New Insights into the Biology and Diagnosis of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphomas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Presentation and Current Care
2.2. Diagnosis
2.2.1. Cytology, Immunophenotype, and Pathology
2.2.2. Cytogenetics
2.3. Molecular Biology
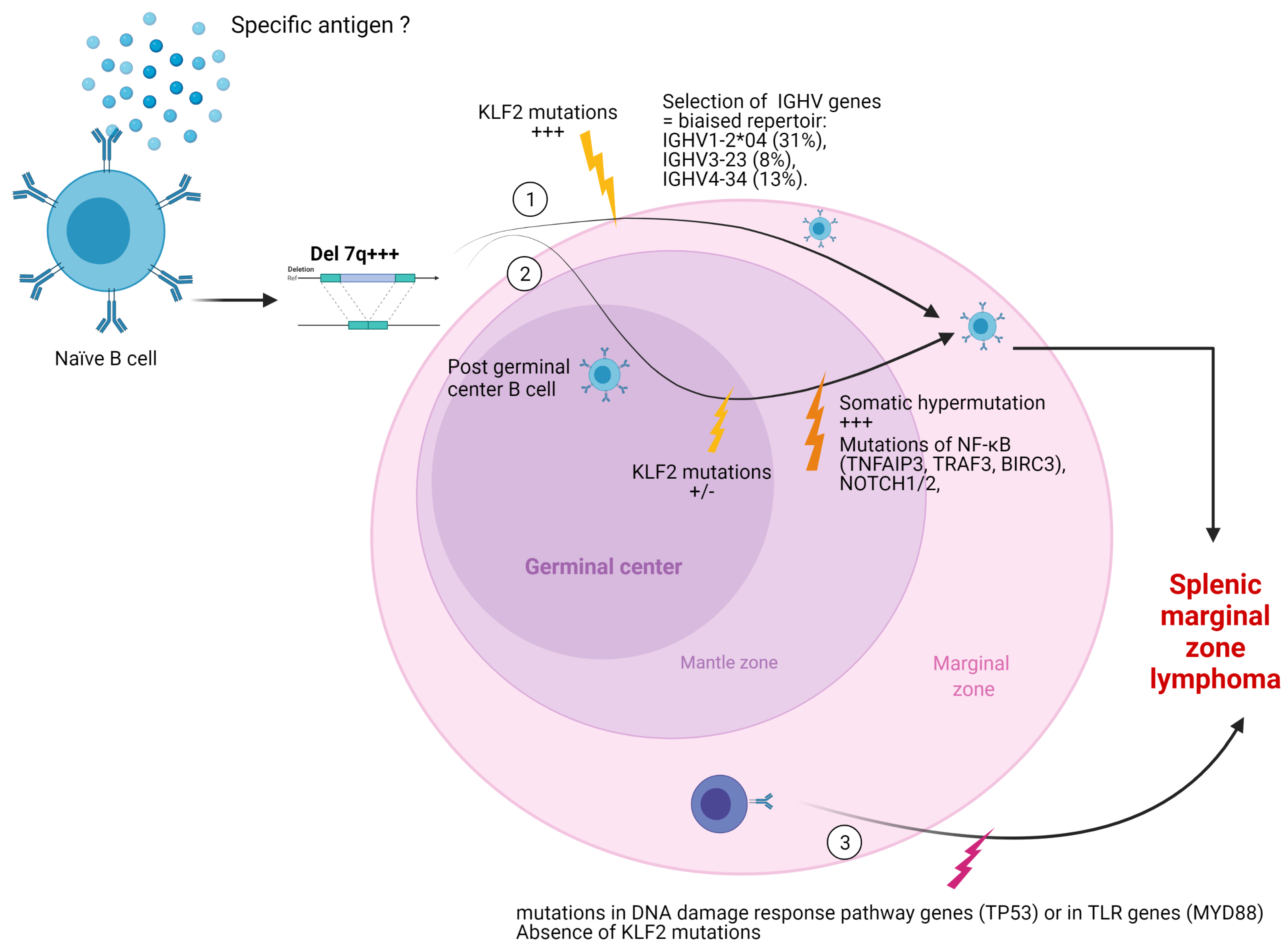
2.3.1. Mutational Status of Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain (IGVH) Genes
2.3.2. MicroRNA
2.3.3. Mutational Landscape
2.3.4. Epigenetic Regulation
2.4. Microenvironment
2.5. Limitations
2.6. Future Perspectives
2.6.1. Future Studies
2.6.2. Potentially Novel Therapeutic Targets
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arcaini, L.; Rossi, D.; Paulli, M. Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: From Genetics to Management. Blood 2016, 127, 2072–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrone, S.; D’Elia, G.M.; Annechini, G.; Ferretti, A.; Tosti, M.E.; Foà, R.; Pulsoni, A. Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Prognostic Factors, Role of Watch and Wait Policy, and Other Therapeutic Approaches in the Rituximab Era. Leuk. Res. 2016, 44, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, A.G.; Caimi, P.F.; Fu, P.; Massoud, M.R.; Meyerson, H.; Hsi, E.D.; Mansur, D.B.; Cherian, S.; Cooper, B.W.; De Lima, M.J.G.; et al. Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Excellent Outcomes in 64 Patients Treated in the Rituximab Era. Hematol. Amst. Neth. 2017, 22, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Risk Stratification for Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Based on Haemoglobin Concentration, Platelet Count, High Lactate Dehydrogenase Level and Extrahilar Lymphadenopathy: Development and Validation on 593 Cases–PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22924582/ (accessed on 2 December 2020).
- Montalban, C.; Abraira, V.; Arcaini, L.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; Guisado-Vasco, P.; Iannitto, E.; Mollejo, M.; Matutes, E.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Salar, A.; et al. Simplification of Risk Stratification for Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: A Point-Based Score for Practical Use. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traverse-Glehen, A.; Baseggio, L.; Salles, G.; Felman, P.; Berger, F. Splenic Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma: A Distinct Clinicopathological and Molecular Entity. Recent Advances in Ontogeny and Classification. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2011, 23, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz Seval, G.; Topcuoglu, P.; Arslan, O.; Gurman, G.; Demirer, T.; Kuzu, I.; Ozcan, M. Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Factors in a Series of 52 Patients. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asatiani, E.; Cohen, P.; Ozdemirli, M.; Kessler, C.M.; Mavromatis, B.; Cheson, B.D. Monoclonal Gammopathy in Extranodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma (ENMZL) Correlates with Advanced Disease and Bone Marrow Involvement. Am. J. Hematol. 2004, 77, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucca, E.; Arcaini, L.; Buske, C.; Johnson, P.W.; Ponzoni, M.; Raderer, M.; Ricardi, U.; Salar, A.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Thieblemont, C.; et al. Marginal Zone Lymphomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bennett, M.; Schechter, G.P. Treatment of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Splenectomy Versus Rituximab. Semin. Hematol. 2010, 47, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, A.; Hollander, P.; Baecklund, E.; Smedby, K.E.; Enblad, G.; Amini, R. Superior Outcome for Splenectomised Patients in a Population-based Study of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma in Sweden. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 194, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noy, A.; de Vos, S.; Coleman, M.; Martin, P.; Flowers, C.R.; Thieblemont, C.; Morschhauser, F.; Collins, G.P.; Ma, S.; Peles, S.; et al. Durable Ibrutinib Responses in Relapsed/Refractory Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Long-Term Follow-up and Biomarker Analysis. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5773–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, F.; Rossi, D.; Zucca, E. Recent Advances in Understanding the Biology of Marginal Zone Lymphoma. F1000Research 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertoni, F.; Rossi, D.; Raderer, M.; Zucca, E. Marginal Zone Lymphomas. Cancer J. 2020, 26, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Martín, Y.; Martínez, N.; Martínez-López, A.; Cereceda, L.; Casado, F.; Algara, P.; Oscier, D.; Menarguez, F.J.; García, J.F.; Piris, M.A.; et al. Clinical and Diagnostic Relevance of NOTCH2 -and KLF2 -Mutations in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Haematologica 2017, 102, e310–e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cascione, L.; Rinaldi, A.; Bruscaggin, A.; Tarantelli, C.; Arribas, A.J.; Kwee, I.; Pecciarini, L.; Mensah, A.A.; Spina, V.; Chung, E.Y.L.; et al. Novel Insights into the Genetics and Epigenetics of MALT Lymphoma Unveiled by next Generation Sequencing Analyses. Haematologica 2019, 104, e558–e561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trøen, G.; Wlodarska, I.; Warsame, A.; Llodrà, S.H.; Wolf-Peeters, C.D.; Delabie, J. NOTCH2 Mutations in Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Haematologica 2008, 93, 1107–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogusz, A.M.; Bagg, A. Genetic Aberrations in Small B-Cell Lymphomas and Leukemias: Molecular Pathology, Clinical Relevance and Therapeutic Targets. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 1991–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, A.; Sreedharanunni, S.; Sachdeva, M.U.S.; Rana, S.; Kashyap, D.; Bose, P.; Bal, A.; Prakash, G.; Malhotra, P.; Das, R.; et al. The Relative Expression Levels of CD148 and CD180 on Clonal B Cells and CD148/CD180 Median Fluorescence Intensity Ratios Are Useful in the Characterization of Mature B Cell Lymphoid Neoplasms Infiltrating Blood and Bone Marrow—Results from a Single Centre Pilot Study. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeur-Rousse, C.; Guy, J.; Miguet, L.; Bouyer, S.; Geneviève, F.; Robillard, N.; Solly, F.; Maar, A.; Bené, M.C.; Mauvieux, L.; et al. CD180 Expression in B-Cell Lymphomas: A Multicenter GEIL Study: CD180 EXPRESSION IN B-CELL LYMPHOMAS. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 2016, 90, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miguet, L.; Lennon, S.; Baseggio, L.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Berger, F.; Perrusson, N.; Chenard, M.-P.; Galoisy, A.-C.; Eischen, A.; Mayeur-Rousse, C.; et al. Cell-Surface Expression of the TLR Homolog CD180 in Circulating Cells from Splenic and Nodal Marginal Zone Lymphomas. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1748–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matutes, E.; Oscier, D.; Montalban, C.; Berger, F.; Callet-Bauchu, E.; Dogan, A.; Felman, P.; Franco, V.; Iannitto, E.; Mollejo, M.; et al. Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Proposals for a Revision of Diagnostic, Staging and Therapeutic Criteria. Leukemia 2008, 22, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlădăreanu, A.-M.; Onisâi, M.; Ciufu, C.; Bumbea, H.; Cîşleanu, D.; Voican, I.; Nicolescu, A.; Radeşi, S.; Vintilescu, A.; Băluţă, C.; et al. Splenectomy—A Therapeutic Option in Splenic Marginal Zone Cell Lymphoma. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 47, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baseggio, L.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Petinataud, F.; Callet-Bauchu, E.; Berger, F.; Ffrench, M.; Couris, C.M.; Thieblemont, C.; Morel, D.; Coiffier, B.; et al. CD5 Expression Identifies a Subset of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphomas with Higher Lymphocytosis: A Clinico-Pathological, Cytogenetic and Molecular Study of 24 Cases. Haematologica 2010, 95, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Favre, R.; Manzoni, D.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Verney, A.; Jallades, L.; Callet-Bauchu, E.; Sujobert, P.; Salles, G.; Baseggio, L. Usefulness of CD200 in the Differential Diagnosis of SDRPL, SMZL, and HCL. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2018, 40, e59–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, A.J.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Zeng, N.; Yan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Braggio, E.; Fonseca, R.; de Leval, L.; et al. An Integrated Genomic and Expression Analysis of 7q Deletion in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watkins, A.J.; Huang, Y.; Ye, H.; Chanudet, E.; Johnson, N.; Hamoudi, R.; Liu, H.; Dong, G.; Attygalle, A.; McPhail, E.D.; et al. Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Characterization of 7q Deletion and Its Value in Diagnosis. J. Pathol. 2010, 220, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresquet, V.; Robles, E.F.; Parker, A.; Martinez-Useros, J.; Mena, M.; Malumbres, R.; Agirre, X.; Catarino, S.; Arteta, D.; Osaba, L.; et al. High-Throughput Sequencing Analysis of the Chromosome 7q32 Deletion Reveals IRF5 as a Potential Tumour Suppressor in Splenic Marginal-Zone Lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 158, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salido, M.; Baró, C.; Oscier, D.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Dierlamm, J.; Matutes, E.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Berger, F.; Felman, P.; Thieblemont, C.; et al. Cytogenetic Aberrations and Their Prognostic Value in a Series of 330 Splenic Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphomas: A Multicenter Study of the Splenic B-Cell Lymphoma Group. Blood 2010, 116, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lefebvre, C.; Callet-Bauchu, E.; Chapiro, E.; Nadal, N.; Penther, D.; Antoine-Poirel, H. Cytogenetics in the Management of Lymphomas and Lymphoproliferative Disorders in Adults and Children: An Update by the Groupe Francophone de Cytogénétique Hématologique (GFCH). Ann. Biol. Clin. 2016, 74, 568–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonstra, R. Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphomas Presenting with Splenomegaly and Typical Immunophenotype Are Characterized by Allelic Loss in 7q31-32. Mod. Pathol. 2003, 16, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibbotson, R.E.; Parker, A.E.; Oscier, D.G. Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: 7q Abnormalities. Methods Mol. Med. 2005, 115, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo, C.; García, J.L.; Benito, R.; Flores, T.; Mollejo, M.; Martínez-Climent, J.Á.; García, E.; Gutiérrez, N.C.; Piris, M.A.; Hernández, J.M. Molecular Characterization of the Region 7q22.1 in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphomas. PloS ONE 2011, 6, e24939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Algara, P. Analysis of the IGVH Somatic Mutations in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Defines a Group of Unmutated Cases with Frequent 7q Deletion and Adverse Clinical Course. Blood 2002, 99, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikos, V.; Karypidou, M.; Stalika, E.; Baliakas, P.; Xochelli, A.; Sutton, L.-A.; Papadopoulos, G.; Agathangelidis, A.; Papadopoulou, E.; Davis, Z.; et al. An Immunogenetic Signature of Ongoing Antigen Interactions in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Expressing IGHV1-2*04 Receptors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traverse-Glehen, A.; Bachy, E.; Baseggio, L.; Callet-Bauchu, E.; Gazzo, S.; Verney, A.; Hayette, S.; Jallades, L.; Ffrench, M.; Salles, G.; et al. Immunoarchitectural Patterns in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Correlations with Chromosomal Aberrations, IGHV Mutations, and Survival. A Study of 76 Cases. Histopathology 2013, 62, 876–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisou, G.; Verney, A.; Wenner, T.; Baseggio, L.; Felman, P.; Callet-Bauchu, E.; Coiffier, B.; Berger, F.; Salles, G.; Traverse-Glehen, A. A Restricted IGHV Gene Repertoire in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Is Associated with Autoimmune Disorders. Haematologica 2014, 99, e197–e198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zibellini, S.; Capello, D.; Forconi, F.; Marcatili, P.; Rossi, D.; Rattotti, S.; Franceschetti, S.; Sozzi, E.; Cencini, E.; Marasca, R.; et al. Stereotyped Patterns of B-Cell Receptor in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikos, V.; Darzentas, N.; Hadzidimitriou, A.; Davis, Z.; Hockley, S.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Algara, P.; Santoro, A.; Gonzalez, D.; Mollejo, M.; et al. Over 30% of Patients with Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Express the Same Immunoglobulin Heavy Variable Gene: Ontogenetic Implications. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warsame, A.A.; Aasheim, H.-C.; Nustad, K.; Trøen, G.; Tierens, A.; Wang, V.; Randen, U.; Dong, H.P.; Heim, S.; Brech, A.; et al. Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma with VH1-02 Gene Rearrangement Expresses Poly- and Self-Reactive Antibodies with Similar Reactivity. Blood 2011, 118, 3331–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateo, M.-S.; Mollejo, M.; Villuendas, R.; Algara, P.; Sanchez-Beato, M.; Martínez, P.; Piris, M. Molecular Heterogeneity of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphomas: Analysis of Mutations in the 5′ Non-Coding Region of the Bcl-6 Gene. Leukemia 2001, 15, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arribas, A.J.; Gómez-Abad, C.; Sánchez-Beato, M.; Martinez, N.; Dilisio, L.; Casado, F.; Cruz, M.A.; Algara, P.; Piris, M.A.; Mollejo, M. Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Comprehensive Analysis of Gene Expression and MiRNA Profiling. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ballesteros, E.; Mollejo, M.; Mateo, M.; Algara, P.; Martínez, P.; Piris, M.A. MicroRNA Losses in the Frequently Deleted Region of 7q in SMZL. Leukemia 2007, 21, 2547–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemaki, P.I.; Letsos, P.A.; Zoupa, I.C.; Katsaraki, K.; Karousi, P.; Papageorgiou, S.G.; Pappa, V.; Scorilas, A.; Kontos, C.K. The Multifaceted Role and Utility of MicroRNAs in Indolent B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouteloup, M.; Verney, A.; Rachinel, N.; Callet-Bauchu, E.; Ffrench, M.; Coiffier, B.; Magaud, J.-P.; Berger, F.; Salles, G.A.; Traverse-Glehen, A. MicroRNA Expression Profile in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Correspondence. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 156, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Gal, S.; Dunlop, H.M.; Pushkaran, B.; Liggins, A.P.; Pulford, K.; Banham, A.H.; Pezzella, F.; Boultwood, J.; Wainscoat, J.S.; et al. Detection of Elevated Levels of Tumour-Associated MicroRNAs in Serum of Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehle, A.; Hoefig, K.P.; Repsilber, D.; Thorns, C.; Ziepert, M.; Wesche, K.O.; Thiere, M.; Loeffler, M.; Klapper, W.; Pfreundschuh, M.; et al. MicroRNA Signatures Characterize Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas and Follicular Lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo Oquendo, C.; Parker, H.; Oscier, D.; Ennis, S.; Gibson, J.; Strefford, J.C. Systematic Review of Somatic Mutations in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, D.; Deaglio, S.; Dominguez-Sola, D.; Rasi, S.; Vaisitti, T.; Agostinelli, C.; Spina, V.; Bruscaggin, A.; Monti, S.; Cerri, M.; et al. Alteration of BIRC3 and Multiple Other NFΚB Pathway Genes in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Blood 2011, 118, 4930–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, V.; Rossi, D. NFΚB Deregulation in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 39, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Watkins, A.J.; Kocialkowski, S.; Zeng, N.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Isaacson, P.G.; de Leval, L.; Wotherspoon, A.; Du, M.-Q. BCR and TLR Signaling Pathways Are Recurrently Targeted by Genetic Changes in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphomas. Haematologica 2012, 97, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, D.; Navarro, A.; Martinez-Trillos, A.; Molina-Urra, R.; Gonzalez-Farre, B.; Salaverria, I.; Nadeu, F.; Enjuanes, A.; Clot, G.; Costa, D.; et al. NOTCH1, TP53, and MAP2K1 Mutations in Splenic Diffuse Red Pulp Small B-Cell Lymphoma Are Associated With Progressive Disease. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiel, M.J.; Velusamy, T.; Betz, B.L.; Zhao, L.; Weigelin, H.G.; Chiang, M.Y.; Huebner-Chan, D.R.; Bailey, N.G.; Yang, D.T.; Bhagat, G.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies Recurrent Somatic NOTCH2 Mutations in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1553–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, D.; Trifonov, V.; Fangazio, M.; Bruscaggin, A.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; Monti, S.; Vaisitti, T.; Arruga, F.; Famà, R.; et al. The Coding Genome of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Activation of NOTCH2 and Other Pathways Regulating Marginal Zone Development. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1537–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peveling-Oberhag, J.; Wolters, F.; Döring, C.; Walter, D.; Sellmann, L.; Scholtysik, R.; Lucioni, M.; Schubach, M.; Paulli, M.; Biskup, S.; et al. Whole Exome Sequencing of Microdissected Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: A Study to Discover Novel Tumor-Specific Mutations. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanmugam, V.; Craig, J.W.; Hilton, L.K.; Nguyen, M.H.; Rushton, C.K.; Fahimdanesh, K.; Lovitch, S.; Ferland, B.; Scott, D.W.; Aster, J.C. Notch Activation Is Pervasive in SMZL and Uncommon in DLBCL: Implications for Notch Signaling in B-Cell Tumors. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, M.; Rose-Zerilli, M.J.J.; Gibson, J.; Ennis, S.; Walewska, R.; Forster, J.; Parker, H.; Davis, Z.; Gardiner, A.; Collins, A.; et al. Whole Exome Sequencing Identifies Novel Recurrently Mutated Genes in Patients with Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oquendo, C.J.; Parker, H.; Oscier, D.; Ennis, S.; Gibson, J.; Strefford, J.C. The (Epi)Genomic Landscape of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma, Biological Implications, Clinical Utility, and Future Questions. J. Transl. Genet. Genom. 2021, 5, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clipson, A.; Wang, M.; de Leval, L.; Ashton-Key, M.; Wotherspoon, A.; Vassiliou, G.; Bolli, N.; Grove, C.; Moody, S.; Escudero-Ibarz, L.; et al. KLF2 Mutation Is the Most Frequent Somatic Change in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma and Identifies a Subset with Distinct Genotype. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jallades, L.; Baseggio, L.; Sujobert, P.; Huet, S.; Chabane, K.; Callet-Bauchu, E.; Verney, A.; Hayette, S.; Desvignes, J.-P.; Salgado, D.; et al. Exome Sequencing Identifies Recurrent BCOR Alterations and the Absence of KLF2, TNFAIP3 and MYD88 Mutations in Splenic Diffuse Red Pulp Small B-Cell Lymphoma. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parry, M.; Rose-Zerilli, M.J.; Ljungström, V.; Gibson, J.; Wang, J.; Walewska, R.; Parker, H.; Parker, A.; Davis, Z.; Gardiner, A.; et al. Genetics and Prognostication in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Revelations from Deep Sequencing. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4174–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trøen, G.; Warsame, A.; Delabie, J. CD79B and MYD88 Mutations in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. ISRN Oncol. 2013, 2013, 252318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, N.; Almaraz, C.; Vaqué, J.P.; Varela, I.; Derdak, S.; Beltran, S.; Mollejo, M.; Campos-Martin, Y.; Agueda, L.; Rinaldi, A.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Reveals Mutations in Genes Involved in Marginal Zone Differentiation. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bassarova, A.; Trøen, G.; Spetalen, S.; Micci, F.; Tierens, A.; Delabie, J. Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma and Marginal Zone Lymphoma in the Bone Marrow: Paratrabecular Involvement As an Important Distinguishing Feature. Blood 2014, 124, 5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadeh, F.; MacNamara, S.P.; Aguilera, N.S.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Cook, J.R. MYD88 L265P Mutation Analysis Helps Define Nodal Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lopez, A.; Curiel-Olmo, S.; Mollejo, M.; Cereceda, L.; Martinez, N.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Almaraz, C.; Revert, J.B.; Piris, M.A. MYD88 (L265P) Somatic Mutation in Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Wang, M. Mantle Cell Lymphoma: 2019 Update on the Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Prognostication, and Management. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 710–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rose-Zerilli, M.J.J.; Forster, J.; Parker, H.; Parker, A.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Chaplin, T.; Gardiner, A.; Steele, A.J.; Collins, A.; Young, B.D.; et al. ATM Mutation Rather than BIRC3 Deletion and/or Mutation Predicts Reduced Survival in 11q-Deleted Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Data from the UK LRF CLL4 Trial. Haematologica 2014, 99, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diop, F.; Moia, R.; Favini, C.; Spaccarotella, E.; De Paoli, L.; Bruscaggin, A.; Spina, V.; Terzi-di-Bergamo, L.; Arruga, F.; Tarantelli, C.; et al. Biological and Clinical Implications of BIRC3 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frazzi, R. BIRC3 and BIRC5: Multi-faceted Inhibitors in Cancer. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, U.; Rinaldi, A.; Kwee, I.; Nandula, S.V.; Rancoita, P.M.V.; Compagno, M.; Cerri, M.; Rossi, D.; Murty, V.V.; Zucca, E.; et al. The NFΚB Negative Regulator TNFAIP3 (A20) Is Inactivated by Somatic Mutations and Genomic Deletions in Marginal Zone Lymphomas. Blood 2009, 113, 4918–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, R.; Deaglio, S.; Famà, R.; Buonincontri, R.; Scarfò, I.; Bruscaggin, A.; Mereu, E.; Serra, S.; Spina, V.; Brusa, D.; et al. The Krüppel-like Factor 2 Transcription Factor Gene Is Recurrently Mutated in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Leukemia 2015, 29, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruga, F.; Vaisitti, T.; Deaglio, S. The NOTCH Pathway and Its Mutations in Mature B Cell Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mensah, A.A.; Rinaldi, A.; Ponzoni, M.; Canzonieri, V.; Uccella, S.; Rossi, D.; Bhagat, G.; Gaidano, G.; Zucca, E.; Bertoni, F. Absence of NOTCH1 Gene Mutations in MALT Lymphomas: Correspondence. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 157, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arribas, A.J.; Rinaldi, A.; Mensah, A.A.; Kwee, I.; Cascione, L.; Robles, E.F.; Martinez-Climent, J.A.; Oscier, D.; Arcaini, L.; Baldini, L.; et al. DNA Methylation Profiling Identifies Two Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Subgroups with Different Clinical and Genetic Features. Blood 2015, 125, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.W.; Gascoyne, R.D. The Tumour Microenvironment in B Cell Lymphomas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, P.G.; Du, M.-Q. MALT Lymphoma: From Morphology to Molecules. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Lv, R.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Zou, D.; Qiu, L.; Yi, S. Prevalence of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Viral Infections in Various Subtypes of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Confirmation of the Association with Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wickenden, K.; Nawaz, N.; Mamand, S.; Kotecha, D.; Wilson, A.L.; Wagner, S.D.; Ahearne, M.J. PD1hi Cells Associate with Clusters of Proliferating B-Cells in Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verney, A.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Callet-Bauchu, E.; Jallades, L.; Magaud, J.-P.; Salles, G.; Genestier, L.; Baseggio, L. Toll-like Receptor Expression and Function Differ between Splenic Marginal Zone B Cell Lymphoma and Splenic Diffuse Red Pulp B Cell Lymphoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 23589–23598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franco, G.; Guarnotta, C.; Frossi, B.; Piccaluga, P.P.; Boveri, E.; Gulino, A.; Fuligni, F.; Rigoni, A.; Porcasi, R.; Buffa, S.; et al. Bone Marrow Stroma CD40 Expression Correlates with Inflammatory Mast Cell Infiltration and Disease Progression in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Blood 2014, 123, 1836–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puga, I.; Cols, M.; Barra, C.M.; He, B.; Cassis, L.; Gentile, M.; Comerma, L.; Chorny, A.; Shan, M.; Xu, W.; et al. B Cell-Helper Neutrophils Stimulate the Diversification and Production of Immunoglobulin in the Marginal Zone of the Spleen. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 13, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deniset, J.F.; Surewaard, B.G.; Lee, W.-Y.; Kubes, P. Splenic Ly6Ghigh Mature and Ly6Gint Immature Neutrophils Contribute to Eradication of S. Pneumoniae. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1333–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapini, P.; Cassatella, M.A. Location in the Spleen Dictates the Function of Murine Neutrophils. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1207–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, C.L.; Cutucache, C.E. Murine Models of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma: A Role for Cav1? Front. Oncol. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carey, C.D.; Gusenleitner, D.; Lipschitz, M.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Stack, E.C.; Gjini, E.; Hu, X.; Redd, R.; Freeman, G.J.; Neuberg, D.; et al. Topological Analysis Reveals a PD-L1-Associated Microenvironmental Niche for Reed-Sternberg Cells in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2017, 130, 2420–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, N.H.; Cheah, C.Y.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Gribben, J.; Neelapu, S.S.; Ghia, P.; Bollard, C.; Ansell, S.; Curran, M.; Wilson, W.H.; et al. Role of the Tumor Microenvironment in Mature B-Cell Lymphoid Malignancies. Haematologica 2016, 101, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, M.; Gershon, M.D. Netrins and DCC in the Guidance of Migrating Neural Crest-Derived Cells in the Developing Bowel and Pancreas. Dev. Biol. 2003, 258, 364–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, J.G.; Gribben, J.G. Microenvironment Abnormalities and Lymphomagenesis: Immunological Aspects. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 34, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wahlin, B.E.; Aggarwal, M.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Gonzalez, L.F.; Roncador, G.; Sanchez-Verde, L.; Christensson, B.; Sander, B.; Kimby, E. A Unifying Microenvironment Model in Follicular Lymphoma: Outcome Is Predicted by Programmed Death-1-Positive, Regulatory, Cytotoxic, and Helper T Cells and Macrophages. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lipson, E.J.; Drake, C.G. Ipilimumab: An Anti-CTLA-4 Antibody for Metastatic Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6958–6962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savoia, P.; Astrua, C.; Fava, P. Ipilimumab (Anti-Ctla-4 Mab) in the Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma: Effectiveness and Toxicity Management. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meti, N.; Esfahani, K.; Johnson, N. The Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cancers 2018, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carreras, J.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Roncador, G.; Villamor, N.; Colomo, L.; Martinez, A.; Hamoudi, R.; Howat, W.J.; Montserrat, E.; Campo, E. High Numbers of Tumor-Infiltrating Programmed Cell Death 1-Positive Regulatory Lymphocytes Are Associated with Improved Overall Survival in Follicular Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toki, M.I.; Merritt, C.R.; Wong, P.F.; Smithy, J.W.; Kluger, H.M.; Syrigos, K.N.; Ong, G.T.; Warren, S.E.; Beechem, J.M.; Rimm, D.L. High-Plex Predictive Marker Discovery for Melanoma Immunotherapy–Treated Patients Using Digital Spatial Profiling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5503–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Bordeaux, J.M.; Kim, J.-Y.; Vaupel, C.A.; Rimm, D.L.; Ho, T.H.; Joseph, R.W.; Daud, A.I.; Conry, R.M.; Gaughan, E.M.; et al. Quantitative Spatial Profiling of PD-1/PD-L1 Interaction and HLA-DR/IDO-1 Predicts Improved Outcomes of Anti-PD-1 Therapies in Metastatic Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5250–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Jacobs, R.; Ghosh, N. Checkpoint Inhibitors Hodgkin Lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2018, 13, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, J.B.; Jacob, M.K.; Parajuli, P. Review of immune checkpoint inhibitors in immuno-oncology. In Advances in Pharmacology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 91, pp. 111–139. ISBN 978-0-12-823562-1. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, P.G.; Sperling, A.S.; Gibson, C.J.; Pozdnyakova, O.; Wong, W.J.; Manos, M.P.; Buchbinder, E.I.; Hodi, F.S.; Ebert, B.L.; Davids, M.S. A Deep Molecular Response of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma to Front-Line Checkpoint Blockade. Haematologica 2020, 106, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent-Fabert, C.; Soubeyran, I.; Velasco, V.; Parrens, M.; Jeannet, R.; Lereclus, E.; Gachard, N.; Feuillard, J.; Faumont, N. Inflamed Phenotype of Splenic Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphomas with Expression of PD-L1 by Intratumoral Monocytes/Macrophages and Dendritic Cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjwani, P.K.; Charu, V.; DeLisser, M.; Molina-Kirsch, H.; Natkunam, Y.; Zhao, S. Programmed Death-1 Ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 Show Distinctive and Restricted Patterns of Expression in Lymphoma Subtypes. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 71, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, J.C.; Grajales-Cruz, A.F.; Volpe, V.O.; Turba, E.P.; Nodzon, L.; Sahakian, E.; Rozario, N.; Pinilla Ibarz, J. A Phase II Trial of Ibrutinib and PD-1 Blockade in Asymptomatic High Risk Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia to Improve Immune Function. Blood 2019, 134, 5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruga, F.; Gyau, B.B.; Iannello, A.; Vitale, N.; Vaisitti, T.; Deaglio, S. Immune Response Dysfunction in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Dissecting Molecular Mechanisms and Microenvironmental Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, P.; Hu, B.; Ma, X.; Yang, Z.; Yu, M.; Sun, H.; Huang, A.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; et al. New Insight into BIRC3: A Novel Prognostic Indicator and a Potential Therapeutic Target for Liver Cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 6035–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, M.-X.; Liu, Y.-M. The Role of Oncogenic Notch2 Signaling in Cancer: A Novel Therapeutic Target. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 837–854. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duechler, M.; Shehata, M.; Schwarzmeier, J.D.; Hoelbl, A.; Hilgarth, M.; Hubmann, R. Induction of Apoptosis by Proteasome Inhibitors in B-CLL Cells Is Associated with Downregulation of CD23 and Inactivation of Notch2. Leukemia 2005, 19, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Biomarker | Role of the Protein | Consequence at Protein Level | Frequency | Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7q deletion | - | - | 30%–40% | [26,29,30,31,32] |
| Trisomy 3 | - | - | 25% | [29,30] |
| Trisomy 12 | - | - | 10% | [29,30] |
| Trisomy 12 | - | - | 8% | |
| Preferential usage of specific IGHV genes: | - | - | [29,34,37,39] | |
| IGHV1-2*04 | 31% | |||
| IGHV3-23 | 8% | |||
| IGHV4-34 | 13% | |||
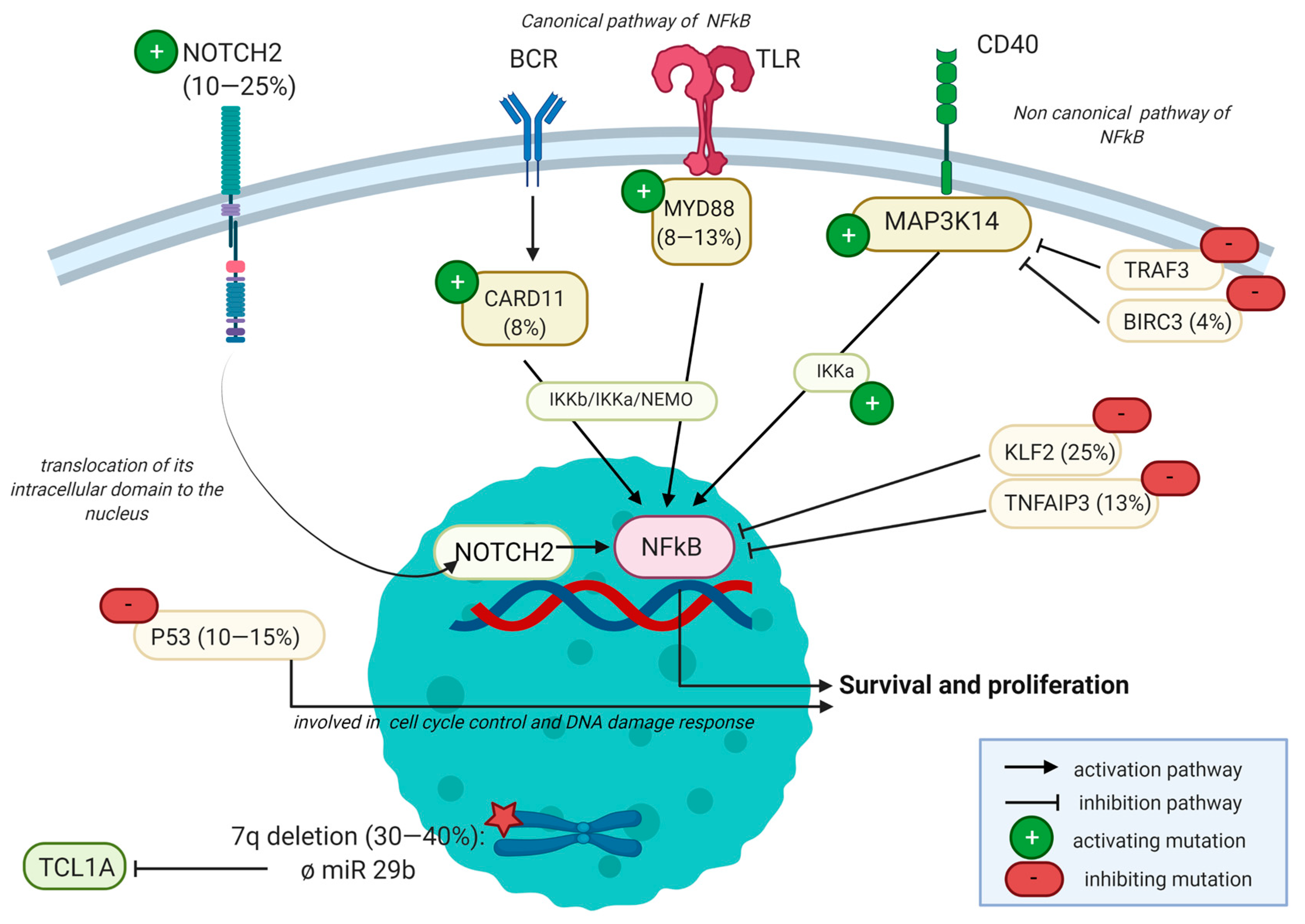
| NOTCH2 | NFκB activation | Activation | 10%–25% | [17,54,73] |
| KLF2 | NFκB inhibition | Inactivation | 12%–40% | [59,60,72] |
| MYD88 | NFκB activation from the Toll-like receptors | Activation | 5%–18% (p.L265P 65%) | [48,60,62,65,66] |
| CARD11 | NFκB activation from the B cell receptors | Activation | 5%–9% | [48,54,62] |
| P53 | DNA damage and cycle cell control | Inactivation | 15% | [29,52,61] |
| BIRC3 | MAP3K14 inactivation | Inactivation by disruption of the RING domain | 5%–11% | [49,54] |
| TRAF3 | MAP3K14 inactivation | Inactivation | 3%–10% | [49,54] |
| MAP3K14 | NFκB activation | Activation | 1%–8% | [49,54] |
| SPEN | Notch inhibition | repress Notch signaling | 5%–10% | [48,54] |
| TNFAIP3 | NFκB inhibition | Inactivation | 7%–13% | [48,71] |
| IKBKB | NFκB activation | Activation | 7% | [54] |
| KMT2D | Epigenetic regulation | Inactivation | 9%–15% | [48,58] |
| ARID1A | DNA damage, cycle cell control, and epigenetic regulation | Inactivation | 4%–6% | [58,61] |
| EP300 | Epigenetic regulation | Inactivation | 2% | [58] |
| CREBBP | Epigenetic regulation | Inactivation | 5% | [58,61] |
| TBL1XR1 | Epigenetic regulation | Inactivation | 1% | [58] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donzel, M.; Baseggio, L.; Fontaine, J.; Pesce, F.; Ghesquières, H.; Bachy, E.; Verney, A.; Traverse-Glehen, A. New Insights into the Biology and Diagnosis of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphomas. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 3430-3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050297
Donzel M, Baseggio L, Fontaine J, Pesce F, Ghesquières H, Bachy E, Verney A, Traverse-Glehen A. New Insights into the Biology and Diagnosis of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphomas. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(5):3430-3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050297
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonzel, Marie, Lucile Baseggio, Juliette Fontaine, Florian Pesce, Hervé Ghesquières, Emmanuel Bachy, Aurélie Verney, and Alexandra Traverse-Glehen. 2021. "New Insights into the Biology and Diagnosis of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphomas" Current Oncology 28, no. 5: 3430-3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050297
APA StyleDonzel, M., Baseggio, L., Fontaine, J., Pesce, F., Ghesquières, H., Bachy, E., Verney, A., & Traverse-Glehen, A. (2021). New Insights into the Biology and Diagnosis of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphomas. Current Oncology, 28(5), 3430-3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050297




