Cuproptosis-Related Gene DLAT as a Novel Biomarker Correlated with Prognosis, Chemoresistance, and Immune Infiltration in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Preliminary Study Based on Bioinformatics Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Processing
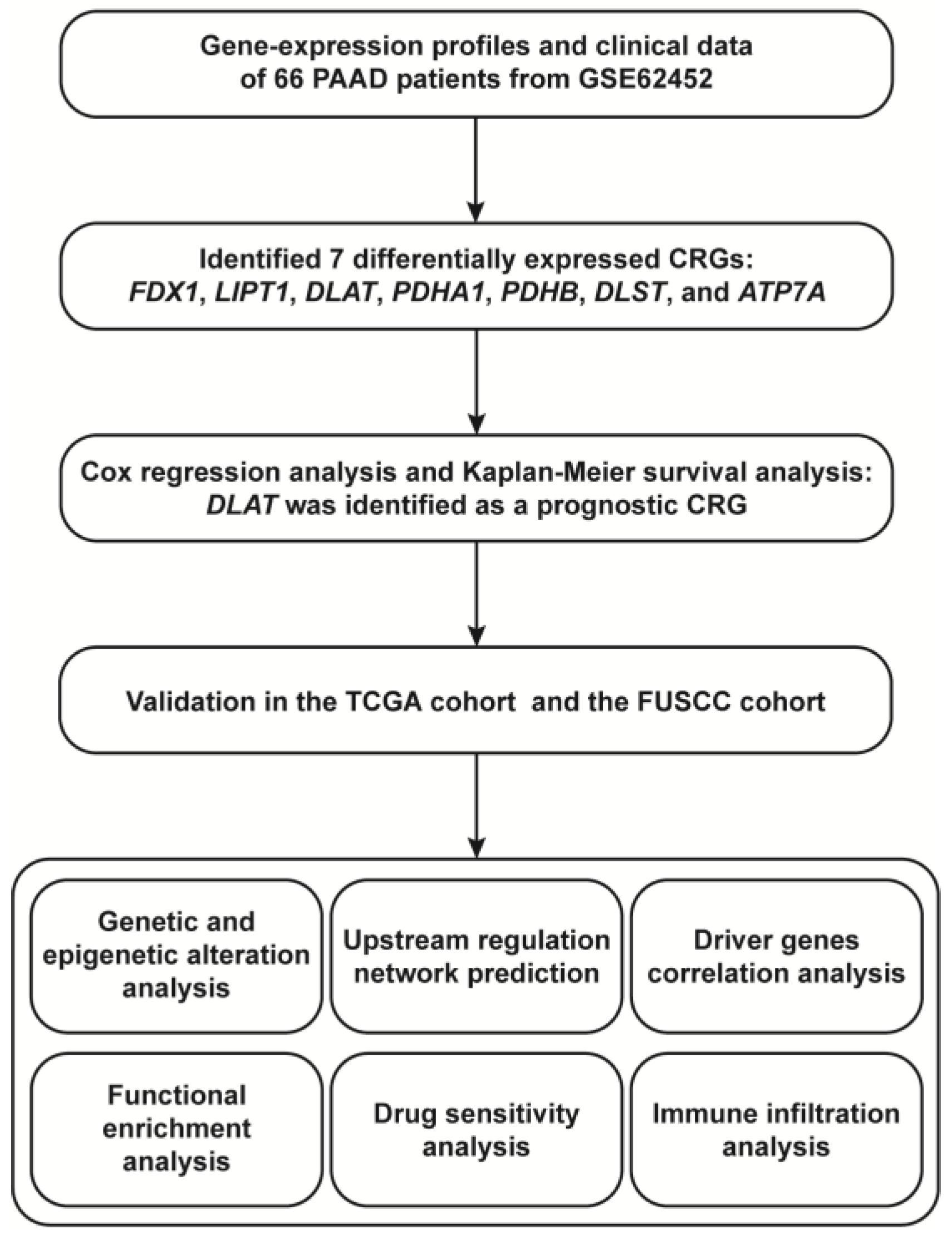
2.2. Identification of Prognostic CRGs
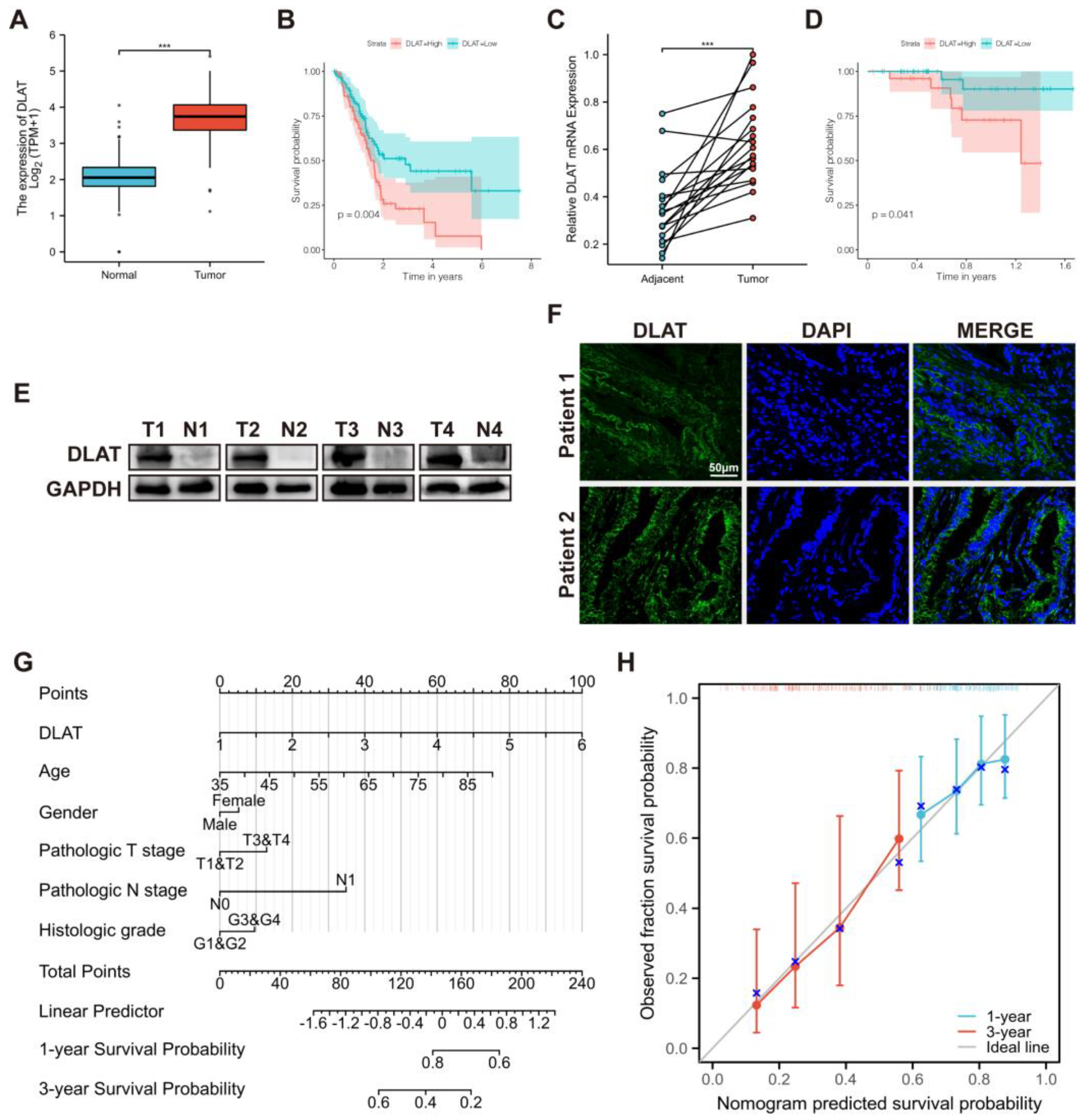
2.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Immunofluorescence
2.6. Analyses of Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations
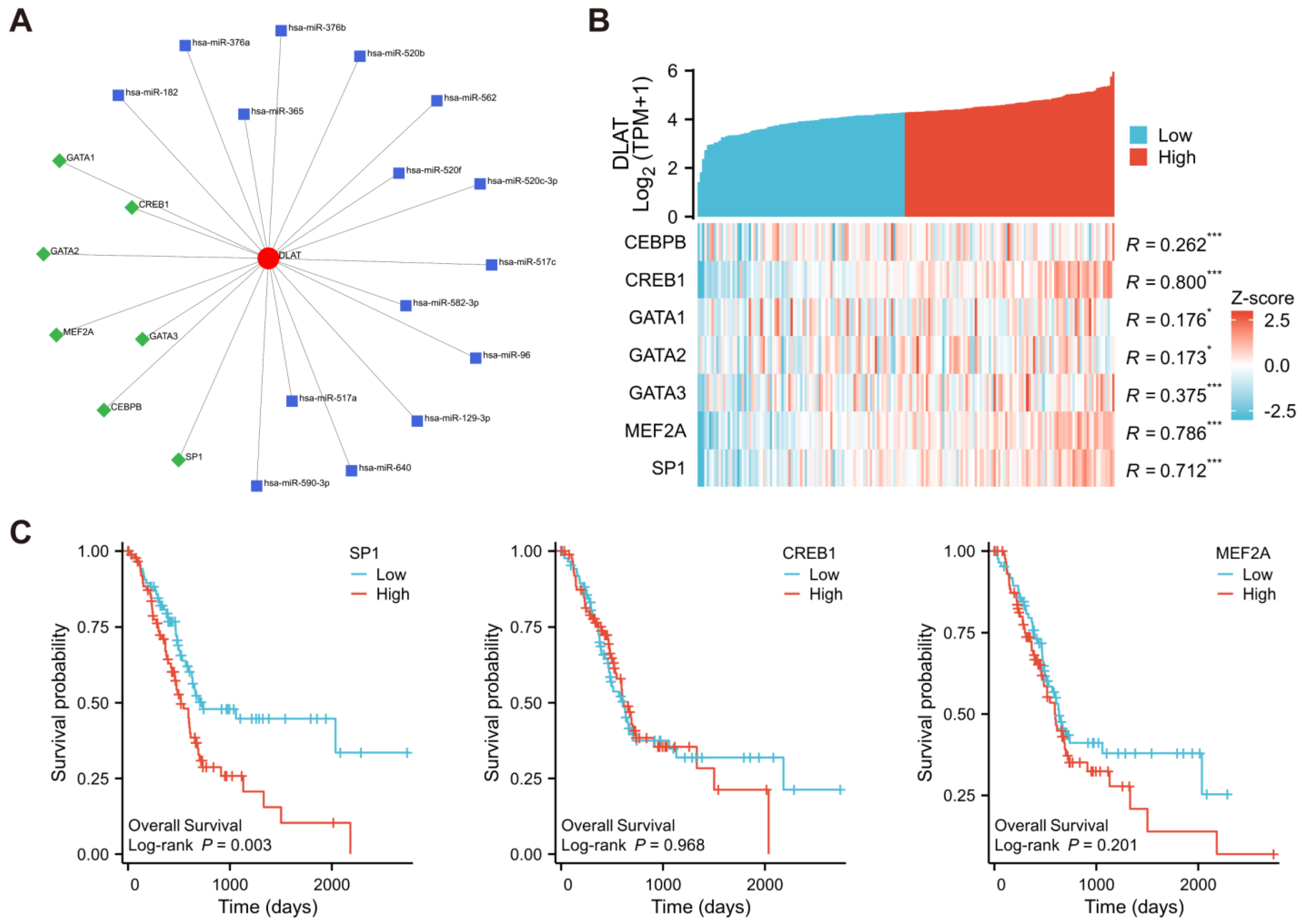
2.7. Prediction of TFs and miRNAs
2.8. Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.9. Drug Sensitivity Analysis
2.10. Evaluation of Immune Infiltration
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DLAT Was Identified as a Prognostic CRG
3.2. Analyses of Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations
3.3. Prediction of TFs and miRNAs Potentially Regulating DLAT
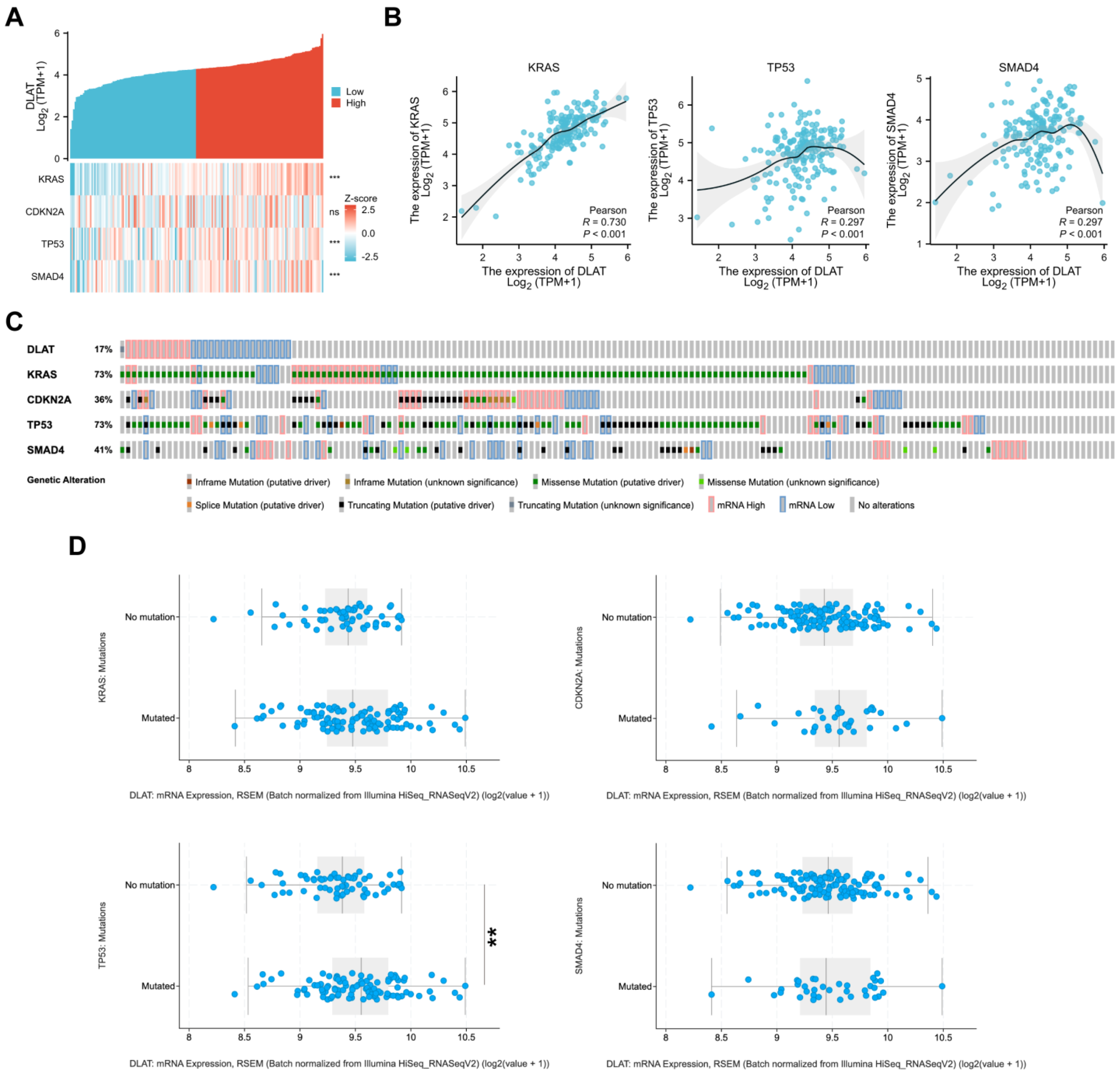
3.4. Correlations between DLAT and Major Driver Genes in PAAD
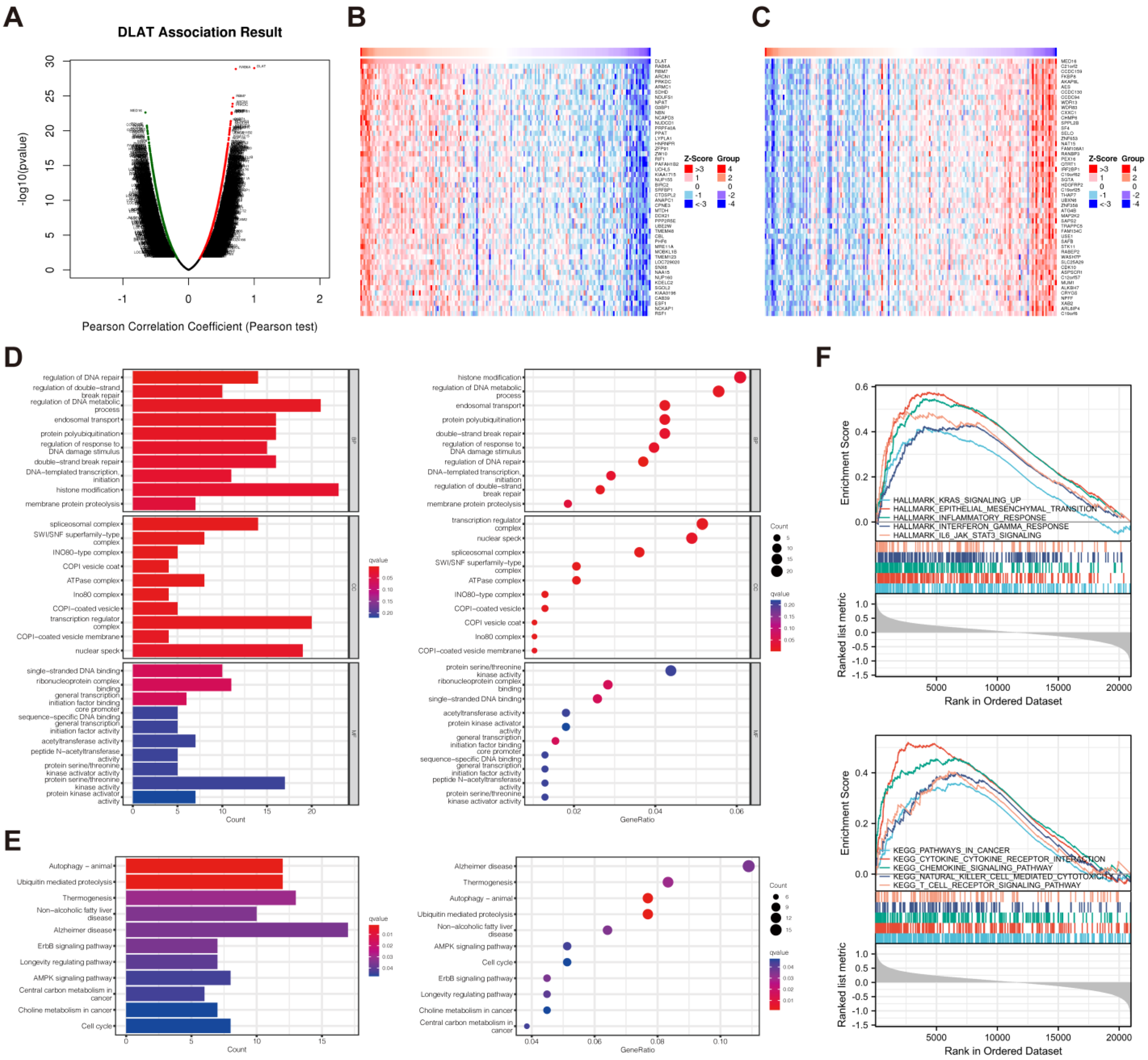
3.5. Functional Enrichment Analysis
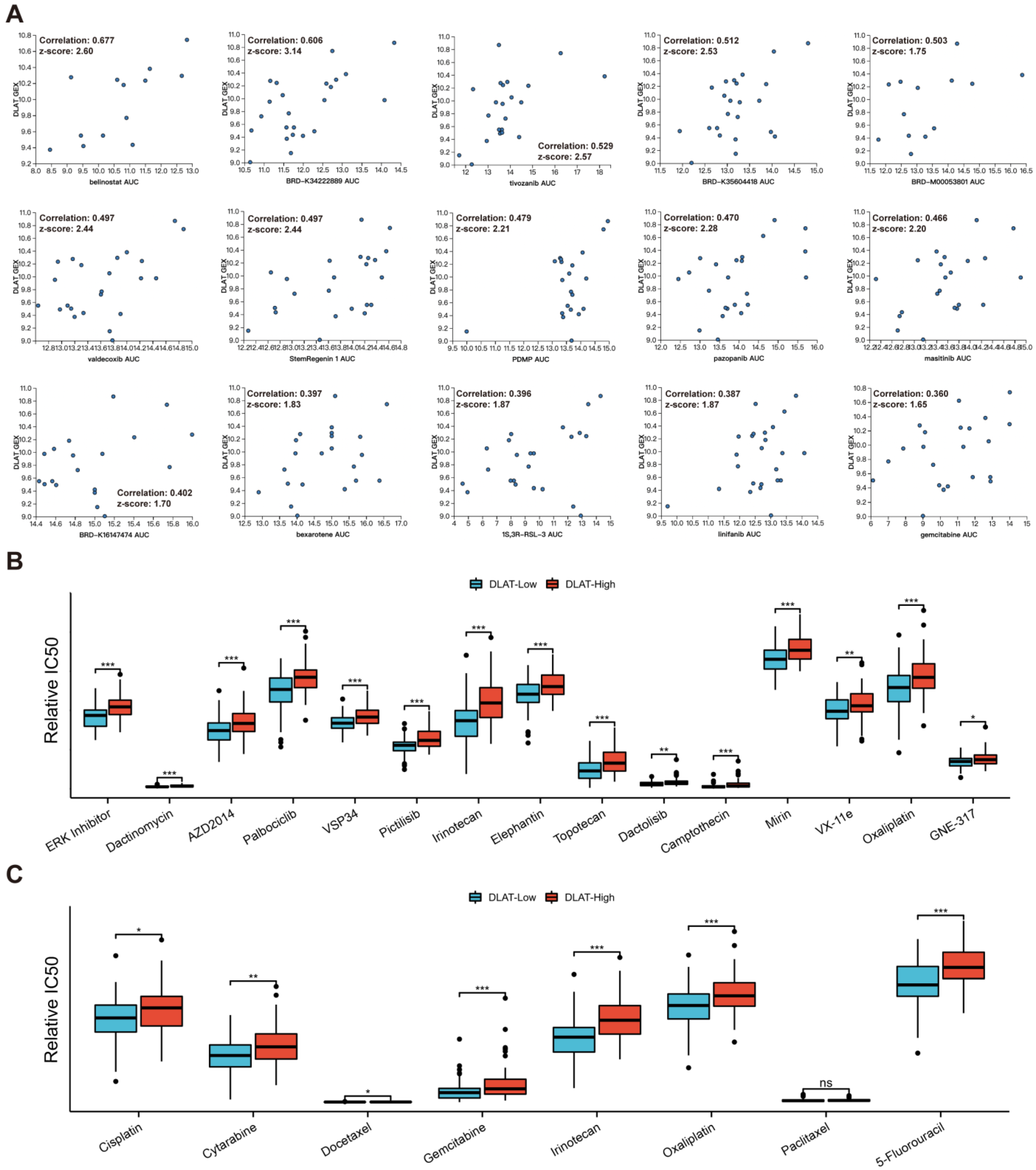
3.6. Drug Sensitivity Analysis
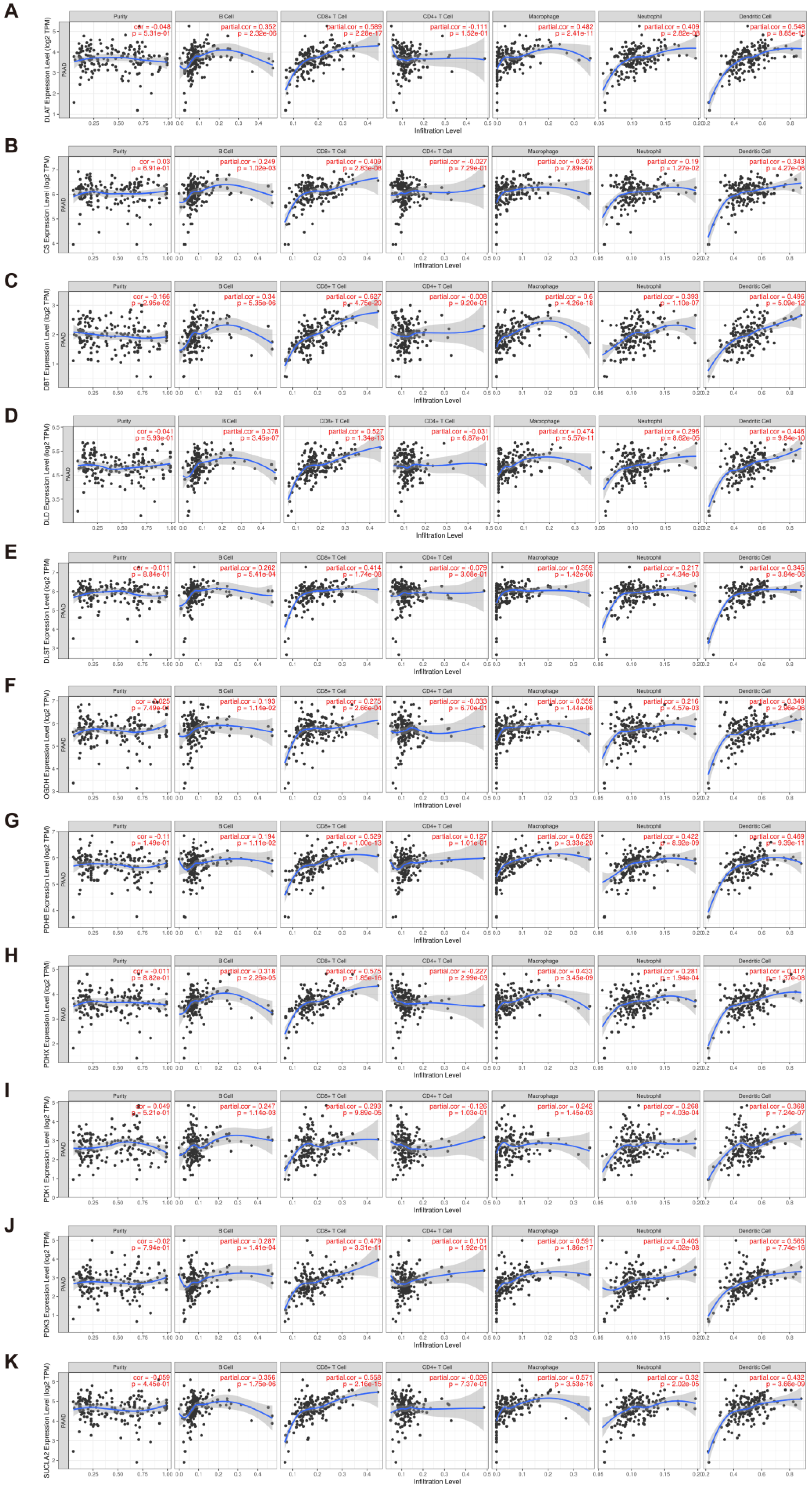
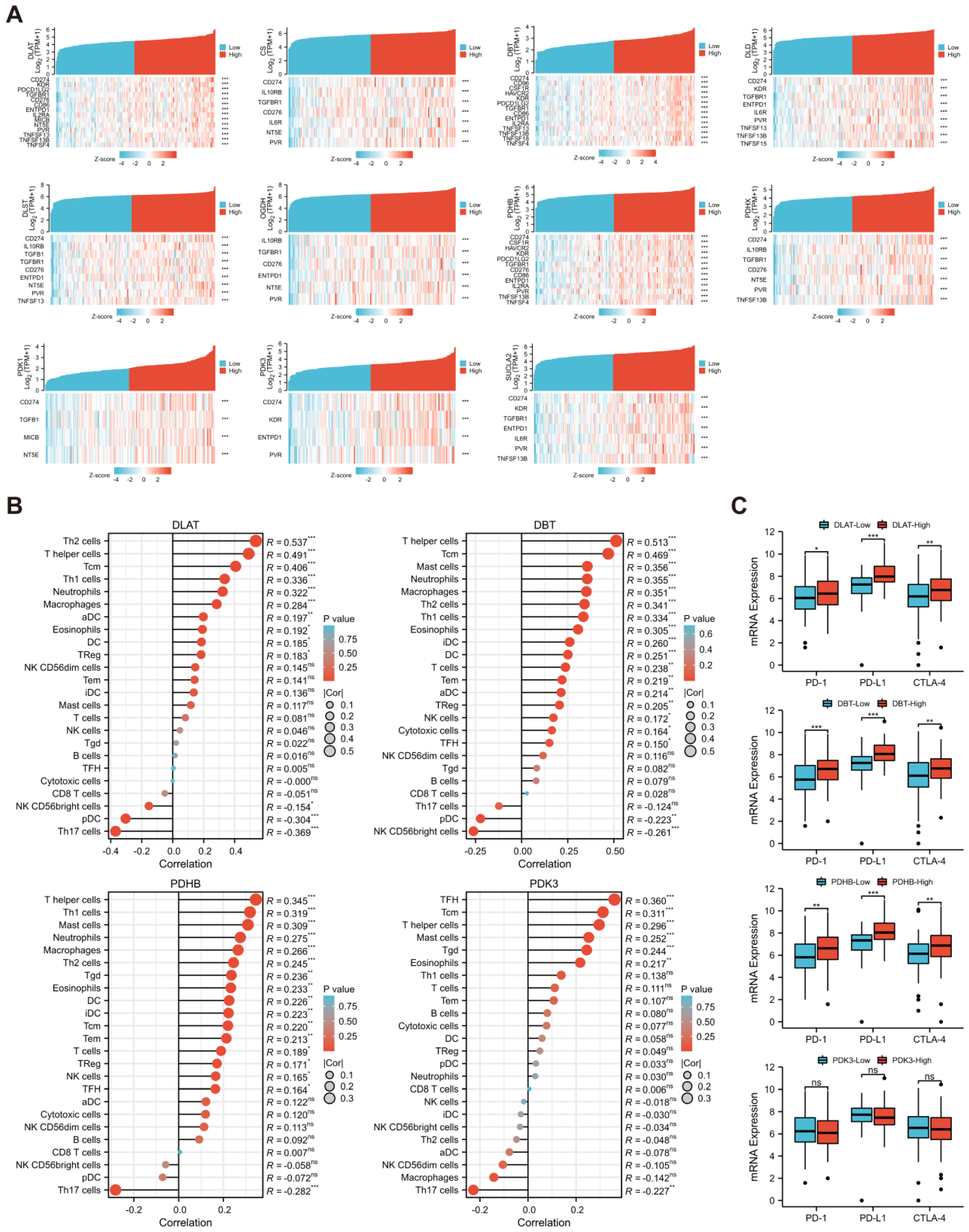
3.7. Evaluation of Immune Infiltration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryan, D.P.; Hong, T.S.; Bardeesy, N. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Chawla, A.; O’Reilly, E.M. Pancreatic Cancer: A Review. Jama 2021, 326, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 395, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenson, E.S.; Jaffee, E.; Azad, N.S. Current and emerging therapies for patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A bright future. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e135–e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.E.; Nevitt, T.; Thiele, D.J. Mechanisms for copper acquisition, distribution and regulation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, N.J.; Winge, D.R. Copper metallochaperones. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 537–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lutsenko, S. Human copper homeostasis: A network of interconnected pathways. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, E.J.; Bush, A.I.; Casini, A.; Cobine, P.A.; Cross, J.R.; DeNicola, G.M.; Dou, Q.P.; Franz, K.J.; Gohil, V.M.; Gupta, S.; et al. Connecting copper and cancer: From transition metal signalling to metalloplasia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, S.; Andreux, P.; Poitry-Yamate, C.; Auwerx, J.; Hanahan, D. Bioavailable copper modulates oxidative phosphorylation and growth of tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19507–19512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsvetkov, P.; Detappe, A.; Cai, K.; Keys, H.R.; Brune, Z.; Ying, W.; Thiru, P.; Reidy, M.; Kugener, G.; Rossen, J.; et al. Mitochondrial metabolism promotes adaptation to proteotoxic stress. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkov, P.; Coy, S.; Petrova, B.; Dreishpoon, M.; Verma, A.; Abdusamad, M.; Rossen, J.; Joesch-Cohen, L.; Humeidi, R.; Spangler, R.D.; et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science 2022, 375, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, B.; Wong, C.N.; Tong, Y.; Zhong, J.Y.; Zhong, S.S.W.; Wu, W.C.; Chu, K.C.; Wong, C.Y.; Lau, C.Y.; Chen, I.; et al. TISIDB: An integrated repository portal for tumor-immune system interactions. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4200–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Shi, S.; Qin, Y.; Meng, Q.; Hua, J.; Hu, Q.; Ji, S.; Zhang, B.; Xu, J.; Yu, X.J. Localisation of PGK1 determines metabolic phenotype to balance metastasis and proliferation in patients with SMAD4-negative pancreatic cancer. Gut 2020, 69, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modhukur, V.; Iljasenko, T.; Metsalu, T.; Lokk, K.; Laisk-Podar, T.; Vilo, J. MethSurv: A web tool to perform multivariable survival analysis using DNA methylation data. Epigenomics 2018, 10, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.P.; Wu, C.; Miao, H.; Wu, H. RegNetwork: An integrated database of transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory networks in human and mouse. Database 2015, 2015, bav095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blake, J.A.; Harris, M.A. The Gene Ontology (GO) project: Structured vocabularies for molecular biology and their application to genome and expression analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2008, 23, 7.2.1–7.2.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasaikar, S.V.; Straub, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. LinkedOmics: Analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer types. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D956–D963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geeleher, P.; Cox, N.; Huang, R.S. pRRophetic: An R package for prediction of clinical chemotherapeutic response from tumor gene expression levels. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Fan, J.; Wang, B.; Traugh, N.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER: A Web Server for Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e108–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshihara, K.; Shahmoradgoli, M.; Martínez, E.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Treviño, V.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Levine, D.A.; et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbie, D.A.; Tamayo, P.; Boehm, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Moody, S.E.; Dunn, I.F.; Schinzel, A.C.; Sandy, P.; Meylan, E.; Scholl, C.; et al. Systematic RNA interference reveals that oncogenic KRAS-driven cancers require TBK1. Nature 2009, 462, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Z.; Liu, F. GEPIA2021: Integrating multiple deconvolution-based analysis into GEPIA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W242–W246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmonson, A.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Lipoic acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 7522–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowland, E.A.; Snowden, C.K.; Cristea, I.M. Protein lipoylation: An evolutionarily conserved metabolic regulator of health and disease. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2018, 42, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevitt, T.; Ohrvik, H.; Thiele, D.J. Charting the travels of copper in eukaryotes from yeast to mammals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1580–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saunier, E.; Benelli, C.; Bortoli, S. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in cancer: An old metabolic gatekeeper regulated by new pathways and pharmacological agents. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacpoole, P.W. Therapeutic Targeting of the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex/Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase (PDC/PDK) Axis in Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djx071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, K.P.; O’Brien, T.W.; Subramony, S.H.; Shuster, J.; Stacpoole, P.W. The spectrum of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency: Clinical, biochemical and genetic features in 371 patients. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 105, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anwar, S.; Shamsi, A.; Mohammad, T.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I. Targeting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase signaling in the development of effective cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxhaj, G.; Manning, B.D. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Dong, X.; Yap, J.; Hu, J. The MAPK and AMPK signalings: Interplay and implication in targeted cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulendran, B.; Davis, M.M. The science and medicine of human immunology. Science 2020, 369, eaay4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Humeau, J.; Buqué, A.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunostimulation with chemotherapy in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, T.; Kierstead, L.S.; Ranieri, E.; Gesualdo, L.; Schena, F.P.; Finke, J.H.; Bukowski, R.M.; Mueller-Berghaus, J.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Kwok, W.W.; et al. Disease-associated bias in T helper type 1 (Th1)/Th2 CD4(+) T cell responses against MAGE-6 in HLA-DRB10401(+) patients with renal cell carcinoma or melanoma. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, P.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Chaurasiya, S.; Strom, A.; Wang, H.; Liao, W.T.; Cavallaro, F.; Denz, P.; Bernard, V.; et al. Oncogenic KRAS-Driven Metabolic Reprogramming in Pancreatic Cancer Cells Utilizes Cytokines from the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 608–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Monte, L.; Wörmann, S.; Brunetto, E.; Heltai, S.; Magliacane, G.; Reni, M.; Paganoni, A.M.; Recalde, H.; Mondino, A.; Falconi, M.; et al. Basophil Recruitment into Tumor-Draining Lymph Nodes Correlates with Th2 Inflammation and Reduced Survival in Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Monte, L.; Reni, M.; Tassi, E.; Clavenna, D.; Papa, I.; Recalde, H.; Braga, M.; Di Carlo, V.; Doglioni, C.; Protti, M.P. Intratumor T helper type 2 cell infiltrate correlates with cancer-associated fibroblast thymic stromal lymphopoietin production and reduced survival in pancreatic cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvin, P.; Toor, S.M.; Sasidharan Nair, V.; Elkord, E. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: Recent progress and potential biomarkers. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, J.; Chehrazi-Raffle, A.; Reddi, S.; Salgia, R. Development of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors as a form of cancer immunotherapy: A comprehensive review of registration trials and future considerations. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Dai, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Qian, H.; Wang, X. Copper-based nanomaterials for cancer theranostics. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 14, e1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, V. Selective Targeting of Cancer Cells by Copper Ionophores: An Overview. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 841814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
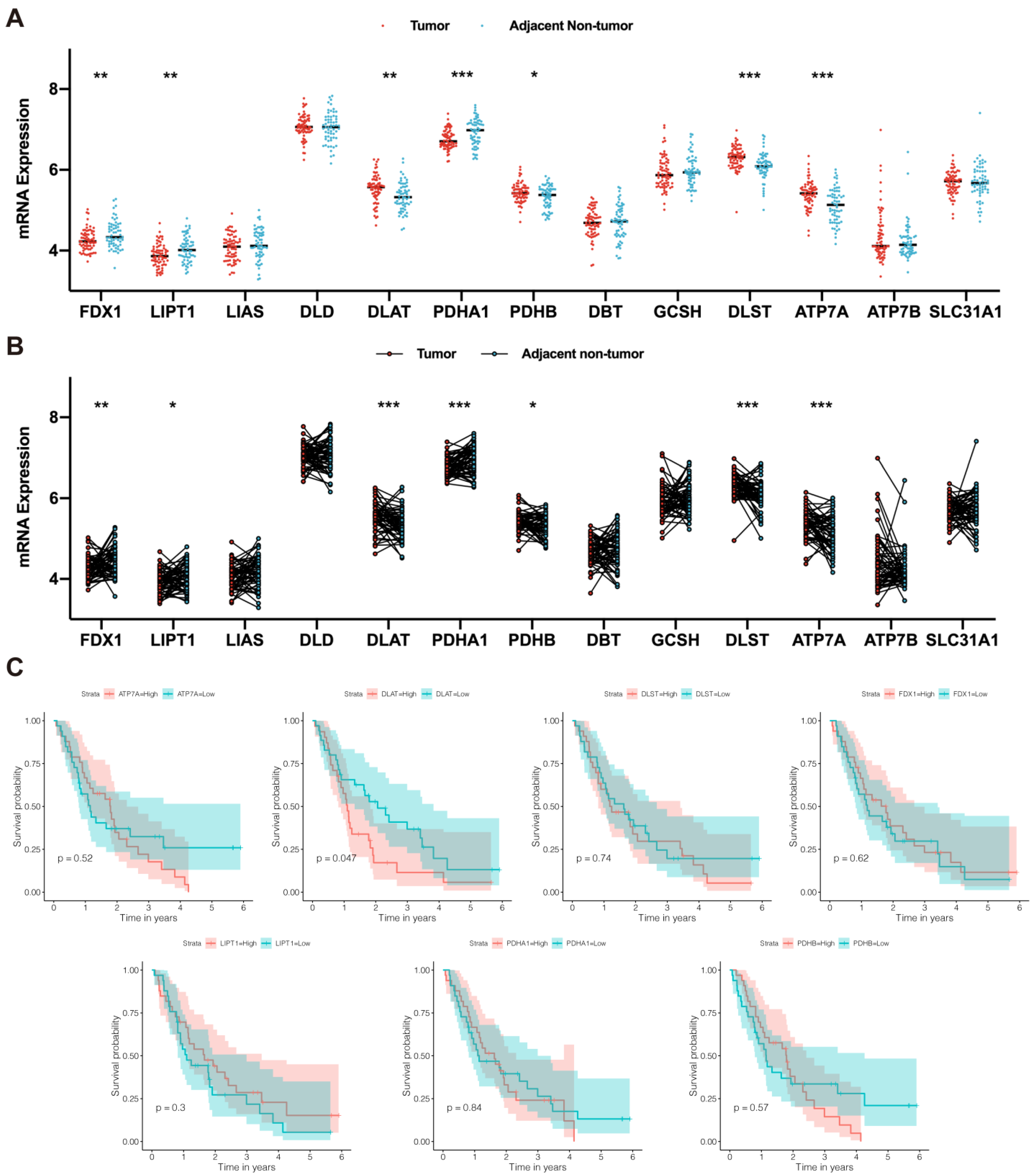



| Gene | HR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATP7A | 1.17 | 0.50–2.69 | 0.720 |
| DLAT | 2.72 | 1.10–6.74 | 0.030 * |
| DLST | 1.58 | 0.64–3.87 | 0.318 |
| FDX1 | 0.77 | 0.24–2.51 | 0.666 |
| LIPT1 | 0.45 | 0.16–1.25 | 0.124 |
| PDHA1 | 0.70 | 0.20–2.41 | 0.568 |
| PDHB | 1.35 | 0.33–5.55 | 0.681 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Hua, J.; Liang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Shi, S.; Yu, X.; Meng, Q.; et al. Cuproptosis-Related Gene DLAT as a Novel Biomarker Correlated with Prognosis, Chemoresistance, and Immune Infiltration in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Preliminary Study Based on Bioinformatics Analysis. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 2997-3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030228
Fang Z, Wang W, Liu Y, Hua J, Liang C, Liu J, Zhang B, Shi S, Yu X, Meng Q, et al. Cuproptosis-Related Gene DLAT as a Novel Biomarker Correlated with Prognosis, Chemoresistance, and Immune Infiltration in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Preliminary Study Based on Bioinformatics Analysis. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(3):2997-3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030228
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Zengli, Wei Wang, Yuan Liu, Jie Hua, Chen Liang, Jiang Liu, Bo Zhang, Si Shi, Xianjun Yu, Qingcai Meng, and et al. 2023. "Cuproptosis-Related Gene DLAT as a Novel Biomarker Correlated with Prognosis, Chemoresistance, and Immune Infiltration in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Preliminary Study Based on Bioinformatics Analysis" Current Oncology 30, no. 3: 2997-3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030228
APA StyleFang, Z., Wang, W., Liu, Y., Hua, J., Liang, C., Liu, J., Zhang, B., Shi, S., Yu, X., Meng, Q., & Xu, J. (2023). Cuproptosis-Related Gene DLAT as a Novel Biomarker Correlated with Prognosis, Chemoresistance, and Immune Infiltration in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Preliminary Study Based on Bioinformatics Analysis. Current Oncology, 30(3), 2997-3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030228





