sPAP/PAAT Ratio as a New Index of Pulmonary Vascular Load: A Study in Normal Subjects and Ssc Patients with and without PH
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Right Heart Catheterization
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethics Statement
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PH | pulmonary hypertension |
| BMI | body mass index, defined as weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| CI | confidence interval |
| DPG | diastolic pulmonary gradient |
| LV | left ventricle |
| PAAT | acceleration time of pulmonary outflow |
| mPAP | mean pulmonary artery pressure |
| PCWP | pulmonary capillary wedge pressure |
| PVR | pulmonary vascular resistance |
| RA | right atrium |
| RV | right ventricle |
| RV FAC | right ventricular fractional area change |
| sPAP | systolic pulmonary artery pressure |
| sPAP/PAAT ratio | systolic pulmonary artery pressure/acceleration time of pulmonary outflow ratio |
| Ssc | systemic sclerosis |
| TAPSE | tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion |
| TPG | transpulmonary gradient |
| TR | tricuspid regurgitation |
| RHC | right heart catheterization |
| WD | Walk distance |
| WU | Wood unit |
References
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawut, S.M.; Taichman, D.B.; Archer-Chicko, C.L.; Palevsky, H.I.; Kimmel, S.E. Hemodynamics and survival in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension related to systemic sclerosis. Chest 2003, 123, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathai, S.C.; Sibley, C.T.; Forfia, P.R.; Mudd, J.O.; Fisher, M.R.; Lechtzin, N.; Boyce, D.; Hummers, L.K.; Housten, T.; Zaiman, A.L.; et al. Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion is a robust outcome measure in scleroderma Associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, A.; Mathai, S.C.; Le Pavec, J.; Zaiman, A.L.; Hummers, L.K.; Boyce, D.; Housten, T.; Champion, H.C.; Lechtzin, N.; Wigley, F.M.; et al. Hemodynamic predictors of survival in scleroderma-related pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedford, R.J.; Mudd, J.O.; Girgis, R.E.; Mathai, S.C.; Zaiman, A.L.; Housten-Harris, T.; Boyce, D.; Kelemen, B.W.; Bacher, A.C.; Shah, A.A.; et al. Right ventricular dysfunction in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badesch, D.B.; Champion, H.C.; Sanchez, M.A.; Hoeper, M.M.; Loyd, J.E.; Manes, A.; McGoon, M.; Naeije, R.; Olschewski, H.; Oudiz, R.J.; et al. Diagnosis and assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol 2009, 54, S55–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, V.V.; Archer, S.L.; Badesch, D.B.; Barst, R.J.; Farber, H.W.; Lindner, J.R.; Mathier, M.A.; McGoon, M.D.; Park, M.H.; Rosenson, R.S.; et al. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: A report of the American College of Cardiology foundation task force on expert consensus documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1573–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Mukerjee, D.; St George, D.; Coleiro, B.; Knight, C.; Denton, C.P.; Davar, J.; Black, C.M.; Coghlan, J.G. Prevalence and outcome in systemic sclerosis associated pulmonary arterial hypertension: Application of a registry approach. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachulla, E.; Gressin, V.; Guillevin, L.; Carpentier, P.; Diot, E.; Sibilia, J.; Kahan, A.; Cabane, J.; Francès, C.; Launay, D.; et al. Early detection of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: A French nationwide pulmonary prospective multicenter study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3792–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.D.; Medsger, T.A. Changes in causes of death in systemic sclerosis, 1972–2002. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franey, L.; Abbas, A.; Marwick, T.; Vlahos, A.; Serra, W.; Al Azizi, K.; Schiller, N.; Lester, S. Assessment of markedly pulmonary vascular resistance by echocardiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, E1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.E.; Franey, L.M.; Marwick, T.; Maeder, M.T.; Kaye, D.M.; Vlahos, A.P.; Serra, W.; Al-Azizi, K.; Schiller, N.B.; Lester, S.J. Noninvasive assessment of pulmonary vascular resistance by Doppler echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2013, 26, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, W.; Chetta, A.; Santilli, D.; Mozzani, F.; Dall’Aglio, P.P.; Olivieri, D.; Cattabiani, M.A.; Ardissino, D.; Gherli, T. Echocardiography may help detect pulmonary vasculopathy in the early stages of pulmonary artery hypertension associated with systemic sclerosis. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2010, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, P.T.; Patel, M.D.; Groh, G.; Choudhry, S.; Murphy, J.; Holland, M.R.; Hamvas, A.; Grady, M.R.; Singh, G.K. Pulmonary artery acceleration time provides a reliable estimate of invasive pulmonary hemodynamics in children. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2016, 29, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Huang, C.H.; Tu, Y.K. Pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary artery acceleration time: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2018, 31, 201–210.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koestenberger, M.; Grangl, G.; Avian, A.; Gamillscheg, A.; Grillitsch, M.; Cvirn, G.; Burmas, A.; Hansmann, G. Normal reference values and Z scores of the pulmonary artery acceleration time in children and its importance for the assessment of pulmonary hypertension. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, e005336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013, 72, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancellotti, P.; Tribouilloy, C.; Hagendorff, A.; Popescu, B.A.; Edvardsen, T.; Pierard, L.A.; Badano, L.; Zamorano, J.L. Scientific Document Committee of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Recommendations for the echocardiographic assessment of native valvular regurgitation: An executive summary from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 14, 611–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guazzi, M.; Bandera, F.; Pelissero, G.; Castelvecchio, S.; Menicanti, L.; Ghio, S.; Temporelli, P.L.; Arena, R. Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion and pulmonary arterial systolic pressure relationship in heart failure: An index of right ventricular contractile function and prognosis. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 305, H1373–H1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, S.; Amsallem, M.; Ouazani, N.; Li, S.; Kudelko, K.; Zamanian, R.T.; Haddad, F.; Chung, L. Non-invasive right ventricular load adaptability indices inpatients with scleroderma-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2018, 8, 2045894018788268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonk-Noordegraaf, A.; Westerhof, B.E.; Westerhof, N. The relationship between the right ventricle and its load in pulmonary hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milnor, W.R. Arterial impedance as ventricular afterload. Circ. Res. 1975, 36, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargani, L.; Voilliot, D.; D’Alto, M.; Agoston, G.; Moreo, A.; Serra, W.; Pieri, F.; Mori, F.; Wierzbowska-Drabik, K.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; et al. Pulmonary Circulation on the Crossroads Between the Left and Right Heart in Systemic Sclerosis: A Clinical Challenge for Cardiologists and Rheumatologists. Heart Fail. Clin. 2018, 14, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, C.; Marra, A.M.; Benjamin, N.; Blank, N.; Cittadini, A.; Coghlan, G.; Distler, O.; Denton, C.P.; Egenlauf, B.; Fiehn, C.; et al. Reduced Right Ventricular Output Reserve in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis and Mildly Elevated Pulmonary Artery Pressure. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
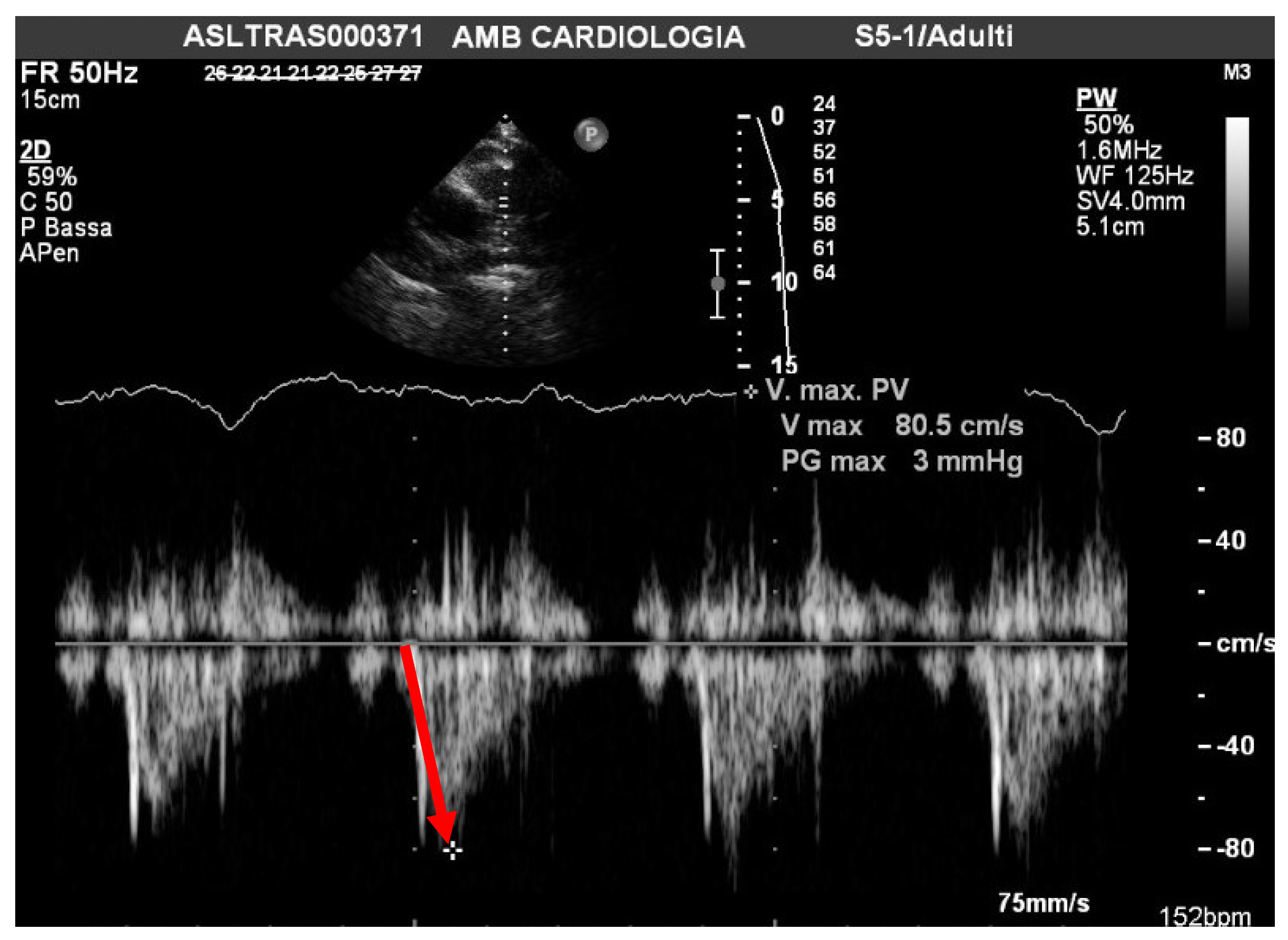
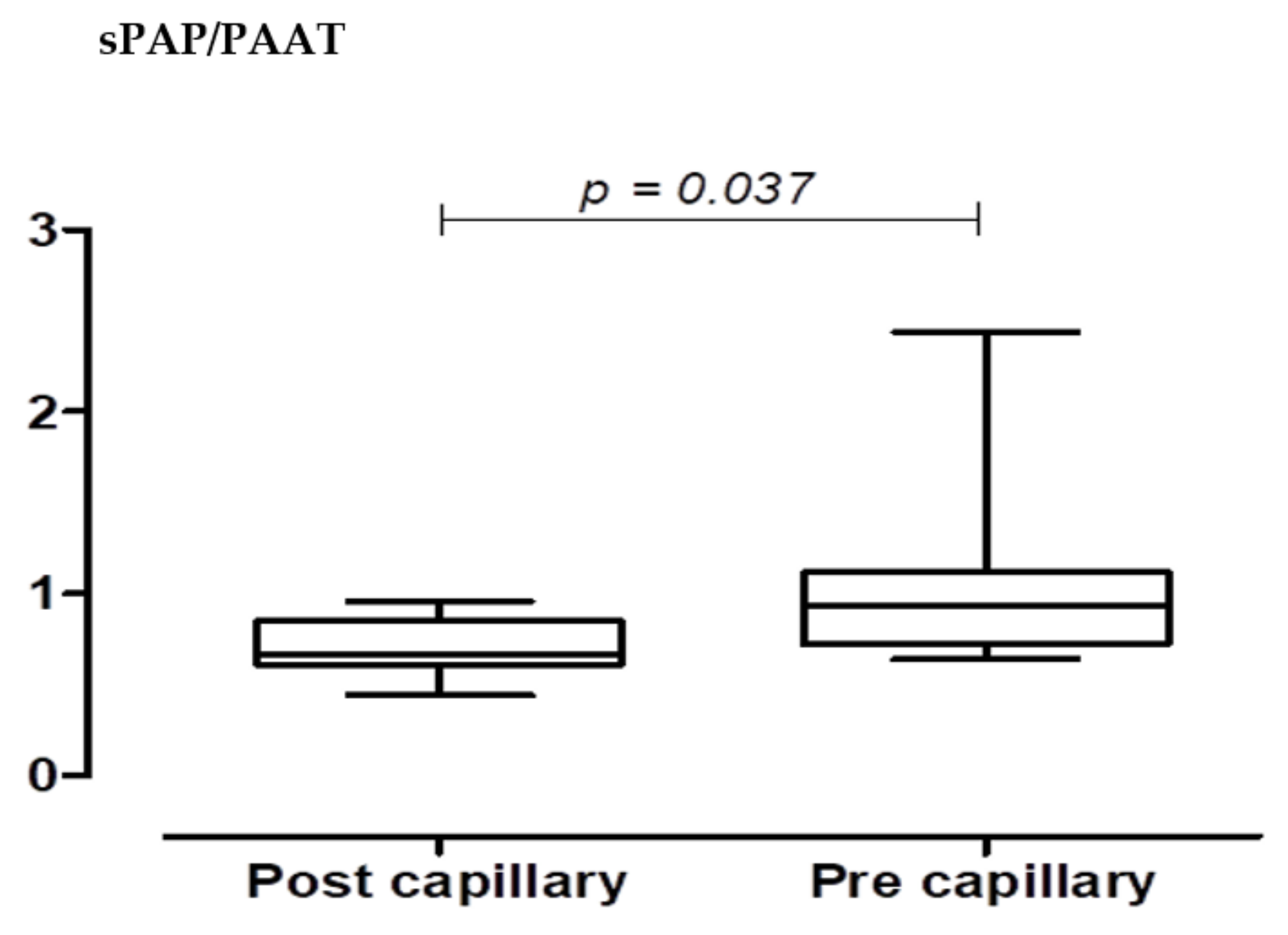
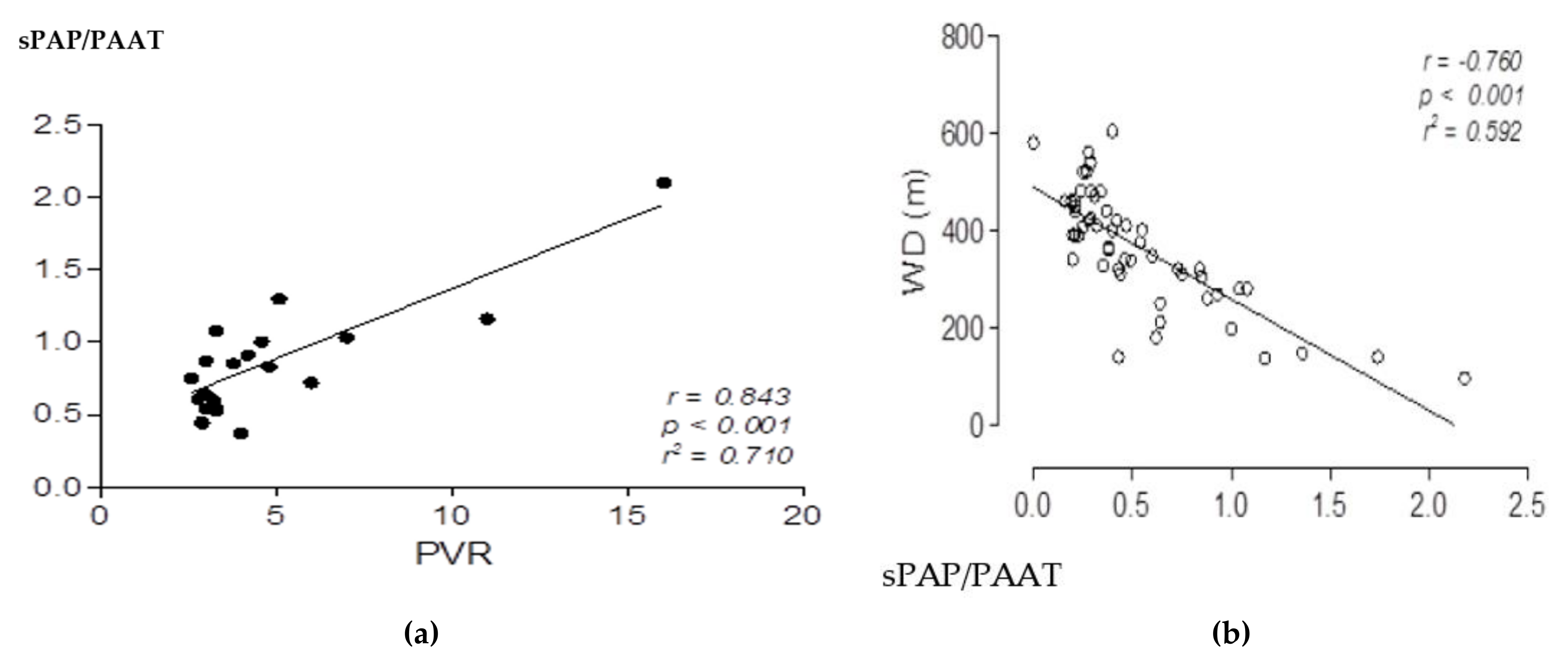
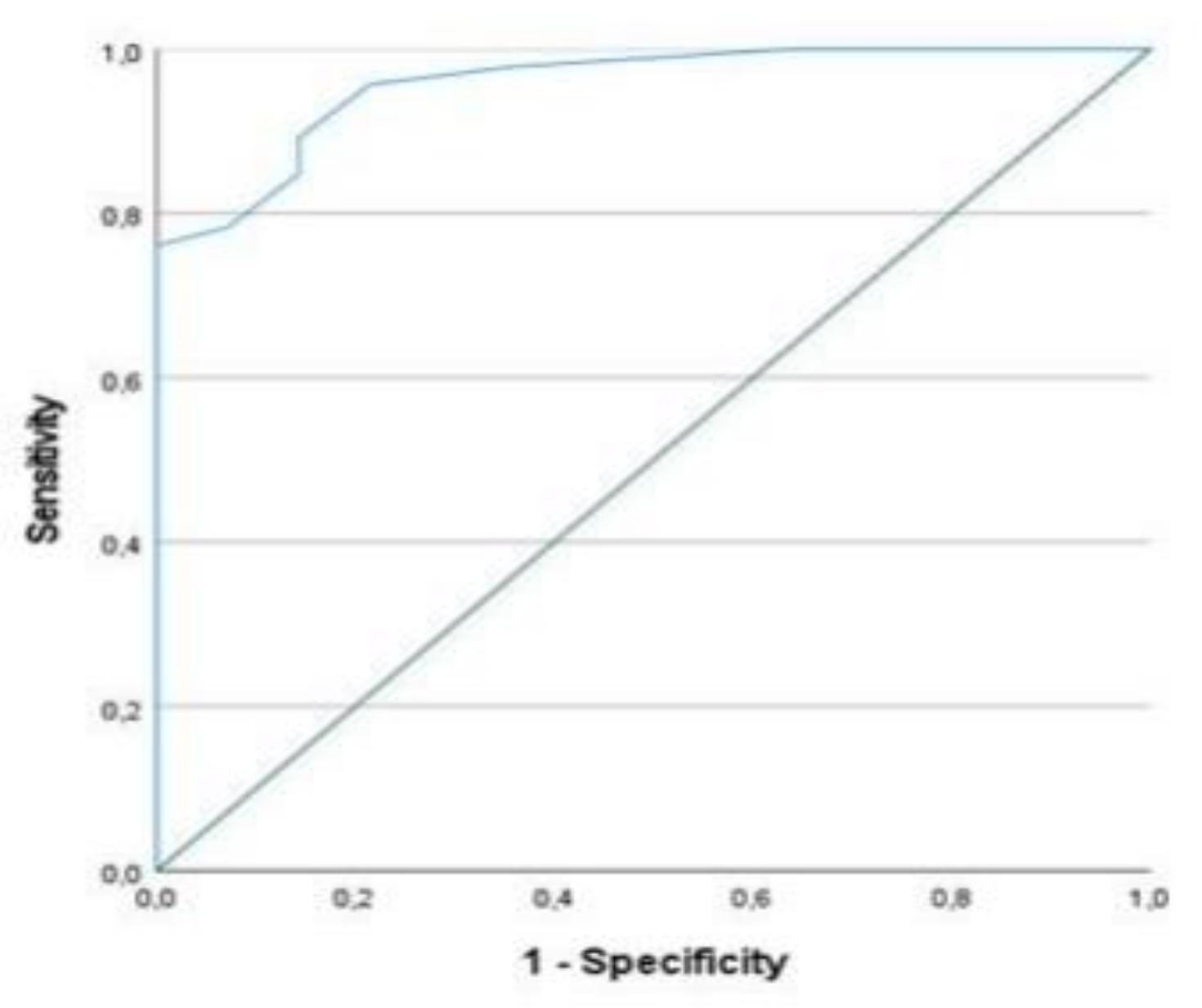
| Total Cohort: |
| (N = 36) |
| Age, years 55.6 ± 9 |
| Female sex 34 |
| NYHA I 26 pts; NYHA II 10 pts |
| Echocardiographic Analysis: |
| LV EF, %58 ± 6 |
| TR pressure gradient mmHg 26.5 |
| Mean PAAT 110 msc |
| TAPSE 23 mm |
| sPAP/PAAT 0.26 |
| Total Cohort |
| (N = 27) |
| Age, years 69.7 ± 8 |
| Female sex (26) |
| NYHA I 15 pts; NYHA II 9 pts; NYHA IV 3 pts |
| Echocardiographic Analysis: |
| LV EF, % 56 ± 6 |
| TR maximum pressure gradient, mmHg 46.5 ± 10 |
| Mean sPAP/PAAT 79.7 ± 7 |
| TAPSE 19.7 mm ± 10 |
| sPAP/PAAT 0.4 |
| Invasive hemodynamic: |
| Heart rate, bpm 85 ± 16 |
| RV systolic, mmHg 58 ± 20 |
| PA systolic, mmHg 60 ± 20 |
| Mean PAP, mmHg 37 ± 13 |
| Mean PCWP, mmHg 15 ± 2 |
| Cardiac output, L/min 4.7 ± 1.3 |
| Pulmonary vascular resistance: 5.63 W.U. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serra, W.; Chetta, A. sPAP/PAAT Ratio as a New Index of Pulmonary Vascular Load: A Study in Normal Subjects and Ssc Patients with and without PH. Pathophysiology 2022, 29, 134-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology29010012
Serra W, Chetta A. sPAP/PAAT Ratio as a New Index of Pulmonary Vascular Load: A Study in Normal Subjects and Ssc Patients with and without PH. Pathophysiology. 2022; 29(1):134-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology29010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerra, Walter, and Alfredo Chetta. 2022. "sPAP/PAAT Ratio as a New Index of Pulmonary Vascular Load: A Study in Normal Subjects and Ssc Patients with and without PH" Pathophysiology 29, no. 1: 134-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology29010012
APA StyleSerra, W., & Chetta, A. (2022). sPAP/PAAT Ratio as a New Index of Pulmonary Vascular Load: A Study in Normal Subjects and Ssc Patients with and without PH. Pathophysiology, 29(1), 134-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology29010012






