Exploring the Role of Hypoxia and HIF-1α in the Intersection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Endometrial Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Mutual Features of T2DM and EC
2.1. Etiology of Diabetes Mellitus
2.2. Etiology of EC
2.3. Adipocytes: Common Ground for T2DM and EC
2.4. Metabolic Reprogramming
3. Signaling Cascades Involving HIF-1α Regulation
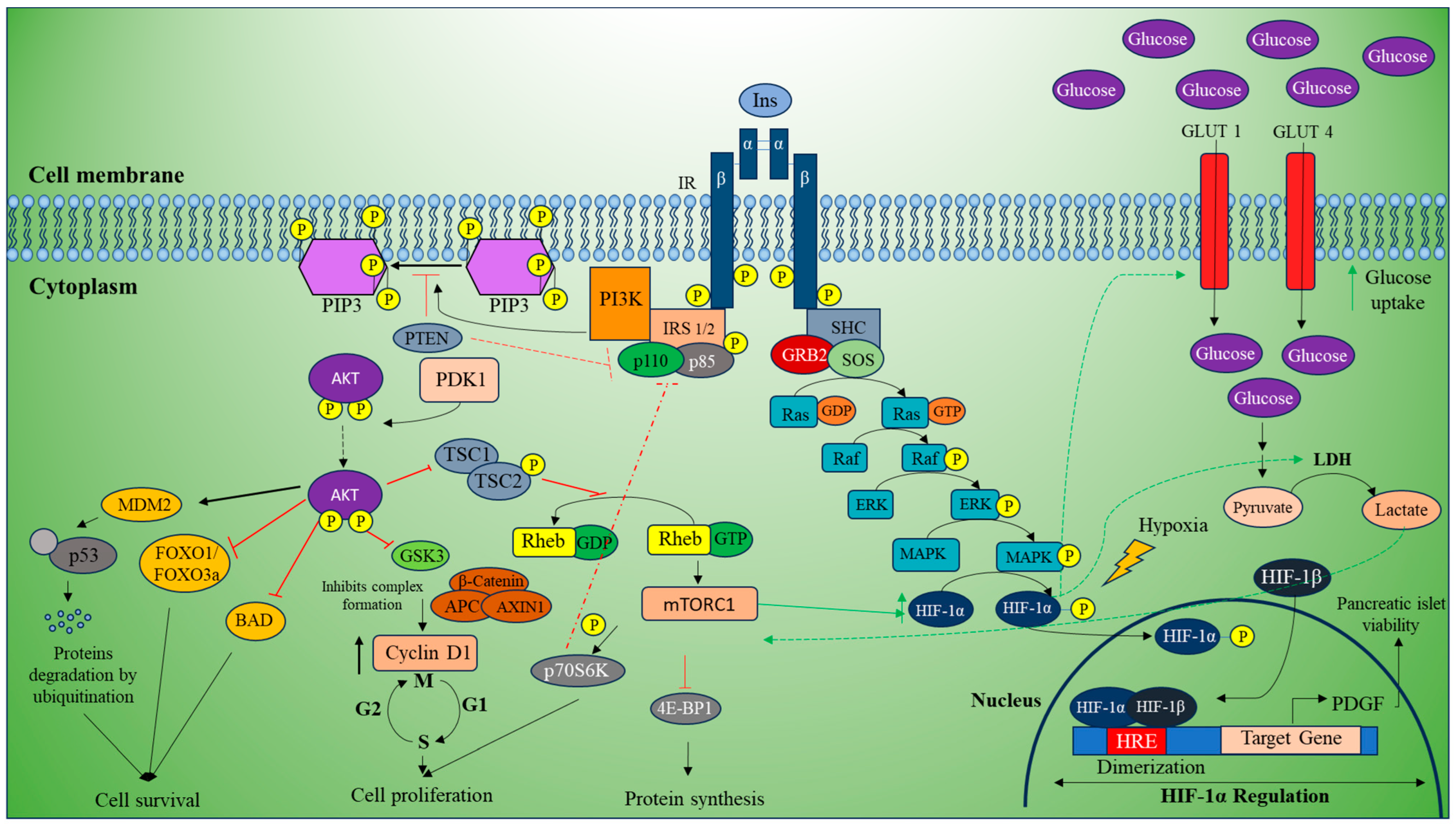
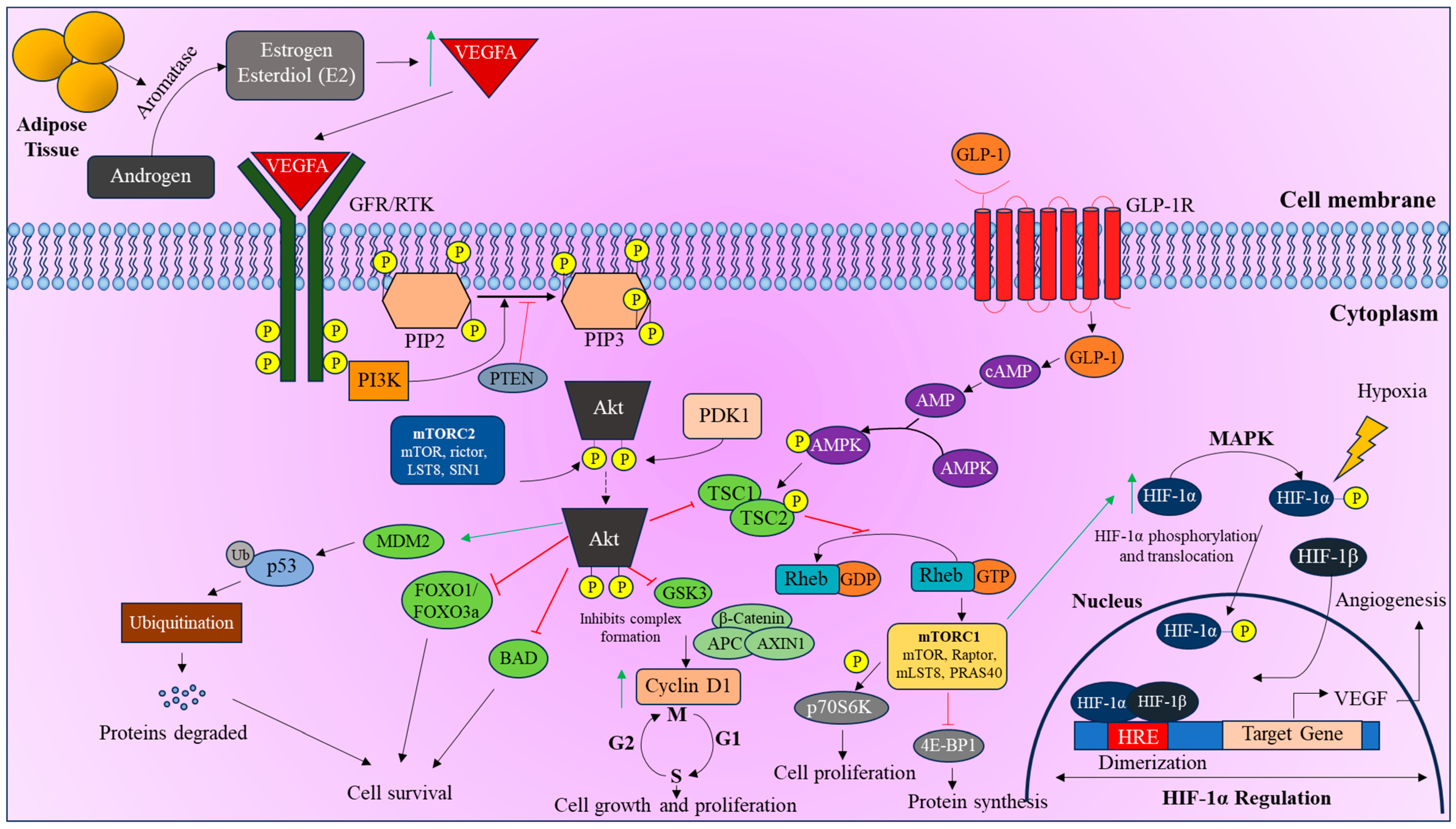
3.1. mTOR Pathway
3.2. PI3K/Akt Pathway
4. Regulation of HIF-1α in T2DM and EC
4.1. Prognosis
4.2. Treatment Strategies
| S. No | Compound/Drug | Source | Mode of Action | Target | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Metformin | Galega officinalis | Promotes the degradation of HIF-1α, inhibits HIF-1α accumulation by AMPK-independent activation | AMPK, GLUT4, mTOR | [88,116] |
| 2 | Topotecan | A semisynthetic analogue of camptothecin isolated from Camptotheca acuminata | Prevents the translation of HIF-1α; decreased transcriptional activity of HIF-1α target genes | Topoisomerase I | [96,101] |
| 3 | Rapamycin | Streptomyces hydroscopicus AY B-994 | Inhibits the mTOR pathway and prevents the translation of HIF-1α under hypoxic conditions | mTOR | [88,117] |
| 4 | Bevacizumab | Humanized monoclonal Ab produced in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) | Targets VEGF, a major downstream target of HIF-1α, and can reduce angiogenesis | VEGFA | [110] |
| 5 | Temsirolimus | Derivative of Rapamycin | Inhibits translation of HIF-1α | mTOR | [104,118] |
| 6 | Everolimus | Derivative of Rapamycin | Inhibits translation of HIF-1α | PI3k/AKT/mTOR | [104,118] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CBP | CREB-binding protein |
| EC | Endometrial cancer |
| GLP1 | Glucagon-like peptidide 1 |
| HIF | Hypoxia-inducible factor |
| HRE | Hypoxia-responsive element |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of Rapamycin |
| OS | Oxidative stress |
| OXPHOS | Oxidative phosphorylation |
| PDK1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 |
| PI3K | Phosphoinoside 3-kinase |
| PTEN | Phosphate and tensin homolog |
| RHEB | Ras homolog enriched in brain |
| RTK | Receptor tyrosine kinase |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Cignarelli, A.; Genchi, V.A.; Caruso, I.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Diabetes and cancer: Pathophysiological fundamentals of a ’dangerous affair’. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 143, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.M.M.; Chua, Z.J.Y.; Tan, J.C.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Diabetes, F.P.-D.T. Treatments and Translational Research. Medicina 2019, 55, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Z. Diabetes and cancer: Epidemiological and biological links. World J. Diabetes 2020, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson-Stuttard, J.; Papadimitriou, N.; Markozannes, G.; Cividini, S.; Kakourou, A.; Gill, D.; Rizos, E.C.; Monori, G.; Ward, H.A.; Kyrgiou, M.; et al. Type 2 Diabetes and Cancer: An Umbrella Review of Observational and Mendelian Randomization Studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 30, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannata, D.; Fierz, Y.; Vijayakumar, A.; LeRoith, D. Type 2 diabetes and cancer: What is the connection? Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2010, 77, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiter, A.; Charokopos, A.; Bailey, S.; Gallagher, E.J.; Hirsch, F.R.; LeRoith, D.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Assessing the association of diabetes with lung cancer risk. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 4200–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lai, T.; Li, Z.; Mao, M.; Jin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R. Role of non-coding RNA intertwined with the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in endometrial cancer (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2023, 28, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G.; Bravi, F.; Serraino, D.; Parazzini, F.; Crispo, A.; Augustin, L.S.A.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C.; Turati, F. Diabetes Risk Reduction Diet and Endometrial Cancer Risk. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicker, L.M.; Cardwell, C.R.; Edge, L.; McCluggage, W.G.; Quinn, D.; Wylie, J.; McMenamin, U.C. Survival outcomes in endometrial cancer patients according to diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 427. [Google Scholar]
- Schlesselman, J.J. Risk of endometrial cancer in relation to use of combined oral contraceptives. A practitioner’s guide to meta-analysis. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 12, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Staa, T.P.; Patel, D.; Gallagher, A.M.; de Bruin, M.L. Glucose-lowering agents and the patterns of risk for cancer: A study with the General Practice Research Database and secondary care data. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H. Author Correction: Targeting oxidative stress in disease: Promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamino, T.; Orimo, M.; Shimizu, I.; Kunieda, T.; Yokoyama, M.; Ito, T.; Nojima, A.; Nabetani, A.; Oike, Y.; Matsubara, H.; et al. A crucial role for adipose tissue p53 in the regulation of insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesmin, J.; Rashid, M.S.; Jamil, H.; Hontecillas, R.; Bassaganya-Riera, J. Gene regulatory network reveals oxidative stress as the underlying molecular mechanism of type 2 diabetes and hypertension. BMC Med. Genom. 2010, 3, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modugno, F.; Ness, R.B.; Chen, C.; Weiss, N.S. Inflammation and endometrial cancer: A hypothesis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 2840–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieszczanski, P.; Januszyk, S.; Zmarzly, N.; Ossowski, P.; Dziobek, K.; Sagan, D.; Boron, D.; Oplawski, M.; Grabarek, B.O. miRNAs Participate in the Regulation of Oxidative Stress-Related Gene Expression in Endometrioid Endometrial Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.J.; Wang, P.H.; Huang, J.Y.; Lee, C.Y.; Lin, C.W.; Lee, C.Y.; Yang, S.F. The lower incidence of endometrial cancer after sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors administration in type 2 diabetes mellitus population: A nationwide cohort study. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 21, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qahremani, R.; Rabizadeh, S.; Mirmiranpoor, H.; Yadegar, A.; Mohammadi, F.; Sahebi, L.; Heidari, F.; Esteghamati, A.; Nakhjavani, M. Lipid profile, ox-LDL, and LCAT activity in patients with endometrial carcinoma and type 2 diabetes: The effect of concurrent disease based on a case-control study. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, F.; Rabizadeh, S.; Mansournia, M.A.; Mirmiranpoor, H.; Salehi, S.S.; Akhavan, S.; Esteghamati, A.; Nakhjavani, M. Inflammatory, oxidative stress and anti-oxidative markers in patients with endometrial carcinoma and diabetes. Cytokine 2019, 120, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karavasilis, A.; Karkalousos, P.; Trapali, M.; Fountzoula, C.; Karikas, G.A.; HIF-, D.O.; Stress, O. Obesity and Other Related Disorders. J. Diabetes Mellit. 2023, 13, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karihtala, P.; Puistola, U. Hypoxia and Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Gynecological Cancers and in Therapeutical Options. Curr. Cancer Ther. Rev. 2011, 7, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.R.; Parikh, R.M. India--diabetes capital of the world: Now heading towards hypertension. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2007, 55, 323–324. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, M. Diabetes Mellitus Review. Urol. Nurs. 2016, 36, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes, A.A. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37 (Suppl. S1), S81–S90. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, C.C.; Philipson, L.H. Update on diabetes classification. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 99, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meglio, D.A.; Evans-Molina, C.; Oram, R.A. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2018, 391, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar]
- Katsarou, A.; Gudbjornsdottir, S.; Rawshani, A.; Dabelea, D.; Bonifacio, E.; Anderson, B.J.; Jacobsen, L.M.; Schatz, D.A.; Lernmark, A. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2017, 389, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.K.; Srivastava, A.K. Diabetes mellitus: Complications and therapeutics. Med. Sci. Monit. 2006, 12, RA130–RA147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brannmark, C.; Nyman, E.; Fagerholm, S.; Bergenholm, L.; Ekstrand, E.M.; Cedersund, G.; Stralfors, P. Insulin signaling in type 2 diabetes: Experimental and modeling analyses reveal mechanisms of insulin resistance in human adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9867–9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makker, V.; MacKay, H.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Levine, D.A.; Westin, S.N.; Aoki, D.; Oaknin, A. Endometrial cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morice, P.; Leary, A.; Creutzberg, C.; Abu-Rustum, N.; Darai, E. Endometrial cancer. Lancet 2016, 387, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saso, S.; Chatterjee, J.; Georgiou, E.; Ditri, A.M.; Smith, J.R.; Ghaem-Maghami, S. Endometrial cancer. BMJ 2011, 343, d3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsa, N. Environmental factors inducing human cancers. Iran. J. Public Health 2012, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Murali, R.; Soslow, R.A.; Weigelt, B. Classification of endometrial carcinoma: More than two types. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e268–e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhouk, A.; McAlpine, J.N. New classification of endometrial cancers: The development and potential applications of genomic-based classification in research and clinical care. Gynecol. Oncol. Res. Pract. 2016, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corr, B.; Cosgrove, C.; Spinosa, D.; Guntupalli, S. Endometrial cancer: Molecular classification and future treatments. BMJ Med. 2022, 1, e000152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burhans, M.S.; Hagman, D.K.; Kuzma, J.N.; Schmidt, K.A.; Kratz, M. Contribution of Adipose Tissue Inflammation to the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Michalczyk, K.; Niklas, N.; Rychlicka, M.; Cymbaluk-Ploska, A. The Influence of Biologically Active Substances Secreted by the Adipose Tissue on Endometrial Cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, I.; Boudreau, A.; Stephens, J.M. Adipose tissue in health and disease. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.; Kelley, D.E.; Yim, J.E.; Spence, N.; Albu, J.; Boxt, L.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Heshka, S.; Group, M.R.I.A.S.G.O.T.L.A.R. Adipose tissue distribution is different in type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, A.; Virbasius, J.V.; Puri, V.; Czech, M.P. Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 9, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.S.; Zhang, X.D.; Hondermarck, H.; Tanwar, P.S. The Emerging Role of the Microenvironment in Endometrial Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.-S.F.; Tsai, K.-B.; Chung, Y.-F.; Chan, T.-F.; Yeh, Y.-T.; Tsai, L.-Y.; Su, J.-H. Aberrant expression and possible involvement of the leptin receptor in endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2004, 92, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onstad, M.A.; Schmandt, R.E.; Lu, K.H. Addressing the Role of Obesity in Endometrial Cancer Risk, Prevention, and Treatment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4225–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, K.M.; Romero, I.L.; Van Houten, B.; Lengyel, E. Adipose tissue and adipocytes support tumorigenesis and metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Fan, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Xue, F. Glucose metabolic reprogramming and its therapeutic potential in obesity-associated endometrial cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J. Energy metabolism of cancer: Glycolysis versus oxidative phosphorylation (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2012, 4, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Dai, Y. Metabolic reprogramming and interventions in endometrial carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimundo, N.; Baysal, B.E.; Shadel, G.S. Revisiting the TCA cycle: Signaling to tumor formation. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Vadhan, A.; Wu, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-K.; Chen, P.-Y.; Nguyen, H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Yuan, S.-S. Fumarate hydratase functions as a tumor suppressor in endometrial cancer by inactivating EGFR signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 50, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Liu, M.; Turner, N. Diabetes and Its Link with Cancer: Providing the Fuel and Spark to Launch an Aggressive Growth Regime. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 390863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Tchernyshyov, I.; Semenza, G.L.; Dang, C.V. HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: A metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netto, L.E.S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Oguro, A.; Hirata, Y.; Imaoka, S. The regulation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1alpha) expression by Protein Disulfide Isomerase (PDI). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246531. [Google Scholar]
- Catrina, S.-B.; Zheng, X. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in diabetes and its complications. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Banno, K.; Kunitomi, H.; Takahashi, T.; Takeda, T.; Nakamura, K.; Tsuji, K.; Tominaga, E.; Aoki, D. Warburg effect in Gynecologic cancers. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2018, 45, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Vandewalle, N.; De Veirman, K.; Vanderkerken, K.; Menu, E.; De Bruyne, E. Targeting mTOR signaling pathways in multiple myeloma: Biology and implication for therapy. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenko, Y.A.; Gonchar, O.O.; Mankovska, I.M.; Drevytska, T.I.; Bratus, L.V.; Mankovsky, B.M. Oxydative stress in type 2 diabetic patients: Involvement of HIF-1 alpha AND mTOR genes expression. Ukr. Biochem. J. 2023, 95, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, S.; Hogan, M.F.; Montminy, M. mTOR links incretin signaling to HIF induction in pancreatic beta cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16876–16882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Kawana, K.; Osuga, Y.; Fujii, T. mTOR Signaling in Endometrial Cancer: From a Molecular and Therapeutic Point of View. Curr. Obstet. Gynecol. Rep. 2015, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, A.A.; Molitoris, K.H.; Koos, R.D. Estrogen rapidly activates the PI3K/AKT pathway and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and induces vascular endothelial growth factor A expression in luminal epithelial cells of the rat uterus. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Reyes, J.A.; Arellano-Plancarte, A.; Castillo-Hernandez, J.R. Angiotensin II and the development of insulin resistance: Implications for diabetes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 302, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabryelska, A.; Karuga, F.F.; Szmyd, B.; Białasiewicz, P. HIF-1α as a Mediator of Insulin Resistance, T2DM, and Its Complications: Potential Links With Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, I.A.; Bhatti, A.; John, P. The prognostic outcome of ‘type 2 diabetes mellitus and breast cancer’ association pivots on hypoxia-hyperglycemia axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-R.; Qin, X.-J.; Fang, Z.-H.; Li, S.; Han, L.-P.; Hui, J.; Guo, M.-F.; Jiang, N.-N. To Explore the Pathogenesis of Vascular Lesion of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 4650906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, I.; Campbell, H. Mechanisms of insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction and the action of the ketogenic diet in bipolar disorder. Focus on the PI3K/AKT/HIF1-a pathway. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 145, 110299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorolla, M.A.; Parisi, E.; Sorolla, A. Determinants of Sensitivity to Radiotherapy in Endometrial Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risinger, J.I.; Hayes, K.; Maxwell, G.L.; Carney, M.E.; Dodge, R.K.; Barrett, J.C.; Berchuck, A. PTEN mutation in endometrial cancers is associated with favorable clinical and pathologic characteristics. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 3005–3010. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bostan, I.S.; Mihaila, M.; Roman, V.; Radu, N.; Neagu, M.T.; Bostan, M.; Mehedintu, C. Landscape of Endometrial Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Target Therapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoerke, J.M.; Makker, V.; Aghajanian, C.; Thomas, P.; Motzer, R.J.; Lauchle, J.O.; Parmar, H.; Gilbert, H.; Lin, W.; O’Keeffe, B.; et al. Abstract A03: Comprehensive predictive biomarker evaluation in two phase II clinical trials of the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor GDC-0980 in metastatic renal cell carcinoma and advanced endometrial cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14 (Suppl. S7), A03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, W.C.; Chow, J.D.Y.; Simpson, E.R. The Multiple Roles of Estrogens and the Enzyme Aromatase. Neuroendocrinol. Norm. Neuroendocr. Syst. 2010, 181, 209–232. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W.; Ning, C.; Luo, X.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Hyperinsulinemia is associated with endometrial hyperplasia and disordered proliferative endometrium: A prospective cross-sectional study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 132, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, R.; Nikpour, P.; Rashidi, B.; Eskandari, N.; Aboutorabi, R. Evaluation of Muc1 Gene Expression at The Time of Implantation in Diabetic Rat Models Treated with Insulin, Metformin and Pioglitazone in The Normal Cycle and Ovulation Induction Cycle. Int. J. Fertil. Steril. 2020, 14, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Sun, N. E74-Like Factor 3 Promotes Endometrial Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion via Regulating Mucin 1/Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α Pathway. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2022, 12, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Wu, F.; Wu, W.; Meng, Z.; Zhu, M.; Miao, C. High glucose mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation via upregulation of ELF3 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredholt, G.; Mannelqvist, M.; Stefansson, I.M.; Birkeland, E.; Bø, T.H.; Øyan, A.M.; Trovik, J.; Kalland, K.-H.; Jonassen, I.; Salvesen, H.B.; et al. Tumor necrosis is an important hallmark of aggressive endometrial cancer and associates with hypoxia, angiogenesis and inflammation responses. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 39676–39691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noer, M.C.; Antonsen, S.L.; Ottesen, B.; Christensen, I.J.; Hogdall, C. Type I Versus Type II Endometrial Cancer: Differential Impact of Comorbidity. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2018, 28, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanders, M.M.; Boll, D.; van Steenbergen, L.N.; van de Poll-Franse, L.V.; Haak, H.R. Effect of diabetes on endometrial cancer recurrence and survival. Maturitas 2013, 74, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholas, Z.; Hu, N.; Ying, J.; Soisson, P.; Dodson, M.; Gaffney, D.K. Impact of comorbid conditions on survival in endometrial cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 37, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle, C.M.; Crosbie, E.J.; Brand, A.; Obermair, A.; Oehler, M.K.; Quinn, M.; Leung, Y.; Spurdle, A.B.; Webb, P.M. and G. Australian National Endometrial Cancer Study, The association between diabetes, comorbidities, body mass index and all-cause and cause-specific mortality among women with endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 150, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeber, L.M.; Horree, N.; van der Groep, P.; van der Wall, E.; Verheijen, R.H.; van Diest, P.J. Necrosis related HIF-1alpha expression predicts prognosis in patients with endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Shen, L.; Ren, Q.; Zeng, Q.; He, X. Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α in Endometrial Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 587420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiar, S.; Harris, A.L. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α as a cancer therapy target. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2006, 13 (Suppl. S1), S61–S75. [Google Scholar]
- Thangarajah, H.; Vial, I.N.; Grogan, R.H.; Yao, D.; Shi, Y.; Januszyk, M.; Galiano, R.D.; Chang, E.I.; Galvez, M.G.; Glotzbach, J.P.; et al. HIF-1α dysfunction in diabetes. Cell Cycle 2014, 9, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Qu, A.; Matsubara, T.; Chanturiya, T.; Jou, W.; Gavrilova, O.; Shah, Y.M.; Gonzalez, F.J. Disruption of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 in Adipocytes Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Decreases Adiposity in High-Fat Diet–Fed Mice. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2484–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunton, J.E. Hypoxia-inducible factors and diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5063–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeber, L.M.; Zweemer, R.P.; Verheijen, R.H.; van Diest, P.J. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 as a therapeutic target in endometrial cancer management. Obstet. Gynecol. Int. 2010, 2010, 580971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerychova, R.; Pavlinkova, G. HIF-1, Metabolism, and Diabetes in the Embryonic and Adult Heart. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Beresford, S.; Chen, C.; Chlebowski, R.; Garcia, L.; Kuller, L.; Regier, M.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Margolis, K.L. Association between diabetes, diabetes treatment and risk of developing endometrial cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, F.L.; Martin, A.R.; Kosasih, M.; Caruana, B.T.; Farrell, R. The Role of Hyperglycemia in Endometrial Cancer Pathogenesis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.J. Metformin: Historical overview. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insin, P.; Prueksaritanond, N. Therapeutic Use of Metformin in Diabetes and Survival Outcomes in Endometrial Cancer Patients with Diabetes. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Jimenez, C.; Gutierrez-Salmeron, M.; Chocarro-Calvo, A.; Garcia-Martinez, J.M.; Castano, A.; De la Vieja, A. From obesity to diabetes and cancer: Epidemiological links and role of therapies. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Di Gennaro, E.; Bruzzese, F.; Avallone, A.; Budillon, A. New perspective for an old antidiabetic drug: Metformin as anticancer agent. Cancer Treat. Res. 2014, 159, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nevadunsky, N.S.; Van Arsdale, A.; Strickler, H.D.; Moadel, A.; Kaur, G.; Frimer, M.; Conroy, E.; Goldberg, G.L.; Einstein, M.H. Metformin use and endometrial cancer survival. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 132, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.H. Metformin and endometrial cancer risk in Chinese women with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Taiwan. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 138, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemanska, A.; Zaborowski, M.; Spaczynski, M.; Nowak-Markwitz, E. Do endometrial cancer patients benefit from metformin intake? Ginekol. Pol. 2015, 86, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urpilainen, E.; Arima, R.; Karihtala, P.; Puistola, U.; Ahtikoski, A. Metformin Associates With Aggressive Features of Endometrial Cancer in Women With Type 2 Diabetes. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuhashi, A.; Kiyokawa, T.; Sato, Y.; Shozu, M. Effects of metformin on endometrial cancer cell growth in vivo: A preoperative prospective trial. Cancer 2014, 120, 2986–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevinskaite, M.; Kaceniene, A.; Linkeviciute-Ulinskiene, D.; Smailyte, G. The impact of metformin on survival in diabetic endometrial cancer patients: A retrospective population-based analysis. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2024, 23, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas-Vera, Y.M.; Gallardo-Rincon, D.; Ruiz-Garcia, E.; Silva-Cazares, M.B.; de la Pena-Cruz, C.S.; Lopez-Camarillo, C. The Role of Hypoxia in Endometrial Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2022, 23, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccia, A.; Siim, B.G.; Johnson, R.S. HIF-1 as a target for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, D.G.; Batchelor, T.T.; Willett, C.G.; Jain, R.K. VEGF-targeted cancer therapy strategies: Current progress, hurdles and future prospects. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmannsberger, C.; Mross, K.; Jakob, A.; Kanz, L.; Bokemeyer, C. Topotecan—A novel topoisomerase I inhibitor: Pharmacology and clinical experience. Oncology 1999, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.S.; Blessing, J.A.; Lentz, S.S.; Waggoner, S.E. A Phase II Trial of Topotecan in Patients with Advanced, Persistent, or Recurrent Endometrial Carcinoma: A Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2002, 87, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapisarda, A.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Melillo, G. Targeting topoisomerase I to inhibit hypoxia inducible factor 1. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapisarda, A.; Melillo, G. UVC inhibits HIF-1alpha protein translation by a DNA damage- and topoisomerase I-independent pathway. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6875–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapisarda, A.; Uranchimeg, B.; Scudiero, D.A.; Selby, M.; Sausville, E.A.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Melillo, G. Identification of small molecule inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 transcriptional activation pathway. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4316–4324. [Google Scholar]
- Wadler, S.; Levy, D.E.; Lincoln, S.T.; Soori, G.S.; Schink, J.C.; Goldberg, G. Topotecan is an active agent in the first-line treatment of metastatic or recurrent endometrial carcinoma: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3E93. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2110–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, T. The origin story of rapamycin: Systemic bias in biomedical research and cold war politics. Mol. Biol. Cell 2022, 33, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.V.; Tran, C.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; Welsbie, D.S.; Chan, E.; Fueger, B.; Czernin, J.; Sawyers, C.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor determines sensitivity to inhibitors of mTOR in kidney cancer. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, C.C.; Liu, M.; Chiang, G.G.; Otterness, D.M.; Loomis, D.C.; Kaper, F.; Giaccia, A.J.; Abraham, R.T. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression and function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 7004–7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chon, H.S.; Hu, W.; Kavanagh, J.J. Targeted therapies in gynecologic cancers. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2006, 6, 333–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verges, B.; Walter, T.; Cariou, B. Endocrine side effects of anti-cancer drugs: Effects of anti-cancer targeted therapies on lipid and glucose metabolism. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 170, R43–R55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oza, A.M.; Elit, L.; Tsao, M.-S.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Biagi, J.; Provencher, D.M.; Gotlieb, W.H.; Hoskins, P.J.; Ghatage, P.; Tonkin, K.S.; et al. Phase II Study of Temsirolimus in Women With Recurrent or Metastatic Endometrial Cancer: A Trial of the NCIC Clinical Trials Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3278–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Harikumar, P.; Atkinson, E.; Rigsby, P.; Wadhwa, M. The First WHO International Standard for Harmonizing the Biological Activity of Bevacizumab. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Kerbel, R.S. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 2005, 438, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajanian, C.; Sill, M.W.; Darcy, K.M.; Greer, B.; McMeekin, D.S.; Rose, P.G.; Rotmensch, J.; Barnes, M.N.; Hanjani, P.; Leslie, K.K. Phase II trial of bevacizumab in recurrent or persistent endometrial cancer: A Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2259–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatromanolaki, A.; Sivridis, E.; Brekken, R.; Thorpe, P.E.; Anastasiadis, P.; Gatter, K.C.; Harris, A.L.; Koukourakis, M.I. The angiogenic “vascular endothelial growth factor/flk-1(KDR) receptor” pathway in patients with endometrial carcinoma: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. Cancer 2001, 92, 2569–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, N.; Kodama, J.; Hongo, A.; Miyagi, Y.; Yoshinouchi, M.; Kudo, T. Vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor expression are implicated in the angiogenesis of endometrial cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2000, 36, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.W.; Bai, G.H.; Wang, T.L.; Shih, I.M.; Chuang, C.M.; Lo, C.L.; Tsai, M.C.; Chiu, L.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Shen, Y.A. Novel cancer treatment paradigm targeting hypoxia-induced factor in conjunction with current therapies to overcome resistance. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, R.A.; Brady, M.F.; Bookman, M.A.; Fleming, G.F.; Monk, B.J.; Huang, H.; Mannel, R.S.; Homesley, H.D.; Fowler, J.; Greer, B.E.; et al. Incorporation of bevacizumab in the primary treatment of ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2473–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geetha, A.V.S.; Harithpriya, K.; Ganesan, K.; Ramkumar, K.M. Exploring the Role of Hypoxia and HIF-1α in the Intersection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Endometrial Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32020106
Geetha AVS, Harithpriya K, Ganesan K, Ramkumar KM. Exploring the Role of Hypoxia and HIF-1α in the Intersection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Endometrial Cancer. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(2):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32020106
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeetha, Alagappan V. S., Kannan Harithpriya, Kumar Ganesan, and Kunka Mohanram Ramkumar. 2025. "Exploring the Role of Hypoxia and HIF-1α in the Intersection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Endometrial Cancer" Current Oncology 32, no. 2: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32020106
APA StyleGeetha, A. V. S., Harithpriya, K., Ganesan, K., & Ramkumar, K. M. (2025). Exploring the Role of Hypoxia and HIF-1α in the Intersection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Endometrial Cancer. Current Oncology, 32(2), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32020106





