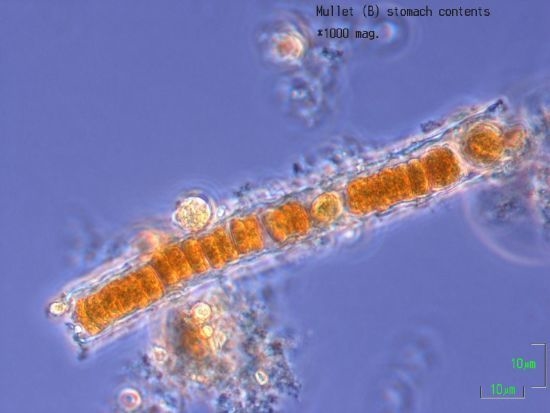
First Report of a Toxic Nodularia spumigena (Nostocales/ Cyanobacteria) Bloom in Sub-Tropical Australia. II. Bioaccumulation of Nodularin in Isolated Populations of Mullet (Mugilidae)
Abstract
Share and Cite
Stewart, I.; Eaglesham, G.K.; McGregor, G.B.; Chong, R.; Seawright, A.A.; Wickramasinghe, W.A.; Sadler, R.; Hunt, L.; Graham, G. First Report of a Toxic Nodularia spumigena (Nostocales/ Cyanobacteria) Bloom in Sub-Tropical Australia. II. Bioaccumulation of Nodularin in Isolated Populations of Mullet (Mugilidae). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 2412-2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9072412
Stewart I, Eaglesham GK, McGregor GB, Chong R, Seawright AA, Wickramasinghe WA, Sadler R, Hunt L, Graham G. First Report of a Toxic Nodularia spumigena (Nostocales/ Cyanobacteria) Bloom in Sub-Tropical Australia. II. Bioaccumulation of Nodularin in Isolated Populations of Mullet (Mugilidae). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2012; 9(7):2412-2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9072412
Chicago/Turabian StyleStewart, Ian, Geoffrey K. Eaglesham, Glenn B. McGregor, Roger Chong, Alan A. Seawright, Wasantha A. Wickramasinghe, Ross Sadler, Lindsay Hunt, and Glenn Graham. 2012. "First Report of a Toxic Nodularia spumigena (Nostocales/ Cyanobacteria) Bloom in Sub-Tropical Australia. II. Bioaccumulation of Nodularin in Isolated Populations of Mullet (Mugilidae)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 9, no. 7: 2412-2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9072412
APA StyleStewart, I., Eaglesham, G. K., McGregor, G. B., Chong, R., Seawright, A. A., Wickramasinghe, W. A., Sadler, R., Hunt, L., & Graham, G. (2012). First Report of a Toxic Nodularia spumigena (Nostocales/ Cyanobacteria) Bloom in Sub-Tropical Australia. II. Bioaccumulation of Nodularin in Isolated Populations of Mullet (Mugilidae). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 9(7), 2412-2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9072412