline soil: The application of a marine bacterial strain isolated from mangrove sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lin, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Hu, H. Insight into metabolic versatility of an aromatic compounds-degrading Arthrobacter sp. YC-RL1. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Qiao, B.; Xu, Q.M.; Cheng, J.S. Potential biotransformation pathways and efficiencies of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin by an activated sludge consortium. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 1, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; ALutovsky, A.C.; Andaker, G.L.; Gough, H.L.; Ferguson, J.F. Cultivation and characterization of bacterial isolates capable of degrading pharmaceutical and personal care products for improved removal in activated sludge wastewater treatment. Biodegradation 2013, 24, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.M.; Machado, M.R.; Costa, G.G.; de Oliveira, G.A.R.; Nunes, H.F.; Maciel Costa Veloso, D.F.; Ishizawa, T.A.; Pereira, J.; Ferreira de Oliveira, T. Influence of different concentrations of plasticizer diethyl phthalate (DEP) on toxicity of Lactuca sativa seeds, Artemia salina and Zebrafish. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, M.R.; Karim, M.R. Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activity of Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate and Anhydrosophoradiol-3-acetate Isolated from Calotropis gigantea (Linn.) Flower. Mycobiology 2009, 37, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henciya, S.; Vengateshwaran, T.D.; Gokul, M.S.; Dahms, H.U.; James, R.A. Antibacterial Activity of Halophilic Bacteria Against Drug-Resistant Microbes Associated with Diabetic Foot Infections. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 3711–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwack, S.J.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, B.M. Comparative Toxicological Evaluation of Phthalate Diesters and Metabolites in Sprague-Dawley Male Rats for Risk Assessment. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2009, 72, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, G.B. Principles for Evaluating Health Risks in Children Associated with Exposure to Chemicals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 237. [Google Scholar]
- Morgana, S.; Estévez-Calvar, N.; Gambardella, C.; Faimali, M.; Garaventa, F. A short-term swimming speed alteration test with nauplii of Artemia franciscana. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J. Evidence That Hormesis Represents an “Overcompensation” Response to a Disruption in Homeostasis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1999, 42, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crobeddu, B.; Ferraris, E.; Kolasa, E.; Plante, I. Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) increases proliferation of epithelial breast cancer cells through progesterone receptor dysregulation. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Baldwin, L.A. Hormesis: A Generalizable and Unifying Hypothesis. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2001, 31, 353–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green-Ojo, B.; Botelho, M.T.; Umbuzeiro, G.d.A.; Gomes, V.; Parker, M.O.; Grinsted, L.; Ford, A.T. Evaluation of precopulatory pairing behaviour and male fertility in a marine amphipod exposed to plastic additives. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green-Ojo, B.; Tan, H.; Botelho, M.T.; Obanya, H.; Grinsted, L.; Parker, M.O.; Ford, A.T. The effects of plastic additives on swimming activity and startle response in marine amphipod Echinogammarus marinus. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, N.C.; Ak, T.P.; Samasas, O. Toxicological effects of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in Gammarus pulex: A biochemical and histopathological assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44442–44451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, K.; Lu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhuang, S. In vitro and in silico investigations of the binary-mixture toxicity of phthalate esters and cadmium (II) to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Zheng, H.; Xu, Q.; Sun, C.; Shi, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, F. Comparative toxicity of the plasticizer dibutyl phthalate to two freshwater algae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 191, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva dos Santos, F.; Neves, R.A.F.; Crapez, M.A.C.; Teixeira, V.L.; Krepsky, N. How does the brown mussel Perna perna respond to environmental pollution? A review on pollution biomarkers. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 111, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellini, T.; Russo, A.; Cincinelli, A.; Santini, S.; Lofrumento, C.; Baini, M.; Ciattini, S.; Conti, L.; Mostardini, F.; Mercatelli, L.; et al. Bioplastics on marine sandy shores: Effects on the key species Talitrus saltator (Montagu, 1808). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Södergren, A. Significance of interfaces in the distribution and metabolism of di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate in an aquatic laboratory model ecosystem. Environ. Pollut. Ser. A Ecol. Biol. 1982, 27, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.Y.; Wei, Q.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, X.Q.; Sun, A.L.; Chen, J.; Shi, X.Z. A comprehensive study of the effects of phthalates on marine mussels: Bioconcentration, enzymatic activities and metabolomics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, X. Antioxidant defenses and metabolic responses of Mytilus coruscus exposed to various concentrations of PAEs (phthalate esters). J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, N.; Zhao, C.; Diao, X.; Han, Q.; Zhou, H. Dynamic responses of antioxidant enzymes in pearl oyster Pinctada martensii exposed to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 54, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Fuster, B.; Alomar, C.; Capó, X.; Paniagua González, G.; Garcinuño Martínez, R.M.; Soliz Rojas, D.L.; Silva, M.; Fernández Hernando, P.; Solé, M.; Freitas, R.; et al. Assessment of the impact of aquaculture facilities on transplanted mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis): Integrating plasticizers and physiological analyses as a biomonitoring strategy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajaraville, M.P.; Cancio, I.; Ibabe, A.; Orbea, A. Peroxisome proliferation as a biomarker in environmental pollution assessment. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 61, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marigómez, I.; Baybay-Villacorta, L. Pollutant-specific and general lysosomal responses in digestive cells of mussels exposed to model organic chemicals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 64, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, C.; Su, X.; Jin, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, T. Characterisation of immune-related gene expression in clam (Venerupis philippinarum) under exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 34, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mincarelli, L.F.; Chapman, E.C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Turner, A.P.; Wollenberg Valero, K.C. Sex and gametogenesis stage are strong drivers of gene expression in Mytilus edulis exposed to environmentally relevant plasticiser levels and pH 7.7. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 23437–23449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mincarelli, L.F.; Turner, A.; Anderson, G.; Wollenberg Valero, K. Exposure to Plasticiser DEHP Affects Eggs Spawned by Blue Mussels: A Possible Risk to Fertilisation? Toxics 2024, 12, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, R.A.F.; Santiago, T.C.; Carvalho, W.F.; Silva, E. dos S.; da Silva, P.M.; Nascimento, S.M. Impacts of the toxic benthic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima on the brown mussel Perna perna: Shell-valve closure response, immunology, and histopathology. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 146, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereycken, J.E.; Aldridge, D.C. Bivalve molluscs as biosensors of water quality: State of the art and future directions. Hydrobiologia 2022, 850, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahouri, A.; Yacoubi, B.; Moukrim, A.; Banaoui, A. Bivalve molluscs as bioindicators of multiple stressors in the marine environment: Recent advances. Cont. Shelf Res. 2023, 264, 105056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbea, A.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M.; Cajaraville, M.P. Interactive effects of benzo(a)pyrene and cadmium and effects of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate on antioxidant and peroxisomal enzymes and peroxisomal volume density in the digestive gland of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. Biomarkers 2002, 7, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| DEHP (mg·L−1) | Cumulative Mortality (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | |
| 0 | 3 (±6) | 20 (±17) | 27 (±21) | 53 (±15) |
| 0.045 | 10 (±10) | 13 (±11) | 13 (±11) | 27 (±15) |
| 0.094 | 10 (±10) | 20 (±17) | 30 (±10) | 37 (±15) |
| 0.187 | 10 (±17) | 10 (±17) | 23 (±15) | 43 (±6) |
| 0.375 | 13 (±6) | 30 (±10) | 33 (±23) | 47 (±15) |
| 0.750 | 13 (±23) | 23 (±25) | 47 (±6) | 60 (±17) |
| 1.50 | 20 (±17) | 43 (±25) | 63 (±25) | 73 (±21) |
| 3.00 | 23 (±15) | 60 (±11) | 47 (±6) | 63 (±6) |
| 6.00 | 27 (±21) | 55 (±10) | 70 (±10) | 70 (±10) |
| DEHP (mg·L−1) | Sublethal Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | |
| 0 | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) |
| 0.045 | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) |
| 0.094 | 0.07 (±0.13) | 0.10 (±0.17) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) |
| 0.187 | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.10 (±0.17) | 0.15 (±0.26) | 1.66 (±0.40) |
| 0.375 | 0.00 (±0.00) | 1.23 (±0.21) | 0.58 (±0.23) | 0.88 (±0.51) |
| 0.750 | 0.03 (±0.06) | 0.68 (±0.53) | 0.82 (±0.17) | 0.26 (±0.70) |
| 1.50 | 0.19 (±0.33) | 0.88 (±0.98) | 0.22 (±0.38) | 1.20 (±0.46) |
| 3.00 | 0.35 (±0.30) | 0.84 (±1.00) | 0.53 (±0.92) | 0.42 (±1.53) |
| 6.00 | 0.40 (±0.70) | 0.42 (±0.35) | 1.53 (±1.52) | 0.22 (±1.52) |
| DEHP (mg·L−1) | Cumulative Mortality (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | |
| 0 | 0 (±0) | 20 (±0) | 53 (±42) | 80 (±35) |
| 0.045 | 67 (±23) | 80 (±43) | 93 (±12) | 100 (±0) |
| 0.094 | 60 (±53) | 93 (±14) | 100 (±0) | 100 (±0) |
| 0.187 | 73 (±12) | 100 (±0) | 100 (±0) | 100 (±0) |
| 0.375 | 40 (±0) | 73 (±38) | 100 (±0) | 100 (±0) |
| 0.750 | 20 (±20) | 47 (±52) | 73 (±31) | 80 (±35) |
| 1.50 | 47 (±12) | 93 (±14) | 100 (±0) | 100 (±0) |
| 3.00 | 100 (±0) | 100 (±0) | 100 (±0) | 100 (±0) |
| 6.00 | 100 (±0) | 100 (±0) | 100 (±0) | 100 (±0) |
| DEHP (mg·L−1) | Cumulative Mortality (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | |
| 0 | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) |
| 0.045 | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) |
| 0.094 | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 7 (±6) | 7 (±6) |
| 0.187 | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 7 (±6) |
| 0.375 | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) |
| 0.750 | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 7 (±6) | 7 (±6) |
| 1.50 | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 20 (±17) | 20 (±17) |
| 3.00 | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 7 (±6) |
| 6.00 | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) |
| DEHP (mg·L−1) | Response to Stimulus | Byssus Production | Cluster Formation | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | |
| 0 | 1.20 (±0.40) | 0.73 (±0.30) | 1.00 (±0.35) | 0.67 (±0.12) | 0.80 (±0.00) | 0.80 (±0.00) | 0.20 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 2.67 (±1.15) | 2.67 (±1.15) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) |
| 0.045 | 1.33 (±0.50) | 1.00 (±0.40) | 1.20 (±0.35) | 0.53 (±0.42) | 0.33 (±0.23) | 0.20 (±0.20) | 0.07 (±0.12) | 0.13 (±0.23) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.67 (±1.15) |
| 0.094 | 1.53 (±0.12) | 1.17 (±0.60) | 0.75 (±0.59) | 0.55 (±0.40) | 0.33 (±0.31) | 0.60 (±0.35) | 0.07 (±0.12) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.67 (±1.15) | 1.33 (±1.15) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) |
| 0.187 | 1.80 (±0.35) | 0.87 (±0.61) | 0.60 (±0.72) | 0.88 (±0.33) | 0.47 (±0.23) | 0.47 (±0.23) | 0.13 (±0.12) | 0.07 (±0.12) | 0.67 (±1.15) | 0.67 (±1.15) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 ±0.00) |
| 0.375 | 1.13 (±0.42) | 1.00 (±0.53) | 0.40 (±0.20) | 0.87 (±0.58) | 0.53 (±0.23) | 0.53 (±0.12) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.07 (±0.12) | 2.00 (±2.00) | 2.33 (±2.08) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) |
| 0.750 | 1.60 (±0.40) | 1.13 (±0.31) | 0.63 (±0.51) | 0.53 (±0.76) | 0.87 (±0.23) | 0.80 (±0.20) | 0.33 (±0.31) | 0.07 (±0.12) | 2.67 (±1.15) | 2.67 (±1.15) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) |
| 1.50 | 1.00 (±0.35) | 1.33 (±0.64) | 0.47 (±0.42) | 0.63 (±0.32) | 0.33 (±0.31) | 0.53 (±0.42) | 0.13 (±0.23) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.67 (±1.15) | 1.33 (±2.3) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) |
| 3.00 | 1.27 (±0.70) | 0.60 (±0.35) | 0.47 (±0.64) | 0.80 (±0.35) | 0.47 (±0.23) | 0.47 (±0.12) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.67 (±1.15) | 0.67 (±1.15) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) |
| 6.00 | 0.93 (±0.23) | 0.80 (±0.00) | 0.93 (±0.81) | 0.53 (±0.76) | 0.67 (±0.23) | 0.60 (±0.20) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.07 (±0.12) | 1.67 (±1.52) | 1.67 (±1.52) | 0.00 (±0.00) | 0.00 (±0.00) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dos Santos, F.S.; Miralha, A.; Coração, A.C.S.; Rodrigues, A.J.S.; Kauai, G.; Borsato, G.T.; Costa, J.S.; Farias, J.d.M.; Pereira, K.B.R.; Feuvrier, O.; et al. The Threat of Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate in Coastal and Marine Environments: Ecotoxicological Assays Using Tropical Species from Different Trophic Levels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22030402
dos Santos FS, Miralha A, Coração ACS, Rodrigues AJS, Kauai G, Borsato GT, Costa JS, Farias JdM, Pereira KBR, Feuvrier O, et al. The Threat of Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate in Coastal and Marine Environments: Ecotoxicological Assays Using Tropical Species from Different Trophic Levels. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(3):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22030402
Chicago/Turabian Styledos Santos, Fernanda Silva, Agatha Miralha, Amanda C. S. Coração, Antonio J. S. Rodrigues, Gabriel Kauai, Geovanna T. Borsato, Jéssica S. Costa, Julia de Morais Farias, Kettollen Brenda Ribeiro Pereira, Odilon Feuvrier, and et al. 2025. "The Threat of Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate in Coastal and Marine Environments: Ecotoxicological Assays Using Tropical Species from Different Trophic Levels" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 3: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22030402
APA Styledos Santos, F. S., Miralha, A., Coração, A. C. S., Rodrigues, A. J. S., Kauai, G., Borsato, G. T., Costa, J. S., Farias, J. d. M., Pereira, K. B. R., Feuvrier, O., Silva, R. A. F., Rodrigues, N., & Neves, R. A. F. (2025). The Threat of Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate in Coastal and Marine Environments: Ecotoxicological Assays Using Tropical Species from Different Trophic Levels. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(3), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22030402









