Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies the VHL Mutation (c.262T > C, p.Try88Arg) in Non-Obstructive Azoospermia-Associated Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient and Clinical Evaluation
2.2. Isolation of Genomic DNA and Whole-Exome Sequencing
2.3. Sanger Verification and Restriction Enzyme Digestion Site Analysis
2.4. Vector Construction, Site-Directed Mutagenesis, Cellular Localization, and Expression Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Findings
3.2. Identification of a Missense Mutation in VHL
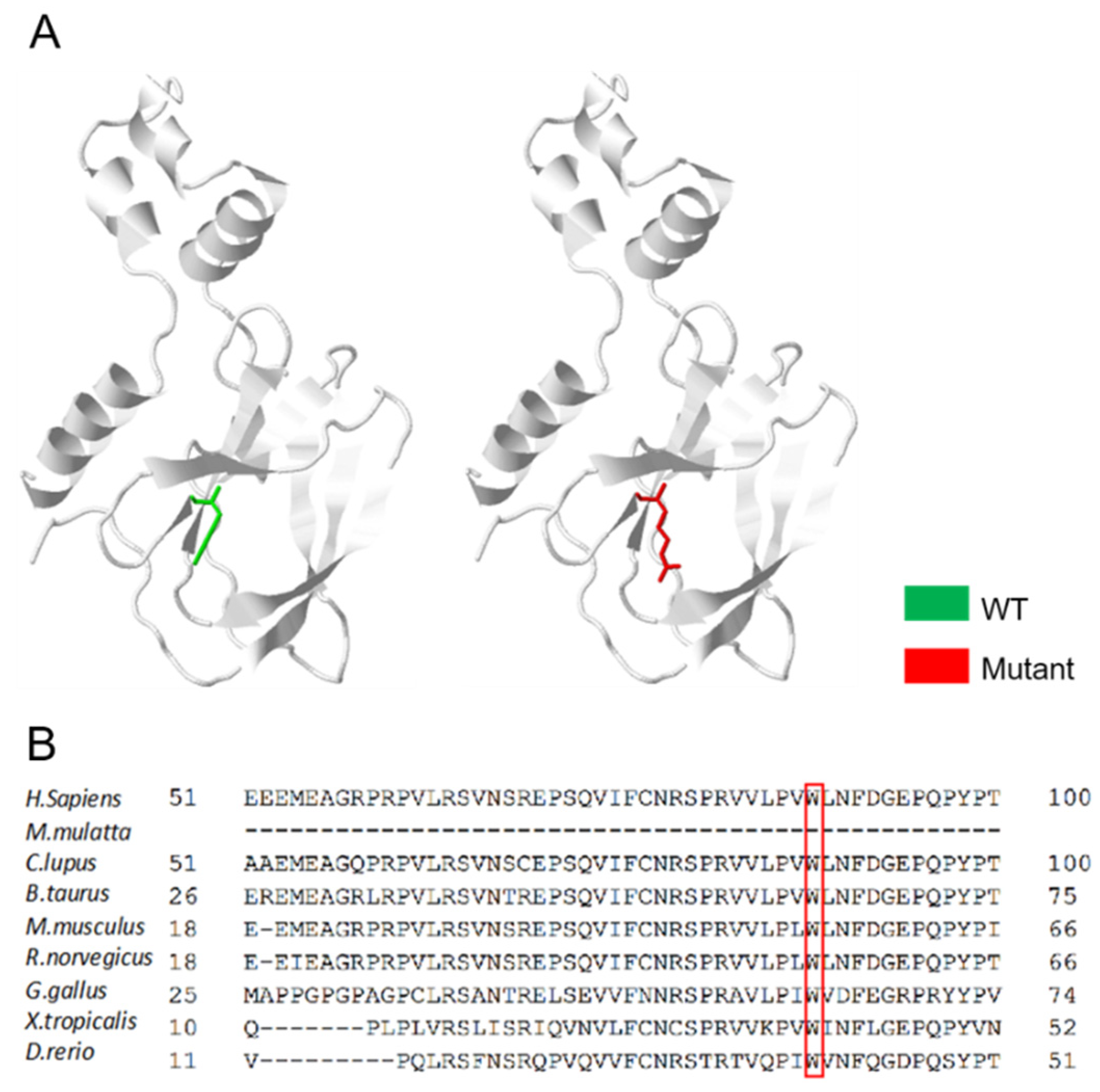
3.3. An Overall Analysis of the VHL p.Trp88Arg Mutation
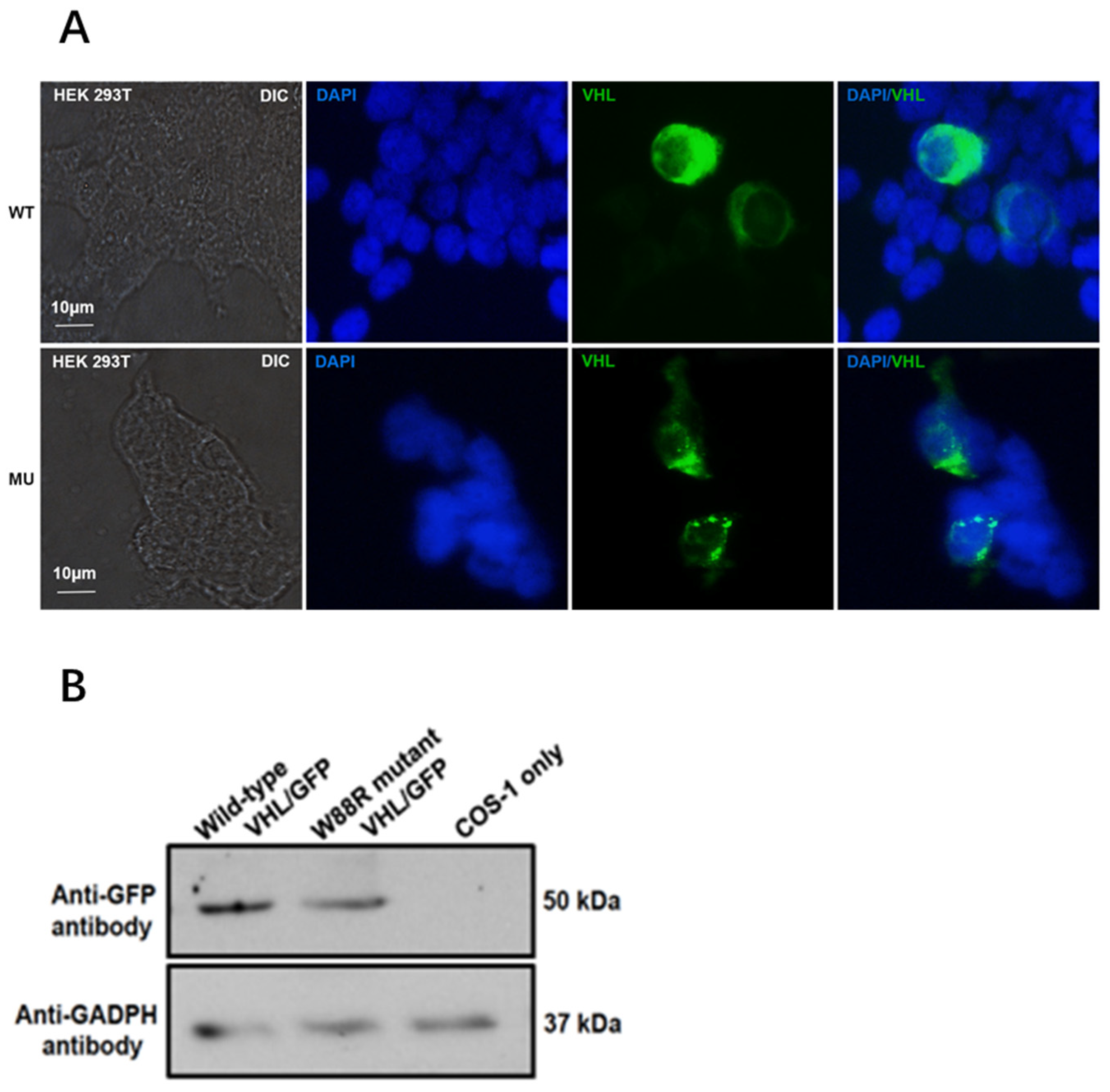
3.4. Mutation Changed Localization of pVHL and Reduced Its Protein Level in Transfected Mammalian Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liss, M.; Natarajan, L.; Hasan, A.; Noguchi, J.L.; White, M.; Parsons, K.J. Physical Activity Decreases Kidney Cancer Mortality. Curr. Urol. 2017, 10, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonerba, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Sonpavde, G. Combination therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nature 2013, 499, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linehan, W.M.; Spellman, P.T.; Ricketts, C.J.; Creighton, C.J.; Fei, S.S.; Davis, C.; Wheeler, D.A.; Murray, B.A.; Schmidt, L. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Papillary Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.; Ricketts, C.J.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Cherniack, A.D.; Shen, H.; Buhay, C.; Kang, H.; Kim, S.C.; Fahey, C.C.; et al. The somatic genomic landscape of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casuscelli, J.; Vano, Y.-A.; Fridman, W.H.; Hsieh, J.J. Molecular Classification of Renal Cell Carcinoma and Its Implication in Future Clinical Practice. Kidney Cancer 2017, 1, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, J.J.; Purdue, M.P.; Signoretti, S.; Swanton, C.; Albiges, L.; Schmidinger, M.; Heng, D.Y.; Larkin, J.; Ficarra, V. Renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallan, A.J.; Parilla, M.; Segal, J.; Ritterhouse, L.; Antic, T. BAP1-Mutated Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 155, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piva, F.; Santoni, M.; Matrana, M.R.; Satti, S.; Giulietti, M.; Occhipinti, G.; Massari, F.; Cheng, L.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Scarpelli, M.; et al. BAP1, PBRM1 and SETD2 in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma: Molecular diagnostics and possible targets for personalized therapies. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.; Schüler, J.; Hoefflin, R.; Korzeniewski, N.; Grüllich, C.; Roth, W.; Teber, D.; Hadaschik, B.; Pahernik, S.; Hohenfellner, M.; et al. Phenotypic drug screening and target validation for improved personalized therapy reveal the complexity of phenotype-genotype correlations in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2014, 32, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Cong, X.; Li, Z.; Ren, M. The Clinicopathological Significance of Epigenetic Silencing of VHL Promoter and Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashouri, K.; Mohseni, S.; Tourtelot, J.; Sharma, P.; Spiess, P.E. Implications of Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome and Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Kidney Cancer VHL 2015, 2, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calzada, M.J. Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome: Molecular mechanisms of the disease. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2010, 12, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Kaelin, W.G. The VHL/HIF axis in clear cell renal carcinoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 23, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, N.; Jing, T.; Ji, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhao, L.; Tian, R.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. Novel Bi-Allelic Variants of FANCM Cause Sertoli Cell-Only Syndrome and Non-Obstructive Azoospermia. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 799886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomella, P.T.; Shin, P.; Srinivasan, R.; Linehan, W.M.; Ball, M.W. Obstructive azoospermia secondary to bilateral epididymal cystadenomas in a patient with von Hippel-Lindau. Urol. Case Rep. 2019, 27, 100922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, N.; Kebede, A.A.; Owusu-Dapaah, H.; Lather, J.; Kaushik, M.; Bhullar, J.S. A Review of Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome. J. Kidney Cancer VHL 2017, 4, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batavia, A.A.; Schraml, P.; Moch, H. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma with wild-type von Hippel-Lindau gene: A non-existent or new tumour entity? Histopathology 2019, 74, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganeshan, D.; Menias, C.O.; Pickhardt, P.J.; Sandrasegaran, K.; Lubner, M.G.; Ramalingam, P.; Bhalla, S. Tumors in von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome: From Head to Toe-Comprehensive State-of-the-Art Review. Radiographics 2018, 38, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satir, P.; Christensen, S.T. Structure and function of mammalian cilia. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 129, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Khouri, E.; Thomas, L.; Jeanson, L.; Bequignon, E.; Vallette, B.; Duquesnoy, P.; Montantin, G.; Copin, B.; Moal, F.D.-L.; Blanchon, S.; et al. Mutations in DNAJB13, Encoding an HSP40 Family Member, Cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia and Male Infertility. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisgrove, B.W.; Yost, H.J. The roles of cilia in developmental disorders and disease. Development 2006, 133, 4131–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gate, D.; Danielpour, M.; Bannykh, S.; Town, T. Characterization of cancer stem cells and primary cilia in medulloblastoma. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 14, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamiok-Ostrowska, A.; Piekiełko-Witkowska, A. Ciliary Genes in Renal Cystic Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Kim, W.Y. Two sides to every story: The HIF-dependent and HIF-independent functions of pVHL. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorak, J.; Sitorova, V.; Nikolov, D.H.; Filipova, A.; Ryska, A.; Melichar, B.; Richter, I.; Buka, D.; Mokry, J.; Filip, S.; et al. Primary cilia in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Neoplasma 2014, 61, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manning, D.K.; Sergeev, M.; van Heesbeen, R.G.; Wong, M.D.; Oh, J.-H.; Liu, Y.; Henkelman, R.M.; Drummond, I.; Shah, J.V.; Beier, D.R. Loss of the ciliary kinase Nek8 causes left-right asymmetry defects. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frank, V.; Habbig, S.; Bartram, M.P.; Eisenberger, T.; Veenstra-Knol, H.E.; Decker, C.; Boorsma, R.A.C.; Göbel, H.; Nürnberg, G.; Griessmann, A.; et al. Mutations in NEK8 link multiple organ dysplasia with altered Hippo signalling and increased c-MYC expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 2177–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zalli, D.; Bayliss, R.; Fry, A.M. The Nek8 protein kinase, mutated in the human cystic kidney disease nephronophthisis, is both activated and degraded during ciliogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1155–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, W.; Tessarollo, L.; Hong, S.-B.; Baba, M.; Southon, E.; Back, T.C.; Spence, S.; Lobe, C.G.; Sharma, N.; Maher, G.W.; et al. Hepatic vascular tumors, angiectasis in multiple organs, and impaired spermatogenesis in mice with conditional inactivation of the VHL gene. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5320–5328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Man, Y.; Shang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Q.; Ma, S.; Shiang, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z. Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies the VHL Mutation (c.262T > C, p.Try88Arg) in Non-Obstructive Azoospermia-Associated Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2376-2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040192
Man Y, Shang X, Liu C, Zhang W, Huang Q, Ma S, Shiang R, Zhang F, Zhang L, Zhang Z. Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies the VHL Mutation (c.262T > C, p.Try88Arg) in Non-Obstructive Azoospermia-Associated Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(4):2376-2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040192
Chicago/Turabian StyleMan, Yonghong, Xuejun Shang, Chunyu Liu, Wei Zhang, Qian Huang, Suheng Ma, Rita Shiang, Feng Zhang, Ling Zhang, and Zhibing Zhang. 2022. "Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies the VHL Mutation (c.262T > C, p.Try88Arg) in Non-Obstructive Azoospermia-Associated Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma" Current Oncology 29, no. 4: 2376-2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040192
APA StyleMan, Y., Shang, X., Liu, C., Zhang, W., Huang, Q., Ma, S., Shiang, R., Zhang, F., Zhang, L., & Zhang, Z. (2022). Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies the VHL Mutation (c.262T > C, p.Try88Arg) in Non-Obstructive Azoospermia-Associated Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Current Oncology, 29(4), 2376-2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040192




