Small Nucleolar RNAs and Their Comprehensive Biological Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biogenesis and Structure of SnoRNAs
3. Biological Functions of SnoRNAs
4. SnoRNA Expression Profiling in HCC and Associated Diseases
5. Clinical Significance of Altered SnoRNAs in HCC
6. SnoRNAs and Liver Carcinogenesis
6.1. From Ribosome Biogenesis to Carcinogenesis
6.2. Noncanonical Functions of SnoRNAs in HCC
6.3. Other SnoRNAs
7. Hepatitis Virus-related Hepatocarcinogenesis
8. Deregulation of SnoRNAs in NAFLD and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: Glo-bocan Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 71, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atiq, O.; Tiro, J.; Yopp, A.C.; Muffler, A.; Marrero, J.A.; Parikh, N.D.; Murphy, C.; McCallister, K.; Singal, A.G. An As-sessment of Benefits and Harms of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance in Patients with Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchard-Bourelle, P.; Desjardins-Henri, C.; Mathurin-St-Pierre, D.; Deschamps-Francoeur, G.; Fafard-Couture, É.; Garant, J.M.; Elela, S.A.; Scott, M.S. Snodb: An Interactive Database of Human Snorna Sequences, Abundance and Interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D220–D225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T. Small Nucleolar RNAs: An Abundant Group of Noncoding RNAs with Diverse Cellular Functions. Cell 2002, 109, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, P.; Kiss, T. Cooperative 2’-O-Methylation of the Wobble Cytidine of Human Elongator Trna(Met)(Cat) by a Nu-cleolar and a Cajal Body-Specific Box C/D Rnp. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.S.; Langouët, M.; Chamberlain, S.J.; Carmichael, G.G. Prader-Willi syndrome: Reflections on seminal studies and future therapies. Open Biol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peffers, M.J.; Chabronova, A.; Balaskas, P.; Fang, Y.; Dyer, P.; Cremers, A.; Emans, P.J.; Feczko, P.Z.; Caron, M.M.; Welting, T.J.M. SnoRNA signatures in cartilage ageing and osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wen, J.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X.-P.; Zhang, B.-X.; Chu, L. Small Nucleolar RNAs: Insight Into Their Function in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falaleeva, M.; Surface, J.; Shen, M.; de la Grange, P.; Stamm, S. Snord116 and Snord115 Change Expression of Multiple Genes and Modify Each Other’s Activity. Gene 2015, 572, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deschamps-Francoeur, G.; Garneau, D.; Dupuis-Sandoval, F.; Roy, A.; Frappier, M.; Catala, M.; Couture, S.; Barbe-Marcoux, M.; Abou-Elela, S.; Scott, M.S. Identification of discrete classes of small nucleolar RNA featuring different ends and RNA binding protein dependency. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 10073–10085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, E.S.; Fournier, M.J. The Small Nucleolar Rnas. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 897–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tollervey, D.; Kiss, T. Function and synthesis of small nucleolar RNAs. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorjani, H.; Kehr, S.; Jedlinski, D.J.; Gumienny, R.; Hertel, J.; Stadler, P.F.; Zavolan, M.; Gruber, A.R. An updated human snoRNAome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 5068–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, T.; Hua, X.; Tang, L.; Wu, W. Sno/scaRNAbase: A curated database for small nucleolar RNAs and cajal body-specific RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 35, D183–D187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-H.; Zhang, X.-C.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Huang, M.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Qu, L.-H. snoSeeker: An advanced computational package for screening of guide and orphan snoRNA genes in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5112–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, T.; Längst, G. Changes in higher order structures of chromatin by RNP complexes. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, S.; Stamm, S. The snoRNA HBII-52 Regulates Alternative Splicing of the Serotonin Receptor 2C. Science 2006, 311, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayet-Lebaron, E.; Atzorn, V.; Henry, Y.; Kiss, T. 18S rRNA processing requires base pairings of snR30 H/ACA snoRNA to eukaryote-specific 18S sequences. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terns, M.; Terns, R. Noncoding Rnas of the H/Aca Family. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006, 71, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ender, C.; Krek, A.; Friedländer, M.R.; Beitzinger, M.; Weinmann, L.; Chen, W.; Pfeffer, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Meister, G. A Human Snorna with Microrna-Like Functions. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalaj, M.; Park, C.Y. snoRNAs contribute to myeloid leukaemogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-S.; Camacho, C.V.; Nagari, A.; Malladi, V.S.; Challa, S.; Kraus, W.L. Activation of PARP-1 by snoRNAs Controls Ribosome Biogenesis and Cell Growth via the RNA Helicase DDX21. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 1270–1285.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Xu, T.; Ganapathy, S.; Shadfan, M.; Long, M.; Huang, T.H.-M.; Thompson, I.; Yuan, Z.-M. Elevated snoRNA biogenesis is essential in breast cancer. Oncogene 2013, 33, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, S.; Shi, L.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Lan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Qiang, W.; Ji, M.; et al. The noncoding RNAs SNORD50A and SNORD50B-mediated TRIM21-GMPS interaction promotes the growth of p53 wild-type breast cancers by degrading p53. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2450–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, W.; Li, S.; You, C.; Tang, F.; Peng, S.; Ma, S.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; et al. Small Nucleolar Rna 71a Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion Via Mapk/Erk Pathway. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2261–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, R.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, X.; Zhu, W.; Han, L.; Su, P.; Fan, Y.; Yan, Y.; et al. Snora72 Activates the Notch1/C-Myc Pathway to Promote Stemness Transformation of Ovarian Cancer Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 583087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, G.; Liao, J.; Huang, Z.; Wen, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Cai, G.; Xu, W.; Ding, Z.; et al. Non-coding small nucleolar RNA SNORD17 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through a positive feedback loop upon p53 inactivation. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 988–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herter, E.K.; Stauch, M.; Gallant, M.; Wolf, E.; Raabe, T.; Gallant, P. snoRNAs are a novel class of biologically relevant Myc targets. BMC Biol. 2015, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, R.D.; Chen, S. Sno-derived RNAs are prevalent molecular markers of cancer immunity. Oncogene 2018, 37, 6442–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, A.B.; Stahly, A.N.; Kasukurthi, M.V.; Barchie, A.A.; Hutcheson, S.B.; Houserova, D.; Huang, Y.; Watters, B.C.; King, V.M.; Dean, M.A. Microrna-Like Snorna-Derived Rnas (Sdrnas) Promote Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Lin, P.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; He, Y.; Dang, Y.; Chen, G. Genomic analysis of small nucleolar RNAs identifies distinct molecular and prognostic signature in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3346–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ma, P.; Liu, P.; Chen, B.; Liu, Z. Small nucleolar RNA U2_19 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zaidi, S.; Rao, S.; Chen, J.-S.; Phan, L.; Farci, P.; Su, X.; Shetty, K.; White, J.; Zamboni, F.; et al. Analysis of Genomes and Transcriptomes of Hepatocellular Carcinomas Identifies Mutations and Gene Expression Changes in the Transforming Growth Factor-β Pathway. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.; Yang, A.; Wang, R.; Xia, X.; Zhai, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Cui, Y.; Xie, W.; Liu, Y.; et al. Germline Duplication of SNORA18L5 Increases Risk for HBV-related Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Altering Localization of Ribosomal Proteins and Decreasing Levels of p53. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Xu, C.; Wu, B.; Tang, H.; Zhao, P.; Qi, Z. SNORD126 Promotes Hepatitis C Virus Infection by Upregulating Claudin-1 via Activation of PI3K-AKT Signaling Pathway. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.I.; Holley, C.L.; Scruggs, B.S.; Sidhu, R.; Brookheart, R.T.; Listenberger, L.L.; Behlke, M.A.; Ory, D.S.; Schaffer, J.E. Small Nucleolar RNAs U32a, U33, and U35a Are Critical Mediators of Metabolic Stress. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Evason, K.J.; Asahina, K.; Stainier, D.Y. Hepatic Stellate Cells in Liver Development, Regeneration, and Can-cer. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koduru, S.V.; Leberfinger, A.N.; Kawasawa, Y.I.; Mahajan, M.; Gusani, N.J.; Sanyal, A.J.; Ravnic, D.J. Non-Coding Rnas in Various Stages of Liver Disease Leading to Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Differential Expression of Mirnas, Pirnas, Lncrnas, Circrnas, and Sno/Mt-Rnas. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitz, N.F.; Wang, J.; Kamboh, M.I.; Koldamova, R.; Lefterov, I. Small nucleolar RNAs in plasma extracellular vesicles and their discriminatory power as diagnostic biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 159, 105481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Yu, L.; Mei, Y.; Guarnera, M.; Shen, J.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, F. Small nucleolar RNA signatures as biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, S.; Yang, J.; Yang, X. New Marker Useful for Predicting Risk of Recurrence of Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patient after Resection, Comprises Nucleic Acid Molecules Encoding Small Nucleolar Rnas Chosen from U15a, U19, Aca21, Aca31, U42b, U52 and Aca61. China Patent CN106282321A, 26 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Xu, H.; Bai, Y.; Xu, C.; et al. Downregulation of snoRNA SNORA52 and Its Clinical Significance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BioMed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 7020637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, H.; Bai, Y.; et al. Re-vealing the Clinical Significance and Prognostic Value of Small Nucleolar Rna Snord31 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20201479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, H.; Bai, Y.; et al. Identification of snoRNA SNORA71A as a Novel Biomarker in Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 8879944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zheng, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, Y. Small nucleolar RNA ACA11 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Chang, L.; Wang, H.; Ma, W.; Peng, Q.; Yuan, Y. Clinical significance of C/D box small nucleolar RNA U76 as an oncogene and a prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2018, 42, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Guarnera, M.A.; Fang, H.; Jiang, F. Small non-coding RNA biomarkers in sputum for lung cancer diagnosis. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Song, X.; Wang, K.; Yu, M.; Ding, S.; Dong, X.; Xie, L.; Song, X. Snord63 and Snord96a as the Non-Invasive Di-agnostic Biomarkers for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yao, D.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Fu, C.; et al. A plasma SNORD33 signature predicts platinum benefit in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer patients. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardocco, M.; Radeghieri, A.; Busatto, S.; Gallorini, M.; Raggi, C.; Gissi, C.; D’Agnano, I.; Bergese, P.; Felsani, A.; Berardi, A.C. RNA-seq reveals distinctive RNA profiles of small extracellular vesicles from different human liver cancer cell lines. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82920–82939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, C.; Cao, J.; Chen, L.; Xi, X.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L.; Ma, L.; Wang, D.; Yin, J.; et al. Noncoding RNAs Serve as Diagnosis and Prognosis Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, R.S.; Mercuri, E.; Darras, B.T.; Connolly, A.M.; Kuntz, N.L.; Kirschner, J.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Saito, K.; Servais, L.; Tizzano, E.; et al. Nusinersen versus Sham Control in Infantile-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, M.; Contreras, A.; Holm, M.; Uechi, T.; Forester, C.M.; Pang, X.; Jackson, C.; Calvert, M.E.; Chen, B.; Quigley, D.A.; et al. A single H/ACA small nucleolar RNA mediates tumor suppression downstream of oncogenic RAS. eLife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Wu, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, N.; Wen, J.; Liao, J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Chu, L. SnoRD126 promotes the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through transcriptional regulation of FGFR2 activation in combination with hnRNPK. Aging 2021, 13, 13300–13317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, P.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, P.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; et al. The C/D box small nucleolar RNA SNORD52 regulated by Upf1 facilitates Hepatocarcinogenesis by stabilizing CDK1. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9348–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Yang, D.; Luo, H.; Wu, S.; Dong, W.; Xiao, J.; Yuan, S.; Ni, A.; Zhang, K.-J.; Liu, X.-Y.; et al. SNORD126 promotes HCC and CRC cell growth by activating the PI3K–AKT pathway through FGFR2. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 9, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, P.; Zhang, H.; Yin, M.; Qin, Z.; Ma, W.; Yuan, Y. Small nucleolar RNA 42 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma through the p53 signaling pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yu, H.; Qu, Y.; Tan, R.; Gao, Y.; He, Y.; Li, L. An SNP reducing SNORD105 and PPAN expression decreases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese population. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e24095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Xu, F.; Lei, J.; Wang, Q.L.; Luo, L.Y.; Cao, H.Y.; Ge, X.; Ran, T.; et al. Lncrna-Lalr1 Upregulates Small Nucleolar Rna Snord72 to Promote Growth and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Aging 2020, 12, 4527–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Qin, F.; Lan, X. Small nucleolar RNA 47 promotes tumorigenesis by regulating EMT markers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Minerva Med. 2017, 108, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siprashvili, Z.; Webster, D.E.; Johnston, D.; Shenoy, R.M.; Ungewickell, A.J.; Bhaduri, A.; Flockhart, R.; Zarnegar, B.J.; Che, Y.; Meschi, F.; et al. The Noncoding Rnas Snord50a and Snord50b Bind K-Ras and Are Recurrently De-leted in Human Cancer. Nat. Genet 2016, 48, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Yang, F.; Ding, C.L.; Zhao, L.J.; Ren, H.; Zhao, P.; Wang, W.; Qi, Z.T. Small Nucleolar Rna 113-1 Suppresses Tu-morigenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.A.Z.; Pang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Qin, Q.; Wang, R.; Li, W.; Jing, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, S. SNORA23 inhibits HCC tumorigenesis by impairing the 2′-O-ribose methylation level of 28S rRNA. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcel, V.; Ghayad, S.E.; Belin, S.; Therizols, G.; Morel, A.-P.; Solano-Gonzàlez, E.; Vendrell, J.A.; Hacot, S.; Mertani, H.C.; Albaret, M.A.; et al. p53 Acts as a Safeguard of Translational Control by Regulating Fibrillarin and rRNA Methylation in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braig, M.; Lee, S.; Loddenkemper, C.; Rudolph, C.; Peters, A.H.; Schlegelberger, B.; Stein, H.; Dörken, B.; Jenuwein, T.; Schmitt, C.A. Oncogene-induced senescence as an initial barrier in lymphoma development. Nature 2005, 436, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccaletto, P.; Machnicka, M.A.; Purta, E.; Piatkowski, P.; Baginski, B.; Wirecki, T.K.; de Crécy-Lagard, V.; Ross, R.; Limbach, P.A.; Kotter, A.; et al. Modomics: A Database of Rna Modification Pathways. 2017 Update. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, D303–D307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryusheva, S.; Talross, G.J.; Gall, J.G. SnoRNA guide activities: Real and ambiguous. RNA 2021, 27, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeing, T.M.; Ramakrishnan, V. What Recent Ribosome Structures Have Revealed About the Mechanism of Translation. Nature 2009, 7268, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeshkina, N.; Jenner, L.; Westhof, E.; Yusupov, M.; Yusupova, G. A new understanding of the decoding principle on the ribosome. Nature 2012, 484, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liang, X.-Z.; Deng, Y.; Liang, Y.-B.; Zhu, X.; Liang, X.-Y.; Luo, D.-Z.; Chen, G.; Fang, Y.-Y.; Lan, H.-H.; et al. Prognostic value of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) for colon adenocarcinoma based on RNA sequencing data. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, O.; Kim, D.-W.; Cheong, J.-Y. Screening Plasma Exosomal RNAs as Diagnostic Markers for Cervical Cancer: An Analysis of Patients Who Underwent Primary Chemoradiotherapy. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurki, S.; Peltonen, K.; Latonen, L.; Kiviharju, T.M.; Ojala, P.M.; Meek, D.; Laiho, M. Nucleolar protein NPM interacts with HDM2 and protects tumor suppressor protein p53 from HDM2-mediated degradation. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, W.; Hayashi, Y.; Yokoyama, W.; Kuroda, T.; Kishimoto, H.; Ito, I.; Kimura, K.; Akaogi, K.; Waku, T.; Yanagisawa, J. The Nucleolar Protein Myb-binding Protein 1A (MYBBP1A) Enhances p53 Tetramerization and Acetylation in Response to Nucleolar Disruption. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 4928–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Li, C.; Guo, T.; Wang, H.; Ma, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ye, Q.; Liu, Z. The human RNA surveillance factor UPF1 regulates tumorigenesis by targeting Smad7 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaki, T.; Shiratori, Y.; Rengifo, W.; Igarashi, K.; Yamagata, M.; Kurokohchi, K.; Uchida, N.; Miyauchi, Y.; Yoshiji, H.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases: Comparative Study of Hepatocellular Car-cinoma Versus Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2003, 37, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmick, M.; Vartak, N.; Papke, B.; Kovacevic, M.; Truxius, D.C.; Rossmannek, L.; Bastiaens, P.I.H. Kras Localizes to the Plasma Membrane by Spatial Cycles of Solubilization, Trapping and Vesicular Transport. Cell 2014, 157, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, Y.; Siprashvili, Z.; Kovalski, J.R.; Jiang, T.; Wozniak, G.; Elcavage, L.; Khavari, P.A. KRAS regulation by small non-coding RNAs and SNARE proteins. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemiju, T.; Abera, S.; Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Alemayohu, M.A.; Allen, C.; Al-Raddadi, R.; Alvis-Guzman, N.; Amoako, Y.; Artaman, A.; et al. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies from 1 990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, Y.; Saigo, K.; Takashima, H.; Minami, M.; Okanoue, T.; Bréchot, C.; Brechot, P.P. Large scaled analysis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA integration in HBV related hepatocellular carcinomas. Gut 2005, 54, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, W.; Yan, H.X.; Luo, T.; Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Wu, F.Q.; Zhang, H.L.; Yu, L.X.; Zheng, L.Y.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus X (Hbx) Induces Tumorigenicity of Hepatic Progenitor Cells in 3,5-Diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-Dihydrocollidine-Treated Hbx Transgenic Mice. Hepatology 2012, 55, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshida, Y.; Fuchs, B.C.; Bardeesy, N.; Baumert, T.F.; Chung, R.T. Pathogenesis and Prevention of Hepatitis C Vi-rus-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, S79–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, P.; Wang, H.; Han, L.; Jing, W.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Up-regulation of small nucleolar RNA 78 is correlated with aggressive phenotype and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 15753–15761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, G.N. Epidemiology and risk-stratification of NAFLD-associated HCC. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Meta-Analytic Assessment of Prevalence, Incidence, and Outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelotti, G.A.; Machado, M.V.; Diehl, A.M. Nafld, Nash and Liver Cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.J.H.; Ng, C.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Pan, X.H.; Tay, P.; Lim, W.H.; Teng, M.; Syn, N.; Lim, G.; Yong, J.N.; et al. Clinical characteristics, surveillance, treatment allocation, and outcomes of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.F.; Wang, F.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, D.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Ke, A.W. Lncrna Snhg3 Induces Emt and Sorafenib Resistance by Modulating the Mir-128/Cd151 Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 2788–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinn, S.; Brandis, K.A.; Ren, A.; Chacko, A.; Dudley-Rucker, N.; Gale, S.E.; Sidhu, R.; Fujiwara, H.; Jiang, H.; Olsen, B.N.; et al. snoRNA U17 Regulates Cellular Cholesterol Trafficking. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sletten, A.C.; Davidson, J.W.; Yagabasan, B.; Moores, S.; Schwaiger-Haber, M.; Fujiwara, H.; Gale, S.; Jiang, X.; Sidhu, R.; Gelman, S.J.; et al. Loss of SNORA73 reprograms cellular metabolism and protects against steatohepatitis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, C.A.; Maxwell, E.S.; Eliceiri, G.L.; Sollner-Webb, B. 5’ets Rrna Processing Facilitated by Four Small Rnas: U14, E3, U17, and U3. RNA 1996, 2, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. Mtor Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 169, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Iadevaia, V.; Averous, J.; Taylor, P.M.; Zhang, Z.; Proud, C.G. Impairing the production of ribosomal RNA activates mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signalling and downstream translation factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 5083–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

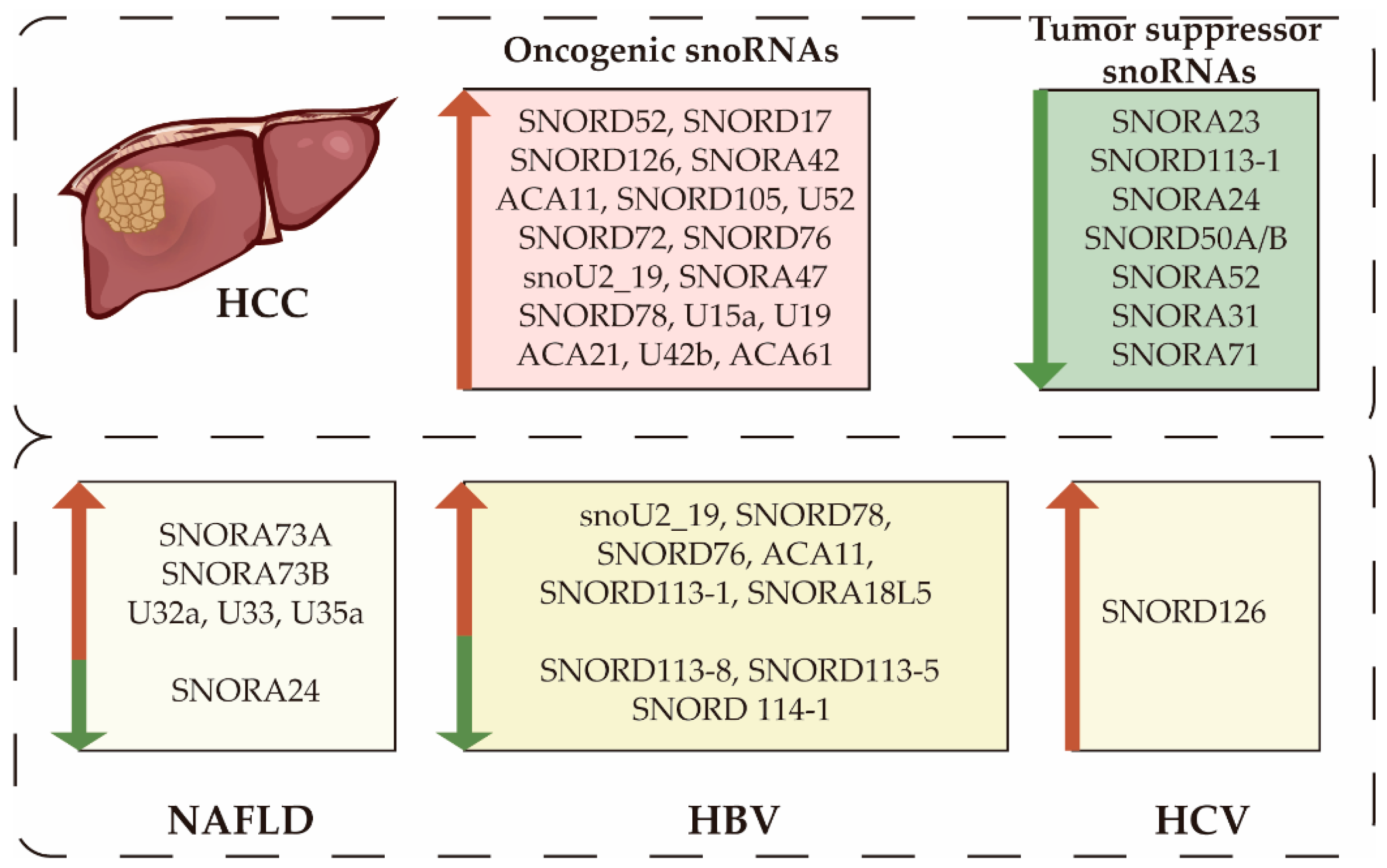
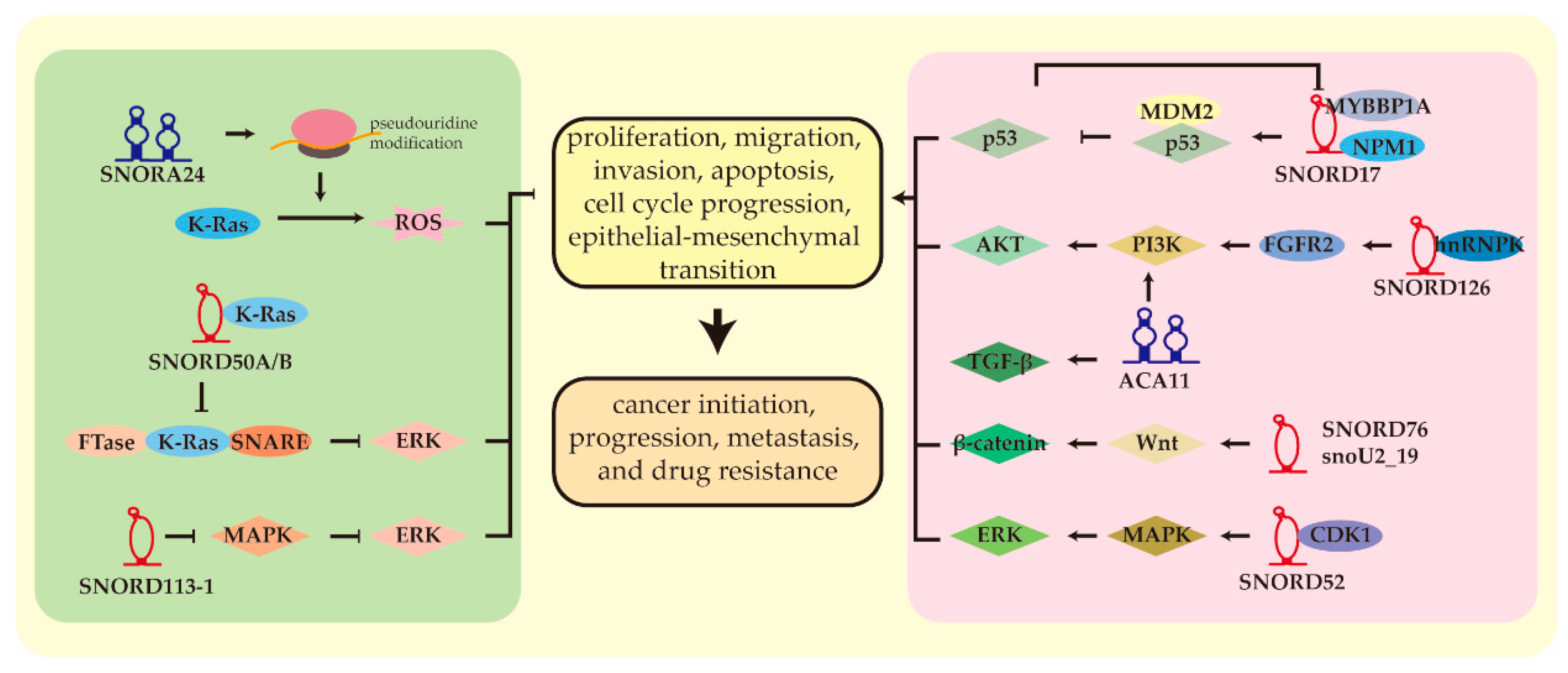
| snoRNA | Chromosomal Location | Host Gene | Role in HCC | Expression | Sample Size, HCC/Control | Targets | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNORD52 | 6p21.33 | SNHG32 | Oncogene | Up | 80/80 | CDK1 | [56] |
| SNORD17 | 20p11.23 | SNX5 | Oncogene | Up | 175/175 | NPM1, MYBBP1A | [28] |
| SNORD126 | 14q11.2 | CCNB1IP-1 | Oncogene | Up | 30/30 | hnRNPK | [55,57] |
| SNORA42 | 1q22 | KHDC4 | Oncogene | Up | 60/60 | P53, p21 | [58] |
| ACA11 | 4p16.3 | NSD2 | Oncogene | Up | 92/92 | - | [46] |
| SNORD105 | 19p13.2 | PPAN-P2Rγ11 | Oncogene | Up | 712/801 | PPAN | [59] |
| SNORD72 | 5p13.1 | - | Oncogene | Up | 46/46 | ID2 | [60] |
| SNORD76 | 1q25.1 | GAS5 | Oncogene | Up | 66/66 | Fibronectin, vimentin | [47] |
| snoU2_19 | 4, 7 | - | Oncogene | Up | 80/80 | β-catenin | [33] |
| SNORA47 | 5q13.3 | ZBED3 | Oncogene | Up | 60/60 | - | [61] |
| SNORA24 | 4q26 | SNHG8 | Tumor suppressor | Down | 91/91 | 18S rRNA | [54] |
| SNORD50A SNORD50B | 6q14.3 | SNHG5 | Tumor suppressor | Down | - | K-Ras | [62] |
| SNORD113-1 | 14q32.31 | MEG8 | Tumor suppressor | Down | 112/112 | ERK1/2, SMAD2/3 | [63] |
| SNORA23 | 11p15.4 | IP07 | Tumor suppressor | Down | - | 28S rRNA | [64] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Xie, W.; Meng, S.; Kang, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, C. Small Nucleolar RNAs and Their Comprehensive Biological Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2022, 11, 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11172654
Liu X, Xie W, Meng S, Kang X, Liu Y, Guo L, Wang C. Small Nucleolar RNAs and Their Comprehensive Biological Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells. 2022; 11(17):2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11172654
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoyu, Wan Xie, Silu Meng, Xiaoyan Kang, Yuhuan Liu, Lili Guo, and Changyu Wang. 2022. "Small Nucleolar RNAs and Their Comprehensive Biological Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cells 11, no. 17: 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11172654
APA StyleLiu, X., Xie, W., Meng, S., Kang, X., Liu, Y., Guo, L., & Wang, C. (2022). Small Nucleolar RNAs and Their Comprehensive Biological Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells, 11(17), 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11172654





