In Silico Analysis of PORD Mutations on the 3D Structure of P450 Oxidoreductase
Abstract
1. Introduction
POR Deficiency (PORD)
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Compilation of Reported POR Genetic Variants
2.2. In Silico Analysis of POR Mutations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Compilation of Reported Cases of POR Mutations
3.2. Bioinformatics Analysis of POR Protein Sequences
3.3. In Silico Analysis of 3D X-ray Crystal Structure of POR Protein
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Pandey, A.V.; Flück, C.E. NADPH P450 oxidoreductase: Structure, function, and pathology of diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flück, C.E.; Mullis, P.E.; Pandey, A.V. Modeling of human P450 oxidoreductase structure by in silico mutagenesis and MD simulation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 313, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flück, C.E.; Tajima, T.; Pandey, A.V.; Arlt, W.; Okuhara, K.; Verge, C.F.; Jabs, E.W.; Mendonça, B.B.; Fujieda, K.; Miller, W.L. Mutant P450 oxidoreductase causes disordered steroidogenesis with and without Antley-Bixler syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdane, D.; Xia, C.; Im, S.-C.; Zhang, H.; Kim, J.-J.P.; Waskell, L. Structure and Function of an NADPH-Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase in an Open Conformation Capable of Reducing Cytochrome P450. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 11374–11384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flück, C.E.; Pandey, A.V. Clinical and Biochemical Consequences of P450 Oxidoreductase Deficiency. Endocr. Dev. 2010, 20, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermilion, J.; Ballou, D.; Massey, V.; Coon, M. Separate roles for FMN and FAD in catalysis by liver microsomal NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyanagi, T.; Mason, H.S. Properties of Hepatic Reduced Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate-Cytochrome C Reductase. Biochemistry 1973, 12, 2297–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.R.; Miller, W.L. Genetic and Clinical Features of P450 Oxidoreductase Deficiency. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2008, 69, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.E.; Imperato-McGinley, J.; Gautier, T.; Shackleton, C. Male pseudohermaphroditism due to multiple defects in steroid-biosynthetic microsomal mixed-function oxidases. A new variant of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 1413–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.L.; O’Leary, K.A.; Kasper, C.B. Association of Multiple Developmental Defects and Embryonic Lethality with Loss of Microsomal NADPH-Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 6536–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, D.M.E.; Henderson, C.J.; Carrie, D.; Davey, M.; Gundersen, T.E.; Blomhoff, R.; Adams, R.H.; Tickle, C.; Wolf, C.R. Identification of Novel Roles of the Cytochrome P450 System in Early Embryogenesis: Effects on Vasculogenesis and Retinoic Acid Homeostasis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 6103–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krone, N.; Reisch, N.; Idkowiak, J.; Dhir, V.; Ivison, H.E.; Hughes, B.A.; Rose, I.T.; O’Neil, D.M.; Vijzelaar, R.; Smith, M.J.; et al. Genotype-Phenotype Analysis in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia due to P450 Oxidoreductase Deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E257–E267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Ren, X.; Song, Y.; Su, C.; Fu, J.; Gong, C. Novel phenotypes and genotypes in Antley-Bixler syndrome caused by cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency: Based on the first cohort of Chinese children. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlt, W.; Walker, E.A.; Draper, N.; Ivison, H.E.; Ride, J.P.; Hammer, F.; Chalder, S.M.; Borucka-Mankiewicz, M.; Hauffa, B.P.; Malunowicz, E.M.; et al. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia caused by mutant P450 oxidoreductase and human androgen synthesis: Analytical study. Lancet 2004, 363, 2128–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Tachibana, K.; Asakura, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Hanaki, K.; Oka, A. Compound heterozygous mutations of cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase gene (POR) in two patients with Antley-Bixler syndrome. Am. J. Med Genet. 2004, 128A, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wudy, S.A.; Hartmann, M.F.; Draper, N.; Stewart, P.M.; Arlt, W. A Male Twin Infant with Skull Deformity and Elevated Neonatal 17–Hydroxyprogesterone: A Prismatic Case of P450 Oxidoreductase Deficiency. Endocr. Res. 2004, 30, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Pandey, A.V.; Agrawal, V.; Reardon, W.; Lapunzina, P.D.; Mowat, D.; Jabs, E.W.; Van Vliet, G.; Sack, J.; Flück, C.E.; et al. Diversity and function of mutations in P450 oxidoreductase in patients with Antley-Bixler syndrome and disordered steroidogenesis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 76, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, M.; Horikawa, R.; Nagai, T.; Tanaka, T.; Naiki, Y.; Sato, N.; Okuyama, T.; Nakai, H.; Soneda, S.; Tachibana, K.; et al. Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase Gene Mutations and Antley-Bixler Syndrome with Abnormal Genitalia and/or Impaired Steroidogenesis: Molecular and Clinical Studies in 10 Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Horikawa, R.; Ohashi, T.; Nishimura, G.; Homma, K.; Ogata, T. Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase Deficiency in Three Patients Initially Regarded as Having 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency and/or Aromatase Deficiency: Diagnostic Value of Urine Steroid Hormone Analysis. Pediatr. Res. 2006, 59, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Nagai, T.; Adachi, M.; Horikawa, R.; Fujiwara, I.; Tajima, T.; Takeda, R.; Fukami, M.; Ogata, T. Urine Steroid Hormone Profile Analysis in Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase Deficiency: Implication for the Backdoor Pathway to Dihydrotestosterone. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 2643–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, L.; Arlt, W.; Shackleton, C.; Kelley, R.; Braddock, S. Linking Antley-Bixler syndrome and congenital adrenal hyperplasia: A novel case of P450 oxidoreductase deficiency. Am. J. Med Genet. Part A 2006, 140A, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershkovitz, E.; Parvari, R.; Wudy, S.A.; Hartmann, M.F.; Gomes, L.G.; Loewental, N.; Miller, W.L. Homozygous Mutation G539R in the Gene for P450 Oxidoreductase in a Family Previously Diagnosed as Having 17,20-Lyase Deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3584–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.M.; Cheon, C.-K.; Kim, G.-H.; Yoo, H.-W. A case of Antley-Bixler syndrome caused by compound heterozygous mutations of the cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase gene. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 168, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukami, M.; Nishimura, G.; Homma, K.; Nagai, T.; Hanaki, K.; Uematsu, A.; Ishii, T.; Numakura, C.; Sawada, H.; Nakacho, M.; et al. Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency: Identification and characterization of biallelic mutations and genotype-phenotype correlations in 35 Japanese patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahakitrungruang, T.; Huang, N.; Tee, M.K.; Agrawal, V.; Russell, W.E.; Crock, P.; Murphy, N.; Migeon, C.J.; Miller, W.L. Clinical, Genetic, and Enzymatic Characterization of P450 Oxidoreductase Deficiency in Four Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4992–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idkowiak, J.; Malunowicz, E.M.; Dhir, V.; Reisch, N.; Szarras-Czapnik, M.; Holmes, D.M.; Shackleton, C.H.L.; Davies, J.D.; Hughes, I.A.; Krone, N.; et al. Concomitant mutations in the P450 oxidoreductase and androgen receptor genes presenting with 46,XY disordered sex development and androgenization at adrenarche. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 3418–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- But, W.M.; Lo, I.; Shek, C.C.; Tse, W.Y.; Lam, S.T.S. Ambiguous genitalia, impaired steroidogenesis, and Antley-Bixler syndrome in a patient with P450 oxidoreductase deficiency. Hong Kong Med. J. 2010, 16, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Herkert, J.C.; Blaauwwiekel, E.E.; Hoek, A.; Veenstra-Knol, H.E.; Kema, I.P.; Arlt, W.; Kerstens, M.N. A rare cause of congenital adrenal hyperplasia: Antley-Bixler syndrome due to POR deficiency. Neth. J. Med. 2011, 69, 281–283. [Google Scholar]
- Idkowiak, J.; O’Riordan, S.; Reisch, N.; Malunowicz, E.M.; Collins, F.; Kerstens, M.N.; Köhler, B.; Graul-Neumann, L.M.; Szarras-Czapnik, M.; Dattani, M.; et al. Pubertal presentation in seven patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to P450 oxidoreductase deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E453–E462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flück, C.E.; Mallet, D.; Hofer, G.; Samara-Boustani, D.; Leger, J.; Polak, M.; Morel, Y.; Pandey, A.V. Deletion of P399_E401 in NADPH cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase results in partial mixed oxidase deficiency. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puiu, M.; Pienar, C.; Chirita Emandi, A.; Arghirescu, S.; Popa, C.; Micle, I. A case of antley bixler syndrome: Diagnosis and outcome. Acta Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaragna-Filho, G.; Castro, C.C.T.D.S.; De Carvalho, R.R.; Coeli, F.B.; Ferraz, L.F.C.; Petroli, R.J.; de Mello, M.P.; Sewaybricker, L.; Lemos-Marini, S.H.V.; D’Souza-Li, L.F.R.; et al. 46,XX DSD and Antley-Bixler syndrome due to novel mutations in the cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase gene. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2012, 56, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Garvín, D.; Albaladejo, S.; Ezquieta, B.; Corripio, R. Disorder of sex development as a diagnostic clue in the first Spanish known newborn with P450 oxidoreductase deficiency. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2013010251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisch, N.; Idkowiak, J.; Hughes, B.A.; Ivison, H.E.; Abdul-Rahman, O.A.; Hendon, L.G.; Olney, A.H.; Nielsen, S.; Harrison, R.; Blair, E.M.; et al. Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Caused by P450 Oxidoreductase Deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E528–E536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boia, E.; Popoiu, M.; Puiu, M.; Stanciulescu, C.; David, V. Antley-bixler syndrome: Surgical management of ambiguous genitalia—A case report. Med Princ. Pract. 2013, 23, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldani, E.; Garel, C.; Bucourt, M.; Carbillon, L. Prenatal diagnosis of antley-bixler syndrome and POR deficiency. Am. J. Case Rep. 2015, 16, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koika, V.; Armeni, A.; Georgopoulos, N. Delayed diagnosis of disorder of sex development (DSD) due to P450 oxidoreductase (POR) deficiency. Hormones 2016, 15, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parween, S.; Roucher-Boulez, F.; Flück, C.E.; Lienhardt-Roussie, A.; Mallet, D.; Morel, Y.; Pandey, A.V. P450 oxidoreductase deficiency: Loss of activity caused by protein instability from a novel L374H mutation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4789–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonamichi, B.D.S.F.; Santiago, S.L.M.; Bertola, D.; Kim, C.; Alonso, N.; Mendonca, B.; Bachega, T.; Gomes, L. Long-term follow-up of a female with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to P450-oxidoreductase deficiency. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 60, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzetis, M.; Konstantinidou, A.; Sofocleous, C.; Kosma, K.; Mitrakos, A.; Tzannatos, C.; Kitsiou-Tzeli, S. Compound heterozygosity of a paternal submicroscopic deletion and a maternal missense mutation inPORgene: Antley-bixler syndrome phenotype in three sibling fetuses. Birth Defects Res. Part A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2016, 106, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, K.; Yamashita, A.; Miyamoto, T.; Takeguch, R.; Furuya, A.; Matsuo, K.; Tanahashi, Y.; Kawamura, M.; Sengoku, K. P450 oxidoreductase deficiency with maternal virilization during pregnancy. Clin. Exp. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 43, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.M.K.H. Two cases of Antley-Bixler syndrome caused by mutations in different genes, FGFR2 and POR. J. Genet. Med. 2016, 13, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency caused by R457H mutation in POR gene in Chinese: Case report and literature review. J. Ovarian Res. 2017, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadilkar, K.S.; Jagtap, V.; Lila, A.; Bandgar, T.; Shah, N.S. Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency: Novel cause of ambiguity with primary amenorrhea. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 21, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Song, J.-S.; Park, J.E.; Jang, S.Y.; Ki, C.-S.; Kim, D.-K. A Case of Antley-Bixler Syndrome with a Novel Likely Pathogenic Variant (c.529G>C) in the POR Gene. Ann. Lab. Med. 2017, 37, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Wang, B.; Chen, H.; Zhu, J.; Sun, H. In vitro fertilization-frozen embryo transfer in a patient with cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency: A case report. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2017, 34, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Guo, J.; Guo, R.; Qi, Z.; Li, W.; Ni, X. Compound heterozygous variants in POR gene identified by whole-exome sequencing in a Chinese pedigree with cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency. Pediatr. Investig. 2018, 2, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Huang, C.; Tan, H.; Wu, L. A case of Antley-Bixler syndrome caused by novel POR mutations. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 2019, 36, 1025–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Oh, A.; Kim, G.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Moon, J.E.; Ko, C.W.; Cheon, C.-K.; Yoo, H.-W. Clinical, endocrinological, and molecular features of four Korean cases of cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 25, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Ren, X.; Huang, B.; Zhu, G.; Yang, W.; Jin, L. Clinical and genetic analysis of cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase (POR) deficiency in a female and the analysis of a novel POR intron mutation causing alternative mRNA splicing. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2020, 37, 2503–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unal, E.; Demiral, M.; Yıldırım, R.; Taş, F.F.; Ceylaner, S.; Özbek, M.N. Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency caused by a novel mutation in the POR gene in two siblings: Case report and literature review. Hormones 2020, 20, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, A.; Xie, M.; Chen, L.; Wu, H.; Shen, Y.; Wang, H. Antley-Bixler syndrome arising from compound heterozygotes in the P450 oxidoreductase gene: A case report. Transl. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 3309–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuki, T.; Ohtsu, Y.; Hiroshima, S.; Sawano, K.; Nagasaki, K. Two cases of cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency with severe scoliosis and surgery requirement. Congenit. Anom. 2021, 61, 202–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfinsen, C.B. Principles that Govern the Folding of Protein Chains. Science 1973, 181, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, D.M.; Goldstein, R.A. Why are proteins marginally stable? Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2001, 46, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, K.B.; Chen, P.; Shakhnovich, E.I. Protein stability imposes limits on organism complexity and speed of molecular evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16152–16157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.V.; Sproll, P. Pharmacogenomics of human P450 oxidoreductase. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flück, C.E.; Pandey, A.V. Impact on CYP19A1 activity by mutations in NADPH cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 165, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Agrawal, V.; Giacomini, K.M.; Miller, W.L. Genetics of P450 oxidoreductase: Sequence variation in 842 individuals of four ethnicities and activities of 15 missense mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
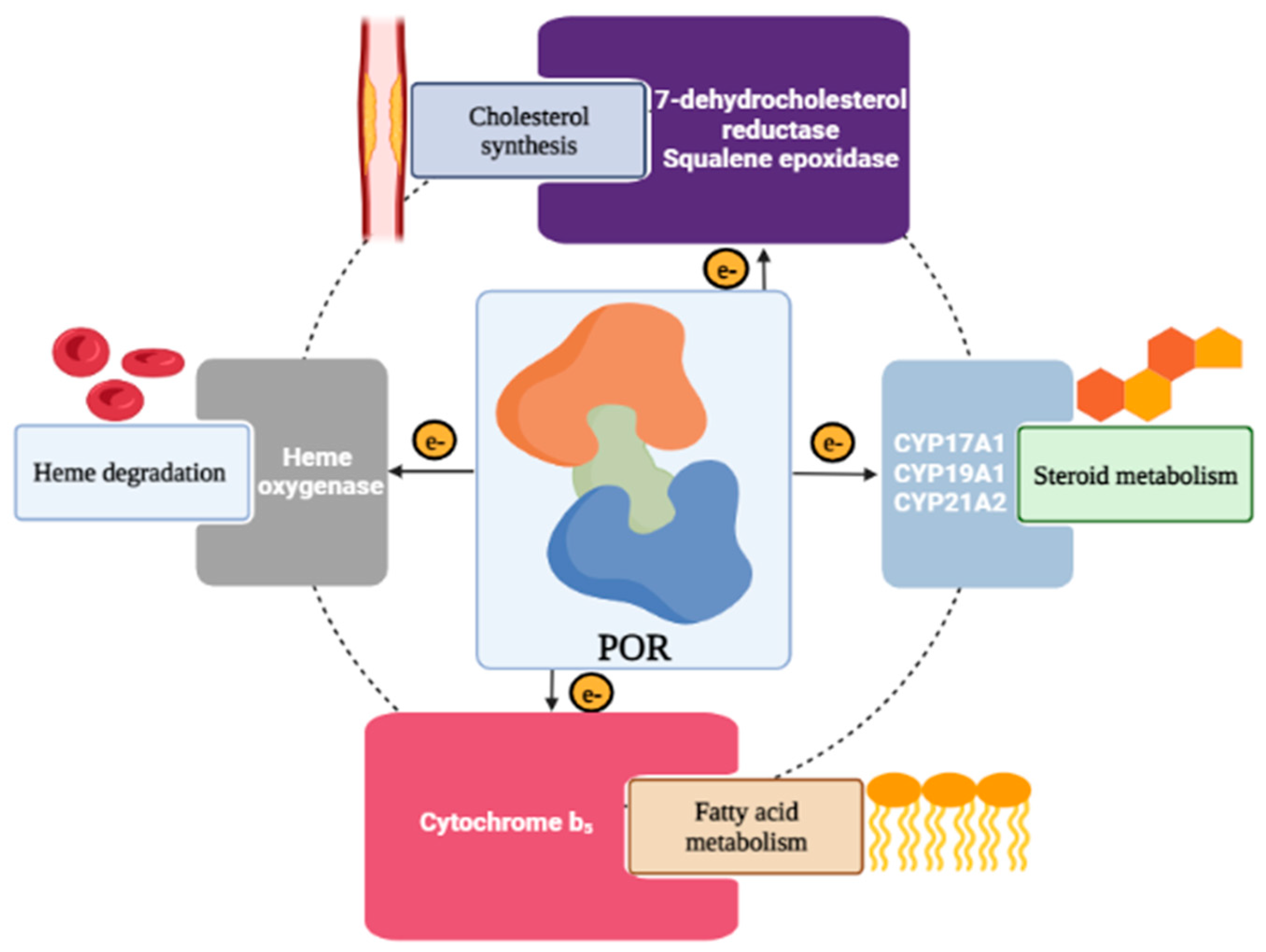
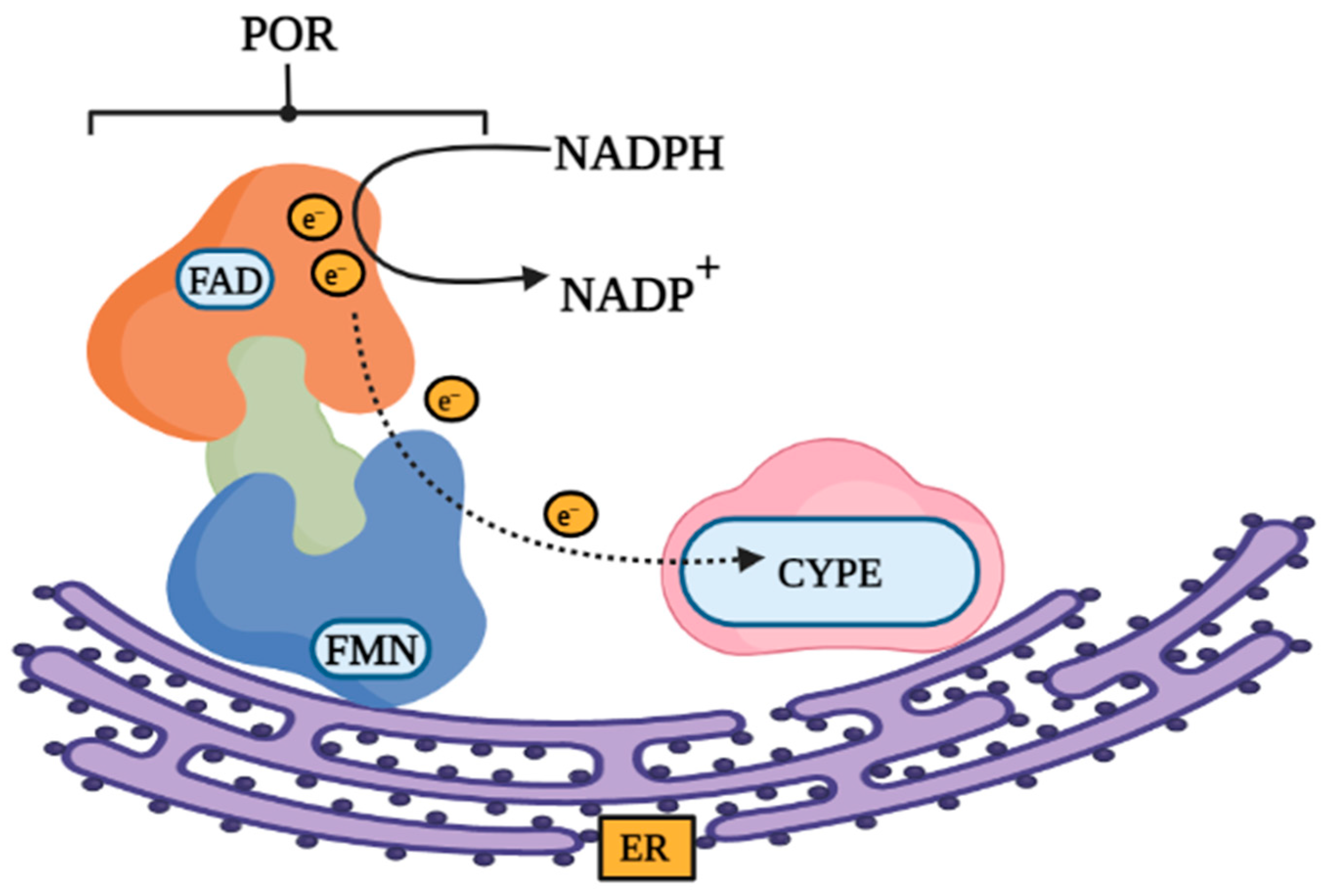






| Patient (n) | Chromosomal Sex 46,XX/46,XY | POR Mutation | Clinical Phenotype | Reported by | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS Features | Abnormal Genitals | Abnormal Steroid Levels | ||||
| 4 | 2/2 | 7/8 a | 2 | 2 | 3 | [3] |
| 3 | 2/1 | 6/6 | 1 | 2 | 3 | [15] |
| 2 | 1/1 | 4/4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | [16] |
| 1 | 0/1 | 2/2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | [17] |
| 19 (32 b) | 6 c/10 c | 34/38 a | 19 (32) | 12 c | 10 c | [18] |
| 10 | 6/4 | 19/20 a | 9 | 9 | 10 | [19] |
| 3 | 2/1 | 6/6 | 0 | 2 | 3 | [20] |
| 7 | 2/5 | 14/14 | 5 | 2 | 7 | [21] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | [22] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 1/2 a,d | 1 | 1 | 1 | [8] |
| 4 | 0/4 | 8/8 | 3 | 3 | 4 | [23] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | [24] |
| 12 (35 e) | 7/5 | 24/24 | 11 | 11 | 12 | [25] |
| 4 | 3/1 | 8/8 | 3 | 3 | 4 | [26] |
| 1 | 0/1 | 2/2 f | 0 | 1 | 1 | [27] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | [28] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | [29] |
| 7 | 5/2 | 14/14 | 7 | 5 | 7 | [30] |
| 2 | 2/0 | 4/4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | [31] |
| 30 | 18/12 | 54/60 a | 27 | 22 | 28 c | [13] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | [32] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | [33] |
| 1 | 0/1 | 2/2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | [34] |
| 20 | 12/8 | 39/40 a | 19 | 12 | N/A | [35] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | [36] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | N/A | [37] |
| 1 | 0/1 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | [38] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | [39] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | [40] |
| 2 | 1 c/0 c | 4/4 | 1 | 1 | N/A | [41] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | [42] |
| 1 | 0/1 | 2/2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | [43] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | [44] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | [45] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | [46] |
| 1 | 0/1 | 2/2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | [47] |
| 1 | 0/1 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | [48] |
| 8 | 3/5 | 16/16 | 7 | 8 | 8 | [14] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | N/A | [49] |
| 4 | 2/2 | 8/8 | 2 | 4 | 2 | [50] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | [51] |
| 2 | 1/1 | 4/4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | [52] |
| 1 | 1/0 | 2/2 | 1 | 1 | N/A | [53] |
| 2 | 1/1 | 4/4 | 2 | 0 | N/A | [54] |
| 170 | 95/71 | 143 (84.1%) | 120 (70.6%) | |||
| No. | Variant | DNA Change | Exon | Domain Affected | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R457H | 1370G > A | 11 | FAD | [3,13,14,15,16,18,19,20,21,24,25,28,30,42,43,44,48,49,50,51,52,53,54] |
| 2 | V492E | 1475T > A | 12 | FAD | [3,18] |
| 3 | A287P | 859G > C | 8 | Below FAD | [3,8,13,15,17,18,22,30,32,35,36,37,40,41] |
| 4 | C569Y | 1706G > A | 13 | NADPH | [3,13,17,18] |
| 5 | V608F | 1822G > T | 14 | NADPH | [3,18] |
| 6 | A115V | 345C > T | 5 | FMN | [18] |
| 7 | T142A | 424A > G | 4 | FMN | [13,18,29,30] |
| 8 | Q153R | 458A > G | 4 | FMN | [18] |
| 9 | Y181D | 541T > G | 5 | FMN | [13,15] |
| 10 | P228L | 683C > T | 6 | FMN | [18] |
| 11 | M263V | 787A > G | 7 | Below FAD | [18] |
| 12 | R316W | 947C > T | 9 | Below FAD | [18] |
| 13 | G413S | 1237G > A | 10 | FAD | [18] |
| 14 | Y459H | 1375T > C | 11 | FAD | [18] |
| 15 | A503V | 1508C > T | 12 | FAD | [18] |
| 16 | G504R | 1510G > A | 12 | FAD | [18] |
| 17 | G539R | 1615G > A | 12 | NADPH | [18,23,34] |
| 18 | L565P | 1694T > C | 12 | NADPH | [18] |
| 19 | Y578C | 1733A > G | 13 | NADPH | [19] |
| 20 | E580Q | 1738G > C | 13 | NADPH | [21] |
| 21 | L577R | 1730T > G | 13 | NADPH | [26] |
| 22 | N185K | 555T > A | 5 | FMN | [26] |
| 23 | Y607C | 1820A > G | 14 | NADPH | [13,27] |
| 24 | R498P | 1493G > C | 12 | FAD | [13,35] |
| 25 | H628P | g.32234A > C | 14 | NADPH | [13,35] |
| 26 | M408L | 1223T > A | 10 | FAD | [33] |
| 27 | A259G | 758G > C | 7 | Below FAD | [38] |
| 28 | L374H | 1121A > G | 10 | FAD | [39] |
| 29 | G144S | 430G > A | 4 | FMN | [45] |
| 30 | G177R | 529G > C | 5 | FMN | [46] |
| 31 | D210G | 629A > G | 5 | FMN | [14] |
| 32 | Y326D | 976C > T | 10 | FAD | [47] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nurhafizuddin, M.; Azizi, A.; Ming, L.C.; Shafqat, N. In Silico Analysis of PORD Mutations on the 3D Structure of P450 Oxidoreductase. Molecules 2022, 27, 4646. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144646
Nurhafizuddin M, Azizi A, Ming LC, Shafqat N. In Silico Analysis of PORD Mutations on the 3D Structure of P450 Oxidoreductase. Molecules. 2022; 27(14):4646. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144646
Chicago/Turabian StyleNurhafizuddin, Muhammad, Aziemah Azizi, Long Chiau Ming, and Naeem Shafqat. 2022. "In Silico Analysis of PORD Mutations on the 3D Structure of P450 Oxidoreductase" Molecules 27, no. 14: 4646. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144646
APA StyleNurhafizuddin, M., Azizi, A., Ming, L. C., & Shafqat, N. (2022). In Silico Analysis of PORD Mutations on the 3D Structure of P450 Oxidoreductase. Molecules, 27(14), 4646. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144646







