Current Evidence for Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Lung Metastases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Definition of Oligometastatic Disease
3. Number of Metastases
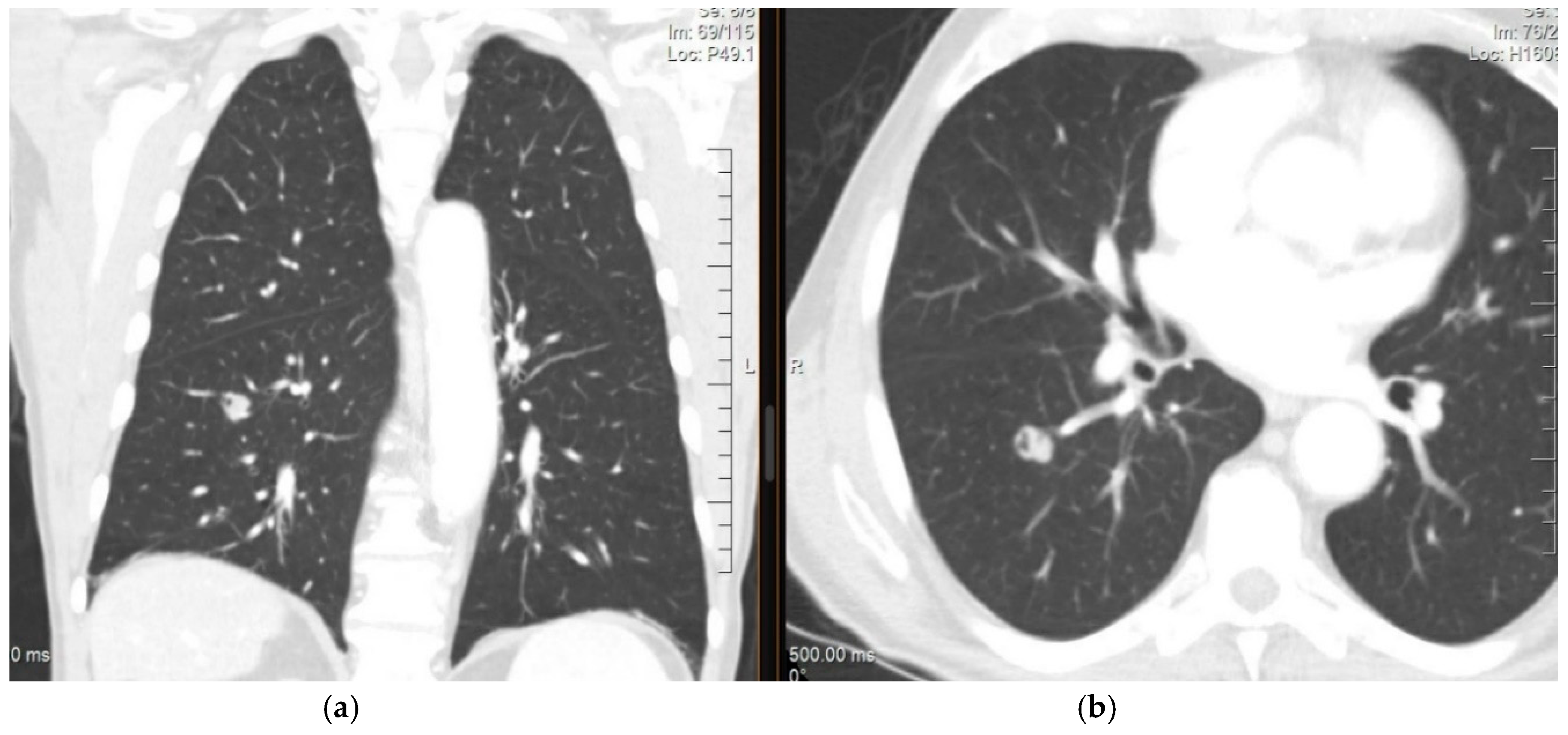
4. Diagnosis and Imaging of Lung Metastases
Imaging Studies
5. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for the Lung
Radiobiological Principles of SBRT
- Repair of sublethal cell damage;
- Cell repopulation followed by radiation;
- Cell redistribution in the cell cycle;
- Re-oxygenation of surviving cells;
6. Eligible Patients
6.1. Considerations of the Number and Size of Metastases
6.2. Peripheral and Central Lesions: Technical, Fractional, and Dose Prescription Differences
7. Treatment Volumes
8. Treatment Dose
9. Technical Requirements
- Modern linear accelerators to enable image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) and motion-management systems;
- Quality controls [72].
9.1. Simulation
9.2. Pretreatment Setup and Treatment Delivery
9.2.1. IGRT and Motion Management Systems
9.2.2. Sophisticated Immobilization Devices
9.2.3. Quality Control
10. Acute and Late Toxicity
11. Prognostic Factors
12. Conclusions
- Lung SBRT is an external beam radiation therapy method that accurately delivers a high dose of radiotherapy within a limited number of fractions, often using biologically effective doses ≥ 100 Gy10.
- Its use in treating lung oligometastases is becoming increasingly prevalent with evidence supporting both a clinical benefit and limited toxicity.
- There is variation in the dose-fractionation schedules used, and an optimal regimen for central or ultracentral tumours has yet to be defined.
- The main technical requirements for SBRT include modern linear accelerators with image-guided radiation therapy, advanced immobilization devices, motion management strategies, and quality controls.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Londero, F.; Grossi, W.; Morelli, A.; Parise, O.; Masullo, G.; Tetta, C.; Livi, U.; Maessen, J.G.; Gelsomino, S. Surgery versus stereotactic radiotherapy for treatment of pulmonary metastases. A systematic review of literature. Futur. Sci. OA 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sauter, E.R.; Bolton, J.S.; Willis, G.W.; Farr, G.H.; Sardi, A. Improved survival after pulmonary resection of metastatic colorectal carcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 1990, 43, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, U.; Buyse, M.; Friedel, G.; Ginsberg, R.J.; Girard, P.; Goldstraw, P.; Johnston, M.; McCormack, P.; Pass, H.; Putnam, J.B. Long-term results of lung metastasectomy: Prognostic analyses based on 5206 cases. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1997, 113, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okunieff, P.; Petersen, A.L.; Philip, A.; Milano, M.T.; Katz, A.W.; Boros, L.; Schell, M. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) for lung metastases. Acta Oncol. 2006, 45, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusthoven, K.E.; Kavanagh, B.D.; Burri, S.H.; Chen, C.; Cardenes, H.; Chidel, M.A.; Pugh, T.J.; Kane, M.; Gaspar, L.E.; Schefter, T.E. Multi-Institutional Phase I/II Trial of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Lung Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, A.; Kunieda, E.; Ohashi, T.; Aoki, Y.; Koike, N.; Takeda, T. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for oligometastatic lung tumors from colorectal cancer and other primary cancers in comparison with primary lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 101, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohopolski, M.J.; Horne, Z.; Clump, D.; Burton, S.A.; E Heron, D.E. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Pulmonary Oligometastases Arising from Non-lung Primaries in Patients without Extrapulmonary Disease. Cureus 2018, 10, e2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomez, D.R.; Blumenschein, G.R., Jr.; Lee, J.J.; Hernandez, M.; Ye, R.; Camidge, D.R.; Doebele, R.C.; Skoulidis, F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gibbons, D.L. Local consolidative therapy versus maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer without progression after first-line systemic therapy: A multicentre randomised, controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Yaremko, B.P. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard of care palliative treatment in patients with oligometastatic cancers (SABR-COMET): A randomised, phase 2, open-label trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greelish, J.P.; Friedberg, J.S. Secondary pulmonary malignancy. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 80, 633–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budczies, J.; Von Winterfeld, M.; Klauschen, F.; Bockmayr, M.; Lennerz, J.K.; Denkert, C.; Wolf, T.; Warth, A.; Dietel, M.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; et al. The landscape of metastatic progression patterns across major human cancers. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnan, K.; Khanna, C.; Helman, L.J. The Molecular Biology of Pulmonary Metastasis. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2006, 16, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, H.H. Progression and metastasis of lung cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stella, G.M.; Kolling, S.; Benvenuti, S.; Bortolotto, C. Lung-seeking metastases. Cancers 2019, 11, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellman, S.; Weichselbaum, R.R. Oligometastases. J. Clin. Oncol 1995, 13, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichselbaum, R.R.; Hellman, S. Oligometastases revisited. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol 2011, 8, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Heo, J.S.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, D.W.; Choi, S.H. Surgical resection of synchronous and metachronous lung and liver metastases of colorectal cancers. Ann. Surg Treat. Res. 2017, 92, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Correa, R.J.M.; Salama, J.K.; Milano, M.T.; Palma, D.A. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Oligometastasis. Cancer J. 2016, 22, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helou, J.; Thibault, I.; Poon, I.; Chiang, A.; Jain, S.; Soliman, H.; Erler, D.; Yeung, L.; Cheung, P. Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy for Pulmonary Metastases: Histology, Dose, and Indication Matter. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.L.; Porceddu, S.; Nakamura, N.; Palma, D.A.; Lo, S.S.; Hoskin, P.; Moghanaki, D.; Chmura, S.J.; Salama, J.K. Definitive Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) for Extracranial Oligometastases. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 40, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligoprogressive cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20160251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanne, D.H.; Heitmann, J.; Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N.H.J. Evolution of treatment strategies for oligometastatic NSCLC patients—A systematic review of the literature. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 80, 101892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Palma, D.; A Haasbeek, C.J.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Dahele, M.; Lock, M.; Yaremko, B.; Olson, R.; Liu, M.; Panarotto, J.; Griffioen, G.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for comprehensive treatment of oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET): Study protocol for a randomized phase II trial. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, D.; Ahn, Y.C.; Seo, J.M.; Shin, E.H.; Park, H.C.; Lim, D.H.; Pyo, H. Potentially curative stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for single or oligometastasis to the lung. Acta Oncol. 2012, 51, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widder, J.; Klinkenberg, T.J.; Ubbels, J.F.; Wiegman, E.M.; Groen, H.J.M.; Langendijk, J.A. Pulmonary oligometastases: Metastasectomy or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy? Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 107, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, J.K.; Hasselle, M.D.; Chmura, S.J.; Malik, R.; Mehta, N.; Yenice, K.M.; Villaflor, V.M.; Stadler, W.M.; Hoffman, P.C.; Cohen, E.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for multisite extracranial oligometastases: Final report of a dose escalation trial in patients with 1 to 5 sites of metastatic disease. Cancer 2012, 118, 2962–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Niibe, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Dekura, Y.; Oh, R.-J.; Yamashita, H.; Kakuhara, H.; Aoki, M.; Jingu, K. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for pulmonary oligometastases from esophageal cancer: Results and prognostic factors. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Correa, R.J.M.; Schneiders, F.; Haasbeek, C.J.A.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Lock, M.; Yaremko, B.P.; Bauman, G.S.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of 4–10 oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET-10): Study protocol for a randomized phase III trial. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomez, D.R.; Tang, C.; Zhang, J.; Blumenschein, G.R.J.; Hernandez, M.; Lee, J.J.; Ye, R.; Palma, D.A.; Louie, A.V.; Camidge, D.R.; et al. Local consolidative therapy vs. maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: Long-term results of a multi-institutional, phase II, randomized study. J. Clin. Oncol 2019, 195, 1113–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.T.; Aronchick, J.M.; Epstein, D.M.; Gefter, W.B. The troublesome nipple shadow. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1985, 145, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahan, W.G.; Shah, J.P.; Castro, E.B. Benign solitary lung lesions in patients with cancer. Ann. Surg 1978, 187, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruickshank, A.; Stieler, G.; Ameer, F. Evaluation of the solitary pulmonary nodule. Intern. Med. J. 2019, 49, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deppen, S.A.; Blume, J.D.; Kensinger, C.D.; Morgan, A.M.; Aldrich, M.C.; Massion, P.P.; Walker, R.C.; McPheeters, M.L.; Putnam, J.B., Jr.; Grogan, E.L. Accuracy of FDG-PET to diagnose lung cancer in areas with infectious lung disease: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2014, 312, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, R.; Fiorentino, A.; Di Paola, G.; Levra, N.G.; Ricchetti, F.; Fersino, S.; Tebano, U.; Pasetto, S.; Ruggieri, R.; Salgarello, M.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy for Lung Oligometastases: Predictive Parameters of Early Response by 18 FDG-PET/CT. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiono, S.; Endo, M.; Suzuki, K.; Yarimizu, K.; Hayasaka, K. The prognostic value of positron emission tomography/computed tomography in pulmonary metastasectomy. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, E.M.; Sanders, G.D.; Trotter, P.R.; Patz, J.E.F.; A Silvestri, G.; Owens, D.K.; Gould, M.K. Validation of two models to estimate the probability of malignancy in patients with solitary pulmonary nodules. Thorax 2008, 63, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evangelista, L.; Panunzio, A.; Polverosi, R.; Pomerri, F.; Rubello, D. Indeterminate lung nodules in cancer patients: Pretest probability of malignancy and the role of18F-FDG PET/CT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwig, D.; Baum, R.P.; Kirsch, C.M. FDG-PET, PET/CT and conventional nuclear medicine procedures in the evaluation of lung cancer: A systematic review. NuklearMedizin 2009, 48, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, M.T.; Viswanathan, C.; Carter, B.W.; Mawlawi, O.; Marom, E.M. PET/CT in the Thorax: Pitfalls. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 52, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebofsky, R.; Decraene, C.; Bernard, V.; Kamal, M.; Blin, A.; Leroy, Q.; Frio, T.R.; Pierron, G.; Callens, C.; Bieche, I.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA as a non-invasive substitute to metastasis biopsy for tumor genotyping and personalized medicine in a prospective trial across all tumor types. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, R.D.; Paulus, R.; Pass, H.I.; Gore, E.M.; Edelman, M.J.; Galvin, J.; Straube, W.L.; Nedzi, L.A.; McGarry, R.C.; Robinson, C.G.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for operable early-stage lung cancer findings from the NRG oncology RTOG 0618 trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videtic, G.M.; Donington, J.; Giuliani, M.; Heinzerling, J.; Karas, T.Z.; Kelsey, C.R.; Lally, B.E.; Latzka, K.; Lo, S.S.; Moghanaki, D.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: Executive Summary of an ASTRO Evidence-Based Guideline. Pr. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 7, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benedict, S.H.; Yenice, K.M.; Followill, D.; Galvin, J.M.; Hinson, W.; Kavanagh, B.; Keall, P.; Lovelock, M.; Meeks, S.; Papiez, L.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy: The report of AAPM Task Group 101. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 4078–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahgal, A.; Roberge, D.; Schellenberg, D.; Purdie, T.; Swaminath, A.; Pantarotto, J.; Filion, E.; Gabos, Z.; Butler, J.; Letourneau, D.; et al. The Canadian Association of Radiation Oncology Scope of Practice Guidelines for Lung, Liver and Spine Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 24, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkbride, P.; Cooper, T. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. Guidelines for Commissioners, Providers and Clinicians: A National Report. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 23, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N.H.; Alheit, H.; Holy, R.; Moustakis, C.; Nestle, U.; A Sauer, O. Definition of stereotactic body radiotherapy: Principles and practice for the treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2014, 190, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, J.M.; Carlson, D.J.; Brenner, D.J. The Tumor Radiobiology of SRS and SBRT: Are More than the 5 Rs Involved? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 88, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.-S.; Kim, W.; Park, I.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, E.; Jung, J.-H.; Cho, L.C.; Song, C.W. Radiobiological mechanisms of stereotactic body radiation therapy and stereotactic radiation surgery. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2015, 33, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanksley, J.; Salama, J.K.; Kirkpatrick, J.P. Rationale for Fractionated SRS and Single SRS Session Approaches. In Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy; Trifiletti, D., Chao, S., Sahgal, A., Sheehan, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Salerno, K.E.; Citrin, D.E. Biology of Radiation-Induced Lung Injury. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 31, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, E.K.; Hui, S.; Brooks, J.; Dasu, A.; Kujawski, M.; Toma-Dasu, I. Radiation-induced Vascular Damage and the Impact on the Treatment Outcome of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. Anticancer. Res. 2019, 39, 2721–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karam, S.D.; Bhatia, S. The radiobiological targets of SBRT: Tumor cells or endothelial cells? Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Griffin, R.J.; Hui, S.; Levitt, S.H.; Song, C.W. Radiation-induced vascular damage in tumors: Implications of vascular damage in ablative hypofractionated radiotherapy (SBRT and SRS). Radiat. Res. 2012, 177, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, C.W.; Park, H.; Griffin, R.J.; Levitt, S.H. Radiobiology of Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. In Technical Basis of Radiation Therapy. Medical Radiology; Levitt, S., Purdy, J., Perez, C., Poortmans, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Fowler, J.F.; Lamond, J.P.; Lanciano, R.; Feng, J.; Brady, L.W. Red Shell: Defining a High-Risk Zone of Normal Tissue Damage in Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 77, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, E.K.; Antonovic, L.; Dasu, A.; Lax, I.; Wersäll, P.; Toma-Dasu, I. Treatment fractionation for stereotactic radiotherapy of lung tumours: A modelling study of the influence of chronic and acute hypoxia on tumour control probability. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toma-Dasu, I.; Sandström, H.; Barsoum, P.; Dasu, A. To fractionate or not to fractionate? That is the question for the radiosurgery of hypoxic tumors. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121 (Suppl. 2), 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirkpatrick, J.P.; Meyer, J.J.; Marks, L.B. The linear-quadratic model is inappropriate to model high dose per fraction effects in radiosurgery. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 18, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocher, M.; Treuer, H.; Voges, J.; Hoevels, M.; Sturm, V.; Müller, R.-P. Computer simulation of cytotoxic and vascular effects of radiosurgery in solid and necrotic brain metastases. Radiother. Oncol. 2000, 54, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Barros, M.; Paris, F.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Lyden, D.; Rafii, S.; Haimovitz-Friedman, A.; Fuks, Z.; Kolesnick, R. Tumor Response to Radiotherapy Regulated by Endothelial Cell Apoptosis. Science 2003, 300, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuks, Z.; Kolesnick, R. Engaging the vascular component of the tumor response. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moding, E.J.; Castle, K.D.; Perez, B.A.; Oh, P.; Min, H.D.; Norris, H.; Ma, Y.; Cardona, D.; Lee, C.-L.; Kirsch, D.G. Tumor cells, but not endothelial cells, mediate eradication of primary sarcomas by stereotactic body radiation therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 278ra34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giuliani, M.E.; Bissonnette, J.-P.; Lo, S.; Teh, B.S.; A Mayr, N.; Machtay, M. Target contouring & treatment planning in lung SBRT. Clin. Insights Stereotact Body Radiat. Ther. Lung Cancer 2013, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahele, M.; Pearson, S.; Purdie, T.; Bissonnette, J.-P.; Franks, K.; Brade, A.; Cho, J.; Sun, A.; Hope, A.; Marshall, A.; et al. Practical Considerations Arising from the Implementation of Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) at a Comprehensive Cancer Center. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grills, I.S.; Hugo, G.; Kestin, L.L.; Galerani, A.P.; Chao, K.K.; Wloch, J.; Yan, D. Image-Guided Radiotherapy via Daily Online Cone-Beam CT Substantially Reduces Margin Requirements for Stereotactic Lung Radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 70, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, R.; Paulus, R.; Galvin, J.; Michalski, J.; Straube, W.; Bradley, J.; Fakiris, A.; Bezjak, A.; Videtic, G.; Johnstone, D. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA 2010, 303, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wegner, R.E.; Abel, S.; Hasan, S.; Schumacher, L.Y.; Colonias, A. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) for Oligometastatic Lung Nodules: A Single Institution Series. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N.; Dieckmann, K.; Hoogeman, M.S.; Hoyer, M.; Hurkmans, C.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Lartigau, E.; Romero, A.M.; Senan, S.; et al. ESTRO ACROP consensus guideline on implementation and practice of stereotactic body radiotherapy for peripherally located early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kilmer, P.D. Review Article: Review Article. J. Theory Pract. Crit. 2010, 11, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, A.; Davis, J.; Rate, W.; Yang, J.; Perry, D.; Pablo, J.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Sharma, S.; Sundararaman, S.; Kolker, J.; et al. Lung metastases treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: The RSSearch® patient Registry’s experience. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernard, M.E.; Critchfield, L.; Kudrimoti, M. Safety of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Seven Ipsilateral Lung lesions. Cureus 2020, 12, e8759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guckenberger, M.; Baus, W.W.; Blanck, O.; Combs, S.E.; Debus, J.; Engenhart-Cabillic, R.; Gauer, T.; Grosu, A.L.; Schmitt, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; et al. Definition and quality requirements for stereotactic radiotherapy: Consensus statement from the DEGRO/DGMP Working Group Stereotactic Radiotherapy and Radiosurgery. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2020, 196, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pennathur, A. Lung SBRT. In Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT); Dwight, E., Ed.; Springer Publishing Company: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 183–200. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.H.; Poon, I.; Erler, D.; Zhang, L.; Cheung, P. The safety and effectiveness of stereotactic body radiotherapy for central versus ultracentral lung tumors. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 129, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmerman, R.; McGarry, R.; Yiannoutsos, C.; Papiez, L.; Tudor, K.; DeLuca, J.; Ewing, M.; Abdulrahman, R.; Desrosiers, C.; Williams, M.; et al. Excessive Toxicity When Treating Central Tumors in a Phase II Study of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Medically Inoperable Early-Stage Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4833–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.N.; Medbery, C.; Sharma, S.; Pablo, J.; Kimsey, F.; Perry, D.; Muacevic, A.; Mahadevan, A. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for centrally located early-stage non-small cell lung cancer or lung metastases from the RSSearch® patient registry. Radiat Oncol. 2015, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bral, S.; Gevaert, T.; Linthout, N.; Versmessen, H.; Collen, C.; Engels, B.; Verdries, D.; Everaert, H.; Christian, N.; De Ridder, M.; et al. Prospective, Risk-Adapted Strategy of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early-Stage Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results of a Phase II Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 80, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lischalk, J.W.; Malik, R.M.; Collins, S.P.; Collins, B.T.; Matus, I.A.; Anderson, E.D. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for high-risk central pulmonary metastases. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milano, M.T.; Chen, Y.; Katz, A.W.; Philip, A.; Schell, M.C.; Okunieff, P. Central thoracic lesions treated with hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 91, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.A.; Tang, C.; Binkley, M.S.; Jin, M.; Wynne, J.F.; von Eyben, R.; Hara, W.Y.; Trakul, N.; Loo, B.W.; Diehn, M. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) for treatment of central and ultra-central lung tumors. Lung Cancer 2015, 89, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezjak, A.; Paulus, R.; Gaspar, L.E.; Timmerman, R.D.; Straube, W.L.; Ryan, W.F.; Garces, Y.I.; Pu, A.T.; Singh, A.K.; Videtic, G.M.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of a Five-Fraction Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Schedule for Centrally Located Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: NRG Oncology/RTOG 0813 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hallaq, H.A.; Chmura, S.; Salama, J.K.; Winter, K.A.; Robinson, C.G.; Pisansky, T.M.; Borges, V.; Lowenstein, J.R.; McNulty, S.; Galvin, J.M.; et al. Rationale of technical requirements for NRG-BR001: The first NCI-sponsored trial of SBRT for the treatment of multiple metastases. Pr. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 6, e291–e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unger, K.; Ju, A.; Oermann, E.; Suy, S.; Yu, X.; Vahdat, S.; Subramaniam, D.; Harter, K.W.; Collins, S.P.; Dritschilo, A.; et al. CyberKnife for hilar lung tumors: Report of clinical response and toxicity. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2010, 3, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rowe, B.P.; Boffa, D.J.; Wilson, L.D.; Kim, A.W.; Detterbeck, F.C.; Decker, R.H. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Central Lung Tumors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuyttens, J.J.; Zyp, N.C.V.D.V.V.; Praag, J.; Aluwini, S.; van Klaveren, R.J.; Verhoef, C.; Pattynama, P.M.; Hoogeman, M.S. Outcome of four-dimensional stereotactic radiotherapy for centrally located lung tumors. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 102, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuyttens, J.J.; Zyp, N.C.V.D.V.V.; Verhoef, C.; Maat, A.; Van Klaveren, R.J.; Van Der Holt, B.; Aerts, J.; Hoogeman, M. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Oligometastases to the Lung: A Phase 2 Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 91, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseltine, J.M.; Rimner, A.; Gelblum, D.; Modh, A.; Rosenzweig, K.E.; Jackson, A.; Yorke, E.D.; Wu, A.J. Fatal complications after stereotactic body radiation therapy for central lung tumors abutting the proximal bronchial tree. Pr. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 6, e27–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindberg, K.; Bergström, P.; Brustugun, O.T.; Engelholm, S.; Grozman, V.; Hoyer, M.; Karlsson, K.; Khalil, A.; Kristiansen, C.; Lax, I.; et al. OA24.05 The Nordic HILUS-Trial—First Report of a Phase II Trial of SBRT of Centrally Located Lung Tumors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, S340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Román, A.; Perez-Rozos, A.; Otero, A.; Jodar, C.; García-Ríos, I.; Lupiañez-Perez, Y.; Medina, J.A.; Gomez-Millan, J. Efficacy and safety of a simplified SBRT regimen for central and peripheral lung tumours. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 22, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, M.J.; Ricardi, U.; Ball, D.; Salama, J.K. Ablative Approaches for Pulmonary Metastases. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2016, 26, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillet, V.; Booth, J.T.; Keall, P. IGRT and motion management during lung SBRT delivery. Phys. Medica 2017, 44, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, T.D.; Balter, J.M.; Benedict, S.H.; Fraass, B.A.; Kavanagh, B.D.; Miyamoto, C.T.; Pawlicki, T.; Potters, L.; Yamada, Y. Quality and safety considerations in stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic body radiation therapy: Executive summary. Pr. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 2, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricardi, U.; Badellino, S.; Filippi, A.R. What do radiation oncologists require for future advancements in lung SBRT? Phys. Medica 2017, 44, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdie, T.; Bissonnette, J.-P.; Franks, K.; Bezjak, A.; Payne, D.; Sie, F.; Sharpe, M.B.; Jaffray, D. Cone-Beam Computed Tomography for On-Line Image Guidance of Lung Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Localization, Verification, and Intrafraction Tumor Position. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2007, 68, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, C.; Grills, I.S.; Kestin, L.L.; McGrath, S.; Ye, H.; Martin, S.K.; Yan, D. Intrafraction Variation of Mean Tumor Position during Image-Guided Hypofractionated Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 1636–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Paysan, P.; Zhang, Z.; Seghers, D.; Brehm, M.; Munro, P. Optimization-Based Reconstruction from Megavoltage Cone-beam CT Data in Image Guided Radiation Therapy. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312068407_Optimization-based_Reconstruction_from_Megavoltage_Cone-beam_CT_Data_in_Image_Guided_Radiation_Therapy/citation/download (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Shah, A.P.; Langen, K.M.; Ruchala, K.J.; Cox, A.; Kupelian, P.A.; Meeks, S.L. Patient Dose from Megavoltage Computed Tomography Imaging. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 70, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, J.K.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Yin, F.-F. Stereotactic body radiotherapy treatment of extracranial metastases. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.P.; Kupelian, P.A.; Waghorn, B.J.; Willoughby, T.R.; Rineer, J.M.; Mañon, R.R.; Vollenweider, M.A.; Meeks, S.L. Real-Time Tumor Tracking in the Lung Using an Electromagnetic Tracking System. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 86, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.D.; Lawrence, Y.R.; Appel, S.; Landau, E.; Ben-David, M.A.; Rabin, T.; Benayun, M.; Dubinski, S.; Weizman, N.; Alezra, D.; et al. Continuous positive airway pressure for motion management in stereotactic body radiation therapy to the lLung: A Controlled Pilot study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 93, 391–399, Earlier versions of this work were accepted for presentation at the third ESTRO Forum, 24–28 April 2015, in Barcelona, Spain, and ISCORT, 27–30 January 2015, in Eilat, Israel Study. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molitoris, J.K.; Diwanji, T.; Snider, J.W.; Mossahebi, S.; Samanta, S.; Onyeuku, N.; Mohindra, P.; Choi, J.I.; Simone, C.B. Optimizing immobilization, margins, and imaging for lung stereotactic body radiation therapy. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasa, I.J.; Cheng, C.-W.; Watts, R.J.; Ahnesjoö, A.; Gibbons, J.; Li, X.A.; Lowenstein, J.; Mitra, R.K.; Simon, W.E.; Zhu, T.C. TG-106 of the Therapy Physics Committee of the AAPM. Accelerator beam data commissioning equipment and procedures: Report of the TG-106 of the Therapy Physics Committee of the AAPM. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 4186–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Radiology. ACR–ASTRO Practice Parameter for Radiation Oncology. [Updated 2018; Cited 2021 March 10]. Available online: https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/Practice-Parameters/radonc.pdf?la=en (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Matsuo, Y. Interinstitutional variations in planning for stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, N.; Biedermann, G.; Yang, W.; Cai, J.; Benedict, S.; Sheng, K.; Kavanagh, B.; Larner, J. Chest Wall Volume Receiving More than 30 Gy Predicts Risk of Severe Pain and/or Rib Fracture Following Lung SBRT. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 72, S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Duijm, M.; Hoop, E.O.-D.; Aerts, J.G.; Verhoef, C.; Hoogeman, M.; Nuyttens, J.J. Survival and prognostic factors of pulmonary oligometastases treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2018, 58, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kessel, K.A.; Grosser, R.C.E.; Kraus, K.M.; Hoffmann, H.; Oechsner, M.; Combs, S.E. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in patients with lung metastases—Prognostic factors and long-term survival using patient self-reported outcome (PRO). BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jingu, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Onishi, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Aoki, M.; Murakami, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Kakuhara, H.; Nemoto, K.; Sakayauchi, T.; et al. Dose Escalation Improves Outcome in Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Pulmonary Oligometastases from Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2017, 37, 2709–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Age | Any |
|---|---|
| ECOG | 0–2 |
| Medically operable patients | Patients who refuse surgical intervention |
| Number of lesions | Range 1–5 |
| Tumor diameter | <50 mm |
| Location | Peripheral Central |
| Medically inoperable patients | Poor lung function: FEV1 < 40% predicted, postoperative FEV1 < 30% predicted, decrease diffusing capacity < 40% predicted, baseline hypoxemia (≤70 mm Hg) and/or hypercapnia (>50 mmHg), and oxygen consumption during exercise < 50% predicted. Important comorbidities: Severe pulmonary hypertension; diabetes mellitus with end-organ damage; severe cerebral, cardiovascular or peripheral vascular disease; or severe chronic heart disease |
| Author/Year | Location | Technique Description | Prescribed Dose | Local Control | Overall Survival | Grade > 3 Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milano et al. 2009 [79] | Central | Relaxed end-expiratory breath holding | Dmean 50 Gy (30–63 Gy) most in 4–5 Gy per fx | 73% at 2 yr | 47% at 2 yr | 5/53 pts w/grade 5 |
| Unger et al. 2010 [83] | Central | CyberKnife system with synchrony fiducial tracking technology | 30–40 Gy in 5 fx | 63% at 1 yr | 54% at 1 yr | 3/20 pts w/severe pneumonitis |
| Rowe et al. 2012 [84] | Central 100% | 4D-CT with ITV and CBCT guidance system | 75% BED 100 Gy 57% 12.5 Gy × 4 fx 25% BED <100 Gy | 75% at 2 yr | _______ | 5/47 patients |
| Nuyttens et al. 2012 [85] | Central | CyberKnife respiratory tumor tracking system | 45–60 Gy/5–6 Fx | 64% at 2 yr | 75% at 2 yr | No grade 4–5 toxicity, 17.12% grade 3 |
| Nuyttens et al. 2014 [86] | Peripheral Size >3 cm | Real-time tumor tracking + radiopaque markers | 60 Gy/3 fx | 90% at 2 yr | 58% at 3 yr | No grade 4–5 toxicity |
| Peripheral Size <3 cm | 30 Gy/1 fx | 74% at 2 yr | ||||
| Central | 60 Gy/5 fx | 100% at 2 yr | 53% at 3 yr | |||
| Central in contact with the esophagus or mediastinum. | 56 Gy/7 fx | 100% at 2 yr | ||||
| Chaudhuri et al. 2015 [80] | Central 50% | IMRT/4D-CT/PET respiratory gating | (78%) 50 Gy/4 fx; (22%) 50.4 Gy/5 fx. Proportionally, more centrally located with 5 fx. | _______ | 73.8% at 2 yr No differences regarding tumor location | 3% at 3 yr |
| Peripheral 50% | _______ | 11.6% at 3 yr | ||||
| Davis et al. 2015 [76] | Central | CyberKnife with synchrony respiratory motion tracking system | Dmean 37.5 Gy (16–60 Gy) in 1–5 fx (media 3 fx), Dmean BED 93.6 Gy | 69.8% at 2 yr | 49.5% at 2 yr | No grade 3–5 toxicity |
| Haseltine et al. 2015 [87] | Central | 4D-CT with ITV and CBCT guidance system | 36–60 Gy in 2–5 fx, 56% received 45 Gy in 5 fx | 77.4% at 2 yr | 63.9% at 2 yr | 12%, four patients with grade 5 |
| Lischalk et al. 2016 [78] | Central | Synchrony respiratory motion tracking system with fiducial markers | 35–40 Gy/5 fx BED 59.5–72 Gy | 57.4% at 2 yr No differences regarding the prescribed dose | 40% at 2 yr No differences regarding the prescribed dose | 15% (one patient with grade 4) |
| Lindberg et al. 2017 [88] | Central ≤1 cm from the proximal bronchial tree | _______ | 56 Gy/8 fx | _______ | _______ | 28% grade 3–5 |
| Tumor Location | Dose to PTV | BED10 of the Prescribed Dose to the PTV |
|---|---|---|
| Peripheral | 3 × 15 Gy (45 Gy) | 113 Gy BED10 |
| Central | 4 × 12 Gy (48 Gy) | 106 Gy BED10 |
| Prescribed Dose for PTV | BED10 of the Prescribed Dose to the PTV |
|---|---|
| 8 × 7.5 Gy (60 Gy) | 105 Gy BED10 |
| 5 × 10 Gy (50 Gy) | 100 Gy BED10 |
| 4 × 12 Gy (48 Gy) | 106 Gy BED10 |
| 3 × 18–20 Gy (54–60 Gy) | 151–180 Gy BED10 |
| 1 × 34 Gy (34 Gy) | 150 Gy BED10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez, E.; Sánchez, I.; Díaz, O.; Valles, A.; Balderrama, R.; Fuentes, J.; Lara, B.; Olimón, C.; Ruiz, V.; Rodríguez, J.; et al. Current Evidence for Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Lung Metastases. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 2560-2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28040233
Gutiérrez E, Sánchez I, Díaz O, Valles A, Balderrama R, Fuentes J, Lara B, Olimón C, Ruiz V, Rodríguez J, et al. Current Evidence for Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Lung Metastases. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(4):2560-2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28040233
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez, Enrique, Irving Sánchez, Omar Díaz, Adrián Valles, Ricardo Balderrama, Jesús Fuentes, Brenda Lara, Cipatli Olimón, Víctor Ruiz, José Rodríguez, and et al. 2021. "Current Evidence for Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Lung Metastases" Current Oncology 28, no. 4: 2560-2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28040233
APA StyleGutiérrez, E., Sánchez, I., Díaz, O., Valles, A., Balderrama, R., Fuentes, J., Lara, B., Olimón, C., Ruiz, V., Rodríguez, J., Bayardo, L. H., Chan, M., Villafuerte, C. J., Padayachee, J., & Sun, A. (2021). Current Evidence for Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Lung Metastases. Current Oncology, 28(4), 2560-2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28040233








