Design of the ASSUT-FF Algorithm for GTO Satellite CNS/BDS Integrated Navigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. GTO Satellite CNS/BDS Integrated Navigation Method
2.1. Navigation System Model
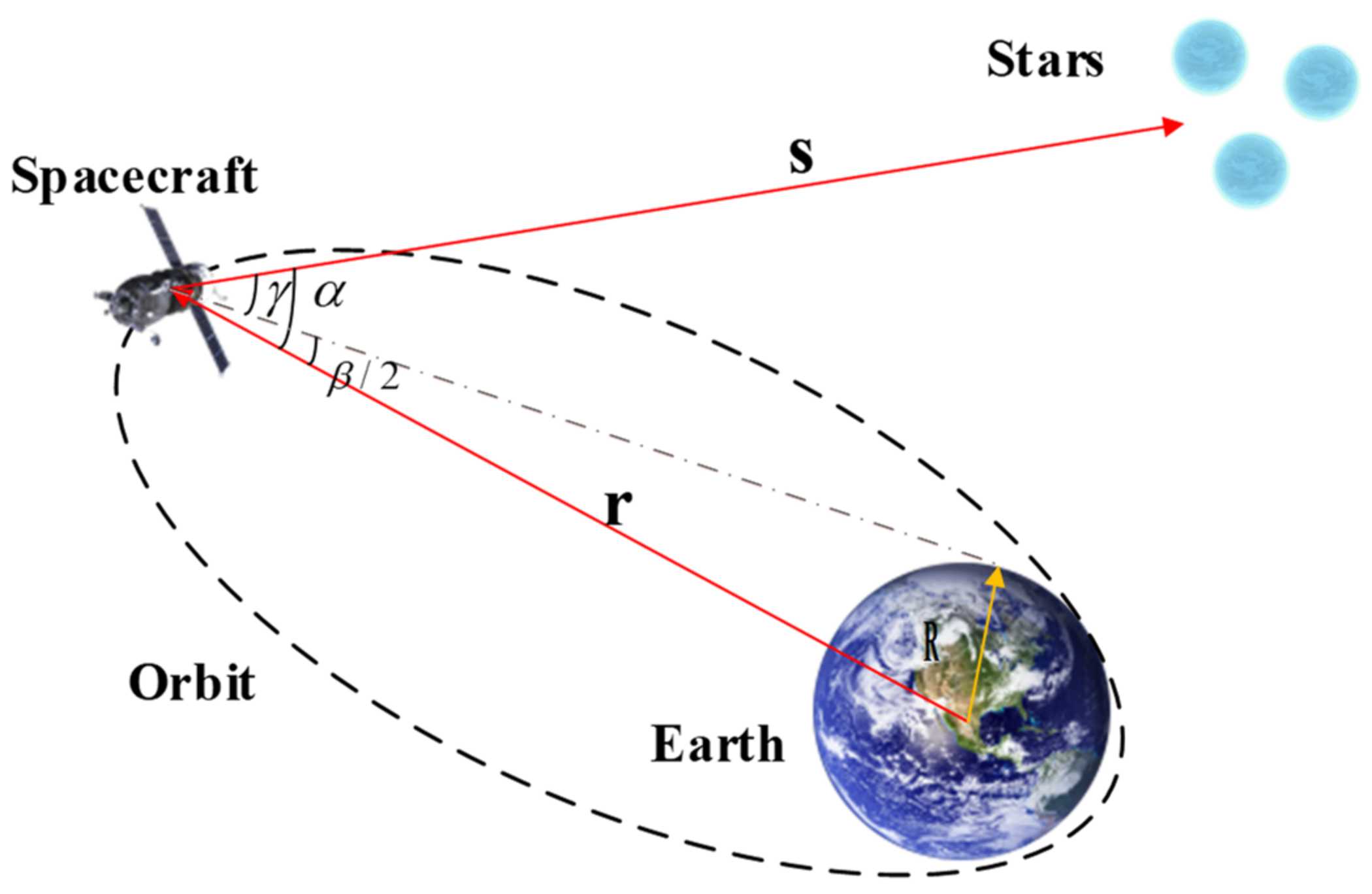
2.2. CNS Measurement Model
2.3. BDS Measurement Model
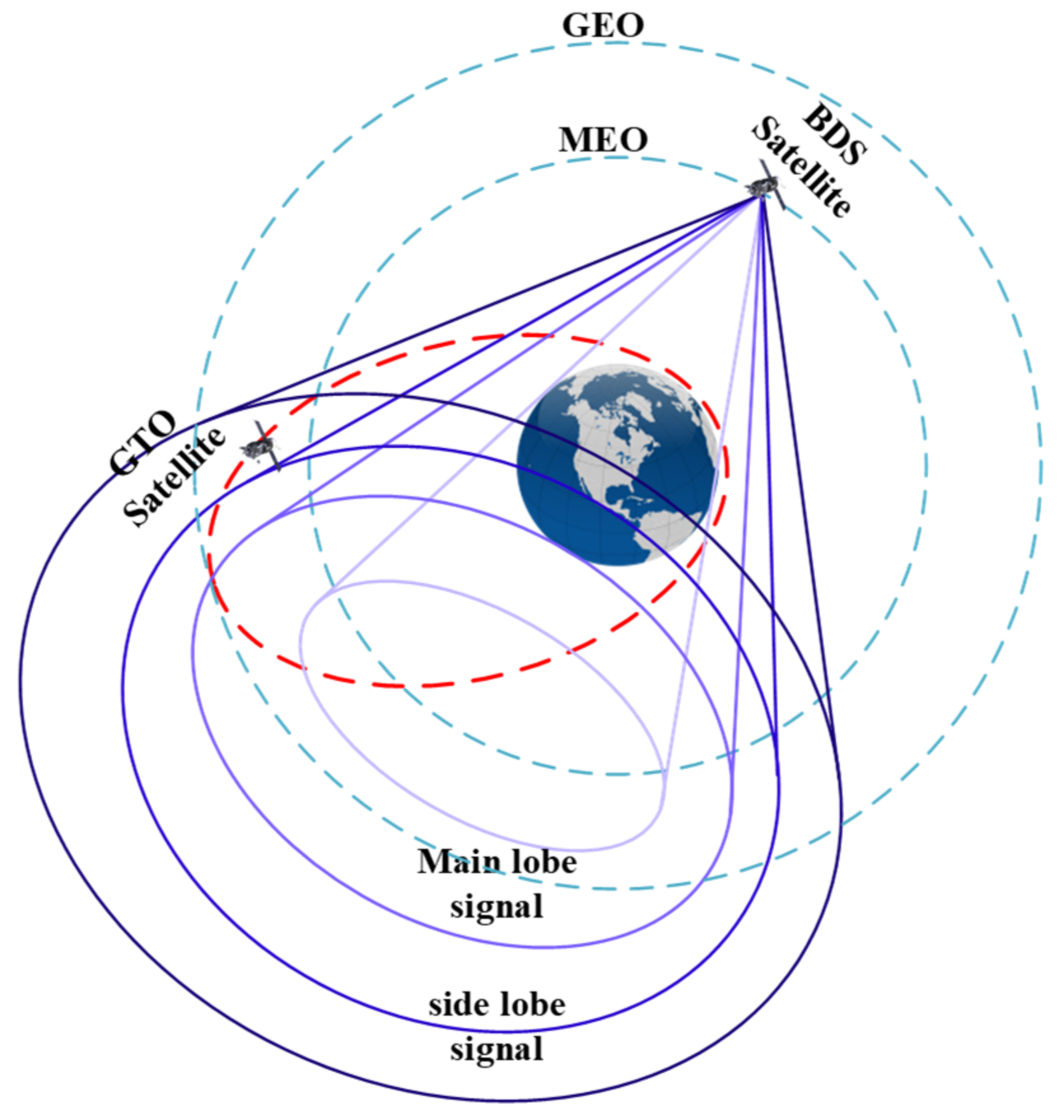
2.3.1. Visibility of BD Satellites
2.3.2. BDS Measurement Equation
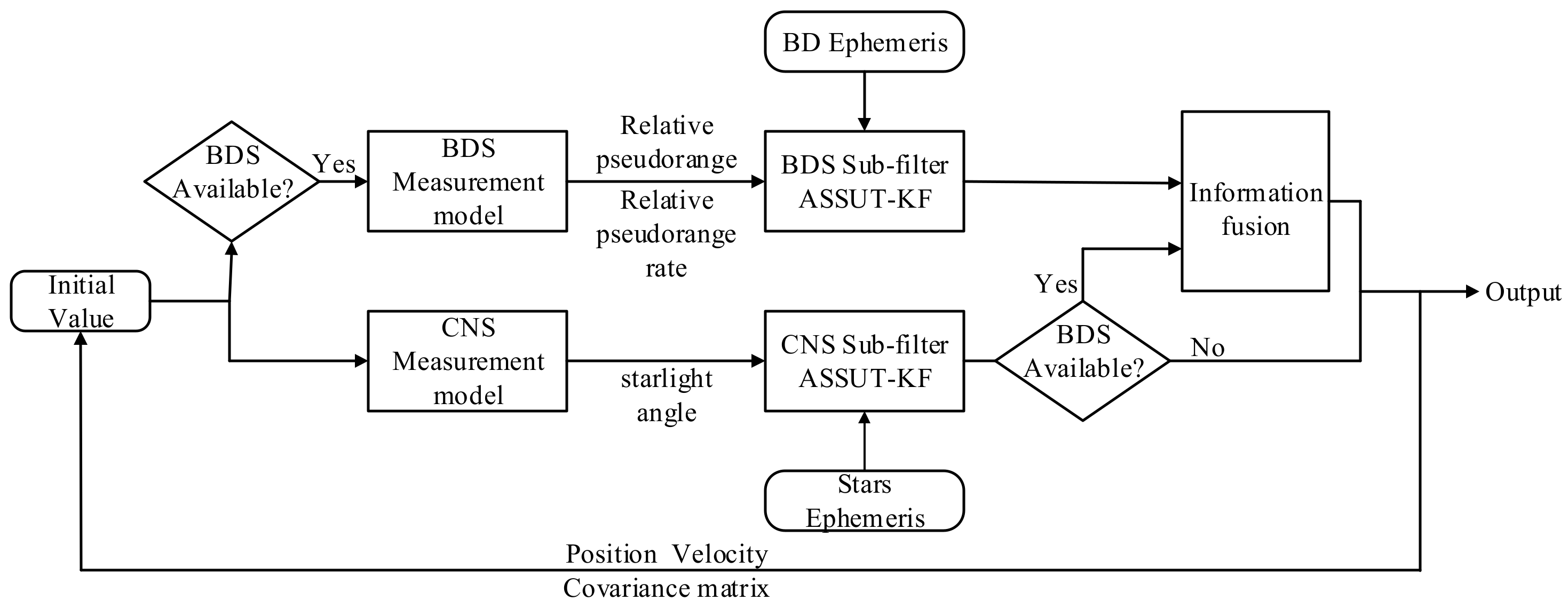
2.4. GTO Satellite CNS/BDS Integrated Navigation Scheme
3. GTO Satellite Integrated Navigation ASSUT-FF Algorithm
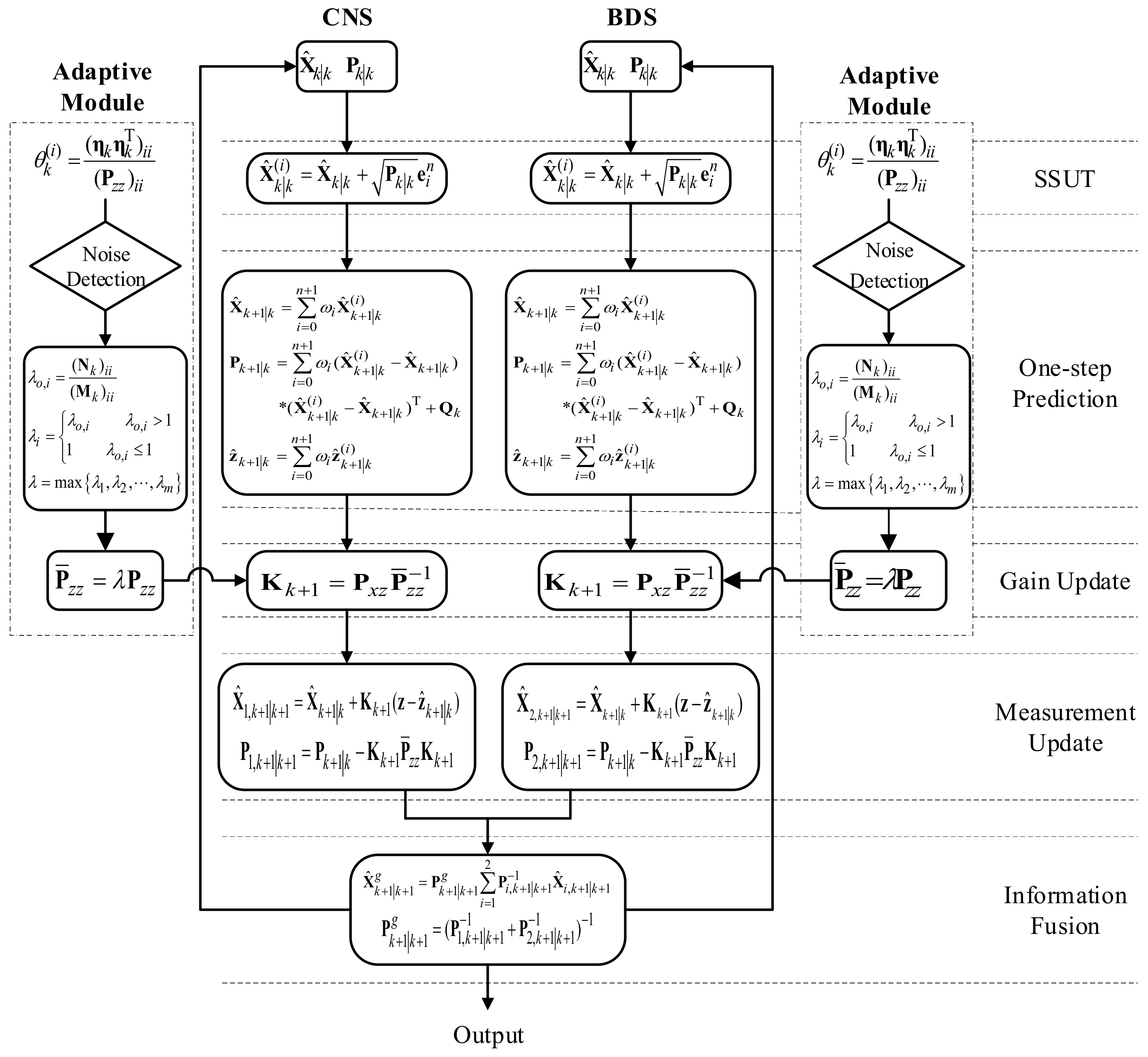
3.1. Spherical Simplex Unscented Transformation Sampling of ASSUT-FF
- Step 1: Determine the weight of each sampling point.where is the weight of the first sampling point determined in advance.
- Step 2: Initialization of vector sequence.
- Step 3: Extension of vector sequence.where is the -th sampling point vector of the -dimensional random variable and is the -dimensional zero vector. Therefore, the spherical simplex unscented transformation of an -dimensional random variable with mean and error covariance matrix is
3.2. Adaptive Method of ASSUT-FF
3.2.1. Measurement Noise Uncertainty Detection
3.2.2. Calculation of Adaptive Factor
3.3. Information Fusion Process of ASSUT-FF
- Step 1: Distribution of public information.
- Step 2: Local information is fused.where is the information distribution coefficient between 0 and 1 that satisfies .
4. Simulation
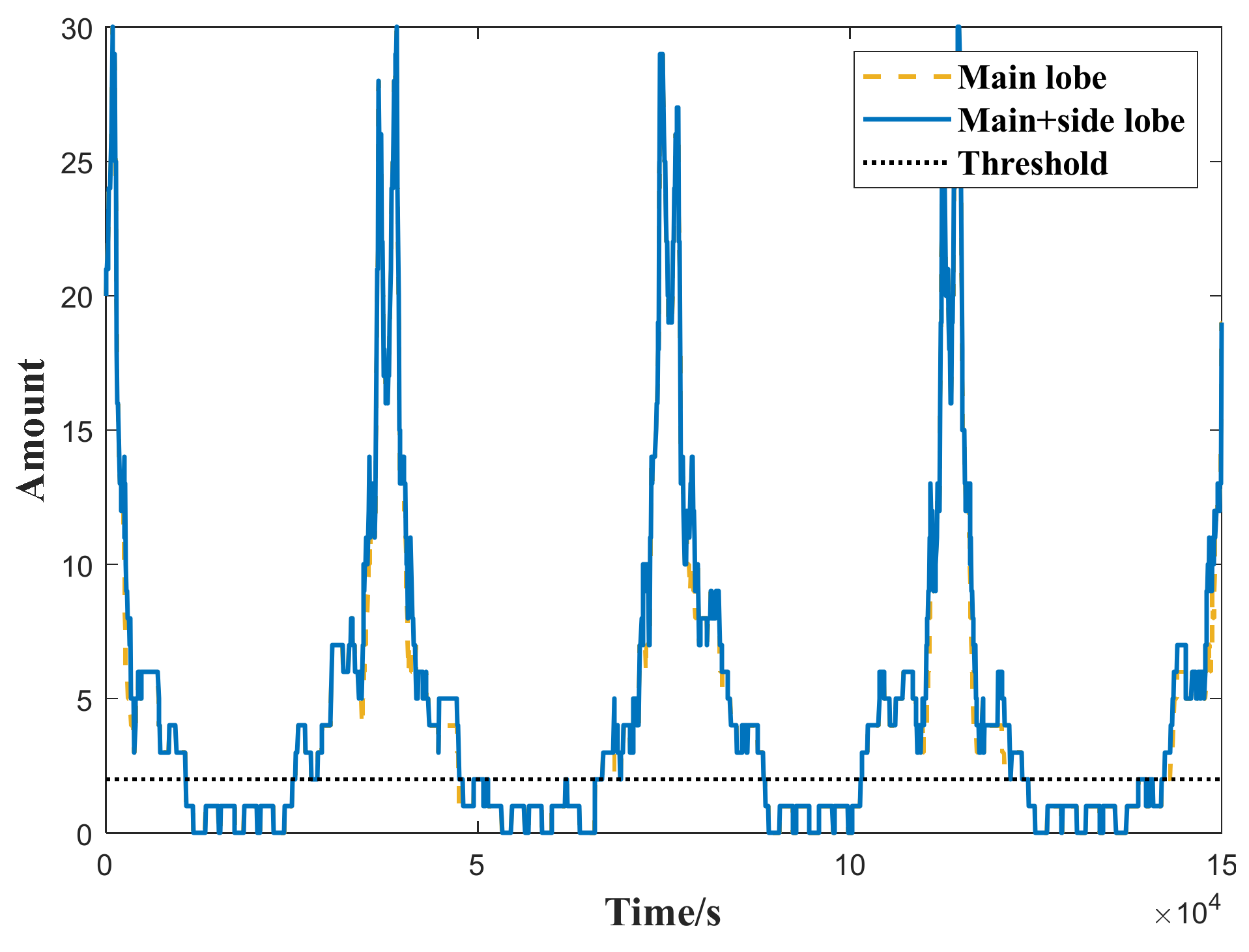
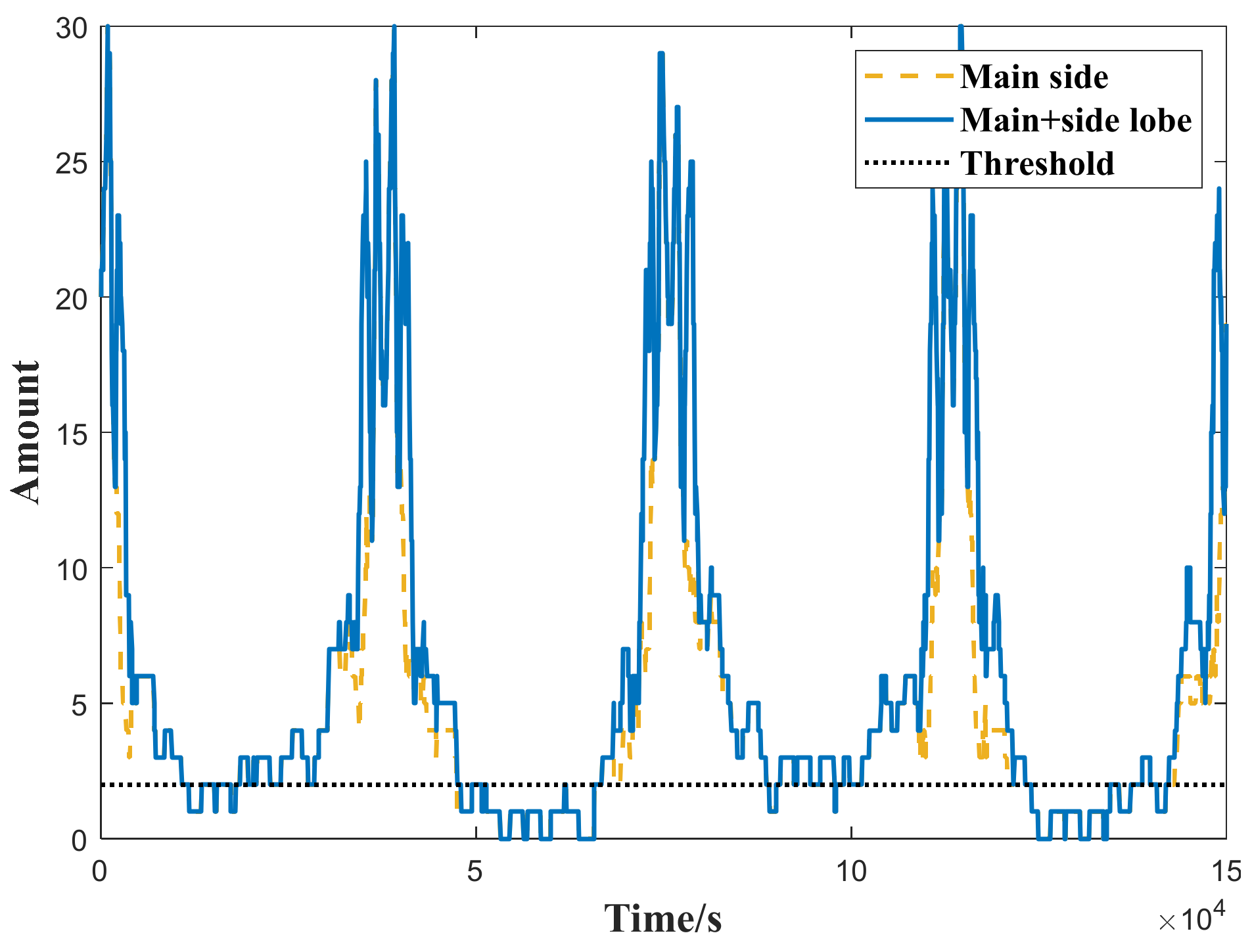
4.1. BDS Availability Analysis
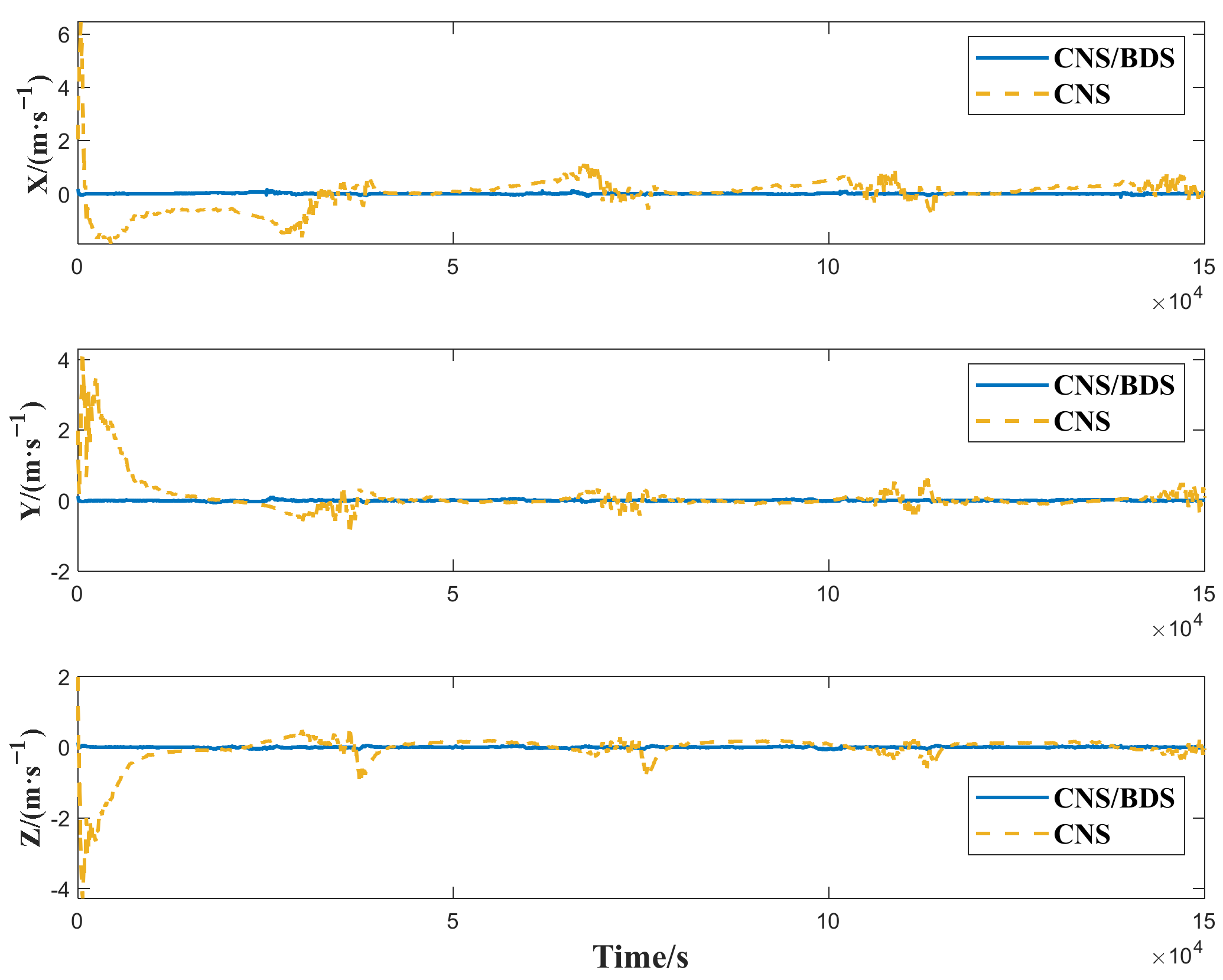
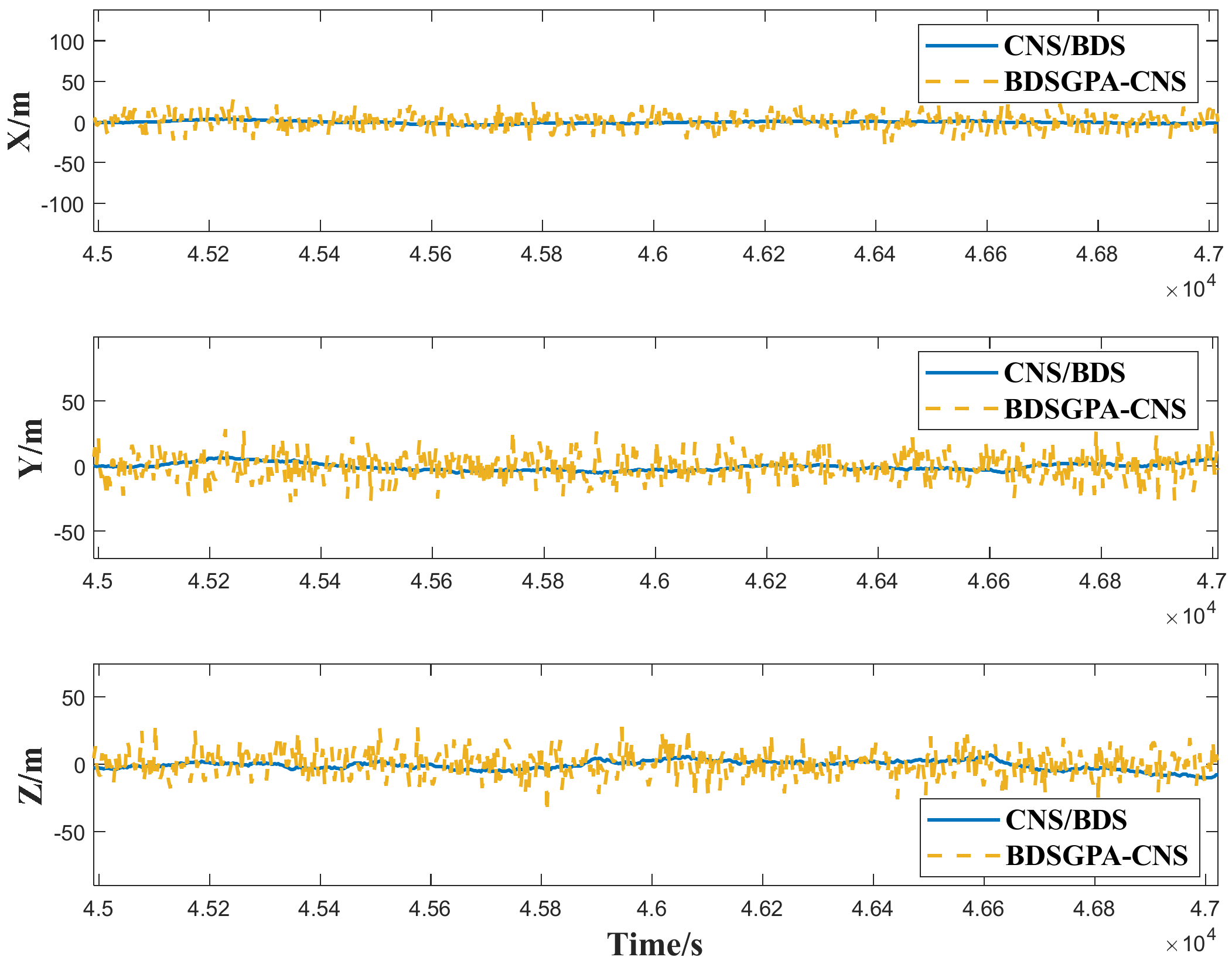
4.2. Comparison of GTO Satellite CNS/BDS Integrated Navigation and CNS Navigation
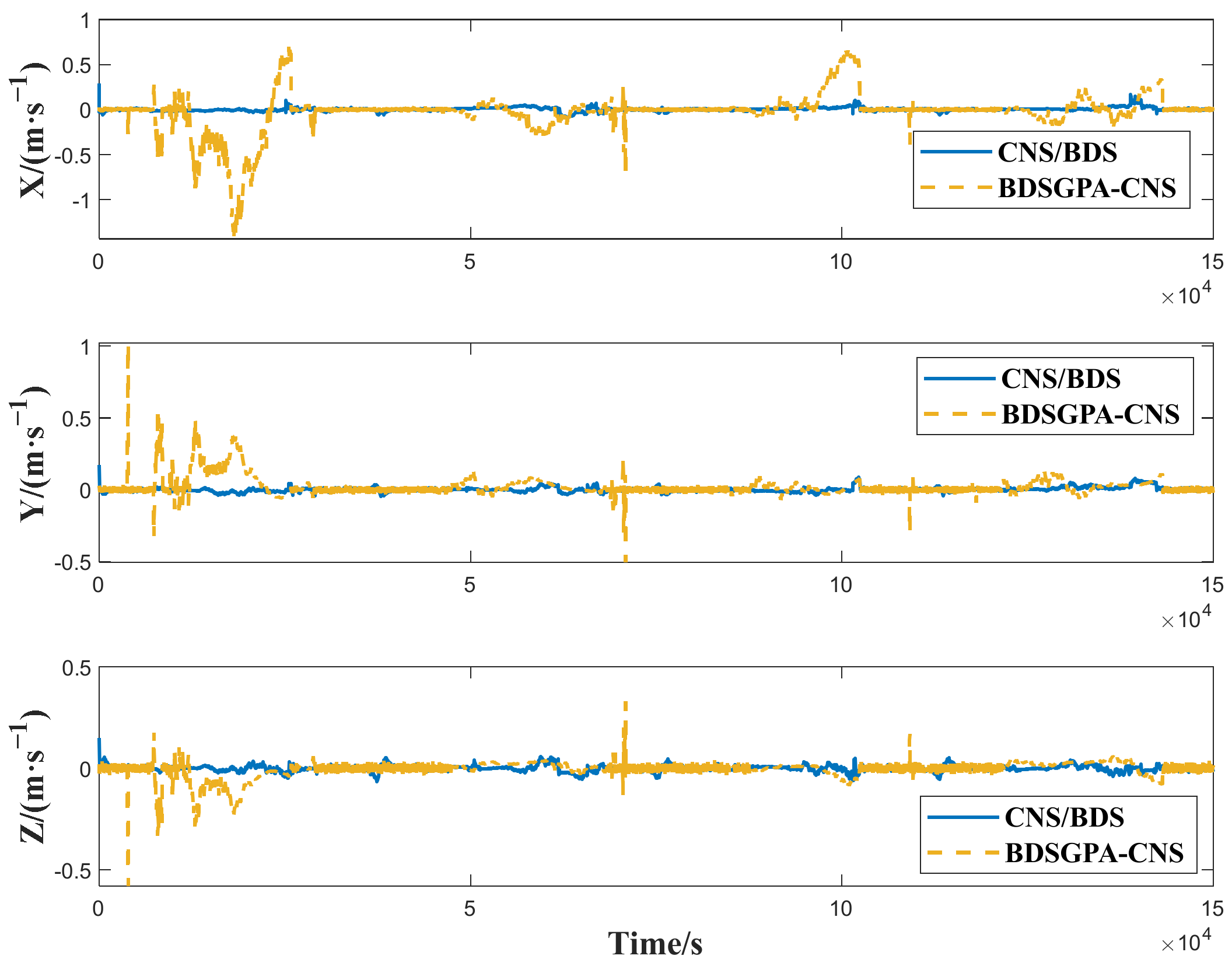
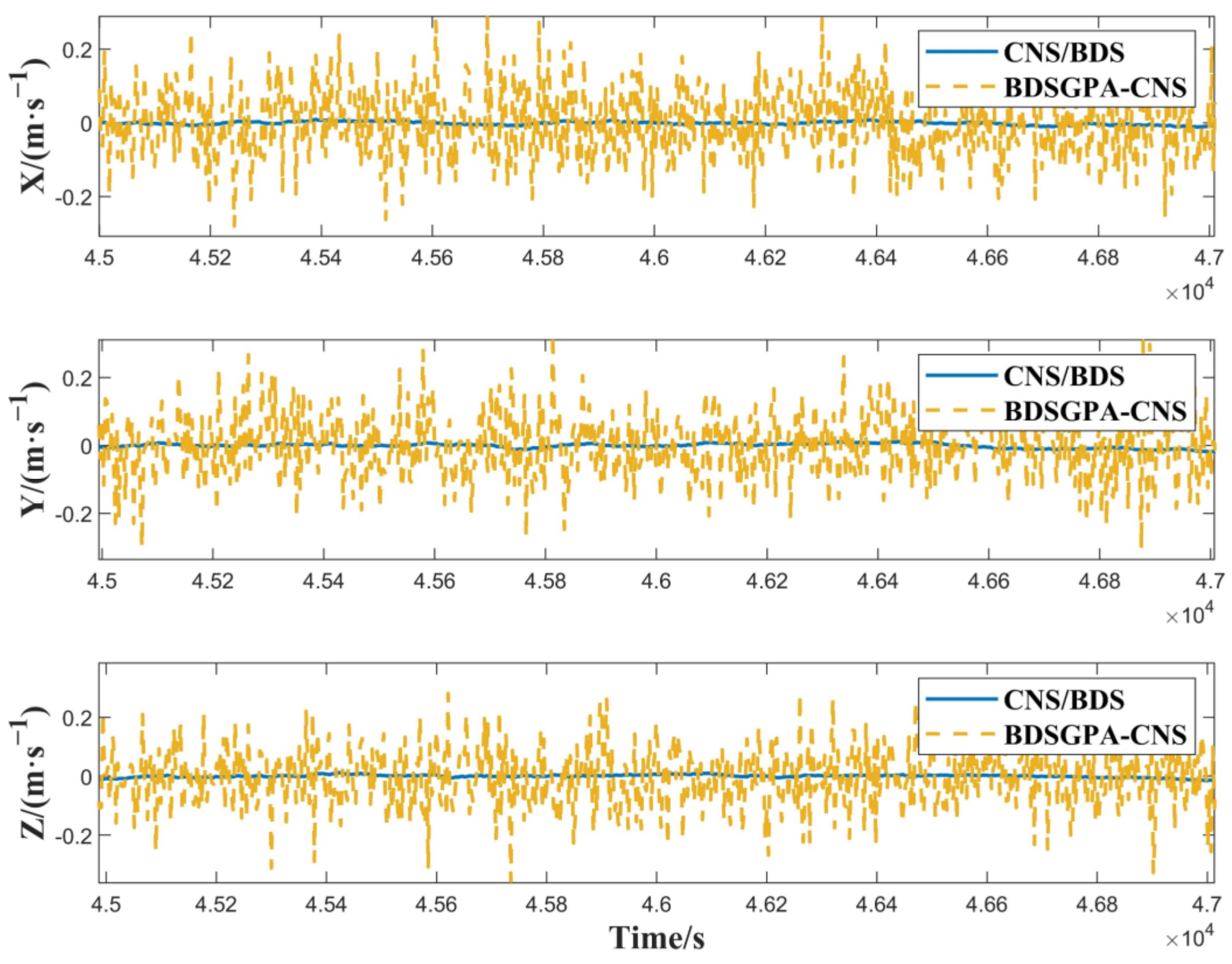
4.3. Comparison of GTO Satellite CNS/BDS Integrated Navigation and BDSGPA-CNS Navigation
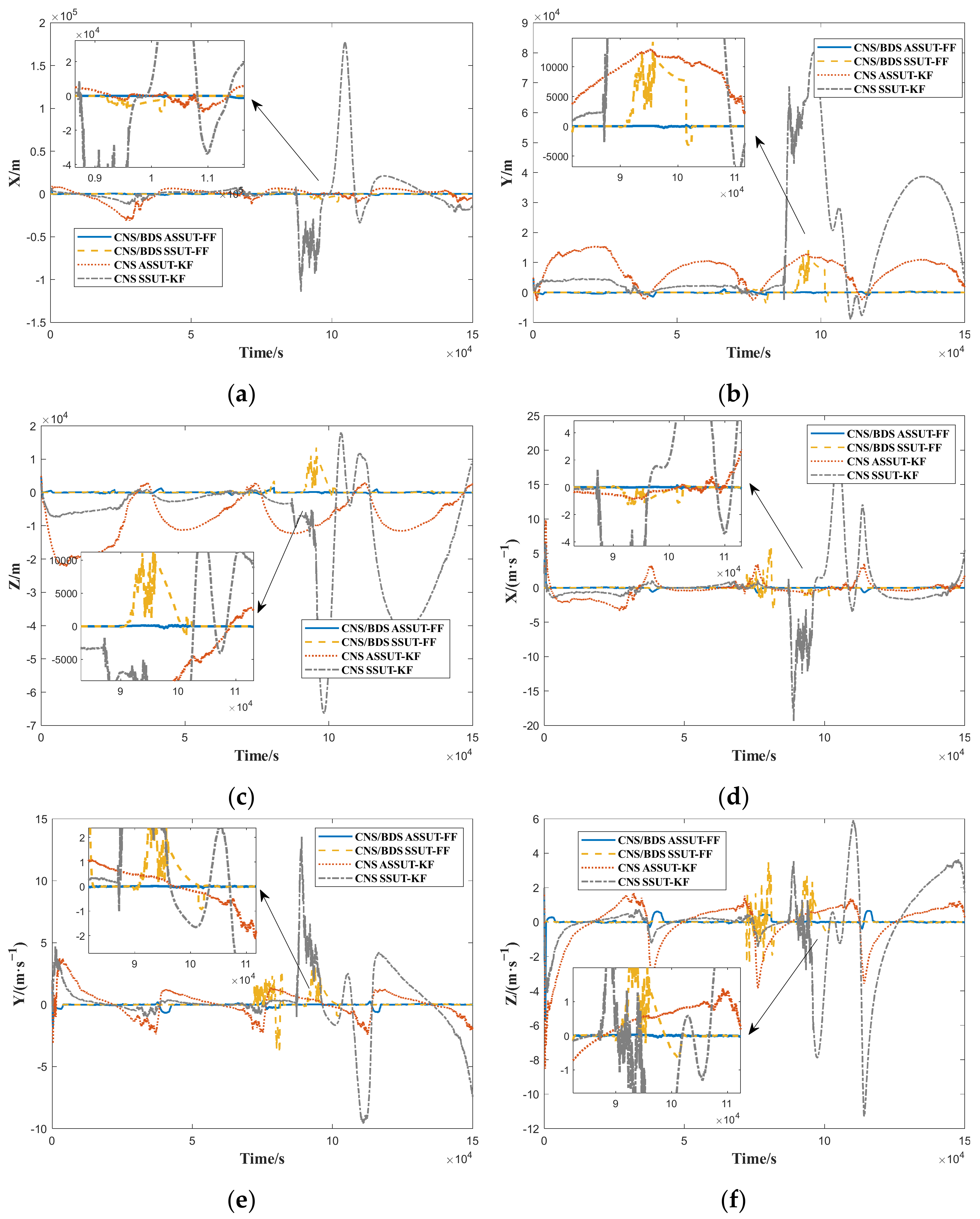
4.4. Case Where Prior Information Is Inaccurate
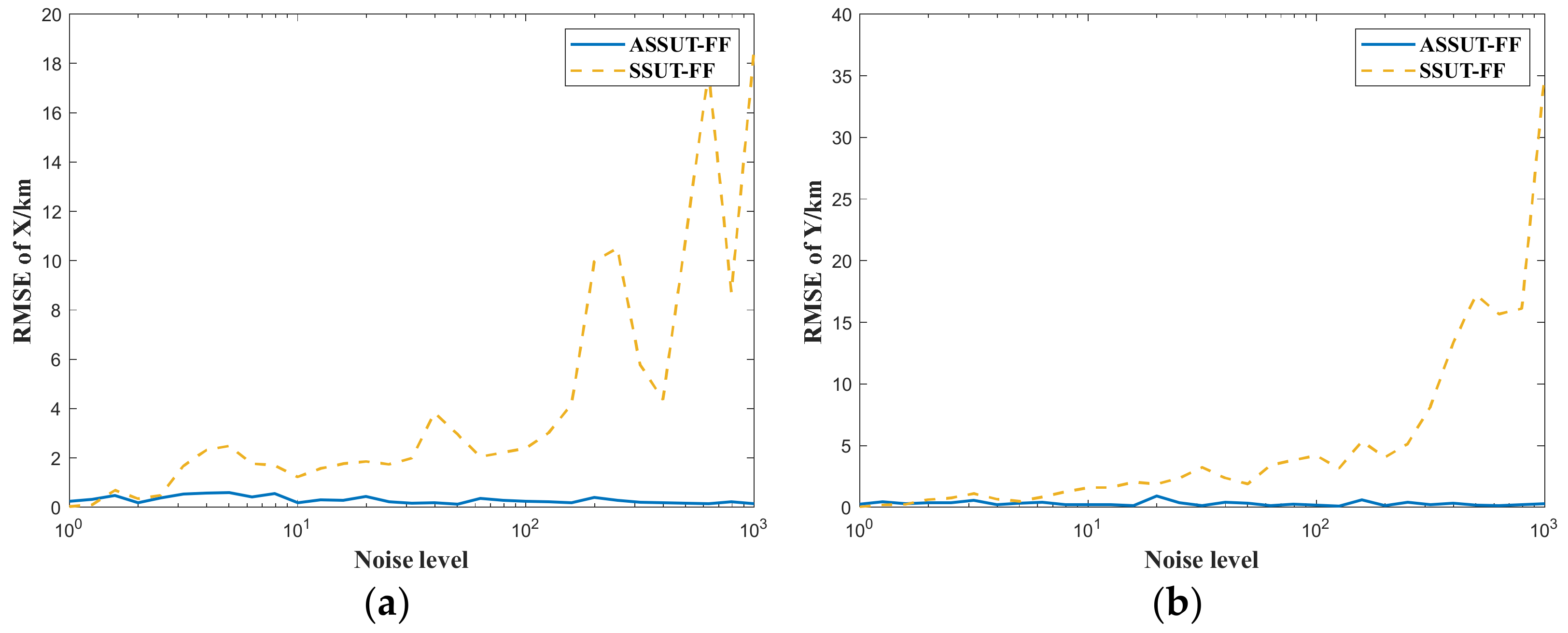
4.5. Case of Different Noise Levels
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Han, C. Low-thrust GEO orbit transfer guidance using semi-analytic method. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. 2018, 162, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Q. Satellite celestial/cadar altimeter integrated navigation method for large elliptical orbits. Chin. J. Inert. Technol. 2012, 20, 300–305. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Ning, X.; Liu, L. New celestial assisted INS initial alignment method for lunar explorer. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2013, 24, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Ning, X.; Fang, J. Analysis of orbital dynamic equation in navigation for a mars gravity-assist mission. J. Navig. 2012, 65, 531–548. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, M.; Xu, T.; Li, M.; Gao, F.; Ma, D. Navigation in GEO, HEO, and Lunar Trajectory Using Multi-GNSS Sidelobe Signals. Remote Sens. 2022, 2, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. GNSS-based orbit determination for highly elliptical orbit satellites. In Proceedings of the International Global Navigation Satellite Systems Society IGNSS Symposium, New York, NY, USA, 1 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liu, R.; Li, B. Application of unscented kalman filter in celestial/geomagnetic autonomous navigation algorithm of aerocraft. J. Chin. Inert. Technol. 2010, 18, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, W.; Fang, J.; Xu, F.; Sheng, W. Hybrid simulation system study of SINS/CNS integrated navigation. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2008, 23, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shirinzadeh, B. Multi-sensor optimal data fusion for INS/GPS/SAR integrated navigation system. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2009, 13, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, X.; Gao, L.; Liu, Z.; Hua, Z. Spacecraft autonomous navigation system based on SINS/Ultraviolet sensor/Star sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Chinese Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference (CGNCC), Nanjing, China, 12–14 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. A new method for autonomous navigation of HEO satellite based on celestial/accelerometer. Chin. J. Inert. Technol. 2014, 22, 525–530. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, M. Research on Autonomous Navigation Technology of High-Orbit Satellites Based on Celestial/GNSS. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Gao, D. Integrated navigation method for large elliptical orbit satellite based on information fusion. J. Astronaut. 2012, 33, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. Celestial navigation method of HEO satellite based on celestial/GPS. Control Decis. 2015, 30, 519–525. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Josep, J.; Gerard, G.; Yuan, J. An efficient statistical adaptive order-switching methodology for kalman filters. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2021, 93, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Wu, Z.; Chambers, J. A New Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter for Cooperative Localization. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, J.; Abdolrahman, R. Performance improvement for mobilerobot position determination using cubature kalman filter. J. Navig. 2018, 71, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonya, K.; Ghorbani, S.; Janabi, S. Unscented kalman filter state estination for manipulating unmanned aerial vehicles. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 446–463. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Guo, R.; He, F.; Liu, L.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Zhao, G.; et al. Improvement of orbit determination accuracy for beidou navigation satellite system with two-way satellite time frequency transfer. Adv. Space Resharch 2016, 58, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Pei, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Gao, S.; Wei, W.; Hu, G. A Quaternion-Based Robust Adaptive Spherical Simplex Unscented Particle Filter for MINS/VNS/GNS Integrated Navigation System. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 8532601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, F.; Ge, S.; Zhang, J.; He, W. Celestial navigation in deep space exploration using spherical simplex unscented particle filter. IET Signal Process 2017, 12, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Pang, X.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Yu, H.; Tang, J. Comparison on three unscented transformation methods for solving probabilistic load flow. In Proceedings of the IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies—Asia (ISGT Asia), Chengdu, China, 21–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, N.; Chambers, J. A novel adaptive kalman filter with inaccurate process and measurement noise covariance matrices. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2018, 63, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwang, H.; Jang, G.; Chan, G.; Gyu, I. The stability analysis of the adaptive fading extended kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, Singapore, 1–3 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Satellite Orbit Attitude Dynamics and Control; Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 49–51. ISBN 978-78-1012-721-9. [Google Scholar]
- Qing, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S. Kalman Filter and Principle of Integrated Navigation; Northwestern Polytechnic University Press: Xi’an, China, 2010; pp. 86–107. ISBN 978-75-6123-350-4. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Tian, X. An adaptive UKF algorithm for process fault prognostics. In Proceedings of the 2th International Conferences on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Changsha, China, 10–11 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Ge, J.; Zong, B.; Lu, W. Strong tracking square root volumetric kalman filtering algorithm for adaptive CS model. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2019, 41, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar]




| Frequency /GHz | Main Lobe Angle/° | Power /dBW | Main Lobe Gain/dB | Side Lobe Gain/dB | Receiver Sensitivity /dBW | Other Losses /dB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5611 | 42.6 | 12 | 15 | 3 | −170/−175/−180 | 3 |
| N | Signal Properties | Probability of Availability of BDS for Receivers of Different Sensitivities | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −170 dBW | −175 dBW | −180 dBW | ||
| 2 | Main + side lobe signal | 66.58% | 82.29% | 96.55% |
| Main lobe signal | 66.58% | 82.29% | 82.29% | |
| 4 | Main + side lobe signal | 46.47% | 49.70% | 82.75% |
| Main lobe signal | 45.67% | 47.07% | 47.07% | |
| Star Sensor | Earth Sensor | Receiver | Pseudorange Error | Pseudorange Rate Error | CNS Noise Variance | BDS Noise Variance | Initial Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −170 dBW | 10 m | 0.1 m/s |
| x/m | y/m | z/m | vx/(m/s) | vy/(m/s) | vz/(m/s) | Increased Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNS | 3607.1 | 1277.7 | 2021.8 | 0.6229 | 0.5025 | 0.4590 | -- |
| CNS/BDS | 132.9 | 83.1 | 96.8 | 0.0203 | 0.0153 | 0.0162 | 96.23% |
| Star Sensor | Earth Sensor | Receiver | Pseudorange Error | Pseudorange Rate Error | CNS Noise Variance | BDS Noise Variance | Initial Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −170 dBW | 10 m | 0.1 m/s |
| x/m | y/m | z/m | vx/(m/s) | vy/(m/s) | vz/(m/s) | Increased Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDSGPA-CNS | 1258.2 | 758.2 | 339.8 | 0.1539 | 0.0657 | 0.0367 | -- |
| CNS/BDS | 170.7 | 87.9 | 78.2 | 0.0237 | 0.0141 | 0.0144 | 84.06% |
| x/m | y/m | z/m | vx/(m/s) | vy/(m/s) | vz/(m/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDSGPA-CNS | 34.5104 | 43.3258 | 13.7668 | 0.0928 | 0.0983 | 0.1096 |
| CNS/BDS | 1.4396 | 2.1284 | 3.0380 | 0.0047 | 0.0058 | 0.0050 |
| Star Sensor | Earth Sensor | Receiver | Pseudorange Error | Pseudorange Rate Error | CNS Noise Variance | BDS Noise Variance | Initial Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −170 dBW | 10 m | 0.1 m/s |
| Algorithm | x/m | y/m | z/m | vx/(m/s) | vy/(m/s) | vz/(m/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNS | SSUT-KF | 30,975.5 | 24,338.6 | 18,419.2 | 4.1487 | 2.5703 | 2.3528 |
| ASSUT-KF | 7691.4 | 8984.2 | 10,274.9 | 1.3007 | 1.0766 | 1.3449 | |
| CNS/BDS | SSUT-FF | 1339.1 | 2184.4 | 1550.2 | 0.5539 | 0.5234 | 0.4313 |
| ASSUT-FF | 420.9 | 248.9 | 239.7 | 0.3283 | 0.1497 | 0.2741 |
| Algorithm | x/m | y/m | z/m | vx/(m/s) | vy/(m/s) | vz/(m/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNS | SSUT-KF | 38,203.1 | 33,384.5 | 6892.3 | 5.6796 | 3.5540 | 1.1270 |
| ASSUT-KF | 4511.2 | 7477.6 | 9498.8 | 1.0734 | 1.0040 | 1.2253 | |
| CNS/BDS | SSUT-FF | 2046.3 | 3281.3 | 2810.5 | 1.3465 | 1.2411 | 1.0291 |
| ASSUT-FF | 163.1 | 192.6 | 332.1 | 0.1466 | 0.1285 | 0.1876 |
| Star Sensor | Earth Sensor | Receiver | Pseudorange Error | Pseudorange Rate Error | CNS Noise Variance | BDS Noise Variance | Initial Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −170 dBW | 10 m | 0.1 m/s |
| Algorithm | x/m | y/m | z/m | vx/(m/s) | vy/(m/s) | vz/(m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSUT-FF | 4159.2 | 5094.4 | 4431.6 | 1.4752 | 1.3752 | 1.2467 |
| ASSUT-FF | 298.2 | 299.8 | 210.3 | 0.1244 | 0.1179 | 0.1025 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, B.; Wei, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z. Design of the ASSUT-FF Algorithm for GTO Satellite CNS/BDS Integrated Navigation. Aerospace 2022, 9, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9070384
Hua B, Wei X, Wu Y, Chen Z. Design of the ASSUT-FF Algorithm for GTO Satellite CNS/BDS Integrated Navigation. Aerospace. 2022; 9(7):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9070384
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Bing, Xiaosong Wei, Yunhua Wu, and Zhiming Chen. 2022. "Design of the ASSUT-FF Algorithm for GTO Satellite CNS/BDS Integrated Navigation" Aerospace 9, no. 7: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9070384
APA StyleHua, B., Wei, X., Wu, Y., & Chen, Z. (2022). Design of the ASSUT-FF Algorithm for GTO Satellite CNS/BDS Integrated Navigation. Aerospace, 9(7), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9070384






