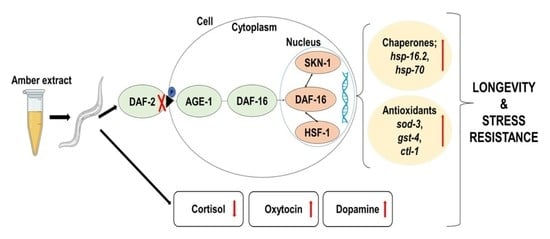
Stress Buffering and Longevity Effects of Amber Extract on Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. AE Increased Lifespan and Improved Health Span in C. elegans
2.2. AE Enhanced Stress Tolerance in C. elegans
2.3. AE Positively Regulated Levels of Stress Biomarkers in C. elegans
2.4. AE Increased the Nuclear Localization of DAF-16 and Expression of HSP-16.2, SOD-3 and GST-4
2.5. AE Increased the Messenger RNA Expression of daf-16 and Its Target Genes
2.6. AE-Mediated Stress Tolerance and Longevity Activity May Be via the IIS Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. AE Preparation and Other Reagents
4.2. C. elegans Strains, Culture and Maintenance
4.3. Longevity Assay
4.4. Health Span Assays
4.4.1. Body Length Determination
4.4.2. Reproduction Capacity Assay
4.4.3. Motility Assay
4.5. Stress Survival Assays
4.5.1. Heat Stress Survival
4.5.2. Oxidative Stress Survival
4.6. Biochemical Analysis
4.6.1. Cortisol Determination
4.6.2. Oxytocin and Dopamine Determination
4.7. Fat Accumulation Determination
4.8. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Determination
4.9. DPPH Assay
4.10. Gene Expression
4.10.1. Green Fluorescence Protein (GFP)
4.10.2. Real Time Quantitative PCR
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Mogilski, J.K.; Wysocki, A.; Reeve, S.D. Stress Hormones, Physiology, and Behavior. In The Oxford Handbook of Evolutionary Psychology and Behavioral Endocrinology; Oxford Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, B.S. Central Effects of Stress Hormones in Health and Disease: Understanding the Protective and Damaging Effects of Stress and Stress Mediators. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 583, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landis, G.N.; Tower, J. Superoxide Dismutase Evolution and Life Span Regulation. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2005, 126, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alschuler, L. HPA Axis & Stress Response: Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis. Available online: https://www.integrativepro.com/articles/the-hpa-axis (accessed on 24 December 2021).
- Sugawara, T.; Sakamoto, K. Quercetin Enhances Motility in Aged and Heat-Stressed Caenorhabditis elegans Nematodes by Modulating Both HSF-1 Activity, and Insulin-like and P38-MAPK Signalling. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broman-Fulks, J.J.; Kelso, K. Stress Management. In Wellness Literacy; Townsend, G.M., Ed.; Kendall Hunt: Dubuque, IA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, L.; Qi, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, L. Emodin Extends Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans through Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling Pathway Depending on DAF-16 and SIR-2.1. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, L.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Antistress and Anti-Aging Activities of Caenorhabditis elegans Were Enhanced by Momordica Saponin Extract. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 1819–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.S.; Lee, H.N.; Oh, J.W.; Yoon, Y.J.; Park, J.S.; Park, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Cha, D.S.; Jeon, H. Moringa oleifera Prolongs Lifespan via DAF-16/FOXO Transcriptional Factor in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2016, 22, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alex, A.; Srivastava, A. Nutraceuticals for Calming and Stress. In Nutraceuticals in Veterinary Medicine; Gupta, R.C., Srivastava, A., Lall, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 417–425. ISBN 9783030046248. [Google Scholar]
- Warmka, L. Compounds Found in Baltic Amber and Their Potential Medicinal Uses—A URS Project. 2017. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11299/190676 (accessed on 24 December 2021).
- Sogo, E.; Zhou, S.; Haeiwa, H.; Takeda, R.; Okazaki, K.; Sekita, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamano, M.; Sakamoto, K. Amber Extract Reduces Lipid Content in Mature 3T3-L1 Adipocytes by Activating the Lipolysis Pathway. Molecules 2021, 26, 4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Otto, A.; Krumbiegel, G.; Simoneit, B.R.T. The Natural Product Biomarkers in Succinite, Glessite and Stantienite Ambers from Bitterfeld, Germany. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2006, 140, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccouri, B.; Rajhi, I. Potential Antioxidant Activity of Terpenes. In Terpenes and Terpenoids—Recent Advances; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; ISBN 9781838819163. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Uchida, T.; Shimizu, E.; Higashio, H.; Ohno, M.; Uesugi, S.; Kimura, K.-I. Anti-Allergy Activities of Kuji Amber Extract and Kujigamberol. Fitoterapia 2018, 127, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tamimi, W.H.; Al-Saadi, S.A.A.M.; Burghal, A.A. Antibacterial Activity and GC-MS Analysis of Baltic Amber against Pathogenic Bacteria. Available online: https://faculty.uobasrah.edu.iq/uploads/publications/1599035651.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- Baltic Amber Jewelry for Women Men Children by Amber Artisans. Available online: https://www.amberartisans.com/baamalme.html (accessed on 24 December 2021).
- Nissen, M.D.; Lau, E.T.L.; Cabot, P.J.; Steadman, K.J. Baltic Amber Teething Necklaces: Could Succinic Acid Leaching from Beads Provide Anti-Inflammatory Effects? BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, S.; Takeda, R.; Okazaki, K.; Sekita, M.; Sakamoto, K. Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Amber Extract in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, S.; Haeiwa, H.; Takeda, R.; Okazaki, K.; Sekita, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamano, M.; Sakamoto, K. Role of Amber Extract in Protecting SHSY5Y Cells against Amyloid Β1-42-Induced Neurotoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.; Snoek, L.B.; De Bono, M.; Kammenga, J.E. Worms under Stress: C. elegans Stress Response and Its Relevance to Complex Human Disease and Aging. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Deng, N.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Chen, L.; Zheng, B.; Liu, R.H. Effects of Orange Extracts on Longevity, Healthspan, and Stress Resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 2020, 25, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontana, L.; Partridge, L.; Longo, V.D. Extending Healthy Life Span—From Yeast to Humans. Science 2010, 328, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannibal, K.E.; Bishop, M.D. Chronic Stress, Cortisol Dysfunction, and Pain: A Psychoneuroendocrine Rationale for Stress Management in Pain Rehabilitation. Phys. Ther. 2014, 94, 1816–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranabir, S.; Reetu, K. Stress and Hormones. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 15, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Valk, E.S.; Savas, M.; van Rossum, E.F.C. Stress and Obesity: Are There More Susceptible Individuals? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2018, 7, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, K.A.; Melhorn, S.J.; Sakai, R.R. Effects of Chronic Social Stress on Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2012, 1, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gems, D.; McElwee, J.J. Broad Spectrum Detoxification: The Major Longevity Assurance Process Regulated by Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling? Mech. Ageing Dev. 2005, 126, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangjan, C.; Rangsinth, P.; Gu, X.; Wink, M.; Tencomnao, T. Lifespan Extending and Oxidative Stress Resistance Properties of a Leaf Extracts from Anacardium occidentale L. in Caenorhabditis elegans. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9012396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rangsinth, P.; Prasansuklab, A.; Duangjan, C.; Gu, X.; Meemon, K.; Wink, M.; Tencomnao, T. Leaf Extract of Caesalpinia mimosoides Enhances Oxidative Stress Resistance and Prolongs Lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayuda-Durán, B.; González-Manzano, S.; Miranda-Vizuete, A.; Dueñas, M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; González-Paramás, A.M. Epicatechin Modulates Stress-Resistance in C. elegans via Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0199483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, C.T.; McCarroll, S.A.; Bargmann, C.I.; Fraser, A.; Kamath, R.S.; Ahringer, J.; Li, H.; Kenyon, C. Genes That Act Downstream of DAF-16 to Influence the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2003, 424, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, O.; Park, S.; Lee, S.-J.V. The Role of Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling in the Longevity of Model Invertebrates, C. elegans and D. melanogaster. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehghan, E.; Zhang, Y.; Saremi, B.; Yadavali, S.; Hakimi, A.; Dehghani, M.; Goodarzi, M.; Tu, X.; Robertson, S.; Lin, R.; et al. Hydralazine Induces Stress Resistance and Extends C. elegans Lifespan by Activating the NRF2/SKN-1 Signalling Pathway. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Jin, S.; Lu, Y.; Chang, S.; Liu, R.; Peng, Y.; et al. Velvet Antler Methanol Extracts (MEs) Protects against Oxidative Stress in Caenorhabditis elegans by SKN-1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.T.; Johnson, T.E. Daf-16 Integrates Developmental and Environmental Inputs to Mediate Aging in the Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-H.; Kim, B.-K.; Park, S.; Park, S.-K. Phosphatidylcholine Extends Lifespan via DAF-16 and Reduces Amyloid-Beta-Induced Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2860642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Xiao, J.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, Q.; Zheng, H.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Rosmarinic Acid Improved Antioxidant Properties and Healthspan via the IIS and MAPK Pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biofactors 2019, 45, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithgow, G.J.; Walker, G.A. Stress Resistance as a Determinate of C. elegans Lifespan. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2002, 123, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Measurement of Antioxidant Activity. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 757–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunquell, J.; Morris, S.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, F.; Westerheide, S.D. The Genome-Wide Role of HSF-1 in the Regulation of Gene Expression in Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.M.; Vale, W.W. The Role of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis in Neuroendocrine Responses to Stress. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 8, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostis, P.; Katsiki, N.; Adamidou, F.; Athyros, V.G.; Karagiannis, A.; Kita, M.; Mikhailidis, D.P. 11beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Inhibitors: Novel Agents for the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity-Related Disorders? Metabolism 2013, 62, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.O.; Kamilaris, T.C.; Chrousos, G.P.; Gold, P.W. Mechanisms of Stress: A Dynamic Overview of Hormonal and Behavioral Homeostasis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1992, 16, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, Z.R.; Abizaid, A. Stress Induced Obesity: Lessons from Rodent Models of Stress. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhama, K.; Latheef, S.K.; Dadar, M.; Samad, H.A.; Munjal, A.; Khandia, R.; Karthik, K.; Tiwari, R.; Yatoo, M.I.; Bhatt, P.; et al. Biomarkers in Stress Related Diseases/Disorders: Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Values. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2019, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuaid, R.J.; McInnis, O.A.; Paric, A.; Al-Yawer, F.; Matheson, K.; Anisman, H. Relations between Plasma Oxytocin and Cortisol: The Stress Buffering Role of Social Support. Neurobiol. Stress 2016, 3, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozbay, F.; Fitterling, H.; Charney, D.; Southwick, S. Social Support and Resilience to Stress across the Life Span: A Neurobiologic Framework. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2008, 10, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrichs, M.; Baumgartner, T.; Kirschbaum, C.; Ehlert, U. Social Support and Oxytocin Interact to Suppress Cortisol and Subjective Responses to Psychosocial Stress. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.-H. Stress and the Dopaminergic Reward System. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1879–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saul, N.; Pietsch, K.; Menzel, R.; Steinberg, C.E.W. Quercetin-Mediated Longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans: Is DAF-16 Involved? Mech. Ageing Dev. 2008, 129, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Chen, W.-D.; Wang, Y.-D. DAF-16/FOXO Transcription Factor in Aging and Longevity. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeister, R.; Schaffitzel, E.; Hertweck, M. Endocrine Signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans Controls Stress Response and Longevity. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 190, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullet, J.M.A.; Hertweck, M.; An, J.H.; Baker, J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Liu, S.; Oliveira, R.P.; Baumeister, R.; Blackwell, T.K. Direct Inhibition of the Longevity-Promoting Factor SKN-1 by Insulin-like Signaling in C. elegans. Cell 2008, 132, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forman, H.J.; Augusto, O.; Brigelius-Flohe, R.; Dennery, P.A.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Mann, G.E.; Radi, R.; Roberts, L.J., 2nd; Vina, J.; et al. Even Free Radicals Should Follow Some Rules: A Guide to Free Radical Research Terminology and Methodology. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 78, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpey, M.M.; Fridovich, I. Methods of Detection of Vascular Reactive Species: Nitric Oxide, Superoxide, Hydrogen Peroxide, and Peroxynitrite. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruber, J.; Ng, L.F.; Poovathingal, S.K.; Halliwell, B. Deceptively Simple but Simply Deceptive—Caenorhabditis elegans Lifespan Studies: Considerations for Aging and Antioxidant Effects. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3377–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Rourke, E.J.; Soukas, A.A.; Carr, C.E.; Ruvkun, G. C. elegans Major Fats Are Stored in Vesicles Distinct from Lysosome-Related Organelles. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escorcia, W.; Ruter, D.L.; Nhan, J.; Curran, S.P. Quantification of Lipid Abundance and Evaluation of Lipid Distribution in Caenorhabditis elegans by Nile Red and Oil Red O Staining. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 133, 57352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saul, N.; Möller, S.; Cirulli, F.; Berry, A.; Luyten, W.; Fuellen, G. Health and Longevity Studies in C. elegans: The “Healthy Worm Database” Reveals Strengths, Weaknesses and Gaps of Test Compound-Based Studies. Biogerontology 2021, 22, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herndon, L.A.; Wolkow, C.A.; Driscoll, M.; Hall, D.H. Effects of Ageing on the Basic Biology and Anatomy of C. elegans. In Healthy Ageing and Longevity; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 9–39. ISBN 9783319447018. [Google Scholar]
- Gusarov, I.; Shamovsky, I.; Pani, B.; Gautier, L.; Eremina, S.; Katkova-Zhukotskaya, O.; Mironov, A.; Makarov, A.A.; Nudler, E. Dietary Thiols Accelerate Aging of C. elegans. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutphin, G.L.; Kaeberlein, M. Measuring Caenorhabditis elegans Life Span on Solid Media. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 27, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugawara, T.; Sakamoto, K. Killed Bifidobacterium Longum Enhanced Stress Tolerance and Prolonged Life Span of Caenorhabditis elegans via DAF-16. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoogewijs, D.; Houthoofd, K.; Matthijssens, F.; Vandesompele, J.; Vanfleteren, J.R. Selection and Validation of a Set of Reliable Reference Genes for Quantitative Sod Gene Expression Analysis in C. elegans. BMC Mol. Biol. 2008, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Somuah-Asante, S.; Sakamoto, K. Stress Buffering and Longevity Effects of Amber Extract on Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). Molecules 2022, 27, 3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123858
Somuah-Asante S, Sakamoto K. Stress Buffering and Longevity Effects of Amber Extract on Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). Molecules. 2022; 27(12):3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123858
Chicago/Turabian StyleSomuah-Asante, Sandra, and Kazuichi Sakamoto. 2022. "Stress Buffering and Longevity Effects of Amber Extract on Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans)" Molecules 27, no. 12: 3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123858
APA StyleSomuah-Asante, S., & Sakamoto, K. (2022). Stress Buffering and Longevity Effects of Amber Extract on Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). Molecules, 27(12), 3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123858