The Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. The Relationship between Clinicopathological Parameters and Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A.; Thandra, K.C.; Saginala, K.; Mohammed, A.; Vakiti, A.; Rawla, P.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma. World J. Oncol. 2020, 11, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidegger, I.; Pircher, A.; Pichler, R. Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment in Renal Cell Cancer Biology and Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bamias, A.; Escudier, B.; Sternberg, C.N.; Zagouri, F.; Dellis, A.; Djavan, B.; Tzannis, K.; Kontovinis, L.; Stravodimos, K.; Papatsoris, A.; et al. Current Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Critical Evaluation. Oncologist 2017, 22, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, R.; Ren, F.; Guo, R.; Zhang, P. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with oral cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20181550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faria, S.S.; Fernandes, P.C., Jr.; Silva, M.J.; Lima, V.C.; Fontes, W.; Eterovic, A.K.; Forget, P. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: A narrative review. Ecancermedicalscience 2016, 10, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mjaess, G.; Chebel, R.; Karam, A.; Moussa, I.; Pretot, D.; Abi Tayeh, G.; Sarkis, J.; Semaan, A.; Peltier, A.; Aoun, F.; et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in urological tumors: An umbrella review of evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 704–713. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Health Estimates 2020: Deaths by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country and by Region. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/mortality-and-global-health-estimates/ghe-leading-causes-of-death (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Díaz-Montero, C.M.; Rini, B.I.; Finke, J.H. The immunology of renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonasch, E.; Atkins, M.B.; Chowdhury, S.; Mainwaring, P. Combination of Anti-Angiogenics and Checkpoint Inhibitors for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Is the Whole Greater Than the Sum of Its Parts? Cancers 2022, 14, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. Anti-angiogenic Agents in Combination With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Promising Strategy for Cancer Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Bersanelli, M.; Gelibter, A.J.; Borsellino, N.; Caserta, C.; Doni, L.; Maruzzo, M.; Mosca, A.; Pisano, C.; Verzoni, E.; et al. Combination Therapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma: The Best Choice for Every Patient? Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes-Sousa, M.; Magalhães, H.; Oliveira, A.; Carneiro, F.; Dos Reis, F.P.; Madeira, P.S.; Meireles, S. Reviewing Treatment Options for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Is There Still a Place for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) Monotherapy? Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 1107–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonacera, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Colaci, M.; Malatino, L. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio: An Emerging Marker of the Relationships between the Immune System and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaac, V.; Wu, C.Y.; Huang, C.T.; Baune, B.T.; Tseng, C.L.; McLachlan, C.S. Elevated neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predicts mortality in medical inpatients with multiple chronic conditions. Medicine 2016, 95, e3832, Erratum in Medicine 2016, 95, e0916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otunctemur, A.; Dursun, M.; Besiroglu, H.; Ozer, K.; Horsanali, O.; Ozbek, E. Clinical Significance of Preoperative Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2016, 42, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allenet, C.; Klein, C.; Rouget, B.; Margue, G.; Capon, G.; Alezra, E.; Blanc, P.; Estrade, V.; Bladou, F.; Robert, G.; et al. Can Pre-Operative Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) Help Predict Non-Metastatic Renal Carcinoma Recurrence after Nephrectomy? (UroCCR-61 Study). Cancers 2022, 14, 5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorec, R. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, past, present and future perspectives. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2021, 122, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setakornnukul, J.; Chanvimalueng, W.; Patumanond, J.; Thephamongkhol, K. Cutoff point of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for predicting survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Medicine 2021, 100, e27095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forget, P.; Khalifa, C.; Defour, J.P.; Latinne, D.; van Pel, M.C.; de Kock, M. What is the normal value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio? BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, K.; Lou, L.; Ye, J.; Zhang, S. Prognostic role of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in renal cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e006404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wu, B.; Jia, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wang, D. Prognostic value of pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Urol. 2020, 20, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalani, A.A.; Xie, W.; Martini, D.J.; Steinharter, J.A.; Norton, C.K.; Krajewski, K.M.; Duquette, A.; Bossé, D.; Bellmunt, J.; van Allen, E.M.; et al. Change in Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in response to immune checkpoint blockade for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Meng, F.; Jiang, R. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Biomarker for Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 746976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, N.; Yao, J.; Cheng, C.; Huang, Z.; Hong, L.; Li, H.; Qiu, J. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of the pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of prognosis in renal carcinoma patients receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 44039–44046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, B.; Guo, L.; Shen, R.; Cao, C.; Xie, R.; Jiang, W.; Wen, L.; Bi, X.; Shi, H.; Zheng, S.; et al. Prognostic Significance of NLR About NETosis and Lymphocytes Perturbations in Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma With Tumor Thrombus. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 771545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Hirobe, M.; Kikushima, T.; Matsuki, M.; Takahashi, A.; Yanase, M.; Ichimatsu, K.; Egawa, M.; Hayashi, N.; Negishi, T.; et al. The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio has a role in predicting the effectiveness of nivolumab in Japanese patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A multi-institutional retrospective study. BMC Urol. 2020, 20, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.J.; Knox, J.J.; Lin, X.; Simantov, R.; Xie, W.; Lawrence, N.; Broom, R.; Fay, A.P.; Rini, B.; Donskov, F.; et al. Change in Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio in Response to Targeted Therapy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma as a Prognosticator and Biomarker of Efficacy. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | N (%) |
|---|---|
| All patients | 74 |
| Age (years) | 62.8 (range 43–88) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 52 (70.3%) |
| Female | 22 (29.7%) |
| Surgical treatment | |
| Radical nephrectomy | 48 (64.8%) |
| Tumour biopsy | 11 (14.8%) |
| Partial nephrectomy | 15(20.2%) |
| The main sites of metastasis | |
| Lungs | 17 (23%) |
| Distant lymph nodes | 10 (13.5%) |
| Liver | 29 (39.2%) |
| Bones | 21 (28.4%) |
| Fuhrman grade | |
| 2 | 35 (47.3%) |
| 3 | 33 (44.5%) |
| 4 | 6 (8.1%) |
| Karnofsky Performance Status | |
| <80% | 17 (23%) |
| ≥80% | 57 (77.0%) |
| Time since diagnosis to treatment | |
| <12 months | 52 (70.3%) |
| ≥12 months | 22 (29.7%) |
| Haemoglobin | |
| <LLN | 41 (55.4%) |
| ≥LLN | 33 (44.6%) |
| LHD | |
| ≥1.5× ULN | 12 (16.2%) |
| <1.5× ULN | 62 (83.8%) |
| Serum-corrected calcium | |
| ≥ULN | 16 (21.6%) |
| <ULN | 58 (78.4%) |
| Platelet count | |
| ≥ULN | 24 (32.4%) |
| <ULN | 50 (67.6%) |
| Neutrophil count | |
| ≥ULN | 11 (14.9%) |
| <ULN | 62 (83.8%) |
| NLR | |
| Median (range) | 3.34 ± 3.06 (1–22) |
| ≥3 | 33 (44.5%) |
| <3 | 41 (55.4%) |
| IMDC score | |
| Favourable | 5 (6.8%) |
| Intermediate | 38 (51.4%) |
| Poor | 31 (41.9%) |
| MSKCC score | |
| Low risk | 8 (10.8%) |
| Intermediate risk | 49 (66.2%) |
| High risk | 17 (23.0%) |
| Variable | p-Value | Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
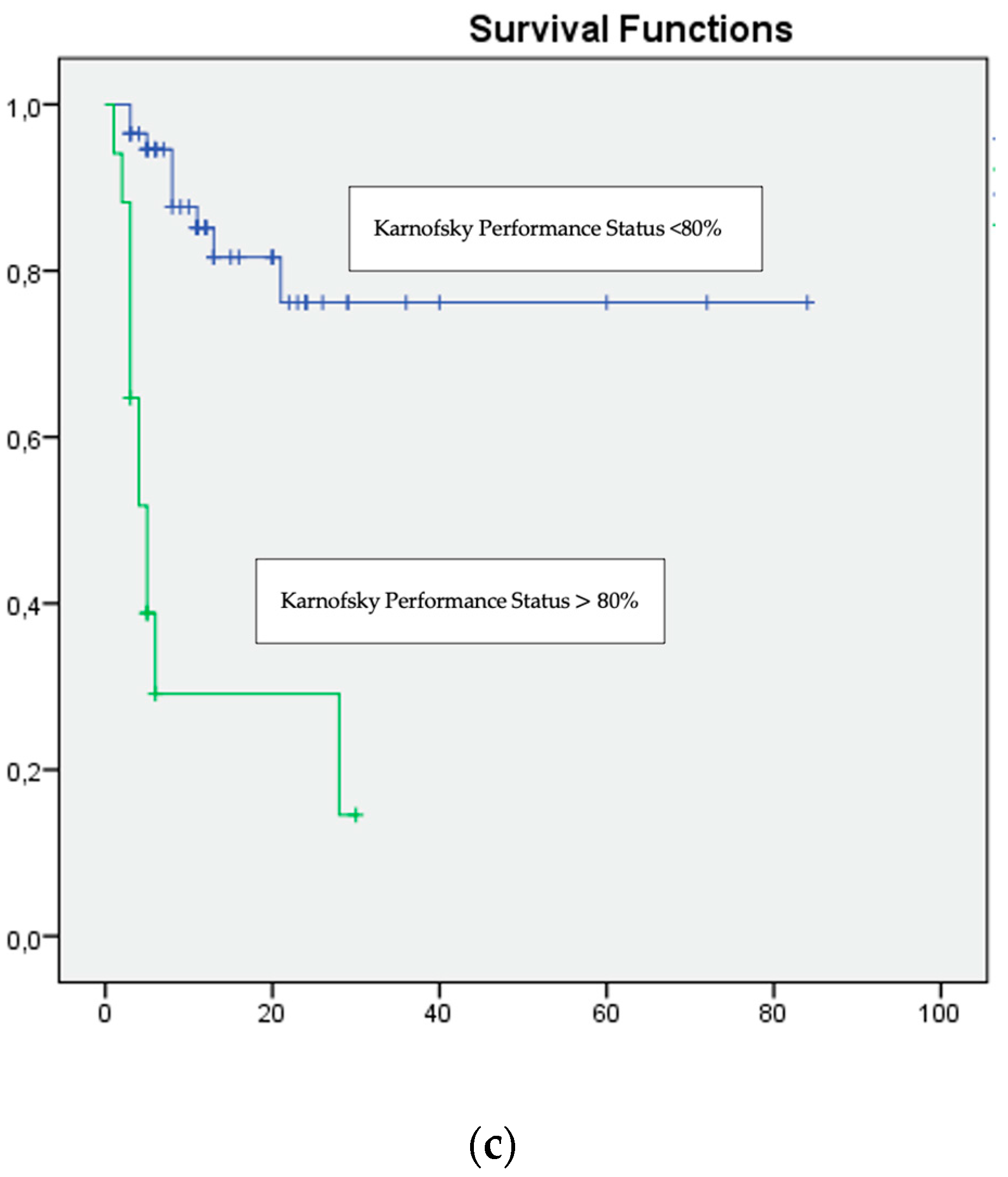
| Karnofsky Performance Status <80% | 0.001 | 2.42 | 1.84–2.76 |
| Time since diagnosis to treatment <12 months | 0.009 | 10.819 | 1.718–68.135 |
| Haemoglobin < LLN | 0.002 | 1.904 | 0.653–5.552 |
| LHD > 1.5× ULN | 0.002 | 1.924 | 0.661–5.597 |
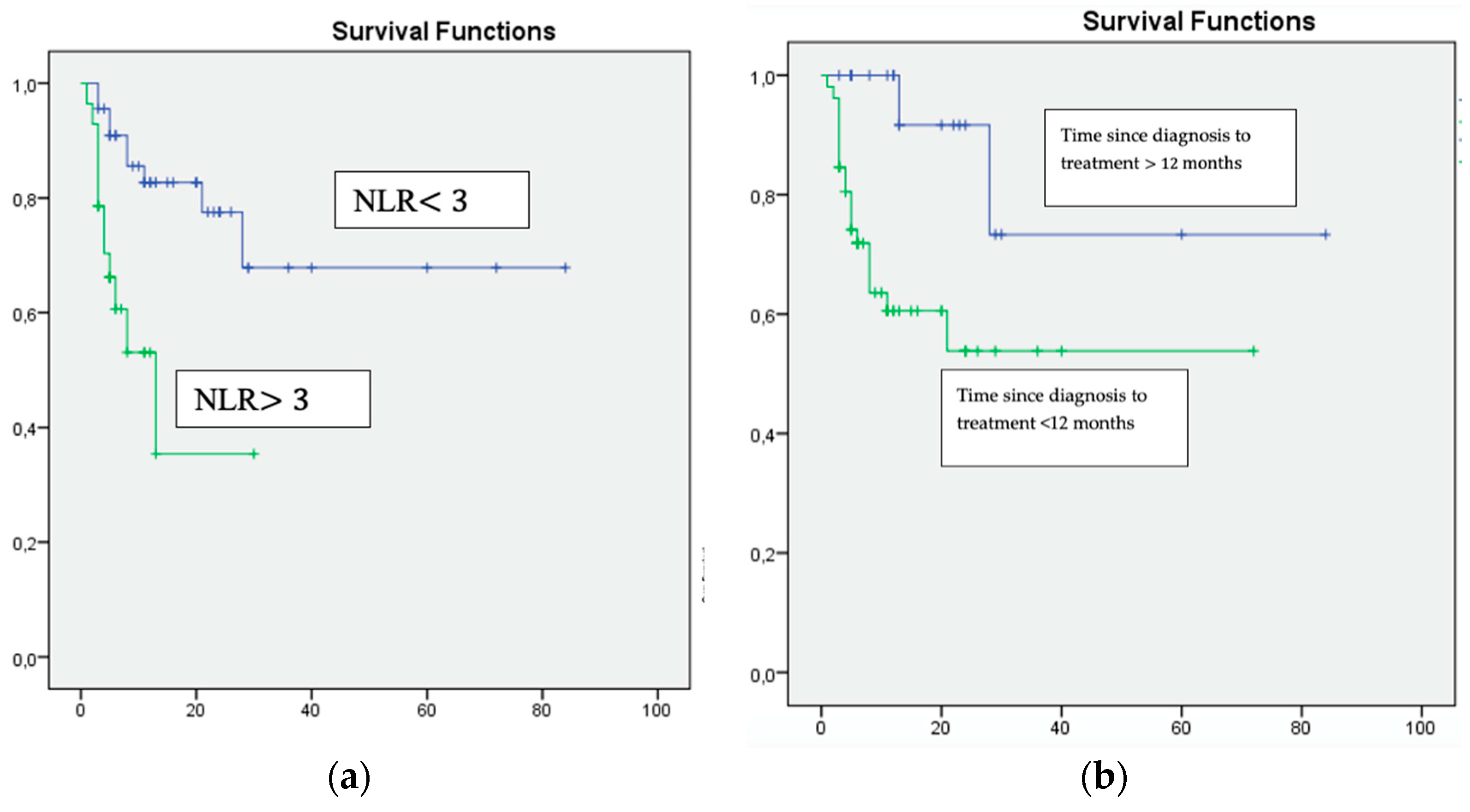
| NLR ≥ 3 | 0.001 | 1.55 | 1.23–1.91 |
| High IMDC and MSKCC scores | 0.001 | 3.30 | 2.22–4.89 |
| Variable | p-Value | Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Karnofsky Performance Status <80% | 0.009 | 16.008 | 1.989–128.86 |
| Time since diagnosis to treatment <12 months | 0.0011 | 10.819 | 1.718–68.135 |
| NLR ≥ 3 | 0.006 | 4.650 | 1.562–13.840 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parosanu, A.I.; Pirlog, C.F.; Slavu, C.O.; Stanciu, I.M.; Cotan, H.-T.; Vrabie, R.C.; Popa, A.-M.; Olaru, M.; Iaciu, C.; Bratu, L.I.; et al. The Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 2457-2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30020187
Parosanu AI, Pirlog CF, Slavu CO, Stanciu IM, Cotan H-T, Vrabie RC, Popa A-M, Olaru M, Iaciu C, Bratu LI, et al. The Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(2):2457-2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30020187
Chicago/Turabian StyleParosanu, Andreea Ioana, Cristina Florina Pirlog, Cristina Orlov Slavu, Ioana Miruna Stanciu, Horia-Teodor Cotan, Radu Constantin Vrabie, Ana-Maria Popa, Mihaela Olaru, Cristian Iaciu, Lucian Ioan Bratu, and et al. 2023. "The Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma" Current Oncology 30, no. 2: 2457-2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30020187
APA StyleParosanu, A. I., Pirlog, C. F., Slavu, C. O., Stanciu, I. M., Cotan, H.-T., Vrabie, R. C., Popa, A.-M., Olaru, M., Iaciu, C., Bratu, L. I., Baicoianu, I. F., Moldoveanu, O., Baston, C., & Nițipir, C. (2023). The Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Current Oncology, 30(2), 2457-2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30020187





