Use of Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreatic Cancer Patients: A Multi-Center Experience
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. IRE Procedure
2.4. Follow-Up
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics and Preoperative Characteristics
3.2. Operative Characteristics
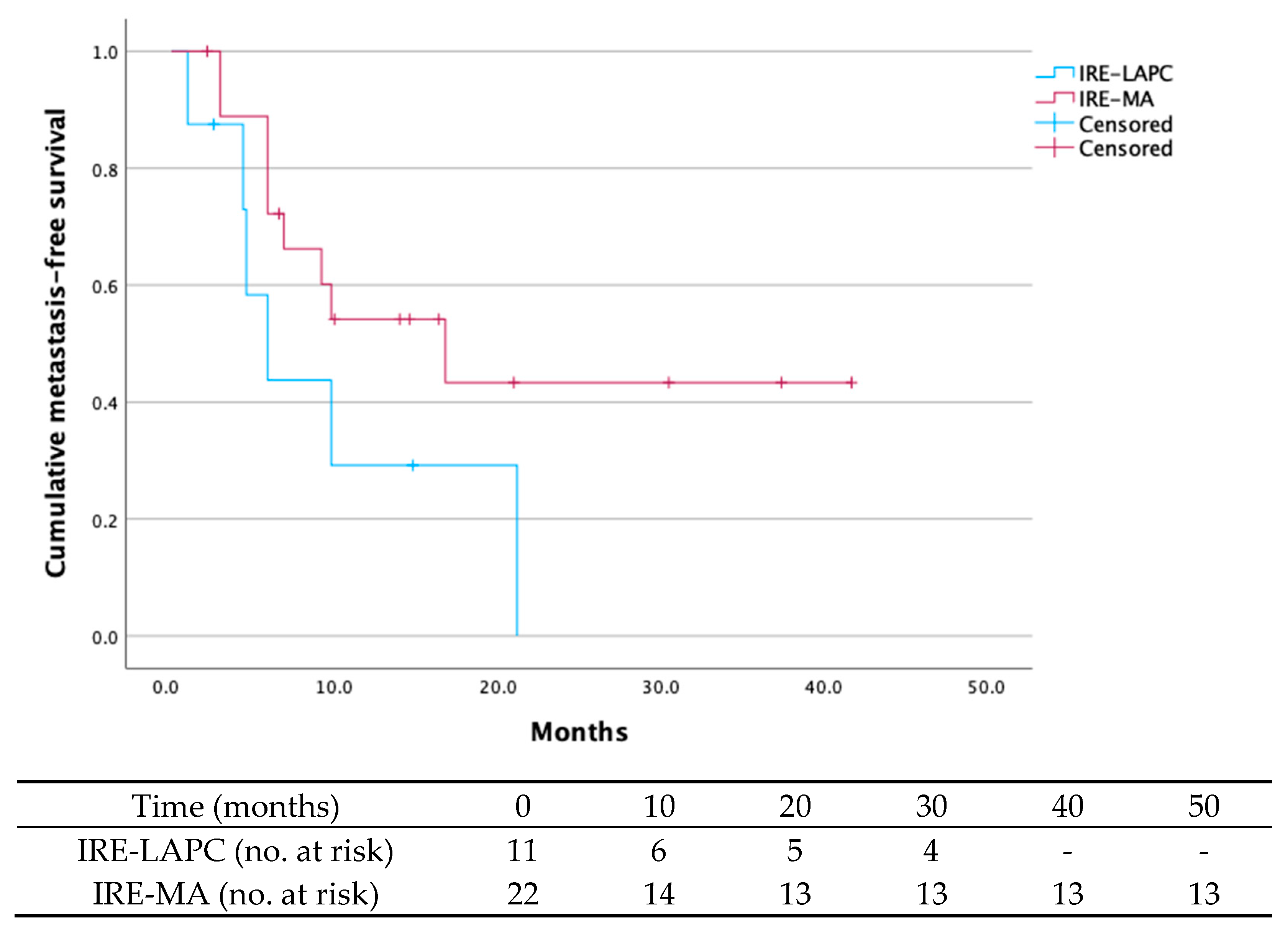
3.3. Postoperative Complications, Follow-Up and Survival Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IRE | Irreversible Electroporation |
| PDAC | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| LAPC | Locally advanced pancreatic cancer |
| BRPC | Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer |
| RPC | Resectable pancreatic cancer |
| IRE-LAPC | Local tumor destruction with IRE in unresectable LAPC |
| IRE-MA | Margin accentuation with IRE during resection in BRPC and RPC |
| SMA | Superior mesenteric artery |
| PV | Portal vein |
| SMV | Superior mesenteric vein |
| IPMN | Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists, Physical Status Classification |
| CCI | Comprehensive Complication Index |
| NSTEMI | Non-ST elevated myocardial infarct |
References
- Bizuayehu, H.M.; Dadi, A.F.; Ahmed, K.Y.; Tegegne, T.K.; Hassen, T.A.; Kibret, G.D.; Ketema, D.B.; Bore, M.G.; Thapa, S.; Odo, D.B.; et al. Burden of 30 cancers among men: Global statistics in 2022 and projections for 2050 using population-based estimates. Cancer 2024, 130, 3708–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Cancer Observatory. 2024. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/en (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Park, W.; Chawla, A.; O’Reilly, E.M. Pancreatic Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, B.; Hartmann, D.; D’Haese, J.G.; Stupakov, P.; Radenkovic, D.; Gloor, B.; Friess, H. Neoadjuvant Treatment for Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Dig. Surg. 2019, 36, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsanic, P.; Mellano, A.; Sottile, A.; De Simone, M. Irreversible electroporation as treatment of locally advanced and as margin accentuation in borderline resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; McFarland, K.; Velanovich, V.; Martin, R.C., 2nd. Borderline and locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma margin accentuation with intraoperative irreversible electroporation. Surgery 2014, 156, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, B.; Al-Leswas, D.; Mohammadi-Zaniani, G.; Littler, P.; Sen, G.; Manas, D.; Pandanaboyana, S. Margin Accentuation Irreversible Electroporation in Stage III Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C., 2nd; McFarland, K.; Ellis, S.; Velanovich, V. Irreversible electroporation therapy in the management of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2012, 215, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C., 2nd; Durham, A.N.; Besselink, M.G.; Iannitti, D.; Weiss, M.J.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Huang, K.W. Irreversible electroporation in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A call for standardization of energy delivery. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 114, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundalia, K.; Hakeem, A.; Papoulas, M.; McPhail, M.; Reddy, S.; Peddu, P.; Kibriya, N.; Atkinson, S.; Prachalias, A.; Srinivasan, P.; et al. Margin Accentuation for resectable Pancreatic cancer using Irreversible Electroporation-Results from the MACPIE-I study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C.G., 2nd; Schoen, E.C.; Philips, P.; Egger, M.E.; McMasters, K.M.; Scoggins, C.R. Impact of margin accentuation with intraoperative irreversible electroporation on local recurrence in resected pancreatic cancer. Surgery 2023, 173, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoulas, M.; Abdul-Hamid, S.; Peddu, P.; Cotoi, C.; Heaton, N.; Menon, K. Irreversible electroporation in borderline resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma for margin accentuation. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2018, 2018, rjy127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.S.; Heard, J.; Brant, N.; Malo, J.; Kong, J.; Osman, H.; Buell, J.; Jeyarajah, D.R. Irreversible Electroporation Margin Accentuation in Pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 31, 8298–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraju, M.O.; Su, Y.; Chang, J.; Katwala, A.; Nayyar, A.; Gordon, D.M.; Abideen, A.; Patel, P.; Smith, R.; Liu, Z. Impact of irreversible electroporation on survival among patients with borderline resectable/locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A single center experience. Surg. Oncol. Insight 2024, 1, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafranceschina, S.; Brunetti, O.; Delvecchio, A.; Conticchio, M.; Ammendola, M.; Currò, G.; Piardi, T.; de’Angelis, N.; Silvestris, N.; Memeo, R. Systematic Review of Irreversible Electroporation Role in Management of Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCCN Guidelines. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. 2021. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1455 (accessed on 22 March 2025).
- Sugumar, K.; Hurtado, A.; Naik, I.; Hue, J.J.; Rothermel, L.D.; Ammori, J.B.; Hardacre, J.M.; Winter, J.M.; Ocuin, L.M. Multimodal therapy with or without irreversible electroporation for unresectable locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. HPB 2022, 24, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, K.; Philips, P.P.; Egger, M.E.; Scoggins, C.R.; McMasters, K.M.; Martin, R.C.G., 2nd. Multi-institutional review of adverse events associated with irreversible electroporation in the treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Surgery 2024, 175, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C., 2nd; Kwon, D.; Chalikonda, S.; Sellers, M.; Kotz, E.; Scoggins, C.; McMasters, K.M.; Watkins, K. Treatment of 200 locally advanced (stage III) pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients with irreversible electroporation: Safety and efficacy. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 486–494; discussion 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.M.; Bhutiani, N.; Kruse, E.J.; Weiss, M.J.; Christein, J.D.; White, R.R.; Huang, K.W.; Martin, R.C.G., 2nd. A prospective, multi-institution assessment of irreversible electroporation for treatment of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Initial outcomes from the AHPBA pancreatic registry. HPB 2019, 21, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, T.; Desseigne, F.; Ychou, M.; Bouché, O.; Guimbaud, R.; Bécouarn, Y.; Adenis, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; De La Fouchardière, C. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N. Eng. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar]
- Timmer, F.E.F.; Geboers, B.; Ruarus, A.H.; Vroomen, L.; Schouten, E.A.C.; van der Lei, S.; Vos, D.J.W.; Dijkstra, M.; Schulz, H.H.; Bakker, J.; et al. MRI-guided stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy versus CT-guided percutaneous irreversible electroporation for locally advanced pancreatic cancer (CROSSFIRE): A single-centre, open-label, randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flak, R.V.; Malmberg, M.M.; Stender, M.T.; Hauberg, A.; Thorlacius-Ussing, O. Irreversible electroporation of pancreatic cancer-Effect on quality of life and pain perception. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leen, E.; Picard, J.; Stebbing, J.; Abel, M.; Dhillon, T.; Wasan, H. Percutaneous irreversible electroporation with systemic treatment for locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2018, 9, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Hosein, P.J.; Arora, G.; Barbery, K.J.; Froud, T.; Livingstone, A.S.; Franceschi, D.; Rocha Lima, C.M.; Yrizarry, J. Percutaneous irreversible electroporation for downstaging and control of unresectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeke, C.S. Resection margins in pancreatic cancer. Pathologe 2013, 34 (Suppl. 2), 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaquist, T.; Fristrup, C.W.; Hasselby, J.P.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; Eld, M.; Pfeiffer, P.; Mortensen, M.B.; Detlefsen, S. Prognostic significance of margin clearance in pancreaticoduodenectomy specimens with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in a Danish population-based nationwide study. HPB 2023, 25, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.M.; Salibi, P.N.; Motz, B.M.; Vrochides, D.; McKillop, I.H.; Iannitti, D.A. Irreversible Electroporation-Assisted Resection for Locally Advanced Pancreas Cancer. Surg. Innov. 2023, 30, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, S. T-cell activation and immune memory enhancement induced by irreversible electroporation in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.; Christians, K.K.; Ritch, P.S.; George, B.; Khan, A.H.; Erickson, B.; Evans, D.B. Multimodality Therapy in Patients With Borderline Resectable or Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: Importance of Locoregional Therapies for a Systemic Disease. J. Oncol. Pract. 2016, 12, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempero, M.A.; Malafa, M.P.; Al-Hawary, M.; Behrman, S.W.; Benson, A.B.; Cardin, D.B.; Chiorean, E.G.; Chung, V.; Czito, B.; Del Chiaro, M.; et al. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brys, E.A.; Gryspeerdt, F.; Rashidian, N.; Lerut, A.V.; Dries, P.; Abreu de Carvalho, L.; Berrevoet, F. Postoperative Refractory Diarrhea After Margin Accentuation of the Superior Mesenteric Artery with Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreaticoduodenectomy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Liang, B.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chang, H.S.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.L. Safety and feasibility of irreversible electroporation for the pancreatic head in a porcine model. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.W.; Shahrouki, P.; Peterson, S.; Tafti, B.A.; Ding, P.X.; Kee, S.T. Safety of Irreversible Electroporation Ablation of the Pancreas. Pancreas 2021, 50, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woeste, M.R.; Wilson, K.D.; Kruse, E.J.; Weiss, M.J.; Christein, J.D.; White, R.R.; Martin, R.C.G., 2nd. Optimizing Patient Selection for Irreversible Electroporation of Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: Analyses of Survival. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 817220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merath, K.; Mehta, R.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Farooq, A.; Sahara, K.; Paredes, A.Z.; Wu, L.; Ejaz, A.; Pawlik, T.M. In-hospital Mortality Following Pancreatoduodenectomy: A Comprehensive Analysis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heger, U.; Mack, C.; Tjaden, C.; Pan, F.; Pausch, T.; Hinz, U.; Sommer, C.M.; Hackert, T. Open irreversible electroporation for isolated local recurrence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma after primary surgery. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluger, M.D.; Epelboym, I.; Schrope, B.A.; Mahendraraj, K.; Hecht, E.M.; Susman, J.; Weintraub, J.L.; Chabot, J.A. Single-Institution Experience with Irreversible Electroporation for T4 Pancreatic Cancer: First 50 Patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiella, S.; Butturini, G.; Frigerio, I.; Salvia, R.; Armatura, G.; Bacchion, M.; Fontana, M.; D’Onofrio, M.; Martone, E.; Bassi, C. Safety and feasibility of Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Results of a prospective study. Dig. Surg. 2015, 32, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.A.; Rombouts, S.J.; de Rooij, T.; van Delden, O.M.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; van Gulik, T.M.; van Hooft, J.E.; van Laarhoven, H.W.; Martin, R.C.; Schoorlemmer, A.; et al. Induction Chemotherapy Followed by Resection or Irreversible Electroporation in Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer (IMPALA): A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 2734–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, H.J.; Vroomen, L.G.; de Jong, M.C.; Melenhorst, M.C.; Zonderhuis, B.M.; Daams, F.; Vogel, J.A.; Besselink, M.G.; van Kuijk, C.; Witvliet, J.; et al. Ablation of Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer with Percutaneous Irreversible Electroporation: Results of the Phase I/II PANFIRE Study. Radiology 2017, 282, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Total n = 35 | IRE-LAPC n = 13 | IRE-MA n = 22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years [mean (SD)] | 65.2 (8.4) | 67.9 (9.6) | 63.6 (7.4) |
| Gender | |||
| Men | 23 (65.7) | 9 (69.2) | 14 (63.6) |
| Women | 12 (34.3) | 4 (30.8) | 8 (36.4) |
| BMI, kg/m2 [(median (IQR)] | 24.1 (21.3–26.6) | 25.2 (23.3–31.4) | 22.5 (21.3–26.4) |
| ASA-classification | |||
| Class I | 3 (8.6) | 1 (7.7) | 2 (9.1) |
| Class II | 16 (45.7) | 4 (30.8) | 12 (64.5) |
| Class III | 15 (42.9) | 7 (53.8) | 8 (36.4) |
| Comorbidities | |||
| None | 16 (45.7) | 7 (53.8) | 9 (40.9) |
| Myocardial infarction | 2 (5.7) | 2 (15.4) | 0 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 3 (8.6) | 2 (15.4) | 1 (4.5) |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 2 (5.7) | 1 (7.7) | 1 (4.5) |
| Congestive heart failure | 1 (2.9) | 1 (7.7) | 0 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 2 (5.7) | 0 | 2 (9.1) |
| Peptic ulcer | 5 (14.3) | 0 | 5 (22.7) |
| Diabetes without damage to end-organs | 11 (31.4) | 5 (38.5) | 6 (27.3) |
| Diabetes with damage to end-organs | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tumor without metastasis | 4 (11.4) | 0 | 4 (18.2) |
| Gastric bypass | 1 (2.9) | 1 (7.7) | 0 |
| Histological diagnosis | |||
| PDAC | 32 (91.4) | 11 (84.6) | 21 (95.5) |
| PDAC following IPMN | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.5) |
| Cholangiocarcinoma | 1 (2.9) | 1 (7.7) | 0 |
| Metastasis of other primary | 1 (2.9) | 1 (7.7) | 0 |
| Location tumor | |||
| Head | 19 (57.5) | 5 (41.7) | 14 (66.7) |
| Body | 11 (33.3) | 6 (50) | 5 (23.8) |
| Neck | 3 (9.1) | 1 (8.3) | 2 (9.5) |
| Tail | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tumor size, mm [mean (SD)] | 31.9 (11.1) | 32.7 (13.3) | 29.5 (8.5) |
| cT stage | |||
| T2 | 6 (17.1) | 1 (7.7) | 5 (22.2) |
| T3 | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.5) |
| T4 | 25 (71.4) | 11 (84.6) | 14 (63.6) |
| cN stage | |||
| N0 | 19 (54.3) | 4 (30.8) | 15 (68.2) |
| Nn | 13 (37.1) | 8 (61.5) | 5 (22.7) |
| cM stage | |||
| M0 | 30 (85.7) | 11 (84.6) | 19 (86.4) |
| Mn | 2 (5.7) | 0 | 2 (9.1) |
| Vascular involvement | |||
| None | 3 (8.6) | 3 (23.1) | 0 |
| Portal vein and/or SMV | 17 (48.6) | 7 (53.9) | 10 (45.5) |
| SMA | 20 (57.1) | 6 (46.2) | 14 (63.6) |
| Coeliac trunk | 10 (28.6) | 4 (30.8) | 6 (27.3) |
| Hepatic artery | 9 (25.7) | 4 (30.8) | 5 (22.7) |
| Resectability | |||
| RPC | 2 (5.7) | 2 (15.4) | 0 |
| BRPC | 9 (25.7) | 1 (7.7) | 8 (36.4) |
| LAPC | 24 (68.6) | 10 (76.9) | 14 (63.6) |
| Neoadjuvant treatment regimen | 30 (85.7) | 11 (84.6) | 19 (86.4) |
| Chemotherapy | 30 (85.7) | 11 (84.6) | 19 (86.4) |
| Folfirinox | 25 (71.4) | 10 (76.9) | 15 (68.2) |
| Gemcitabine | 5 (14.3) | 1 (7.7) | 4 (18.2) |
| Radiotherapy | 4 (11.4) | 0 | 4 (18.2) |
| Characteristics | Total n = 35 | IRE-LAPC n = 13 | IRE-MA n = 22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor resected? | |||
| Yes | 22 (62.9) | 0 | 22 (100) |
| No | 13 (37.1) | 13 (100) | 0 |
| Type of surgery | |||
| Pancreaticoduodenectomy | 13 (37.1) | - | 13 (59.1) |
| Total pancreatectomy | 4 (11.4) | - | 4 (18.2) |
| Distal pancreatectomy | 5 (14.3) | - | 5 (22.7) |
| Additional interventions | |||
| Portal vein reconstruction | 5 (14.7) | - | 5 (23.8) |
| IRE procedure time, min [mean (SD)] | 367 (17.9) | 277 (22.8) | 420 (17.3) |
| Number of probes | 4 (3–5) | 5 (4–6) | 3 (2–4) |
| Electrode spacing, mm [mean (SD)] | 15 (0) | 15 (0) | 15 (0) |
| pT stage | |||
| T1 | 5 (14.3) | - | 5 (22.7) |
| T2 | 8 (24.2) | - | 8 (36.4) |
| T3 | 4 (11.4) | - | 4 (18.2) |
| T4 | 4 (11.4) | - | 4 (18.2) |
| Missing | 1 (2.9) | - | 1 (4.5) |
| pN stage | |||
| N0 | 9 (25.7) | - | 9 (40.9) |
| Nn | 12 (34.3) | - | 12 (64.5) |
| Missing | 1 (2.9) | - | 1 (4.5) |
| pM stage | |||
| M0 | 7 (20) | - | 7 (31.8) |
| Mn | 5 (14.3) | - | 5 (22.7) |
| Missing | 10 (28.6) | - | 10 (45.4) |
| Resection margin | |||
| R0 resection | 14 (40) | - | 14 (63.6) |
| R1 resection | 8 (24.2) | - | 8 (36.4) |
| R2 resection | 0 | - | 0 |
| Characteristics | No. Patients n = 35 | IRE-LAPC n = 13 | IRE-MA n = 22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complications | 18 (51.4) | 3 (23.1) | 15 (68.2) |
| Gastroparesis | 9 (25.7) | 2 (15.4) | 7 (31.8) |
| Infection | 7 (20) | 1 (7.7) | 5 (27.3) |
| Liver abscess | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.6) |
| Abscess at ablated zone | 1 (2.9) | 1 (7.7) | 0 |
| Cholangitis | 3 (8.6) | 1 (7.7) | 2 (9.1) |
| Peritonitis | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.6) |
| Cellulitis | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.6) |
| Other: non-specified | 3 (8.6) | 0 | 3 (13.6) |
| Ascites | 2 (5.7) | 1 (7.7) | 1 (4.6) |
| Pancreatic fistula | 3 (8.6) | 2 (15.4) | 1 (4.6) |
| Grade B | 2 (5.7) | 1 (7.7) | 1 (4.6) |
| Grade C | 1 (2.9) | 1 (7.7) | 0 |
| Colon perforation | 2 (5.7) | 0 | 2 (9.1) |
| Chyle leakage | 8 (22.9) | 0 | 8 (36.4) |
| Portal vein thrombosis | 2 (5.7) | 1 (7.7) | 1 (4.6) |
| Hepatic artery thrombosis | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.6) |
| Diarrhea | 6 (17.1) | 0 | 6 (27.3) |
| Cardiac arrhythmias | 3 (8.6) | 0 | 3 (13.6) |
| GI bleeding | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.6) |
| CCI [median (IQR)] | 22.6 (8.7–40.5) | 8.7 (0–28.7) | 32.7 (14.6–40.9) |
| Severity of complications, Clavien–Dindo grade III or higher | 12 (34.3) | 3 (23.1) | 9 (40.9) |
| In hospital stay, days [mean (SD)] | 14.8 (6.2) | 10.1 (4.2) | 17.7 (5.5) |
| Death within 90 days post IRE | 6 (17.1) | 2 (15.4) | 4 (18.2) |
| Cause of death within 30 days post IRE | |||
| Death of unknown cause | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.6) |
| NSTEMI | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.6) |
| Hepatic artery thrombosis | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.6) |
| Cholangitis | 1 (2.9) | 1 (7.7) | 0 |
| Multi-organ failure | 1 (2.9) | 1 (7.7) | 0 |
| Aortic dissection | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.6) |
| Rehospitalization within 3 months post IRE | 11 (32.4) | 2 (15.4) | 9 (42.9) |
| Reason for rehospitalization | |||
| Malnutrition | 8 (22.9) | 0 | 8 (36.6) |
| Diarrhea | 5 (14.3) | 0 | 5 (27.3) |
| Cholangitis | 1 (2.9) | 1 (7.7) | 0 |
| Sepsis | 1 (2.9) | 0 | 1 (4.6) |
| Pain | 1 (2.9) | 1 (7.7) | 0 |
| Received adjuvant treatment | 28 (80) | 13 (100) | 15 (68.2) |
| Adjuvant treatment regimen | |||
| Chemotherapy | 20 (57.1) | 7 (53.9) | 13 (59.1) |
| Radiotherapy | 6 (17.1) | 5 (41.7) | 1 (4.6) |
| Chemoradiotherapy | 2 (5.7) | 1 (7.7) | 1 (4.6) |
| Time to adjuvant treatment, days [mean (SD)] | 47.1 (15.5) | 43.4 (12.6) | 52.7 (15.4) |
| Characteristics | No. Patients n = 33 | IRE-LAPC n = 11 | IRE-MA n = 22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local tumor recurrence at 24 months | 8 (24.2) | 3 (27.3) | 5 (22.7) |
| Metastases at 24 months | 17 (51.5) | 6 (54.5) | 9 (40.9) |
| Location of metastases | |||
| Lung | 7 (21.2) | 3 (27.3) | 4 (18.2) |
| Liver | 7 (21.2) | 1 (9.1) | 6 (18.2) |
| Peritoneum | 8 (24.2) | 4 (36.4) | 4 (18.2) |
| Overall survival at 24 months | |||
| Alive | 9 (27.3) | 3 (27.3) | 6 (27.3) |
| Death | 23 (69.7) | 7 (63.6) | 16 (72.7) |
| Lost to follow-up | 1 (3.0) | 1 (9.1) | 0 |
| Cause of death | |||
| Tumor progression | 10 (30.3) | 5 (45.5) | 5 (22.7) |
| Multi-organ failure | 7 (21.2) | 1 (9.1) | 6 (27.3) |
| Cardial | 2 (6.1) | 1 (9.1) | 1 (4.5) |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 1 (3.0) | 0 | 1 (4.5) |
| Cholangitis | 1 (3.0) | 1 (9.1) | 0 |
| Euthanasia | 1 (3.0) | 0 | 1 (4.5) |
| Unknown | 1 (3.0) | 0 | 1 (4.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hendrikx, B.; Brys, E.-A.; Dili, A.; Apers, T.; Hartman, V.; Brichard, M.; Gryspeerdt, F.; Bertrand, C.; Roeyen, G.; Berrevoet, F. Use of Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreatic Cancer Patients: A Multi-Center Experience. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100574
Hendrikx B, Brys E-A, Dili A, Apers T, Hartman V, Brichard M, Gryspeerdt F, Bertrand C, Roeyen G, Berrevoet F. Use of Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreatic Cancer Patients: A Multi-Center Experience. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(10):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100574
Chicago/Turabian StyleHendrikx, Bart, Eline-Alice Brys, Alexandra Dili, Thomas Apers, Vera Hartman, Martin Brichard, Filip Gryspeerdt, Claude Bertrand, Geert Roeyen, and Frederik Berrevoet. 2025. "Use of Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreatic Cancer Patients: A Multi-Center Experience" Current Oncology 32, no. 10: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100574
APA StyleHendrikx, B., Brys, E.-A., Dili, A., Apers, T., Hartman, V., Brichard, M., Gryspeerdt, F., Bertrand, C., Roeyen, G., & Berrevoet, F. (2025). Use of Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreatic Cancer Patients: A Multi-Center Experience. Current Oncology, 32(10), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100574





