The Challenge to the Pathologist of PD-L1 Expression in Tumor Cells of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer—An Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Approvals
2.1. Relevant Checkpoint Inhibitors
2.2. FDA and EMA
3. Relevant PD-L1 Scores
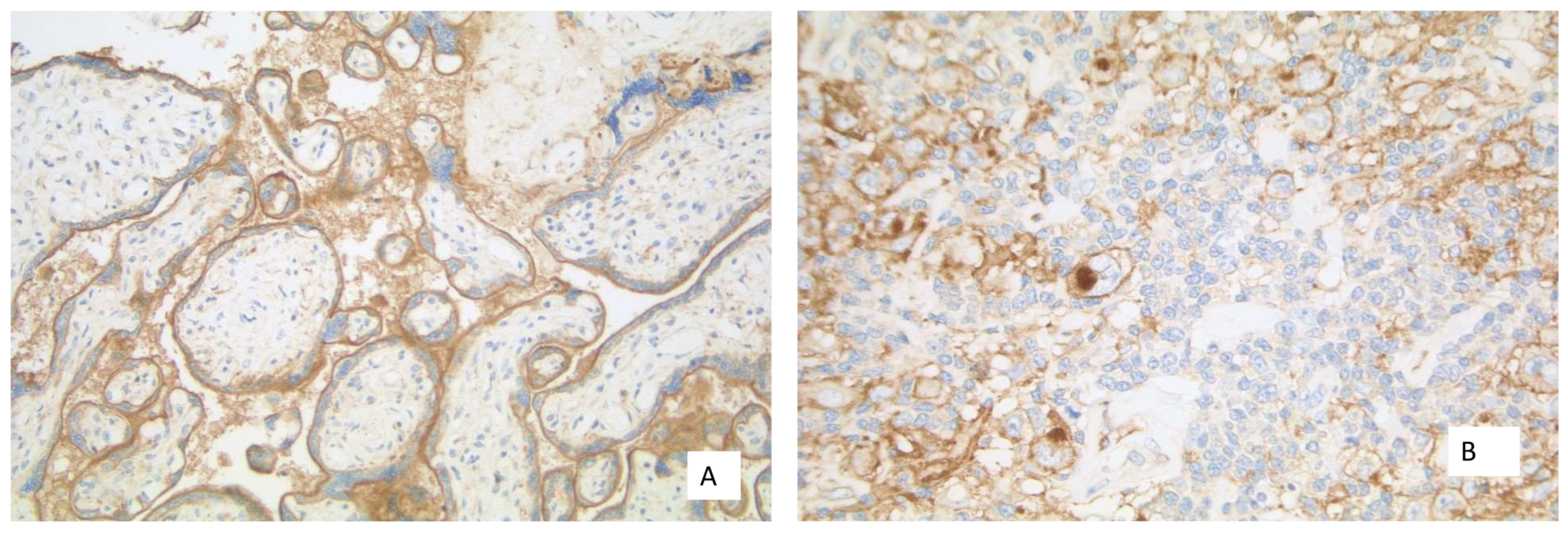
3.1. TPS/TC
3.2. IC
4. General Aspects in the Interpretation, Training, and Reporting of PD-L1 Staining
4.1. Interpretation of PD-L1 Staining
4.2. Training
4.3. Reporting the Results
5. Laboratory Specific aspects
5.1. Laboratory-Developed Tests versus Clinical Trial Tests
5.2. Controls
5.3. Pre-Analytic
6. Tissue-Specific Aspects and Clinical Course
6.1. Tissue Samples versus Cytology
6.2. Primary Tumor versus Metastasis
6.3. Clinical Course
7. Further Developments
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thunnissen, E.; Kerr, K.M.; Herth, F.J.F.; Lantuejoul, S.; Papotti, M.; Rintoul, R.C.; Rossi, G.; Skov, B.G.; Weynand, B.; Bubendorf, L.; et al. The challenge of NSCLC diagnosis and predictive analysis on small samples: Practical approach of a working group. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsoukis, N.; Wang, Q.; Strauss, L.; Boussiotis, V.A. Revisiting the PD-1 pathway. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 pathways: Similarities, differences, and implications of their inhibition. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Francisco, L.M.; Sage, P.T.; Sharpe, A.H. The PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 236, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature 2017, 541, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, S.D.; Shin, H.; Haining, W.N.; Zou, T.; Workman, C.J.; Polley, A.; Betts, M.R.; Freeman, G.J.; Vignali, D.A.A.; Wherry, E.J. Coregulation of CD8+ T cell exhaustion by multiple inhibitory receptors during chronic viral infection. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, T.A.; Yarchoan, M.; Jaffee, E.; Swanton, C.; Quezada, S.A.; Stenzinger, A.; Peters, S. Development of tumor mutation burden as an immunotherapy biomarker: Utility for the oncology clinic. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Drake, C.G.; Pardoll, D.M. Targeting the PD-1/B7-H1(PD-L1) pathway to activate anti-tumor immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinohara, T.; Taniwaki, M.; Ishida, Y.; Kawaichi, M.; Honjo, T. Structure and chromosomal localization of the human PD-1 Gene (PDCD1). Genomics 1994, 23, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Pennell, N.A.; Fidler, M.J.; Halmos, B.; Bonomi, P.; Stevenson, J.; Schneider, B.; Sukari, A.; Ventimiglia, J.; Chen, W.; et al. Phase II study of maintenance Pembrolizumab in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohaegbulam, K.C.; Assal, A.; Lazar-Molnar, E.; Yao, Y.; Zang, X. Human cancer immunotherapy with antibodies to the PD-1 and PD-L1 pathway. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheel, A.H.; Dietel, M.; Heukamp, L.C.; Jöhrens, K.; Kirchner, T.; Reu, S.; Rüschoff, J.; Schildhaus, H.U.; Schirmacher, P.; Tiemann, M.; et al. Predictive PD-L1 immunohistochemistry for non-small cell lung cancer: Current state of the art and experiences of the first German harmonization study. Pathologe 2016, 37, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krigsfeld, G.S.; Prince, E.A.; Pratt, J.; Chizhevsky, V.; Ragheb, J.W.; Novotny, J.J.; Huron, D. Analysis of real-world PD-L1 IHC 28-8 and 22C3 PharmDx assay utilisation, turnaround times and analytical concordance across multiple tumour types. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 73, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, C.; Schwellenbach, H.; Zielinski, D.; Eckstein, S.; Martin-Ortega, M.; D’Arrigo, C.; Schildhaus, H.-U.; Rüschoff, J.; Jasani, B. Optimization and validation of PD-L1 immunohistochemistry staining protocols using the antibody clone 28-8 on different staining platforms. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 1630–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, J.A.; Han, G.; Carvajal-Hausdorf, D.E.; Wasserman, B.E.; Pelekanou, V.; Mani, N.L.; McLaughlin, J.; Schalper, K.A.; Rimm, D.L. Quantitative and pathologist-read comparison of the heterogeneity of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jasani, B.; Oberthür, R.; Bänfer, G.; Diezko, R.; Kumar, G.; Rüschoff, J.; Schildhaus, H.-U. A standardised structured training of pathologists to improve inter- and intra-reader reproducibility for scoring PD-L1 expression levels in non-small cell lung cancer: Results of a worldwide training programme. Virchows Arch. 2019, 475, 1–436. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, W.A.; Russell, P.A.; Cherian, M.; Duhig, E.E.; Godbolt, D.; Jessup, P.J.; Khoo, C.; Leslie, C.; Mahar, A.; Moffat, D.F.; et al. Intra- and interobserver reproducibility assessment of PD-L1 biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4569–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheel, A.H.; Dietel, M.; Heukamp, L.C.; Jöhrens, K.; Kirchner, T.; Reu, S.; Rüschoff, J.; Schildhaus, H.-U.; Schirmacher, P.; Tiemann, M.; et al. Harmonized PD-L1 immunohistochemistry for pulmonary squamous-cell and adenocarcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, F.R.; McElhinny, A.; Stanforth, D.; Ranger-Moore, J.; Jansson, M.; Kulangara, K.; Richardson, W.; Towne, P.; Hanks, D.; Vennapusa, B.; et al. PD-L1 immunohistochemistry assays for lung cancer: Results from phase 1 of the blueprint PD-L1 IHC assay comparison project. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsao, M.S.; Kerr, K.M.; Kockx, M.; Beasley, M.-B.; Borczuk, A.C.; Botling, J.; Bubendorf, L.; Chirieac, L.; Chen, G.; Chou, T.-Y.; et al. PD-L1 immunohistochemistry comparability study in real-life clinical samples: Results of blueprint phase 2 project. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Büttner, R.; Gosney, J.R.; Skov, B.G.; Adam, J.; Motoi, N.; Bloom, K.J.; Dietel, M.; Longshore, J.W.; Lopez-Ríos, F.; Penault-Llorca, F.; et al. Programmed Death-Ligand 1 immunohistochemistry testing: A review of analytical assays and clinical implementation in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3867–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schildhaus, H.-U. Predictive value of PD-L1 diagnostics. Pathologe 2018, 39, 498–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, N.S.; Ferkowicz, M.; Odish, E.; Mani, A.; Hastah, F. Minimum formalin fixation time for consistent estrogen receptor immunohistochemical staining of invasive breast carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 120, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buesa, R.J.; Peshkov, M.V. How much formalin is enough to fix tissues? Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 16, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, B.G.; Skov, T. Paired comparison of PD-L1 expression on cytologic and histologic specimens from malignancies in the lung assessed with PD-L1 IHC 28-8pharmDx and PD-L1 IHC 22C3pharmDx. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. AIMM 2017, 25, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.H.; Schwartz, M.R.; Moriarty, A.T.; Wilbur, D.C.; Souers, R.; Fatheree, L.; Booth, C.N.; Clayton, A.C.; Kurtyz, D.F.I.; Padmanabhan, V.; et al. Immunohistochemistry practices of cytopathology laboratories: A survey of participants in the College of American Pathologists Nongynecologic Cytopathology Education Program. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2014, 138, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubendorf, L.; Conde, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Langfort, R.; Schildhaus, H.-U.; Votruba, J.; Concha-López, Á.; Esteban-Rodriguez, I.; Feng, J.; Devenport, J.; et al. A noninterventional, multinational study to assess PD-L1 expression in cytological and histological lung cancer specimens. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020, 128, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, M.; Long-Mira, E.; Bence, C.; Butori, C.; Lassalle, S.; Bouhlel, L.; Fazzalari, L.; Zahaf, K.; Lalvée, S.; Washetine, K.; et al. Comparative study of the PD-L1 status between surgically resected specimens and matched biopsies of NSCLC patients reveal major discordances: A potential issue for anti-PD-L1 therapeutic strategies. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Nambirajan, A.; Borczuk, A.; Chen, G.; Minami, Y.; Moreira, A.L.; Motoi, N.; Papotti, M.; Rekhtman, N.; Russell, P.A.; et al. Immunocytochemistry for predictive biomarker testing in lung cancer cytology. Cancer Cytopathol. 2019, 127, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munari, E.; Zamboni, G.; Lunardi, G.; Marconi, M.; Sommaggio, M.; Brunelli, M.; Martignoni, G.; Netto, G.J.; Hoque, M.O.; Moretta, F.; et al. PD-L1 expression comparison between primary and relapsed non-small cell lung carcinoma using whole sections and clone SP263. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 30465–30471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Liang, H.; Burnette, B.; Beckett, M.; Darga, T.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Fu, Y.-X. Irradiation and anti-PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Ahn, R.; Yang, K.; Zhu, X.; Fu, Z.; Morin, G.; Bramley, R.; Cliffe, N.C.; Xue, Y.; Kuasne, H.; et al. CD44 promotes PD-L1 expression and its tumor-intrinsic function in breast and lung cancers. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Haihong, P.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y. PD-L1 expression in lung cancer and its correlation with driver mutations: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hastings, K.; Yu, H.A.; Wei, W.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; DeVeaux, M.; Choi, J.; Rizvi, H.; Lisberg, A.; Truini, A.; Lydon, C.A.; et al. EGFR mutation subtypes and response to immune checkpoint blockade treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhong, L.; Li, K.; Nishiyama, A.; Arai, S.; Yano, S.; Wang, W. EGFR-TKI resistance promotes immune escape in lung cancer via increased PD-L1 expression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cai, Y.; Fu, S.; Zhang, N.; Fu, X.; Li, L. IFN-γ-mediated inhibition of lung cancer correlates with PD-L1 expression and is regulated by PI3K-AKT signaling. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurkmans, D.P.; Kuipers, M.E.; Smit, J.; van Marion, R.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Postmus, P.E.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Aerts, J.G.J.V.; von der Thüsen, J.H.; van der Burg, S.H. Tumor mutational load, CD8+ T cells, expression of PD-L1 and HLA class I to guide immunotherapy decisions in NSCLC patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
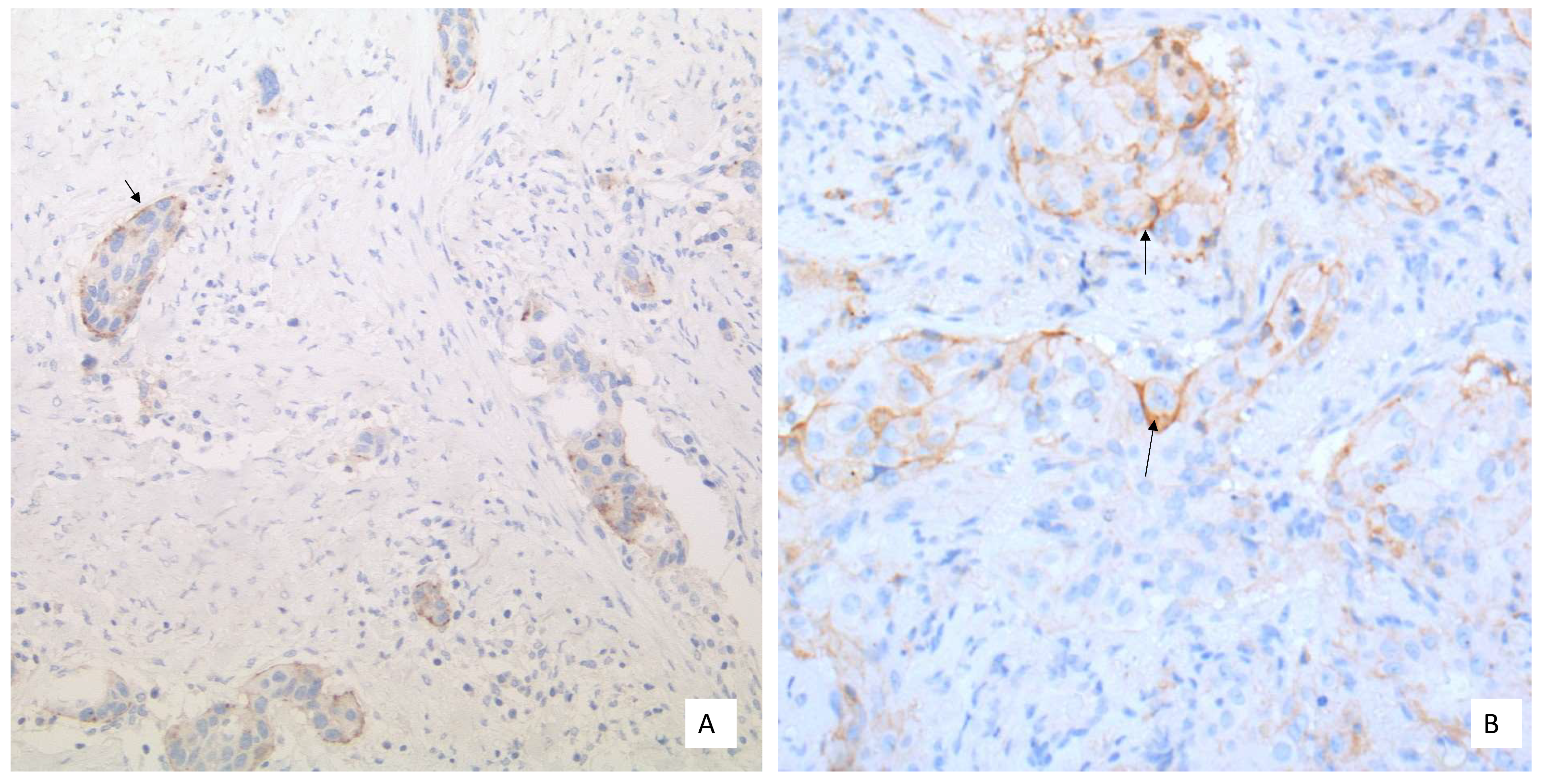
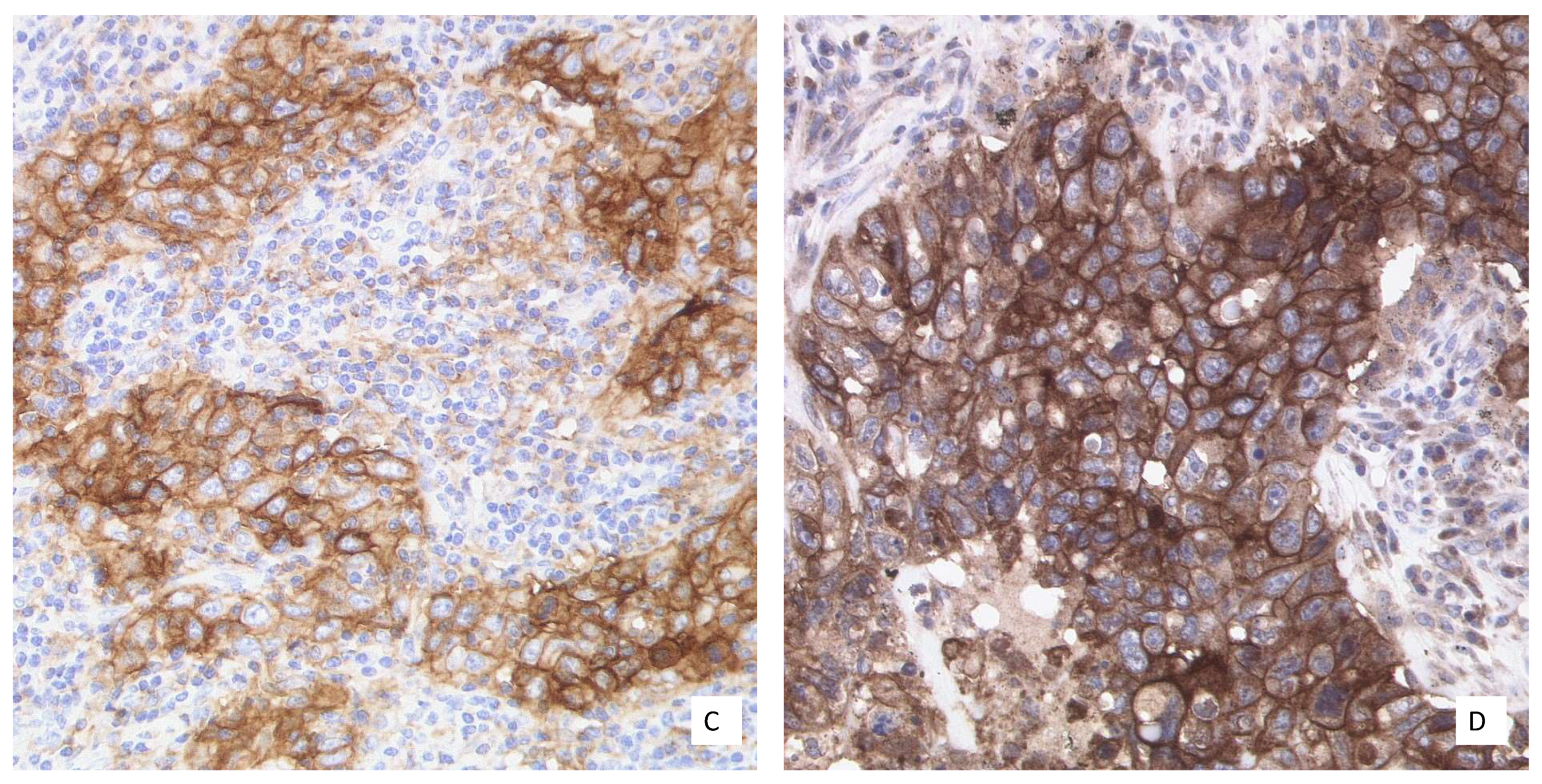


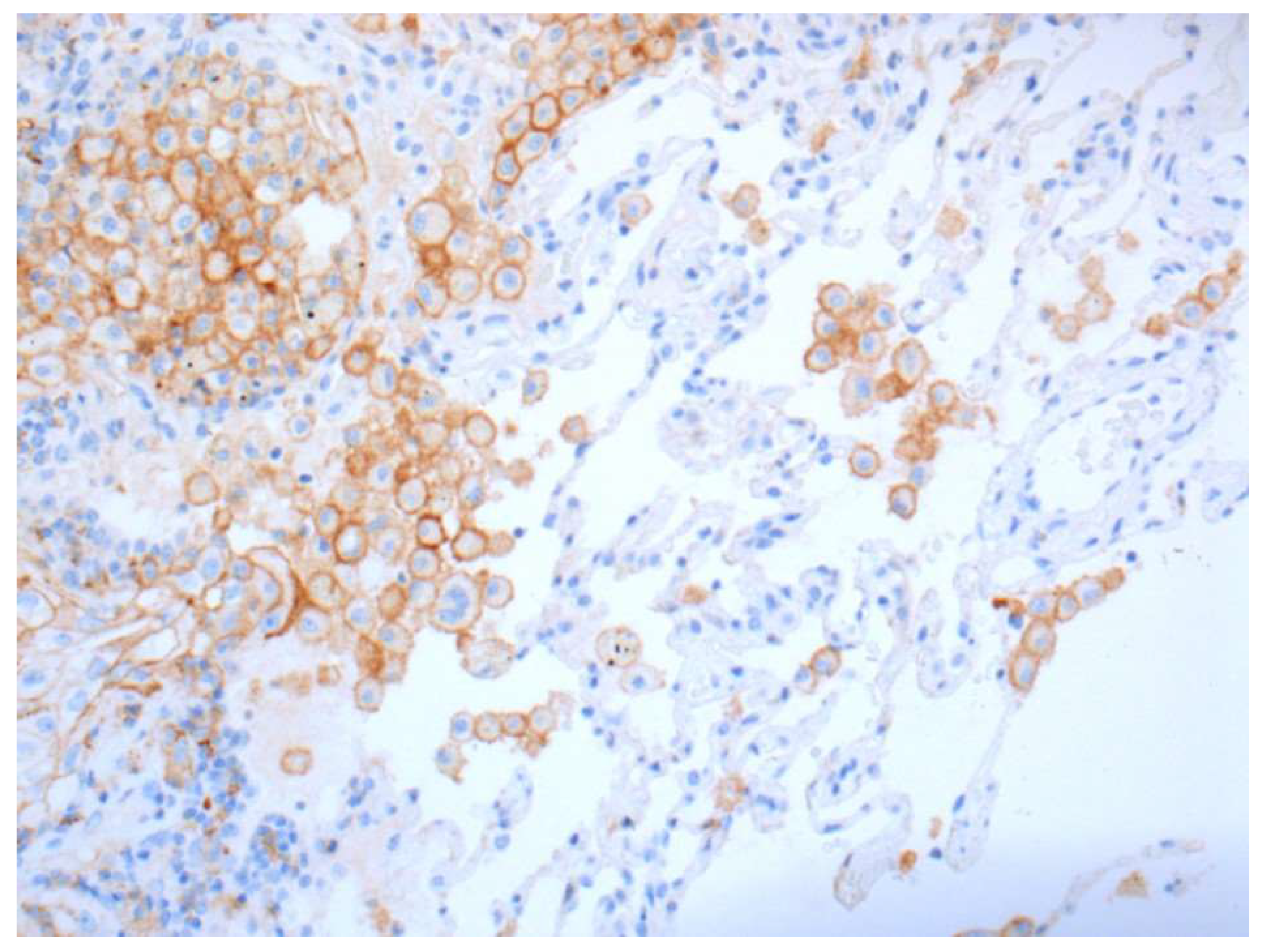
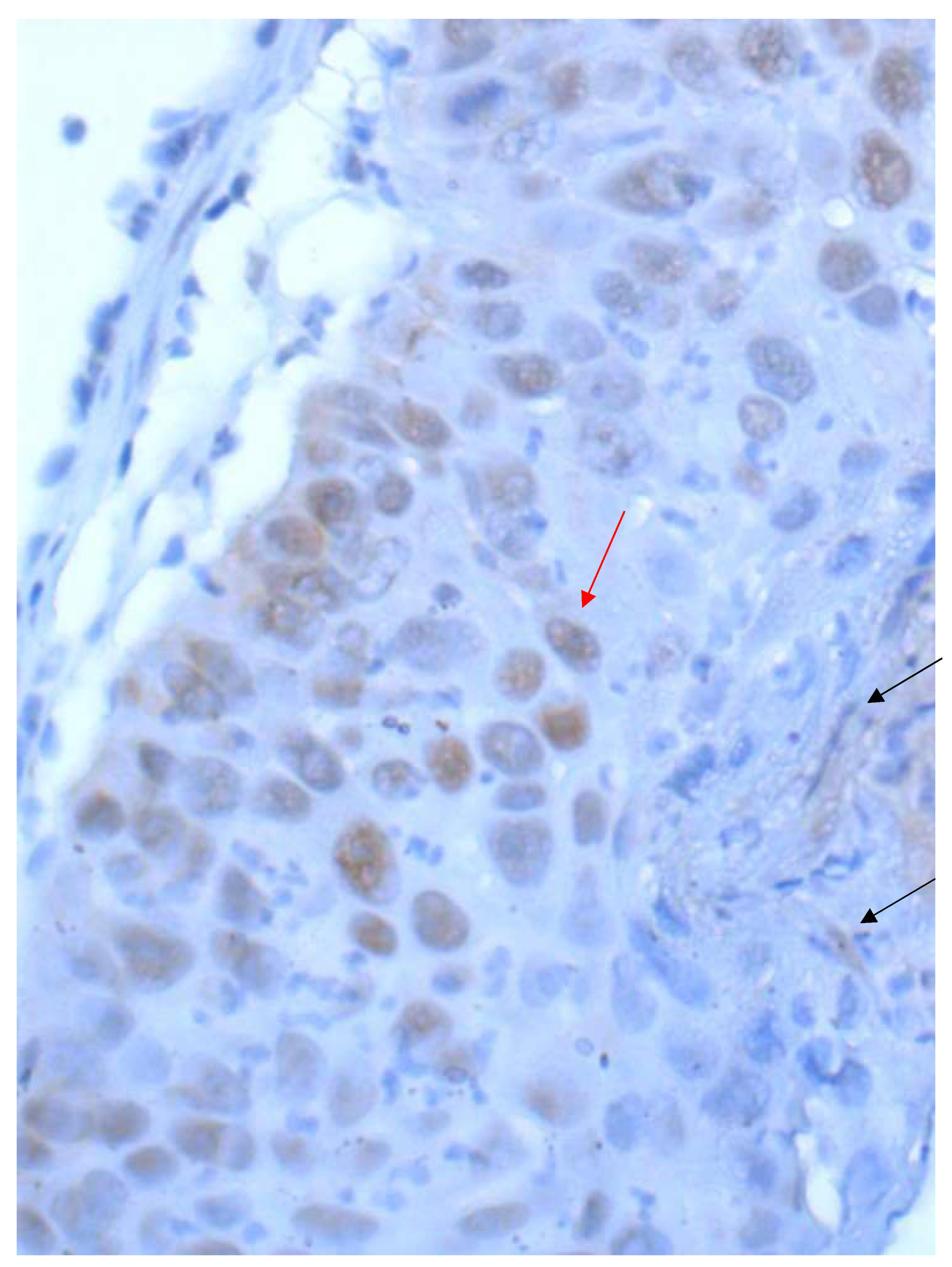

| Drug | Therapy-Line | PD-L1 Test (CTA) | Score | Cut Off | Therapy Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atezolizumab | 1L stage IV | Yes (SP142) | TC or IC | ≥50% TC or ≥10% IC | Monotherapy |
| 2L stage IV | None None | Monotherapy | |||
| Cemiplimab | 1L stage III | Yes (22C3) | TPS | ≥50% | Monotherapy |
| 1L stage IV | |||||
| Durvalumab | 2L stage III | Yes (SP263) | TPS | ≥1% | Monotherapy |
| Ipilimumab | 1L stage IV | None | in combination with Nivolumab and 2 cycles of platinum-based chemotherapy | ||
| Nivolumab | 1L stage IV | None | in combination with Ipilimumab and 2 cycles of platinum-based chemotherapy | ||
| 2L stage IV | None | Monotherapy | |||
| Pembrolizumab | 1L stage IV | Yes (22C3) | TPS | ≥50% | Monotherapy |
| 1L stage IV | None | in combination with pemetrexed and platinum-based chemo- therapy in non squamous NSCLC or in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel or nab-paclitaxel in squamous NSCLC | |||
| 2L stage IV | Yes (22C3) | TPS | ≥1% | Monotherapy |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jöhrens, K.; Rüschoff, J. The Challenge to the Pathologist of PD-L1 Expression in Tumor Cells of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer—An Overview. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 5227-5239. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060437
Jöhrens K, Rüschoff J. The Challenge to the Pathologist of PD-L1 Expression in Tumor Cells of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer—An Overview. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(6):5227-5239. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060437
Chicago/Turabian StyleJöhrens, Korinna, and Josef Rüschoff. 2021. "The Challenge to the Pathologist of PD-L1 Expression in Tumor Cells of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer—An Overview" Current Oncology 28, no. 6: 5227-5239. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060437
APA StyleJöhrens, K., & Rüschoff, J. (2021). The Challenge to the Pathologist of PD-L1 Expression in Tumor Cells of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer—An Overview. Current Oncology, 28(6), 5227-5239. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060437




