Quantitative Analysis of Prostate MRI: Correlation between Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
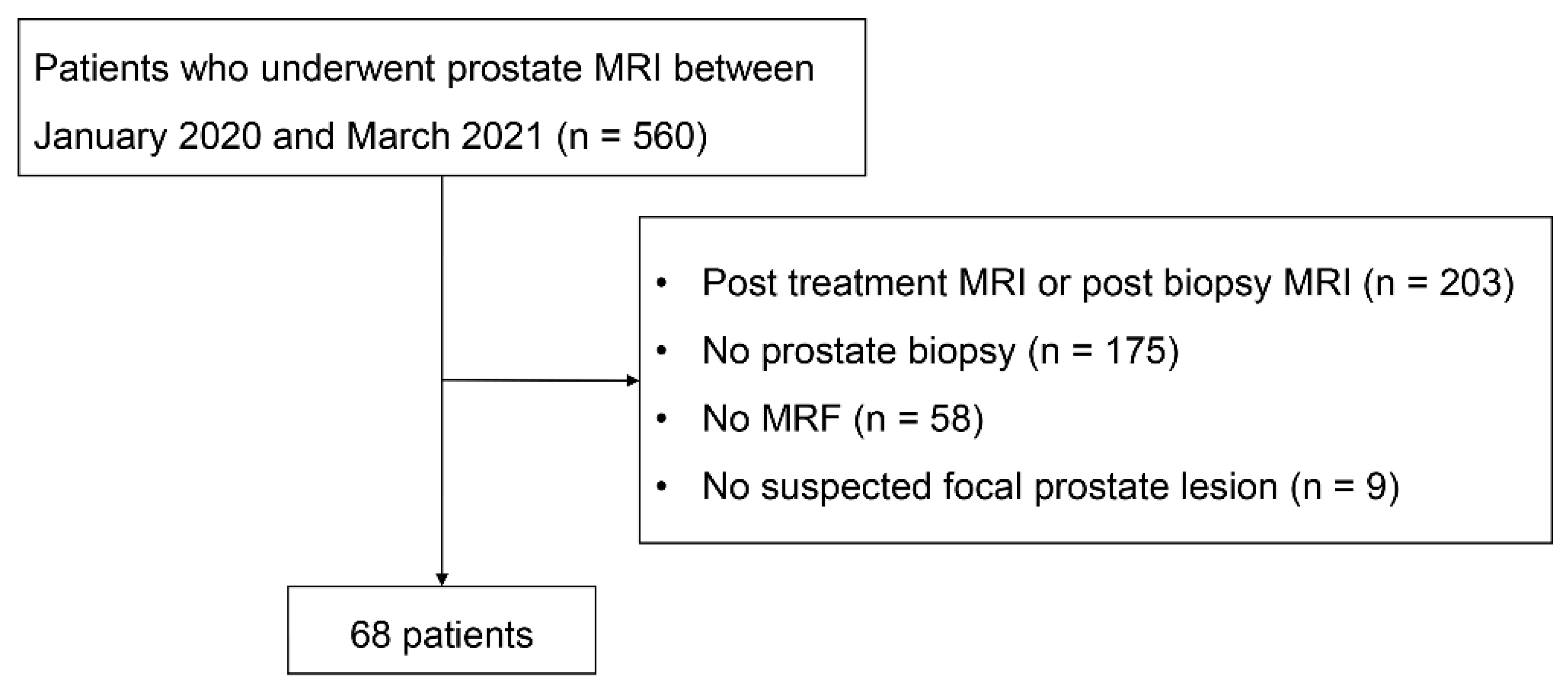
2.1. Patients
2.2. MRI Protocol
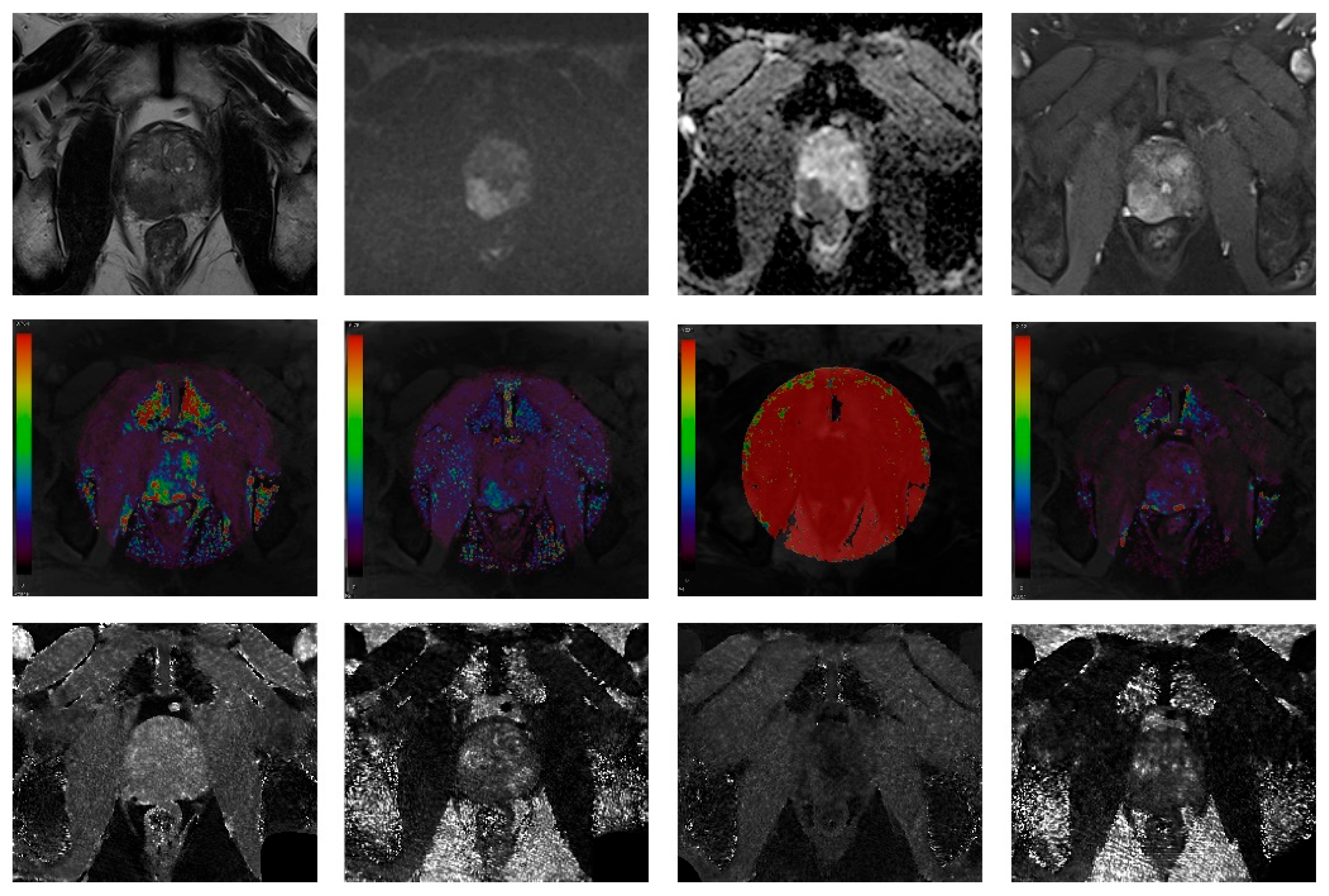
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
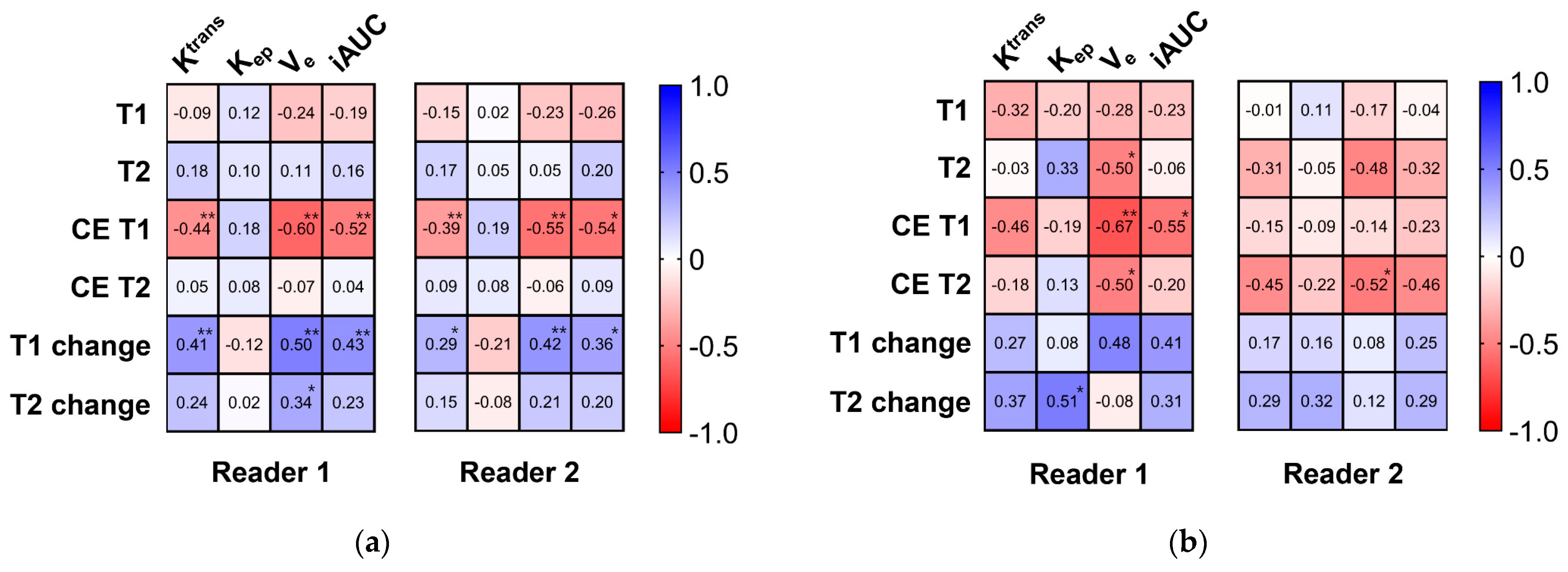
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weinreb, J.C.; Barentsz, J.O.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Haider, M.A.; Macura, K.J.; Margolis, D.; Schnall, M.D.; Shtern, F.; Tempany, C.M.; et al. PI-RADS Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System: 2015, Version 2. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, T.; Kido, A.; Yamamoto, A.; Takeuchi, M.; Miyaji, Y.; Moriya, T.; Sone, T. Comparison of Biparametric and Multiparametric MRI for Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Detection With PI-RADS Version 2.1. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 53, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, C.K.; Bruhn, R.; Kramer, N.; Nebelung, S.; Heidenreich, A.; Schrading, S. Abbreviated Biparametric Prostate MR Imaging in Men with Elevated Prostate-specific Antigen. Radiology 2017, 285, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Campli, E.; Delli Pizzi, A.; Seccia, B.; Cianci, R.; d’Annibale, M.; Colasante, A.; Cinalli, S.; Castellan, P.; Navarra, R.; Iantorno, R.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of biparametric vs multiparametric MRI in clinically significant prostate cancer: Comparison between readers with different experience. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 101, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabile, A.; Giganti, F.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Taneja, S.S.; Villeirs, G.; Gill, I.S.; Allen, C.; Emberton, M.; Moore, C.M.; Kasivisvanathan, V. Multiparametric MRI for prostate cancer diagnosis: Current status and future directions. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2020, 17, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, R.M.; Brown, A.M.; Chang, S.D.; Sankineni, S.; Kadakia, M.; Wood, B.J.; Pinto, P.A.; Choyke, P.L.; Turkbey, B. DCE MRI of prostate cancer. Abdom. Radiol. 2016, 41, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barentsz, J.O.; Richenberg, J.; Clements, R.; Choyke, P.; Verma, S.; Villeirs, G.; Rouviere, O.; Logager, V.; Fütterer, J.J. ESUR prostate MR guidelines 2012. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziayee, F.; Ullrich, T.; Blondin, D.; Irmer, H.; Arsov, C.; Antoch, G.; Quentin, M.; Schimmöller, L. Impact of qualitative, semi-quantitative, and quantitative analyses of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnet resonance imaging on prostate cancer detection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari Mirak, S.; Mohammadian Bajgiran, A.; Sung, K.; Asvadi, N.H.; Markovic, D.; Felker, E.R.; Lu, D.; Sisk, A.; Reiter, R.E.; Raman, S.S. Dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MR imaging: The role of qualitative and quantitative parameters for evaluating prostate tumors stratified by Gleason score and PI-RADS v2. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansford, B.G.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Vannier, M.W.; Antic, T.; Thomas, S.; McCann, S.; Oto, A. Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging Curve-type Analysis: Is It Helpful in the Differentiation of Prostate Cancer from Healthy Peripheral Zone? Radiology 2015, 275, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franiel, T.; Hamm, B.; Hricak, H. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and pharmacokinetic models in prostate cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yuan, Q.; Costa, D.N.; Senegas, J.; Xi, Y.; Wiethoff, A.J.; Rofsky, N.M.; Roehrborn, C.; Lenkinski, R.E.; Pedrosa, I. Quantitative diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced characterization of the index lesion with multiparametric MRI in prostate cancer patients. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 45, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, E.K.; Litjens, G.J.; Kobus, T.; Hambrock, T.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.A.; Barentsz, J.O.; Huisman, H.J.; Scheenen, T.W. Assessment of prostate cancer aggressiveness using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging at 3 T. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.; Chung, D.J.; Yeo, D.M.; Sohn, D.; Son, Y.; Kim, T.; Hahn, S.-T. Optimal cut-off value of perfusion parameters for diagnosing prostate cancer and for assessing aggressiveness associated with Gleason score. Clin. Imaging 2015, 39, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristel, G.; Esposito, A.; Damascelli, A.; Briganti, A.; Ambrosi, A.; Brembilla, G.; Brunetti, L.; Antunes, S.; Freschi, M.; Montorsi, F.; et al. Can DCE-MRI reduce the number of PI-RADS v.2 false positive findings? Role of quantitative pharmacokinetic parameters in prostate lesions characterization. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 118, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Gulani, V.; Seiberlich, N.; Liu, K.; Sunshine, J.L.; Duerk, J.L.; Griswold, M.A. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting. Nature 2013, 495, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, A.; O’Connor, G.; Lo, W.C.; Jiang, Y.; Margevicius, S.; Schluchter, M.; Ponsky, L.E.; Gulani, V. Targeted Biopsy Validation of Peripheral Zone Prostate Cancer Characterization With Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting and Diffusion Mapping. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Obmann, V.C.; Lo, W.C.; Margevicius, S.; Jiang, Y.; Schluchter, M.; Patel, I.J.; Nakamoto, D.; Badve, C.; Griswold, M.A.; et al. MR Fingerprinting and ADC Mapping for Characterization of Lesions in the Transition Zone of the Prostate Gland. Radiology 2019, 292, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Choi, M.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, D.H. Feasibility of Novel Three-Dimensional Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting of the Prostate Gland: Phantom and Clinical Studies. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushentsev, N.; Kaggie, J.D.; Buonincontri, G.; Schulte, R.F.; Graves, M.J.; Gnanapragasam, V.J.; Barrett, T. The effect of gadolinium-based contrast agent administration on magnetic resonance fingerprinting-based T1 relaxometry in patients with prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Choi, M.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Han, D.; Kim, D.H. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting in prostate cancer before and after contrast enhancement. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20210479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenod, C.A.; Balvay, D. Perfusion and vascular permeability: Basic concepts and measurement in DCE-CT and DCE-MRI. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2013, 94, 1187–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocak, I.; Bernardo, M.; Metzger, G.; Barrett, T.; Pinto, P.; Albert, P.S.; Choyke, P.L. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of prostate cancer at 3 T: A study of pharmacokinetic parameters. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 189, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesnais, A.L.; Niaf, E.; Bratan, F.; Mege-Lechevallier, F.; Roche, S.; Rabilloud, M.; Colombel, M.; Rouvière, O. Differentiation of transitional zone prostate cancer from benign hyperplasia nodules: Evaluation of discriminant criteria at multiparametric MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2013, 68, e323–e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oto, A.; Kayhan, A.; Jiang, Y.; Tretiakova, M.; Yang, C.; Antic, T.; Dahi, F.; Shalhav, A.L.; Karczmar, G.; Stadler, W.M.; et al. Prostate cancer: Differentiation of central gland cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia by using diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2010, 257, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.J.; Wienke, A.; Surov, A. Can dynamic contrast enhanced MRI predict gleason score in prostate cancer? A systematic review and meta analysis. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 784.e17–784.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noworolski, S.M.; Henry, R.G.; Vigneron, D.B.; Kurhanewicz, J. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in normal and abnormal prostate tissues as defined by biopsy, MRI, and 3D MRSI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 53, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Axial T2WI (TSE) | Coronal T2WI (TSE) | Sagittal T2WI (TSE) | 3D T2WI (CS 3D SPACE) | T1WI (TSE) | DWI | MRF | DCE MRI (GRASP) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TR (ms) | 2500–3000 | 2510 | 4220 | 1800 | 500–700 | 5200–6000 | 16 | 4 |
| TE (ms) | 103 | 103 | 100 | 104 | 9 | 76 | 4 | 2 |
| Field of views (mm) | 180 × 180 | 180 × 180 | 180 × 180 | 200 × 200 | 180 × 180 | 200 × 180 | 160 × 160 | 200 × 200 |
| Matrix | 320 × 320 | 640 × 640 | 640 × 640 | 577 × 577 | 320 × 320 | 120 × 108 | 256 × 256 | 224 × 224 |
| Resolution (mm) | 0.6 × 0.6 | 0.3 × 0.3 | 0.3 × 0.3 | 0.3 × 0.3 | 0.6 × 0.6 | 1.7 × 1.7 | 0.6 × 0.6 | 0.9 × 0.9 |
| Flip angle (degrees) | 136 | 136 | 120 | 135 | 120 | 90 | Sinusoidal flip angle | 12 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0.6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Gap | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NEX | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2, 2, 9, 9 | 1 | 1 |
| B values (s/mm2) | - | - | - | - | - | 0, 100, 1000, 1500 | - | - |
| Acquisition time (min:s) | 3:32 | 3:17 | 3:17 | 4:55 | 3:35 | 5:58 | 3:48 | 3:41 |
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of patients | 68 |
| Age (years) | 70.0 ± 10.0 |
| PSA (ng/mL) | 37.7 ± 112.2 |
| PI-RADS classification (n [%]) | |
| 3 | 1 (1.5) |
| 4 | 32 (47.1) |
| 5 | 35 (51.5) |
| Location of the focal lesion (n, [%]) | |
| Peripheral zone | 46 (67.6) |
| Transition zone | 22 (32.4) |
| Prostate cancer (n, [%]) | 51 (75.0) |
| Peripheral zone | 35 (68.6) |
| Transition zone | 16 (31.4) |
| Gleason grade group (n, [%]) | |
| 1 | 4 (5.9) |
| 2 | 14 (20.6) |
| 3 | 18 (26.5) |
| 4 | 10 (14.7) |
| 5 | 5 (7.4) |
| Parameters | ICC | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| MRF | ||
| T1 value (,) | 0.825 | <0.001 |
| T2 value (ms) | 0.898 | <0.001 |
| CE T1 value (ms) | 0.968 | <0.001 |
| CE T2 value (ms) | 0.859 | <0.001 |
| T1 change (%) | 0.892 | <0.001 |
| T2 change (%) | 0.708 | <0.001 |
| DCE MRI | ||
| Ktrans | 0.870 | <0.001 |
| Kep | 0.854 | <0.001 |
| Ve | 0.854 | <0.001 |
| iAUC | 0.904 | <0.001 |
| Parameters | Reader 1 | Reader 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noncancer (n = 11) | Prostate Cancer (n = 35) | p Value | Noncancer (n = 11) | Prostate Cancer (n = 35) | p Value | |
| MRF | ||||||
| T1 value (ms) | 1626.1 ± 171.1 | 1488.2 ± 137.0 | 0.009 | 1622.4 ± 169.5 | 1489.7 ± 210.9 | 0.064 |
| T2 value (ms) | 99.6 ± 27.7 | 83.1 ± 12.6 | 0.081 | 95.17 ± 22.84 | 79.62 ± 11.70 | 0.051 |
| CE T1 value (ms) | 624.9 ± 77.7 | 593.3 ± 96.7 | 0.330 | 640.1 ± 125.6 | 608.4 ± 101.2 | 0.397 |
| CE T2 value (ms) | 95.04 ± 26.58 | 74.9 ± 11.2 | 0.032 | 96.41 ± 26.55 | 71.93 ± 10.51 | 0.019 |
| T1 change (%) | 61.41 ± 4.29 | 60.0 ± 6.34 | 0.491 | 60.76 ± 4.85 | 58.83 ± 6.79 | 0.386 |
| T2 change (%) | 3.999 ± 8.771 | 9.424 ± 7.349 | 0.047 | −1.935 ± 16.863 | 6.904 ± 5.786 | 0.116 |
| DCE MRI | ||||||
| Ktrans | 0.209 ± 0.100 | 0.332 ± 0.101 | 0.001 | 0.241 ± 0.104 | 0.328 ± 0.107 | 0.021 |
| Kep | 0.857 ± 0.382 | 1.181 ± 0.358 | 0.013 | 0.857 ± 0.260 | 1.146 ± 0.402 | 0.031 |
| Ve | 0.242 ± 0.056 | 0.298 ± 0.107 | 0.105 | 0.279 ± 0.089 | 0.307 ± 0.122 | 0.489 |
| iAUC | 0.196 ± 0.059 | 0.301 ± 0.078 | 0.001 | 0.227 ± 0.091 | 0.299 ± 0.084 | 0.018 |
| Parameters | Reader 1 | Reader 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noncancer (n = 6) | Prostate Cancer (n = 16) | p Value | Noncancer (n = 6) | Prostate Cancer (n = 16) | p Value | |
| MRF | ||||||
| T1 value (ms) | 1596.0 ± 115.1 | 1575.8 ± 143.7 | 0.762 | 1608.9 ± 141.8 | 1547.9 ± 188.7 | 0.483 |
| T2 value (ms) | 81.77 ± 15.22 | 76.61 ± 7.93 | 0.306 | 76.32 ± 11.44 | 74.19 ± 9.52 | 0.662 |
| CE T1 value (ms) | 519.87 ± 72.06 | 591.62 ± 94.44 | 0.109 | 490.1 ± 48.8 | 607.5 ± 103.8 | 0.016 |
| CE T2 value (ms) | 80.32 ± 9.94 | 70.02 ± 8.13 | 0.021 | 72.02 ± 5.56 | 65.00 ± 7.37 | 0.048 |
| T1 change (%) | 67.15 ± 6.05 | 62.48 ± 4.67 | 0.068 | 69.32 ± 4.29 | 60.79 ± 4.26 | <0.001 |
| T2 change (%) | 0.003 ± 14.261 | 8.629 ± 4.679 | 0.202 | 4.107 ± 14.595 | 12.138 ± 4.957 | 0.061 |
| DCE MRI | ||||||
| Ktrans | 0.372 ± 0.165 | 0.376 ± 0.139 | 0.954 | 0.322 ± 0.173 | 0.384 ± 0.118 | 0.342 |
| Kep | 1.042 ± 0.464 | 1.247 ± 0.372 | 0.292 | 0.998 ± 0.527 | 1.313 ± 0.420 | 0.159 |
| Ve | 0.356 ± 0.063 | 0.306 ± 0.079 | 0.178 | 0.318 ± 0.055 | 0.302 ± 0.076 | 0.650 |
| iAUC | 0.320 ± 0.137 | 0.340 ± 0.116 | 0.730 | 0.286 ± 0.154 | 0.343 ± 0.100 | 0.317 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, M.-H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Han, D.; Kim, D.-H. Quantitative Analysis of Prostate MRI: Correlation between Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Parameters. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 10299-10310. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30120750
Choi M-H, Lee Y-J, Han D, Kim D-H. Quantitative Analysis of Prostate MRI: Correlation between Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Parameters. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(12):10299-10310. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30120750
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Moon-Hyung, Young-Joon Lee, Dongyeob Han, and Dong-Hyun Kim. 2023. "Quantitative Analysis of Prostate MRI: Correlation between Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Parameters" Current Oncology 30, no. 12: 10299-10310. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30120750
APA StyleChoi, M.-H., Lee, Y.-J., Han, D., & Kim, D.-H. (2023). Quantitative Analysis of Prostate MRI: Correlation between Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Parameters. Current Oncology, 30(12), 10299-10310. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30120750






